Human A&P, Ch. 5
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Integumentary System
Most visible & largest organ system
Protection from the environment
Thermoregulation
Excretes some waste products
Lipid storage
Immune response (1st line of defense against pathogens)
Sense stimuli: temperature, pressure, touch, & pain
The Integumentary System has _____ tissue types.
All
Keratinocytes
Dead/dying
Most common cell
Produce keratin
Melanocytes
Pigment cells
Produce melanin
What are the 4 layers of the Epidermis (thin skin)? What is the layer only found in thick skin?
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum (thick skin only)
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
Stratum Basale
The deepest, basal layer
Melanocytes
Merkel cells: touch sensors
Basal cells: become keratinocytes
Attachment to basal lamina
Stratum Spinosum
Keratinocytes have now developed
Melanocytes (squid-looking)
Langerhans: trigger immune response (find & attack pathogens)
Stratum Granulosum
Last layer where cells have nuclei
Keratinocytes start making keratin & keratohyalin
Fully mature cells start making keratin (water-proof protein). Blocks water from coming in & leaving the cell.
Callus formation
Stratum Lucidum
Only found in thick skin
Stacks of dead/dying cells
High amounts or keratin
Cells lack organelles & nuclei
Stratum Corneum
Dead cells
Most superficial layer
Sebaceous & sweat glands maintain these cells
Epidermal Ridges
Finger prints
Generated by the presence of dermal papillae
Valleys: epidermal ridges
Peaks: dermal papillae
What factors influence skin color?
Thickness of stratum corneum (thicker = lighter skin)
Dermal blood supply
Blushing: red color hemoglobin
Pallor: anemia, drop in BP
Bruise: hematoma in skin
Carotene: yellow-orange (dietary)
Melanin
Brown, yellow-brown, & black
