AP Classrooms Unit 7
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
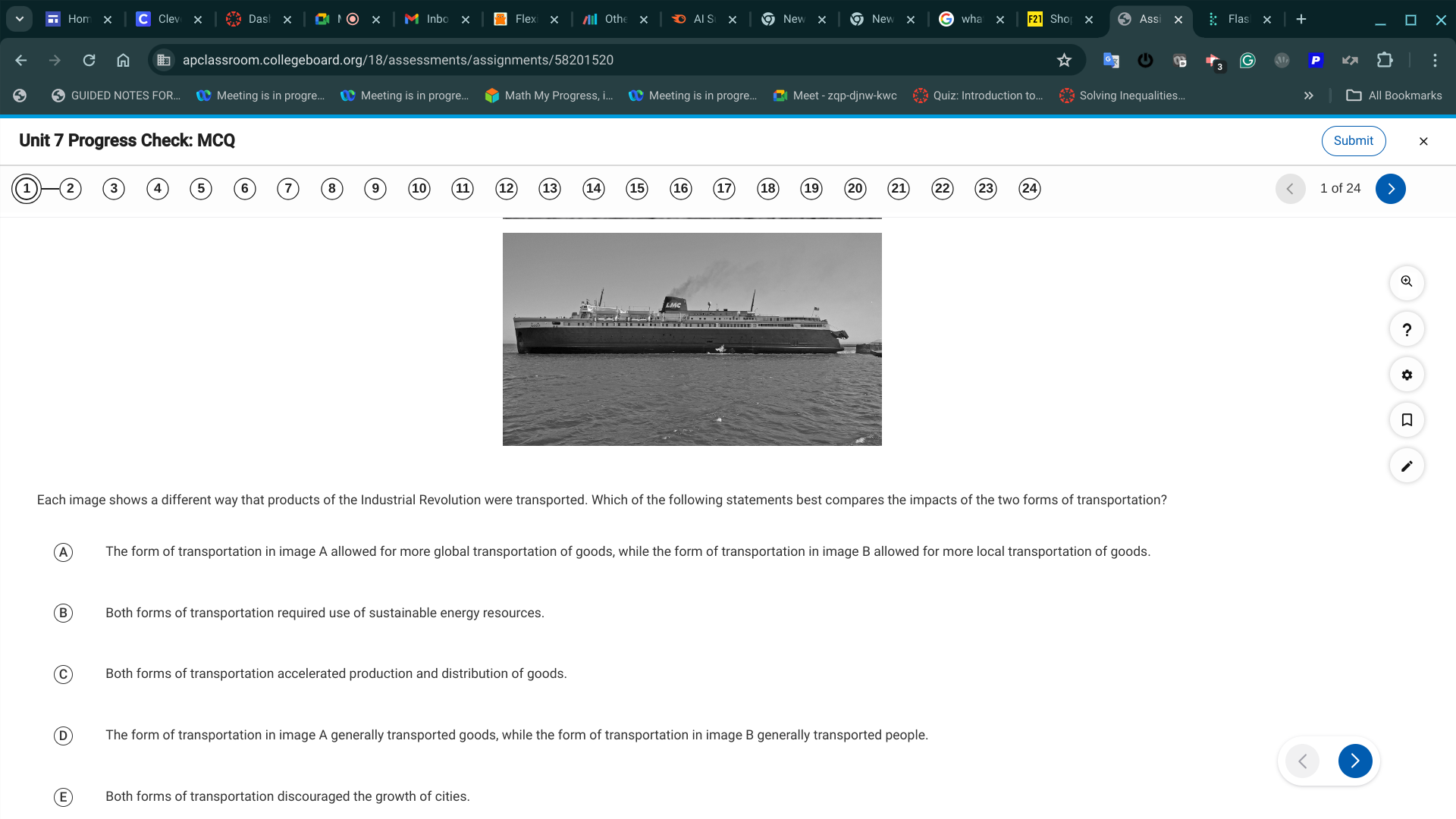
C. Both forms of transportation accelerated production and distribution of goods.
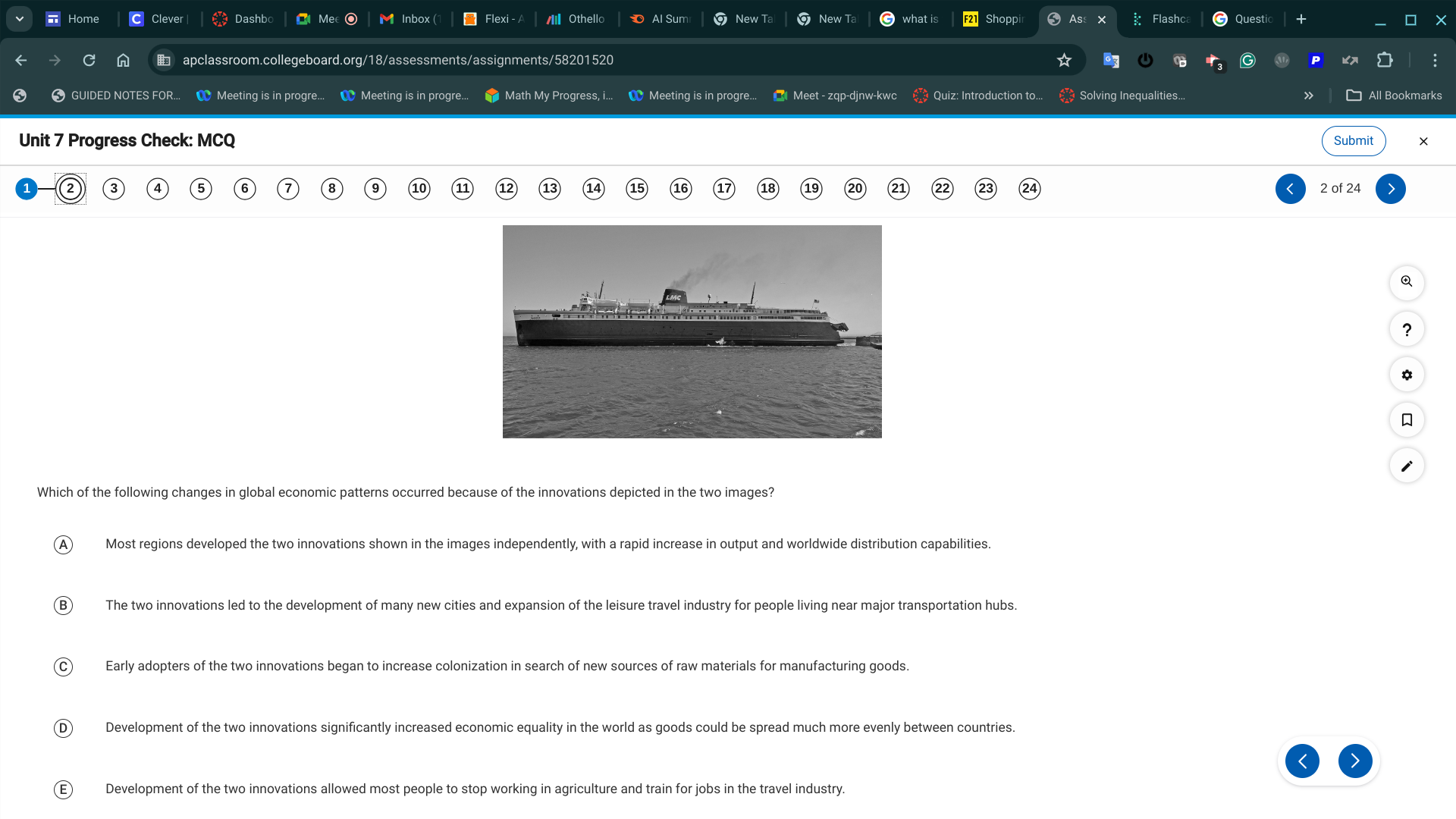
C. Early adopters of the two innovations began to