Describe the A&P of the cardiovascular system (TEAS7)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
cardiovascular system
The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes; composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
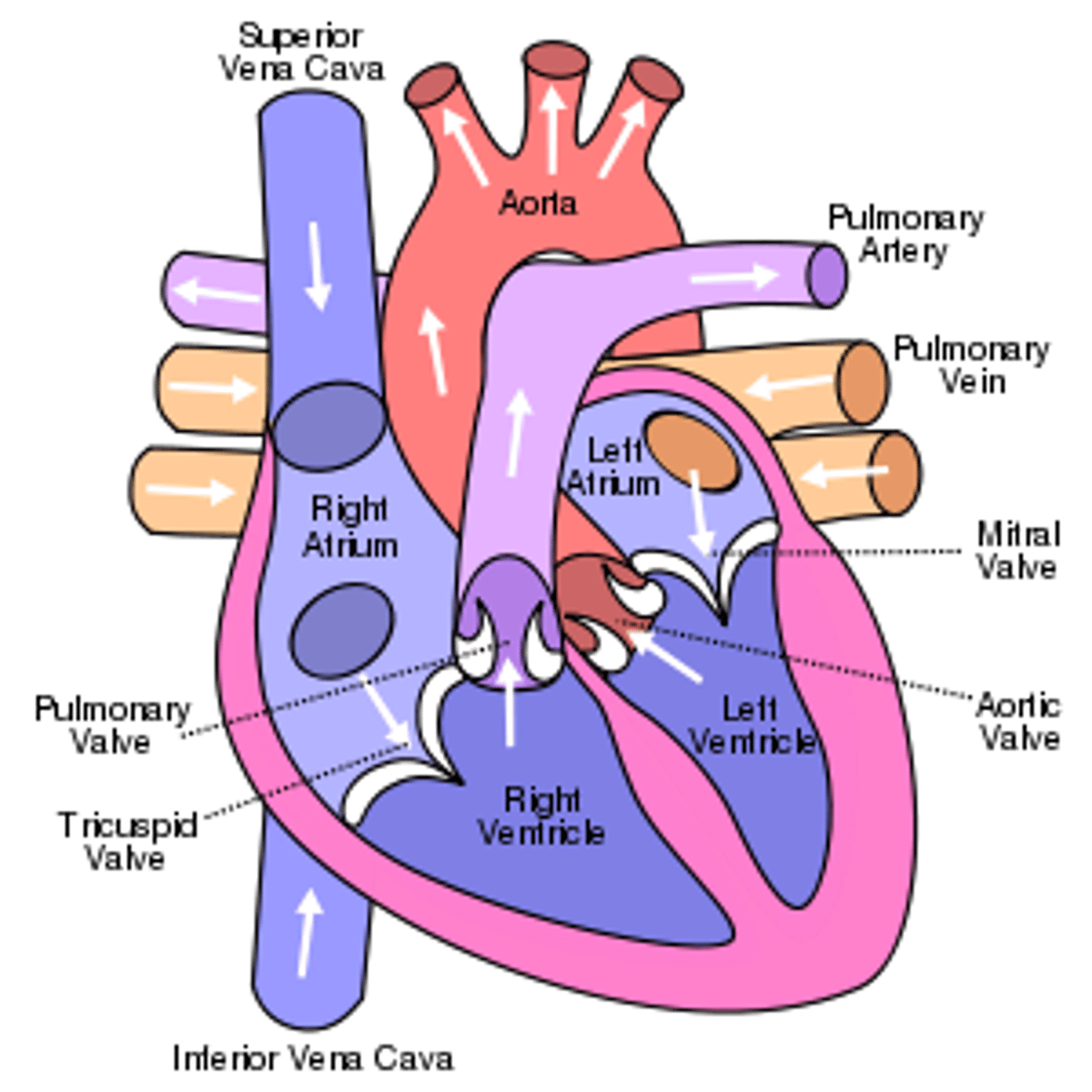
Arteries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart toward the other body parts (thick-wall)
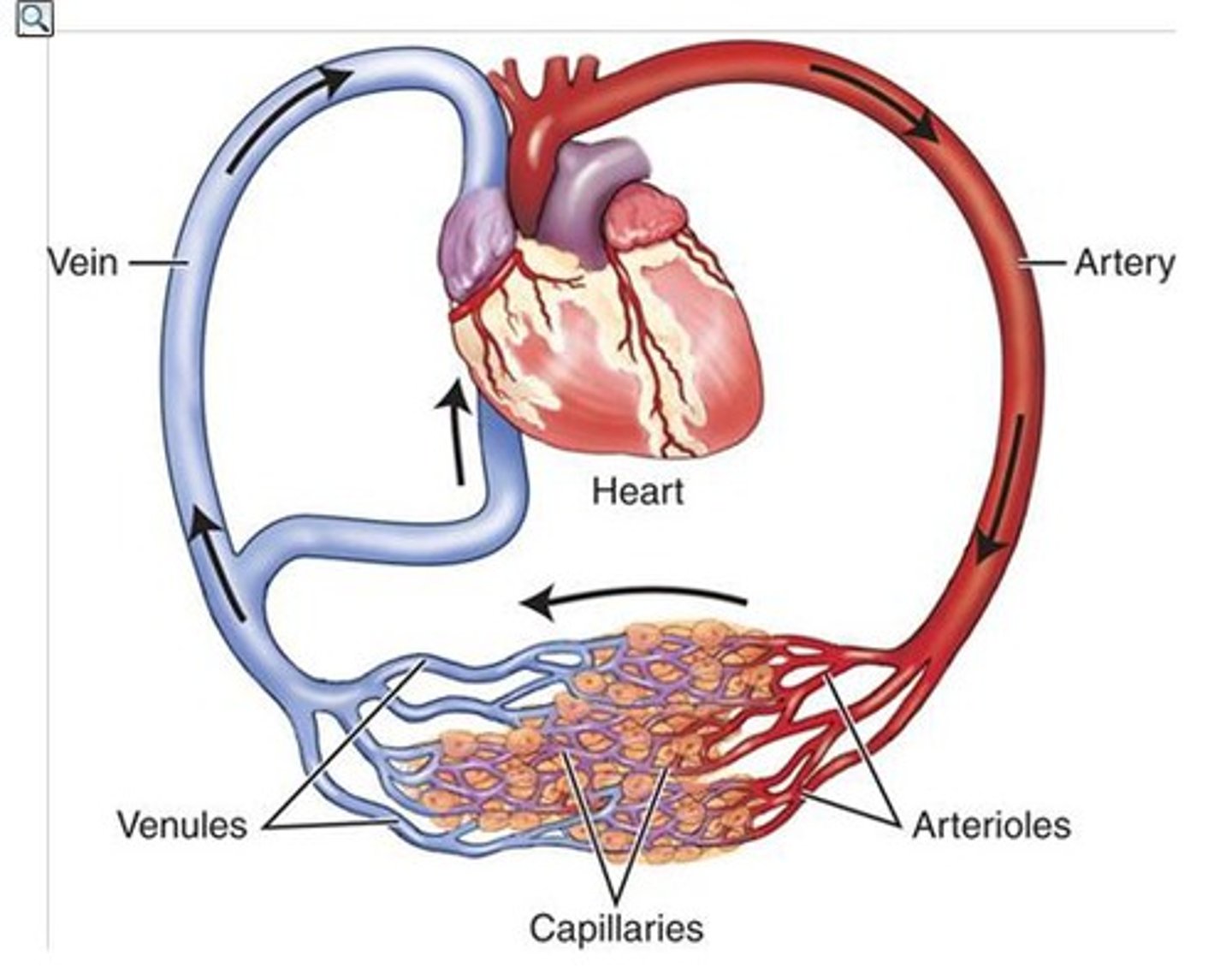
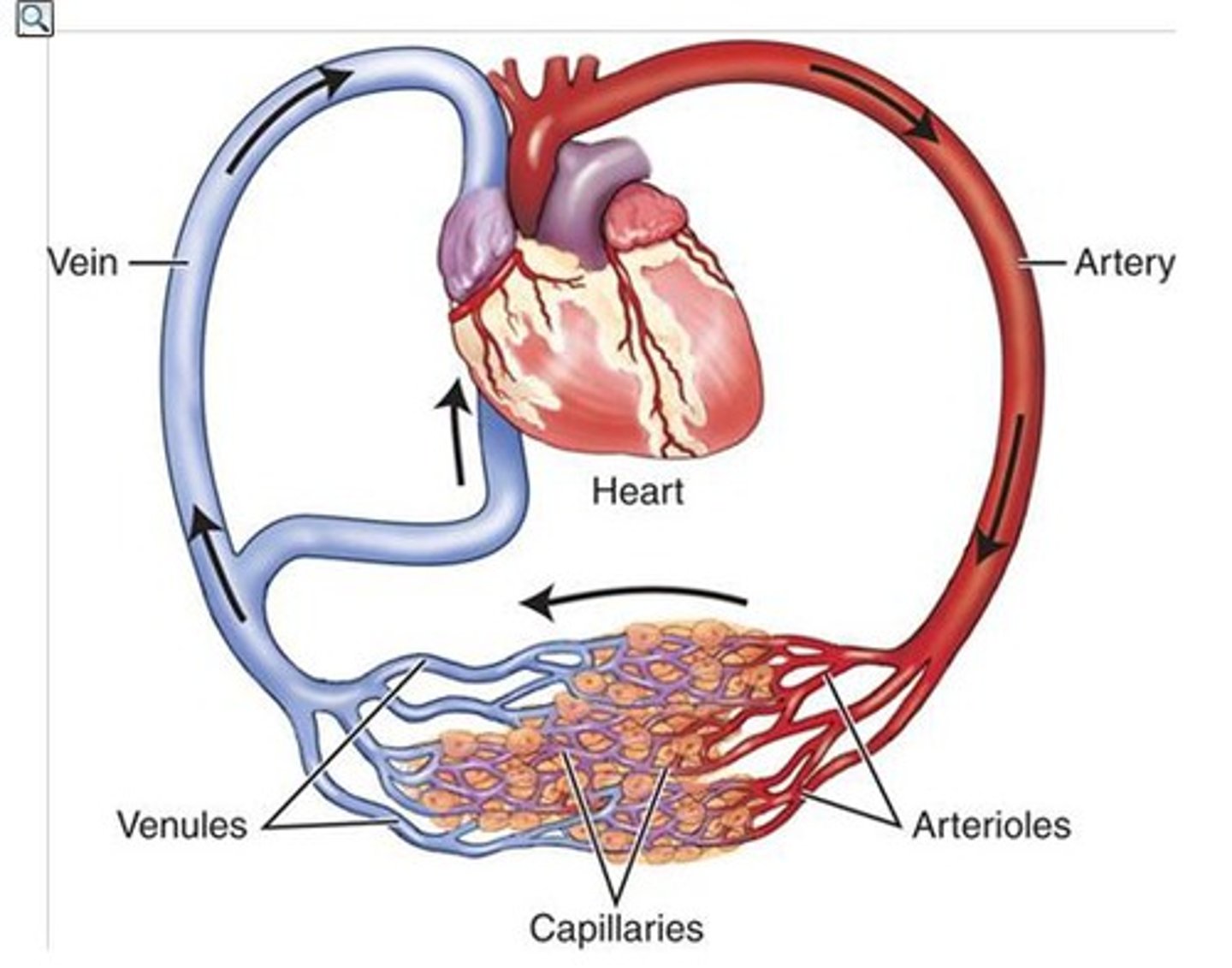
veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart from other body parts (thin-wall)
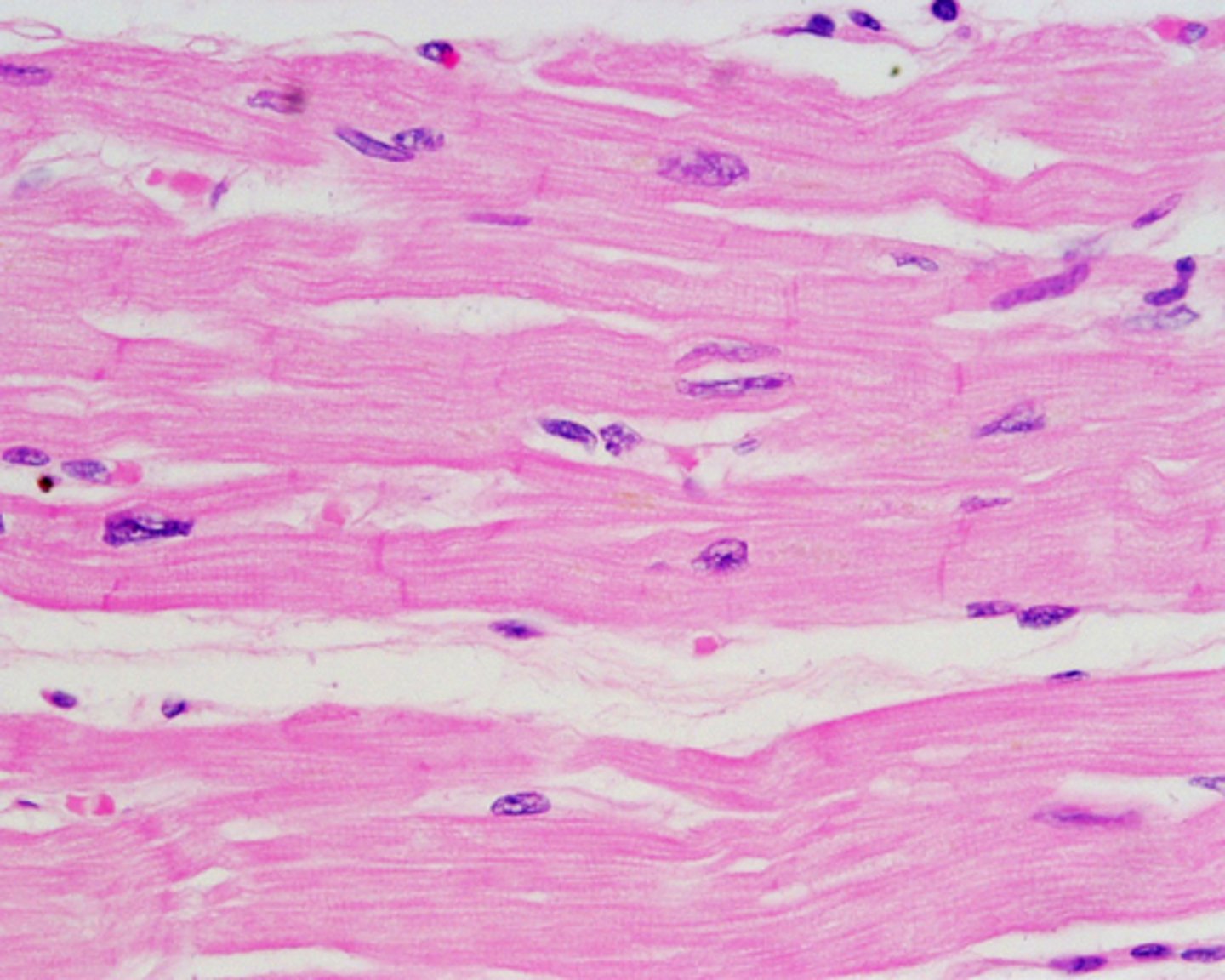
cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue is found only in the heart. comprised of heart and blood vessels.
Capillaries
any of the fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the arterioles[u and venules.

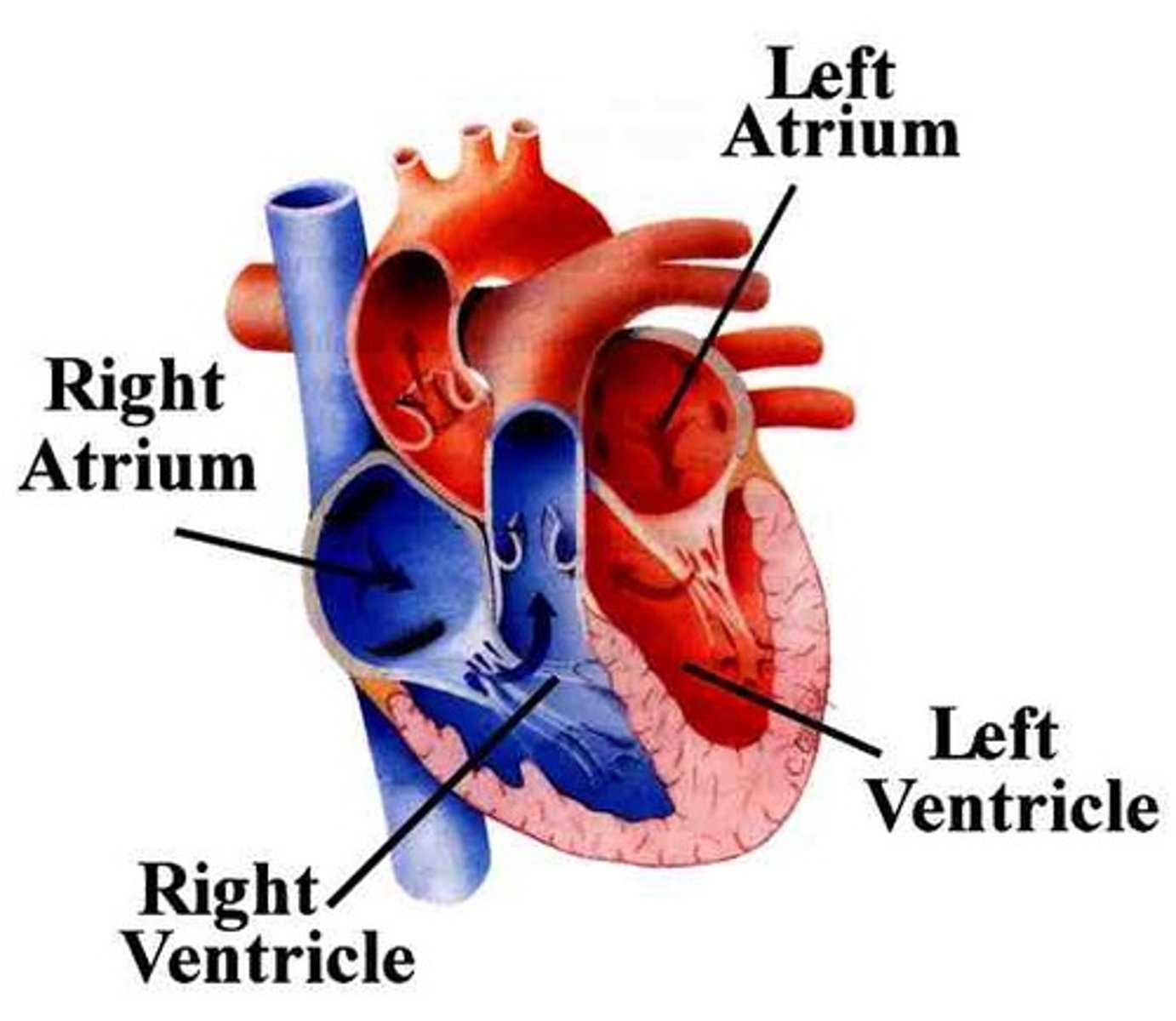
atria
2 upper chambers of the heart
ventricles
the two lower chambers of the heart
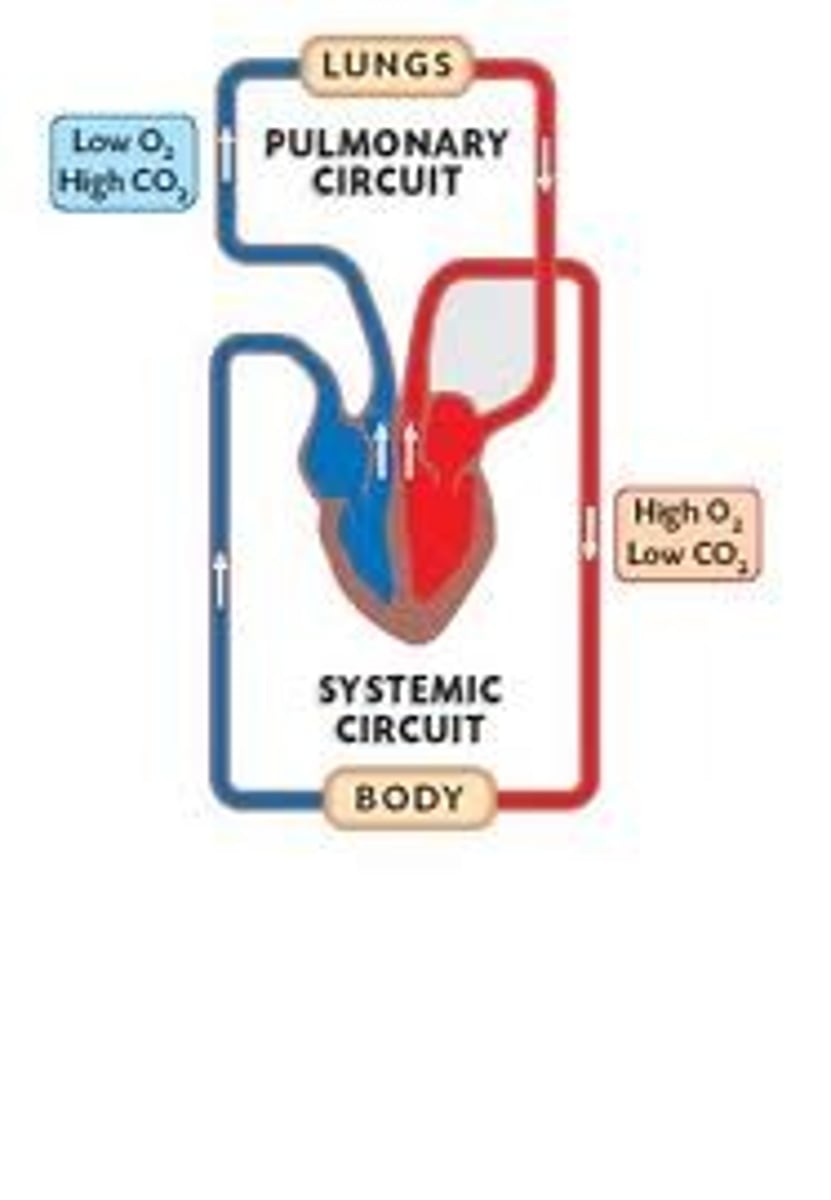
blood flow through the cardiovascular system
