Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
matter
anything with mass + occupies space
All matter consists of
92 naturally-occurring elements
elements
cannot be broken down into substances with different properties
CHNOPS
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur → comprise 95% of organisms' body weight
atom
smallest unit of an element that retains its properties
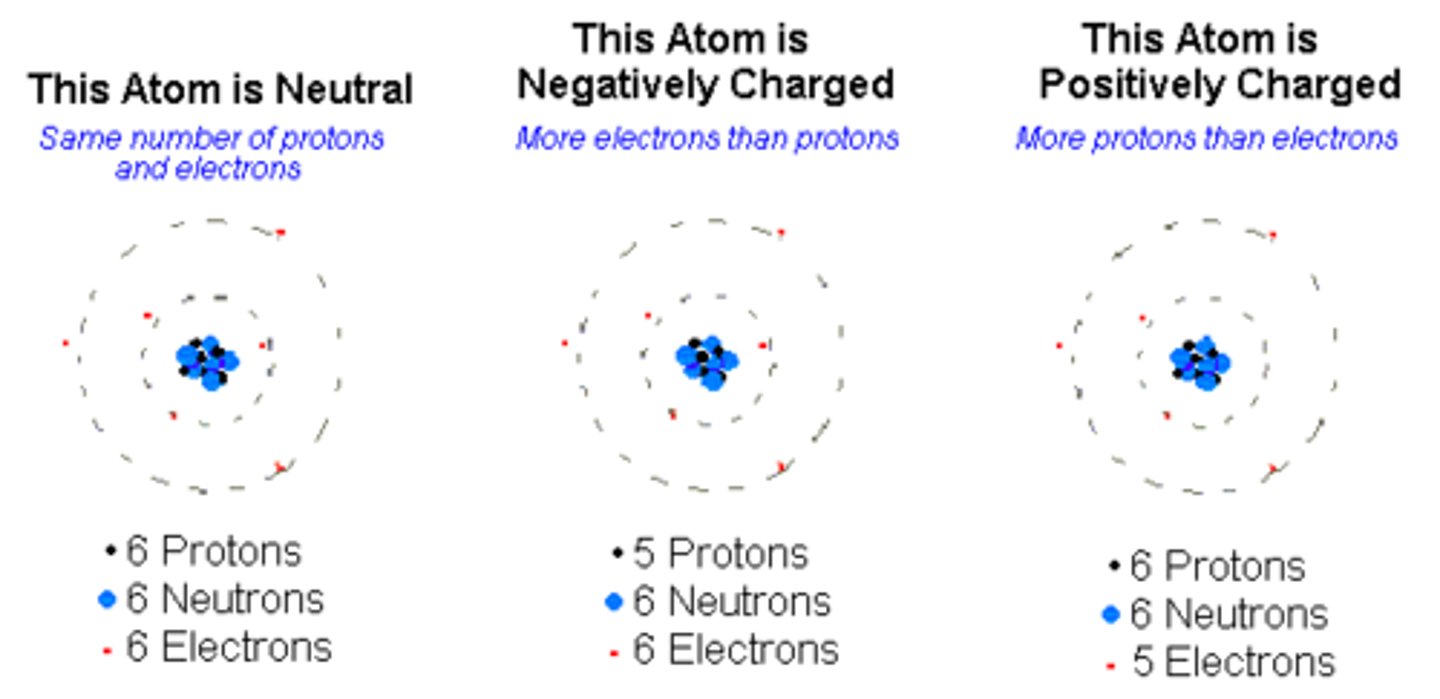
protons
positively charged particles that define the element
neutrons
neutral particles in an atom whose number can vary
electrons
negatively charged particles in an atom whose number can vary
atomic number
number of protons in an atom
mass number
protons + neutrons
both protons and neutrons =
1AMU
atomic mass
weighted average of all isotopes of an element
isotopes
same element, different number of neutrons
unstable isotopes
undergo radioactive decay (release energy)
# of protons usually
equals the # of electrons
valence shell
outermost electron shell of an atom
Bohr Model
1st shell - 2 electrons; outer shells - 8 electrons
octet rule
atoms are most stable when valence shell is full (2 or 8 electrons)
≤ 3 electrons
≥ 5 electrons
→ atoms tend to donate
→ atoms tend to receive
molecule
2+ atoms bonded together
compound
2+ different elements bonded together (ex: CO₂, H₂O, C₆H₁₂O₆)
chemical bonds
caused by interactions between valence electrons
ionic bond
transfer of electrons between donor and acceptor; opposites attract
covalent bond
sharing of electrons between atoms (single, double, or triple bond)
nonpolar covalent bond
equal sharing of electrons (H-H, O-O)
polar covalent bond
unequal sharing of electrons, depends on electronegativity
Electronegativity
ability of an atom to attract electrons
water
polar molecule (not symmetrical)
hydrogen bonds
weak bonds between molecules due to attraction between slightly positive and slightly negative atoms
solvent
most abundant component in a solution
solute
dissolved component in a solution
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water
Hydrophobic
water hating
pure water
neutral
Acid
adds H⁺ ions (ex: HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻)
Base
adds OH⁻ ions (ex: NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻)
pH scale
measure of H⁺ concentration; <7 = acidic, 7 = neutral, >7 = basic
buffers
substances that resist pH changes, maintaining homeostasis in biological systems.
pH < 7.0
pH > 7.8
acidosis
alkalosis
Period
a horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
Group
Vertical column of elements in the periodic table, Contains elements with similar properties because of their simlar electron configurations.
