Mycology review
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
219 Terms
A patients sputum specimen contains a dimorphic fungus. If the sputum is put on a slide and a coverslip added, what would you expect to observe?
a. Aseptate hyphae
b. Septate hyphae
c. Aerial hyphae
d. Yeasts
d. Yeasts
Penicillium produce what type of conidia?
a. Annelloconidia
b. Phialoconidia
c. Blastoconidia
d. Poroconidia
b. phialoconidia
Bipolaris produce what type of conidia?
a. Annelloconidia
b. Phialoconidia
c. Blastoconidia
d. Poroconidia
d. poroconidia
Microconidium are
a. Septate
b. Aseptate
c. Pseudohyphae
d. Microaleuriospores
d. microaleuriospores
Blastoconidia that have elongated are termed:
a. Chlamydospores
b. Mother cells
c. Pseudohyphae
d. True hyphae
Pseudohyphae
A patient is seen by his physician for a hard, nonmoving nodule below the skin on his right index finger. There are no other symptoms. Circle the letter of the correct answer. The infection that this patient is most likely presenting is:
a. Superficial
b. Cutaneous
c. Subcutaneous
d. Systemic
c. subcutaneous
The taxonomic phylum Zygomycota is distinct in that the hyphae are usually
______________ . The typical asexual reproductive structures are ______________ , and the sexual stage is characterized by the formation of
