IB Biology SL - Genetics
1/329
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
330 Terms
Allele
one of the possible forms of a gene, occupying a specific position on a chromosome, that controls a particular trait.
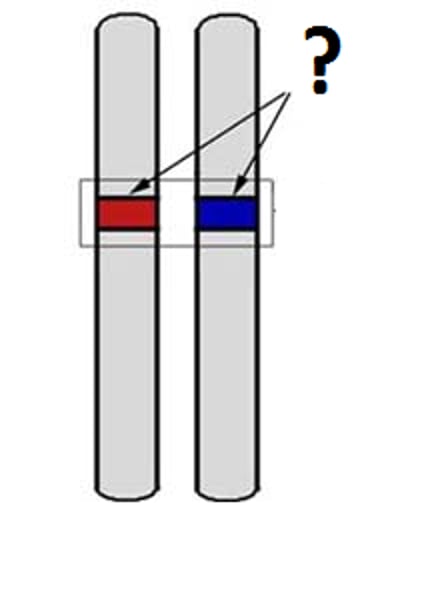
Base Sequence
the order of nitrogenous bases in a DNA molecule.
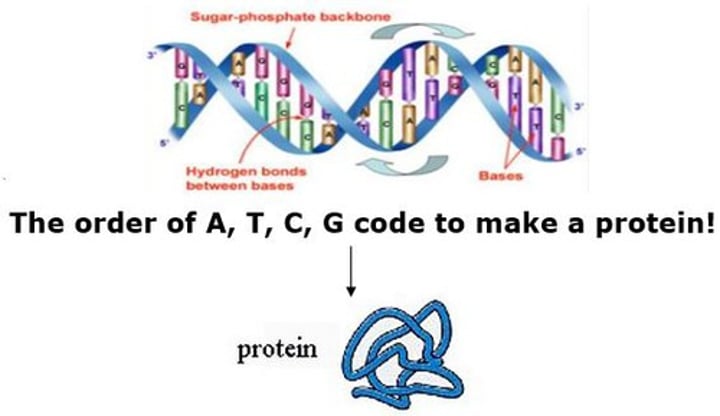
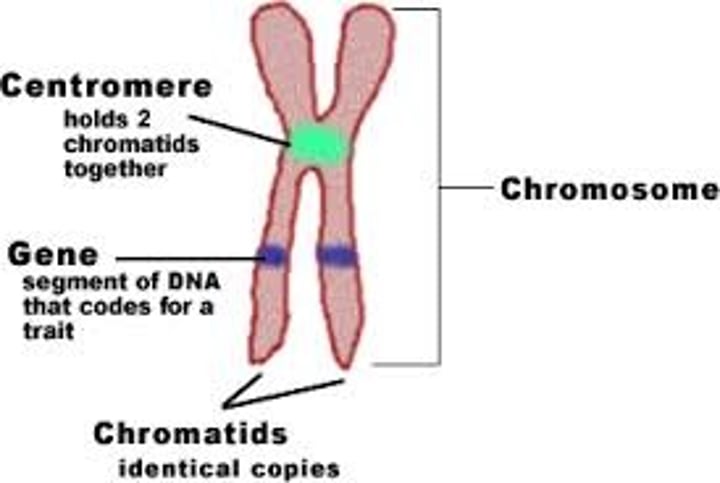
Chromosome
a structure within the cell that bears the genetic material as a thread-like linear strand of DNA with the genes in a linear order (the human species has 23 pairs).
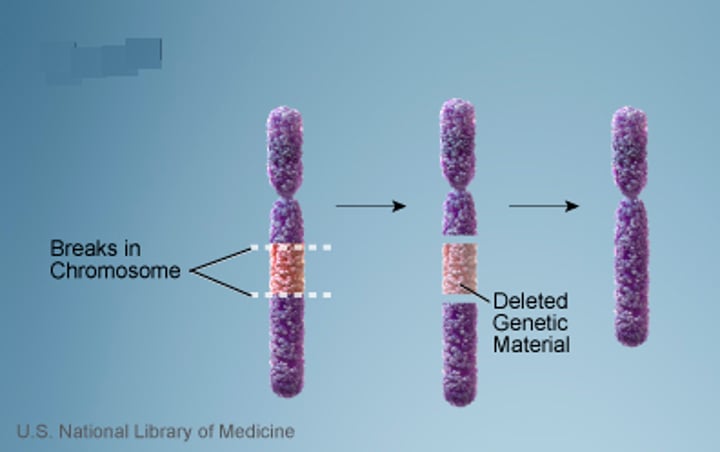
Chromosome Deletion
a type of chromosomal aberration in which a segment of the chromosome is removed or lost.
Frame shift
a genetic mutation, caused by a deletion or insertion in a DNA sequence, that shifts the way the sequence is read.
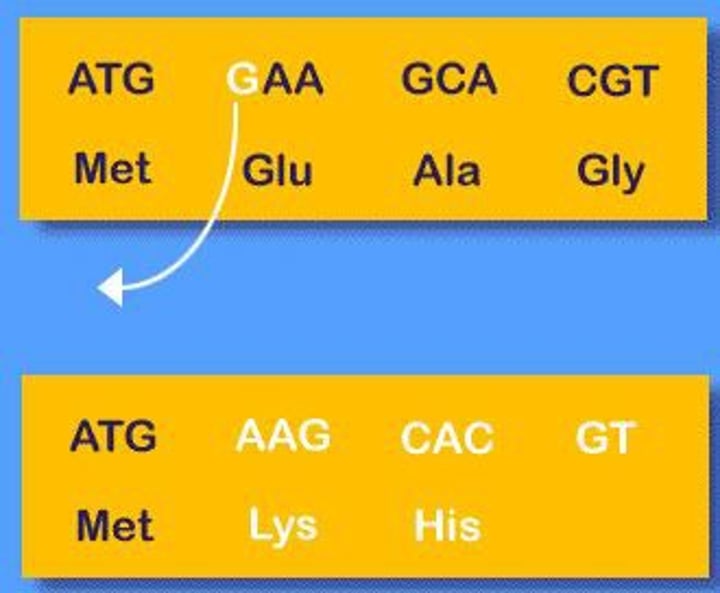
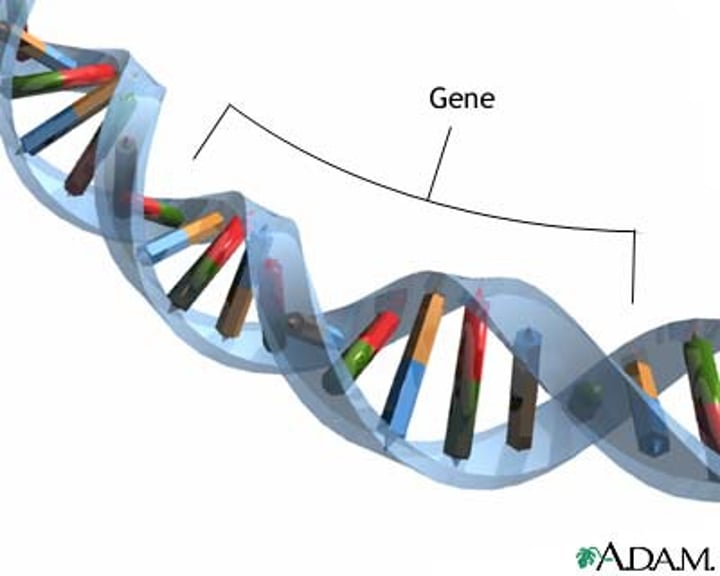
Gene
a hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism.
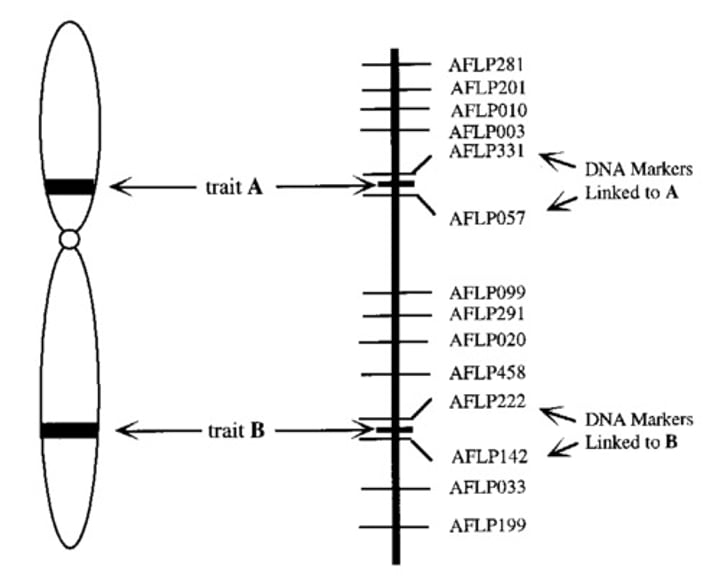
Gene mapping
the process of determining the locus for a particular biological trait.
Genome
the total genetic material of an organism.
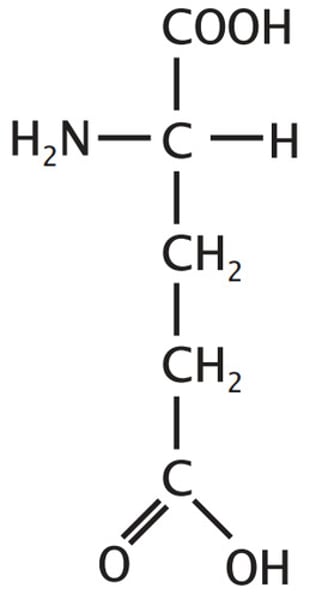
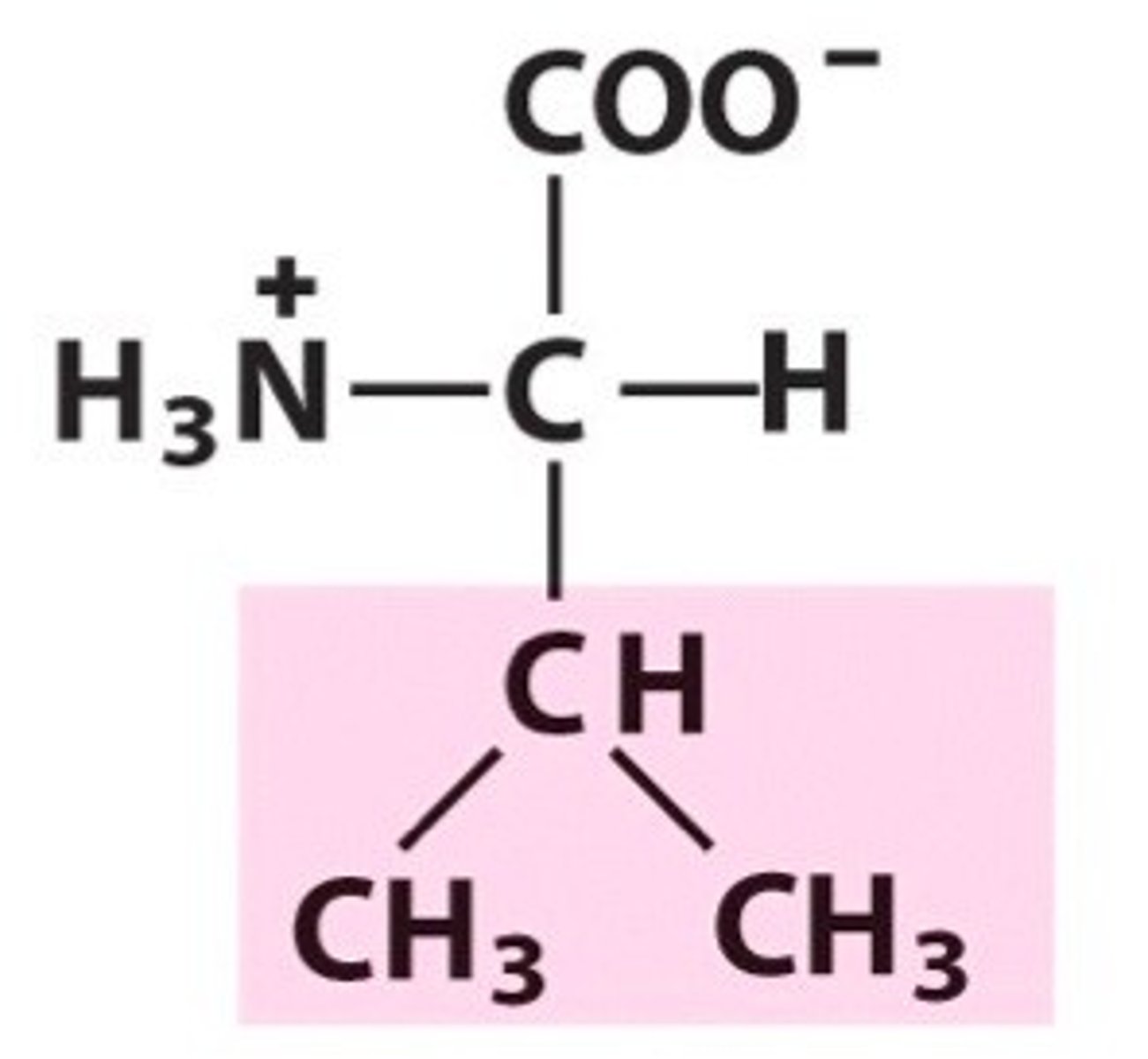
Glutamic acid
a polar amino acid, occurring in proteins, that is replaced by valine in case of sickle cell anaemia.
