VetA&P Cardiovascular
1/298
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
299 Terms
cardiovascular system consists of __ (3)
heart, blood vessels, lymph vessels
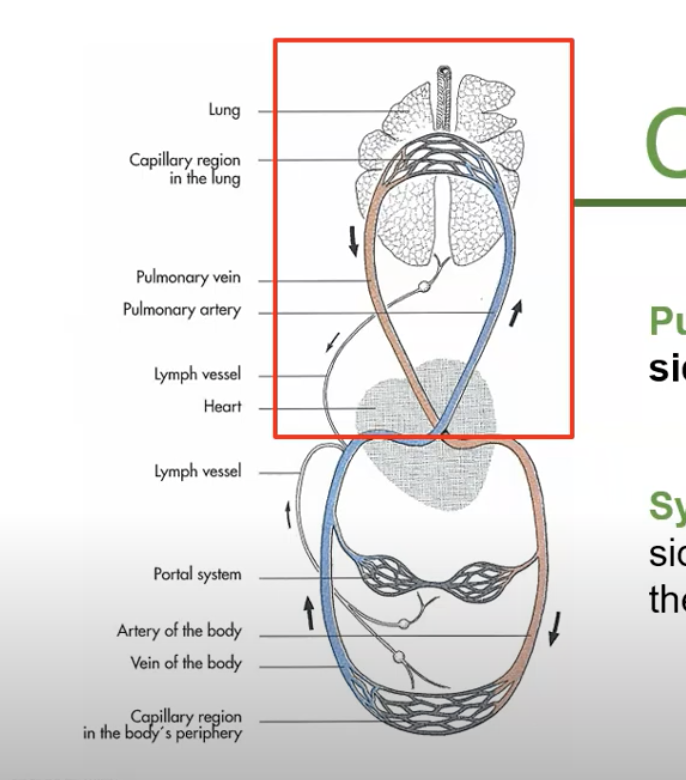
in pulmonic circulation blood moves from __ side of heart to __
right, lungs
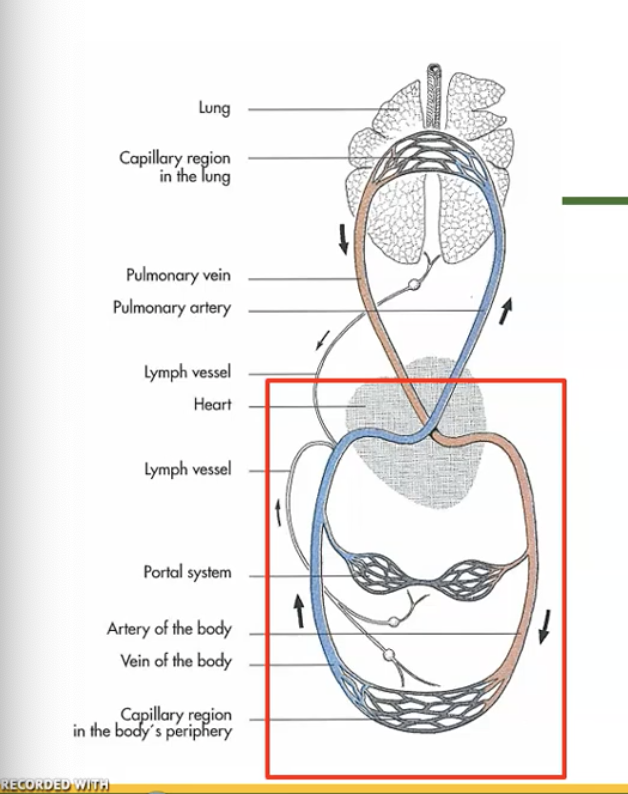
in systemic circulation blood moves from __ side of heart to __
left, body
blood is __% of total body weight
6-8%
circulation time is __ seconds in large animals and __ in small animals
30, 7
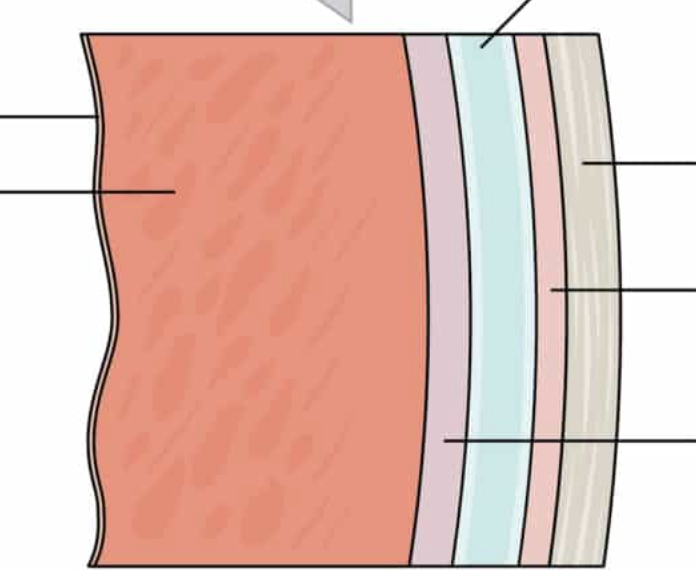
very far left
endocardium of heart wall

thick red layer
myocardium of heart wall

purplish layer
epicardium of heart wall (visceral layer of serous pericardium)

