Nervous System Physiology & Pharmacology: Action Potentials, Synapses, Receptors, and Autonomic Drugs
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What initiates the generation of an action potential?
Graded depolarization at the dendrite.
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
-71 mV
What happens during the depolarization phase of an action potential?
Activation of sodium channels makes the cell membrane more positive.
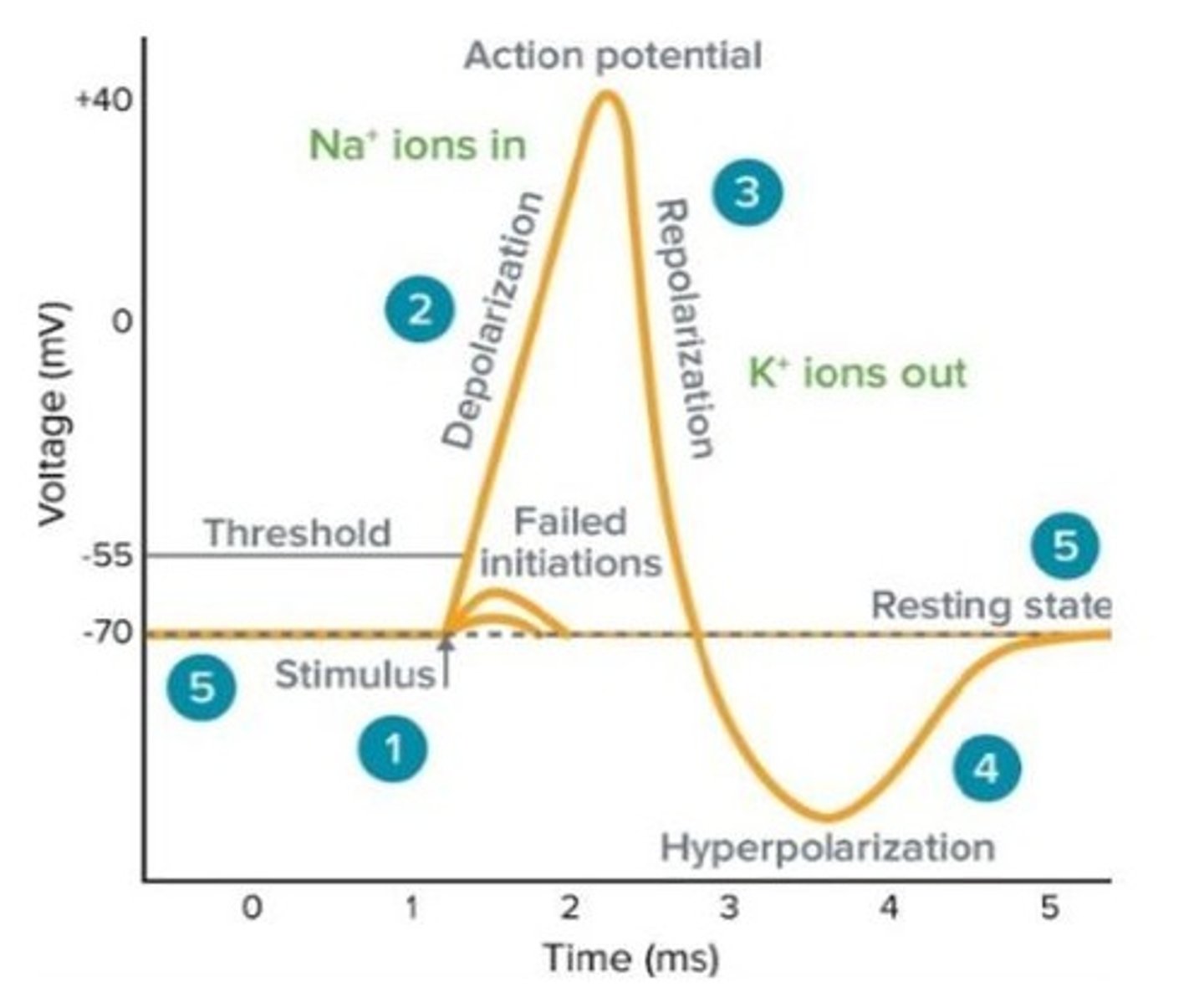
What is the role of potassium channels during an action potential?
They are activated during repolarization, making the membrane more negative.
What is the refractory period?
A state following an action potential where it is more difficult to generate another action potential.
What are the two types of synaptic transmission?
Chemical and electrical synaptic transmission.
What is the first step in chemical synaptic transmission?
Action potential arrives at the axon terminal.
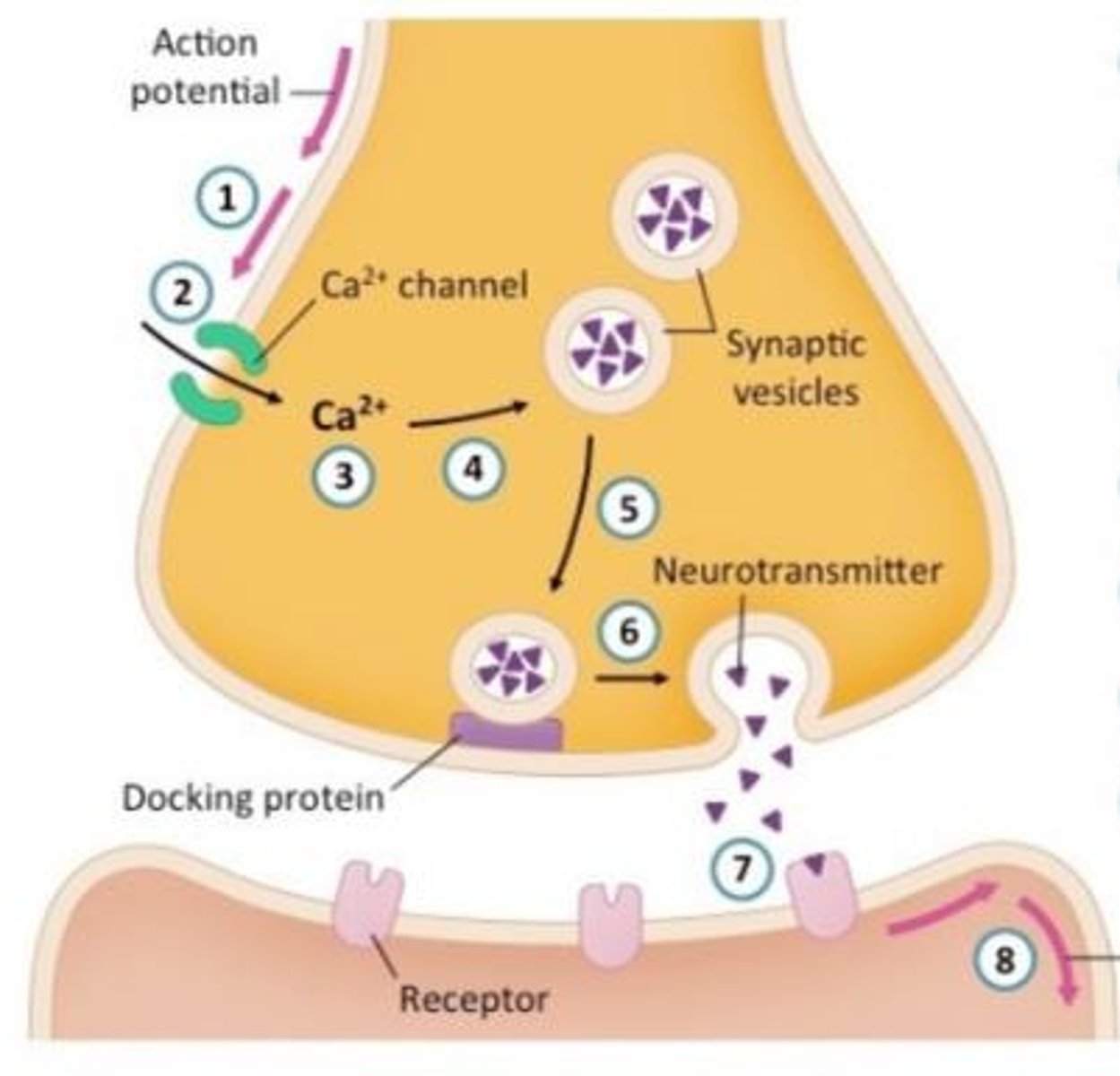
What role do calcium ions play in neurotransmitter release?