Hemoglobin
the oxygen-carrying pigment of red blood cells that gives them their red colour and serves to convey oxygen to the tissues.

Human Genome Project
an international scientific research project to determine the sequence of chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, and to identify and map all of the genes of the human genome.
Insertion
the addition by mutation of one or more nucleotides to a chromosome.
Mutation
a change of the DNA sequence within a gene or chromosome of an organism that results in the creation of a new character or trait not found in the parental type.
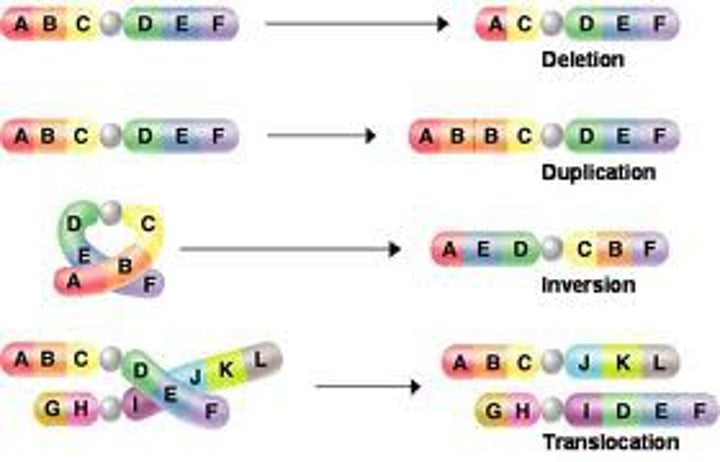
Point mutation
the exchange of a single nucleotide for another in the DNA sequence of a gene.
Polypeptide
a peptide, such as a small protein, containing many molecules of amino acids, typically between 10 and 100.
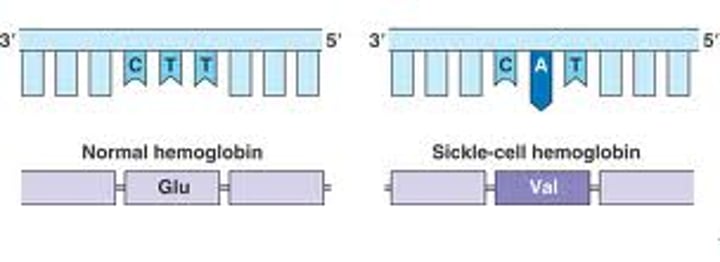
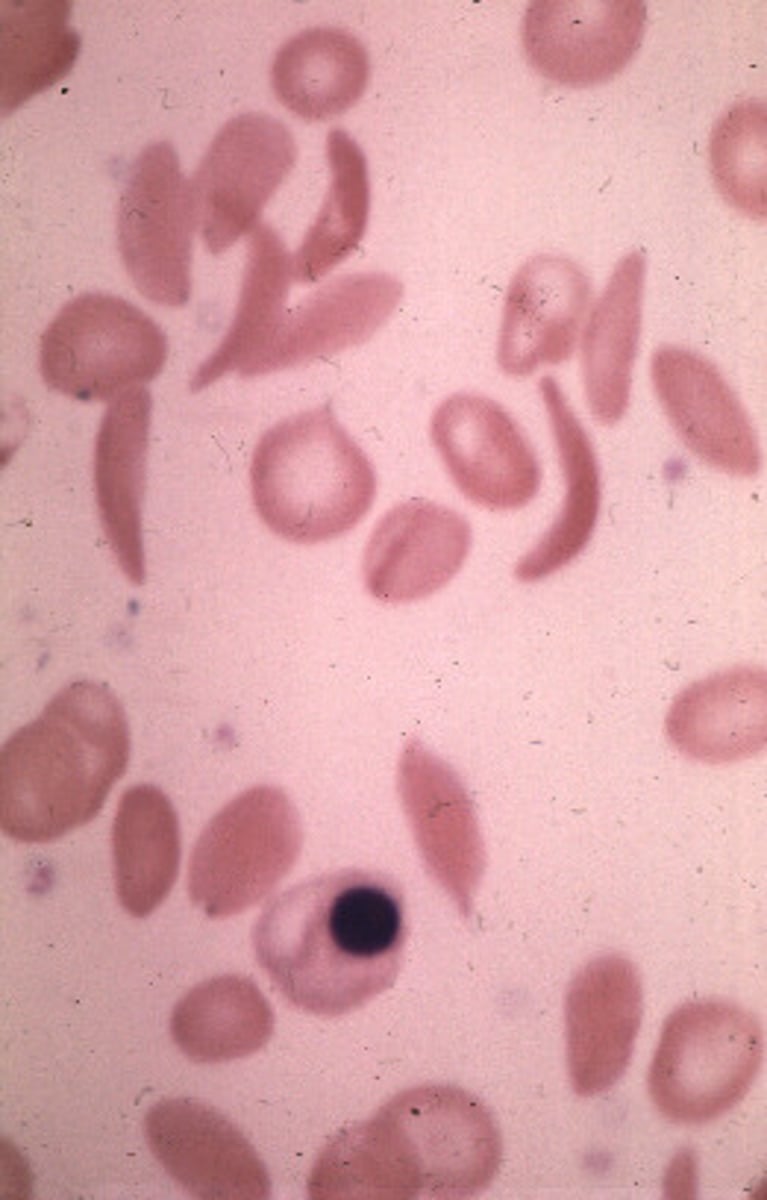
Sickle cell anemia
an autosomal recessive anemia due to substitution of a single amino acid (valine for glutamic acid) characterized by red blood cell becoming sickle-shaped and non-functional.
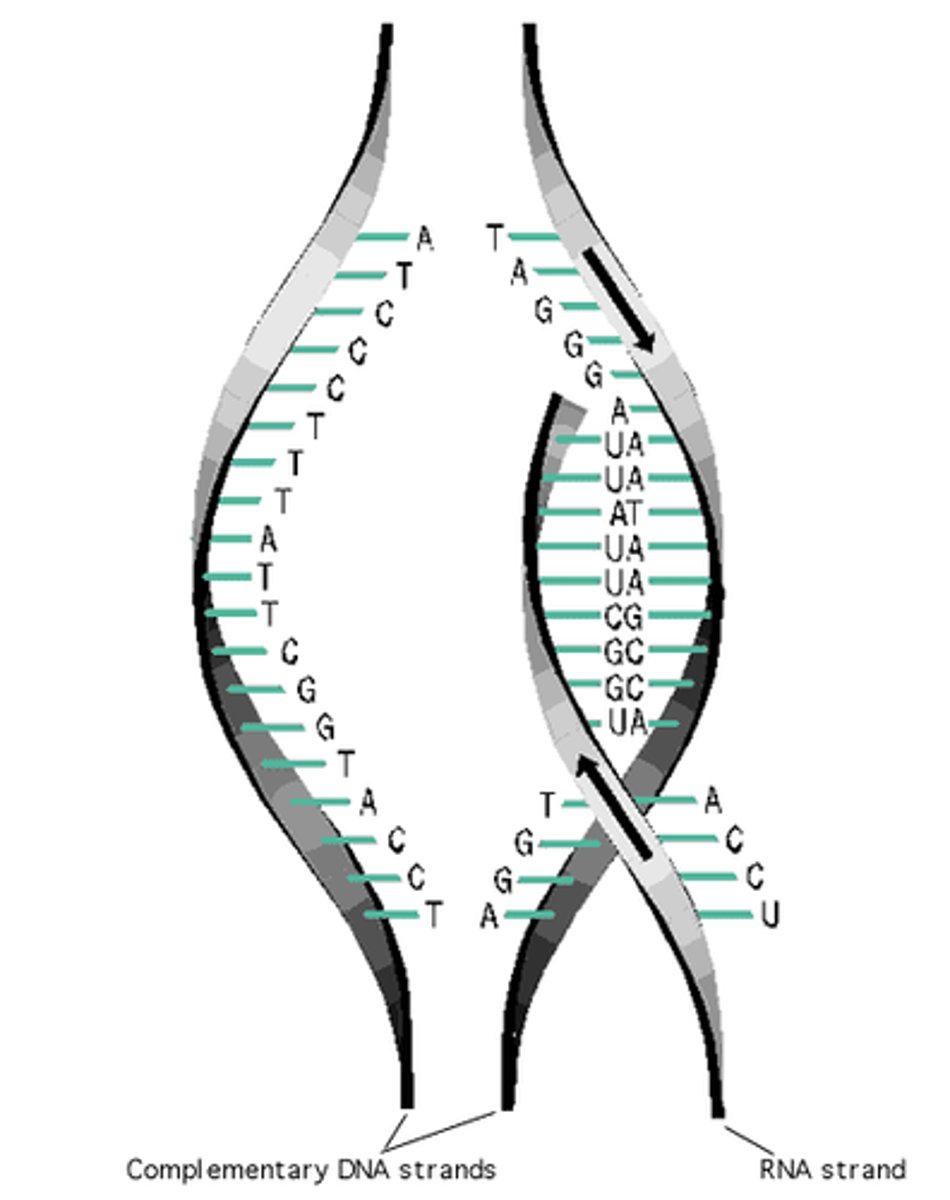
Transcription
the process of copying of DNA into messenger RNA in gene expression.
Valine
an essential amino acid occurring in proteins that replaces glutamic acid in cases of sickle cell anaemia.
Autoradiography
technique that relies on the emission of radioactive particles from within the subject to produce an image.
Autosomes
chromosomes that do not determine sex.
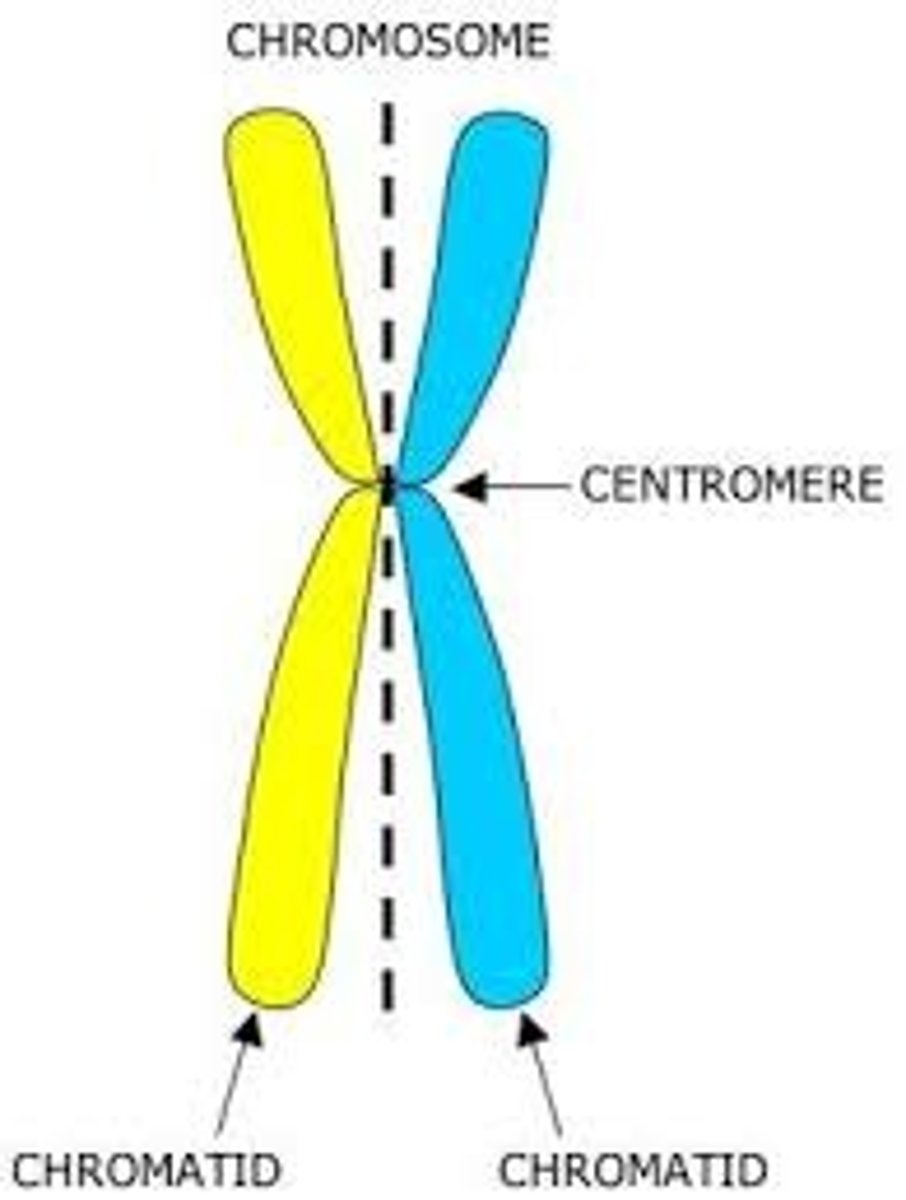
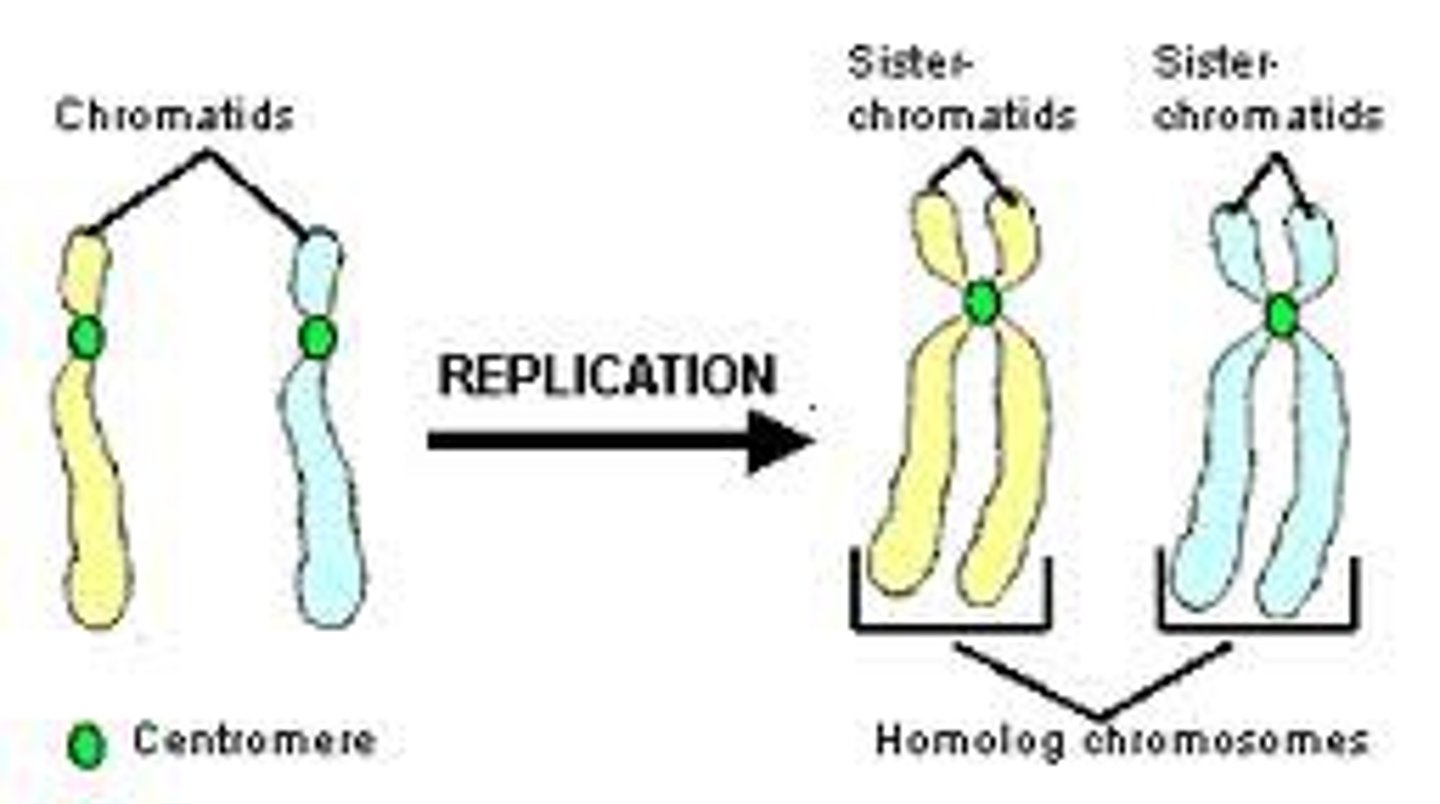
Centromere
region of the chromosome that becomes attached to the spindle fibres during cell division.