Produced by melanocytes
Synthesized & stored in melanosome
Melanosome enter keratinocytes
The more melanin you have, the more resistant you are to UV damage
What does excessive exposure to UV do? (3)
Sunburn
Skin cancer
Damage to fibrocytes
Premature wrinkling
Abnormal connective tissue (leathery skin)
What are the 2 layers of the Dermis?
Papillary layer
Reticular layer
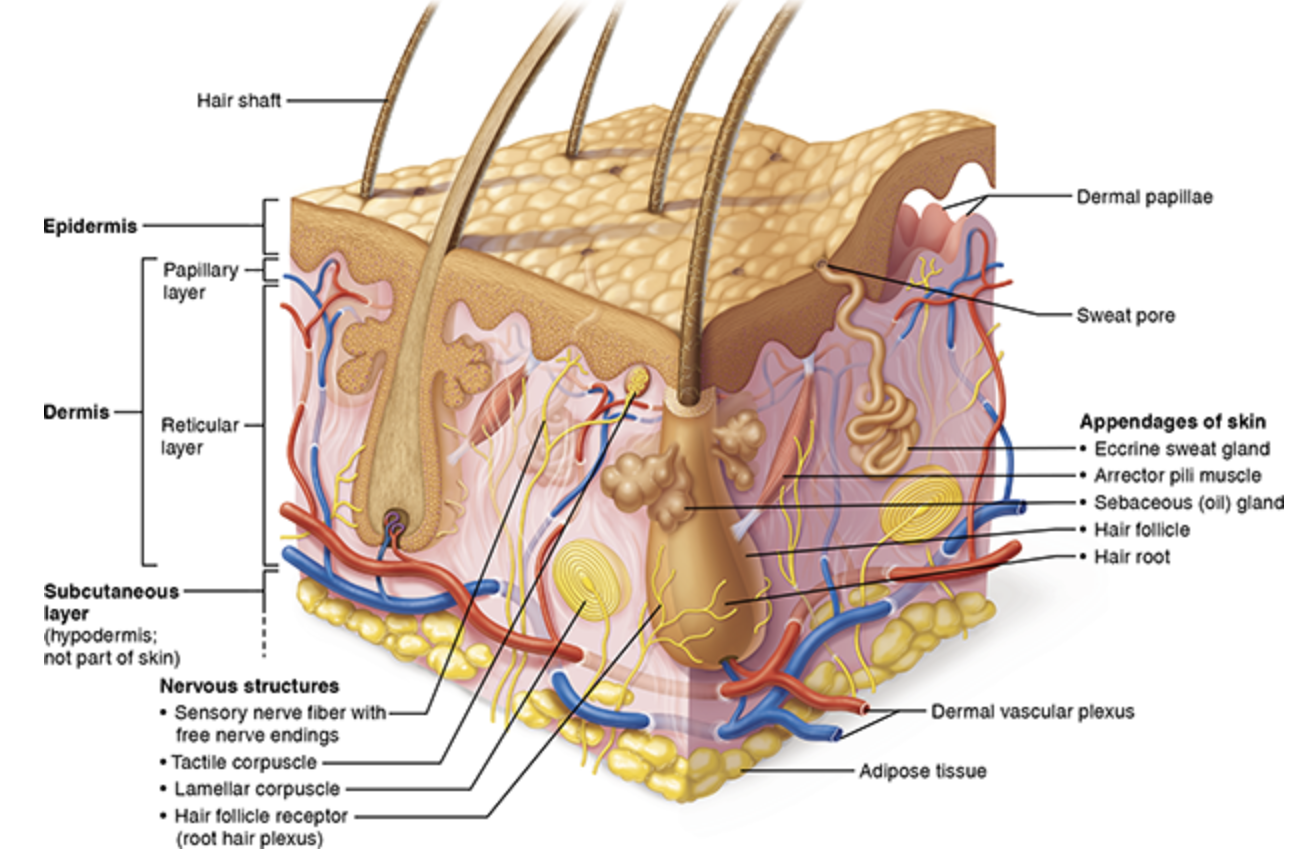
Papillary Layer
Loose connective layer
Dermal papillae
Capillaries
Axons of neurons
Attachment to epidermis
Reticular Layer
Dense irregular connective tissue
Hair follicles
Sweat glands
Sebaceous glands
Collagen fibers provide ______ ______.
Tensile strength
Elastic fibers allow skin to ______ & ______.
Stretch & recoil
What are stretch marks?
Broken reticular fibers
Due to pregnancy & weight gain
Skin doesn’t recoil; causes wrinkles & creases.
What are tension lines?
Collagen & elastic fibers organized in a parallel pattern.
