Archaeology Exam 1 - 9/25
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
field walking
non-invasive method of surveying an archaeological site and collegting without digging or altering the site
dendrochronology
materials/sites can be dated by tree ring growth
techniques of geophysical survey
magnetometry, ground-penetrating radar, earth electrical resistance, aerial photography, LiDAR (light detection and ranging)
what category of scientific dating is dendrochronology?
monumental
half-life
the time it takes for an element to reduce to half its original value
half-life of carbon-14
5730 ± 40 years
common phrase for radiocarbon dating
scientific dating
what category of scientific dating is carbon dating?
radiometric
principle of superposition
what is above is more recent than what is below and vice versa
stratigraphy
as debris accumulates over time, material laid down earlier will be underneath newer. layers of sediment build up over each other.
terminus post quem
time after which
event happed after “___”
terminus ante quem
time before which
event happened before “___”
heirloom effect
heirloom artifacts are kept long after their date of production and not deposited until long after
surface survey
mapping, geophysical prospection and remote sensing, field walking, settlement pattern survey
seriation
changes in proportions of types through time
typology
definition of types by shape and decoration
correlation and cross-dating
comparison of finds in one context with discovery having a continuous record, particularly written, or with a precise date
Joann Winckelmann
Renaissance classicist who came up with the periods of the ancient world
terminus ante quem for the appearance of true bronze in the Aegean
3000 BCE
changes in agriculture from Neolithic to the Bronze age
domesticated animals (plowing, carts)
secondary products (milk, wool, hair, blood)
olive and grape cultivation
copper tools
what do agricultural changes tell us about socio-economic development from the neolithic to the bronze age?
suggests some people have more land
indirect evidence of inequalities
corridor house
ex. House of Tiles at Lerna
administrative and economic centers
The House of Tiles
Lerna, The Argolid
EH II
ca. 2700-2200 BCE
most famous example of a corridor house
activities and practices taken place in a corridor house
feasting
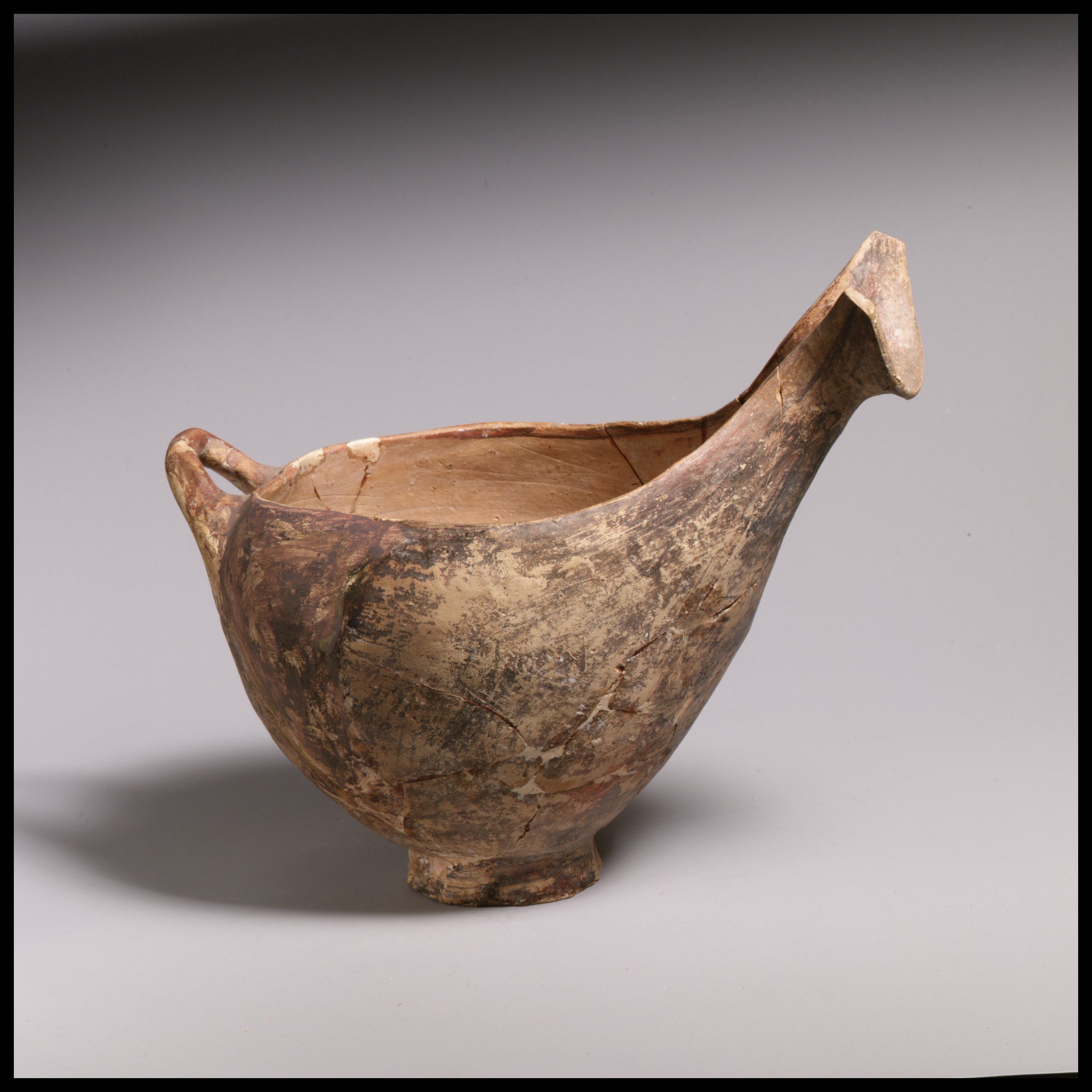

sauceboat
Troy and Peloponnesos
used for drinking
skeuomorph
something meant to resemble something else
decorative stone features
assemblage
a collection or gathering of things
ex. items buried with the dead