increase colonization in search of new sources of raw materials for manufacturing goods.
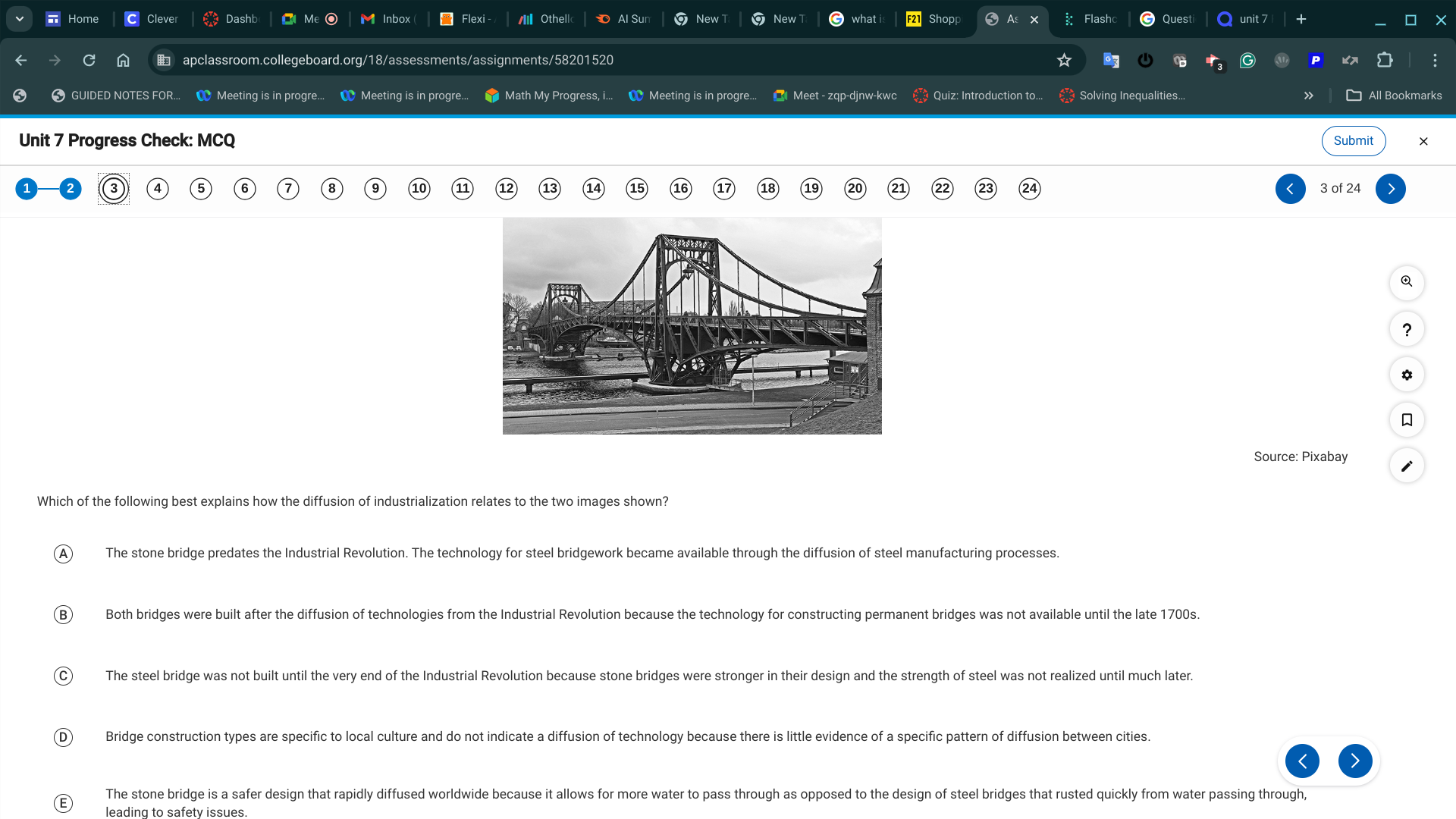
A. The stone bridge predates the Industrial Revolution. The technology for steel bridgework became available through the diffusion of steel manufacturing processes.