Making an incision along a tension line can significantly reduce scarring.
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer)
Not technically considered a part of the Integumentary System
Help stabilizes Integumentary System
Consists of: adipose tissue & major blood vessels
Due to location of vessels: hypodermic needles & subcutaneous injections
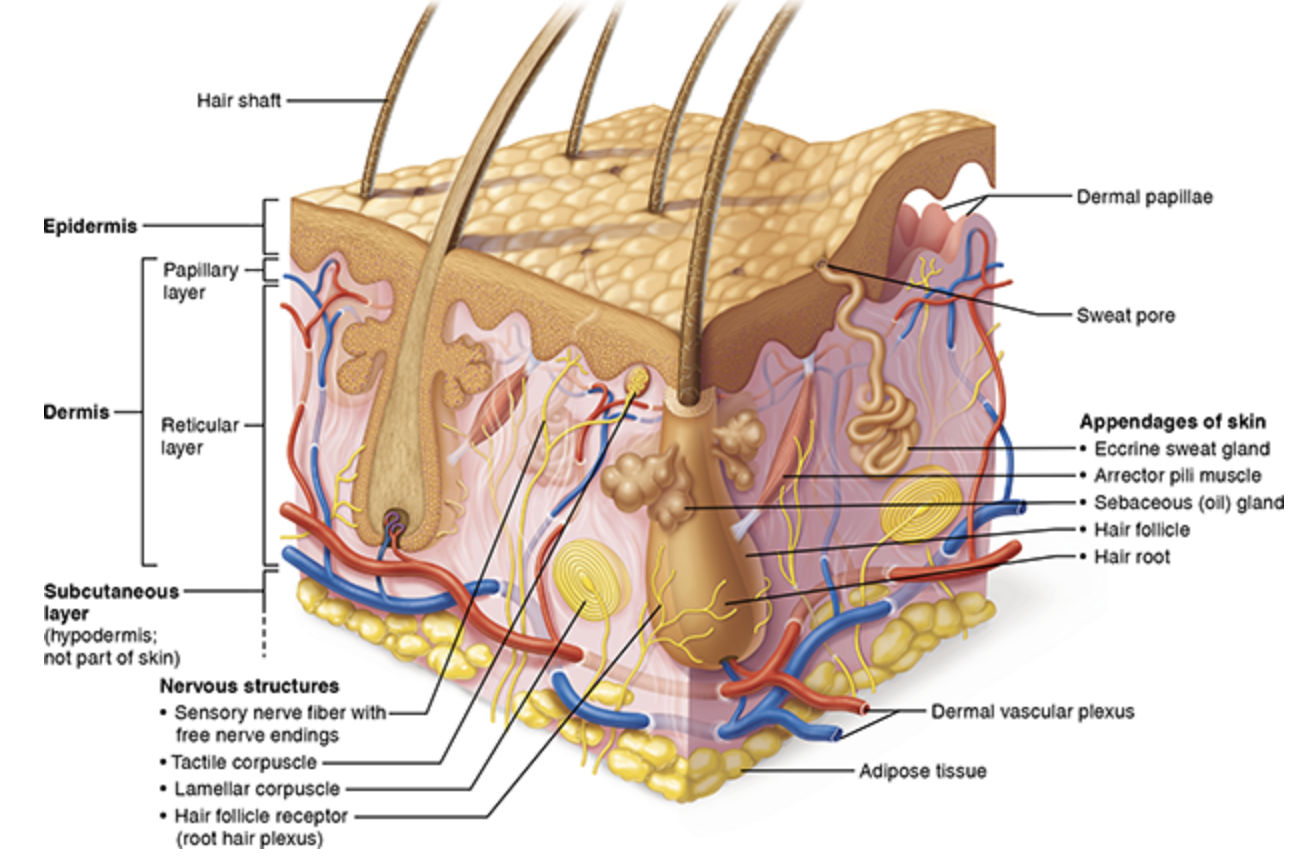
Hypodermis accessory structures (3)
Hair follicles
Exocrine glands
Nails
Also includes mammary & ceruminous glands
Sub-papillary Plexus: blood vessels
Smaller blood vessels
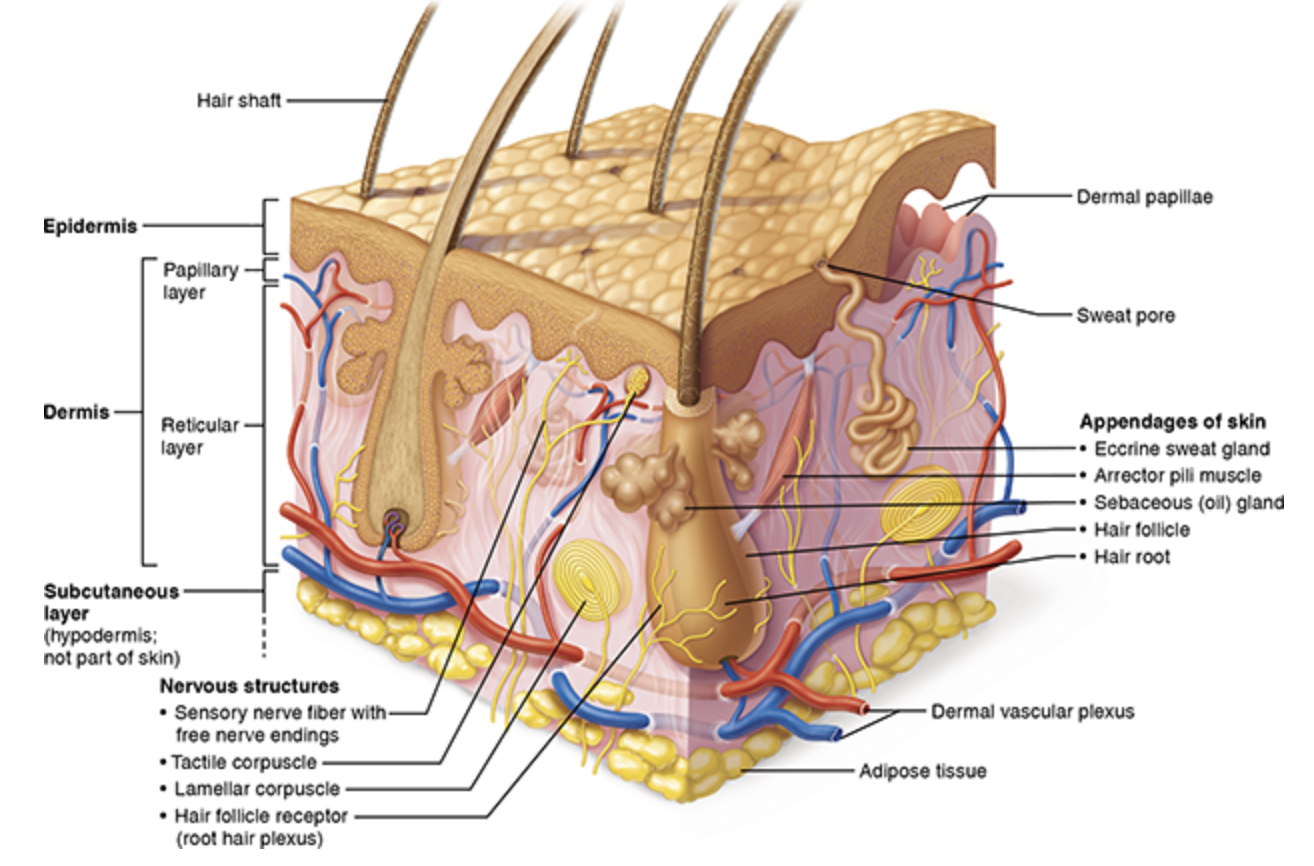
Cutaneous Plexus: blood vessels
Main arteries & veins
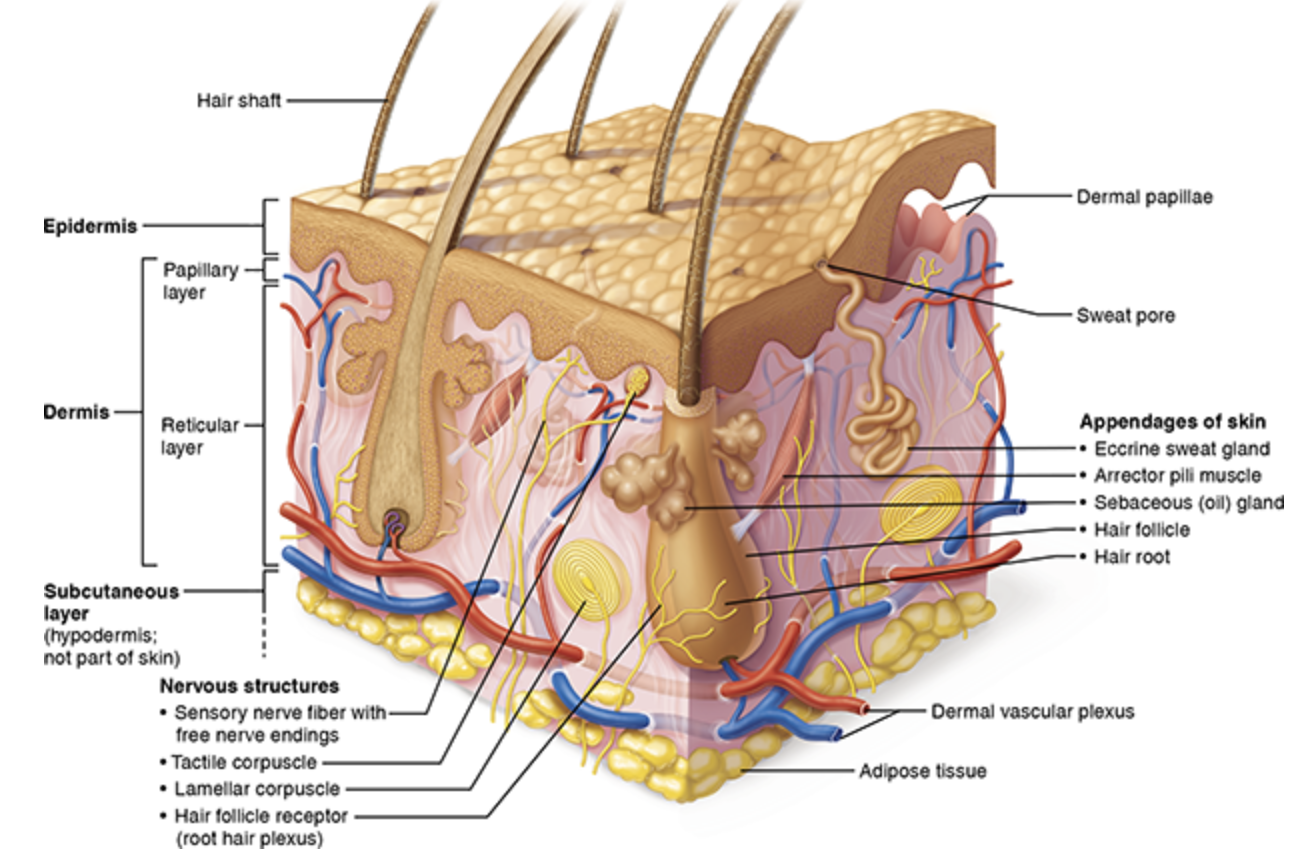
Nerve fibers
Controls blood flow to skin
Adjusts gland secretion rates
Monitors sensory receptors
Proprioception
Allos us to know what our limbs are doing w/o having to look at them.