look in book or youtube
pulmonary circulation
Circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs
-carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the heart to the lungs where it is oxygenated and returns oxygenated blood to the left atrium
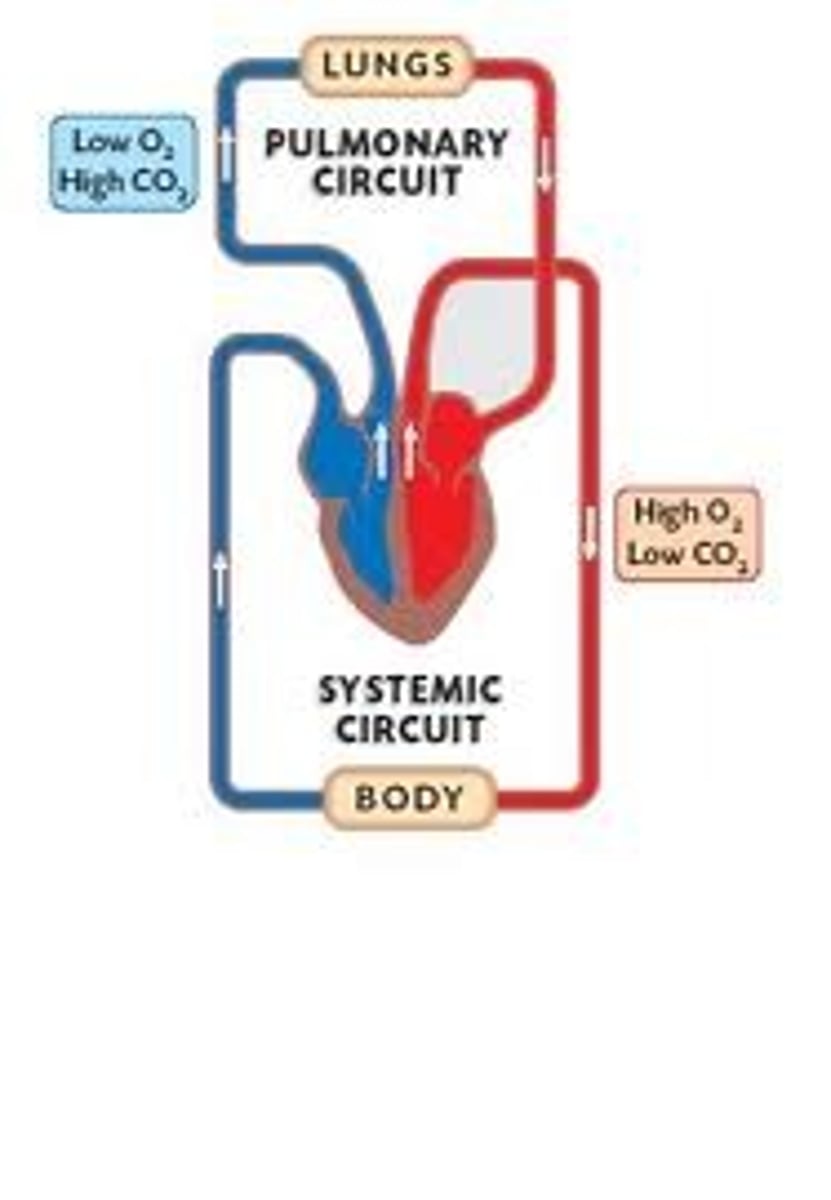
systemic circulation
circulation that supplies blood to all the body except to the lungs
-carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body, returning deoxygenated blood to the right atrium
