I. Fundamental Hematology Principles
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Whole Blood Includes…?
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, and plasma
Buffy Coat
Small white layer btn RBCs & plasma
Appears when specimen is centrifuged
Leukocytes and platelets
Plasma
Liquid portion of unclotted blood OR component produced when blood contains anticoagulant
Serum
fluid remaining after coagulation and a clot has formed
Plasma vs Serum
contains ALL coag factors vs LACKING fibrinogen group (I, V, VIII, XIII) coag proteins
Homeostasis
the process that maintains stable internal conditions in the body, including blood clotting and fluid balance.
Normal Osmotic Concentration
aka Isotonic = osmotic pressure is balanced with cells, preventing net movement of water.
Hypotonic Solution
↑ H2O, ↓ Solute conc.
Cells swell → lyse
Hypertonic Solution
↓ H2O, ↑ Solute conc.
Cells crenate
pH reference range: venous vs. arterial blood
venous: 7.36-7.41
arterial: 7.38-7.44
Body Temp Normal Range
37°C (97-99°F)
MCV (mean corpuscular volume) range, definition, and importance
80-100 fL
avg. vol. of RBC
↑ = megaloblastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, liver disease, norm newborn
↓ = iron defic. anemia, thalessemia, sideroblastic anemia, lead poisoning
MCH (mean corpuscular HgB) range, definition, and importance
26-34 pg
avg. weight of HgB in RBC
↑ = macroytic anemia
↓ = microcytic, hyperchromic anemia
MCHC (mean corpuscular HgB conc.) range, definition, and importance
32-37 g/dL
avg. conc of HgB in RBC
↑ = error or spherocytes, hyperchromic
↓ = hypochromic RBCs → iron defic. and thalessemia
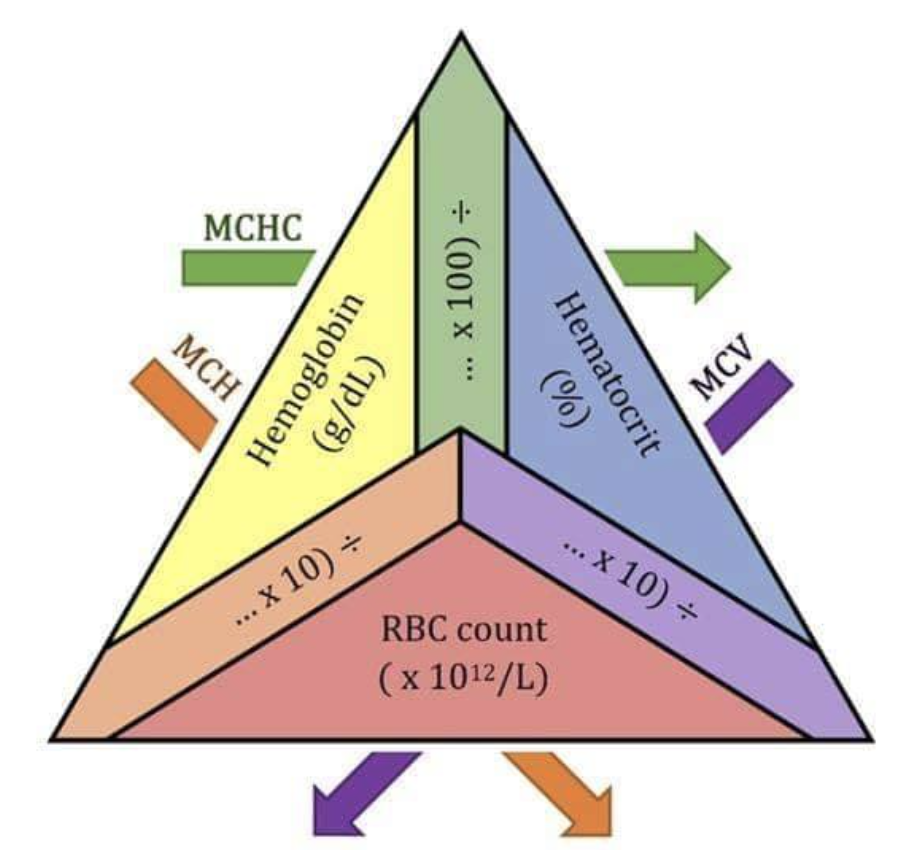