Calcium enters the presynaptic neuron and signals vesicles to release neurotransmitters.
What is acetylcholine's role in the peripheral nervous system?
It is the primary neurotransmitter for the parasympathetic division.
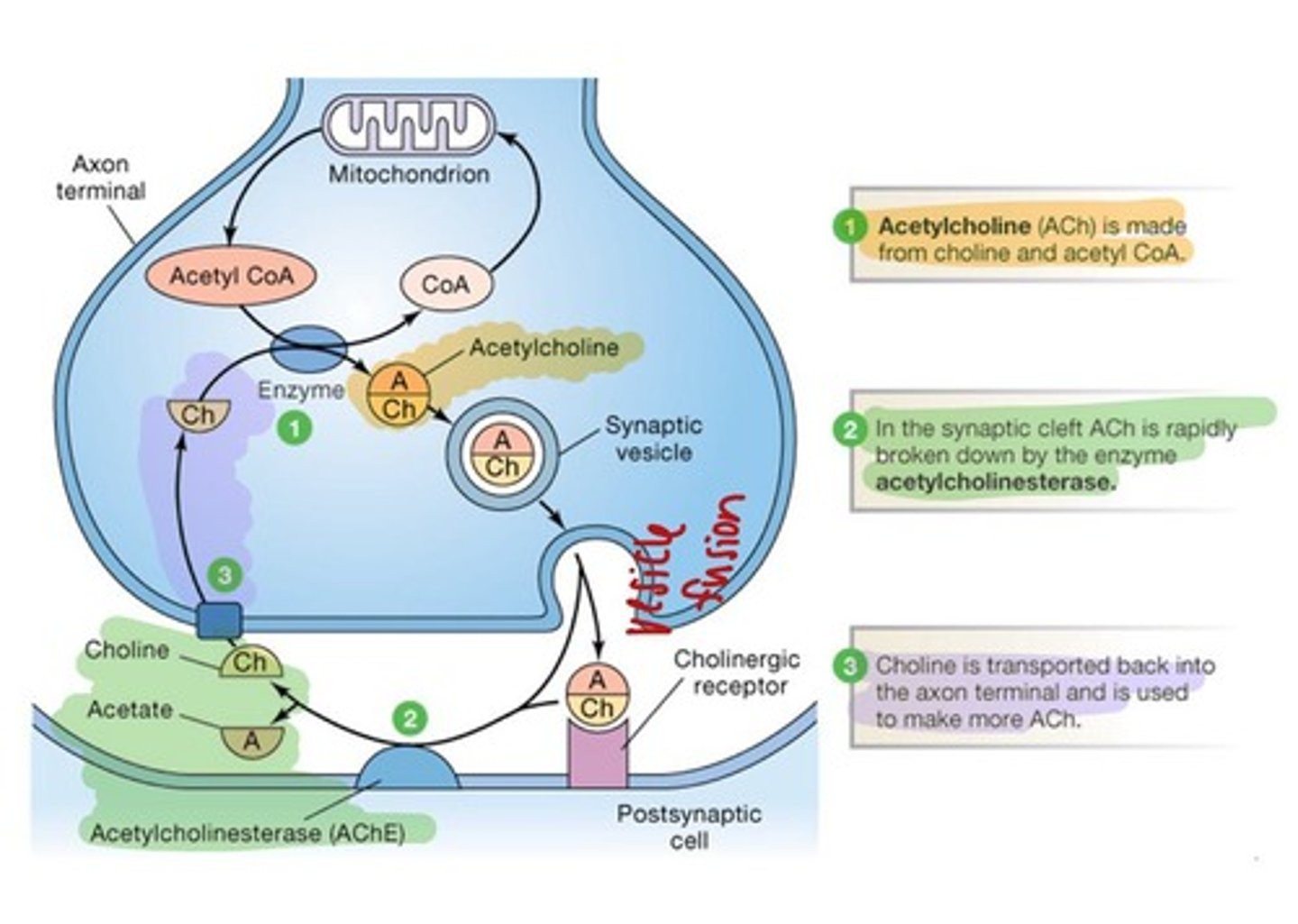
How is acetylcholine synthesized?
From acetyl CoA and choline by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase.
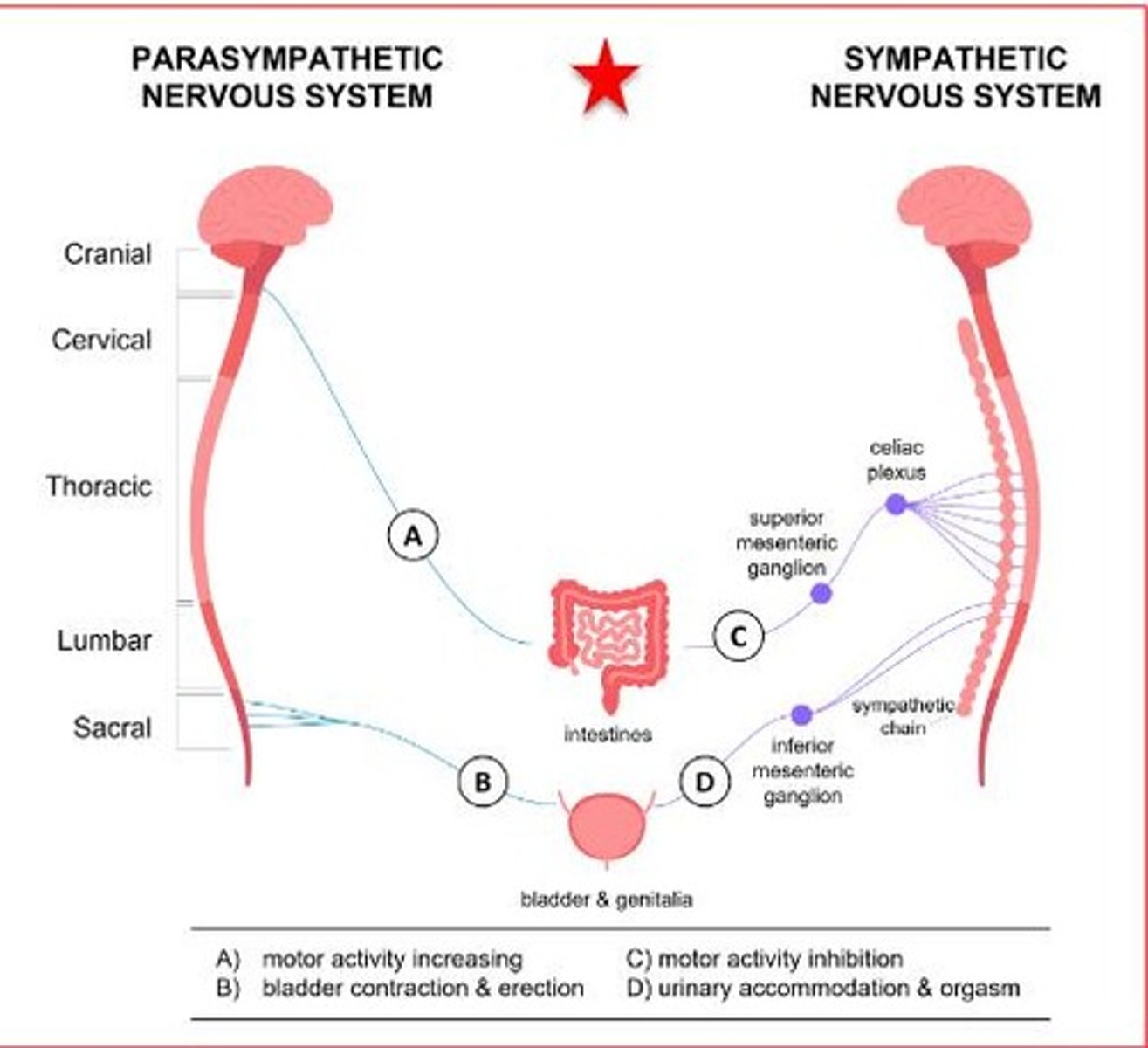
What is norepinephrine's primary function in the sympathetic nervous system?