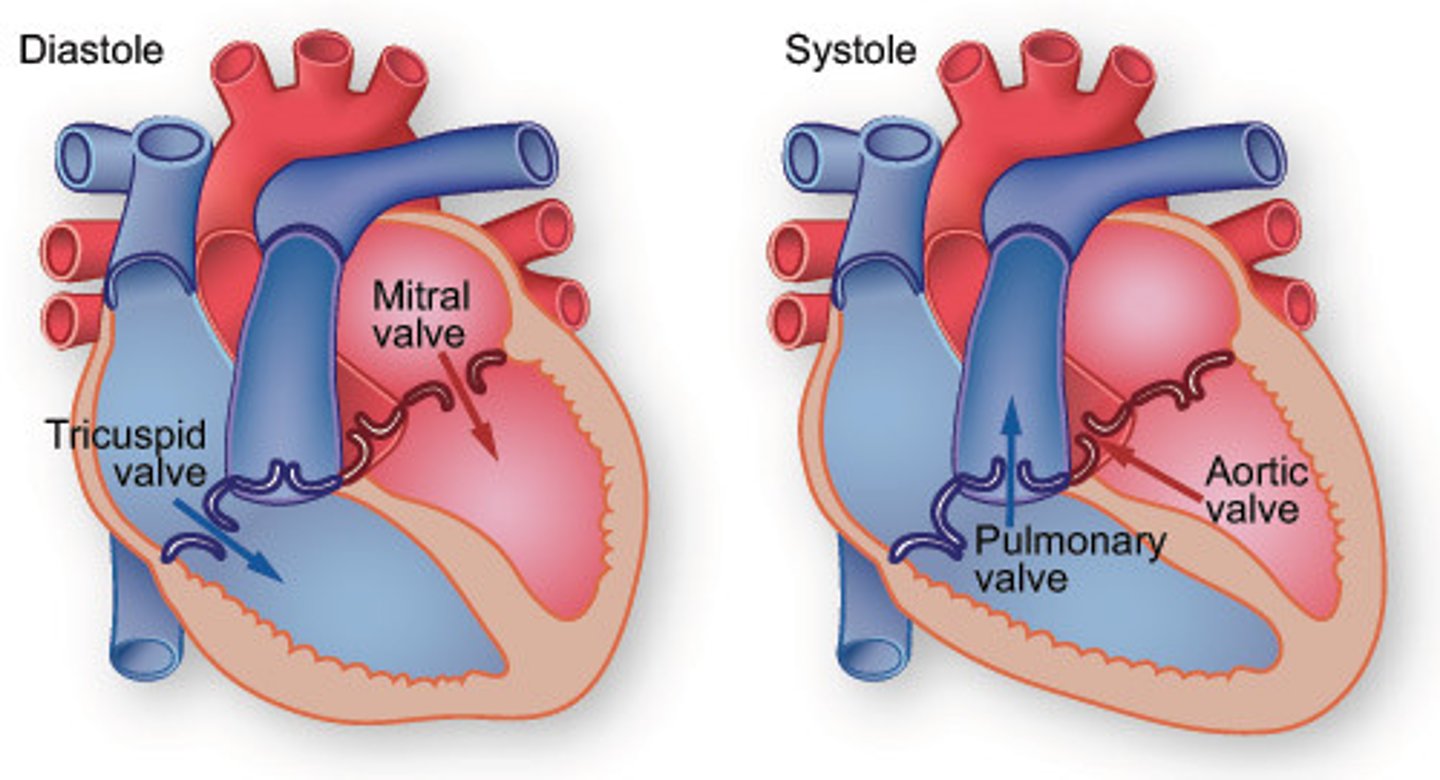
Systole
Contraction of the heart (bigger # ex. 120)

Diastole (smaller # exp 80)
Relaxation of the heart
plasma
Fluid portion of blood
-contains nutrients, hormones, antibodies

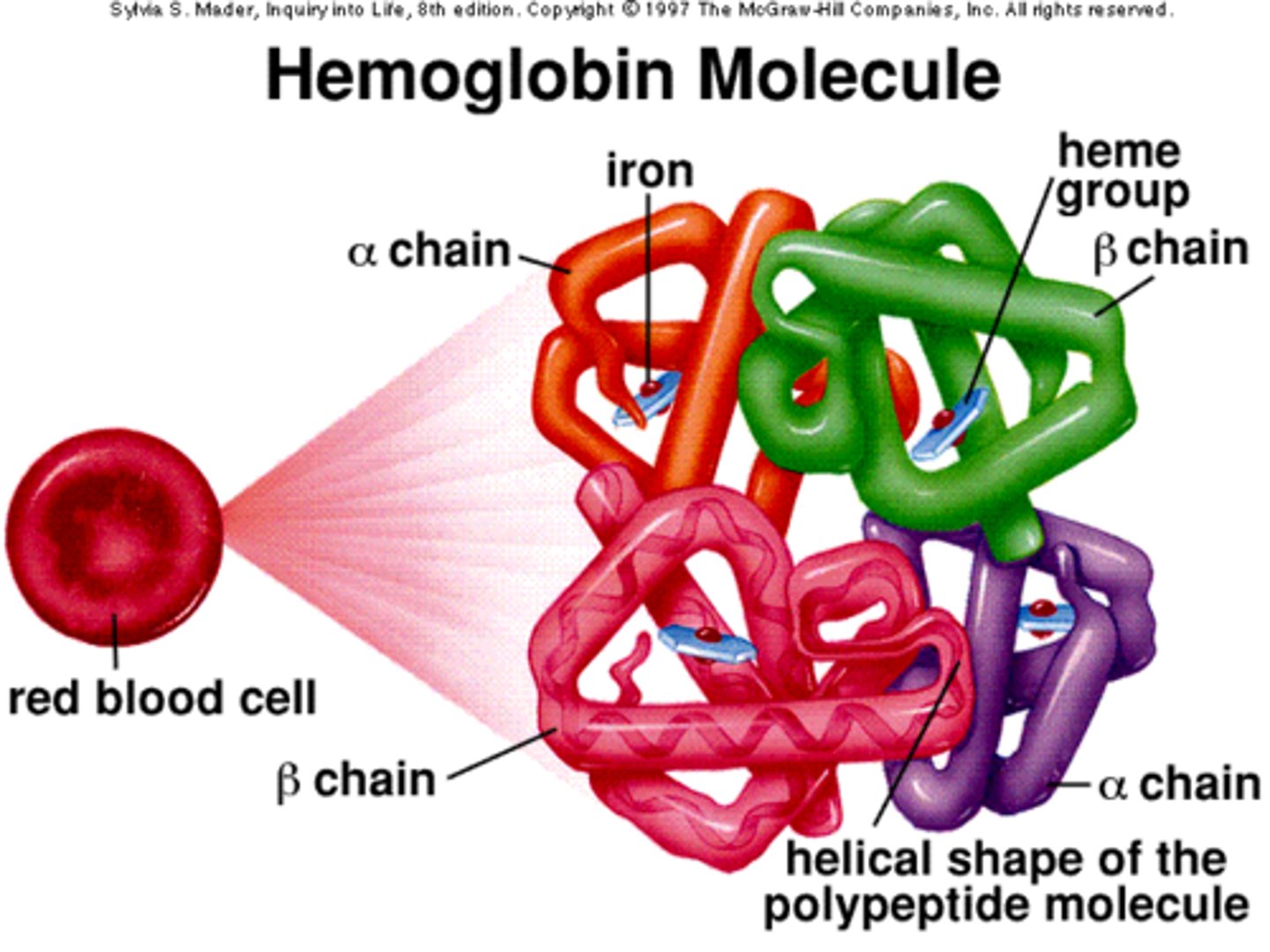
Hemoglobin
The protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body
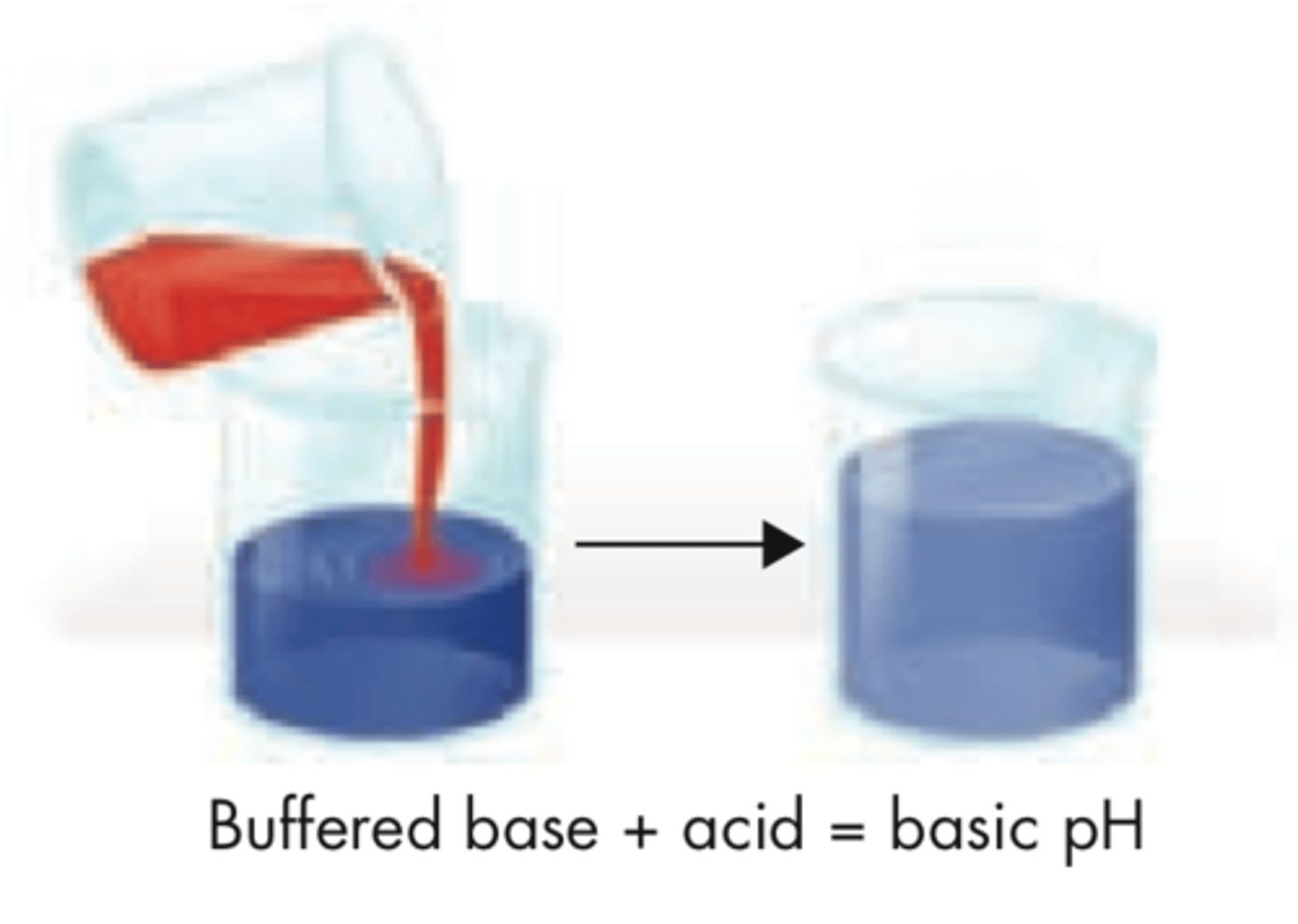
Buffer
a solution of a weak acid and its conjugated base or a weak base and its conjugated acid. buffers maintain the proper pH balance of the body.
