Genotype and Nucleic Acid Quantification
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards includes key vocabulary terms and definitions from a lecture on genotype, phenotype, mutations, nucleic acid quantification, and related concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an organism, determined by the DNA passed to it by its parents.
Genomics
The study of genes and their functions.
Phenotype
The observable physical and behavioral characteristics of an organism.
Mutation
A change in the nucleotide sequence of a short region of a genome.
Polymorphism
Naturally occurring genetic variations among organisms in the same species, present in greater than 1% of the population.
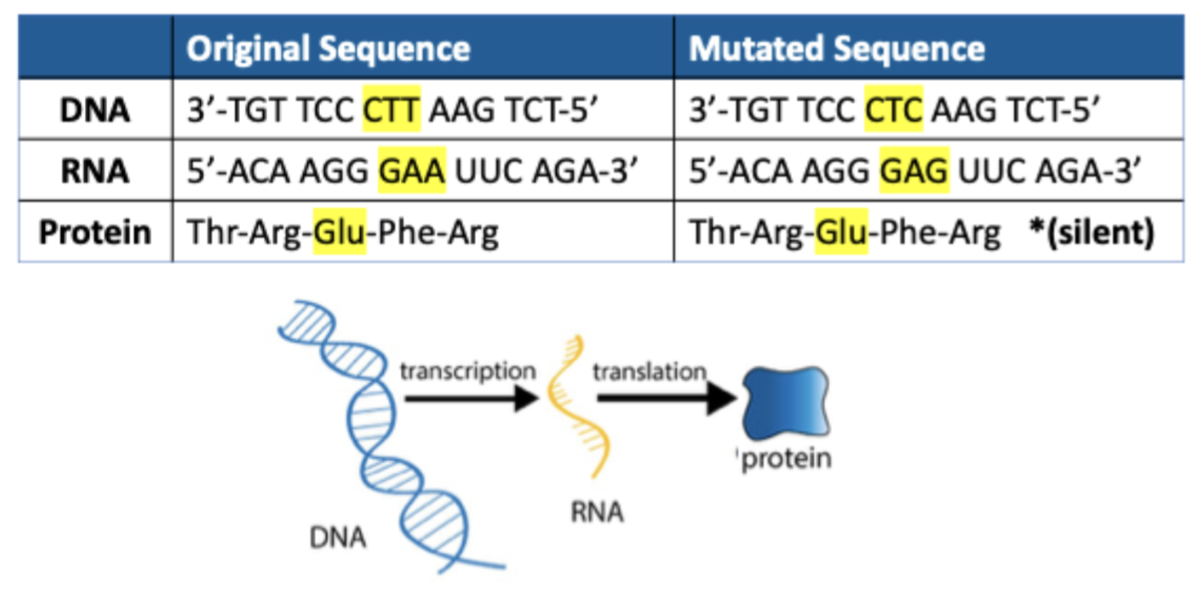
Silent Mutation
A mutation that does not result in a change to the translated amino acid.
Restriction Enzyme
An enzyme that cuts DNA at specific recognition sites, often used in recombinant DNA technology.
pGLO Plasmid
A circular DNA molecule consisting of 5371 base pairs with multiple restriction enzyme recognition sites.
Codon
A three-nucleotide sequence of RNA that codes for a particular amino acid.
Beer-Lambert’s Law
A linear relationship between absorbance and concentration in a solution, used to quantify nucleic acids.
OD260/OD280 Ratio
A measurement used to assess the purity of nucleic acid samples.
λmax
The wavelength at which a substance exhibits maximum absorbance.
Electrophoresis
A technique used to separate DNA fragments based on size.
Nucleic Acid Quantification
The process of measuring the concentration of DNA or RNA in a sample.
EcoRI
A restriction enzyme first isolated from Escherichia coli RY13 strain, known for cutting at a specific sequence.
Hind III
A restriction enzyme isolated from the Haemophilus influenzae Rd strain, used in DNA analysis.
Extinction Coefficient
A measure of how strongly a chemical species absorbs light at a particular wavelength.
Extinction Coefficient (ε) for Double-Stranded DNA
0.020 (μg/mL)−1cm−1.
Extinction Coefficient (ε) for Single-Stranded RNA
0.025 (μg/mL)−1cm−1.
UV Absorbance of Proteins
Proteins exhibit a λmax at 280 nm, which can interfere with DNA purity assessments by raising absorbance at 260 nm.
NanoDrop Measurements
Instruments that use short pathlengths (1.0 mm to 0.05 mm) to measure high-concentration nucleic acid samples with minimal dilution.
Absorbance Units Detection Limit for NanoDrop
The internal spectrometer detection limit is ~1.5 Absorbance units, but shorter path lengths can extend the absorbance range.
λmax for DNA and RNA
Both DNA and RNA are colorless with a maximum absorbance at 260 nm, making it difficult to distinguish them using spectrophotometric analysis.
Presence of RNA in DNA Samples
The presence of RNA cannot accurately be detected with spectrophotometric analysis since they share the same λmax.
Purity Assessment of Nucleic Acid Samples
A common lab practice to ensure samples are free from proteins and contaminants by measuring absorbance at various wavelengths.
Degenerate Codons
Different codons can translate to the same amino acid, showcasing the redundancy in the genetic code.
Mutagenesis
The process by which a change in a nucleotide occurs in a DNA sequence, potentially leading to mutations in the organism.
Impact of Mutations on Restriction Sites
Prevent the enzyme from cutting the DNA, affecting the resulting fragments observed in DNA electrophoresis.
DNA Structure
A double helix that can fold and coil itself into more complex shapes, appearing very small and compact when coiled.
DNA Digestion
When digested with enzymes, it unfolds and increases in length.
Supercoiling
The DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.
Nicked DNA
During the extraction process, creating hooks in the circular DNA.
Concentration Measurement for DNA
Expressed in mass/volume (e.g., ng/mL) rather than molarity.
RNA in Gel Electrophoresis
Smaller than DNA and migrates faster in agarose gel electrophoresis.
Impact of pH and Wavelength on Absorbance
Small changes in pH and the accuracy of the spectrophotometer will cause the OD260/OD280 ratio to vary.