It is involved in the fight or flight response, elevating blood pressure and heart rate.
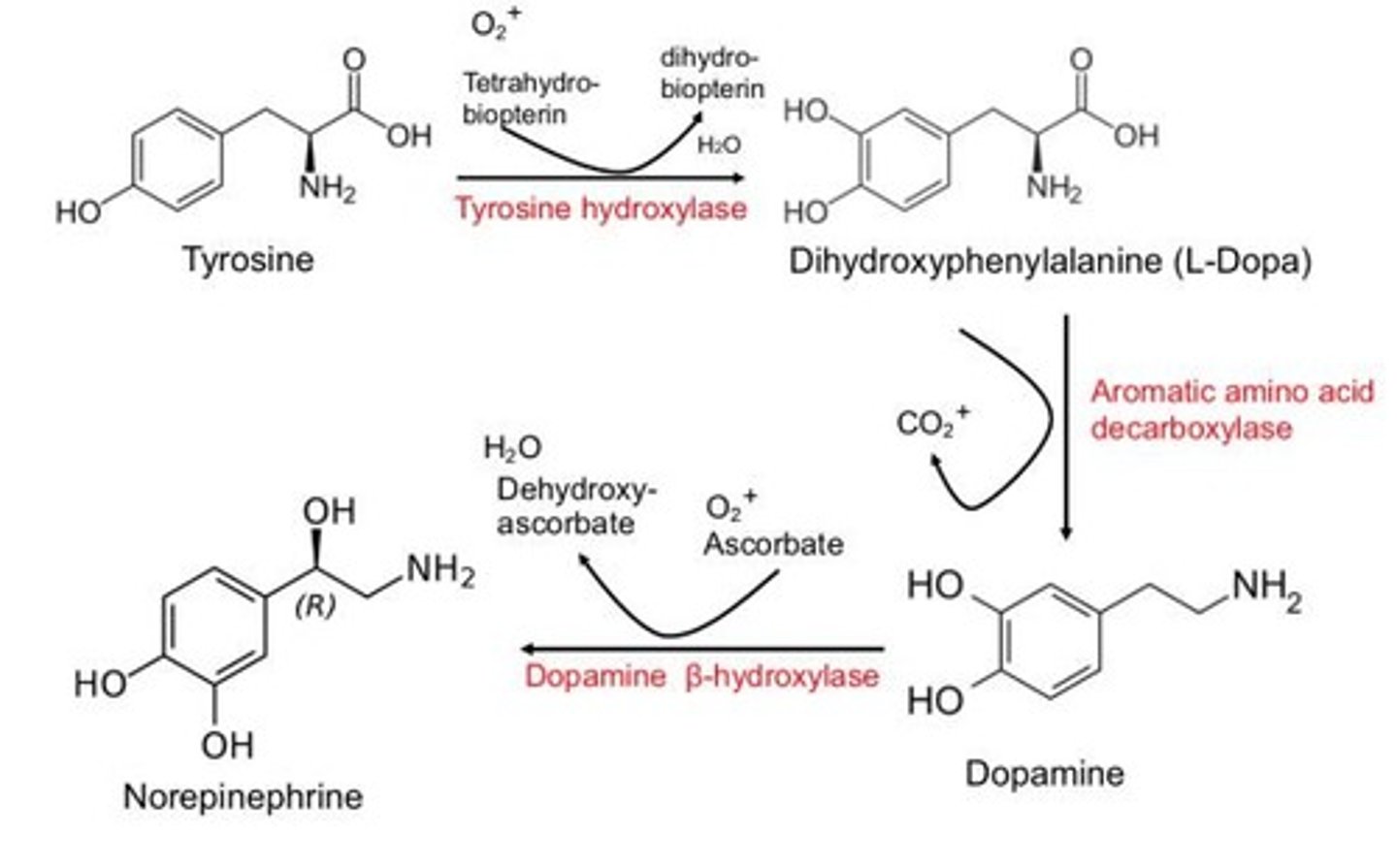
What is the precursor amino acid for norepinephrine?
Tyrosine.
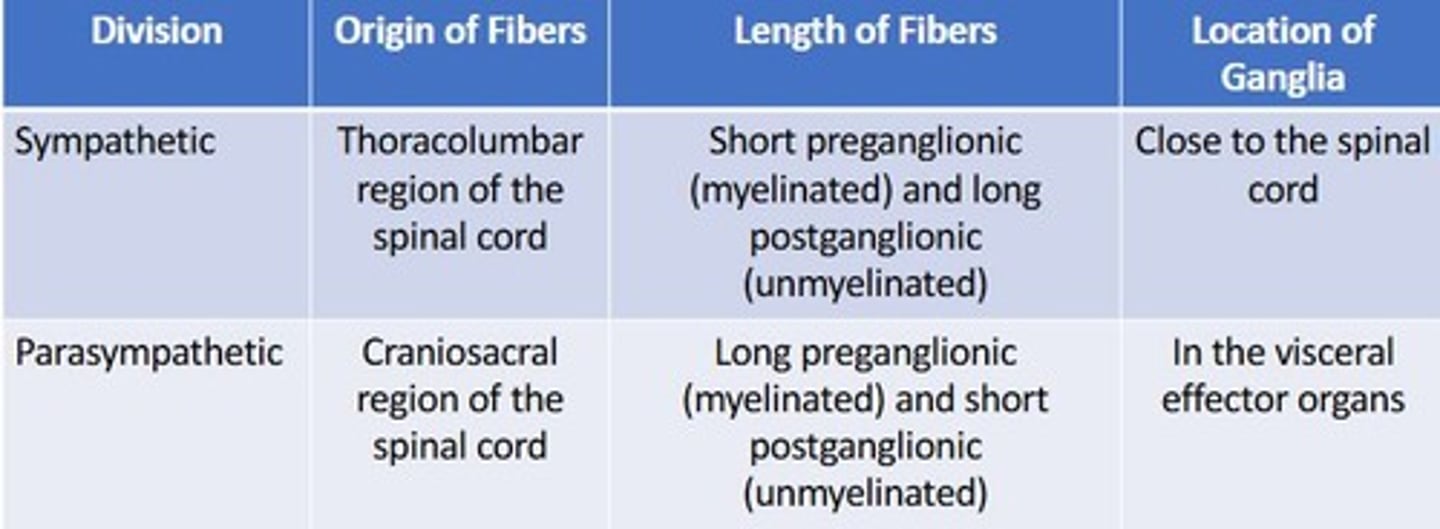
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Sympathetic division and parasympathetic division.