cycladic frying pan
spiral motif
used in decoration and religious ceremonies
made from stone and earthenware
how have looting and forgery made interpretation of FAFs difficult?
smuggled out of country
justified by claiming artistic heritage of Greek work
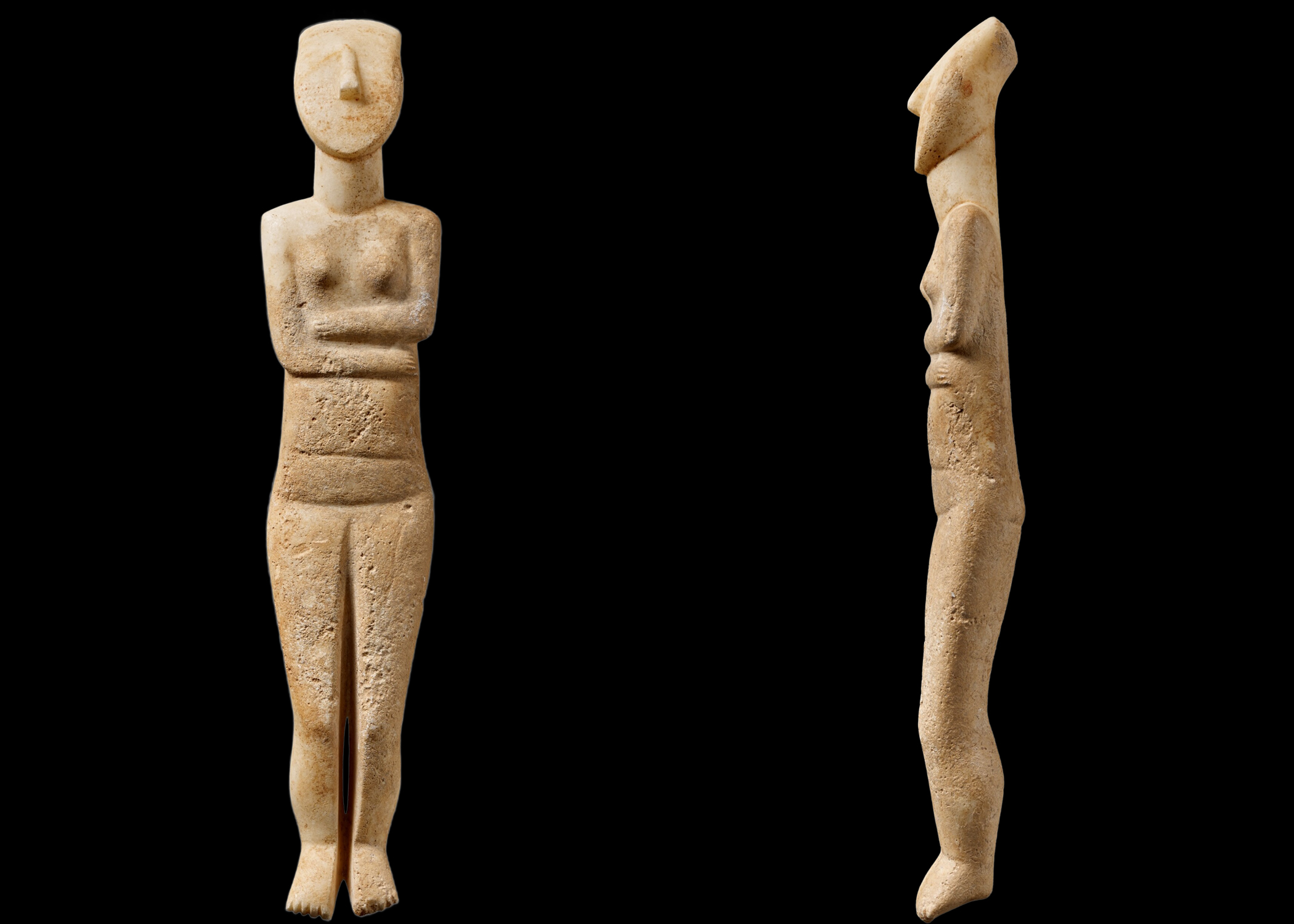

folded arm figure (FAF)
nude figure (usually female) with wedge-shaped heads and arms crossed over the chest
painted to emphasize individual personhood
most are fake
obsidian
glass-like volcanic rock
cyclades have abundant:
limestone
marble
soapstone
pumice
emery
obsidian
important line of evidence of different regional traditions (especially community values)
differences in mortuary customs
individual burials in north central crete
house tombs in east crete
tholos tombs in south crete
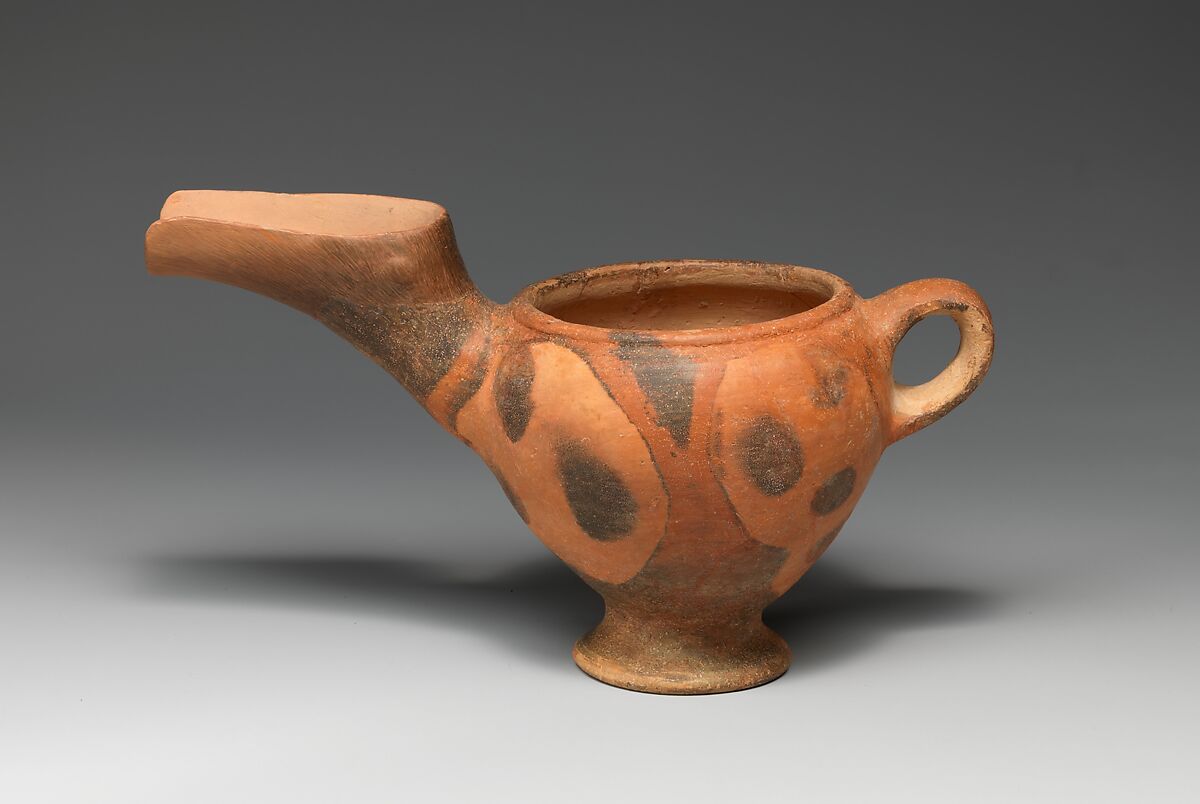

