[PART 3] [THYROID/PARATHYROID GLAND] Clinical Chemistry [RODRIGUEZ]
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Endocrinology
The scientfc study of the functon and pathology of the endocrine gland
Hormone
Chemical substance that send message to another cell in the body
somatotropin
GROWTH HORMONE is also know as?
somatostatn
GROWTH HORMONE (somatotropin) Inhibitor
You've come this far! Take a break!
You've come this far! Take a break!

Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF-1)
Preferred test for assessing GH defciency or excess during childhood and/or adolescent development
o Also used for monitoring recombinant human growth hormone treatment
o Also used for monitoring of treatment of individuals with acromegaly and gigantsm
YES!
Magiging doctor kaba?

Thyroid gland
- is positoned in the lower anterior neck and is shaped like a buterfy, made up of two lobes, restng on each side of the trachea, bridged by the isthmus
Parathyroid gland
posterior/just beneath the thyroid gland.
Regulate serum calcium levels
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
The MOST USEFUL TEST for assessing thyroid function
SECOND-GENERATION TSH
immunometric assays efectvely screen for hyperthyroidism
THIRD-GENERATION TSH
chemiluminometric assays give fewer false-negatve results and more accurately distnguish between "euthyroidism and hyperthyroidism"
THIRD-GENERATION ULTRASENSITIVE TSH TEST (S-TSH)
preferred method for monitoring and adjustng thyroid hormone REPLACEMENT therapy and screening for abnormal thyroid hormone producton in the clinical setting
FOURTH-GENERATION ASSAY
exists providing a 10-fold increase in sensitvity compared to thirdgeneraton assays, it is used primarily for "research purposes"
0.3-4.2 mIU/L - baliktad na number ni CURRY (30) at KOBE (24)
The reference range for s-TSH is
0.4-4.0 mIU/L
reference range for T4
20%
Thyroid gland produces only how many percent (%) of T3?
80%
how many percent (%) of T3 is form from Deiodinaton: conversion of T4 to T3
80-200 ng/dL
The reference range for total T3
FREE THYROXINE (FT4)
It is used as a SECOND-LINE TEST AFTER TSH in the evaluaton of suspected thyroid disorders and, when used in conjuncton with TSH
0.9-1.7 ng/dL
FT4 reference range
Free Triiodothyronine (FT3)
may be required to evaluate clinically euthyroid patents who have an altered distributon of thyroid binding proteins as seen during pregnancy or in patents with dysalbuminemia
2.8-4.4 pg/m