blue
pericardial cavity

pink
parietal layer of serous pericardium

tan
fibrous pericardium
the pericardium is a __ walled membrane
double
the __ pericardium is outer and __ pericardium is inner
fibrous, serous
the __ is found between two layers of serous pericardium
pericardial cavity
the pericardial space is filled with __ which helps __
pericardial fluid, prevent friction between heart and pericardium
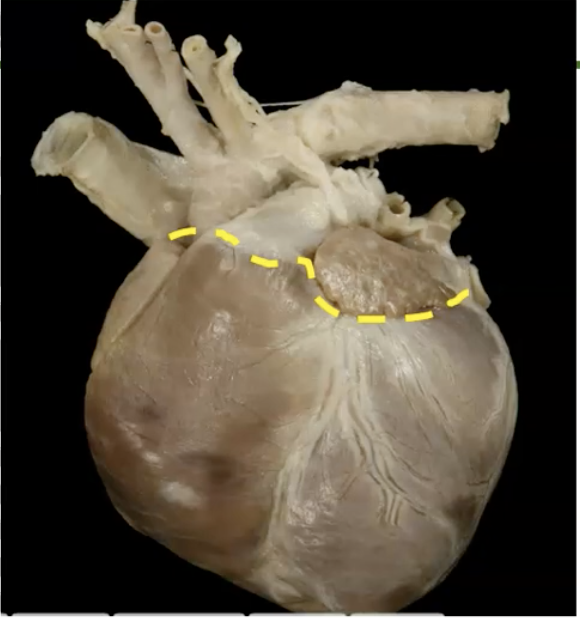
separates artia and ventricles externally
coronary groove
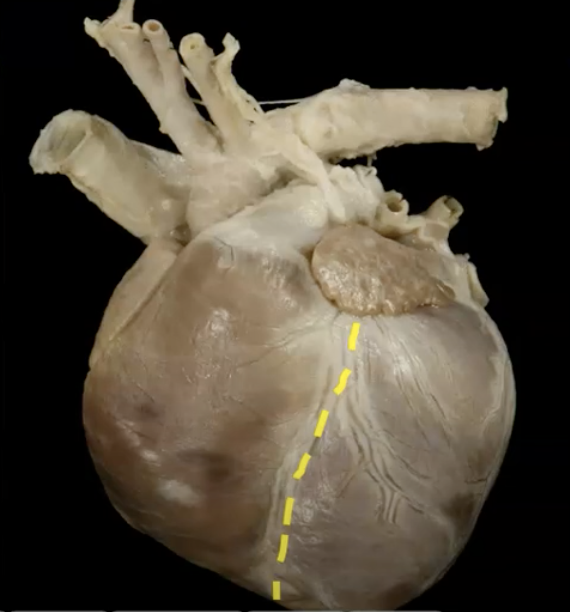
separates ventricles externally
interventricular groove
the __ interventricular groove is on the left side