vasiliki ware
early minoan
“tea pots” or “egg cups” meant to resemble egyptian stonework but made from wet wood
first interregional style
evidence of structured deposition

koumasa figurine
north crete
resembles folded arm figure

early Minoan tholos tomb
circular building
used for rite of passages
three courtyard complexes developed in EM III / MM I
Knossos (central courtyard)
Malia (staple foods and workshops)
Phaistos (food storage)
how are minoan courtyards oriented?
series of wings surrounding a central court
includes a lustral basin and pillar crypt
what do minoan courtyards have in common with tholos tombs?
tombs
thick walls
domed roof
located in cemeteries or burial grounds
courtyard
multipurpose spaces
located in palace complexes

kouloura
subsurface pit with stone
Phaistos, Knossos, Malia
store excess harvest
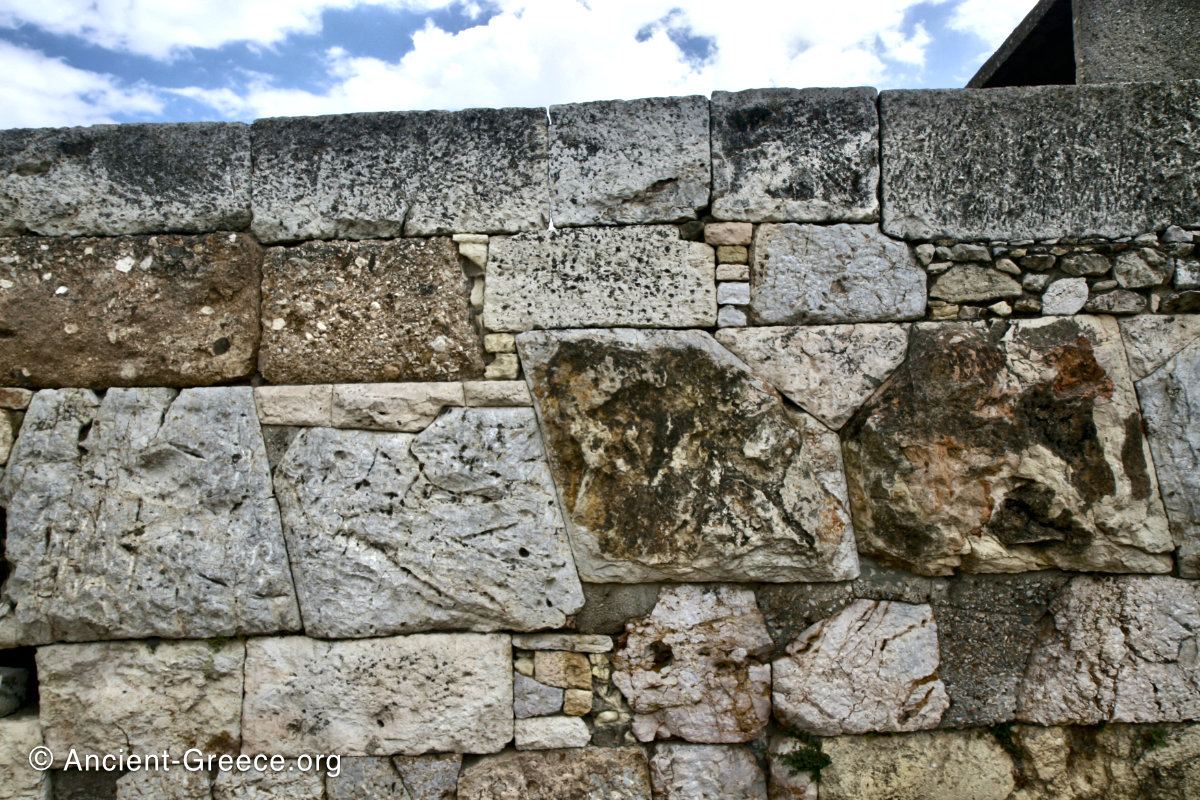

ashlar masonry
building block carved into a rectangular shape
ex. tholos tombs
two types of Minoan ritual sites
cave sanctuaries & peak sanctuaries
rhytons, ceramic body parts as votive offerings
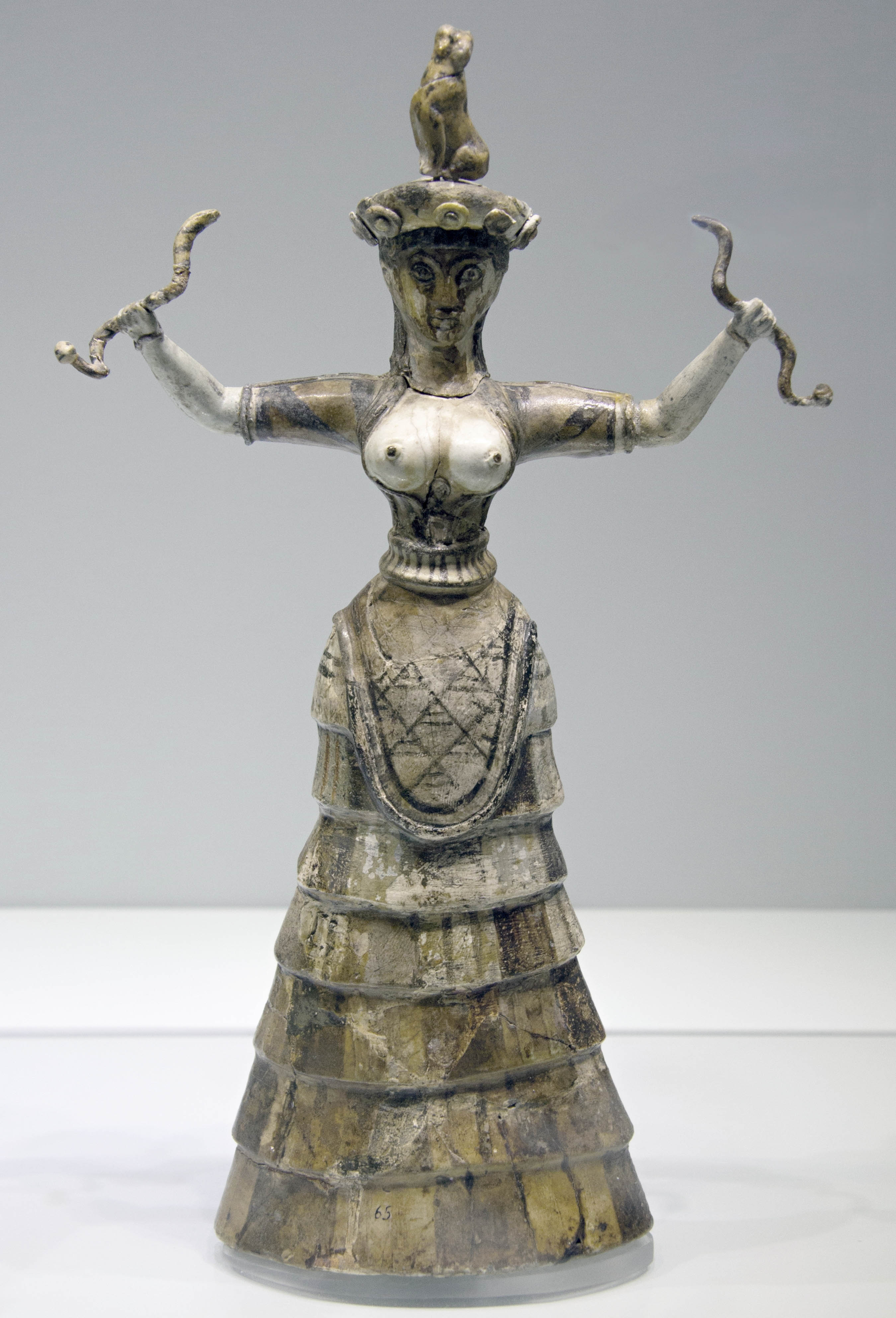