The reference range for FT3 is
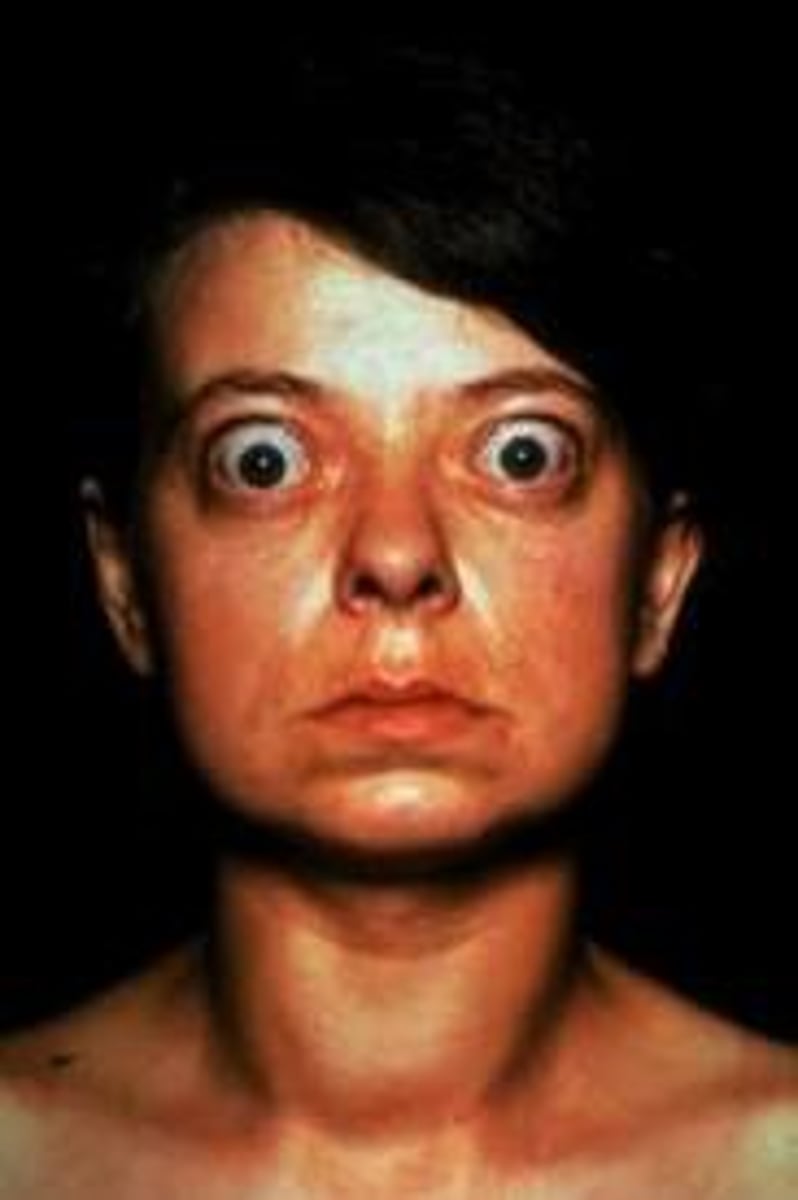
Graves disease
Most common cause of hyperthyroidism
HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS
chronic lymphocytic thyroidits is known as?
HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS
The common cause of hypothyroidism
TPO antbody
Most appropriate test for HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS?
Radioactve iodine
useful in assessing the metabolic actvity of thyroid tssue
Assistng in the evaluaton and treatment of thyroid cancer
Fine Needle Aspirate Biopsy
OFTEN frst step and most accurate tool in the evaluaton of thyroid nodules in the absence of hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
defned as low FT4 with a normal or high TSH
Hyponatremia
can also occur from the combinaton of increased urinary sodium excreton and an ability to inappropriate release of ADH
Primary
Thyroid gland dysfuncton
Secondary
Pituitary dysfuncton
Tertiary
Hypothalamic dysfuncton
Levothyroxine (T4)
treatment of choice for hypothyroidism (Hashimoto's thyroidits)
Thyrotoxicosis
excess of thyroid hormone
Amiodarone
- (drug used to treat cardiac arrythmias) interferes with normal thyroid functon o Blocks T4 to T3 conversion
o Leads to hyperthyroidism
Postpartum thyroidits
most common form of subacute thyroidits
Plummer's Disease
T3 Thyotoxicosis is also known as?
T3
Most active form of thyroid hormone
T4
Principal secretory product of thyroid hormone
Riedle's Thyroiditis
Thyroid Hormone becomes woody/ stony hard mass in appearance
Graves disease
Most common cause of thyrotoxicosis
Reverse T3
END product of T4 Metabolism
Thyroxine- Binding Globulin (TBG)
Transports majority of T3
Transports 70-78% of total T4
Thyroxine-BindingPrealbumin(transthyretin)
It transports 15-20% of total T4
T3 has no affinity
Thyroxine-Binding Albumin
It transport T3 and 10% of T4
Hyperthyroidism
It refers to an excess of circulating thyroid hormone.
De Quervain' thyroiditis (painful thyroiditis)
it is associated with neck pain, low-grade fever and swings in thyroid function tests.
Hypothyroidism
bradycardia, weight gain, coarsened skin, cold intolerance and mental dulness is sign of?
Myxedema
it describes the peculiar nonpitting swelling of the skin.
Clinical features: "puffy" face, weight gain, slow speech, eyebrows thinned, dry and yelow skin, andanemia
Radioactive lodine Uptake (RAIU)
it is used to measure the ability of the thyroid gland to trap iodine.