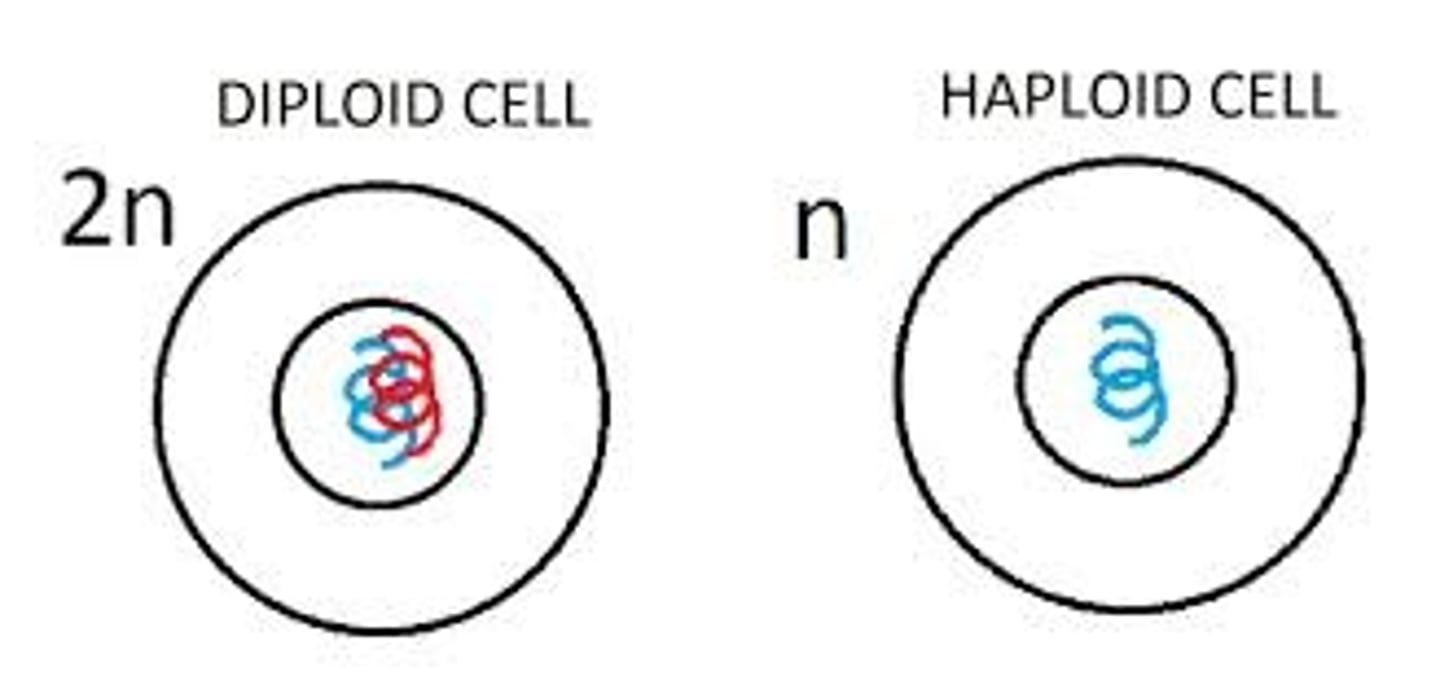
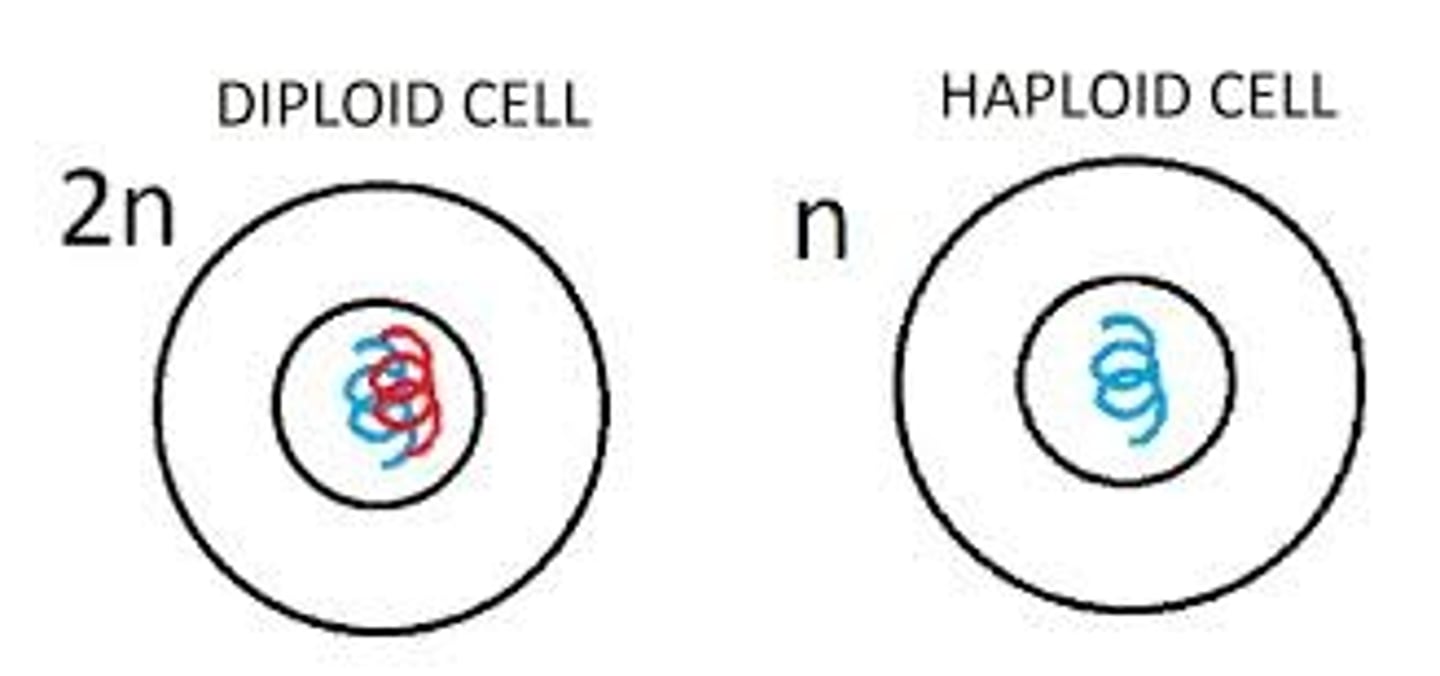
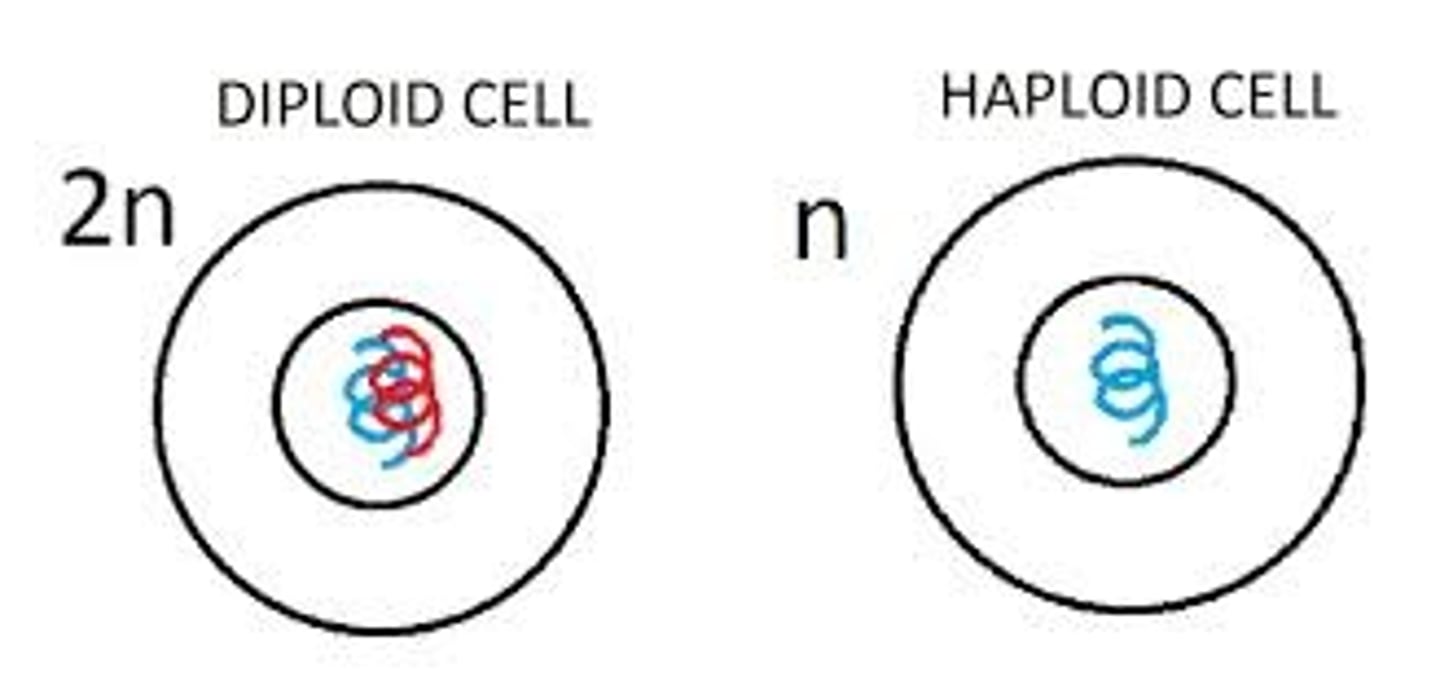
Diploid cells
have nuclei containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one set from each parent.