D. The country has access to shipping lanes and inexpensive transport options that lead to establishment of factories close to raw materials or to markets, depending on the manufacturing process
D. Core countries have the highest percentage of workers in the tertiary sector and the lowest percentage of workers in the primary sector because of the economic emphasis on services.
A. manufacturing output and service industry employment
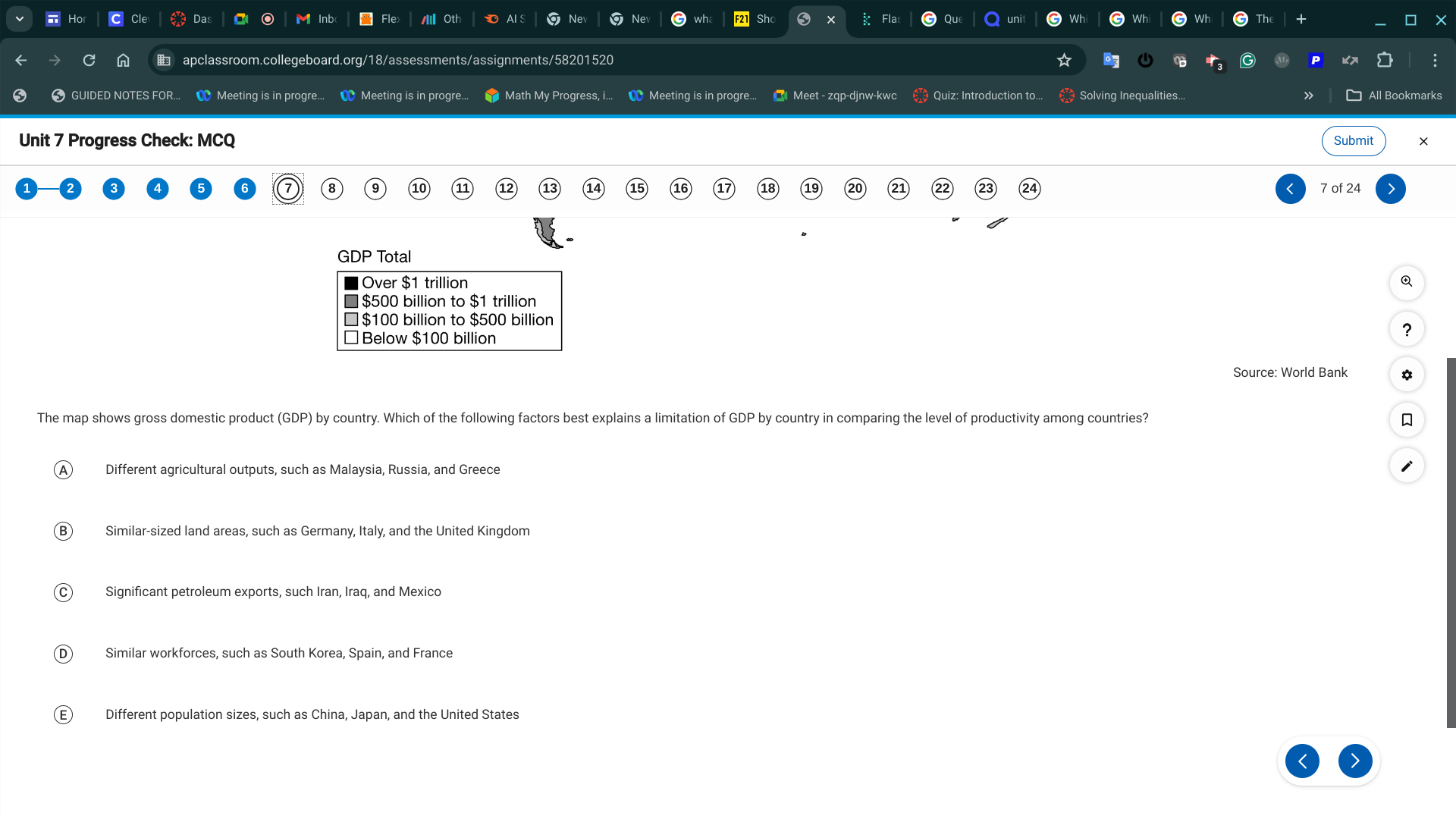
E. Different population sizes, such as China, Japan, and the United States
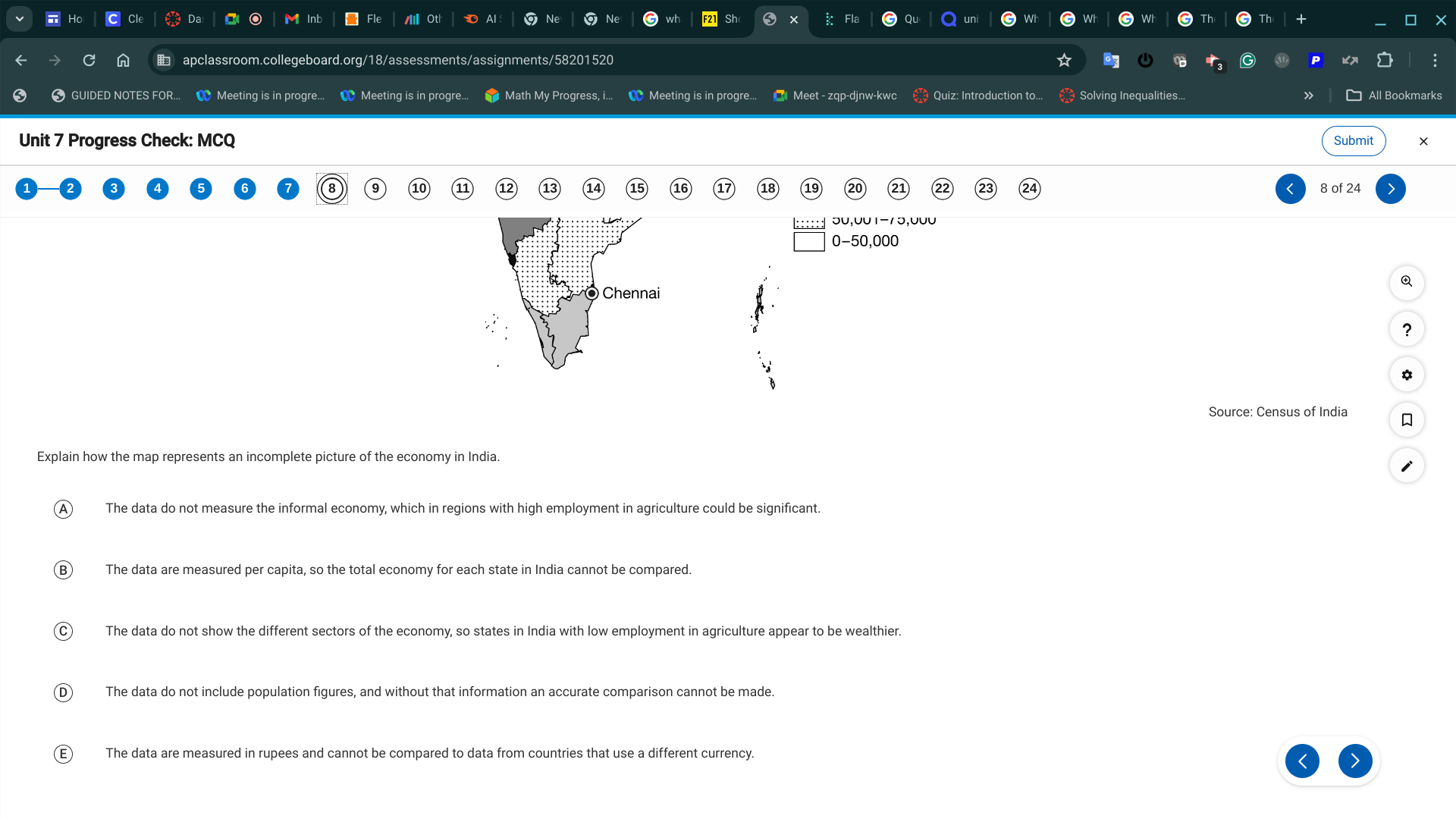
A. The data do not measure the informal economy, which in regions with high employment in agriculture could be significant.
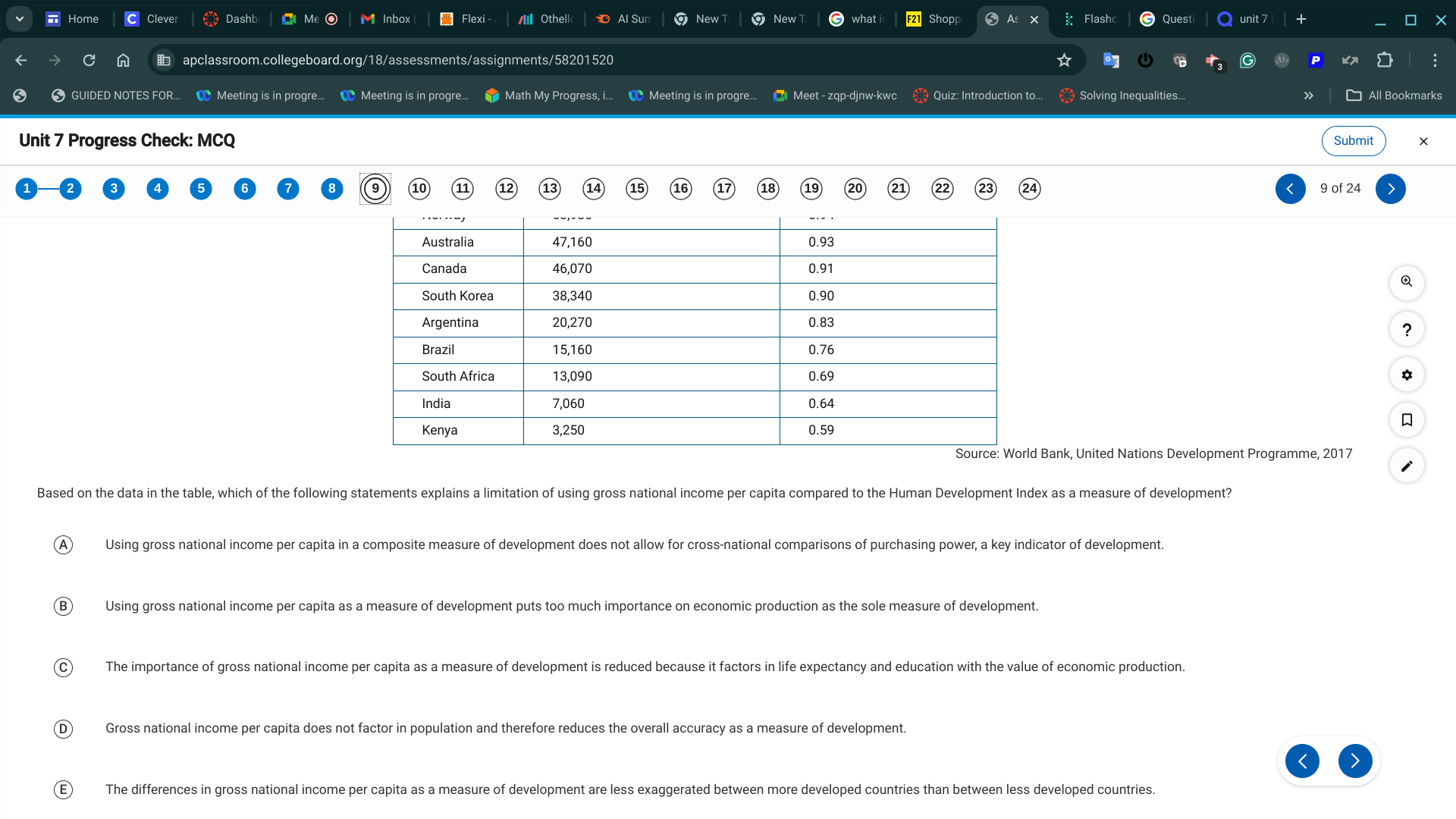
B. Using gross national income per capita as a measure of development puts too much importance on economic production as the sole measure of development.
