6. history of European colonization: chapter 6: tools of empire
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1. politics - systems - strategies - actors 2. gender 3. missionary work 4. economy 5. development
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
power centers
metropole
secretary of state, minister,…
councils, lobbyists,…
little representation
exceptions ex naoroji
colony
governor, viceroy,…
large turnover in order to keep link with metropole
councils, lobbyists,…
armies (important power center): force publique (congo), KNIL (royal netherlands east india company), sepoys,…
little representation
evolutions ex India
dadabhai naoroji
1825-1917
1885 co-founder indian national congress
1892-95 first asian MP in UK house of commons (very rare representation)
representation in india
started evolving after defeat great mutiny, result of different protests and rebellions
1858, 1892, 1909: legislative & executive councils
advisory and indirect elections
1882: municipal council act
elected by landowners and tax payers
at least 2/3 indian members
1921: provincial governments
at least ¾ indian members
1935: autonomy to provinces
1937: one on six indians participate in elections => more than in Europe = exceptional
much variety in rule
direct and indirect rule
especially great britain
assimilation & association (—> lower degree of linking colony to colonial rule)
especially france
military rule
especially germany and italy
segregation
especially Belgium and some white settler colonies
indirect rule
local rulers remain on their thrones (europeans rule indirectly through them)
minor competences (administration, jurisprudence, rite)
not: army, fiscality, foreign policy,… (core powers)
sided and controlled by a european resident
mainly in less strategic (land locked,…) and in poorer regions
advantages
power without responsibility
cheaper: loyal elite (satisfied with system)
legitimation colonial rule
european “respect” for local tradition (not imperialists)
european sharing of power (european civilization) vs local despotism and decadence (authoritarian governance local princes)
==> example majarajas being extremely rich having elephants, rolls-roys,…
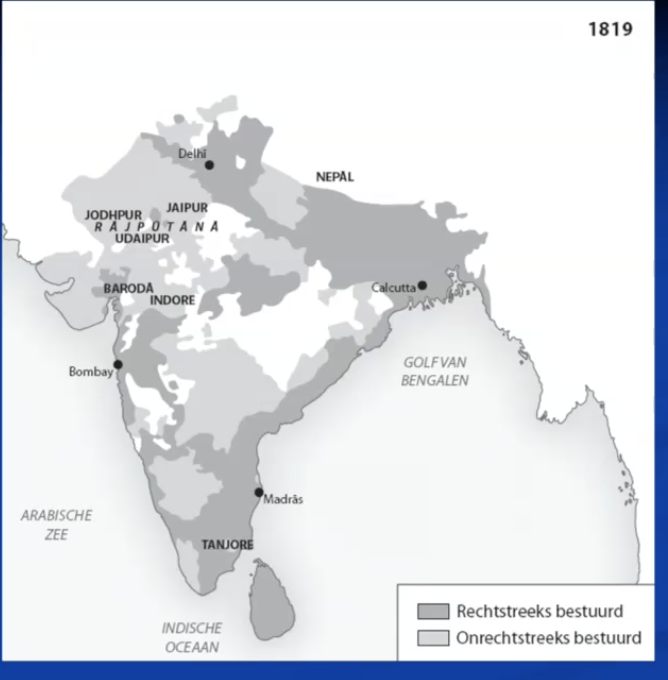
direct and indirect rule in british india
double government under Clive of India (since beginning of british rule in india)
mawab: puppet in British hands (had some competences)
east india company: army & taxes
by 1857-58: about 580 princes (wouldn’t change afterwards)
mawabs, nizam, raja’s, maharaja’s, rani’s, maharani’s
more or less half of british india’s territory
also in other british colonies
direct and indirect rule in belgian congo
King Kwet Mabiine
only symbolical role kings
direct and indirect rule Dutch indies
Batavia: governor-general
not all of them were Dutch (belgians)
provinces (buitengewesten): princes (sultans) and residenten
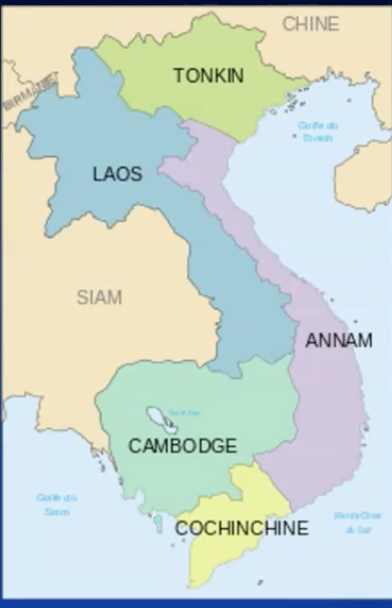
direct and indirect rule french indochina
federation
one directly governed colony (cochinchina)
saigon as a major colonial city
four protectorates
tonkin, Annam: emperor of Vietnam
Cambodia: king
Laos: king of Luang Prabang
assimilation french empire
what?
