higher biology - unit 2.7: genetic control of metabolism
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
wild strain
the typical form, existing in nature, non-mutated version
a wild strain that produces a desired trait may still lack other important features such as...
genetic stability, ability to grow on low cost nutrients, overproduction of desired products, easy harvesting of product
how can wild strains be improved?
mutagenesis and recombinant DNA technology
exposure to UV light and other forms of radiation or mutagenic chemicals result in...
mutations, some of which may produce an improved strain
recombinant DNA technology
involves the use of recombinant plasmids and artificial chromosomes as vectors
vector
dna molecule use to carry foreign genetic information into another cell
what can a microbe be genetically modified to produce?
substances useful to human e.g. human insulin
where are artificial chromosomes preferable to plasmids?
as vectors when larger fragments of foreign DNA are required to be inserted
what cuts open plasmids?
restriction endonucleases
genetic engineering step 1
select a particular DNA sequence for a desirable characteristic from the donor organism
genetic engineering step 2
splice it into the DNA of a vector
genetic engineering step 3
insert the vector into the host cell
what leaves sticky ends?
restriction endonucleases when they cut open plasmids and specific genes
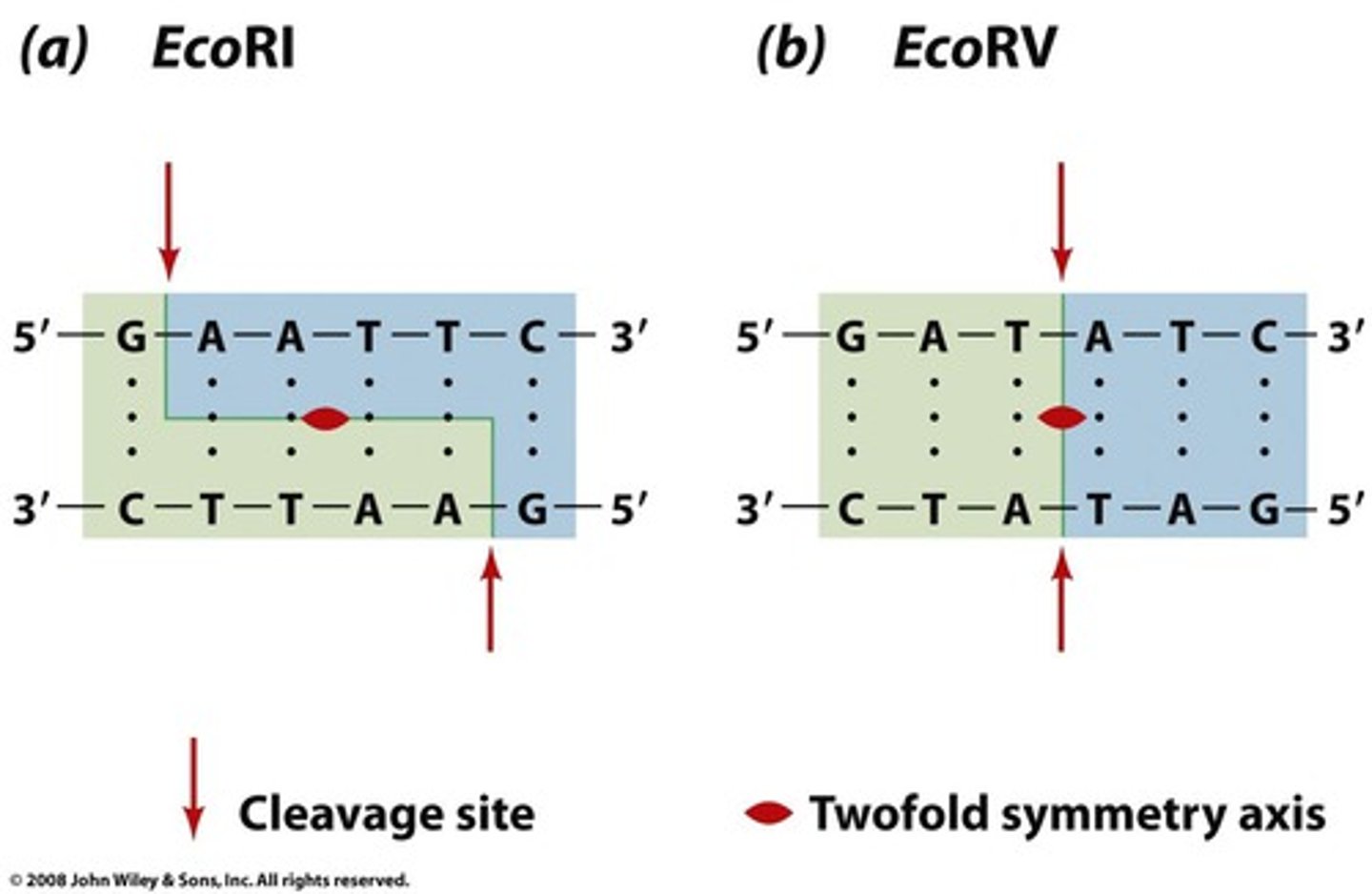
how are complementary sticky ends produced?
when the same restriction endonuclease is used to cut open the plasmid and the gene from the chromosome
what seals the gene into the plasmid?
ligase
restriction sites
contain target sequences of DNA where specific restriction endonucleases cut
regulatory sequences
control gene expression
origin of replication
allows self-replication of the plasmid or artificial chromosome
why is the origin of replication important?
allows many copies to be made, meaning the product can be produced by fewer cells
selectable markers
such as antibiotic resistance, protect micro-organisms from a selective agent that would normally kill them or prevent their growth
what is the purpose of antibiotic resistance genes in selectable markers?
ensure that only micro-organisms that have taken up the vector grow in the presence of the selective agent
as a safety mechanism, genes are often introduced that prevent...
the survival of the micro-organism in an external environment
what can be genetically modified to produce active forms of the protein which are inactive in bacteria?
yeast cells
what can result in polypeptides being folded incorrectly?
plant or animal recombinant DNA expressed in bacteria
recombinant plasmids and artificial chromosomes contain...
restriction sites, regulatory sequences, and origin of replication and selectable markers