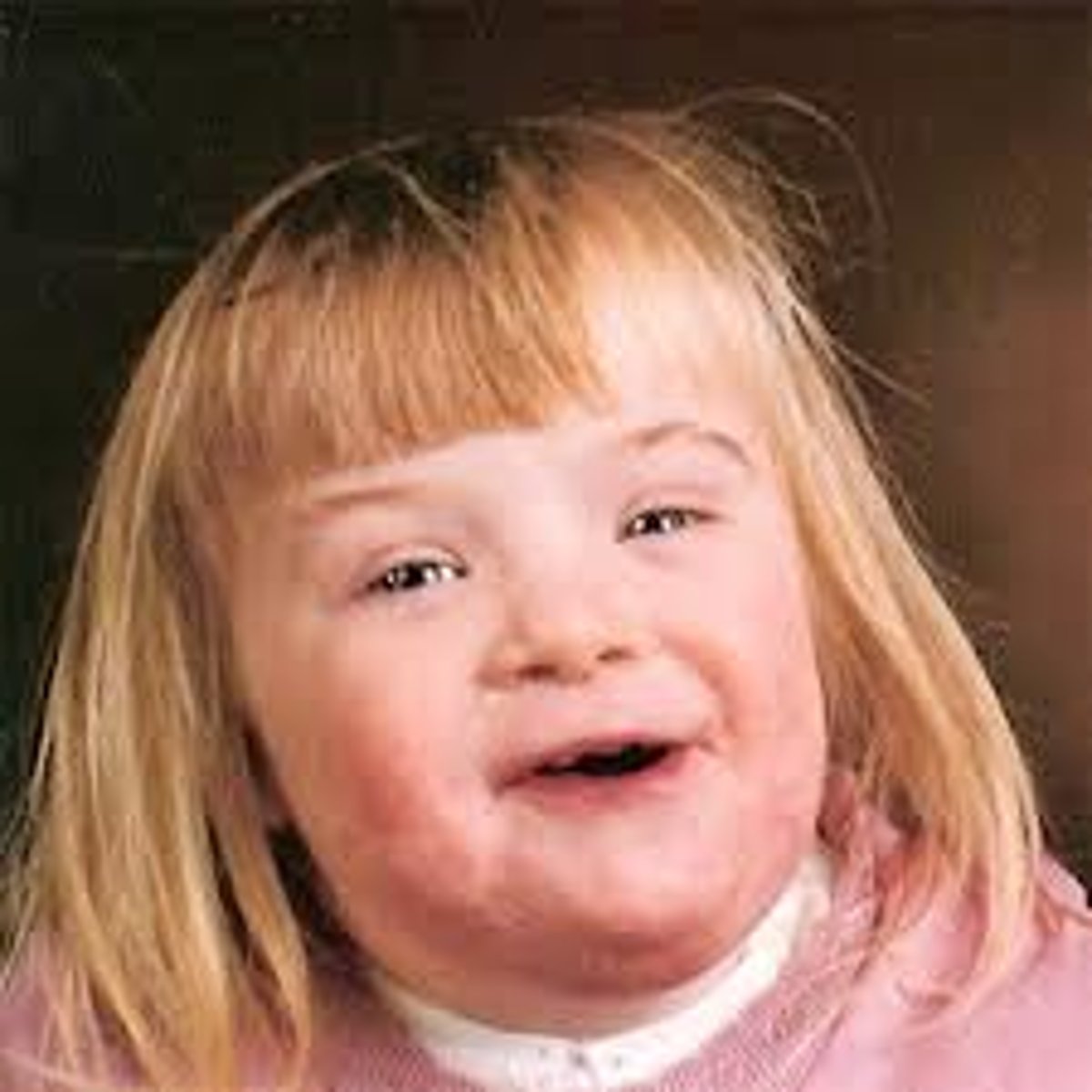
Down syndrome
a human genetic disease resulting from having an extra chromosome 21 (characterized by having a delay in mental development).
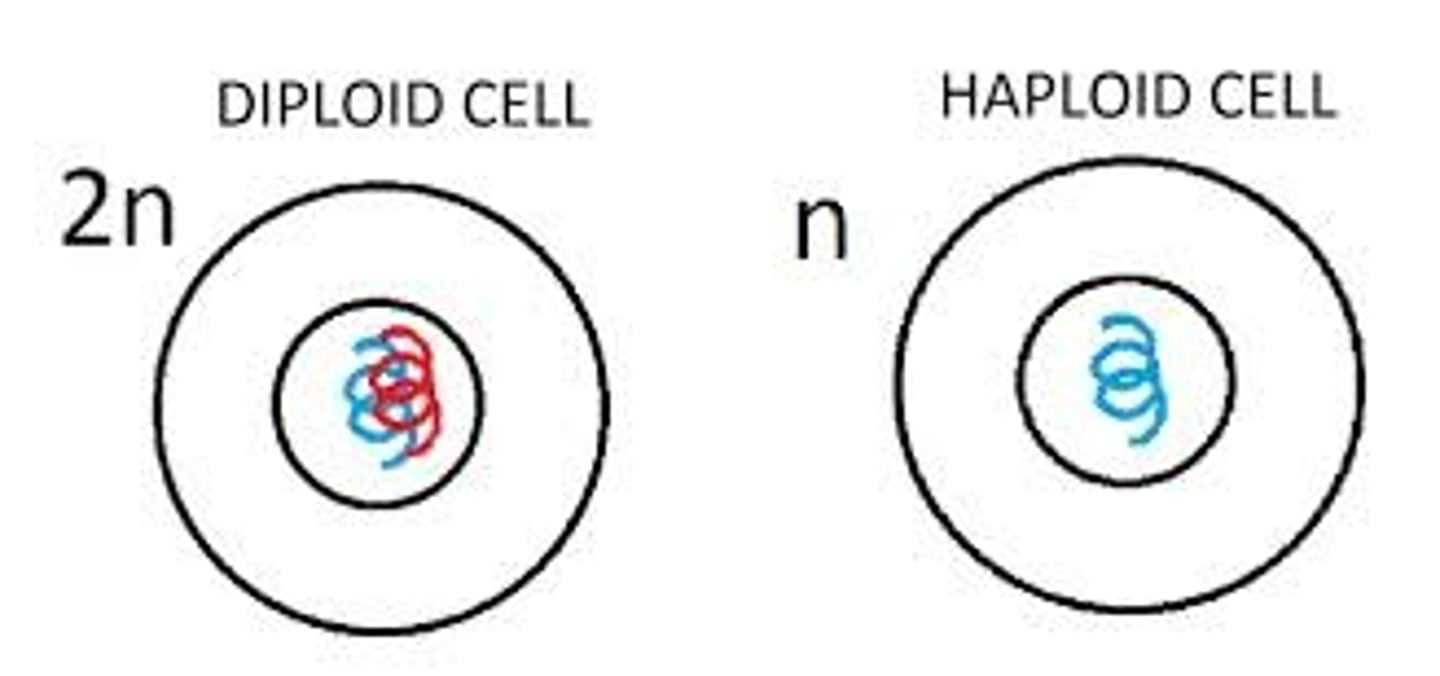
Haploid cells
have one chromosome of each pair (have one full set of the chromosomes that are found in its species).
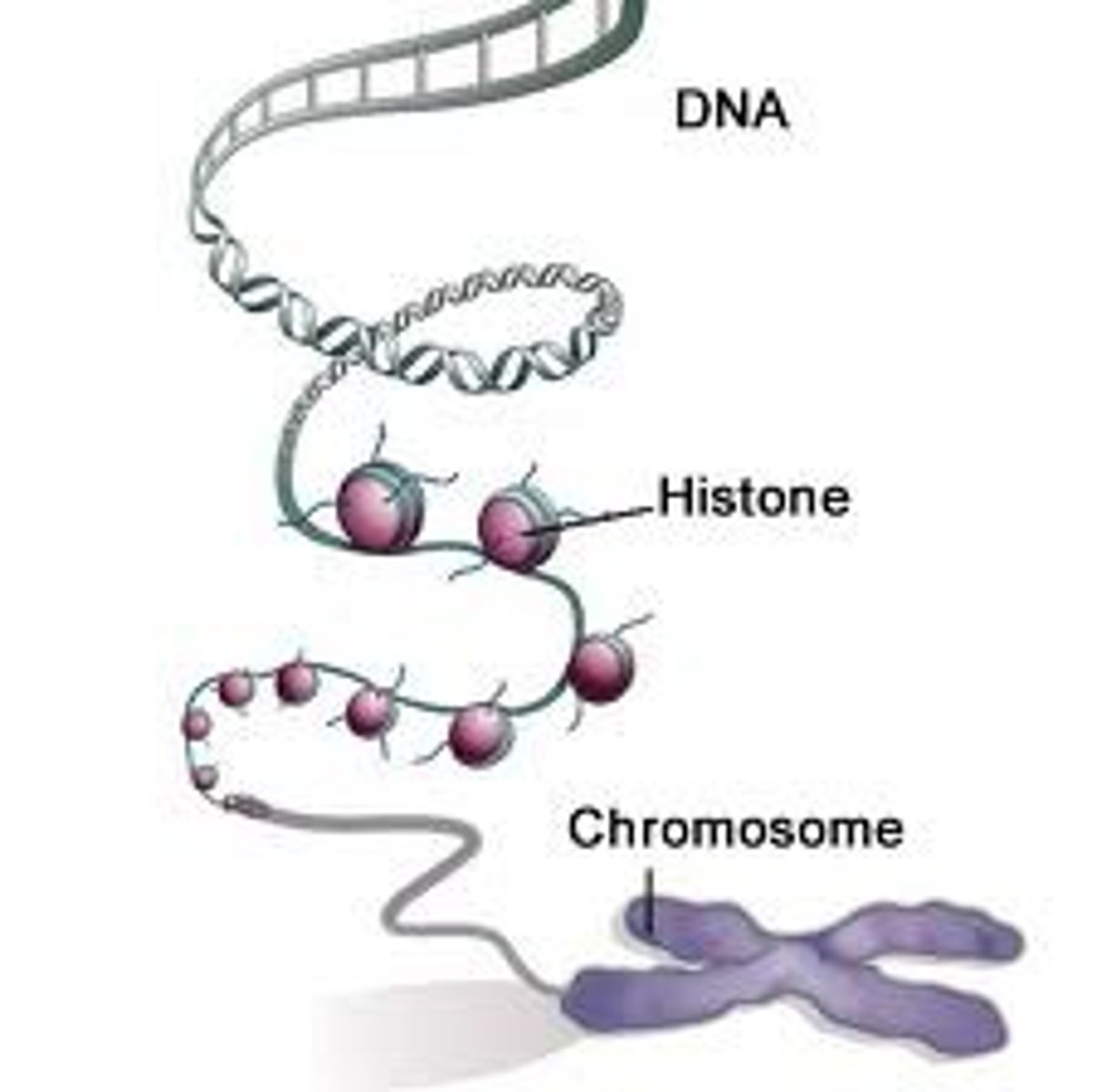
Histones
globular proteins associated to chromosomes in eukaryotic cells.
Homologous chromosomes
chromosome pairs with genes for the same characteristics at corresponding loci.
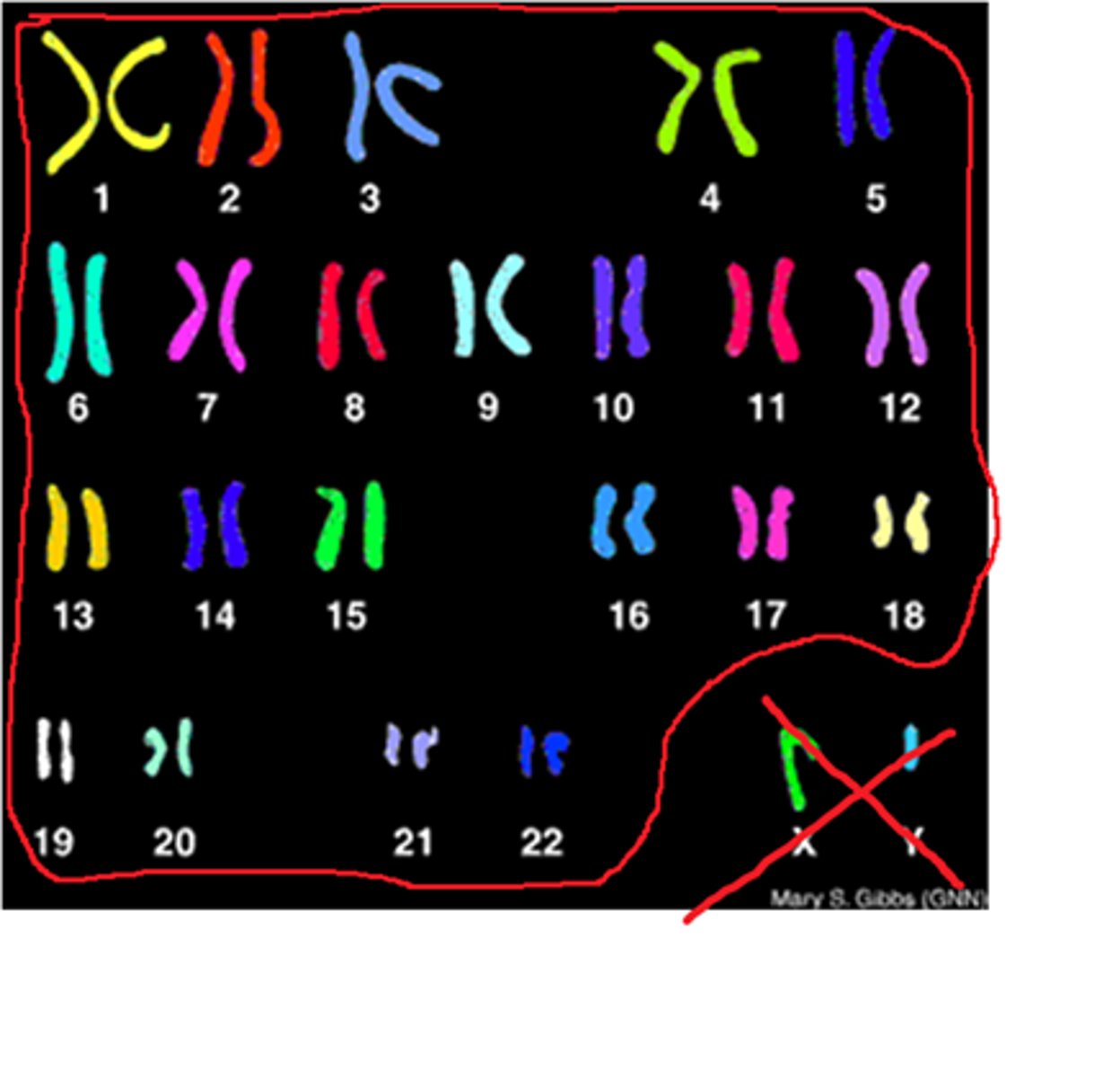
Karyogram
shows the chromosomes of an organism in homologous pairs of decreasing length.