What is the function of the enteric nervous system?
It controls the gastrointestinal system.
What regulates the balance of autonomic activity?
The hypothalamus.
What neurotransmitter is primarily used in the sympathetic division?
Norepinephrine.
What is the difference between excitatory and inhibitory signals?
Excitatory signals promote action potential firing, while inhibitory signals inhibit it.
What is the effect of a strong stimulus on action potentials?
It increases the amplitude of the graded potential and the frequency of action potentials.
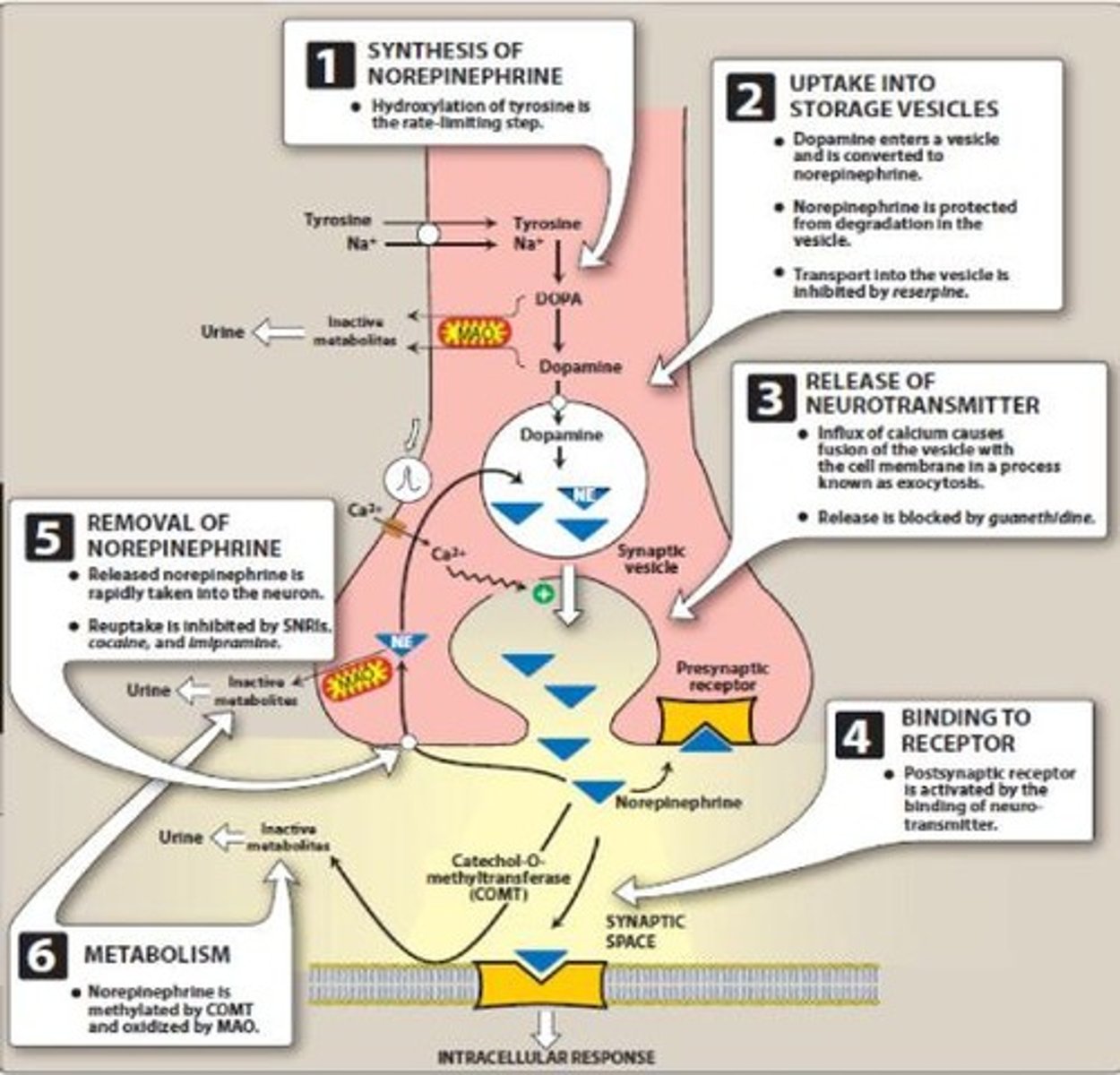
What is the difference between muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors?
Muscarinic receptors are G-protein coupled, while nicotinic receptors are ionotropic.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in synaptic transmission?
They diffuse across the synapse to continue transmission to the next neuron or target cell.
How does the sympathetic division affect digestive activity?
It reduces digestive activity.
What happens during hyperpolarization?
The membrane potential becomes more negative, making it harder to generate an action potential.
What is the significance of gap junction proteins in electrical synapses?
They allow rapid transmission of signals between neurons.