snake goddess
Knossos
1600 BCE, New Palace Period
structured deposition, destroyed and buried with seashells
forgeries developed in 20th century

fresco painting
painting while plaster is wet with details added later
ex. “Ladies in Blue” at Knossos

chrystelephantine
gold and ivory
votive/cult statues
ceremonial architecture
tripartite facades
pillar crypts
pier-and-door partitions
horns of consecration
minoan religious symbols and motifs
bulls
double axes
women
purpose of pier-and-door partitions
flow of traffic
ceremonial
ventilation
Xeste 3
red streaks represent saffron, flowers, or menstrual blood
goddess represented by monkey and griffin
haircut reflects social status
coming of age ceremony
walls are like a big instruction manual
example of courtyard building/complex
ashlar masonry & horns of consecration
4.2 ka BP event
Late 3rd Millennium Mega-drought
supra-reigonal rapid climatic change occurring between 2200 and 2000 BCE
changes after mega drought
sites destroyed by fires or abandoned
rebuilt on top of
example of monumentalizing during EH
EH II
Lerna, Kolonna
ex. corridor houses, tholos tombs
intentional
Middle Helladic Period
2000-1700/1600 BCE
regrowth of population
beginning of shaft grave era

minyan ware
fine gray burnished ware
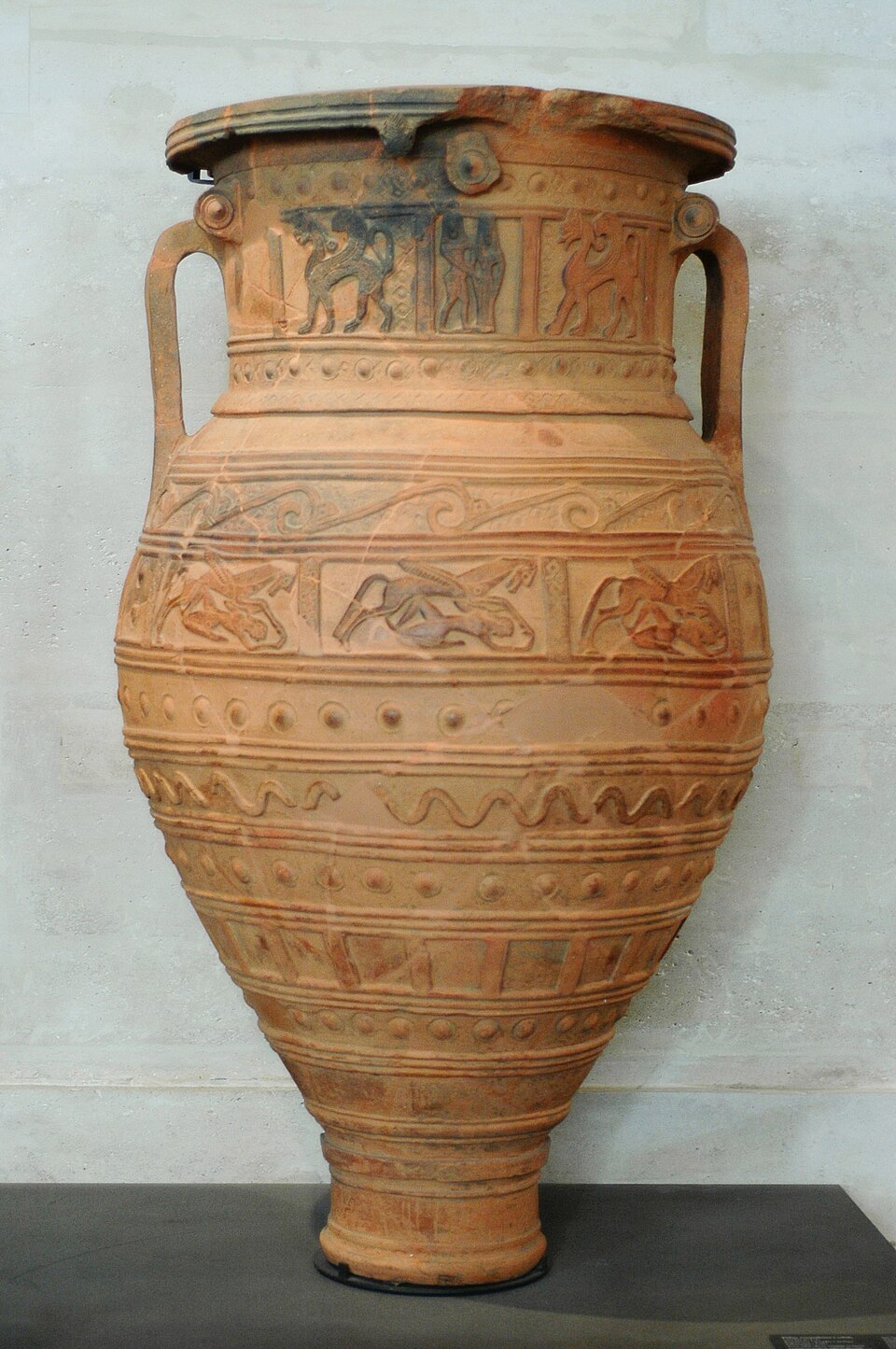

pithos
storage jar

tumulus
artificial mound
warrior’s shaft
ex. Griffin Warrior
bronze vessels and weapons
gemstone
gold signet ring