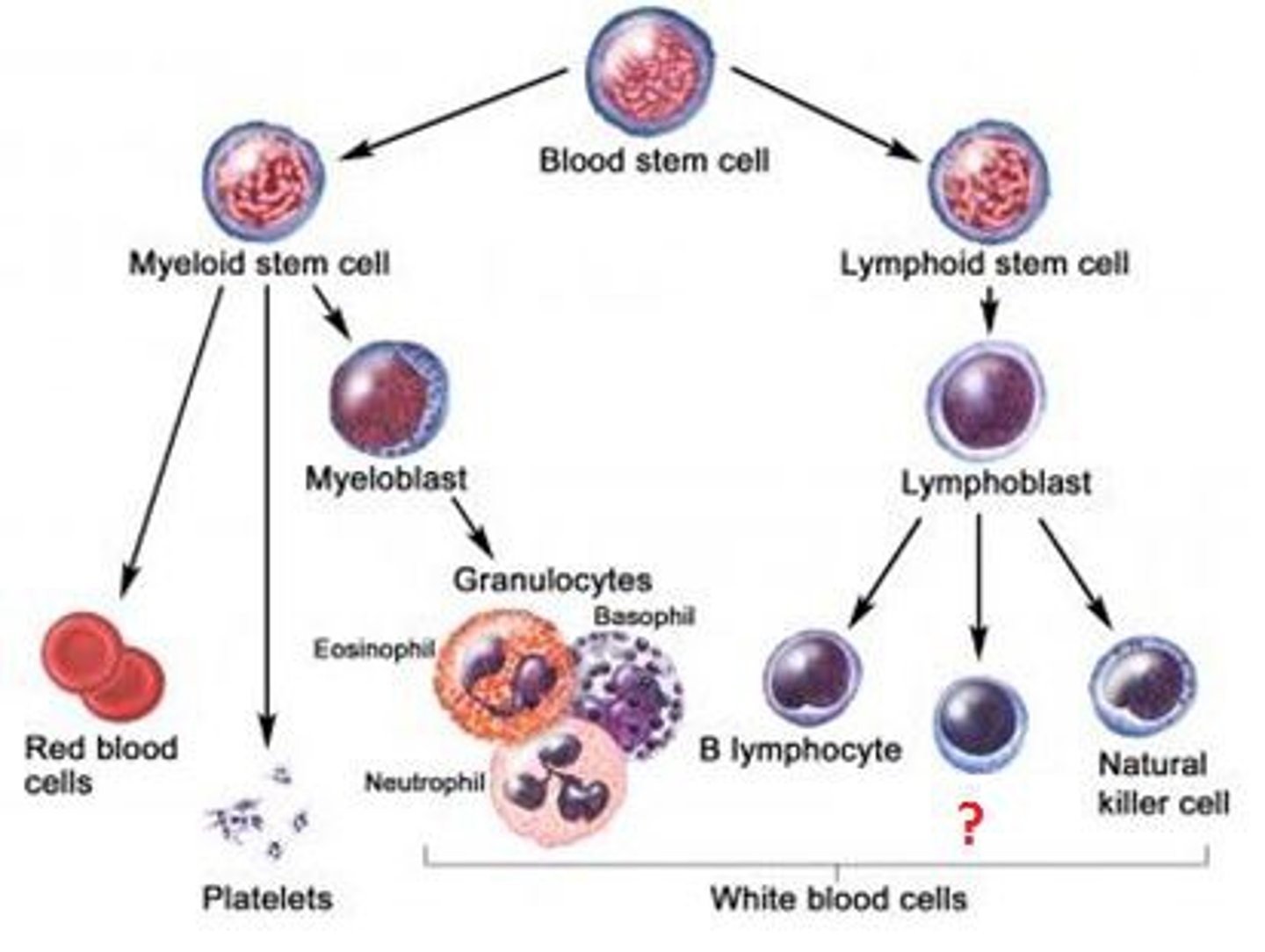
Lymphocytes
a category of white blood cells that includes natural killer cells, B cells, helper T cells, and cytotoxic T cells
lymph
Clear fluid that moves throughout the lymphatic system to fight disease
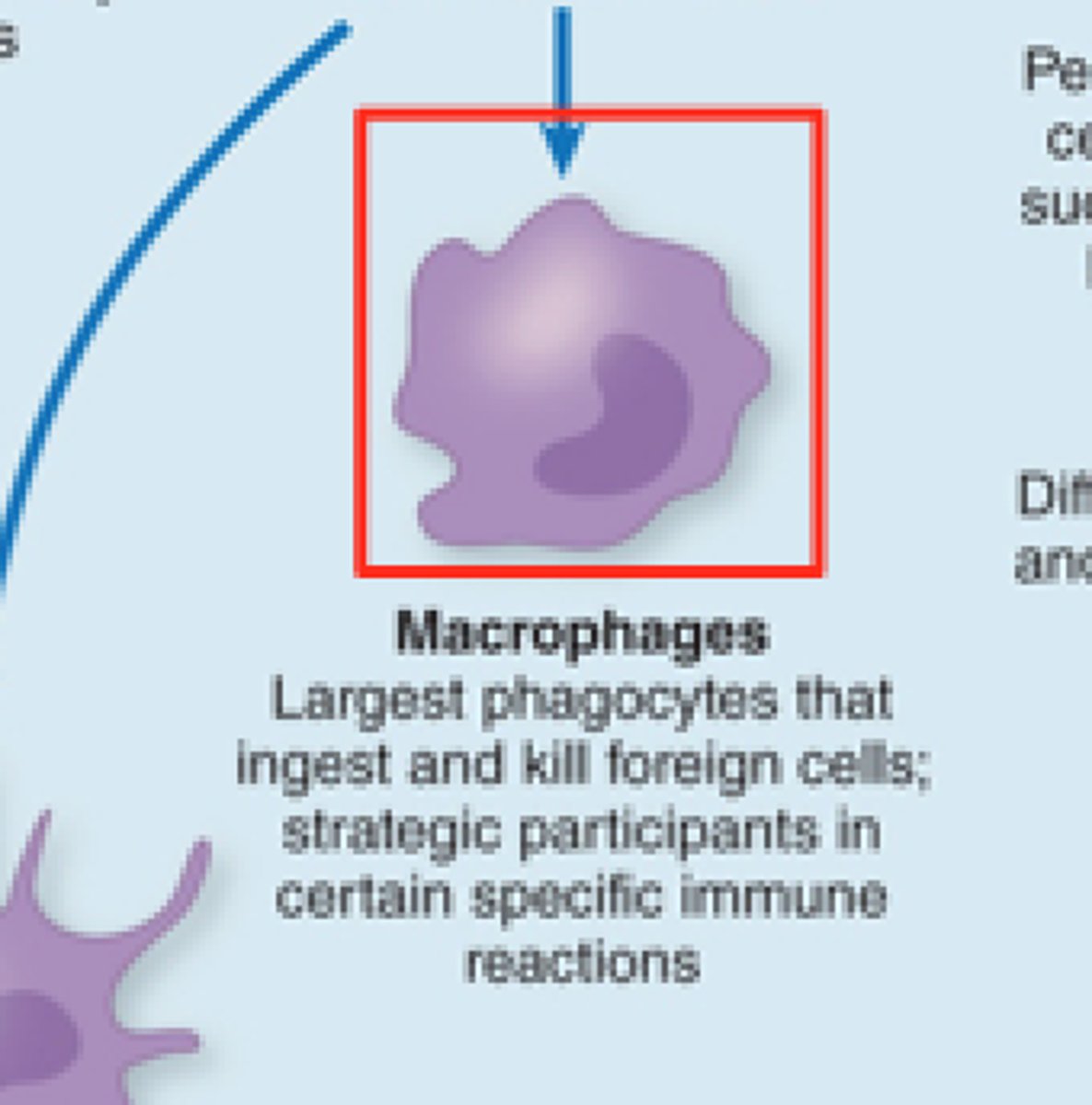
Macrophages
a large white blood cell that ingests foreign material
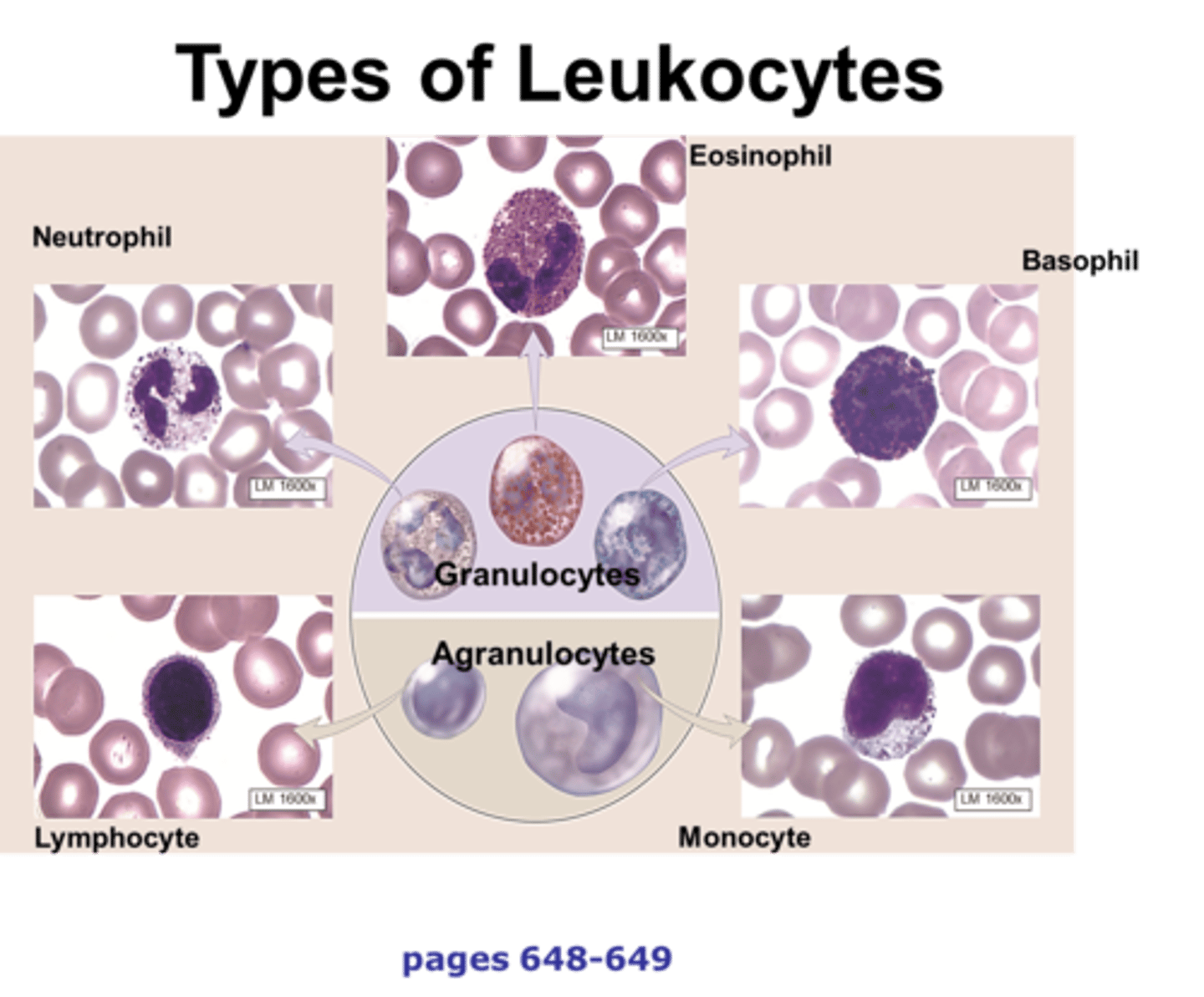