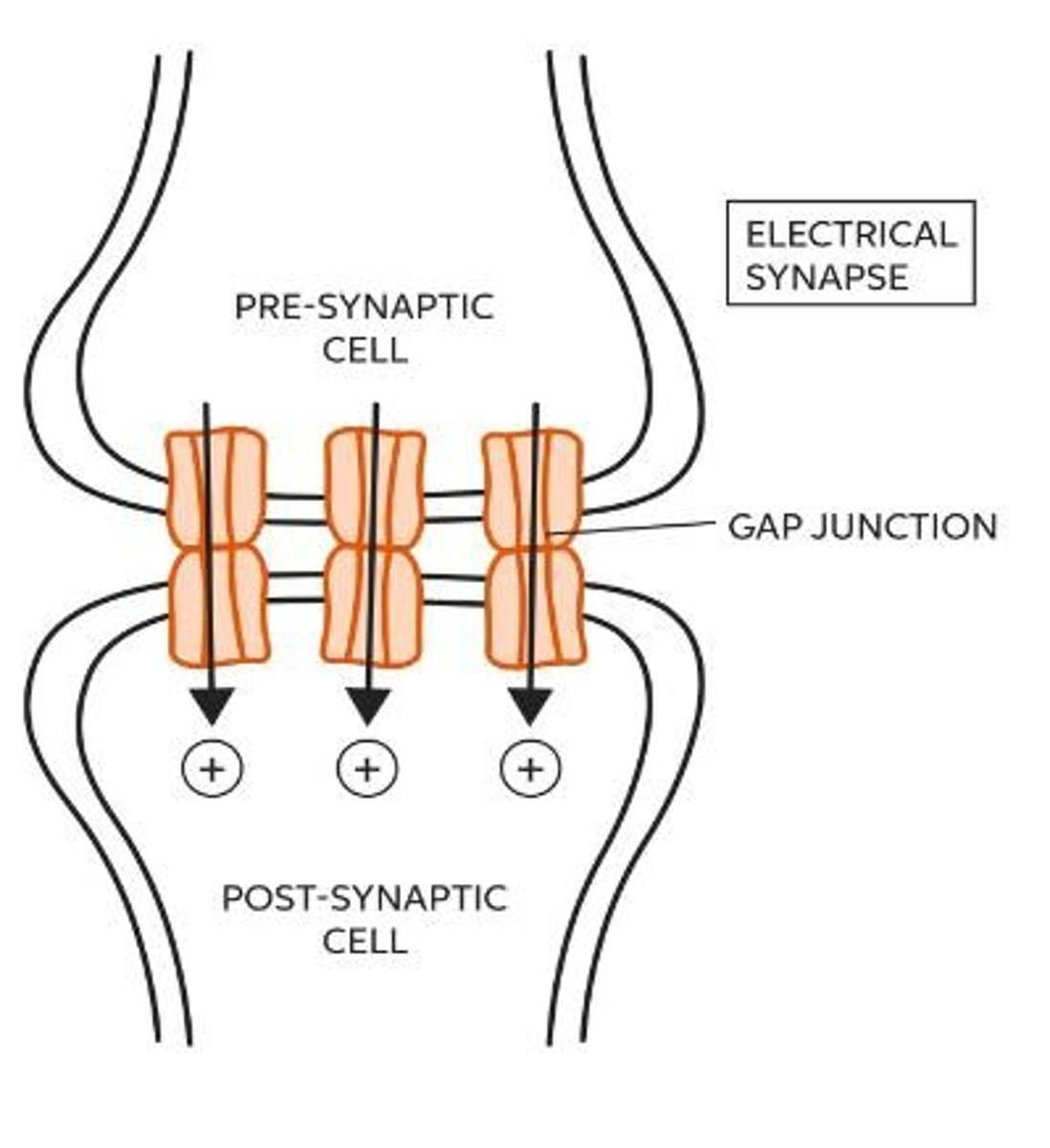
What are the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
What is the primary function of the sympathetic nervous system?
To prepare the body for 'fight or flight' responses, using and releasing energy.
What does the parasympathetic nervous system primarily promote?
Rest and digest functions, conserving energy.
What is the role of afferent signals in the nervous system?
Afferent signals carry information to the brain from sensory receptors.
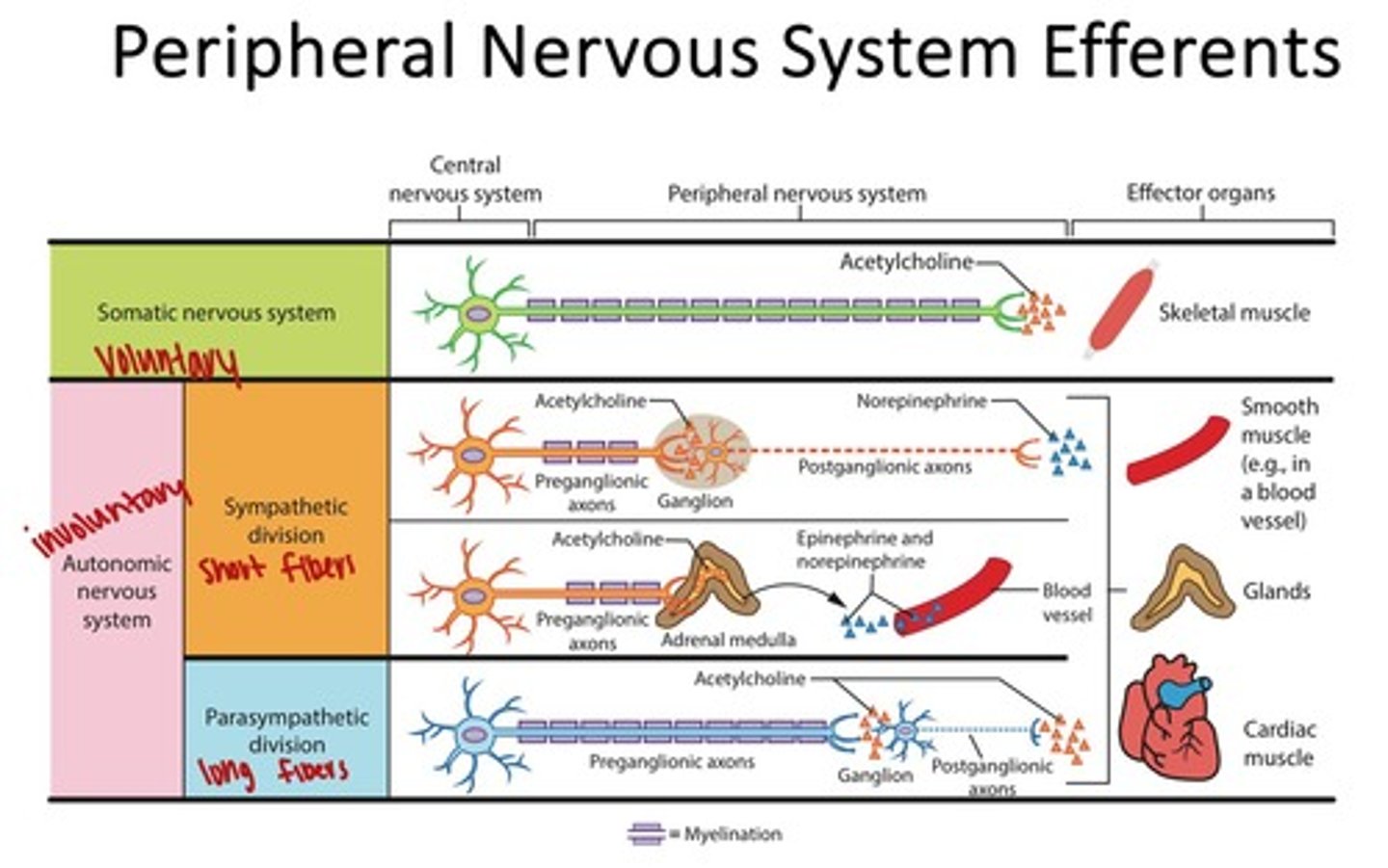
What do efferent signals do?
Efferent signals carry commands from the brain to muscles and glands.
What type of muscle does the somatic nervous system control?
Skeletal muscle, which is under voluntary control.
What distinguishes the autonomic nervous system from the somatic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions, while the somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements.
What is the structure of the autonomic nervous system's pathway?
It consists of a two-neuron pathway: preganglionic and postganglionic neurons.
Where do sympathetic nerve fibers exit from?
Thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord.
What are the effects of the sympathetic division on the cardiovascular system?
Increases heartbeat and blood supply to cardiac muscle, raising blood pressure.
What is the primary neurotransmitter used by cholinergic receptors?