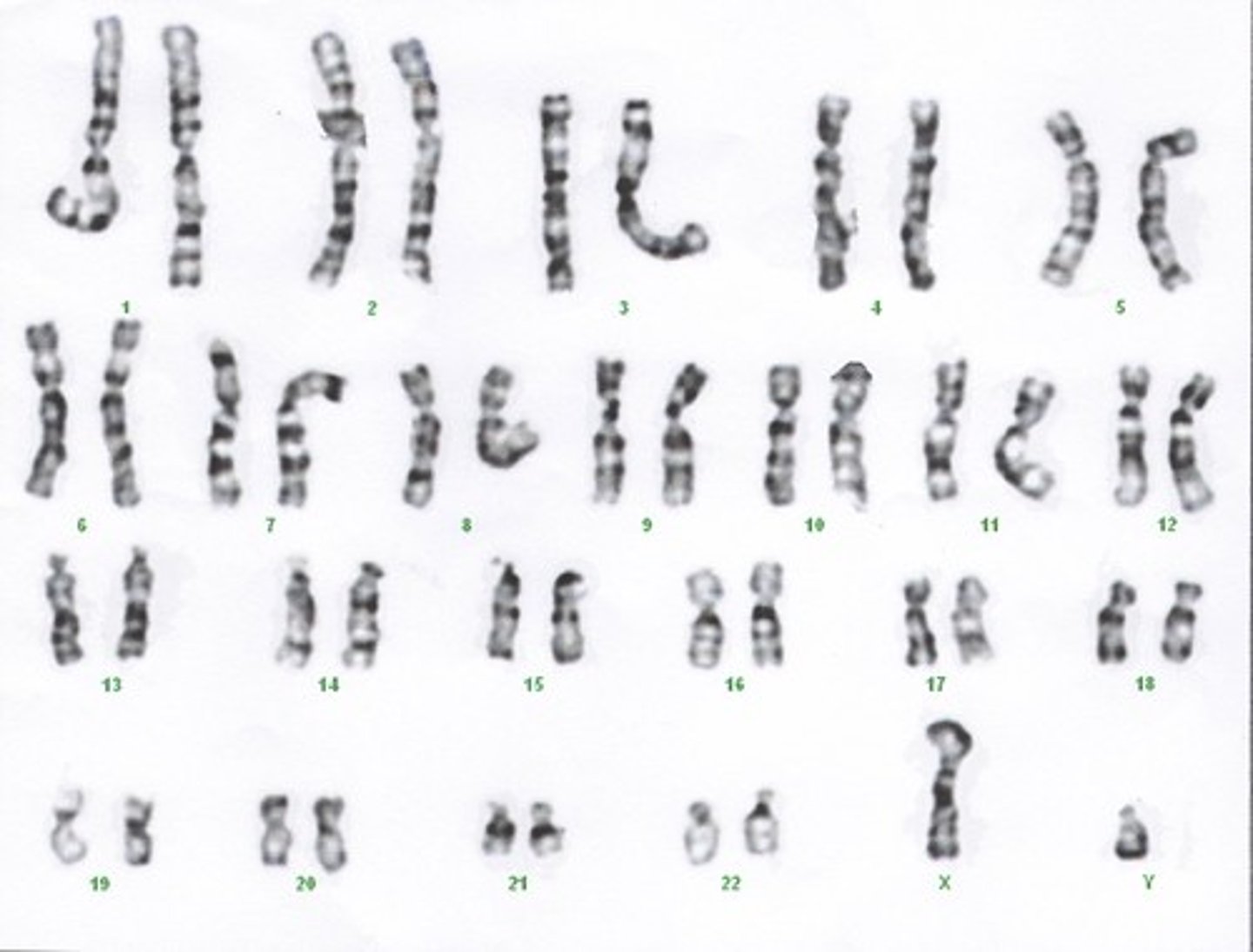
Karyotype
The number and visual appearance of the chromosomes in the cell nuclei of an organism or species. Also a method of organizing the chromosomes of a cell in relation to number, size, and type.
Locus
the position of the gene on the chromosome (loci plural).
Naked DNA
the DNA in prokaryotic cells that is not associated with proteins.
Plasmid
a small circular piece of extra-chromosomal DNA, in a prokaryote.
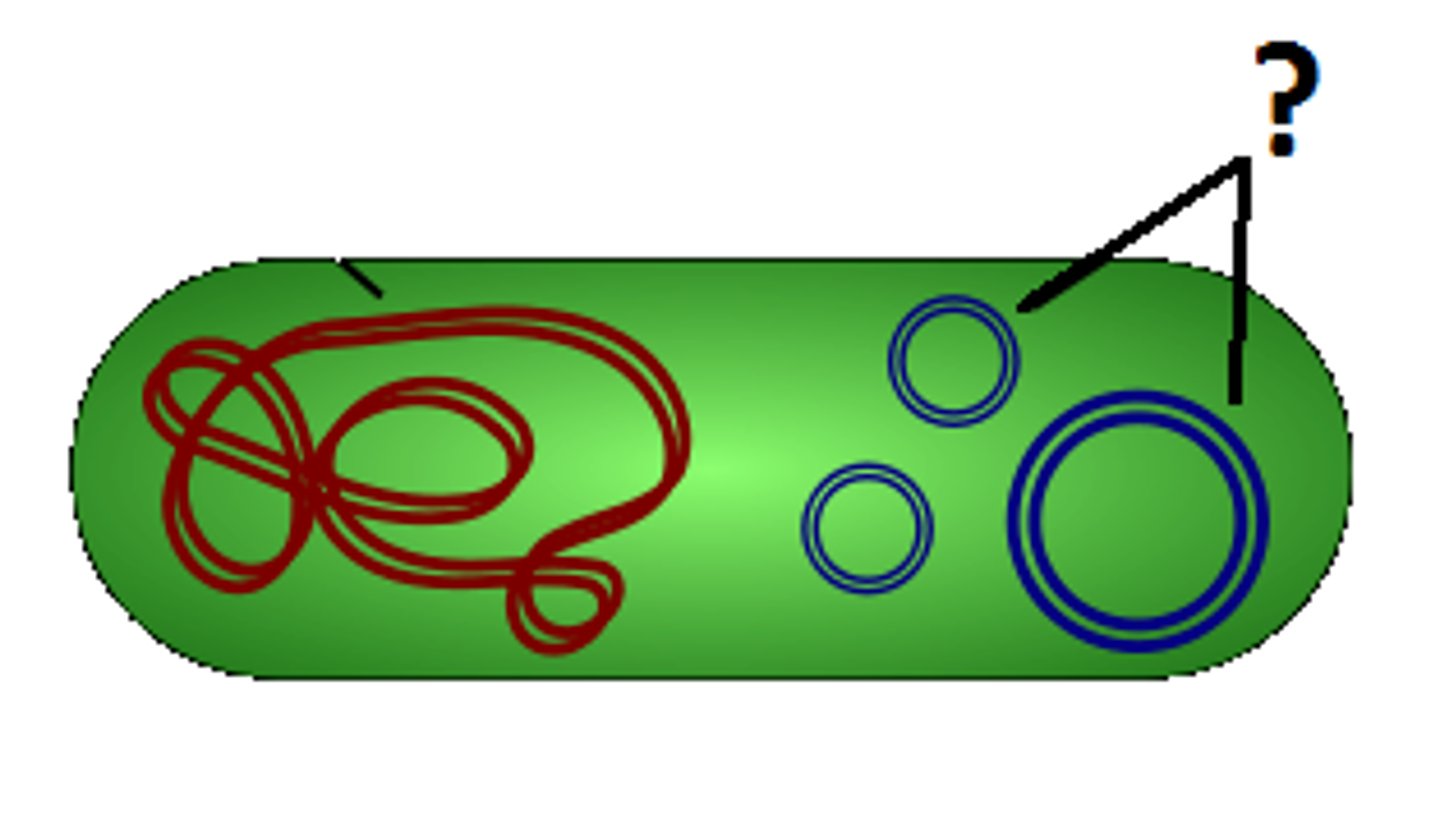
Sequencing of DNA
to determine the order of nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule.
Sex chromosomes
the pair of chromosomes responsible for determining the sex of an individual.
Sister chromatids
replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis.
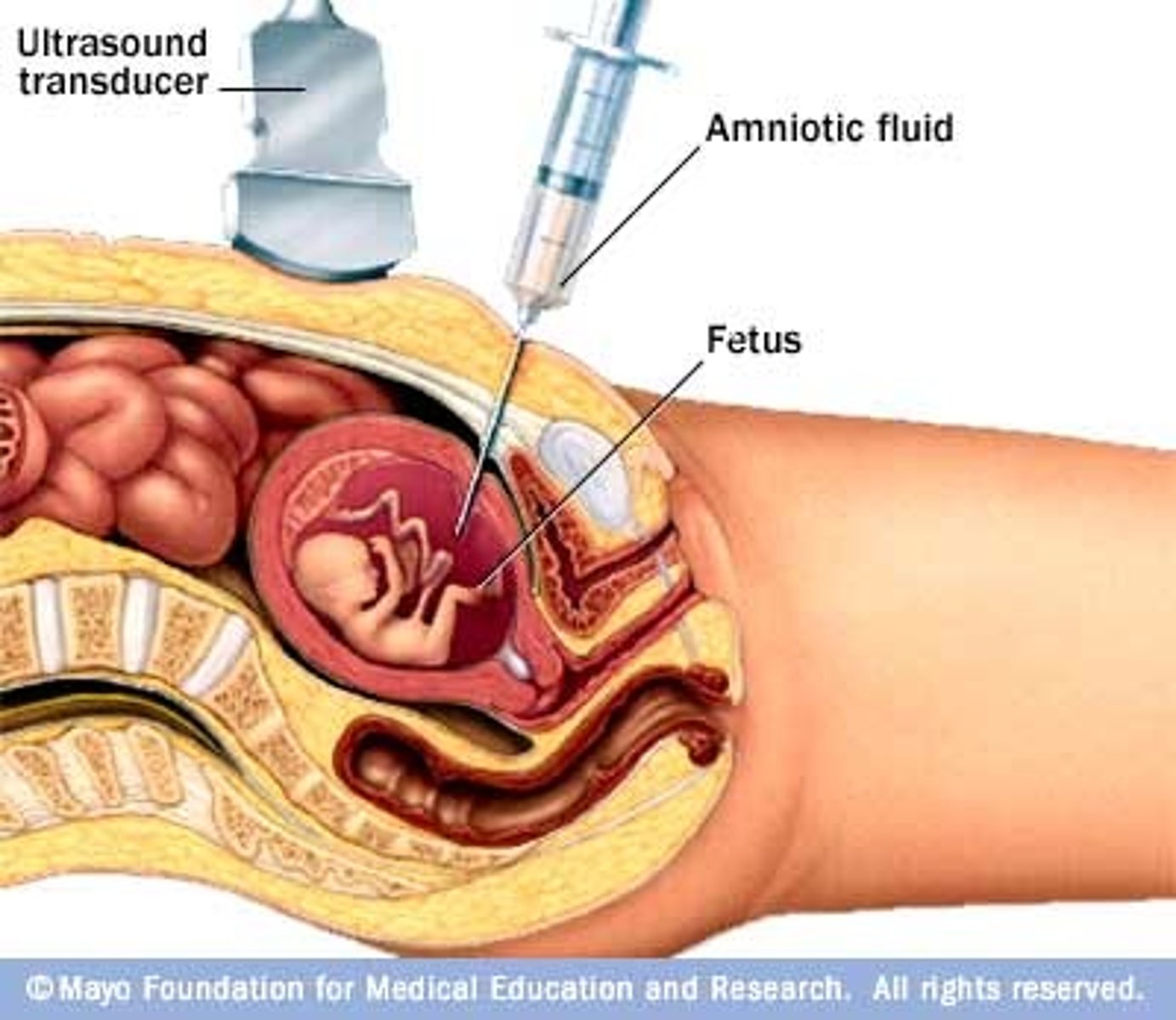
Amniocentesis
a procedure used to diagnose genetic defects in the early stages of pregnancy; it involves collecting amniotic fluid using a needle and syringe.