make colonies little overseas frances
turn colonized into french citoyens of different colour (should be christians,…)
why?
french revolution: universalism
napoleon: institutional centralism
hangovers after 1815 and 1870
when and where?
especially in 19th c in vieilles colonies
difficult due to enormous variety
==> ex in algeria,…
association french colonies
what? a step back
humanité rather than égalité
bilateral relationship with metropole, esp economic = no longer departments of french nation
centralization does not change
why?
other colonies didn’t apply assimilation either
darwinism and racism
Félix Eboué
1884-1944
born in Cayenne
1901 scholarship for France
1909-1912 administrateur en chef in oubangui-chari (central african republic)
1912-1932 back in french guyana
1932-: governor in, subsequently, Martinique, guadeloupe (antilles) and chad
typical example of product of french imperialism
discussed political strategies
divide and rule
violence
disease
famine
divide and rule
enforcing existing inequalities within one colony
ex ethnic, religious or social differences
not always familiar to the very people classified
made absolute by the colonizer
ex castes in india registered in censuses
siding with minority groups (turn them into collaborators)
included in governance ex tutsi’s in ruanda (hutu’s and tutsi’s are colonial categories)
military => overrepresented in colonial armies so became collaboraters in systems of oppression ex ambonese in dutch indies or sikhs in british india (‘martial race’)
=> creating division and weakness (colonized don’t unite against colonizer)
violence
military superiority
from gunboats to maxim gun (1884) = most important innovation that allowed for quick conquest of africa, first automatic rifle
matabele war (1893): 5000 matabele against 50 british with 4 maxim guns, 1500 casualties at matablele side, 4 at british
omdurman: GB & Egypt lost 40 soldiers, mahdi 11000
wars and destruction
ex Herero rising (south-west africa (namibia) 1904-1907)
uprising against land appropriation and bad treatment
Lothar von Trotha’s extermination order (october 1904) = vernichtungsbefehl
repression: 75-80% of 60-100.000 Herero died
German type of military campaign and racism?