Acetylcholine.
What are nicotinic receptors and where are they found?
Ionotropic receptors responsive to nicotine, found in the CNS and autonomic ganglia.
What are muscarinic receptors and their function?
Metabotropic receptors that respond to muscarine, involved in signaling through G proteins.
What are the two major classes of adrenergic receptors?
Alpha receptors (A1 and A2) and beta receptors (B1, B2, B3).
What is the effect of alpha adrenergic receptors on blood vessels?
Stimulate contraction of smooth muscle, leading to vasoconstriction.
What is the function of beta-1 adrenergic receptors?
Increase heart rate and force of contraction.
What is the role of the parasympathetic nervous system in digestion?
Stimulates secretion of digestive juices and increases the rate of digestion.
How does the sympathetic division affect respiratory function?
Causes relaxation of airway smooth muscles, leading to dilation of bronchioles.
What is the effect of the parasympathetic division on heart rate?
Decreases heart rate by approximately 25 beats per minute.
What is dual innervation in the context of the eye?
The eye receives input from both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems for different functions.
What happens to the pupil under sympathetic stimulation?
The pupil dilates to enhance vision in low light conditions.
What is the primary function of the adrenal medulla in the sympathetic response?
Secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine directly into the bloodstream.
What is the effect of the parasympathetic division on the urinary system?
Promotes relaxation of sphincters, facilitating urination.
What is the significance of the sympathetic trunk ganglia?
They lie in a vertical row alongside the vertebral column and innervate organs above the diaphragm.
What is the function of the canal of Schlemm?
It reduces interocular pressure by facilitating the drainage of aqueous humor.
What neurotransmitter increases in the eye to reduce interocular pressure?
Acetylcholine
How do parasympathetic and sympathetic tones affect heart rate?
They have opposing effects to balance heart rate.
What type of control does the parasympathetic division exert?
Short-lived, highly localized control.
What type of effects does the sympathetic division exert?
Long-lasting diffuse effects.
What is a Lewy body?
An abnormal intranural cytoplasmic inclusion composed mainly of misfolded alpha-synuclein.
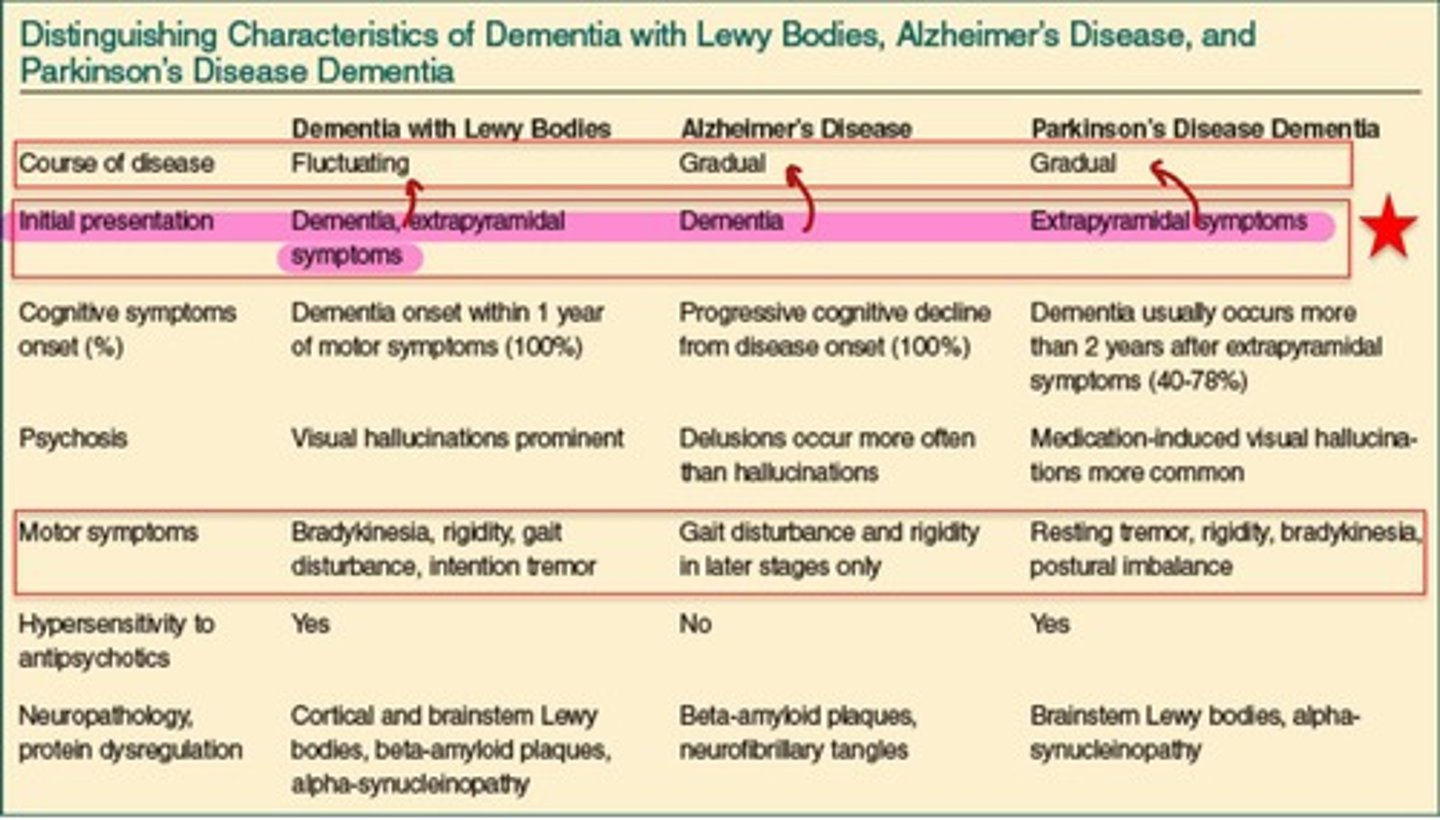
What condition is associated with the accumulation of Lewy bodies?
Lewy body dementia.
Which disease primarily affects the central nervous system?
Alzheimer's disease.
What is the role of baroreflexes in blood pressure regulation?
They are responsible for rapid adjustments in blood pressure.
Where do baroreflexes originate?
In baroreceptors located in the carotid sinus.
What happens to baroreceptor activity when blood pressure falls?
Discharges by baroreceptors are reduced, increasing sympathetic outflow.
What is baroreflex failure?
Loss of baroreflex buffering leading to labile hypertension and other symptoms.
What triggers vasovagal syncope (VVS)?
Emotional or environmental triggers, such as prolonged standing or seeing blood.
What is serotonin syndrome?
A life-threatening toxicity caused by excess serotonin.
What are common causes of serotonin syndrome?
Antidepressant medications like SSRIs, TCAs, MAOIs, and certain opioids.
What are the signs of autonomic hyperactivity in serotonin syndrome?
Tachycardia, hypertension, diaphoresis, mydriasis, flush skin, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
What is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
A rare but serious post-infectious immune-mediated neuropathy.
What triggers the immune response in Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Molecular mimicry between certain proteins, often following infections or vaccinations.
What is diabetic autonomic neuropathy?
A condition caused by hyperglycemia leading to autonomic dysfunction.