paraconal
the __ interventricular groove is on the right side
subsinousal
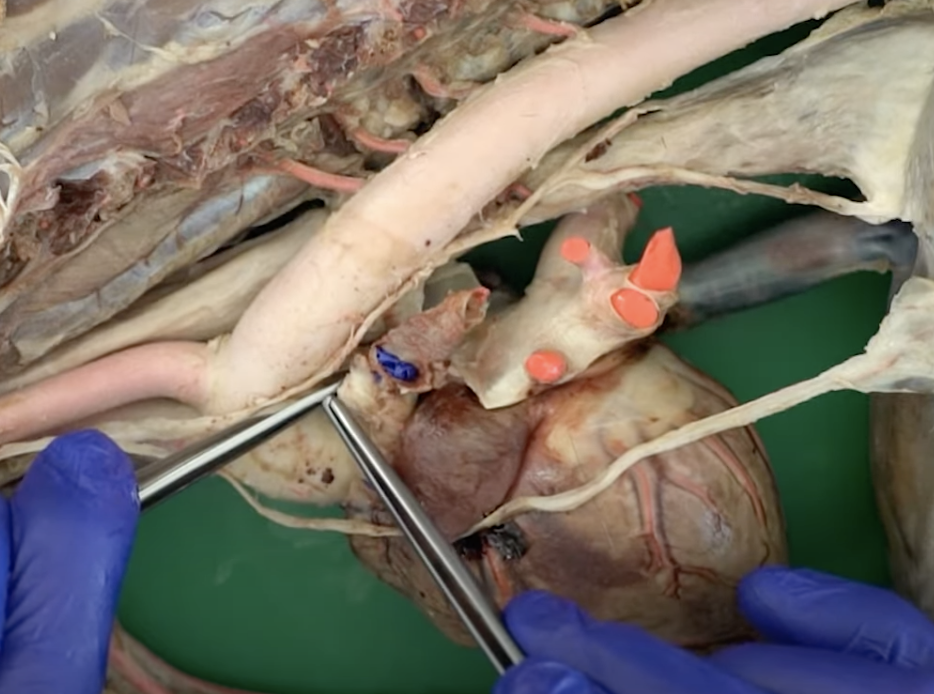
the __ is in between pulmonary trunk and aorta
ligamentum arteriosum (Botalli’s ligament)
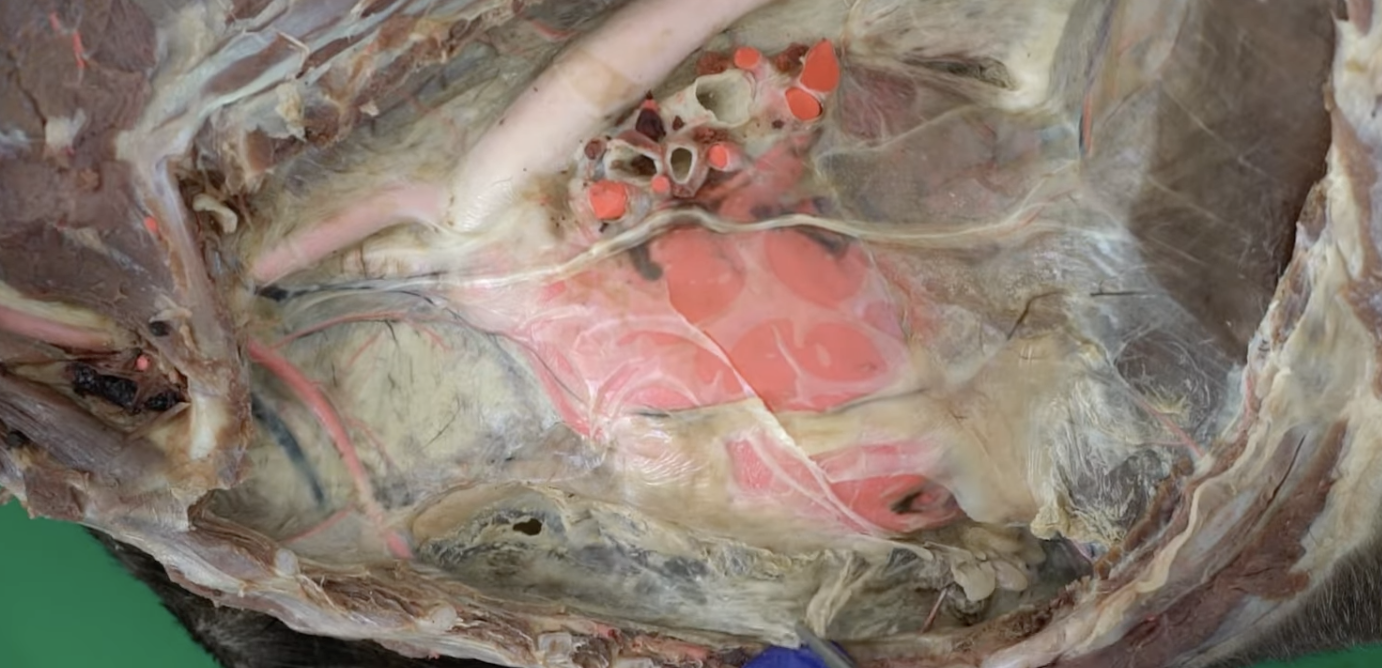
fixes heart and pericardium in place (all animals)
sternopericaridiac ligamennt
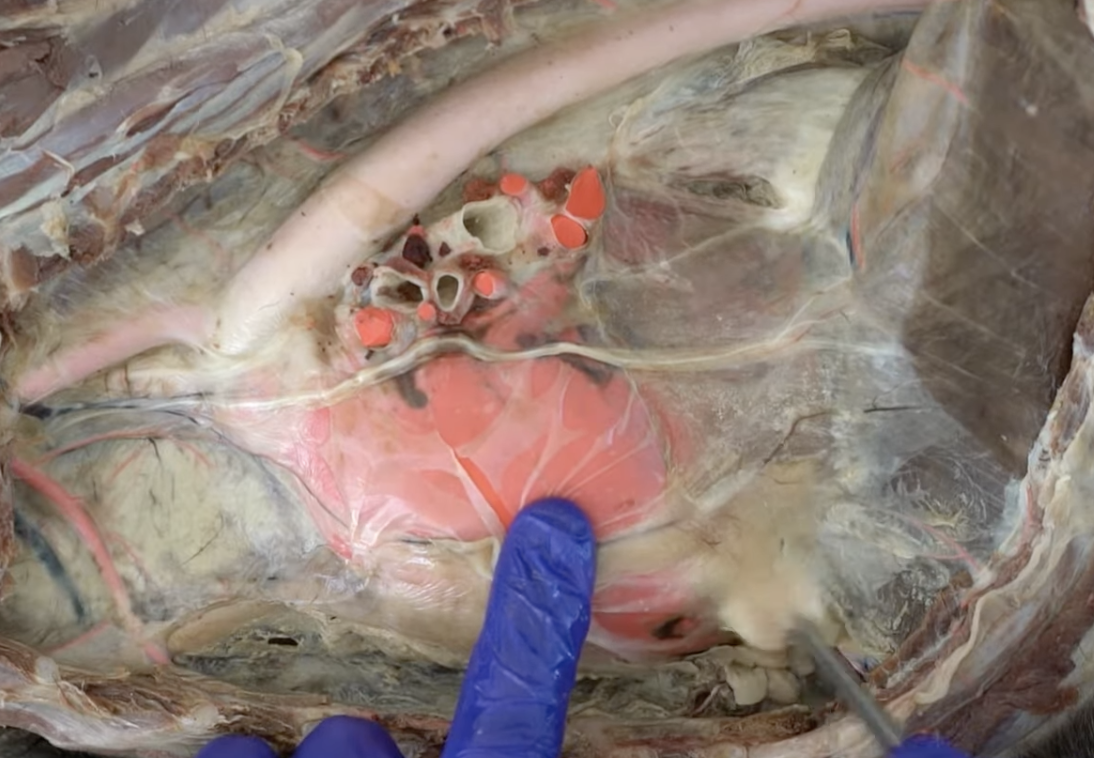
connects pericardium and diaphragm, only found in dog
phrenopericardiac ligament
the __ ligament extends between pericardium and diaphragm, only found in the dog
phrenopericardiac
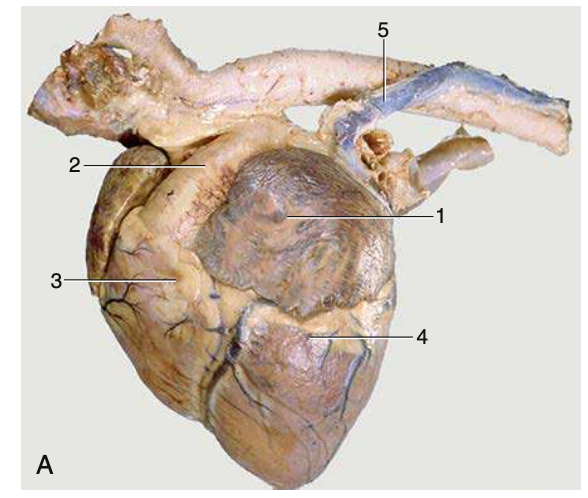
L heart, 1
left auricle