repression = occured everywhere
diseases
several diseases
smallpox in australia, measles in fiji, leprosy in hawaii
sometimes deliberate genocide
hispaniola in 16th c, tasmania in 19th c
sometimes '‘collateral damage’ (but quite fitted into european agenda)
no natural immunity
malaria in india facilitated by irrigation schemes
much amnesia or selective memories
pater damiaan
spread of aids
famines
examples in British India
Bengal famine of 1770
1/3 of bengal population died
great famine 1876-78
indian famine 1899-1900
bengal famine 1943-44 = deliberate famine, consciously triggered by british
not only due to climate but also colonialism
indifferent attitudes colonial administrators
high taxation
other priorities ex during war
local superstition (ex xhosa sacrificed cattle in 1856)
rulers at home
colonial party
political, commercial, scientific,… supporters of active imperialist policy and lobbying (even leuven professors)
advocates of colonialism
Jules Ferry (1880-81 and 1883-85 PM france)
francesco crispi (1887-91 and 1893-96 PM italy)
benjamin disraeli (1868 and 1874-1880 PM britain)
salisbury (1885-86, 1886-92, 1895-1902 PM GB)
joseph chamberlain (1895-1903 secretary of state for colonies GB)
more reluctant politicians
WIlliam Gladstone (1868-74, 1886, 1892-94 PM of GB) = withdrew british indian army from afghanistan, reluctant to colonize egypt,…
rulers oversea
politicians
Lord George Curzon (1859-1925)
1899-1905: viceroy of india
1919-1924: foreign secretary
curzon line = between poland and soviet union proposed by him
soldiers
kitchener
1850-1916
field marchal
command in the mahdist war and second boer war
victor of Khartoum
1902-09: commander-in-chief in india
1914-16: secretary of state for war
on recruitment poster GB
gallieni
1849-1916
military commander french colonial empire
became minister of war during first world war
lyautey
military officer france
became résident géneral in morocco (ruler)
tomb in same palace as napoleon
==> all started soldiers and became commanders, all men
masculinity colonization
a male business
moustaches and uniforms
safari costumes with pith helmets
local dresses (like chinese gordon, kitchener
women colonialism
female pioneers
Mary Kingsley = explorer in south africa
Gertrude Bell = author, journalist, administrator, spy, archeologist => “mother of Iraq”
female colonizers
wives, nuns,… —> in belgian congo more than half of missionaries female
general features
greater freedom than at home
better contact with indigenous people
female freedom fighter
ex Lalla Fatma N’Soumer (algerian female freedom fighter)
male colonizers heroic individuals?
individuals?
role of indigenous people
local geographical knowledge, translators, porters,…
ex Stanley 1874: 4 europeans and 356 Africans
heroic?
violence
expedition of voulet & chanoine (1898) = bad reputation, they were even killing eachother, scandal in france
drugs
most of them some of the time
some of them most of the time
sexual practices
homo-eroticism colonizers
stanley’s problems with women
Rhodes’s notorious homosexuality (only male servants)
Baden-Powell and Kenneth ‘the boy’ McLarren (close intimate relationship
Kitchener’s correspondence with his sister
pederasts: hector macdonald (‘fighting mac’)
prostituion
widespread in colonial cities
“caused by moral corruption of women”
STDs
women saw gynecological examination as indignity
colonizers pursued an inadequate policy
fascination with exotic nude
ex Tahiti and Bali: women legendary for their beauty, praised in books, paintings,…
photography: showing half naked women
eroticization exotic nude
wild, primitive and naked => sexually available
versus oppressed sexuality in Europe
polygamy => alleged libertinage & free love
colonizers as male bachelors (initially)
restriction of emigration of European women
officially: physical hazards of life in tropics
not suitable for european women (not well enough adapted)
in reality: economic reasons
transportation costs
women might press for repatriation (paying for transport again)
women might engage in private trade and encroach on the company’s monopoly
children would become sickly (families would again have to return home)
concubinage (unofficial relations) with local women
tolerance and promotion of extramarital relations
petite épouse, deuxième lit, huishoudsters,…
nyai (java and sumatra), congai (indochina),…
european men in better health
vs prostitution causing veneric diseases
prevention from unnatural liaisons (homosexual relations)
protection against the ill health that sexual abstention, isolation and boredom were thought to bring
other advantages of local women
fewer financial and emotional demands
also useful as guides and domestic servants
regulated relations with women
arguments
political and economic
male and sexual and racist
examples regarding (hidden) stimulation sexual relations with local women
VOC selected male bachelors for more than 200 years
India, 1929: british employees prohibited from marriage for three first years
