L18 - Injuries to the Head, Neck or Spine
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What clues do you check the scene during the size-up to whether a head, neck, or spine injury may have occurred?
Is unresponsive
Was involved in a motor vehicle crash or subjected to another significant force
Was injured as a result of a fall from greater than the person's standing height
Is wearing a safety helmet that is broken
Complains or neck or back pain
Has tingling or weakness in the extremities
Is not fully alert
Appears to be intoxicated
Appears to be frail
Is older than 65 years
Is a child younger than three years with evidence of head or neck injury
If victim is responsive, what question could you ask to further assess the situation?
Does your head, neck, or back hurt?
What happened?
Where specifically does it hurt?
Can you move your hands and feet?
Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spine injuries
Understand situations that may indicate serious head, neck or spine injury
List signs and symptoms of head, neck and spine injuries
Changes in level of consciousness
Severe pain or pressure in the head, neck, or spine
Tingling or loss of sensation in the extremities
Partial or complete loss of movement of any body part
Observable, unusual bumps or depressions on the head or neck
Sudden loss of memory
Blood or other fluids in the ears or nose
Profuse external bleeding of the head, neck or back
Seizures in a person who does not have a seizure disorder
Impaired breathing or impaired vision as a result of injury
Nausea or vomiting
Persistent headache
Loss of balance
Bruising of the head, especially around the eyes or behind the ears
Describe how to care for specfic injuries to these areas
Minimize movement of the head, neck, or spine by asking the person to remain still
Because excessive movement of the head, neck, or spine can damage the spinal cord irreversibly, remind the person to remain as still as possible and provide comfort and reassurance to them until 9-1-1 arrives and takes over.
If the person is wearing a helmet, did not remove it unless you are specifically trained to do so and it is necessary to assess the person's airway.
Check for life-threatening conditions.
Monitor responsiveness and breathing.
Control any external bleeding with direct pressure unless the bleeding is located directly over suspected fracture.
Do not apply direct pressure if there's any signs of an obvious skull fracture.
Do not attempt to remove a penetrating object rather, stabilize it with a bulky dressing.
Wear disposable gloves.
Take steps to minimize shock.
Keep the person from becoming chilled or overheated.
If the person vomits while you are with them, log-roll the person onto their side while keeping the spine aligned, to clear the airway.
If you need to leave the person such as to call 911 or to get an AED, carefully place them in the recovery position to protect their airway if they begin to vomit. However do not place a person with a head, neck, or spinal injury in the recovery position if you are unable to remain with the person and monitor their condition.
What if… you suspect an injury to the spine and the person is not breathing? Which is more important -keeping the spine from moving or giving CPR?
While the general rule is to always leave a person's head, neck, or spine in the position found without any movement or alignment with the body → if the person is unresponsive and not breathing, giving CPR must take precedence over not moving the head or neck
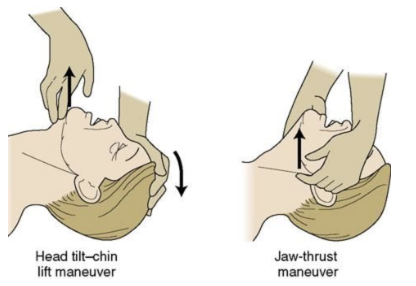
Perform a jaw thrust to open the airway instead of a head-tilt-chin-lift technique
List the specific injuries to Head, Neck, Spinal
Concussion
Scalp
Nose
Mouth
Dental
Cheek
Eye
Ear
Define Concussion
A common type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) that involves a temporary loss of brain function
CAUSE
Concussions are particularly common sports related injuries, but they can occur whenever a person experiences a bump, below, or jolt to the head or body that results in rapid movement of the head
RESULT
A concussion can result from even a seemingly minor bump, blow, or jolt and may be tricky to recognize
Steps for Care for Concussion
Every suspect a concussion should be treated seriously
The person should always follow up with the healthcare provider for a full evaluation
If you are unsure of the seriousness of the concussion, call 9-1-1
While waiting for healthcare providers to arrive, monitor the person for any changes in their condition and try to comfort and reassure the person
Encourage the person to talk with you to help keep the person calm
Define Scalp Injuries
Scalp bleeding can be minor or severe. However, minor lacerations can appear to bleed heavily because the scalp contains many blood vessels.
Steps for Care for Scalp Injuries
If the person has an open wound to the scalp, control the bleeding with direct pressure:
Apply several dressings and hold them in place with your gloved hand. If gloves are not available, use a protective barrier.
Be sure to press gently at first because the skull may be fractured
If you feel a depression, spongy area or bone fragments, do not put direct pressure on the wound
Attempt to control bleeding with pressure on the area around the wound.
Secure the dressing with a roller bandage or triangular bandage
Examine the injured area carefully because the person's hair may hide part of the wound. Call 9-1-1 if you are unsure about the extent of the injury.