Eletronegativity
the tendency of an atom to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself
Atom
The most basic unit of matter; the smallest particle of an element
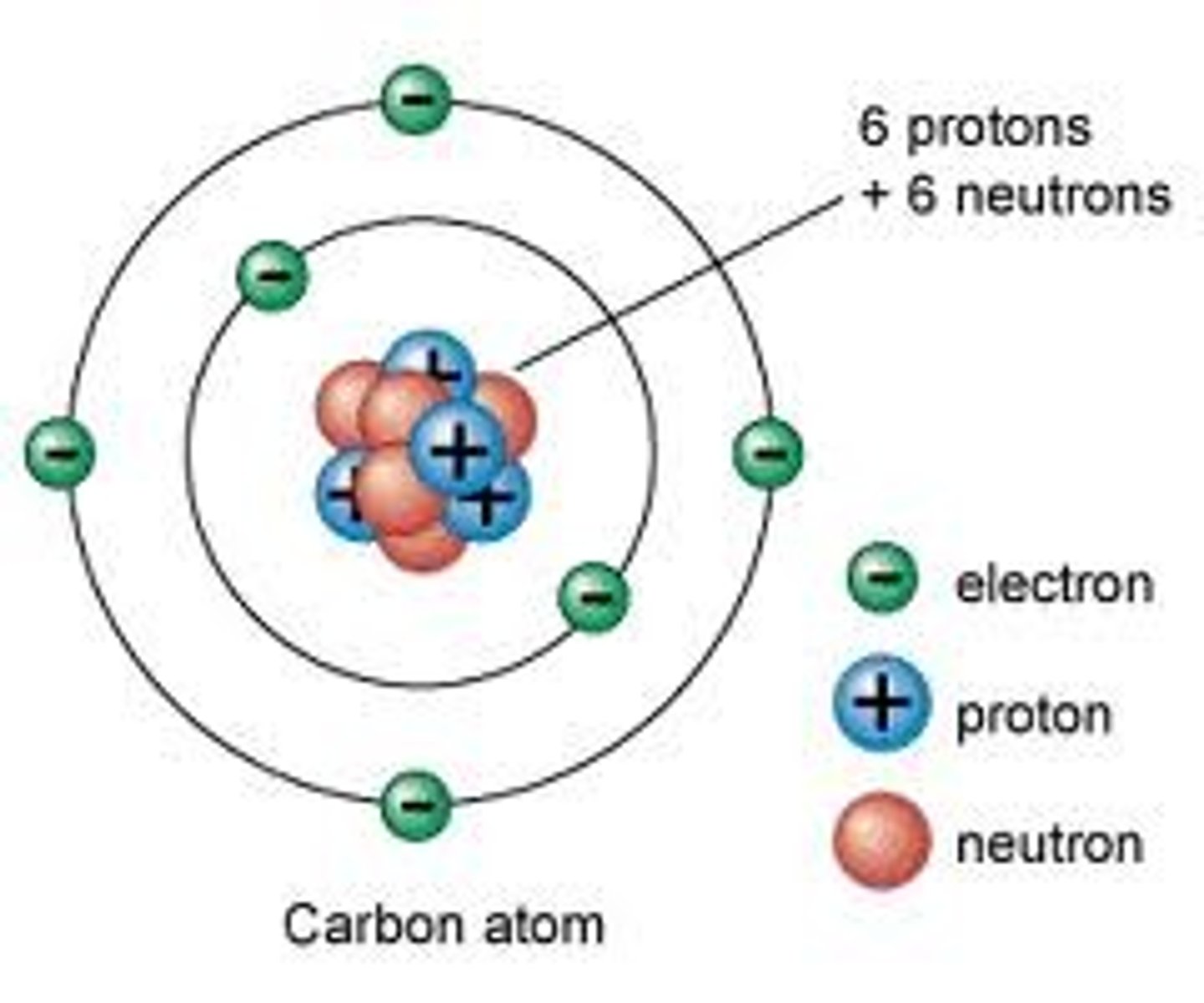
Structure of an Atom
Consists of mostly empty space; Protons (+) and neutrons (0) make up the tiny, dense nucleus. Electrons (-) exist in orbitals at various energy levels surrounding the nucleus. The electrons involved in forming chemical bonds occupy the outermost energy level (AKA the valence shell)
Ion
An atom with a positive or negative electric charge