AP bio- chemistry of life 1.2
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What are the most common elements in nature?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
What are the 4 functional groups?
Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, Amino, and Phosphate
Where is Hydroxyl found in?
Carbohydrates
Where is Carboxyl found in?
Proteins
Where is amino found in?
Proteins
Where is Phosphate found in?
DNA and ATP
How are macromolecules formed?
Through synthesis, the joining of monomers into a chain called a polymer
What is dehydration synthesis?
When 2 monomers make a polymer by forming covalent bonds, removing water molecules as H+ and OH-
What is Hydrolysis?
The desynthesizing of a macromolecule by breaking of a covalent bond by adding H+ and OH-
Why does carbon bond with so many elements?
It has 4 valence electrons allowing for strong covaalence bonds
What are the 4 macromolecules?
Lipids, Nucleic acids, carbohydrates, Proteins
What is the chemical makeup of Carbohydrates?
C6H12O6
How are carbohydrates connected?
Through covalent bonds
What do carbohydrates do?
Provide energy
What are the types of Carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides, Diasaccharides, Polysaccharides
What do all monosaccharides and disaccharides end in?
-ose
What is glycogen?
The excess glucose stored in the liver as a form of energy
What is glucose?
The sugar in your bloodstream used for energy.
What happens when you have high blood sugar?
The pancreas releases glycogen which turns into glucose, increasing the blood sugar level.
What happens when you have low blood sugar?
The pancreas releases insullin which removed sugar from the blood
What does insulin do?
Removes sugar from the blood
What does glycogen and glucose do?
Maintain the homeostasis of blood sugar
What is the polarity of lipids?
They are non polar making them hydrophobic
What are the purposes of lipids?
They store energy, create waterproof barriers, are hormones, keep insulation, and are key part of nerves
What is the ratio of C:H:O in Lipids?
C:2H:2O
What are the 2 common monomers that Lipids are made out of?
Glycerol and Fatty Acids
What is Glycerol?
alcahol with 3 oxygen groups
What’s the difference between saturated and unsaturated fat?
Saturated fat is solid at room temperature while unsaturated fat is usually liquid and has at least 1 double bond
What are the main type of lipids?
Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Steroids/waxes
How do phospholipids relate to the cell?
They make up the cell membrane
How do Phospholipid keep extra and intracellular water out of the cell membrane?
The phosphate head is hydrophillic and interacts with the water while the fatty acids chain are hydrophobic and in the center of the cell membrane.
What macromolecule are Steroids made out of?
Lipids with 4 rings bonded together
What are Steroids used as?
Horomones
What type of molecules are nucleic acids?
Biomolecules
What do nucleic acids do?
create “blueprints” for making proteins and transmit genetic info
What are nucleic acids made of?
CHONP (carbon. hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus)
Where are nucleic acids used?
In DNA and RNA
What monomer makes up nucleic acids?
Nucleotide
What is a nucleotide made up of?
A sugar molecule, a Phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
What are the 2 types of sugar molecules that can make up a nucleotide?
Deoxyribose and ribose
What’s the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
Ribose has 2 OH bonds on the 3rd and 4th carbon while Deoxyribose has one OH bond and one H+ bond on the 3rd and 4th Carbons
What does the 5th prime carbon do on a nucleotide’s sugar molecule?
it is bonded to the phosphate base
What does she 3rd prime carbon do in a nucleotides sugar molecule?
Bond with the OH base
What does she prime carbon do in a nucleotides sugar molecule?
Bonds with the nitrogenous base
How does DNA differ from RNA?
DNA is made up of deoxyribose, is a double helix, is hydrogen bonded together, has genetic hereditary material
How does RNA differ from DNA?
Uses ribose, has additional OH-, single strand, reads DNA s\trands to make proteins, uses Uracel instead of Thymine
Why does RNA use Uracel instead of Thymaine?
Conserves energy and has no CH3
What are proteins made up of ?
Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, sometimes sulfur in R group
What is the monomer of protein?
amino acids
What are proteins made out of?
Polypeptides
What is a polypeptide
several chains of amino acids put together
What do proteins do?
make up muscles, bones, cartilage, and hair
What do amino acids do?
buildup proteins by joining together to form a chain through dehydration synthesis
How do 2 amino acids bond together?
Through dehydration synthesis
What groups in an amino acid bond together?
Carboxyl and N group
What is the name of the bond between the Carboxyll group and the N group?
Through covalent peptide bonds
What are emergent properties?
properties that individual components of a system don’t have
What are the different solubilities of molecules?
Nonpolar-insoluble, polar covalent-soluble, ionic-soluble
What does it mean when a molecule is hydrophilic?
It means that the molecule interacts well with water and is charged
What does it mean when a molecule is hydrophobic?
The molecule doesn’t interact well with water and is likely nonpolar
Explain what happens when something is hydrophobic
water molecules stick to each other and push nonpolar molecules away
What is the difference between intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are attractive and repulsive forces between separate molecules while Intramolecular forces are the attractive and repulsive forces between elements in a molecule
What is the difference between dissolving and dissociating?
Disolving is when a substance breaks apart into individual molecules and spreads evenly throughout the water while Dissociating is when an ionic compound breaks apart into its own ions
What does a buffer do ?
A buffer resists ph change and keeps a solutions pH at a constant
What is a buffer made of?
Its made of either a weak acid and a conjugate base or a weak base and conjugate acid
How does a buffer work?
The weak acid/ base reacts with excess OH- or H++, neutralizing the solution
What is cohesion?
When water molecules stick together creating surface tension due to their hydrogen bonds
What is adhesion?
Adhesion allows water molecules to stick to other surfaces due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds
Why does water have a high heat capacity?
Due to its intermolecular bonds between molecules
What are the 5 properties of water?
Cohesion, Adhesion, Universal Solvent, High heat capacity, High heat of vaporization
How does each property of water keep the homeostasis of the living world?
Universal solvent- helps cells transport needed substances
High heat capacity- maintains temperature for homeostasis in organisms
Cohesion and Adhesion- properties of movement of wate rin plants
High heat of vaporization- takes a lot of energy and time for liquid water to be changed to gas allowing for moderate climate son earth for gas
What monomer is this and what macromolecule
Its a monosaccharide and it makes up a carbohydrate

What type of macromolecule is this?
Lipid

What macromolecule is this and what is the molecule called?
Its a lipid and called a triglyceride
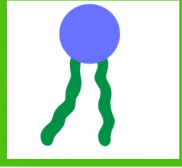
What type of macromolecule is this and what is the molecule called?
its a lipid and its called a phospholipid
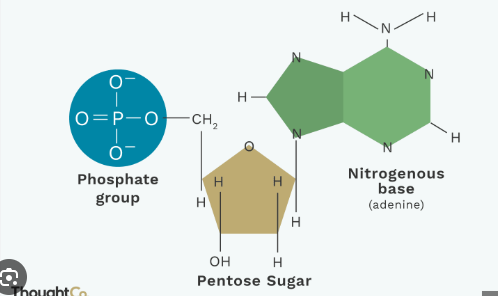
What type of macromolecule is this?
Its a nucleic acid
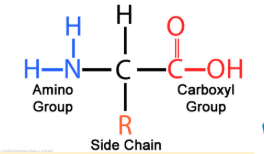
What macromolecule is this?
Protein