Tactile corpuscles (receptor)
Light touch receptors
Ruffini corpuscles (receptor)
Stretch receptors
Lamellar corpuscles (receptor)
Deep pressure & vibration receptors
Hair follicles & hair: function
Thermo-regulation (can dissipate sweat)
Secondary sex characteristic
Protection from UV light
Insulation
Contraction of arrector pili muscles; goose bumps
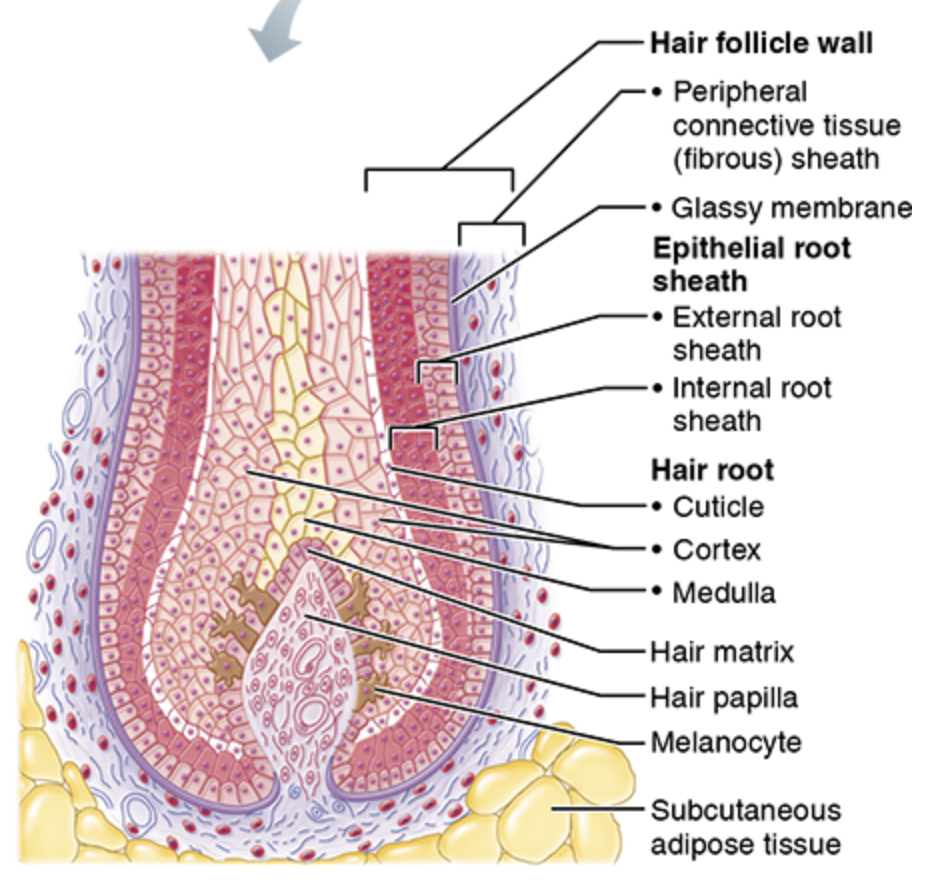
Hair shaft
Non-living, visible portion of hair
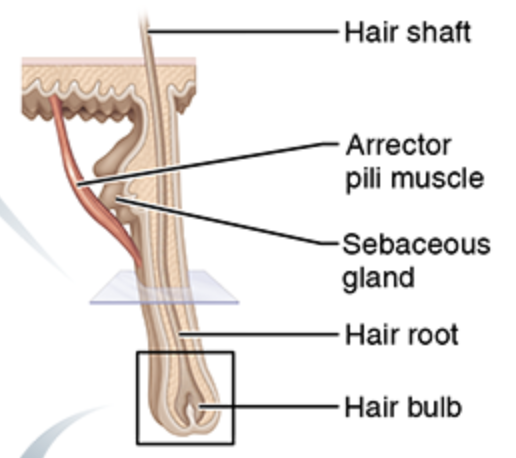
Hair root
Portion of hair in follicle being formed; anchors hair
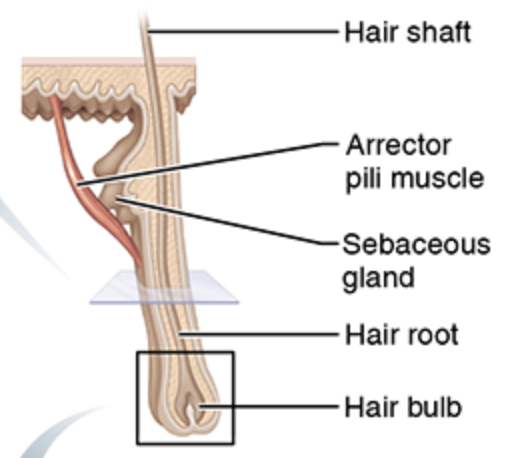
Hair follicle
Organ that form hair
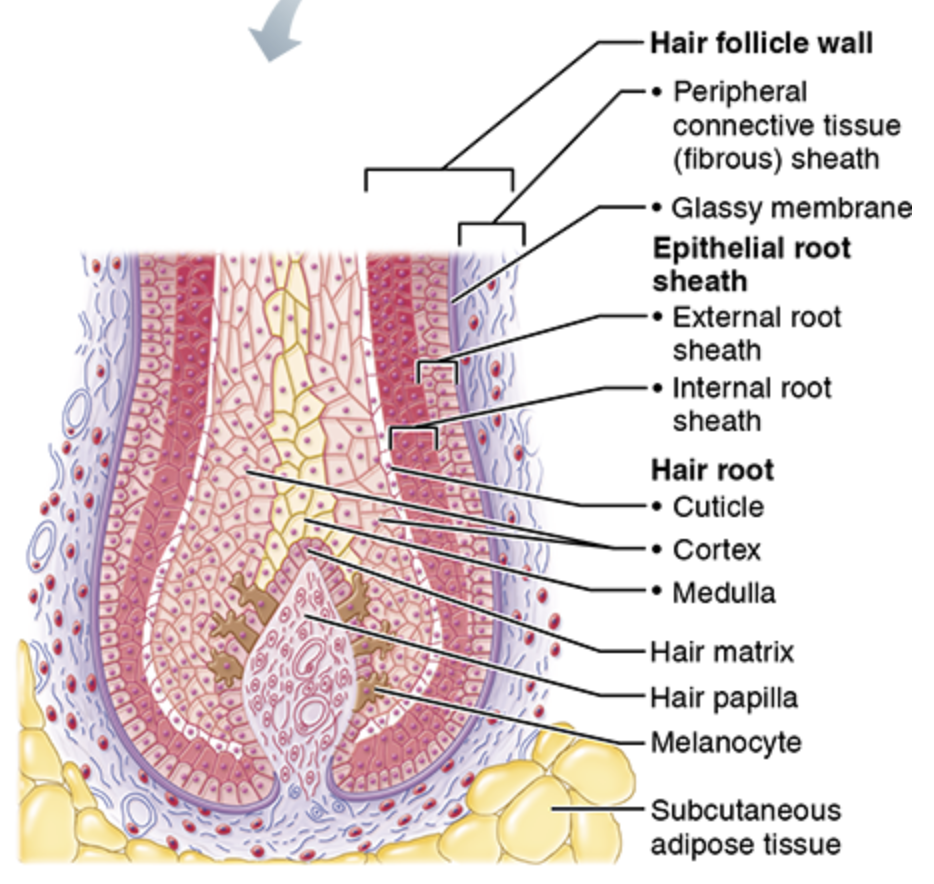
Hair papilla
Nerve & blood supply; supports matrix
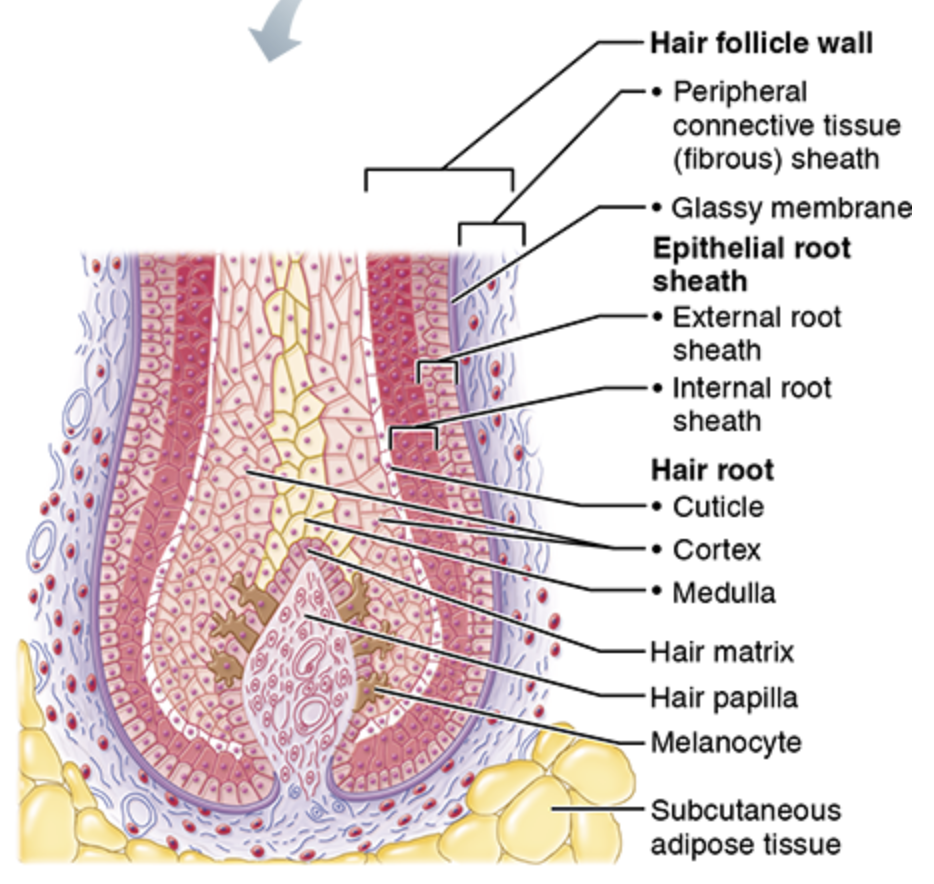
Hair matrix