______________ .
a) Sporangiospores
b) Arthroconidia
c) Ascospores
d) Aseptate
e) Zygospores
f) Basidiospores
g) Septate
d. aseptate
a. sporangiospores
e. zygospores
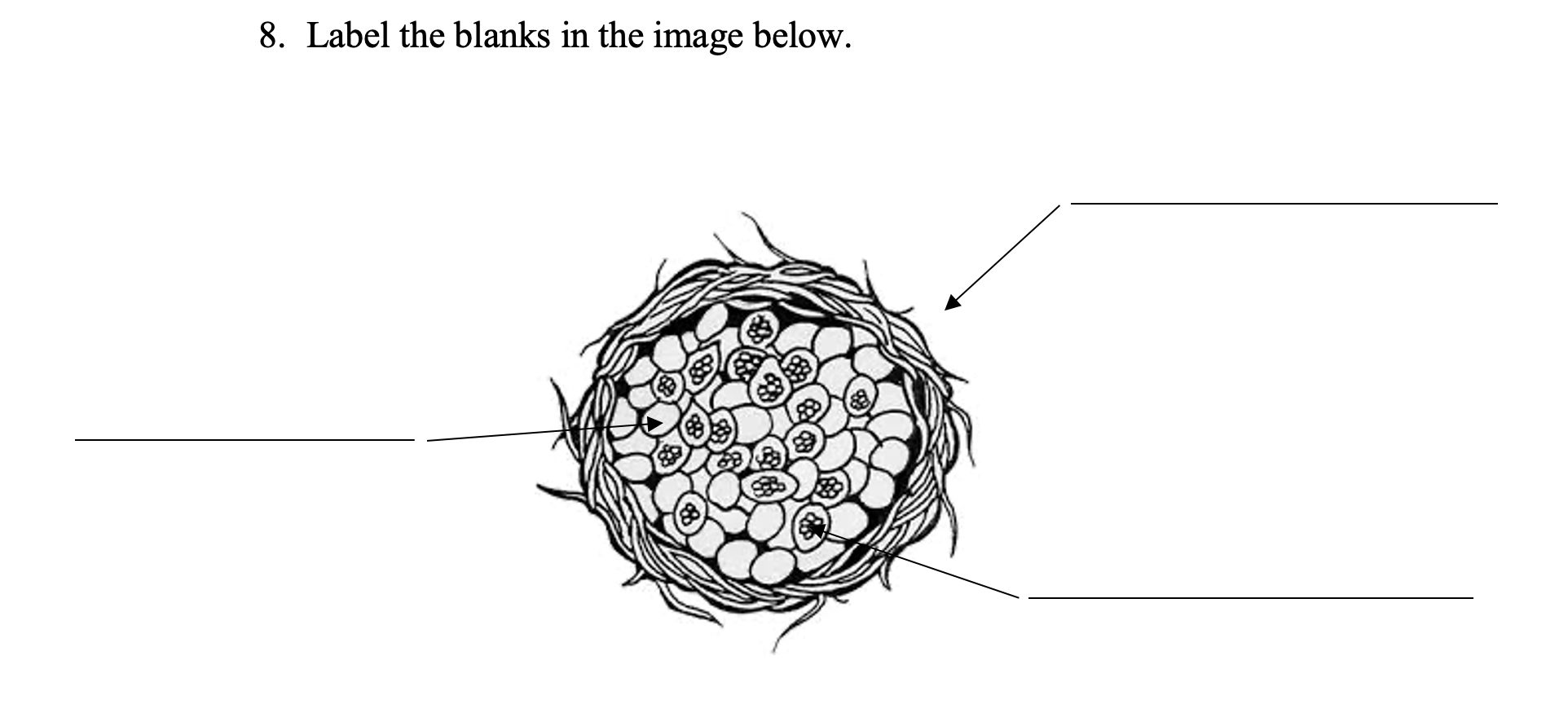
left: Ascus
right top: Cleistothecium
Right bottom: Ascospores
1. The fungal organism most acommonly found in vaginal infections is:
a. Geotrichum candidum
b. Coccidioides immitis
c. Candida albicans
d. Cryptococcus neoformans
C. candida albicans
1. Which is the most useful mounting fluid for nail scrapings?
a. Saline
b. Potassium hydroxide
c. Acetic acid
d. Lactophenol cotton blue
B. Potassium Hydroxide
1. List 3 general rules for good collection of fungal specimens.
a.
b.
c.
a. spec. collected rom correct site
b. sterile collection technique
c. adequate specimen delivered promptly and adequately labeled
Two fungi that may be found in CSF are _______ and________.
crypto. neoformans and candida spp.
T /F Granules from subcutaneous lesions only represent necrotic material and therefore should be disregarded.
False
T/F Fungal growth can be easily detected in blood culture bottles because the broth medium quickly becomes cloudy/turbid like bacteria.
False
1. The best medium to isolate fungal opportunists from a nonsterile site is:
a) Inhibitory mold agar
b) Brain Heart infusion agar with blood, gentamicin, chloramphenicol and cycloheximide
c) BHI agar with blood
d) Dermatophyte test medium
A inhibitory mold agar
1. The best medium to isolate Cryptococcus neoformans in bronchial washings from an AIDS patient is:
a. Sabouraud brain heart infusion agar
b. MacConkey agar
c. Inhibitory mold agar
d. Birdseed agar
D. birdseed agar
What is considered an intermediate growth rate for fungus?
mature colony in 6-10 days
T/F Potato dextrose agar promotes sporulation?
True
1. Canoe/Banana shaped macrophialoconidia with foot cells are diagnostic of:
a. Paecilomyces spp.
b. Curvularia spp.
c. Fusarium spp.
d. Nigrospora spp
C. Fusarium spp.
T /F Dematiaceous organisms exhibit light-colored hyphae and/or conidia.
False
T/F Aspergillus fumigatus produces phialides and phialoconidia only at the end of the vescicle.
True
T /F The cornea of the eye is easily susceptible to infection.
False
T/F In aspergillosis the etiologic fungus may be isolated only once and still be considered significant.
True
Otomycosis involves:
a. Deep inner ear infections
b. Middle ear infections
c. External ear infections
d. A deep understanding of Macro-economics
C. external ear infections
T /F Acremonium exhibits repeatedly forking conidiophores with terminal balls of conidia.
False
T/ F Potato dextrose agar promotes sporulation?
True
Circle the letter(s) of the statement(s) that pertain to the genus Trichophyton.
a. Smooth, thin-walled macroconidia
b. Generally numerous macroconidia
c. Microconidia in grapelike clusters
d. Numerous or few microconidia
e. Rough spindle-shaped macroconidia
a, c, d
T/F Epidermaphyton produces no microconidia
True
T/F, E. floccosum macroconidia may be confused with those of T.
verrucosum
False
Circle all that apply: Test(s) that help differentiate T. mentagrophytes from T.
rubrum.
a. Urease test
b. Trichophyton nutritional agar tests
c. Red pigment on potato destrose agar
d. Polished rice grains test
e. In vitro hair perforation
A, c, e
T/F All dermatophytes infecting humans cause cutaneous mycoses, but not all cutanoueous mycoses are elicited by dermatophytes
True
Hair fluorescence is produced from infection with organisms of
the ________________ genus.
microsporum
T/F Dermatophytes are usually rapid growers.