examples regarding local women
ex prohibitinng european men from returning to the netherlands with native wives and children
indies civil code of 1848: native women had no rights over children recognized by a white man
consequences relationships with local women
for the social structure
reinforcement of social and racial hierarchies
number of men exceeded that of women
for the locals
women: dependent on their European partners
men: competition with european supervisors
children: mixed-blood children (not recognized by either societies) = metis,…
white women colonialism
from late 19th c
following technological possibilities
general narrative: women introduced segregation (mainstream narrative)
housing, compounds, dress codes, social taboos, education,…
women “wanted to be protected from local barbarism”
but: adviced by male doctors
paranoia of the black ‘peril’
white men imagined their wives to be desired
need of protection from the ‘primitives‘ sexual urges
citizen militias and ladies rifle clubs (teach wives to protect themselves)
rape laws: race-specific
sexual abuse of black women was not classified as rape
beginning of missionaries
europeans in asia
jordanus de severac (1321-1330 in Quilon, India)
john de marignolli (1338-53 in china, india & ceylon)
saint francis xavier in India and Japan (1541-1552) = close with founders of jesuits
portuguese in congo
1491: king of kongo converted to christianity
his son: king afonso I of kongo (1509-1543)
his grandson: bishop henrique kinu a mvemba
spanish in latin america
religious emigrants in north america
decline missionaries in 18th century
general trend: age of enlightenment
1773: suppression of the jesuits (until 1814)
also in the colonies
ex british india: fascination with the local culture
colonizers learned local languages
respected or re-established ‘traditional’ structures
political: maharaja’s and nawabs
judicial: code of gentoo laws (hindu and genta)
ex rousseau’s admiration of the ‘noble savage’ = untouched, unspoiled,…
“discourse on the origins of inequality among men” (1754)
resurrection missionaries in 19th century
new rise of christianity
new devotion, new congregations,…
commerce and industrial revolution
new markets —> free trade(18th century: monopoly, control, bans,…)—> free movement
abolitionism (movement to end slavery)
new aim for mobilization after abolishment slavery
darwinism and scientific racism
hierarchy of races
example from fascination to civilization
british india 1810s
—> “to create a class of persons Indian in colour and blood, but english in tastes, opinions, morals and intellect” (1832)
not everyone = elite
imposed english
1816: hindu college in calcutta (first english language college)
1835: english replaced persian (moghuls) as official language
1857: universities in Bombay, calcutta & madras
fought barbaric customs
sati: widow-burning
thugs: ritual killers of travelers in the name of kali (religious+economic reasons) => strangled
not: more widespread customs
missionaries allowed from 1813 onwards
missionaries active in many places example Belgium
across the world
not only in belgian colonies
not only spreading christianity but also had individual initiatives
belgian missionaries in India: jesuits, capucines, carmelites, filles de la croix, ursulines of tildonk, zusters van liefde, sisters of de jacht
new catholic institutions
society for the propagation of faith (lyon 1822)
scheut (congregation of the immaculate heart of mary)
established in 1862 by théophile verbist
1862: belgian mission to china
1863: scheutveld college
1865: died in inner mongolia (north china)
later also to mongolia, philippines, the congo,…
pères blancs (white fathers) (algiers 1868)
lavigerie: archbishop of algiers and carthage, primate of africa
new protestant institutions
britain (end 18th c beginning 19th c)
germany (19th c)
denmark, sweden, norway, US,…
women and missionary
wives of (protestant) missionaries
domestic, medical, educational,… roles
acces to places and communities not accessible to men
missionary nuns
soeurs de st-joseph de l’apparition (tunis, 1843)
soeurs blanches (algiers 1870)
de jacht sisters (india 1879): de meester & devos
women gradually majority of foreign missionaries
british india: 1840s onwards
belgian congo: 1930s onwards
activities missionaries
religious
build churches (chapels, bigger churches, cathedrals)
social work
hospitals, leper houses, dispensaries (pharmacy)
orphanages, beggars’ homes, vagrants’ colonies
science and education
village schools and boarding schools
industrial schools and teaching of handcrafts
agricultural and horticultural projects
printing and publishing ventures
varieties between missionaries in different colonial empires examples
state or church?
france: public instructional system
separation of church and state in france
GB, Belgium, germany: only subsidies to missions
congo 1941: 5252 mission schools & 6 state schools
mass or elite?
