reliability and external validity (in scale development)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
what is reliability across time?
test-retest reliability
involves two administrations of the scale
assumes that the construct is stable across time
what is internal consistency (in reliability)?
split-half reliability/Cronbach’s alpha/McDonald’s omega hierarchal and omega total
involves only one administration of the scale
most common way papers test reliability
what does test-retest reliability measure?
consistency of our measurement when used under the same conditions with the same participants
doesn’t work if studying a construct that is expected to vary across time points
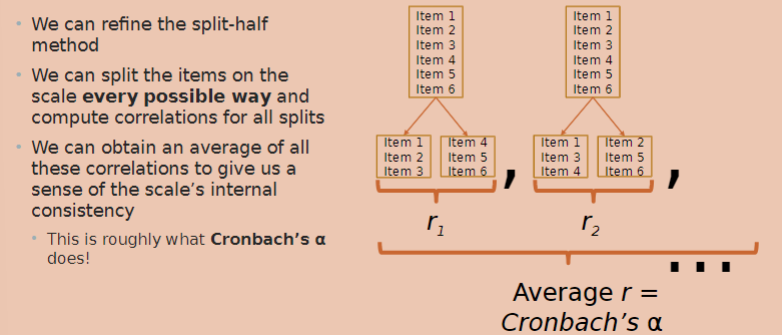
what does split-half reliability measure?
internal consistency estimates relate to item homogeneity; to what extent items measure the same construct
involves splitting a scale into two halves and calculating an average score for each half of the scale
calculate correlation between those half-scale scores; string correlation = high split-half reliability
reliability will depend on how you split the data
interpreting Cronbach’s alpha
interpret the same as Pearson’s r
varies from 0 (no internal consistency) to 1 (perfect internal consistency) but no negative values
acceptable reliability: α ≥ .7 (but depends on other factors)
other statistics that help interpret Cronbach’s alpha
α if item removed - calculates the alpha but leaves out each item one at a time; if α improves the scale is more reliable without it
item-total correlation - correlation between the score on an item and score on the scale as a whole
sources of misuse of Cronbach’s alpha
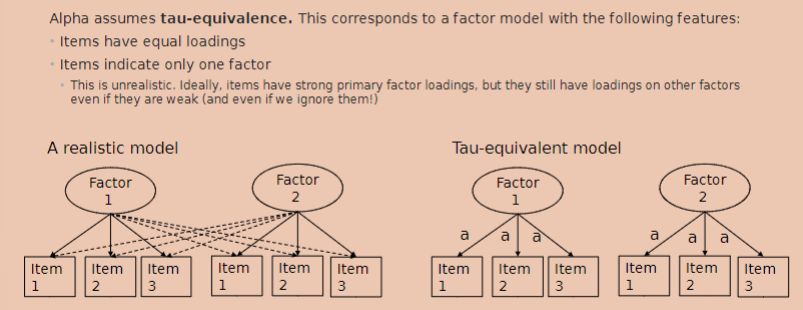
it makes assumptions about the shape of the factor model; if these assumptions are not met, it can be misleading
using it as evidence of a scale’s dimensionality
it is sensitive to the number of items in a scale
alpha and unidimensionality
alpha is designed to be computed for scales with only one factor or it doesn’t work properly however it cannot be used as a measure of unidimensionality

key characteristics of McDonald’s Omega
measure of internal consistency
McDonald’s Omega hierarchical and Omega total
does not assume tau-equivalence or unidimensionality
assumes the existence of a general factor
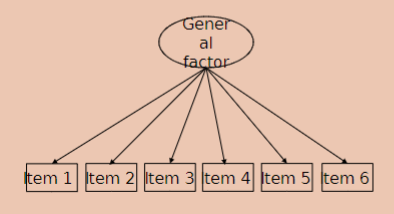
when do you use Omega hierarchical?
unidimensional scales; items share variance with a general factor
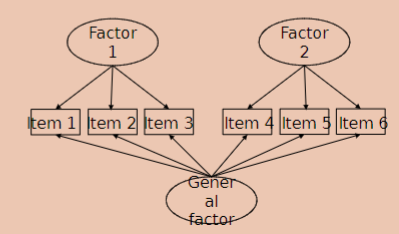
when do you use Omega total?
multidimensional scales; items share variance with both the extracted factors and the the general factor
what are reverse-coding items?
items that measure the same idea but on the opposite direction
what is a composite score?
a single score obtained by aggregating (e.g. summing, averaging) the items from a scale
what is convergent validity?
tests whether constructs that should be related in theory are related in reality (i.e. their measures correlate)
what is discriminant validity?
tests whether constructs should not be related in theory are not related in reality (i.e. their measures don’t correlate)