A. The increased access to microlending institutions for women, such as the Grameen Bank
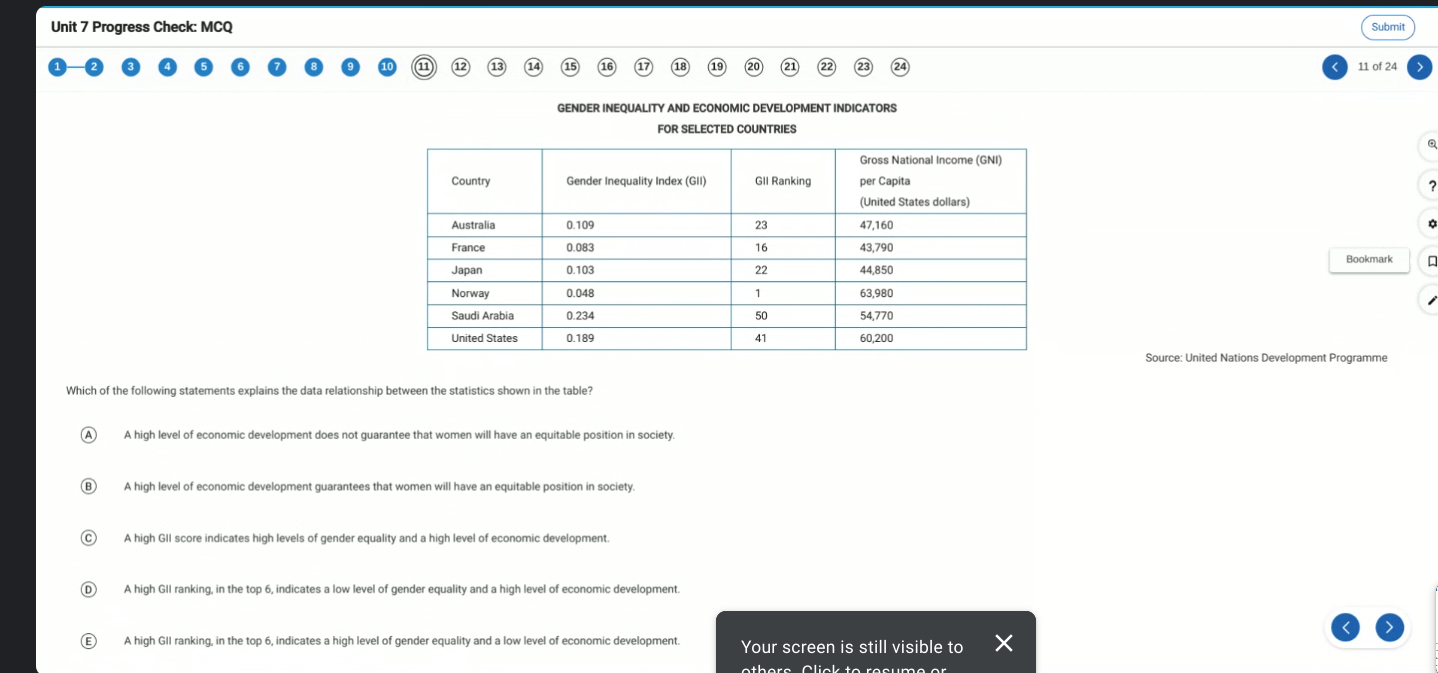
A. A high level of economic development does not guarantee that women will have an equitable position in society.
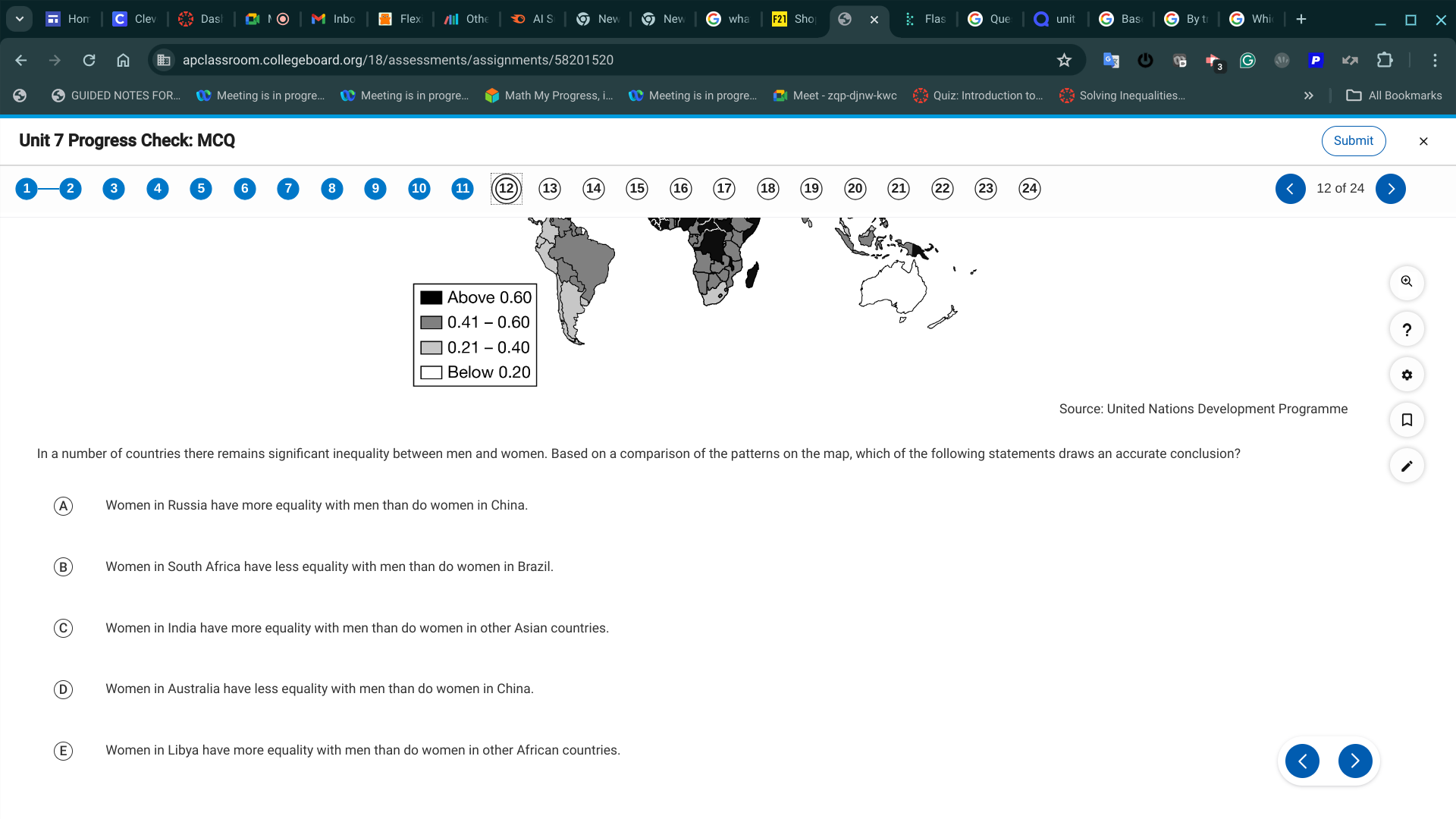
E. Women in Libya have more equality with men than do women in other African countries.
B. places emphasis on developed nations having less developed nations to exploit for resources
D. World system theory provides little explanation about how a country like South Korea could rise from a peripheral country to a core economy.
B. Rostow made the inaccurate assumption that all countries want modernization as defined in the model and would pass through the outlined stages in order.
D. the economic principle of comparative advantage
E. Increased funding opportunities for individuals in less developed countries have led to increased economic stability on a local level and trade opportunities with other countries.
C. Because the global financial system is interconnected, banks in other countries were negatively affected by the crisis in the United States.