India: anglicisation of indian elite
congo: widespread primary eductaion
european or indigenous languages?
france: assimilation, later association
belgium: more local languages and no flemish
positive or negative effects missionaries?
social and economic upheaval
humanitarian and philantropic motives and outcoms
health care, education,… (not very much: 20 doctors in all of congo)
against inequity, poverty and discrimination
BUT: impact on local culture
motives and outcoms? religious - conversion
education? spread of european languages and views
discrimination? racism and complex of inferiority
inequity? sexual abuse
also existent in Western Europe but possibly more in the colonies
problematic clergy sent to colonies?
difficult to make over statements about the extent of abuse
were missions monologue or dialogue
unilateral imposition of eurocentric values
destruction of indigenous cultures
but: outcome of complex negotiations
accommodations
2-way influence
religious figures, customs,… adapted to local communities
syncretic religions = new religions as result of dialogues
ex voodoo, santeria,…
resurgence of non-christian religions after 1815
competition with christianity
new technologies: easier travel, spread of printed texts
Ram Mohan Roy: one of first Indians who learnt English and applied new knowledge into spreading hinduism
Swami Vivekananda = important in spread of hindu sympathies to western world => yoga
mission imperial or not?
co-ordinating imperial government policies
from spanish conquistadores to education in congo
but: not always closely linked with states
before and after imperial processes
ex germans: 1828 gold coast (generations before they joined scramble for africa), 1834 India, 1842 Namibia, 1951 nigeria
outside of impreial territory
ex belgians in china and the philippines
subjects of non-colonial nations
americans (congo), swedes (congo),…
trade dominated by metropolitan centres
needed colonial commerce:
growing industrialization (started in Britain)
greater demand for resources (cotton,…)
greater need for overseas markets (selling industrial products)
growing population (along with industrialization: drop of mortality and high natality)
greater demand for food & luxuries
drain of wealth
by indian minister in britain
18th c: export of indian advanced textile to britain
19th c: import of british industrial textile to india
variety chronology and geography
early modern age: aspiration for monopoly (portugal!)
Britain: commitment to free trade
british india: already in 1813 and 1833 (certain domains of economy)
britain: 1846
1870-1895: stagnation and depression
Britain: non-interventionism (-thomas malthus) => had same approach to the famines in India (demography)
other metropoles: protectionism
all: imperialism to stimulate overseas demand (and solve economic depression)
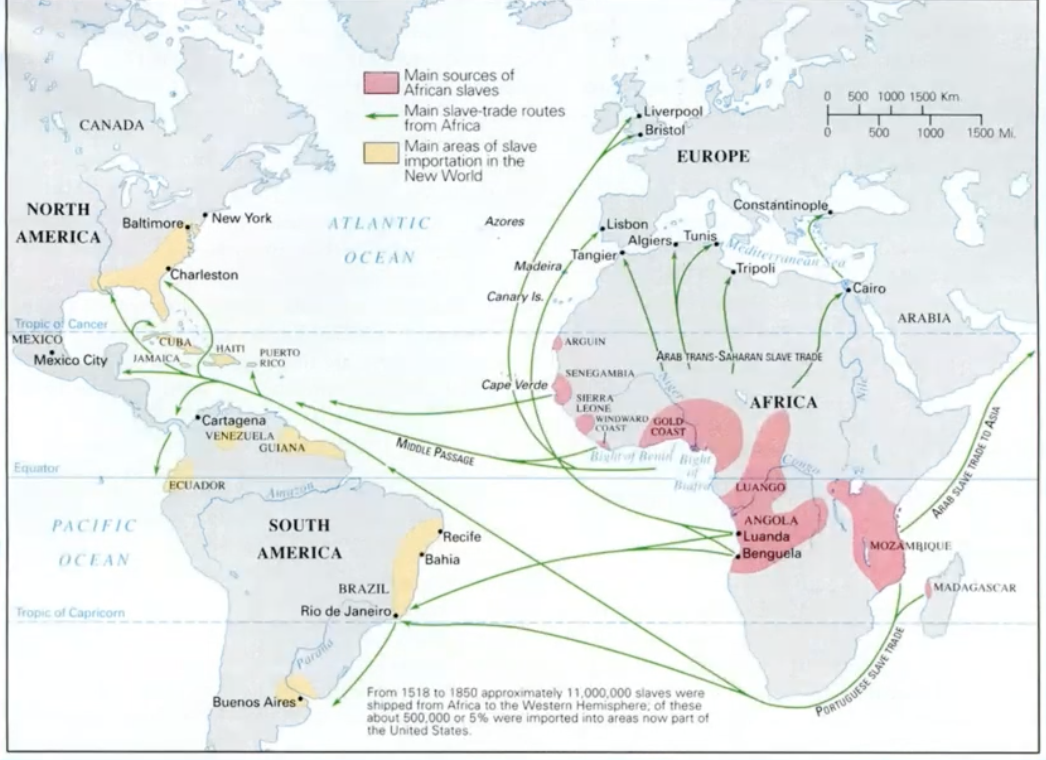
atlantic triangular trade
europe-africa: copper, cloth, glass beads, guns
africa-america: slaves
america-europe: sugar, rum, cotton, gold, tobacco