False
common name for dermatophytosis of the foot or tinea pedis
is ______________________.
athletes foot
his organism is an etiologic agent of epidemic dermatophytosis of the foot in
summer camps and institutions. It does not infect hair.
a. Trichophyton violaceum
b. Epidermophyton floccosum
c. Microsporum audouinii
d. Trichophyton mentagrophytes
e. Trichosporon beigelii
epidermophyton floccosum

c,d,e,f
c
D
B
B
D
Choose all that apply: Torulopsis glabrata may be normal flora of:
a. Vagina
b. Throat
c. Stool
d. All of the above
e. B and C
D. all of the above
T /F All Candida albicans produce germ tubes and chlamydospores.
False
1. On a vaginal culture, a cream-colored yeast grows on SABHI medium. On corn meal-Tween 80 agar, only small oval blastoconidia are observed. This organism is most likely:
a. Candida albicans
b. Trichosporon beigelii
c. Torulopsis glabrata
d. Rhodotorula rubra
e. Geotrichum candidum
C
1. On a urine bacteriology culture blood agar plate at 24 hours, over 100,000 small, white colonies are observed. They are catalase positive and a slide coagulase is negative. Your next step is to:
a. Report over 100,000 Staphylococcus epidermidis/mL of urine
b. Perform a Gram stain
c. Inoculate a gram-positive susceptibility test
d. Set up a tube coagulase test
e. Ask for a repeat culture
B
T /F A germ tube is constricted at its point of attachment to the mother cell.
F
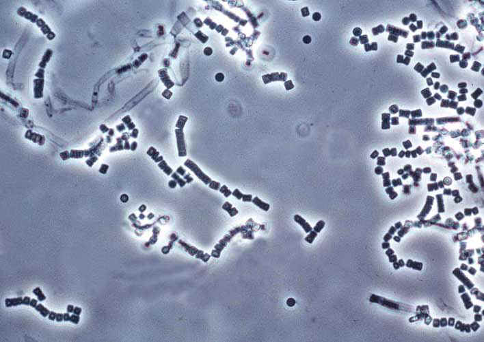
1. This corn meal-Tween 80 microscopic morphology is characteristic of the fungus (genus and species) ________________________. Note: There are no blastoconidia
Geotrichichum candidum
1. On corn meal-Tween 80 agar, a fungus produces terminal round chlamydospores and clusters of numerous blastoconidia. The organism also forms germ tubes within 3 hours and assimilates sucrose but does not ferment it. This organism is named (genus and species) ________________________.
C. albicans

D
C
F
B
A
T F Only fungi and funguslike bacteria may produce granules in tissue
False
1. Which of the following exhibits polymorphism, in which more than one type of conidial arrangement may be observed?
a. Cladosporium carrionii
b. Phialophora verrucosa
c. Fonsecaea compacta
d. Fonsecaea pedrosoi
e. A, C and D
f. All of the above
Cladosporium carrionii
Fonsecaea compacta
Fonsecaea pedrosoi
1. The subcutaneous disease with an endogenous origin is:
a. Actinomycosis
b. Sporotrichosis
c. Phaeohyphomycosis
d. Eumycotic mycetoma
e. Chromoblastomycosis
Actinomycosis
1. Cladosporium trichoides and Cladosporium carrionii appear similar culturally and microscopically. They may be speciated by all of the following except:
a. C. trichoides grows at 42˚C, C. carrionii does not.
b. C. trichoides produces sclerotic bodies, C. carrionii does not.
c. C. trichoides has a predilection for neural tissue, C. carrionii does not.