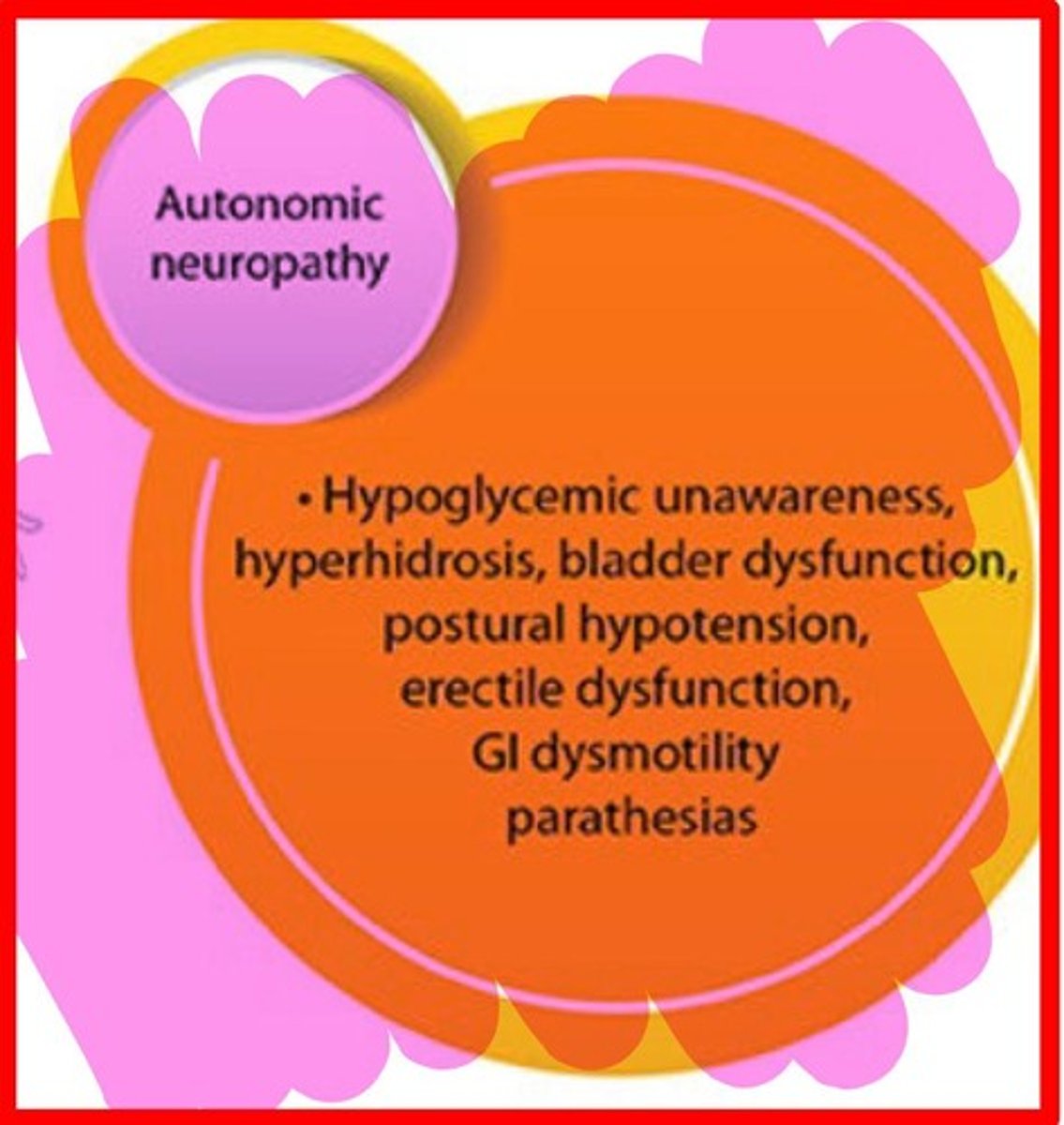
What are the major sites of action for drugs affecting adrenergic signaling?
They include catecholamine storage, release, and inactivation.
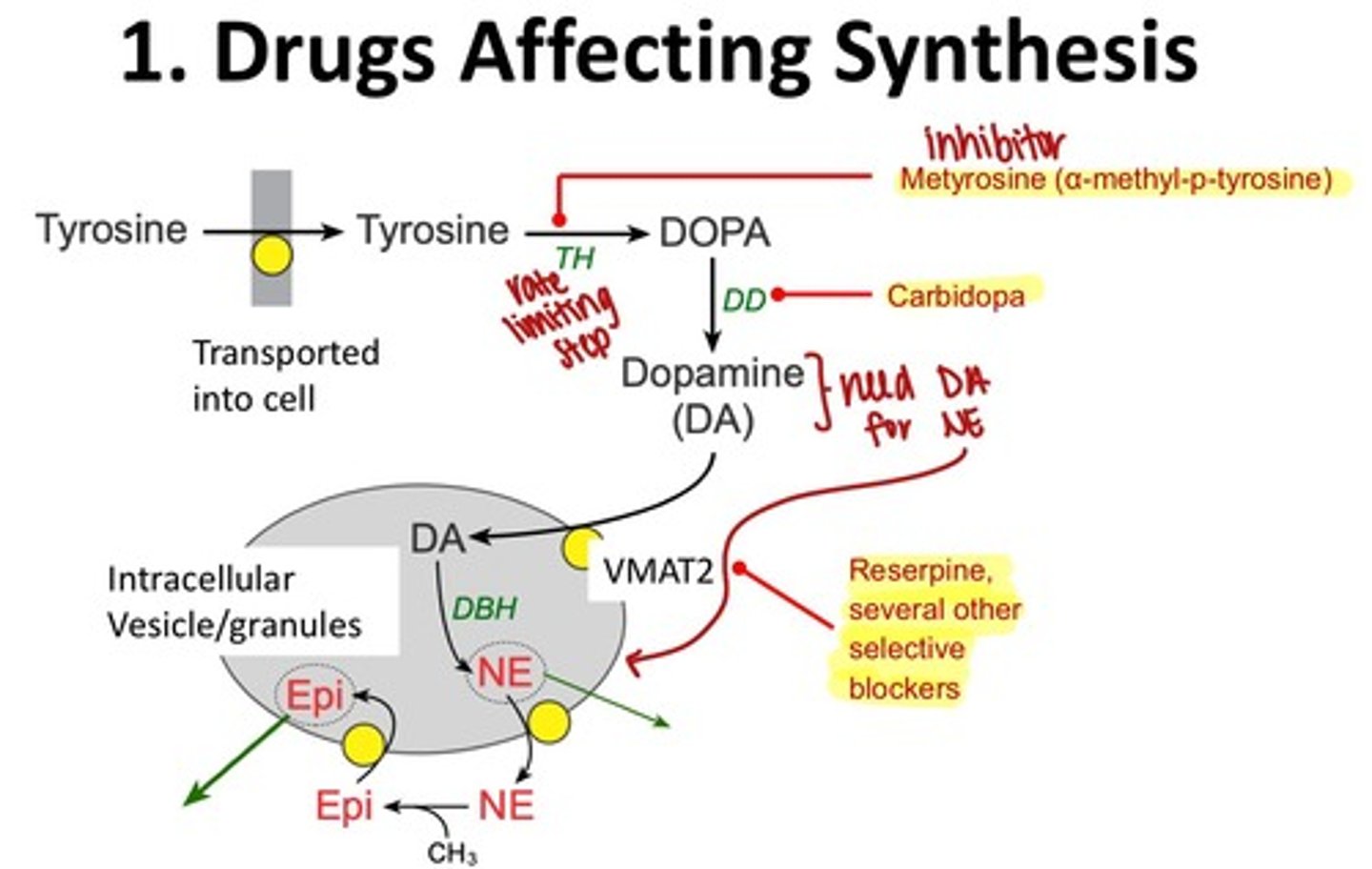
What are false neurotransmitters?