Leukocytes
white blood cells that protects the body from diseases
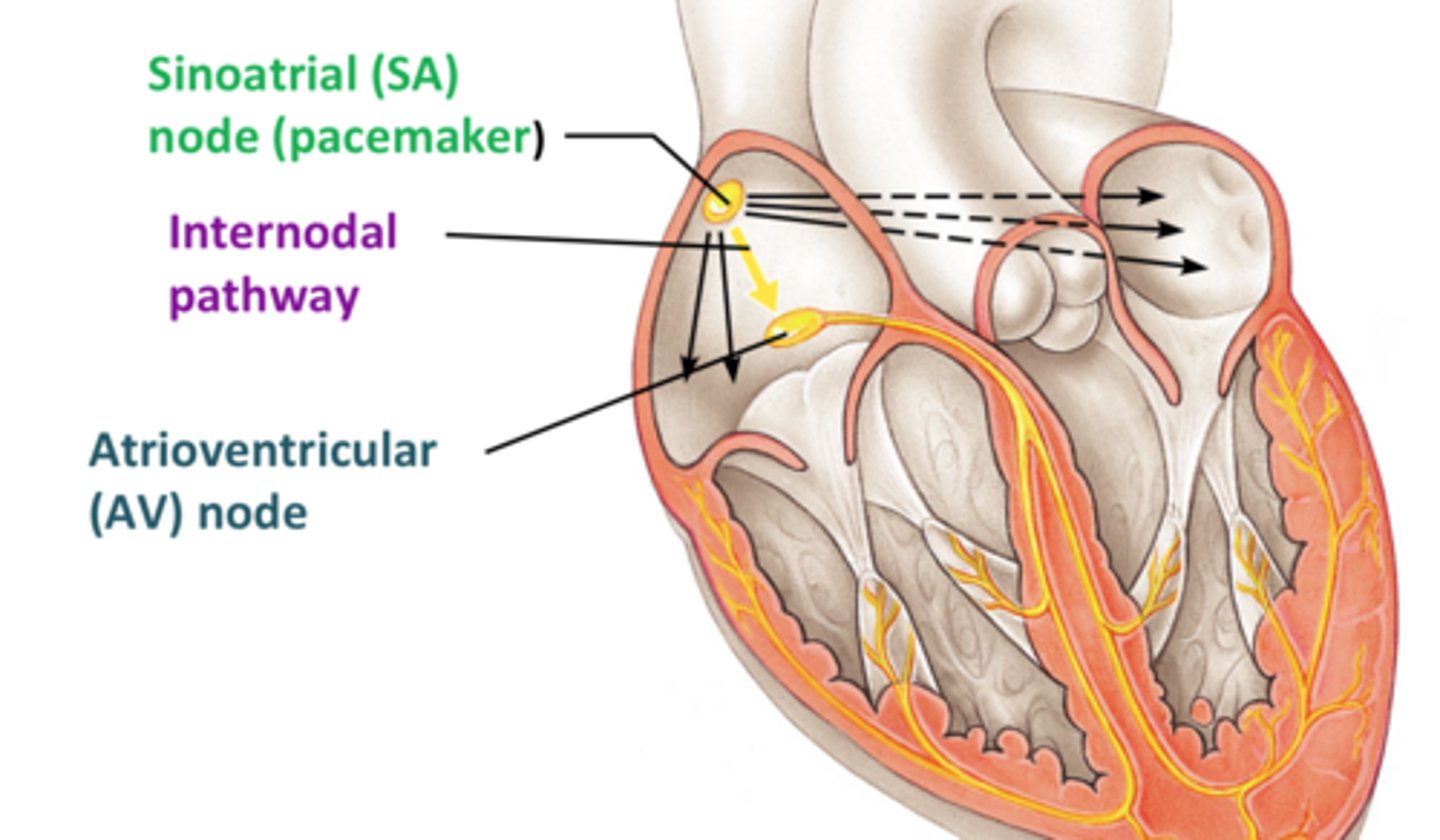
SA node (sinoatrial node)
-pacemaker of the heart
-sets the heartbeat rate 60-100bpm
--located in the right atrium
-causes atria to contract
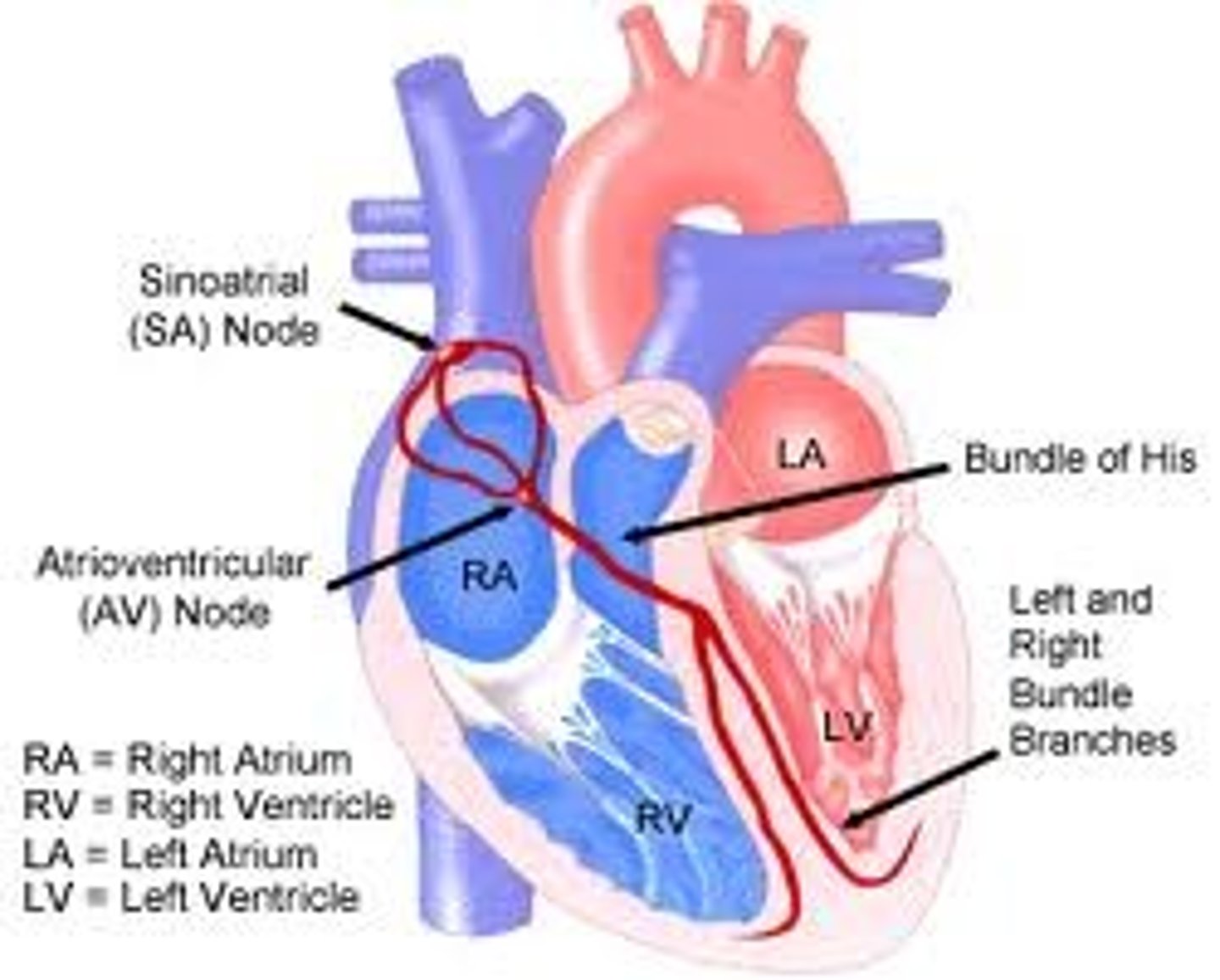
AV node (atrioventricular node)