L heart, 2
pulmonary trunk

L heart, 3
right ventricle

L heart, 4
left ventricle

L heart, 5
left azygous vein
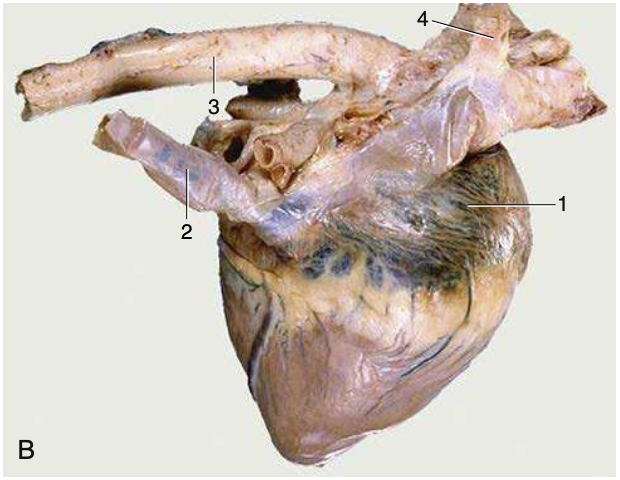
R heart, 1
right atrium

R heart, 2
caudal vena cava

R heart, 3
aorta

R heart, 4
right azygous vein (opening into cranial vena cava)
in the ascending aorta (just above aortic valve after it leaves the left ventricle) are the __
aortic sinuses
the first branch of the aorta is the __
right and left coronary arteries