Define Nose Injuries
Facial trauma can range from minor injuries (lacerations and abrasions, bruises, bloody noses and knocked out teeth) to more severe injuries, such as fracture of one or more of the facial bones
CAUSE
Falling or getting hit in the nose can result in a nosebleed
RESULT
A person with a facial injury may also have a head, neck ,or spinal injury, such as a concussion
Steps for Care for Nose Injuries
In most cases, you can stop nose bleed by having the person put a piece of gauze at the nostrils and pinch their nostrils together and while sitting with the head tilted slightly forward
Sitting with the head tilted forward helps to keep blood from pooling in the back of the throat, which can cause choking or if the blood is swallowed, vomiting
Keep the nostrils pinched for at least five minutes before checking to see if the bleeding is stopped
If the bleeding has not stopped after five minutes keep the nostril shut for another five minutes if the bleeding is severe or gushing, call 9-1-1
Define Mouth Injuries
Injuries to the mouth may cause breathing problems if blood or loose teeth block the airway, so make sure the person is able to breathe
Steps for Care for Mouth Injuries
f the person is bleeding from the mouth and you do not suspect a serious head, neck, or spinal injury, place the person in a seated position leaning slightly forward
This will allow any blood to drain from the mouth. If this position is not possible, place the person on their side in the recovery position
Have the person hold a gauze pad at the site of bleeding and apply direct pressure to stop the bleeding
(If the person is responsive, having the person apply direct pressure to a wound inside their own mouth is easier and safer than doing it for the person.)
Define Dental Injuries
If a tooth is knocked out, control the bleeding by placing a rolled gauze pad in the space left by the missing tooth and have the person gently bite down to maintain pressure.
Steps for Care for Dental Injuries
Try to locate and save the tooth, because the dentist or other healthcare provider may be able to re-implant it
Place the tooth in Hanks Balanced Salt solution (Save-A-Tooth if available)
If you do not have Hanks Balance Salt solution, place the tooth in egg white, coconut water, or whole milk. If these are not available, place the tooth in the injured person's saliva
Be careful to pick up the tooth only by the crown (the part of the tooth that is normally visible above the gum line rather than by the root.)
The person should seek dental or emergency care as soon as possible after the injury
The sooner the tooth is re-implanted, the better the chance that it will survive
Ideally re-implantation should take place within 30 minutes
Define Cheek Injuries
Injury to the cheek usually involves only soft tissue
If an object passes completely through the cheek and becomes embedded, and you cannot control bleeding with the object in place, the object should be removed so that you can control bleeding and keep the airway clear
This circumstance is the only exception to the general rule not to remove embedded objects from the body
Steps for Care for Cheek Injuries
Remove the object by pulling it out in the same direction it entered.
Fold or roll several dressings and place them inside the mouth. Also, apply dressings to the outside of the cheek. Be sure not to obstruct the airway.
If there are no suspected head, neck, or spinal injuries, place the person in a seated position, leaning slightly forward, so that the blood will not drain into the throat. As with any severe bleeding or embedded object, call 9-1-1.
Define Eye Injuries
Injuries to the eye can involve the bone and soft tissue surrounding the eye or the eyeball
CAUSE
Blunt objects, such as a fist or a baseball, may injure the eye area, or a smaller object may penetrate the eyeball. Injuries that penetrate the eyeball are very serious it can cause blindness.
Foreign bodies, such as dirt, sand, or slivers of wood or metal that get in the eye are irritating and can cause significant damage.
RESULT
Pain from the irritation is often severe → The person may have difficulty opening the eye because light further irritates it.
Steps for Care for Eye Injuries (foreign body)
Try to remove the foreign body by telling the person to blink several times, then try gently flushing the eye with water.
If the object remains, the person should receive more advanced medical care. The eye should be flushed continuously until EMS personnel arrive.
Flushing the eye with water is also appropriate if the person has any chemical in the eye. Flush the eye continuously until advanced medical personnel arrive. If only one eye is affected, make sure you do not let the water run into the unaffected eye. (The bad eye is below the good eye under the running water as seen in the picture).
Steps for Care for Eye Injuries (embedded object)
Place the person in a face-up position and enlist someone to help stabilize the person's head.
Do not attempt to remove any object embedded in the eye.
Stabilize the object by encircling the eye with a gauze dressing or soft sterile cloth, being careful not to apply any pressure to the area.
Position bulky dressings, such as a roller gauze, around the impaled object and then cover it with a shield such as a paper cup. Do not use Styrofoam type materials as small particles can break off and get into the eye.
The shield should not touch the object. Bandage the shield and dressing in place with a self adhering bandage and roller bandage covering the persons injured eye, as well as the uninjured eye, to keep the objects stable and minimize movement. (eyes track together, so make sure to cover BOTH eyes).
Comfort and reassure the person. Do not leave the person unattended.
Define Ear Injuries
Injuries to the ear are common
CAUSE
Open wounds, such as lacerations or abrasions, can result from recreational injuries, such as being struck with a racquetball or falling off a bike
An avulsion of the ear can occur when a pierced earring catches on something and tears away from the ear
The ear can also be injured internally
A foreign object, such as dirt, an insect or cotton, can easily become lodged in the ear canal
A direct blow to the head may rupture the eardrum
Sudden pressure changes, such as those caused by an explosion or a deep-water dive, can also injure the ear internally.
RESULT
The person may lose hearing or balance or experience inner ear pain → These injuries require more advanced medical care
Steps for Care for Ear Injuries
If you can easily see and grasp the object, remove it.
Do not try to remove an object by using a pin, toothpick, or similar sharp item
You could force the object farther back or puncture the eardrum.
If you cannot easily remove the object the person should seek more advanced medical care.
If the person has a serious head injury, blood or other fluids may be in the ear canal or maybe draining from the ear
Do not attempt to stop this drainage with pressure. Instead, loosely cover the ear with a sterile dressing
Call 9-1-1 or the designated emergency number
Understand prevention principles
Correctly wear safety belts
Correctly wear approved helmets, eyewear, faceguards and mouthgaurds where recommended
Use non-slip mats to showers and tubs
Use proper lifting techniques when lifting heavy objects
Do not dive into a body of water if you don’t know the depth
Think and talk about safety