cyclopean masonry
MH Kolonna on Aegina
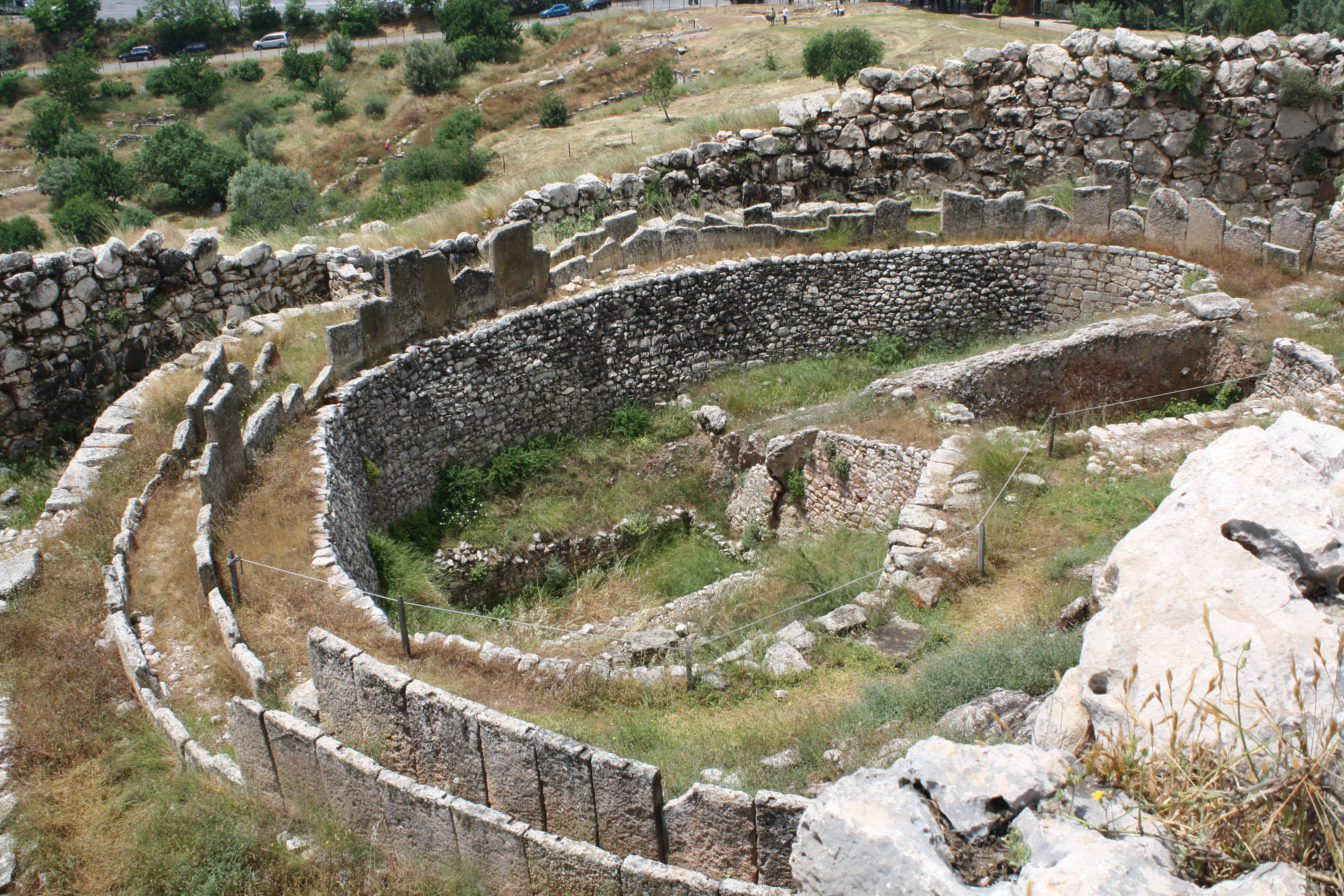

shaft grave
grave at the bottom of deep shaft
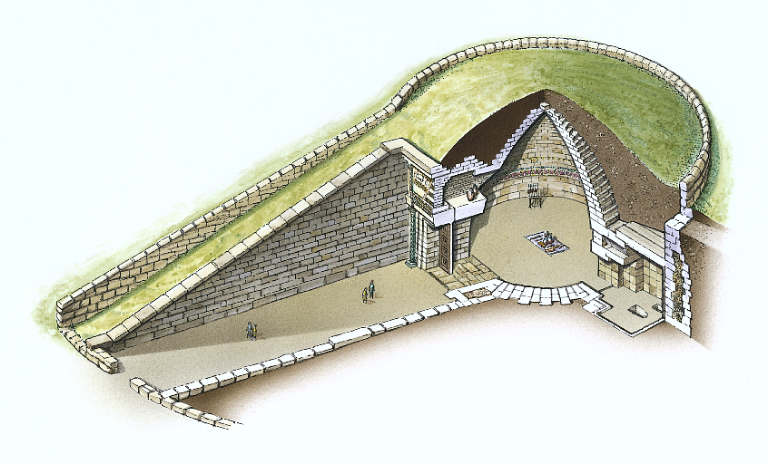
Late Helladic tholos tomb
settlement nucleation
creating a communal area instead of individual houses
apsidal houses

matt-painted ware
lustrous
depicts scenes of sailing and armed persons
were Mycenae’s trade connections more or less than Kolonna?
More because of it’s central location and palace-controlled economy
examples of wealth in Mycenaen grave circles
Grave Circle B
poorer
35 persons in 26 graves
quartz crystal, Baltic amber, death mask
Grave Circle A
richer
19 persons in 6 shafts
gold jewelry for women
death masks, breast plates, and weapons for men
sources of wealth in Mycenae
pottery
gems, jewelry, glass
metalworks