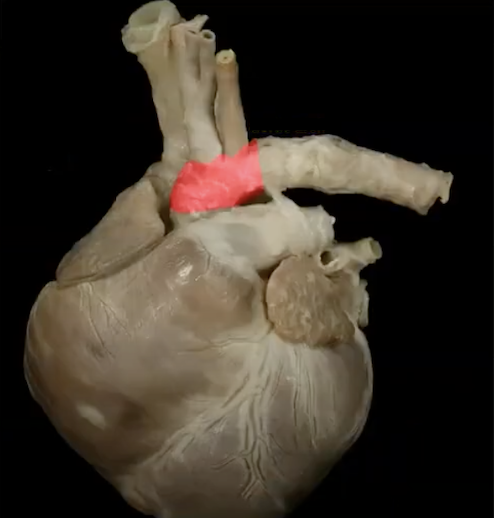
continuation of ascending aorta
aortic arch
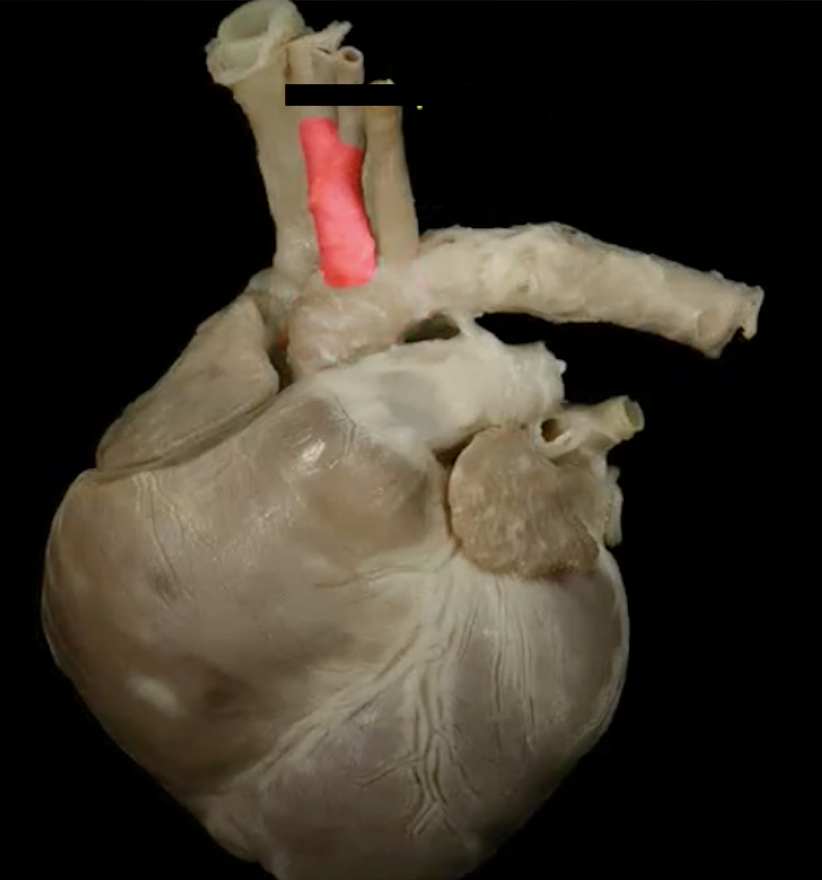
brachiocephalic trunk
the brachiocephalic trunk gives rise to the __
L common carotid artery, R common carotid artery, R subclavian artery
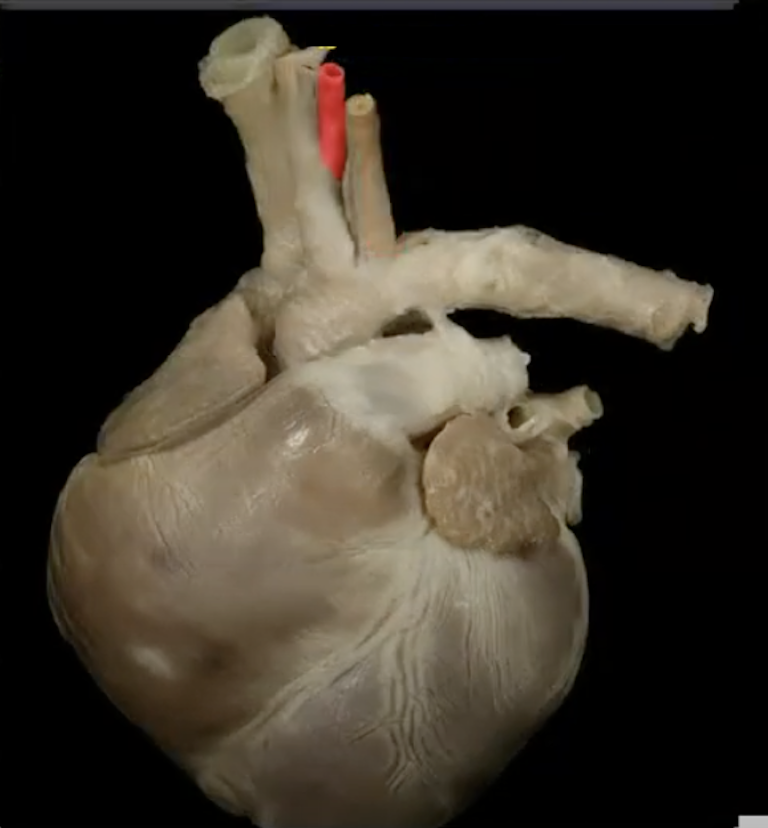
L common carotid artery
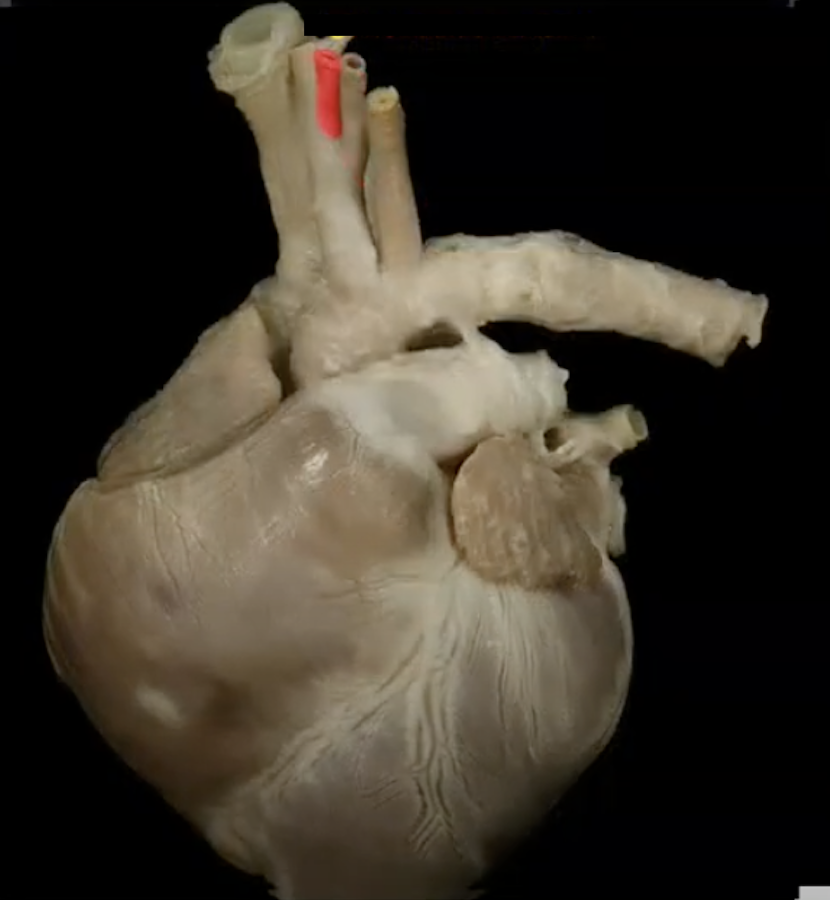
R common carotid artery
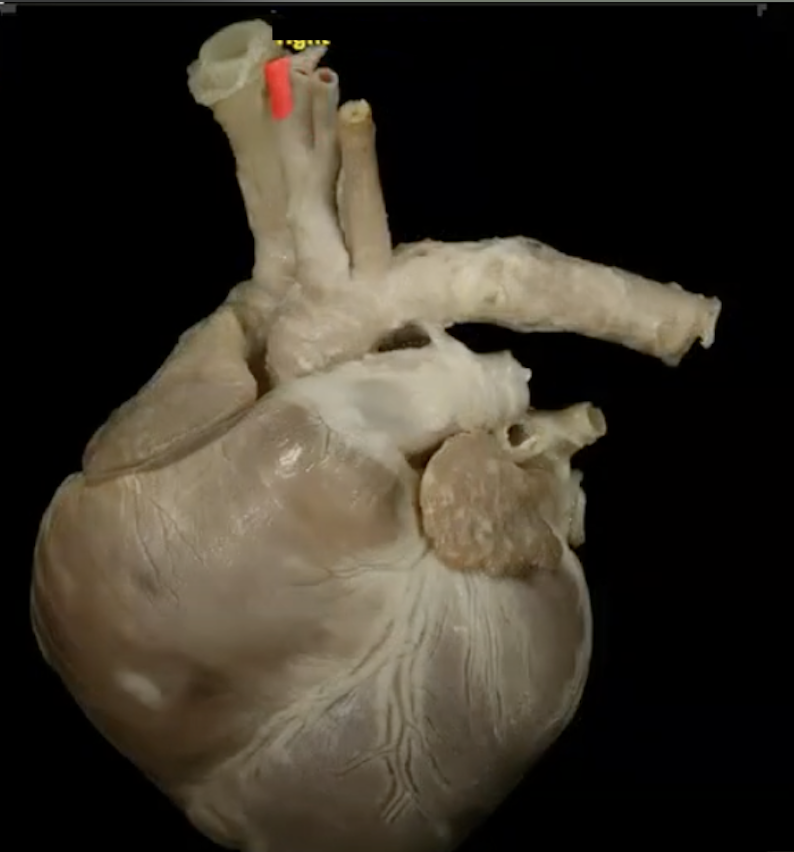
R subclavian artery