numbers of slaves traded
about 11 million slaves shipped from africa to the western hemisphere
especially by portugal and britain
especially to brazil and the caribbean (plantations)
sources abolitionism
religious minorities such as Quakers
enlightenment & french revolution
american independence war
first mass movement abolitionism
clapham sect (William Wilberforce), 1783
first modern pressure group (mobilizaiton of masses)
==> Britain: 1807 Slave Trade Act; 1833 Slavery Abolition
==> France 1848 (had already tried to abolish it after french revolution but it restarted), Netherlands 1863, US 1863, Brazil 1888
2 new states after abolition movement
sierra leone: a colony (-britain)
1787: Freetown for escaped american slaves
1791: sierra leone company
1807: given to british government
many thousands of slaves freed from captured vessels released into sierra leone
liberia: an independent country (-US)
1821: Monrovia by freed american slaves
helped by American Colonial Society
1847: republic of liberia
different views on the right of land
europeans: terra nullius => right to occupation and ownership
indigenous: custodians and users instead of owners
different uses of land by colonizers
taxes (on yields of agriculture)
gathering of naturally occuring products
cultivation on plantation
different systems of land use
indentured labour
the culture system in the dutch east indies
land tax systems in british india
zamindari system (north 1793)
mughal tax (zamindar) collectors were given property right => as if they were respecting local culture and practices
aim: loyal landowners (to british) paying taxes
but: misuse and oppression
raiyatvari system (south, early 19th c)
peasants pay taxes directly
aim: create closer connection with british
but: oppression by tax collectors
sedentarization for tax revenues
nomads as ‘criminal tribes’ = very difficult to control
campaign against thugs: civilization or land revenues?
gathering of naturally occuring products
especially in the beginning and in Africa
ivory, timber, …
rubber: invention of rubber tyre (1888) by John Dunlop
palm oil: soap, lubricants, lightning fuel, margarine,…
plantations
early modern age: Caribbean and Guyana’s
french Indochina: rice, maize and rubber,… (Michelin 1889)
dutch east indies: coffee, indigo (color fex cloth), cane sugar,…
british india: tea and opium
kamerun, kenya,…: cocoa, bananas, tea,…
new systems for labout migration after abolition of slavery
day labourers
indentured servants
contracted labour without (or low) salary ex for five years
were “payed” in accommodation and living
breach of contract falls under criminal law
poor living circumstances = on paper free but in reality many similarities to slavery
migration of Chinese or Indian ‘coolies’
population increase
ex java 3,5 mil 1800 → 40,9 mill 1930
ethnic diversity
ex suriname
the culture (cultivation) system
dutch east indies 1830-1870
financial losses following java war and belgian independence
boosting dutch east indies’ export
what?