Recombinant Human TSH
It is used to test patients with thyroid cancers for the presence of residual or recurrent disease.
parathyroid
What gland prevents hypocalcemia?
Primary hyperparathyroidism
It is the most common cause of hypercalcemia
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
it develops in response to decrease serum calcium.
True
True or False
Low calcium level will lead to TETANY
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Increase Calcium, Decrease PTH
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
Increase Calcium, Increase PTH
Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism
Increase PTH, Calcium precipitates, Increase Phosphate
Secondary Hypothyroidism
↓ TSH | ↓T4
Primary Hyperthyroidism
↓ TSH | ↑T4
Secondary Hyperthyroidism
↑ TSH | ↑T4
Secondary Hyperthyroidism
(N) TSH | ↑T4
Secondary Hypothyroidism
(N) TSH | ↓T4
Primary Hypothyroidism
↑ TSH | ↓T4
Subclinical Hypothyroidism
↑ TSH | (N) T4
Subclinical Hyperthyroidism
↓ TSH | (N) T4
NORMAL
(N) TSH | (N) T4
<0.4 IU/mL
Anti Tg Antibodies Ref range:
<0.9 IU/mL
Thyroperoxidase (TPO) Anitbodies Ref Range:
1.75 IU/mL
Thyrotropin receptor antibodies (TRAb) Ref Range:
Long Acting Thryeoid Stimulator or Thyroid Stimulation Immunoglobulins
Thyrotropin receptor antibodies (TRAb) is also known as
C terminal - C= Cement kaya solid
Solid phase Ab is what terminal?
N terminal - May "N" sa sig(N)al eh
Signal Ab is what terminal?
Sandwich Technique
Common TSH assay uses what technique?
Claim your Price!
Claim your Price!

Follicular cells
Parafollicular or C cells (Calcitonin)
What are the 2 types of cells of THYROID GLAND
Thyroglobulin
is a glycoporotein; it acts as a preformed matrix containing tyrosyl groups; it is stored in the follicular colloid of the thyrcid gland.
Calcitonin
Parafollicular or C secretes?
Thyroperoxidase (TPO)