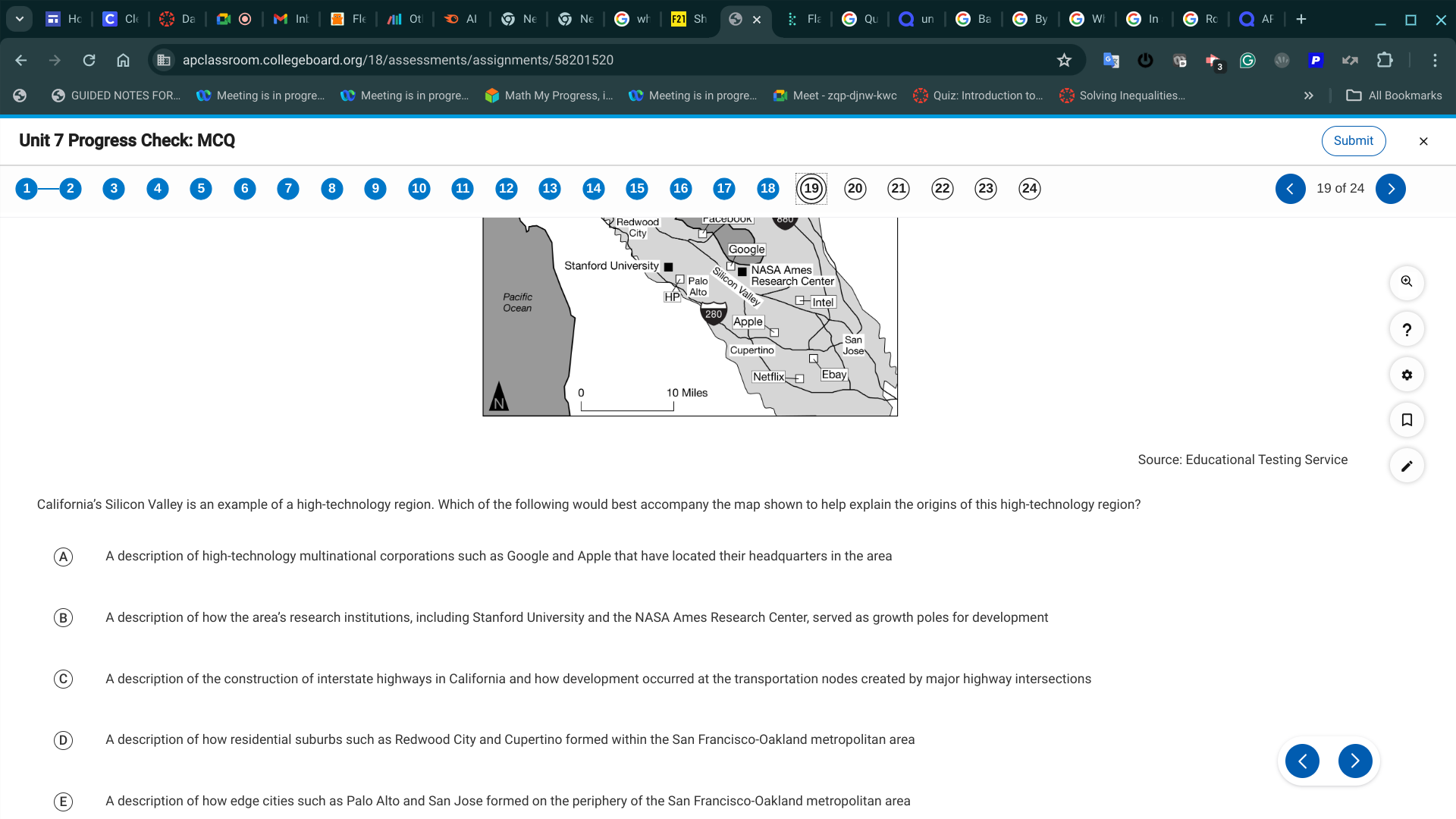
B. A description of how the area’s research institutions, including Stanford University and the NASA Ames Research Center, served as growth poles for development