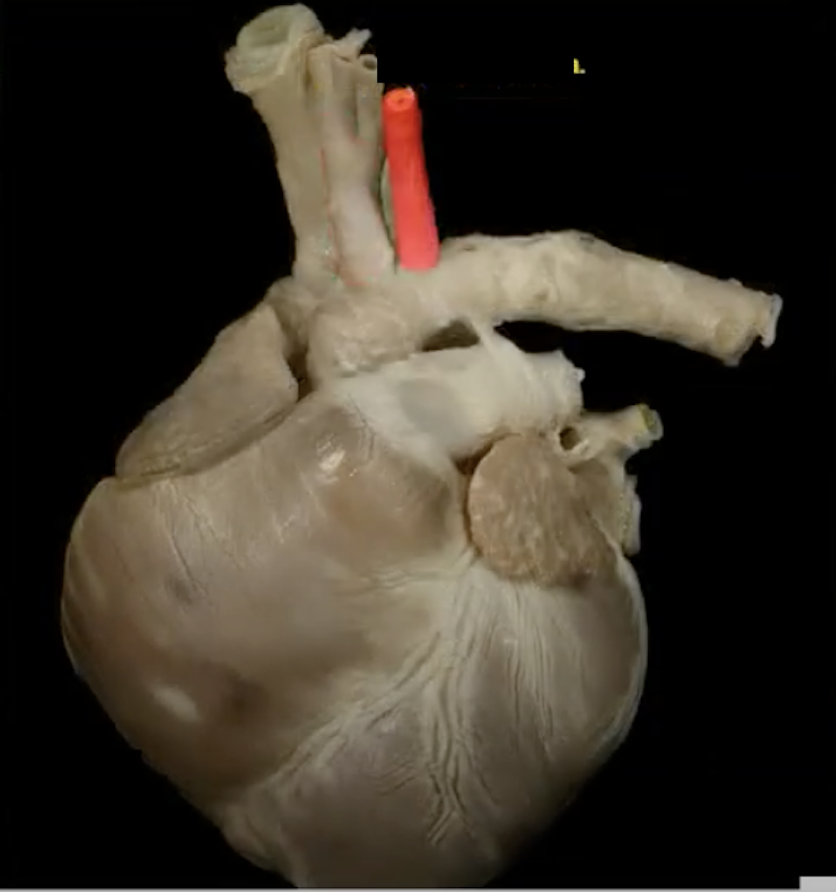
L subclavian artery
The R and L subclavian arteries supply __
neck, thoracic limb, cranial thoracic wall
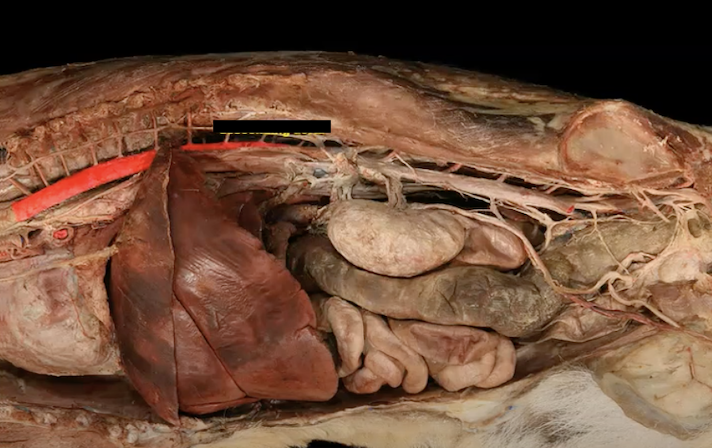
descending aorta
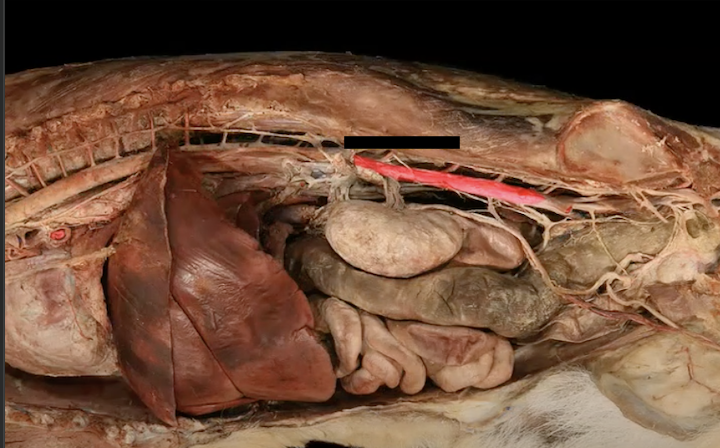
abdominal aorta
aorta gives rise to __ (2)
brachiocephalic trunk, L subclavian artery
brachiocephalic trunk gives rise to __ (3)
common carotids, R subclavian
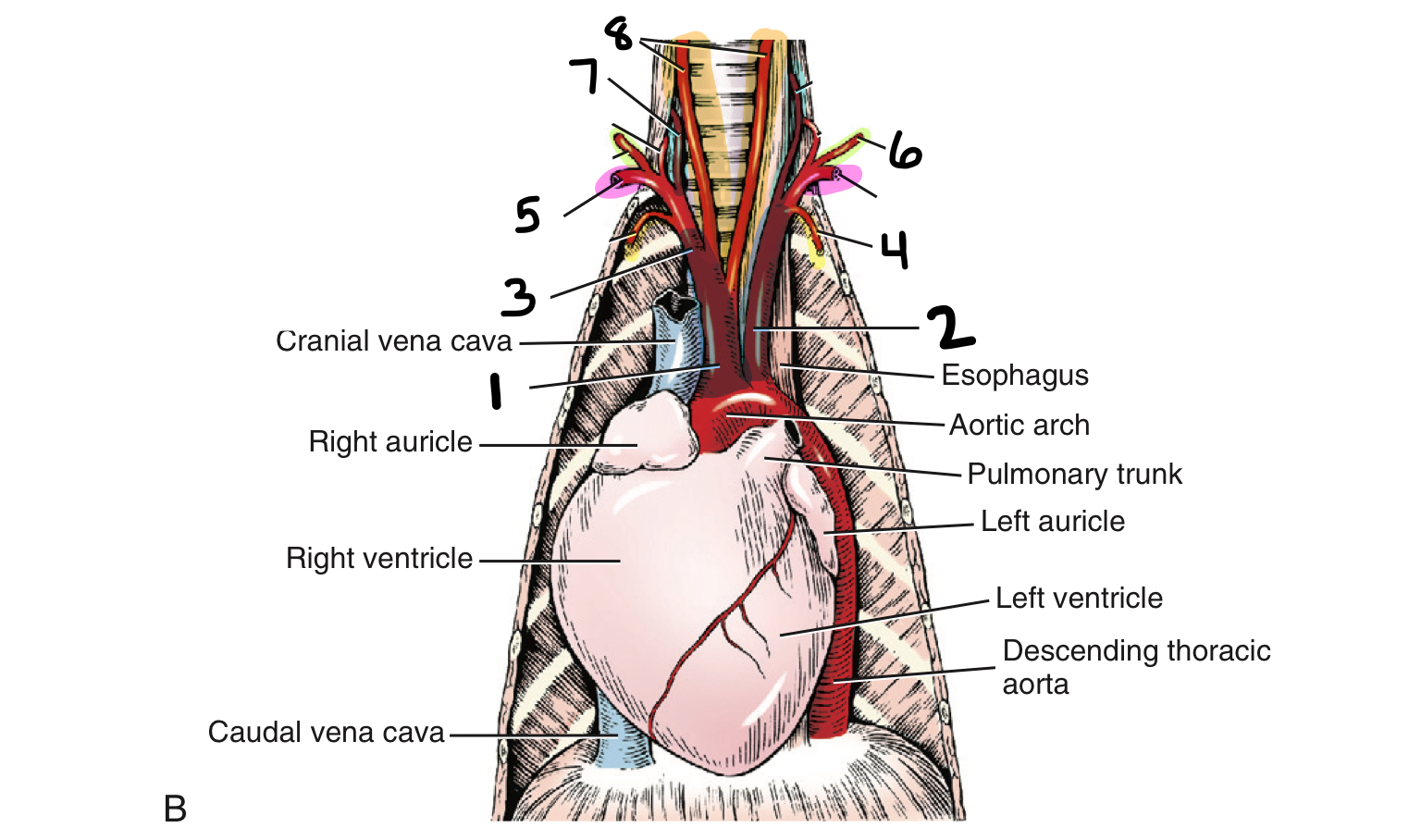
1
brachiocephalic trunk