region of the heart between the right atrium and right ventricle from which electrical impulses spread to the ventricles during a heartbeat .. 40-60bpm
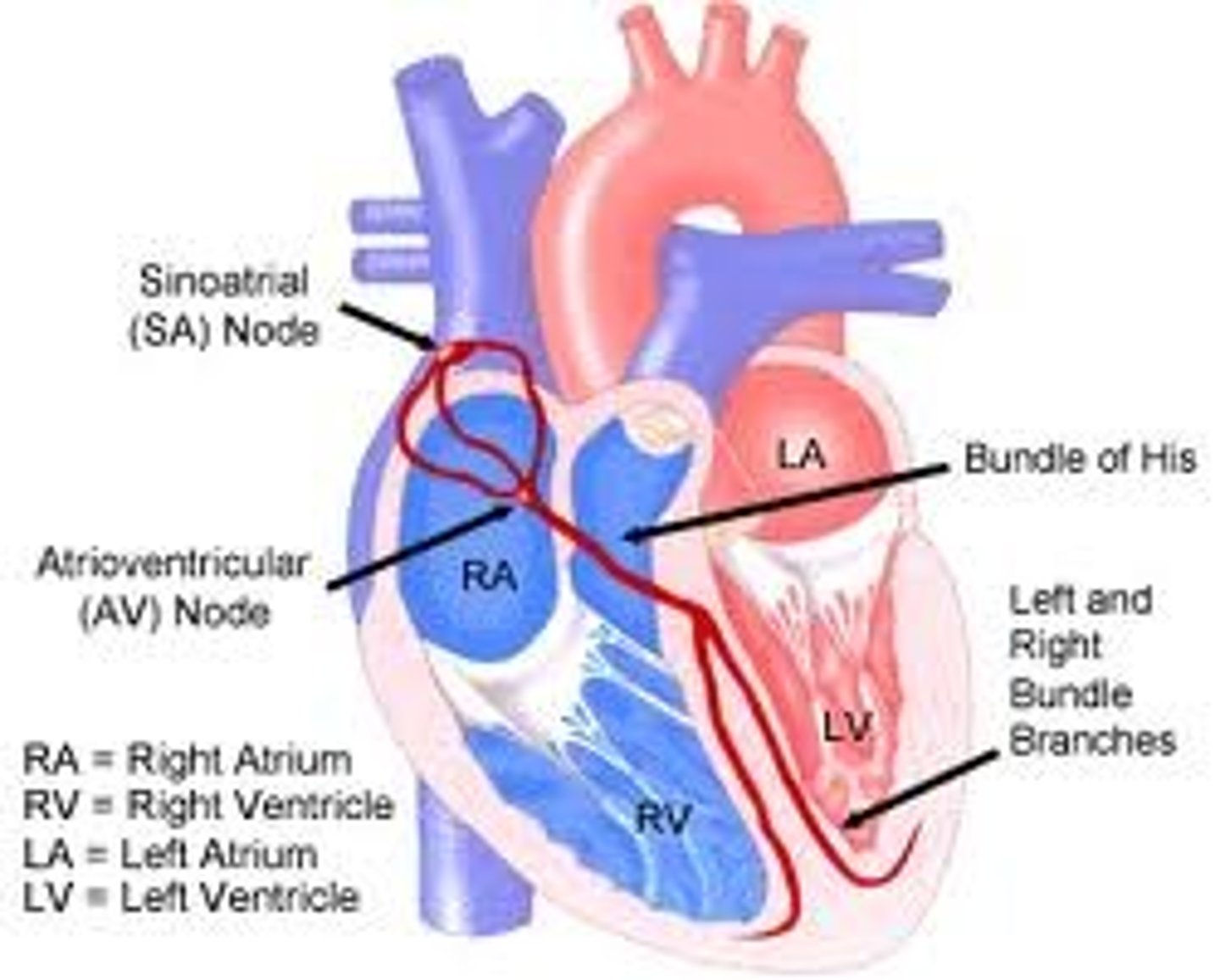
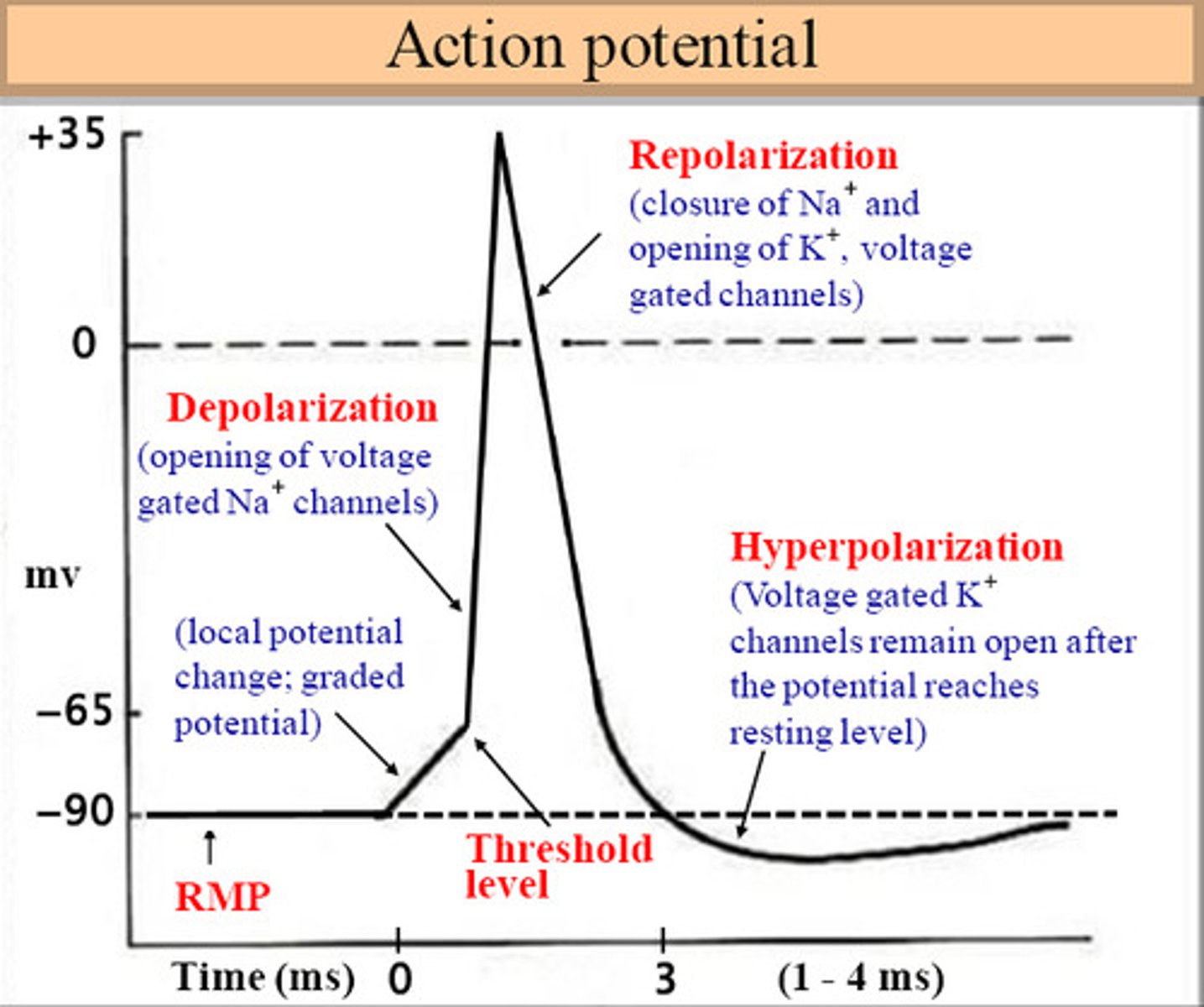
Depolarization
electrical event that leads to systole (contraction)
internodal pathways
Interconnect the SA Node with the AV Node, conducts impulses throught to the atrial working cells.