Substances that can be taken up and released by neurons but are not the normal neurotransmitters.
How do drugs inhibit catecholamine release?
By direct interference with release machinery or stimulation of autoreceptors.
What enzymes are involved in catecholamine inactivation?
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT).
What is the effect of presynaptic uptake (uptake I) on norepinephrine?
It rapidly clears norepinephrine from the synaptic space.
What is the role of postsynaptic synaptic uptake (uptake II)?
Inhibitors include glucocorticoids like cortisone/hydrocortisone and normentanephrine.
What are the effects of adrenergic receptors in the CNS?
A1 and b1/b2 receptors promote arousal and attention, while a2A receptors inhibit norepinephrine release, leading to sedation and impulse-control effects.
What is the significance of noradrenergic neurons in the brain?
They constitute only 0.0005% of brain neurons, explaining how small changes can have significant effects.
What do sympathomimetic drugs do?
They mimic the effects of the sympathetic nervous system by stimulating adrenergic receptors.
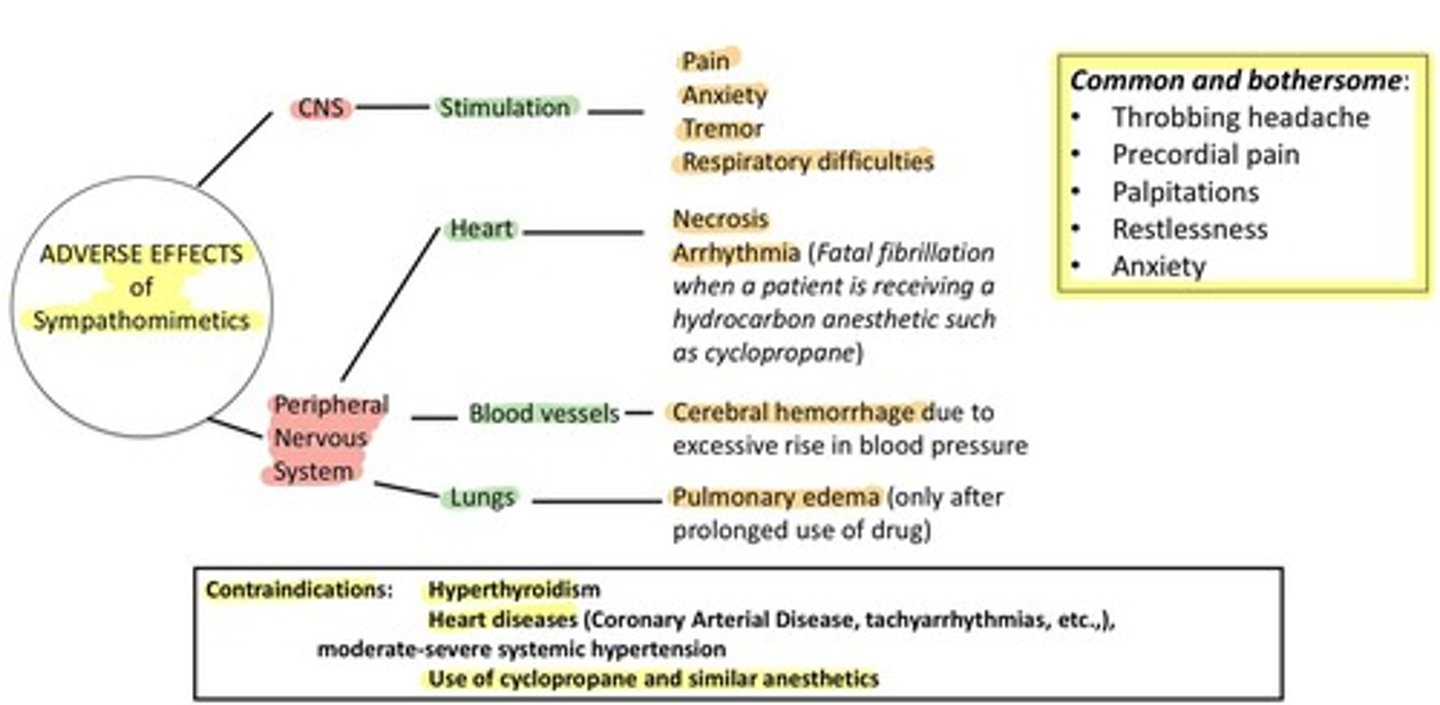
How does activation of sympathetic adrenergic nerves affect blood pressure?
It releases norepinephrine, which acts on beta1 receptors to increase heart rate and cardiac output, thus increasing blood pressure.
What is the rate-limiting step in norepinephrine biosynthesis?
Tyrosine hydroxylase.
What is the structure-activity relationship (SAR) for phenylethanolamine agents?
They require a primary or secondary amine separated by two carbons from the ring, and must be positively charged at pH 7.4.
What happens to alpha receptor activity as R1 substituent size increases?
Alpha receptor activity diminishes, leading to beta selectivity.
What are the effects and clinical uses of alpha 1 agonists?
They induce vasoconstriction, mydriasis, and bladder sphincter contraction; used for nasal decongestion, hypotension, and eye exams.
What are the adverse effects of alpha 1 agonists?
Hypertension, reflex bradycardia, and urinary retention.
What is the mechanism of action (MOA) for clonidine?
It activates presynaptic a2 autoreceptors to prevent further release of norepinephrine.
What are the clinical uses of tizanidine?
It is used for muscle spasticity, spinal cord injury, and cerebral palsy.
What is the clinical use of brimonidine?
It is used in ophthalmic preparations for glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
What is the MOA of methyldopa?
It is a prodrug that is transported into the CNS, where it is decarboxylated and hydroxylated to the active compound.
What are the effects of non-selective beta agonists?
They increase heart rate and contractility (b1) and cause bronchodilation and vasodilation (b2).
What is the clinical use of isoproterenol?
It is used for bradycardia, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and bronchospasm.
What is the MOA of albuterol?
It is a short-acting bronchodilator administered via inhalation.
What are the clinical uses of selective beta 2 agonists?
They are used for asthma, COPD, and preterm labor.
What is the effect of selective beta 3 agonists?
They increase bladder capacity.
What are the adverse effects of alpha 2 agonists?
Hypotension, bradycardia, dry mouth, sedation, and rebound hypertension upon withdrawal.
What is the clinical use of phenylephrine?
It is used for decongestion and as a vasopressor.
What is the effect of oxymetazoline?
It causes vasoconstriction and is used as a nasal decongestant.
What is the clinical use of dobutamine?
It is used as a cardiac stimulant, especially in acute heart failure.
What is the effect of tizanidine on motor neurons?
It increases presynaptic inhibition of motor neurons.
What are the effects of beta 1 agonists?
They increase cardiac output and renin release.