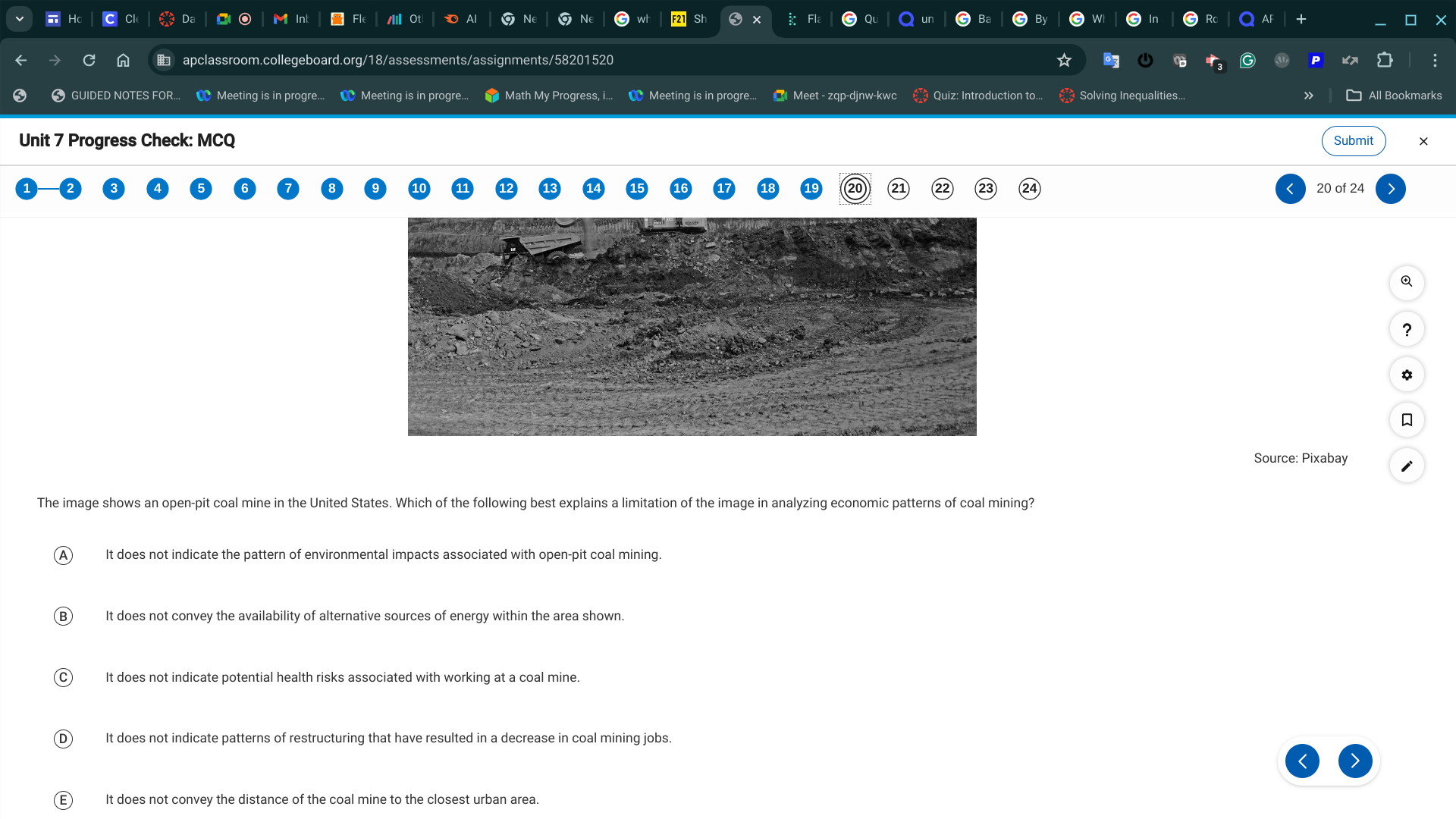
D. It does not indicate patterns of restructuring that have resulted in a decrease in coal mining jobs.
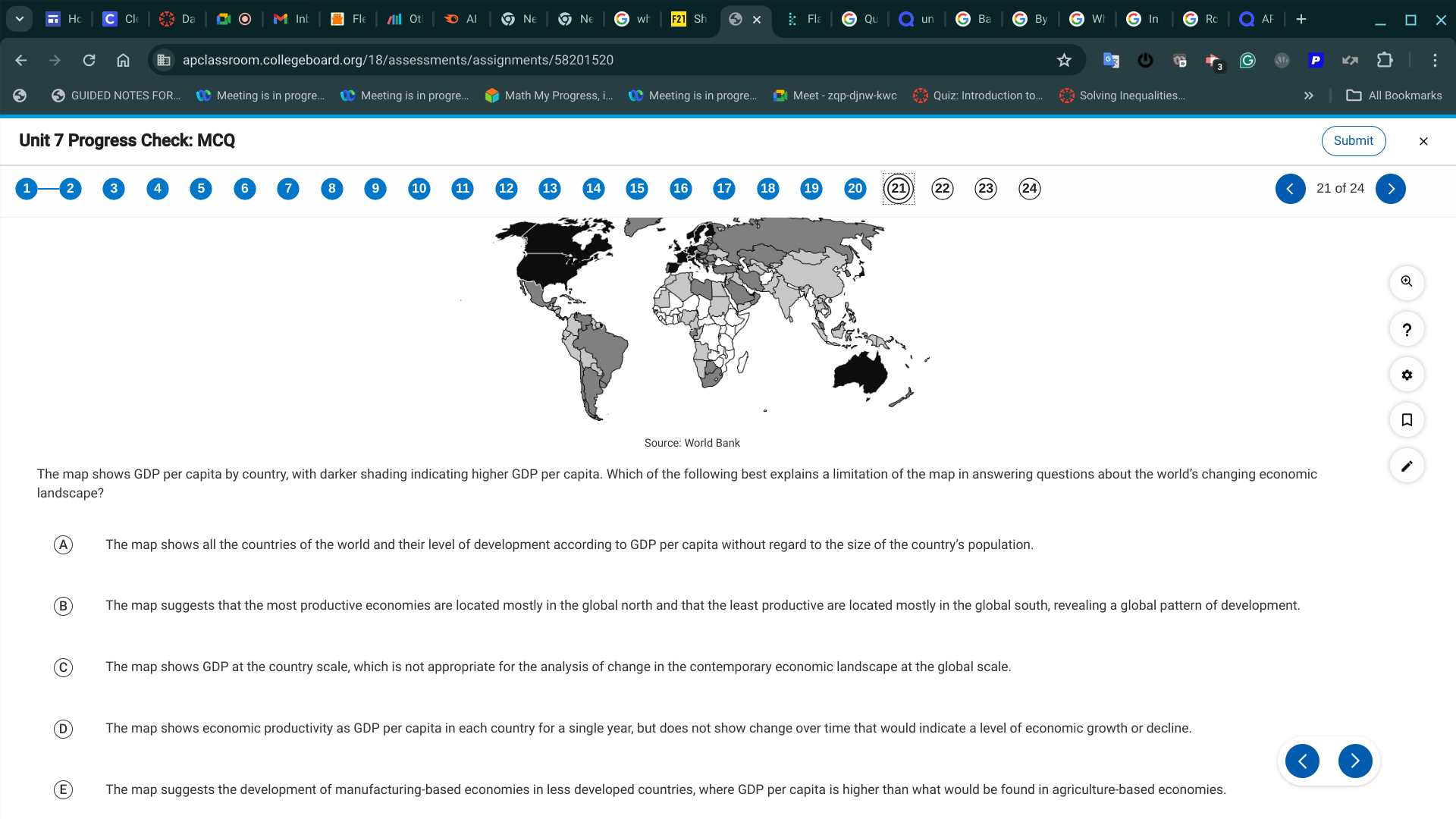
D. The map shows economic productivity as GDP per capita in each country for a single year, but does not show change over time that would indicate a level of economic growth or decline.
C. Global ecotourism does not necessarily lead to local economic sustainability, as workers might not be paid a living wage at ecotourism resorts.
E. Microfinance loans enable people to start small businesses, which contributes to the goal of ending poverty.
E. The development of small, locally owned lodges near ecological preserves in the Brazilian Amazon due to tourists’ desire to benefit the local economy and minimize their environmental impact