peasants compelled (by force) to cultivate government-pwned export crops on a fifth of their land, or to work 66 days a year on government estates or projects
single-crop plantations (sugar, coffee, indigo) => single-crop economy
extremely lucrative
batig slat (‘yielding treasury’)
criticism culture system
imposed by force and much misuse
stagnation since no incentive to innovate (among peasants in dutch indies)
native population had no access to capital market
=> Max Havelaar - Multatuli
liberal period (1870-1901) dutch indies
successor to culture system
agriculture open to private and corporate plantations
new crops: tea, tobacco, rubber, cocoa and palm oil
criticism more liberal period
een ereschuld - Conrad theodor van deventer
ethical policy dutch east indies (1901-1930/42)
successor liberal period
moral obligation to increase dutch indies’ wealth (local population)
social (education & health), economic (irrigation & communication), political (local responsibility),…
failed
mining
making quick fortunes
means of payment for infrastructural development (in service of economic development of mining industry)
little industry in colonies
colonies rather markets for finished products
varieties in mineral extraction among colonies examples
gold rushes in white settlers’ colonies
minerals in the belgian congo
minerals in british india
petrol in the dutch indies and the middle east
gold rushes
US: california (1849), colorado (1859-65)
Australia (1850s) and New Zealand (1870s)
increase of white population
south africa
diamonds in Kimberley (1867)
Gold in witwatersrand (1884)
mechanised gold mining in the gold coast
1877 following the third ashanti war (1873-74)
minerals in the belgian congo
extremely rich soil (especially katanga)
initially thought to be poor and isolated
copper, cobalt, diamond, uranium and other ores
huge mining companies
forminière: société internationale forestière et minière
UMHK: union minière du haut-katanga
also built infrastructure
including hospitals and schools
political administration and police force
—> state in a state
minerals in India
no interest from European investors
focus on trade, taxes, opium and tea
long indian tradition of artisan skills
development stimulated by british
profited from infrastructure (rail network)
indian plants
tata iron and steel works
Jamsetji Tata: indian man who created it himself, tata dynasty => now also cars and phones, hotel (the taj in mumbai)
WWII: largest steel producer of British empire
petrol in the middle east
discoveries in the mid-19th century
1850s: galicia (poland), romania, baku (azerbajan); 1860s: united states
refining paraffin and keresene from crude oil
discoveries at the turn of the century
1885: sumatra; 1908: persia (petrol discovered in colonies)
internal combustion engine
oil companies
anglo-persian oil company (1908), —> British Petrol (1954)
royal dutch petroleum company (1890) —> royal dutch shell (1907)
other seven sisters: american
mutual effect colonization and transport
transport on colonisation
arteries of empire
shrinkage of imperial distances
greater homogenization of colonial empires
colonization on transport
impetus to development
competition in europe
waterways
rivers as the first ‘highways’
mekong, zambezi, congo,…
many new river canals
ex ganges canal (1854): transport and irrigation
important sea canals
suez canal (1869): french (ferdinand de lesseps)
london-bombay: almost half the distance
ex suez about 20.000 egyptian labourers died
massive financial burden for egyptian people
panama canal (1914): US
1880-1900: French but fraud and mismanagment so Americans took over
-1999 US territory of the canal zone
railways
much variety
Brits built very dense network of railroads in India
Congo: short railways to bypass difficult river sections
great investment
originally funded by private companies
India: railway guarantee scheme (1849): 5% return rate
often lacked the means
physical obstacles —> control of the state
mountains (darjeeling and Shimla = summer capitals)
railway stations: palaces (temples of modernity)
most famous one in Bombay (mumbai)
unfulfilled projects
cape-to-cairo
trans-saharan: from dunkirk to brazzaville
colonies as laboratories
experiments with fex gyrobus
air transport
colonization fueled/triggered development of airplanes
imperial airways (1924, after merges)
1927: cairo-basra, 1932 cairo-cape town (no longer need to cape-to-cairo railway)
1938: british airways as a separate european carrier
KLM (1919)
1924: amsterdam-batavia (20 stops, 1 oct - 24 nov)