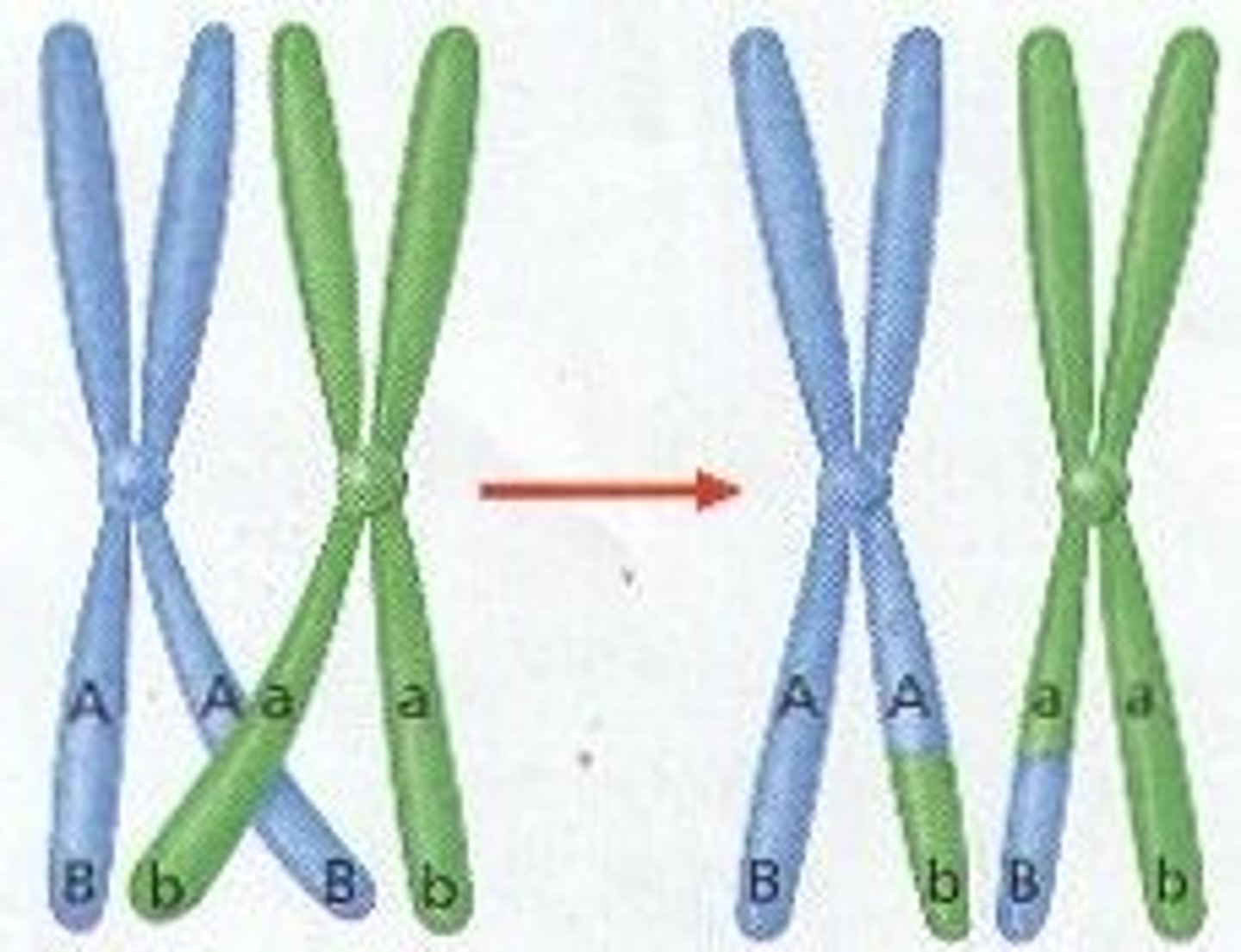
Crossing over
exchange of genetic material between homologous non-sister chromatids during meiosis I.
Diploid
a cell containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one from each parent.
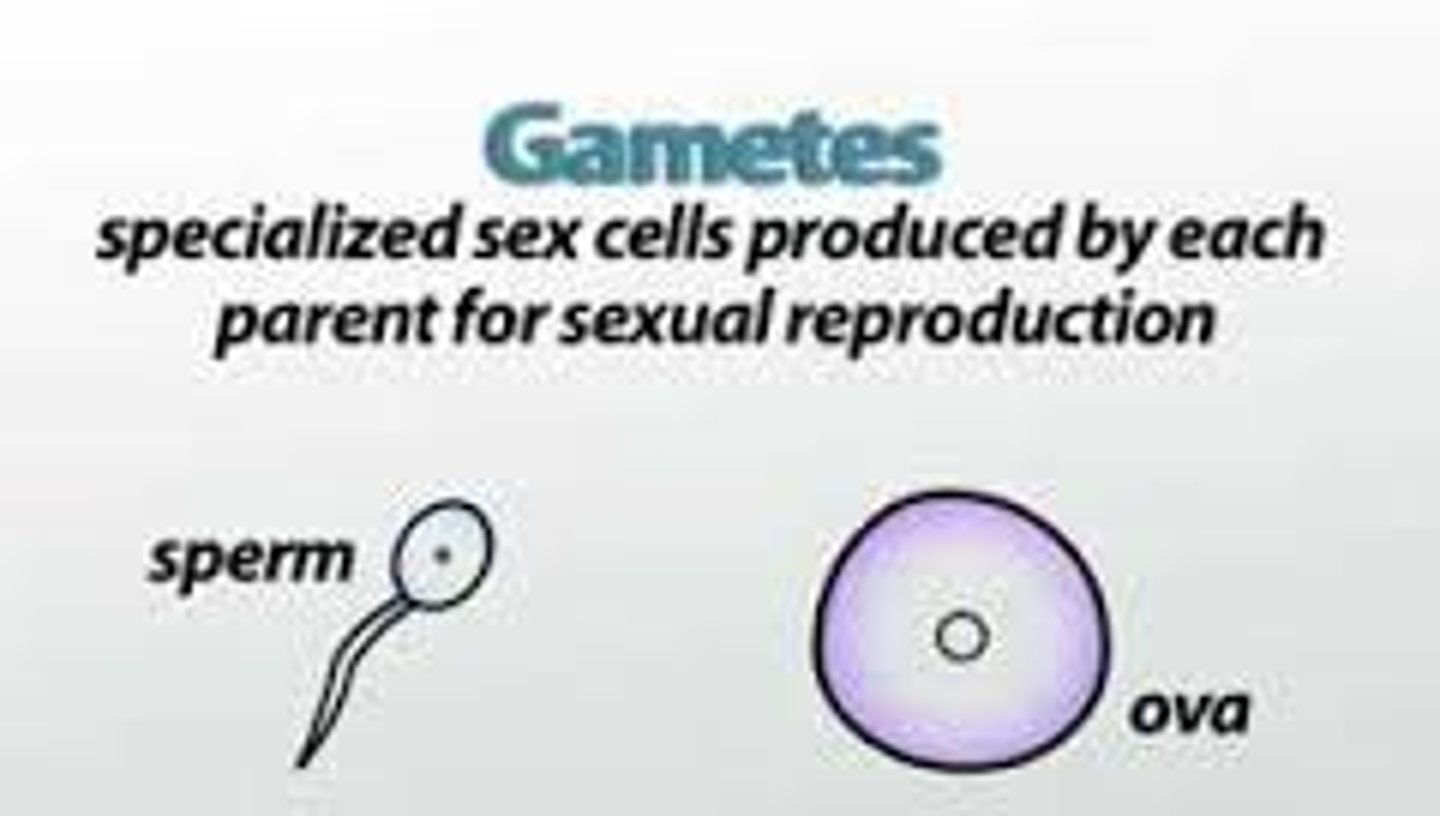
Gametes
one of two haploid reproductive cells, egg or sperm, whose union is necessary in sexual reproduction to produce a diploid zygote.
Haploid cells
have one chromosome of each pair (have one full set of the chromosomes that are found in its species).
Meiosis
the process of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that reduces the number of chromosomes in reproductive cells from diploid to haploid.
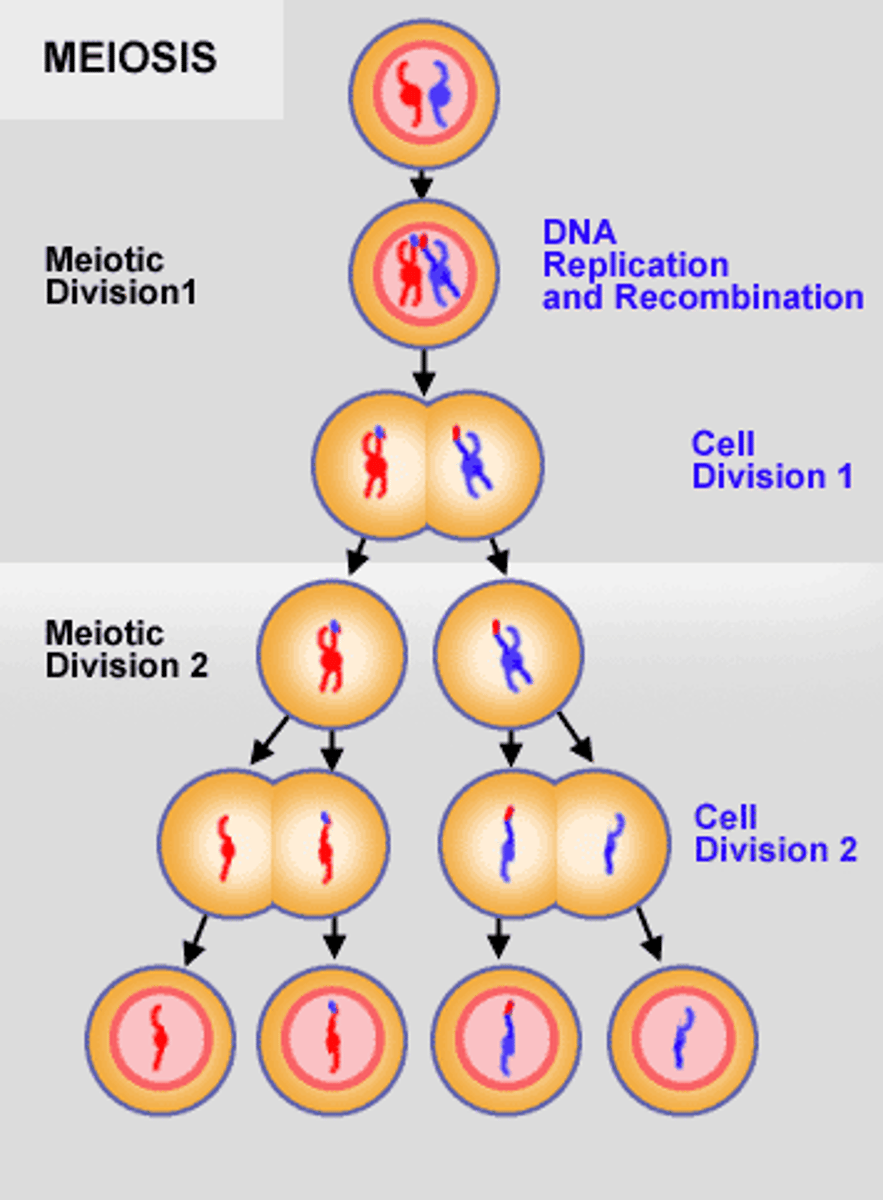
Non-disjunction
an error during mitosis or meiosis in which both members of a pair of homologous chromosomes or both sister chromatids fail to move apart.
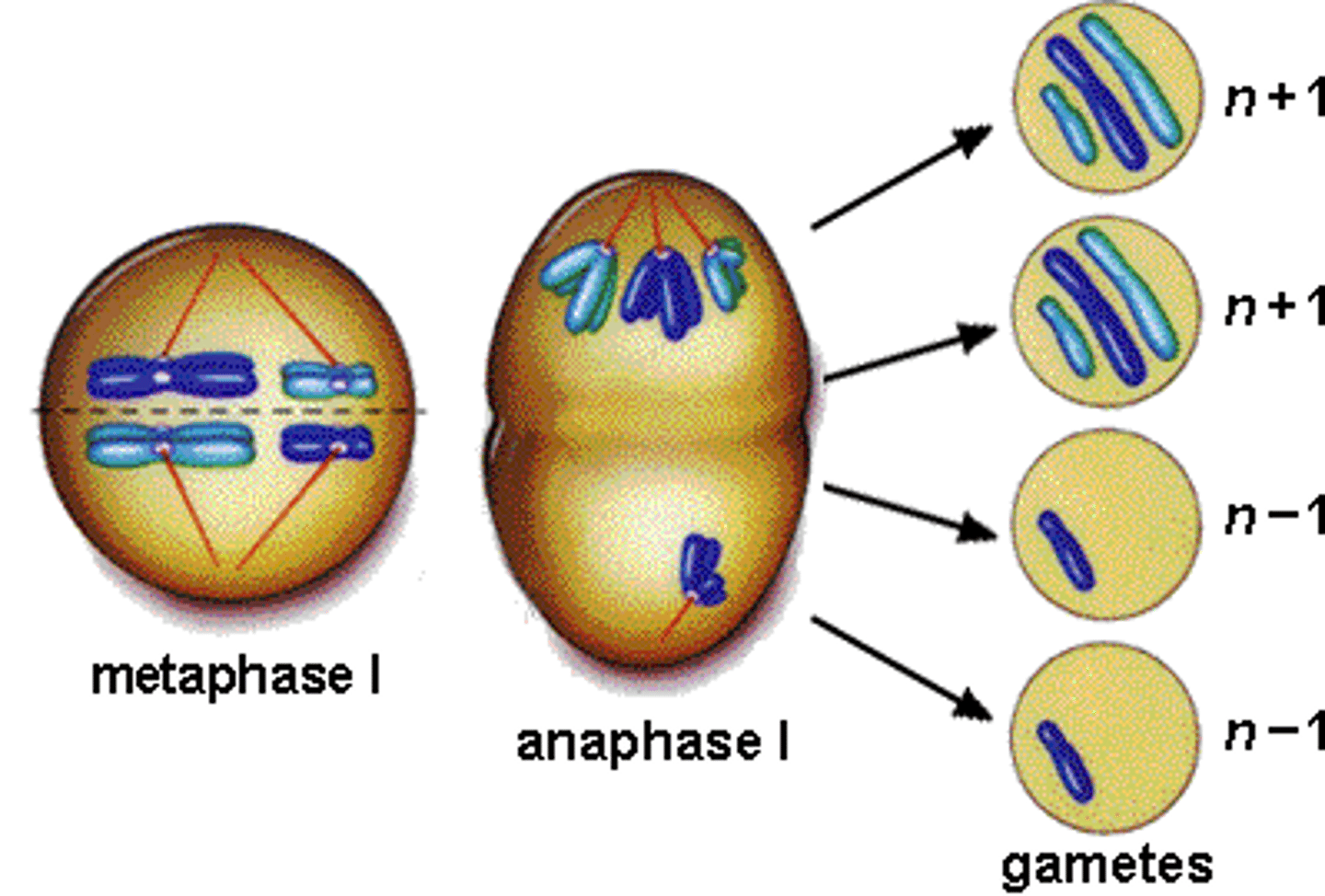
Random orientation
the orientation of homologous chromosomes in the spindle axis during metaphase I is random and either maternal or paternal homologue may orient towards a given pole. Leads to independent assortment.