d. C. trichoides grows more rapidly than C. carrionii
e. C. trichoides exhibits larger blastoconidia than C. carrionii
C. trichoides produces sclerotic bodies, C. carrionii does not.
1. T F Characteristic sulfur-colored granules are usually present in both actinomycosis and mycetoma produced by the same organism
True
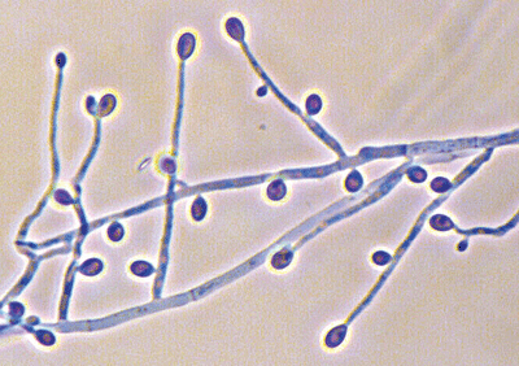
1. This fungus is the leading cause of eumycotic mycetoma in the U.S.
a. Cladosporium carrionii
b. Sporothrix schenkckii
c. Scedosporium apiospermum
d. Fonsecaea pedrosoi
e. Fonsecaea compacta
Scedosporium apiospermum

c,d
a
b,c
b,c
A

B,C
D,E
A
E
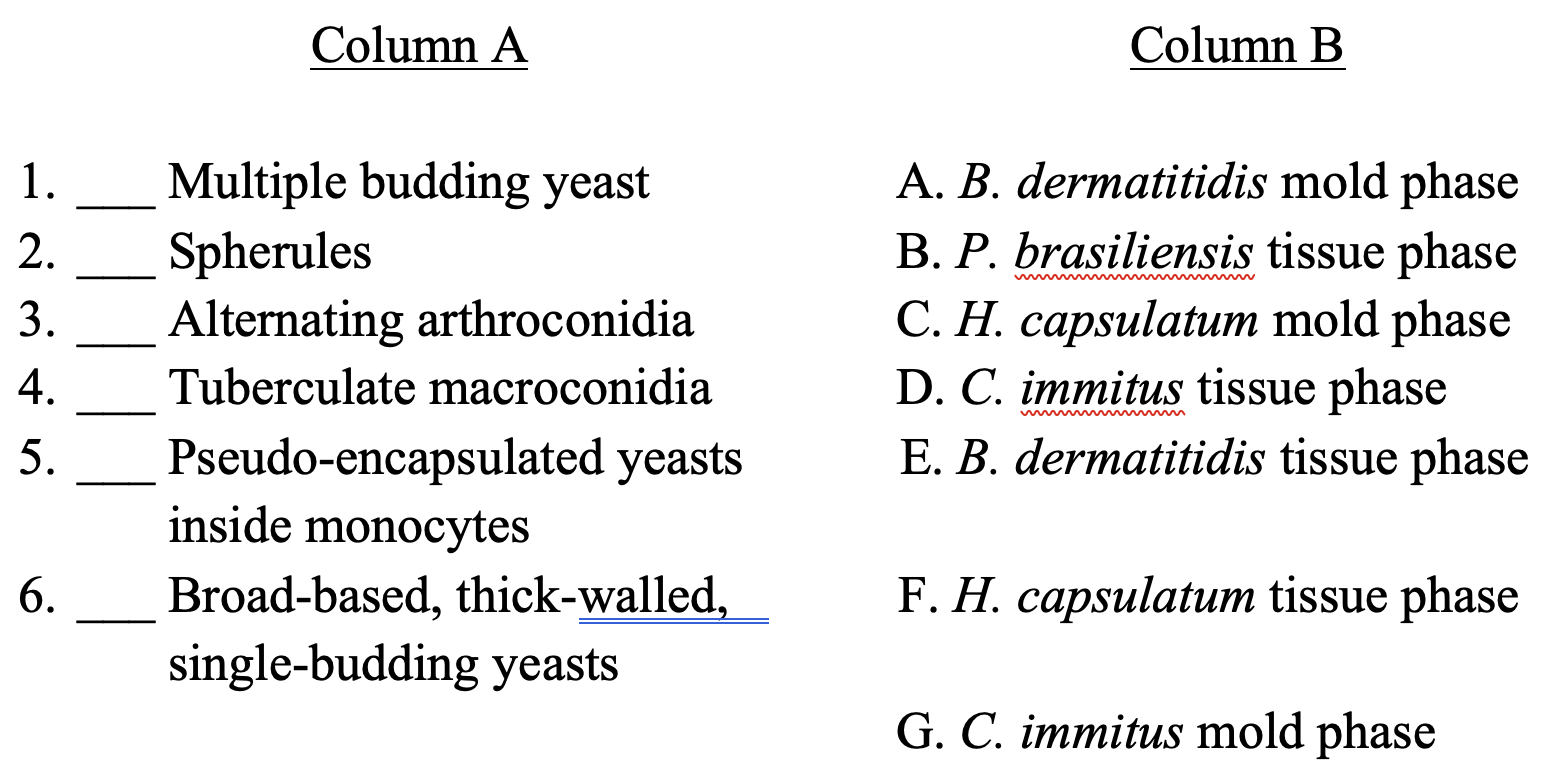
B
D
G
C
F
E
Ascomycota
sexual reproduction resulting in ascospores
Basidiomycota
sexual reproduction resulting in basidospores
Zogomycota
asexual reproduction resulting in zygospores
Deuteromycota
asexual reproduction resulting in conidia
(includes most pathogenic fungi)
Clinically important fungi
all have an asexual name
(anamorph)
some have a sexual name
(teleomorph)
Conidiogenesis
asexual formation of conidia
Conidiophore
supportive stalk for the conidia
may be conidiogenous or support the conidiogenous cells.