1930: passenger service
1940: six days; after WWII: less than 24 hrs
Sabena (1923)
flights to confo cf SN brussels airlines today
communication
post
1840: penny post in the UK (send a letter for just one penny)
1854: penny post introduced in India
telegraph
1837/44: morse telegraph in line in Bengal
decisive in Great Mutiny (1857)
first submarine cable to India: 1870
radio
from 1912 onwards
mutual effect colonization and science
science on colonization
exploit the resources
mining, agriculture,…
ex Edmond Leplae (leuven professor) => cash crops suchaas cotton to congo
control the colonized
expertise, infrastructure, weapons,…
also development antropology,…
ex Edouard de Jonghe (leuven) => developed african studies, basically trained colonials
conolization on science
new data
Alexander von Humboldt => voyaged to discover flora around the world
new research questions
Eugène Dubois => looking for link between humans and animals (apes)
==> institutionalization of tropical sciences
botanical gardens
geographical sciences
Institute of tropical medicine (Antwerp
==> universities and the colonial past
closely involved with colonies
geography
acquisition of geographical knowledge
need: practical guides
capacity: travelling and instuments => possibility to make greater voyages
mapping the world
great trigonometrical survey of India
1802-1841
rivers, lands, altitudes
a surveyor general of India: George Everest
admiralty hydrographer in Britain (1795)
fourth Hydrographer (1829-1855): Francis Beaufort (beaufort scale measuring winds)
subjectivity of geography
metaphores of power
ex center (mercator map with Europe in center of the world), color (color all territories belonging to metropole), names (appropriating by naming),…
instruments of rule
ex borders
first: drawing lines with limited knowledge
then: boundary comissions for adjustment
local people not represented
vs non-european views
fluid borders
nomadic peoples being tributary rather than sovereign
place names
new names
places: New York, New Zealand,…
royalty and rulers: Montreal, Leopoldville,…
Saints: San Francisco, Sao Tomé, Natal,…
Colonizers: Pennsylvania, Rhodesia, Brazzaville, Stanleyville…
old names
ex Massachusetts, Delaware,…
new trends
koisan (called bushmen, hottentots), inuits (eskimos),…
native americans (US), first nations (Canada), Amerindians (South America),…
anthropology
knowledge
insight into social conditions
power and control
appropriate plans for dealing with population
classification
creating absolute boundaries along ethnic, cultural, regional, linguistic and religious lines
racism
measuring physical appearance (and categorizing based off of measurements)
hierarchy between categories
indigenous people on display
places
zoo’s,…
shows, circusses,… = performances
villages on world fairs
involved people
carl hagenbeck: “father of the modern zoo” => organizer of many of the human zoos
saartjie baartman or hottentot venus
khoi slave with large buttocks and elongated inner labia
1810-15: exibited as freak show attraction in UK & France
-1974: preserved genitals exhibited in Paris Musée de l’homme
2002: remains repatriated to south africa
transformation of the landscape
ex clearance of forests
Australia: 87,6 million hectares cleared before 1920
several reasons
for direct revenues: timber (teak),…
for agricultural and pastoral purposes: plantations
economic progress?
profits for Europe
focused on the promotion of commercial crops
risks of salinity and malaria
hunting
great numbers
40000-60000 elephants killed per annum in 19th c
tiger became an endangered species by the 1930s
different resons
indigenous: food
europeans: sport, prestige, masculinity, dominance,…
changing attitude
first: concern for conservation of species and habitat
first national parks: 1920s
now: indignance about local poachers
cities
old
often deep local roots of urban development
…and new
segregation (civil lines only inhabited by white people)
laboratories for experiments on urban modernity
new delhi: multi lane highways, great mansions,…
variety
french: less planning and more population mixing
british: more residential segregation
belgians: ‘most thorough practitioners of segregation’ (ville europeenne and cite indigene
but: white cities and african ‘villages’ in most of africa’
architecture
variety ex within british empire
wood in georgetown, guyana
saracene (mimic asian/arab style) style in kuala lumpur, malaysia
colors and ironwork in Cape Town, south africa
grandeur in new delhi
mixed styles
orientalism => “all in the east”
ex sfinx in India,..