Autosomal genes
chromosomes that do not determine sex.
Co-dominant alleles
two alleles at a particular locus that have different effects and are distinguishable in a heterozygous individual (e.g. AB blood groups).
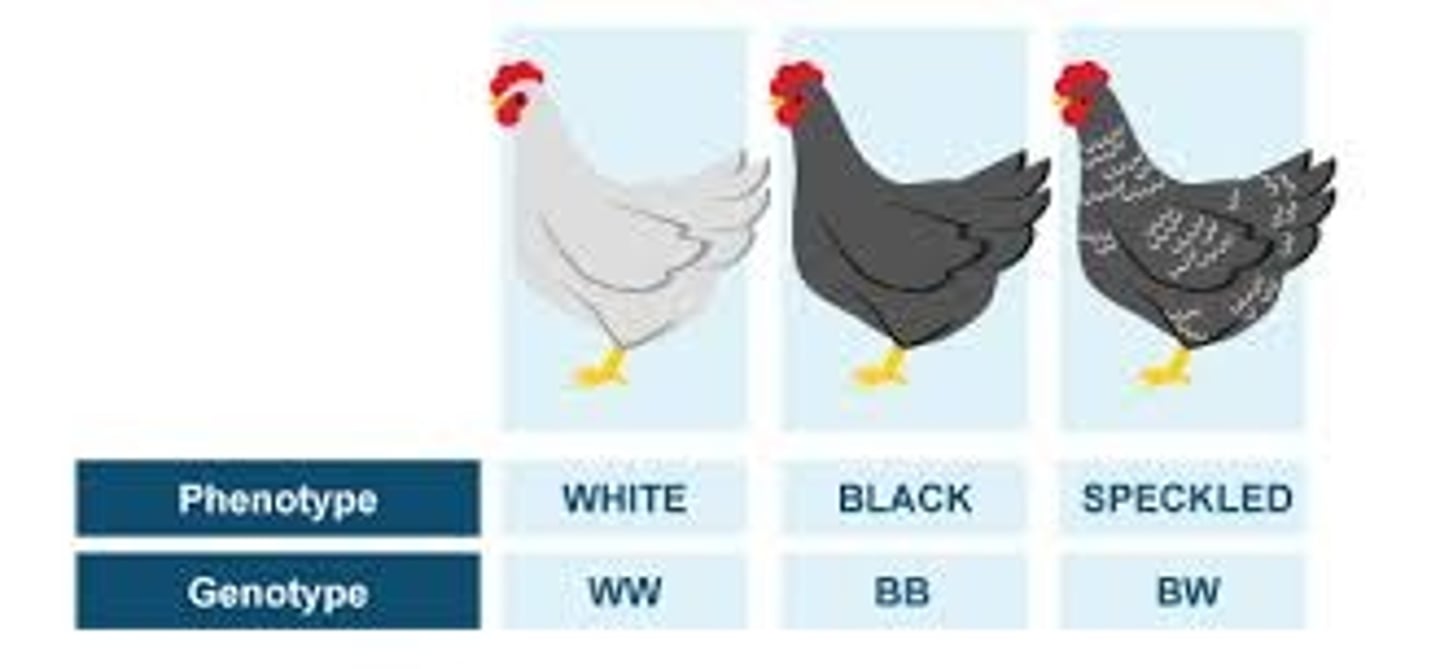
Color blindness
an abnormal condition caused by an X-linked recessive allele and characterized by the inability to clearly distinguish different colours of the visible light spectrum.

Dominant alleles
the allele that is fully expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygote.

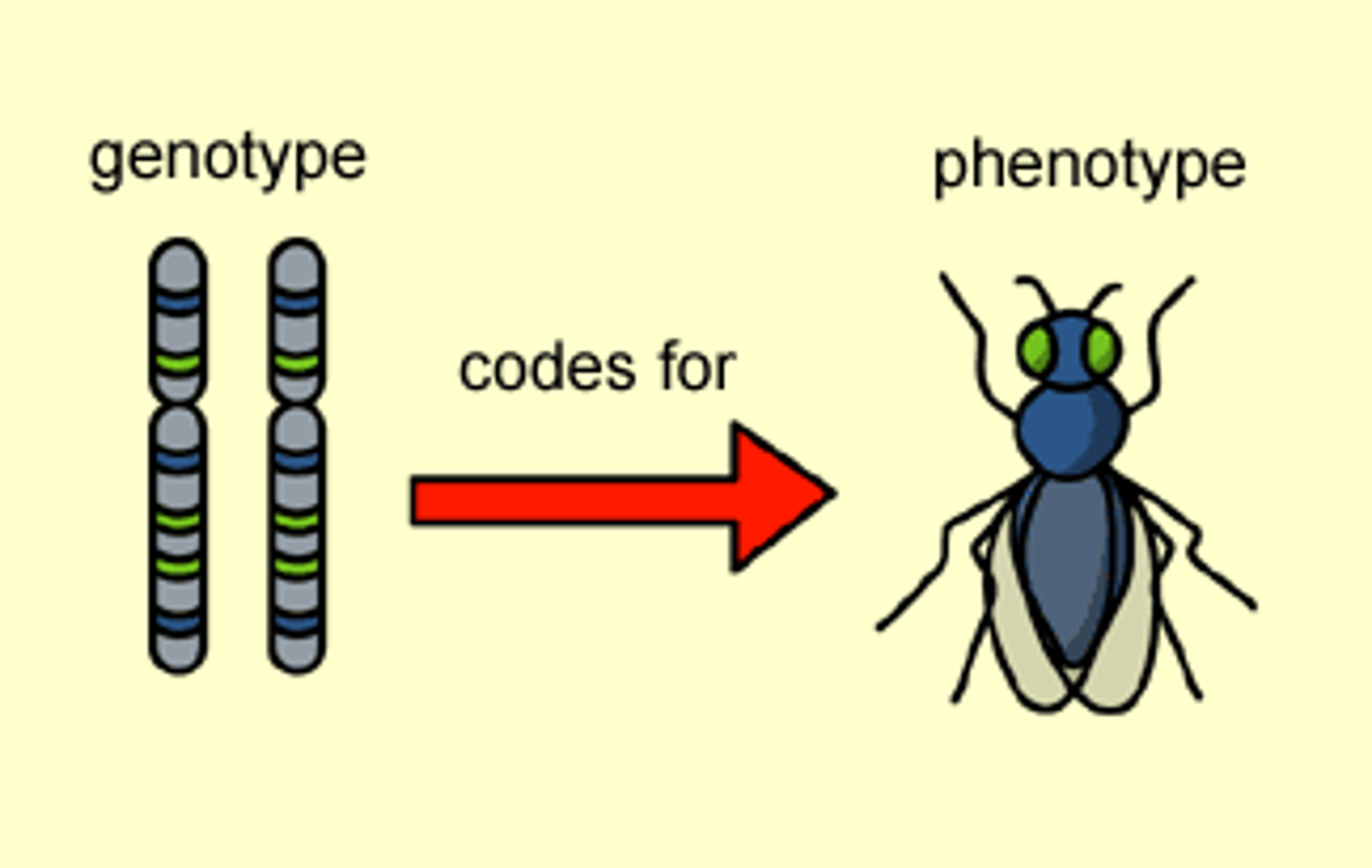
Genotype
the genetic constitution of an organism.
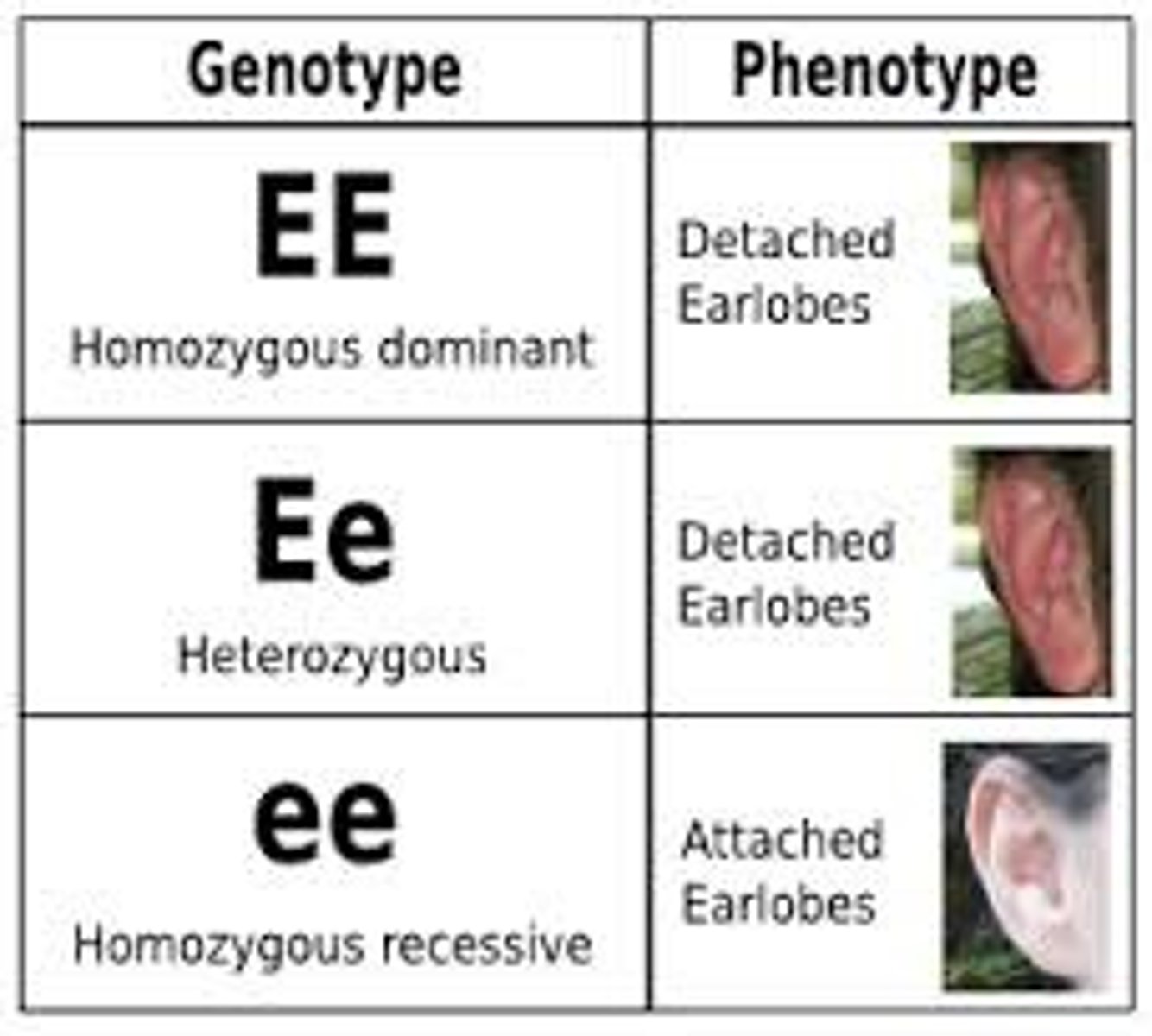
Hemophilia
a sex-linked inheritable disease characterized by loss or impairment of the normal clotting ability of blood, so that a minor wound may result in fatal bleeding.
Huntington's disease
autosomal dominant genetic defect on chromosome 4; caused by a CAG repeat in the DNA. Lethal in the homozygous dominant condition.
Mutagen
a chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.

Phenotype
the physical and physiological traits of an organism.
Punnett grid (or Punnett square)
a tool that helps to show all possible allelic combinations of gametes in a cross of parents with known genotypes in order to predict the probability of their offspring possessing certain sets of alleles.
Recessive allele
an allele that has an effect on the phenotype only when present in the homozygous state.