MCH (pg) formula
Hgb (g/dL) x 10 / RBC count ( x 10^12/L)
MCV (fL) formula
HCT (%) x 10 / RBC count (x 10^12/L)
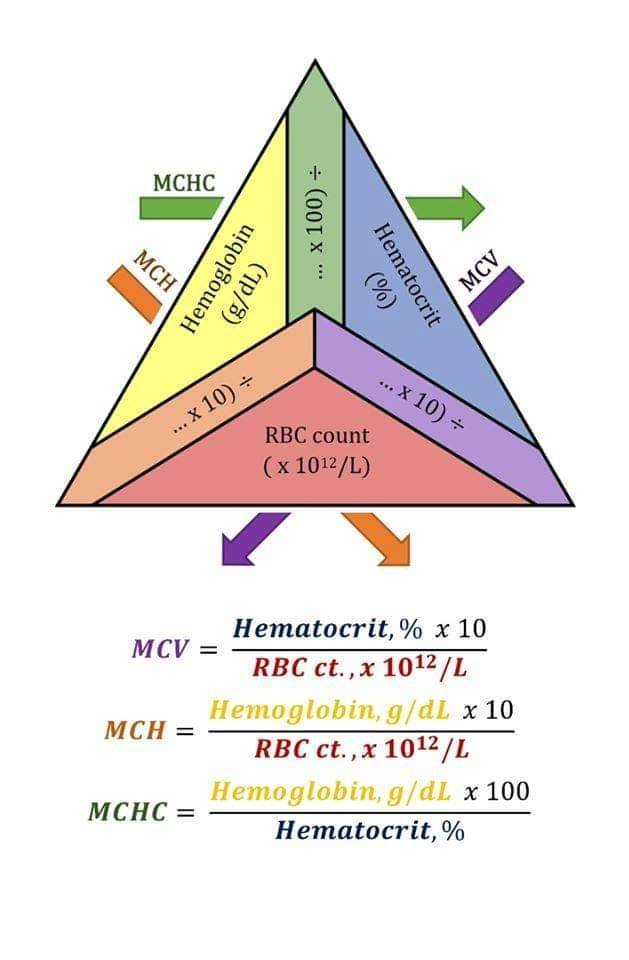
MCHC (g/dL) formula
Hgb (g/dL) x 100 / Hct (%)
RBC indicies triangle
Hgb (Hemoglobin) Reference Range
Males: 13.5-17.5 g/dL
Females: 12.0-16.0 g/dL
Platelets Reference Range
150 - 450 × 10^9/L (150,000-450,000/uL)
MPV (mean platelet volume)
6.8 - 10.2 fL
*Note: MPV is analagous to MCV for RBCs
Relative vs Absolute Count
Proportion of a cell type in WBC count % vs. actual cells per blood volume #.
Relative Lymphocytosis
inc. in % of lymphocytes, associated w/ neutropenia
Absolute Lymphocytosis
inc. in # of lymphocytes
Relative vs Absolute polycythemia
increase in RBCs, distinguishing between % and actual # of cells.
Most common: Wright stain
Contains Methylene blue: basic dye that stains acidic (DNA and RNA) blue
Contains Eosin: acidic dye that stains basic (Hgb and eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules) red-orange
Methanol Fixative
Phosphate Buffer: 6.4-6.8
Nonvital (dead cell) polychrome (Romanowsky)
Causes of RBCs too red and WBC nuclei poorly stained
< 6.4 pH, excess buffer, dec. staining time, inc. washing time, thin, expired stains
Causes of RBCs and WBC nuclei poorly stained
> pH 6.8, too little buffer, inc. staining time, poor washing, thick smear, inc. protein, heparinized blood sample
Nonvital Monochrome Stain
Ex: Prussian blue stain, used to identify iron granules
New methylene blue: stains RNA in reticulocytes
Measure level of erythropoiesis
Neutral red w/ brilliant cresyl green: visualize heinz bodies
shows G6PD deficiency, unstable HgB
Supravital Monochrome Stain