What autoantibody is involved in the tissue destructive process (Hashimoto's disease)?
TSH receptor (TR)
What autoantibody is is involved in Grave's disease
Hyperthyroidism
It refers to an excess of circulating thyroid hormone.
Graves' disease: (diffuse toxic goiter)
It is the most common cause of thyrotoxicosis
Plummer's disease
T3 thyrotoxicosis is also known as?
It occurs 6x more commonly in women than in men.
True or False
Graves' disease is more commonly in WOMEN than in MEN.
6x
Graves' disease occurs how many times more commonly in women than in men.
exophthalmos (bulgingeyes) and pritibial myxedema (may edema sa paa)
Give 2 Graves' disease features. Ano itchura ng pasyente
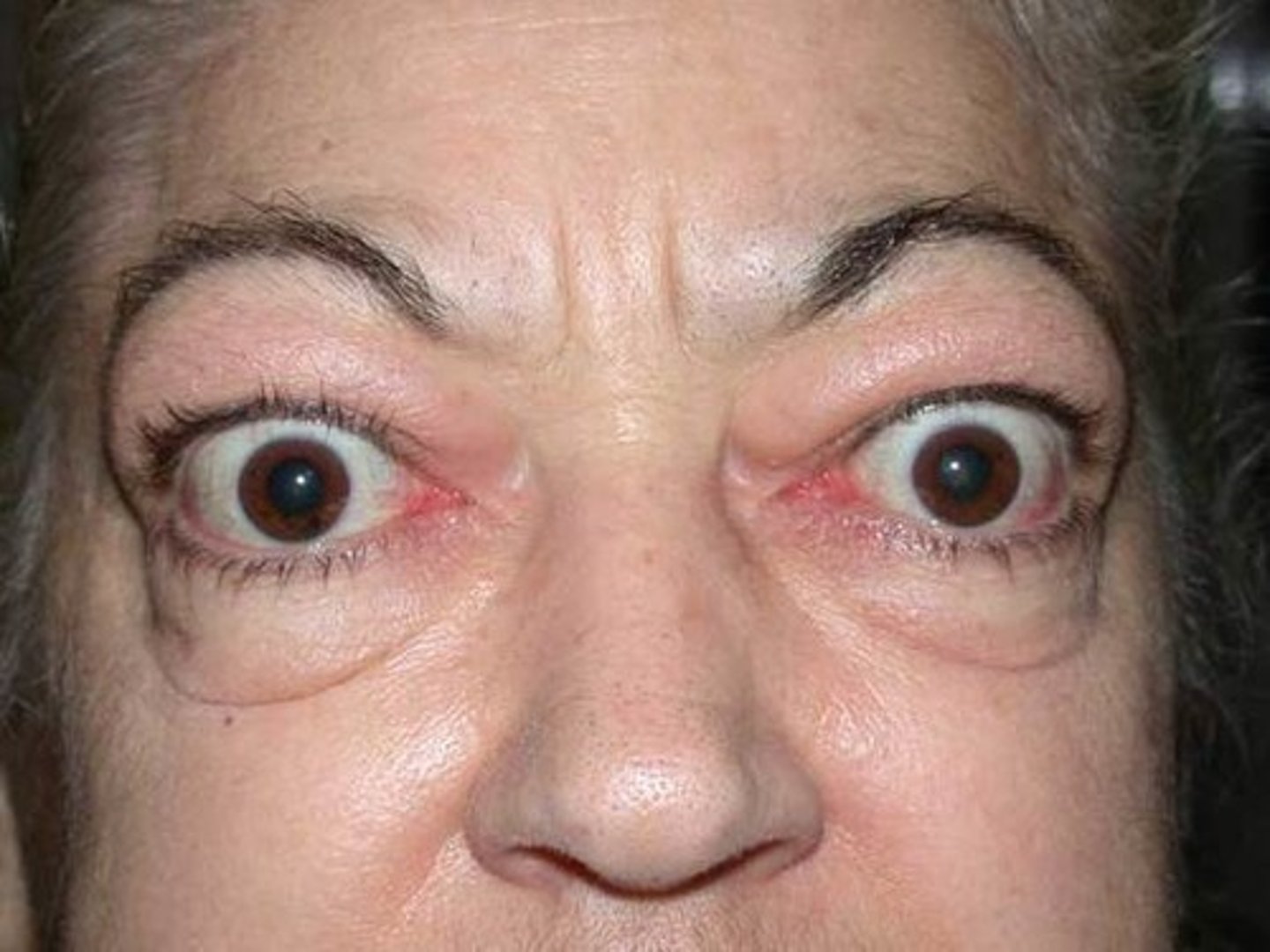
Subclinical hyperthyroidism
shows no clinical syrnptoms but TSH level is low, and FT, and FT normal
TSH receptor antibody test
Graves' disease Diagnostic test:
Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis / De Quervain' thyroiditis
painful thyroiditis is known as?
Hypothyroidism
It develops whenever insufficient amounts of thyroid hormone are available to tissues.
Hypothyroidism
bradycardia, weight gain, coarsened skin, cold intolerance and mental dullness are SYMPTOMS of what thyroid disease?
Primary hypothyroidism
it si primarily due todeficiency of elemental iodine
Hashimoto's disease (chronic autoimmune thyroiditis)
It is the most commoncause of primary HYPOthyroidism.
Hashimoto's disease
What disease is associated with enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter)?
T3,T4 [low]
TSH [high]
TPO antibody [+]
Hashimoto's disease lab result
T3,T4 [high]
TSH [low]
TSH Receptor antibody [+]
Grave's disease lab result
Myxedema
it describes the peculiar nonpittingswelling of the skin.
clinical features: "puffy" face, weight gain, slow speech, eyebrowsthinned, dry and yellow skin, andanemia
Myxedema coma
It is the severe form of primary hypothyroidism