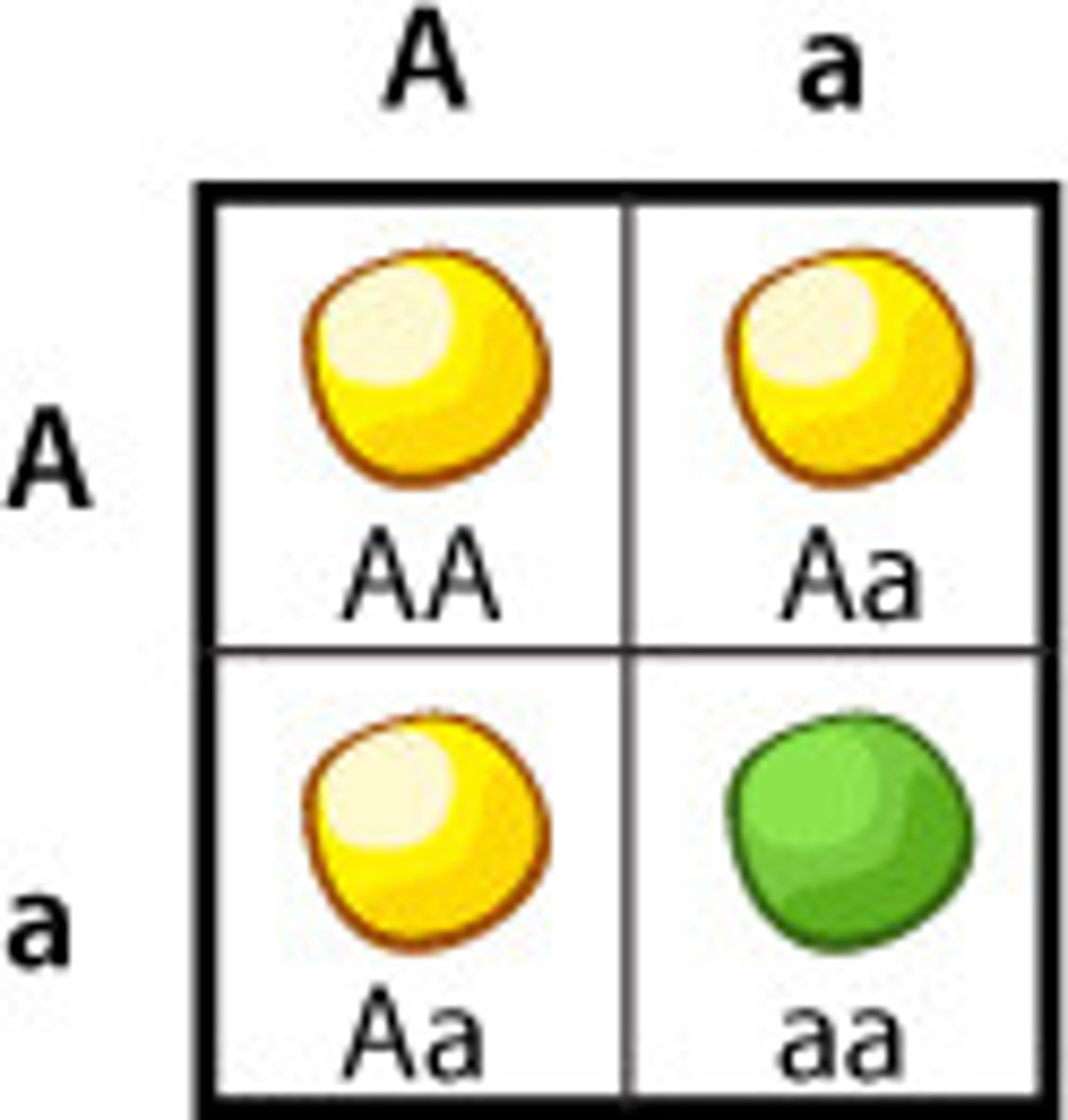
Sex-linked inheritance
traits controlled by genes located on one sex chromosome but not the other.
Zygotes
the diploid product of the fusion of haploid gametes (a fertilized egg).
Clones
a group of genetically identical cells or individuals.

DNA profiling (DNA fingerprinting)
the analysis of a small amount of genetic material, which is as unique per individual as a fingerprint is, as an aid to identification.
Embryo
the earliest stages in the development of a new plant or animal from a fertilized ovum and entirely dependent on nutrients supplied by the parent.
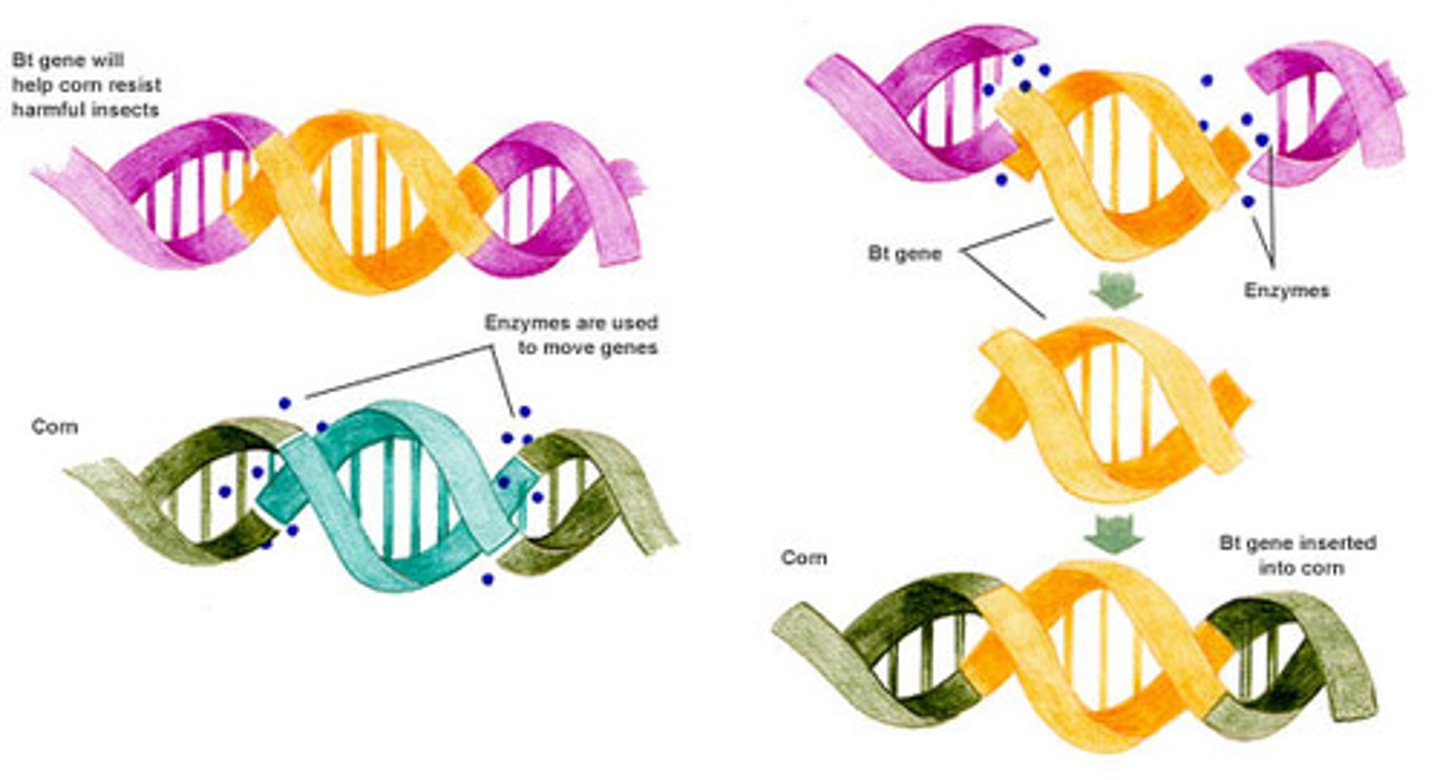
Genetic modification
the change to the genetic constitution of an organism by artificial methods.
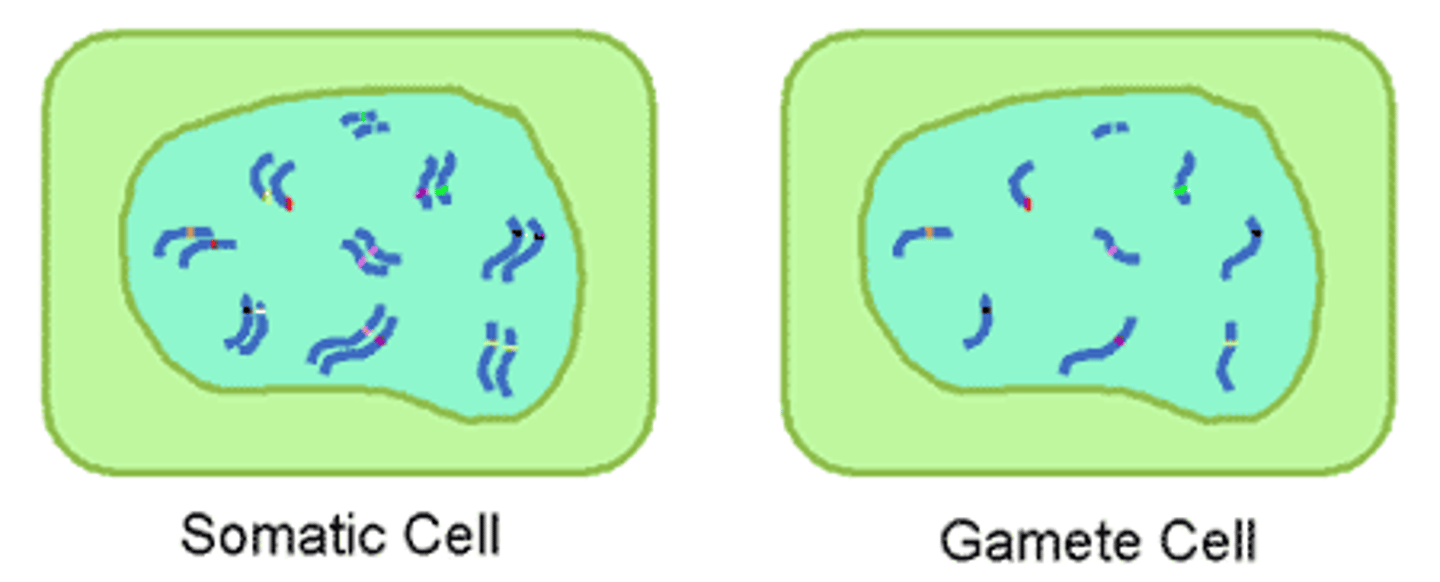
Somatic cell
all body cells except sex cells (cells producing gametes).
Gene
A heritable factor that influences a specific characteristic- a feature such as height or blood group
Heritable factor
A section of DNA passed from parent to offspring
Chromosomes
Subsections of an organism's total DNA
Homozygous
When a pair of chromosomes have the same allele
Heterozygous
When a pair of chromosomes have different alleles
Mutation
A change in the base sequence of DNA
Genome
The total genetic information in an organism
Prokaryote
Single-celled organisms without a membrane-bound nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryote
An organism of complex cells with DNA contained in a membrane-bound nucleus and with other membrane-bound organelles.
How do chromosomes occur in diploid cells?
In homologous pairs
How can you identify different chromosomes?
Look at the shape under a microscope
How do alleles differ from one another?
By a few differences in DNA base sequence
How do you know which gene it is on a chromosome?
By its locus
What outside factors can cause gene mutations?
Radiation, UV and chemicals
How does a gene mutation affect someone's characteristics?
Change in DNA -> Change in mRNA transcription -> Change in protein translation
Single base substitution
One base in a DNA sequence is changed for another
WHere is the genome found in prokaryotes?
In a single chromosome which takes the form of a circular molecule of DNA (majority) and the plasmids
Where is the genome found in eukaryotes?
In the nucleus, and some also found in the mitochondria, plasmids and chloroplasts
Example of a disease caused by single base substitution
Sickle Cell Anaemia
Human Genome Project
A map of the entire human genome
Which gene is substituted in Sickle Cell Anaemia?
One for haemoglobin and the codon in the gene- GAG is changed to GTG.
Results in polar amino acid glutamate being replaced by non-polar amino acid valine
Where is sickle cell anemia most common?
Africa- particularly where there are high rates of malaria
What are symptoms of sickle cell anaemia?
Blood clots which lead to pain and infection.
Sickle Cells are also destroyed quickly, which leads to anaemia due to less oxygen being transported.
What is the treatment for Sickle Cell Anaemia?
Lifelong treatment. Only cure is bone marrow transplant, which has a high risk.
What does the single base substitution for sickle cell anemia cause?
Glutamic acid is changed to valine. The mRNA also changes from GAG to GUG
WHat does a change from glutamic acid to valine cause?
Protein forms long fibres in the red blood cells, which sickles the red blood cells and makes haemoglobin less soluble in water
Why is sickle cell anaemia so common in areas with high rates of malaria?
Because the heterozygous carriers of sickle cell anaemia have a higher survival rate from malaria, so more of these are passed on to offspring.
Heterozygote Advantage
Greater reproductive success of heterozygous individuals compared to homozygotes; tends to preserve variation in gene pools.
How can a genome be used in medicine?
To determine if offspring will have a genetic disease. (genetic screening)
What is comparative genomics used for?
One can construct evolutionary trees to find common ancestors and determine target genes for biological modelling in the lab.
Comparative genomics
Comparing genomes of different species
Plasmid
A small, circular section of DNA that contains a small number of genes, and can replicate itself
Histone
protein associated in the "packaging" of DNA
Centromere
The region of the chromosomes that join the two sister chromatids togethr
Diploid cells
Contain homologous pairs of chromosomes
Haploid cells
Contain individual chromosomes
Somatic cells
"body" cells
Autosomal Chromosomes
Chromosomes that do not determine sex
Karyotype
A property of a cell; how many chromosomes it has and their pairs
Why is it better to look at base sequences than comparative genomics to find relations?
Because different bases can use the same amino acids