2
left subclavian

3
right subclavian

4
internal thoracic artery

5
axillary artery

6
superficial cervical artery

7
vertebral artery

8
common carotid arteries
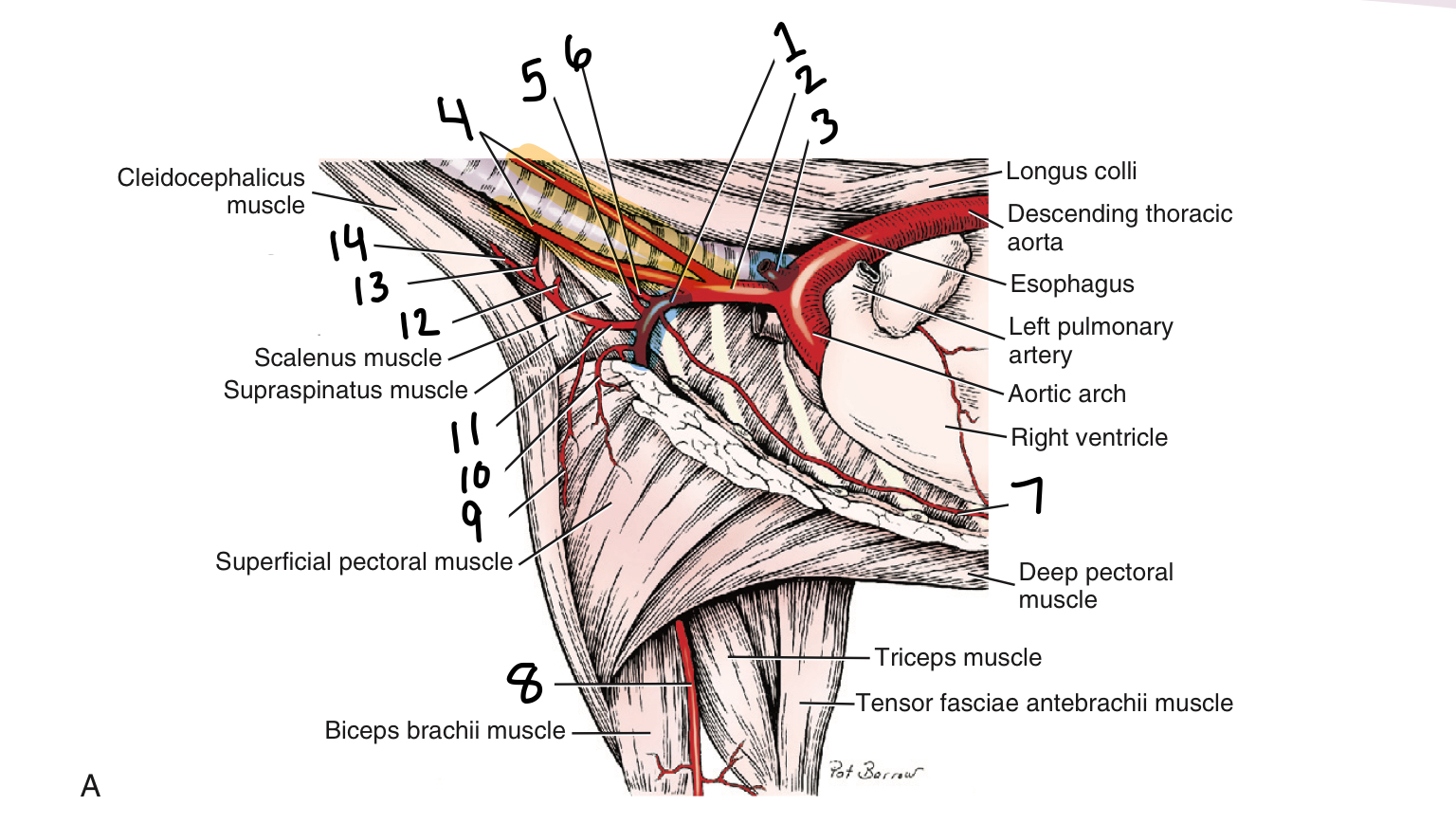
1
right subclavian artery

2
brachiocephalic trunk

3
left subclavian artery

4
common carotid arteries

5
costocervical trunk

6
vertebral artery

7
internal thoracic artery

8
brachial artery

9
deltoideus branch

10
external thoracic artery

11
superficial cervical artery

12
suprascapular artery

13
acrominal branch

14
ascending branch
the brachiocephalic trunk gives rise to __
R common carotid artery, L common carotid artery, R subclavian artery
the common carotid arteries give rise to __ (2)
internal carotid artery, external carotid artery
internal carotid artery supplies the __, external carotid artery supplies the __
brain, face
the __ artery is a direct continuation of the external carotid artery
maxillary
the circle is willis (arterial circle) is located __
ventral to hypothalamus circling infundibular stalk
the circle is willis (arterial circle) is formed by __
paired internal carotid artery and basilar artery
the circle of willis is a __ at the base of the brain
circulatory anastomosis
the basilar artery arises from the __ (2)
vertebral artery, ventral spinal artery
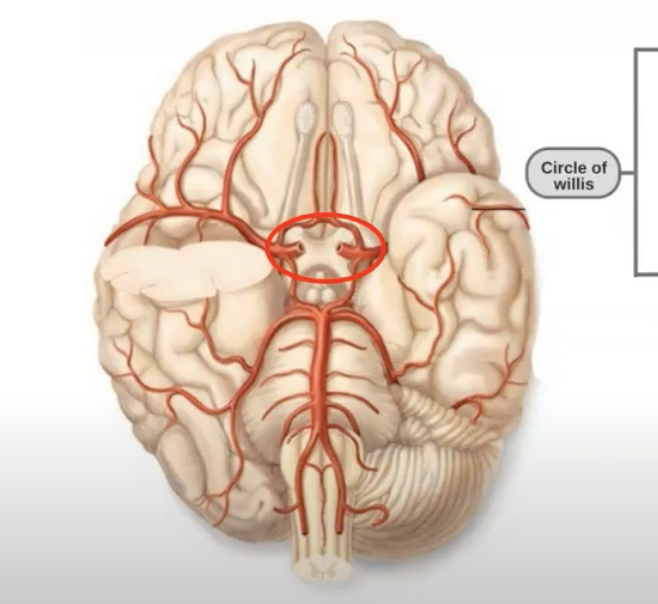
the circle of willis serves as a backup system for blood flow because __
if one artery becomes narrowed, other arteries can preserve cerebral perfusion (pressure) to prevent symptoms of ischemia
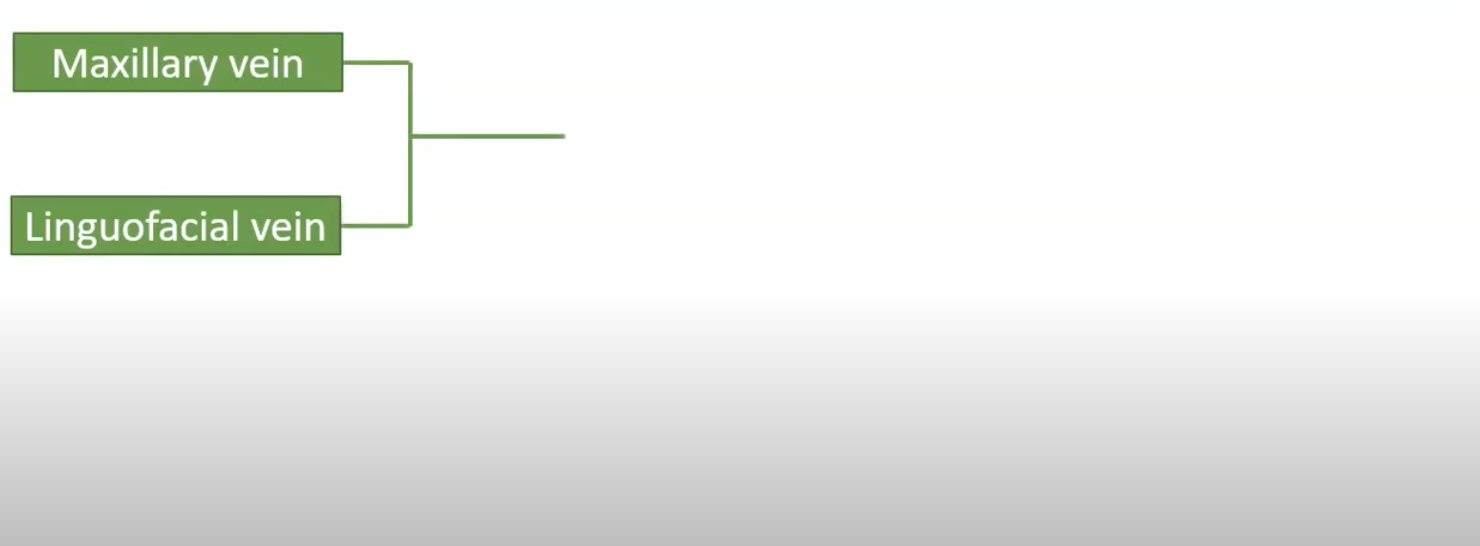