_
Mask of Agamemnon
Heinrich Schliemann
fake
filigree
ornamental work of fine gold or silver wire
niello
engraved designs in black sulfur
pyxis
wooden box for death mask
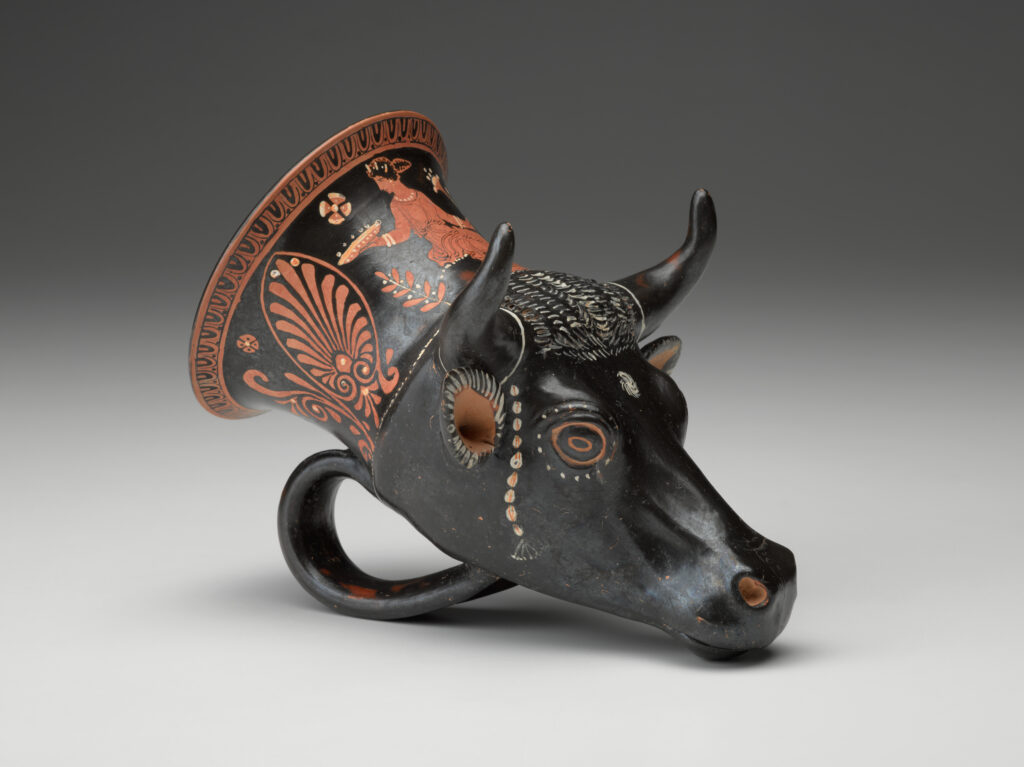