Blastic
type of conidiogenesis where the parent cell enlarges and a septum separates the enlarged portion into a daughter cell.
Thallic
A septum forms first and then the growing point ahead of it becomes the daughter cell.
Arthric
A daughter cell fragments within the hyphal strand.
Holo
all wall layers of the parent cell are involved in daughter conidium development
Blastoconidia
holoblastic conidia formed by budding along hyphae, pseudophyphae, or a single cell (i.e. yeast)
Poroconidia
holoblastic conidia produced through a pore in the parent cell wall.
Phialoconidia
conidia arising from a phialide, - first is developed holoblastically
- the rest are enteroblastically derived
phialide
vase-shaped cell that may be ringed at the top by a cup-shaped collarette.
Annelloconidia
conidia arising from an annellide
- the first one develops holloblastically
- the subsequent are enteroblastically derived
annellide
a vase-shaped cell that exhibits a new ring of material as each conidium passes through.
Chlamydoconidia
thick-walled hyphal survival conidium formed during poor environmental conditions, which germinate and produce conidia when a better climate occurs
- may be terminal, sessile, or intercalary
Chlamydospore
thick-walled vesicle of C. albicans and some other yeast which neither germinates nor produces conidia when mature.
Arthroconidia
conidia produced by fragmentation of the hyphal strand through separation points
- may form adjacently or separated by disjunctor cells.
Sporangia
- asexual sac-like structures at the tip of support stalk.
- contain sporangiospores
- produced by Zygomycota
Microconidia
- smaller conidia in fungi that produce both large and small conidia
- usually single-celled, round, ovoid, pear shaped, or club shaped
Macroconidia
- larger conidia in fungi that produce both
- may be single celled, but usually multicelled.
Antheridium
male cell
Ascogonium
female cell
Ascus
zygote
Ascospores
formed by nuclear division within the ascus
Ascocarp
protective sac which houses the asci & ascospores
Cleistothecium
completely enclosed ascocarp
Basidium
- club-shaped mother cell from which basidiospores arise
(Filobasidiella neoformans)
(( Cryptococcus neoformans ))
Basidiospores
- sexual spore formed by the fusion of two compatible nuclei and cells into a zygote
Basidiocarp
- protective structure which houses basidia and basidiospores
Zygophore
- arm of hyphae that extends toward another compatible arm to produce a zygospore
Zygospore
- sexual spore formed by fusion of two compatible hyphal arms
Zygosporangium
- thick outer layer covering a zygospore
Mycelia sterilia
no reproductive structures just lots of hyphae
Morphology :
Cottony / Wooly
Very high dense aerial mycelium
Morphology:
Velvety
low aerial mycelium
Morphology:
granular or powdery
dense production of conidia
Morphology:
Glabrous
waxy, smooth, no aerial mycelium
Morphology:
Rugose
Deep furrows irregularly radiating from center
Morphology:
Umbonate
button-like central elevation
Morphology:
Verrucose
wrinkled, convoluted surface
Hyaline
lightly colored conidia and hyphae
Calcofluor white
- binds to chitin
- fluoresces under UV
SAB
Sabourad Dextrose Agar
nonselective media
- acid pH of 5.6
nutritionally poor - limits bacterial growth but allows opportunist and pathogens to grow
BHI with blood
nutritionally richer for specimens with normally sterile body sites