Bundle of His (AV bundle)
located next to the AV node; provides the transfer of the electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles
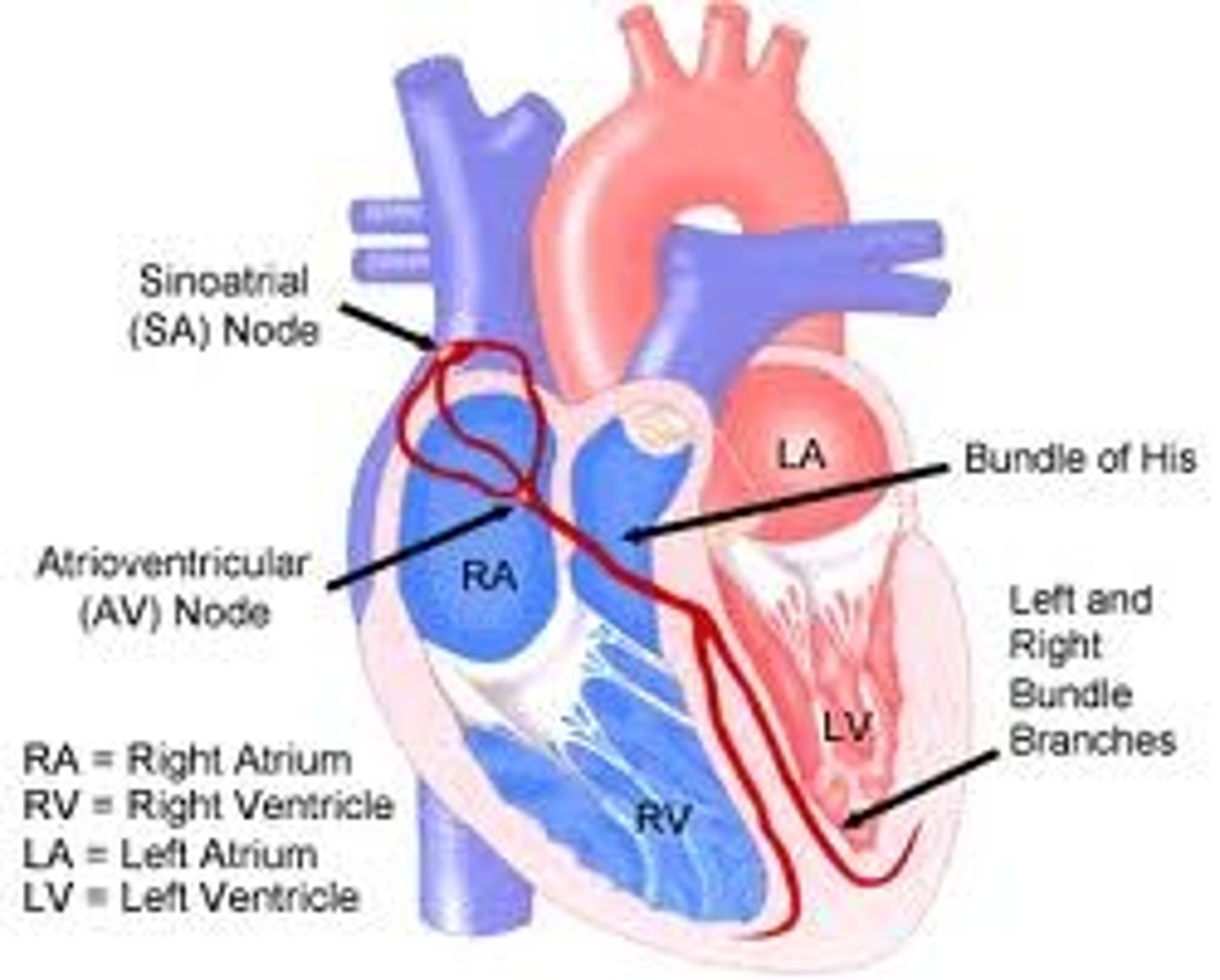
bundle branches
branches of the AV bundle that divide to the right and left sides of the interventricular septum

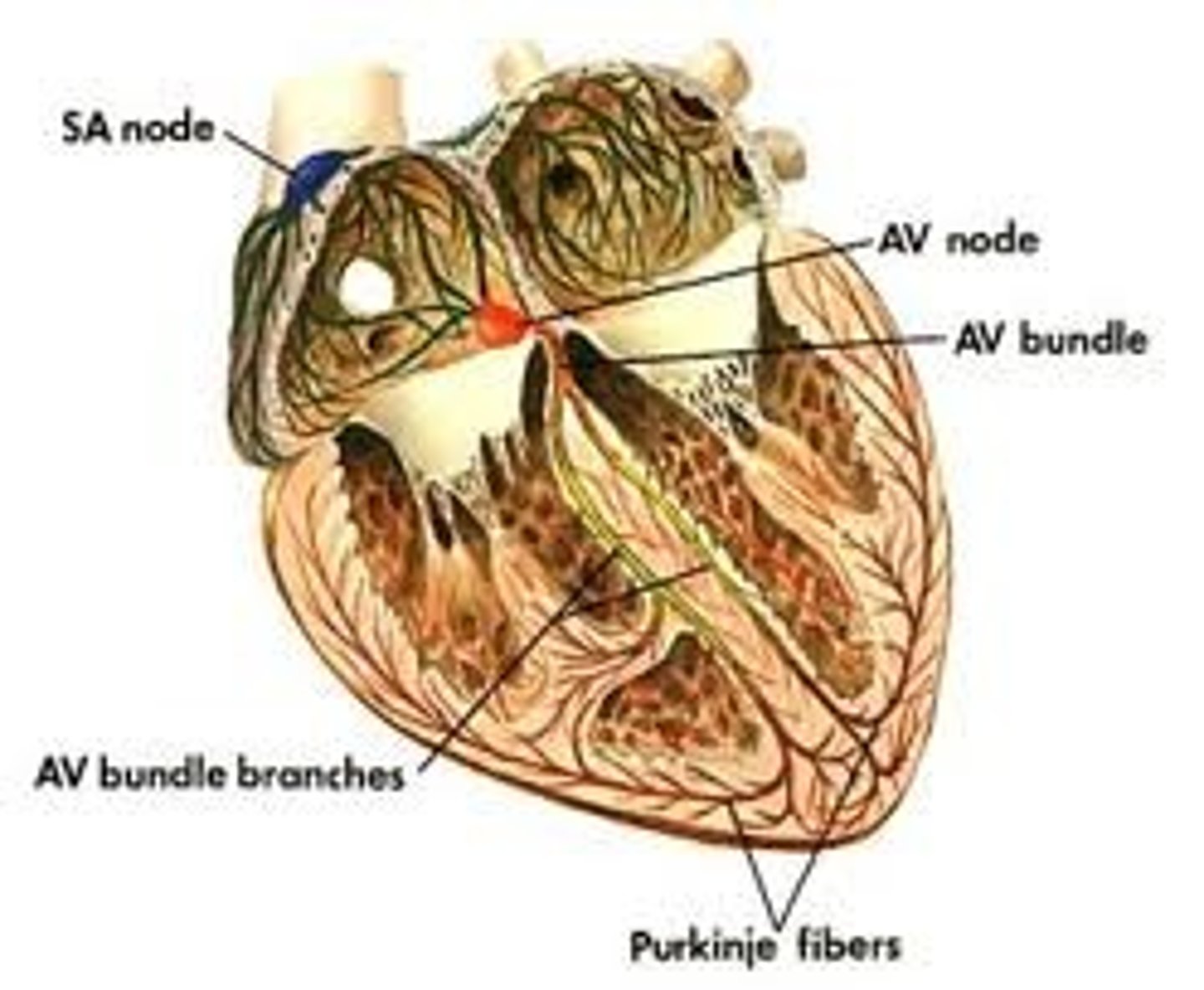
Purkinje fibers
fibers in the ventricles that transmit impulses to the right and left ventricles, causing them to contract..40 bpm
Reploarization
relaxation
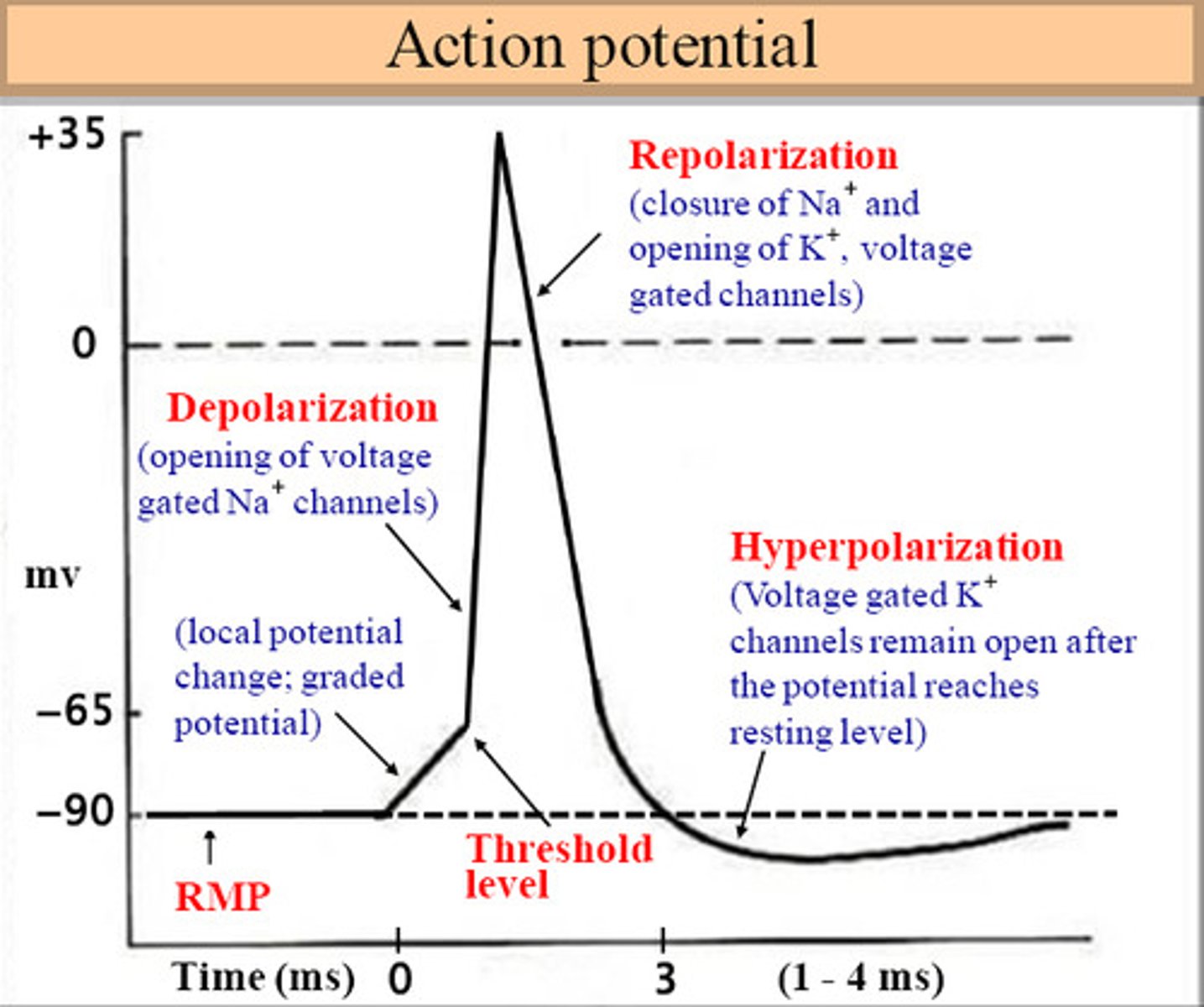
SA node starts repolarizing after it sends its contraction impulses to
the AV node; it has already done its job is time to relax.
SA node depolarization
-Through the property of automaticity, the heart's pacemaker cells spontaneously depolarize
-They have what can be described as an unstable resting membrane potential
Repolarization starts with Purkinje fibers moving
upwards; up the bundle of branches; up the bundle of his and up the AV node.
-blood moves to the body and lungs at this stage.
P waves
Indicates atrial depolarization
Q, R, S waves
depolarization of the ventricles
T waves
ventricular repolarization
Depolarization
contraction
normal sinus rhythm (NSR)
60/100 bpm
Bradycardia
Slow heart rate less than 60bpm
Tachycardia
rapid heart rate over 100 beats per minute
sphygmomanometer
instrument to measure blood pressure