Basal cells that divide to become hair
Types of Hair: Vellus
Covers most of body; lacks a medulla
Types of Hair: Terminal
Head, eyebrows, eyelashes
Types of Hair: Hair Color
More melanin → darker hair
Decreased production → gray hair
Lack of melanin in hair shaft → white hair
Influenced by: genetics, hormones, & environmental factors
Types of Hair: Hair Shape
Based on follicle shape
Circular follicle: straight
Oval follicle: wavy
Flat follicle: curly
Growth & replacement of hair
Active stage (2-5 years) → resting stage → stays in place → brushing hair/shedding → hair becomes a club hair → leaves head → increases productivity of follicle → regrows hair
Hair grows about ___ ___ per day
0.33 mm
What are the 2 main categories of glands in skin?
Sebaceous (oil) glands
Sweat glands
Apocrine glands
Ceruminous glands
Mammary glands
Eccrine glands
Sebaceous glands
Make sebum
Sebum: lipid mixture
Lubricate epidermis & hair
Antimicrobial properties
No glands on palms or soles
High concentration on forehead, face, & upper back
Sebaceous follicles
Large sebaceous glands, no hair
Apocrine sweat glands
What we think of as a standard/classic sweat gland
Active at puberty (“human musk glands”), produce an odorous secretion
High density in armpit & areola
Secretions can contain pheromones
Eccrine secretion
Eccrine sweat glands
Found all over body
High concentrations on palms & soles (b/c those areas lack sebaceous glands)
Sweat (thermo-regulation, waste excretion, antimicrobial activity)
Eccrine secretion
Nails
Provides protection for distal-most phalanges
Made of keratin