rhyton
bull’s head, lion’s head, stag
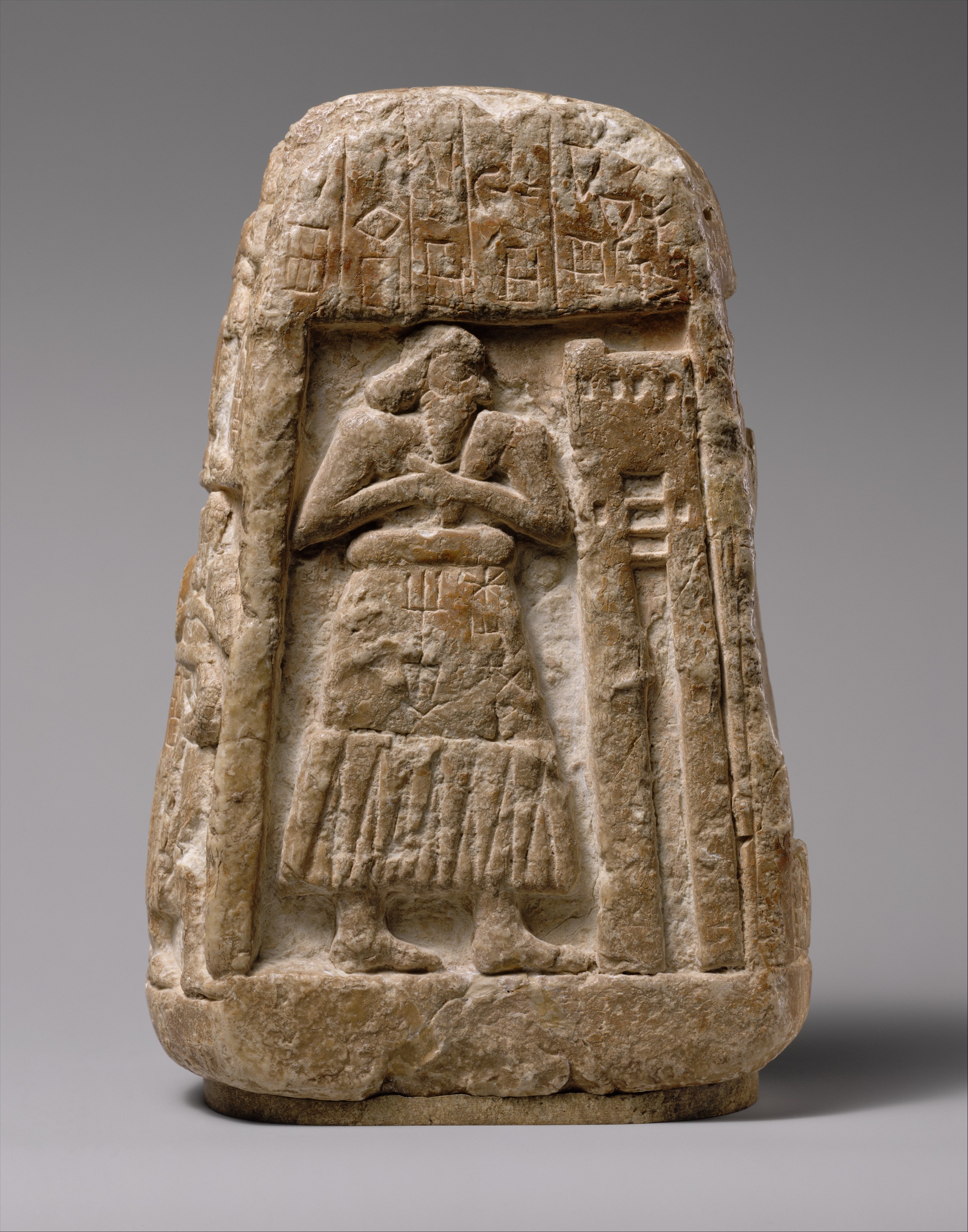

stela
upright slab of stone
inlays of Grave Circle A swords & daggers
hunting
abstract waves
Nilotic landscapes
during heyday of House of Tiles, what else was happening?
Keros-Syros and FAFs in Cyclades
Pyramids in Old Kingdom
House graves and tholos tombs in Crete
three Mycenaean palaces
Mycenae
lion’s gate
linear b
Tiryns
lion’s gate
linear b
Pylos
linear b
kind of masonry in Mycenaean sites
cyclopean
how is corbeling used?
stacking progressively smaller rings of stone on top of one another and trimming the inner corners to create a smooth, beehive-like dome
how do LH tholos tombs differ from EM?
Mainland
vaulted roofs
buried under mounds
sophisticated construction
only for ruling elite
Minoan
above ground
smaller w/ rough masonry
communal
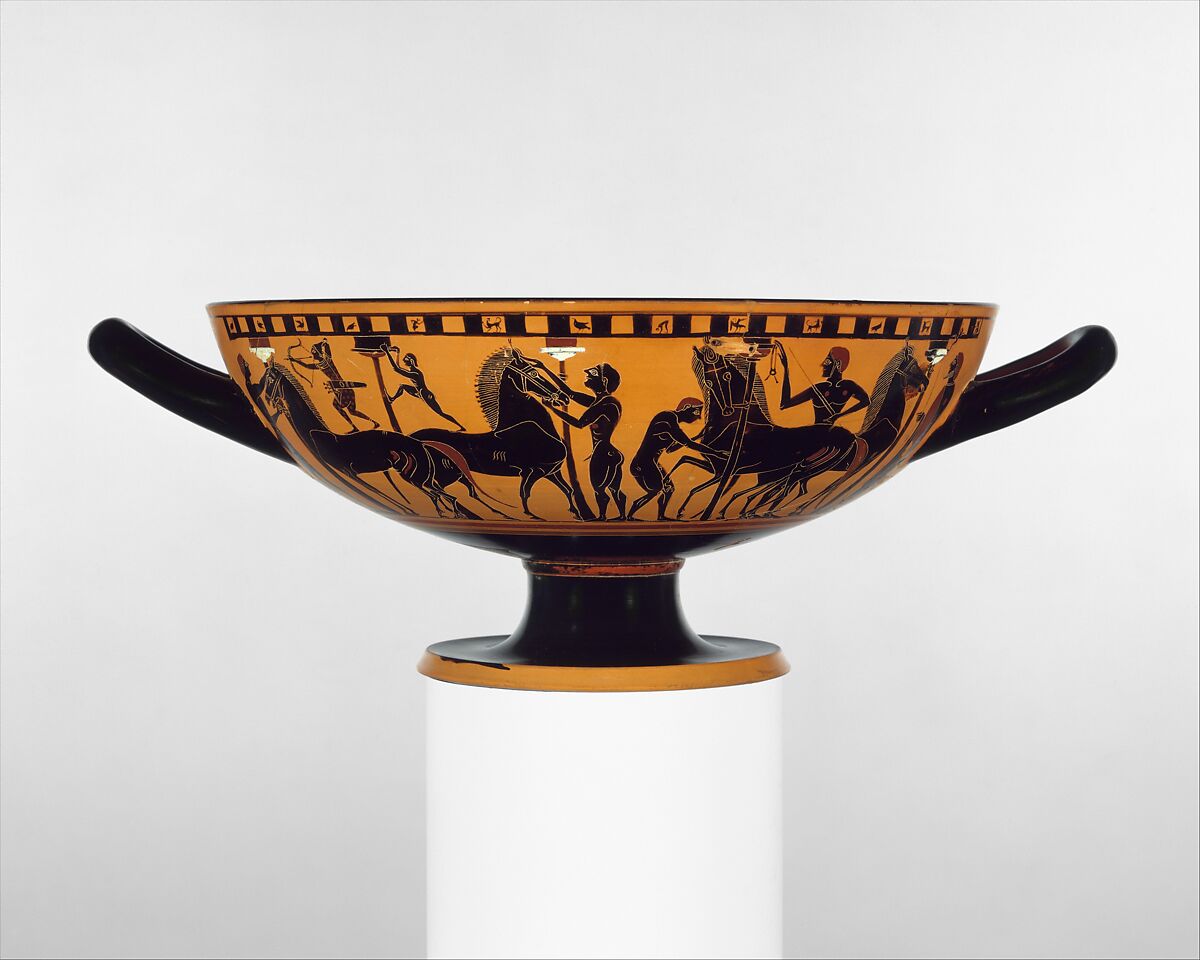