external jugular vein
brachiocephalic vein
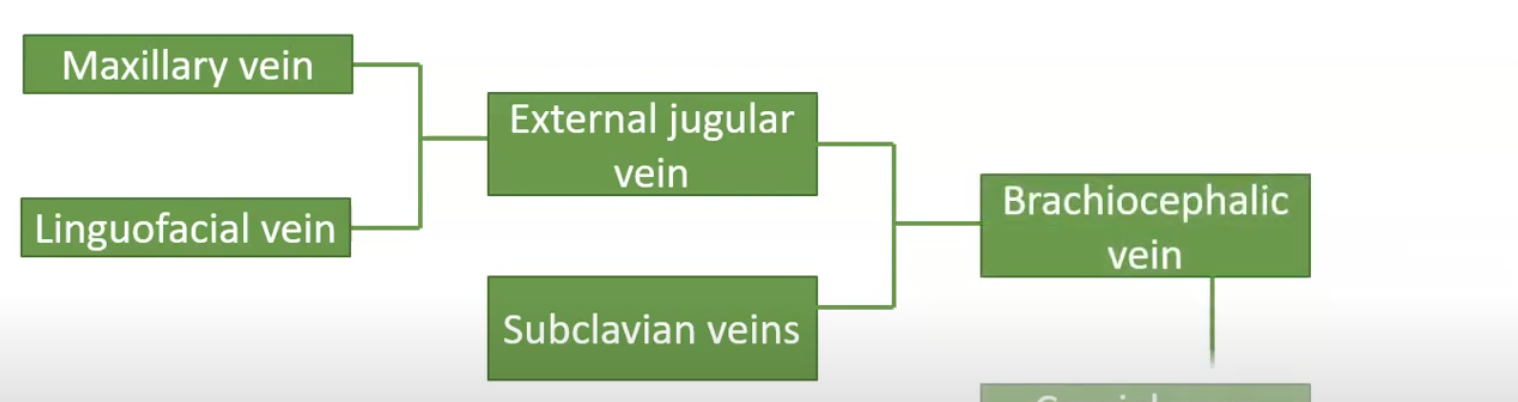
cranial vena cava
the arterial system of thoracic limb arises from __ artery
subclavian
the __ artery is a direct continuation of subclavian
axillary
thoracic limb arteries: ? → ? → ? → ?
axillary → brachial → median → radial
thoracic limb veins: ? → ? → ?
cephalic; median → brachial → axillary
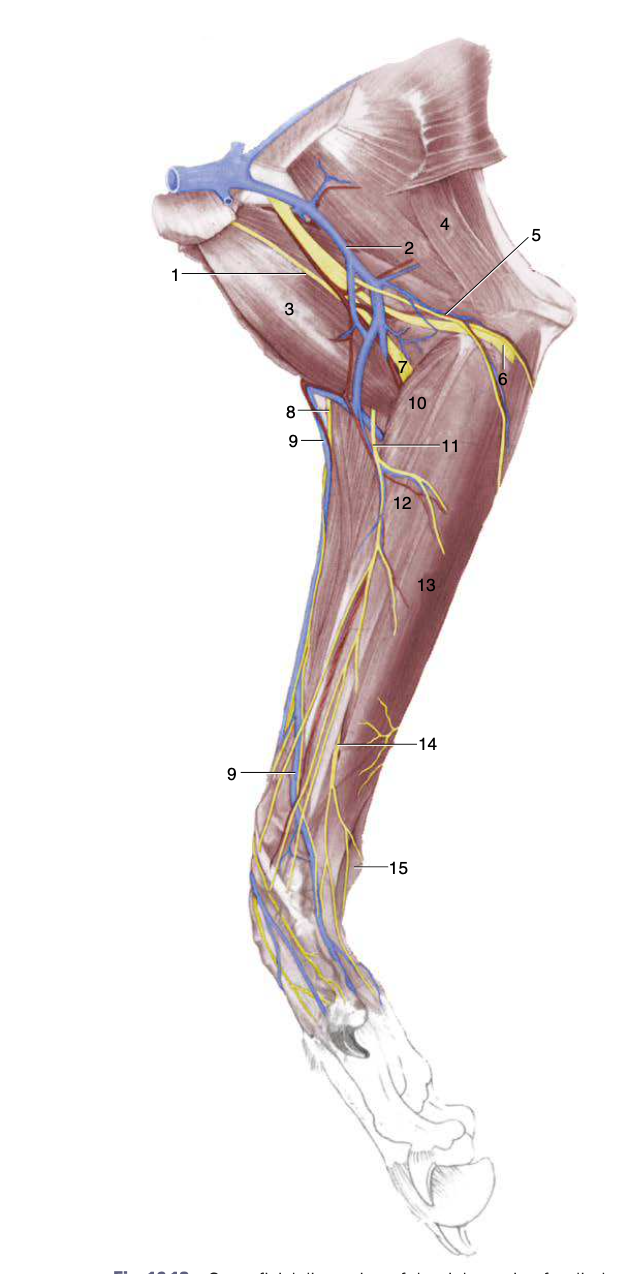
1
musculocutaneous n.

2
brachial vein

3 (right limb)
biceps brachii

4
tensor fasciae antebrachii

5
caudal cutaneous antebrachial nerve and collateral ulnar vessels

6
ulnar nerve

7
median nerve and brachial artery

8
median branch of superficial radial nerve

9
cephalic vein

10 (right limb)
pronator teres m.

11
medial cutaneous antebrachial nerve

12
flexor carpi radialis

13
superficial digital flexor

14
inconstant cutaneous branch of ulnar nerve

15
accessory carpal bone