kylix
drinking cup
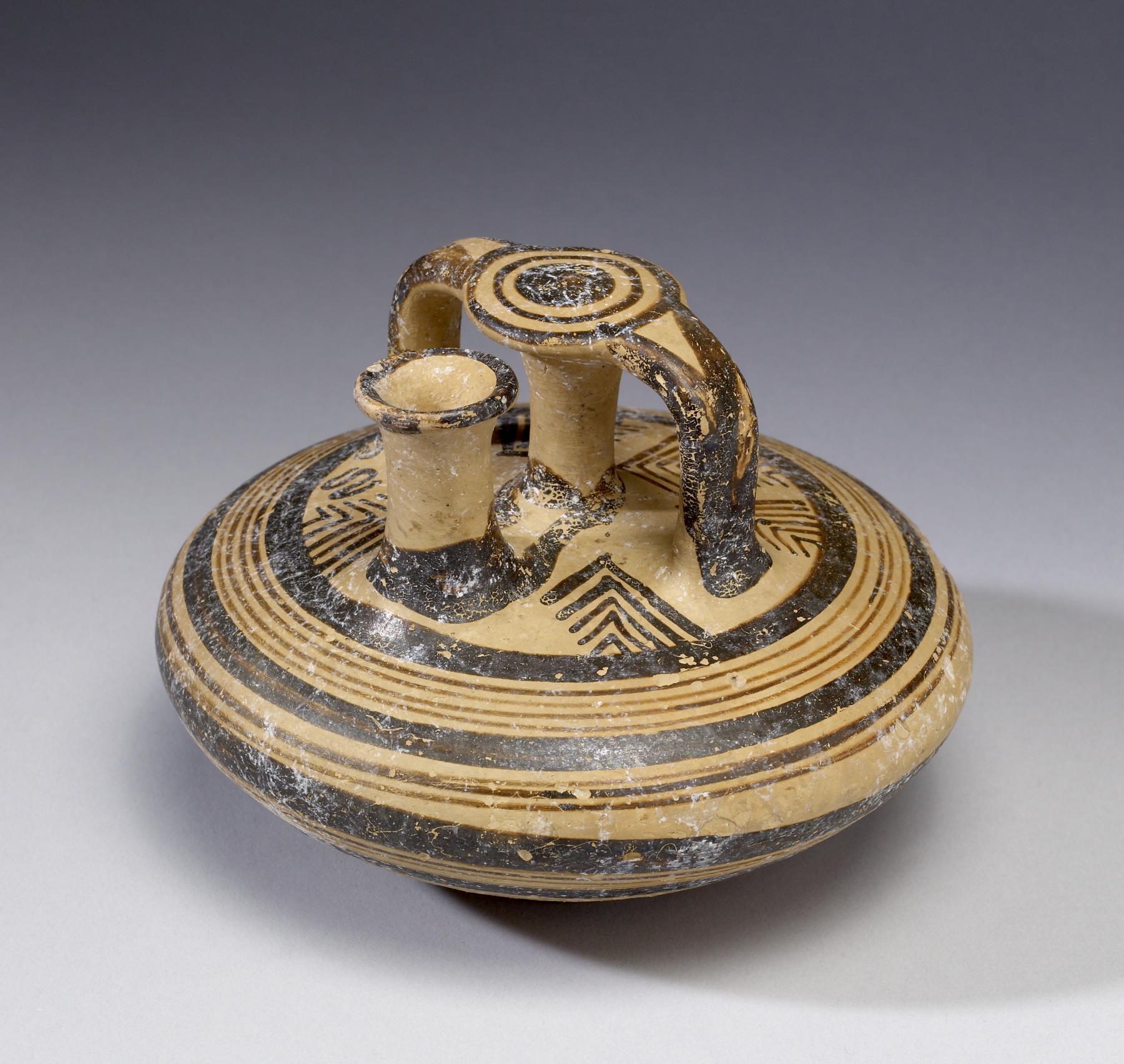

stirrup jar
stirrup like handles
used for holding oil
megaron
large rectangular room with a hearth at center
contains porch, vestibule, and throne/hearth room
__
dromos
avenue leading into a temple or tomb
stomion
deep doorway of post and lintel construction (under a relieving triangle)
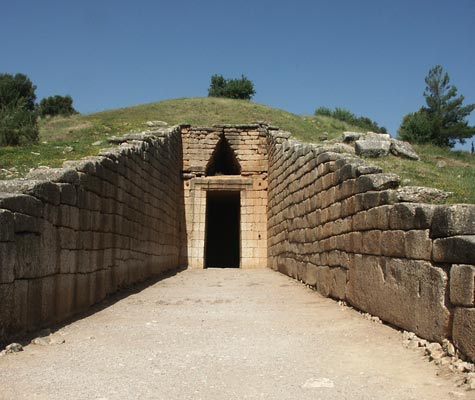

relieving triangle
triangular space above lintel to transfer weight
Cretan influence on Mycenean material culture
procession fresco
gold signet rings
frescoes of warfare
Knossos
center of political power on Crete after eruption of Thera
evidence of Greek-speaking administration
Linear B texts
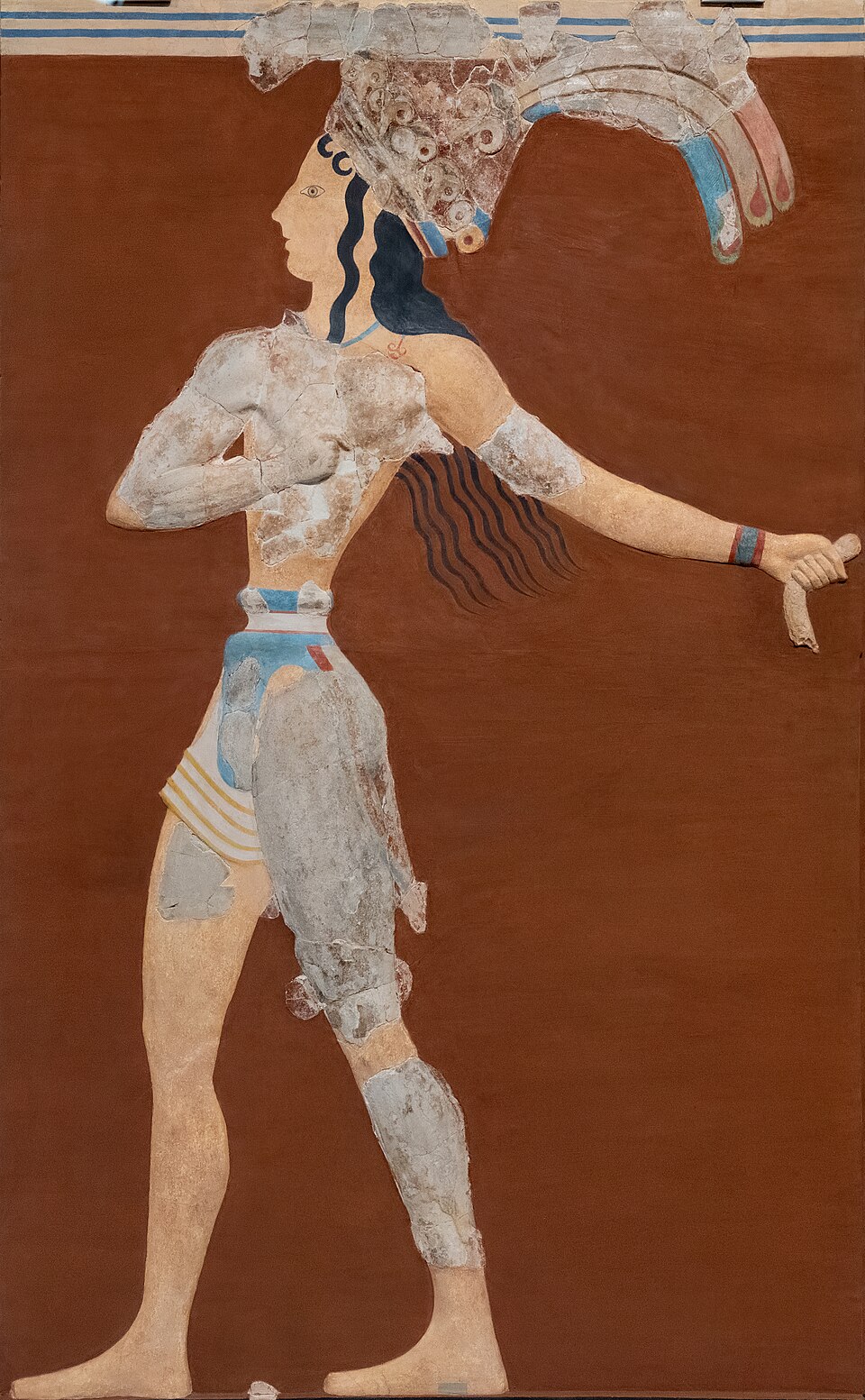

Prince of Lilies
modern reconstruction at Knossos
arms and legs and headdress mismatch
lustral basin
indoor sunken area resembling a walk in pool