Conjugation and Stability of Dienes and Allyl Cations
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
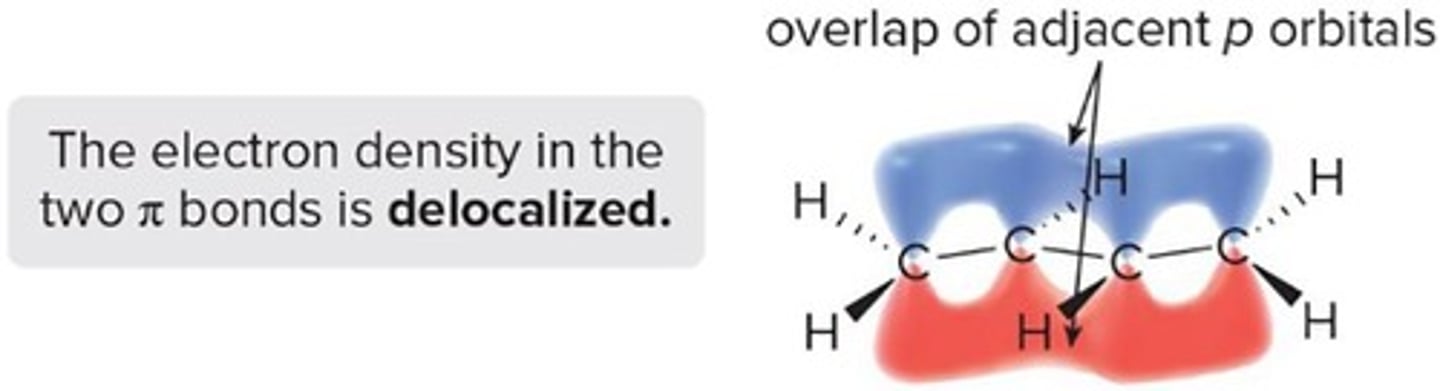
Conjugation
Overlap of p orbitals on adjacent atoms.
p Orbital
A type of atomic orbital involved in bonding.
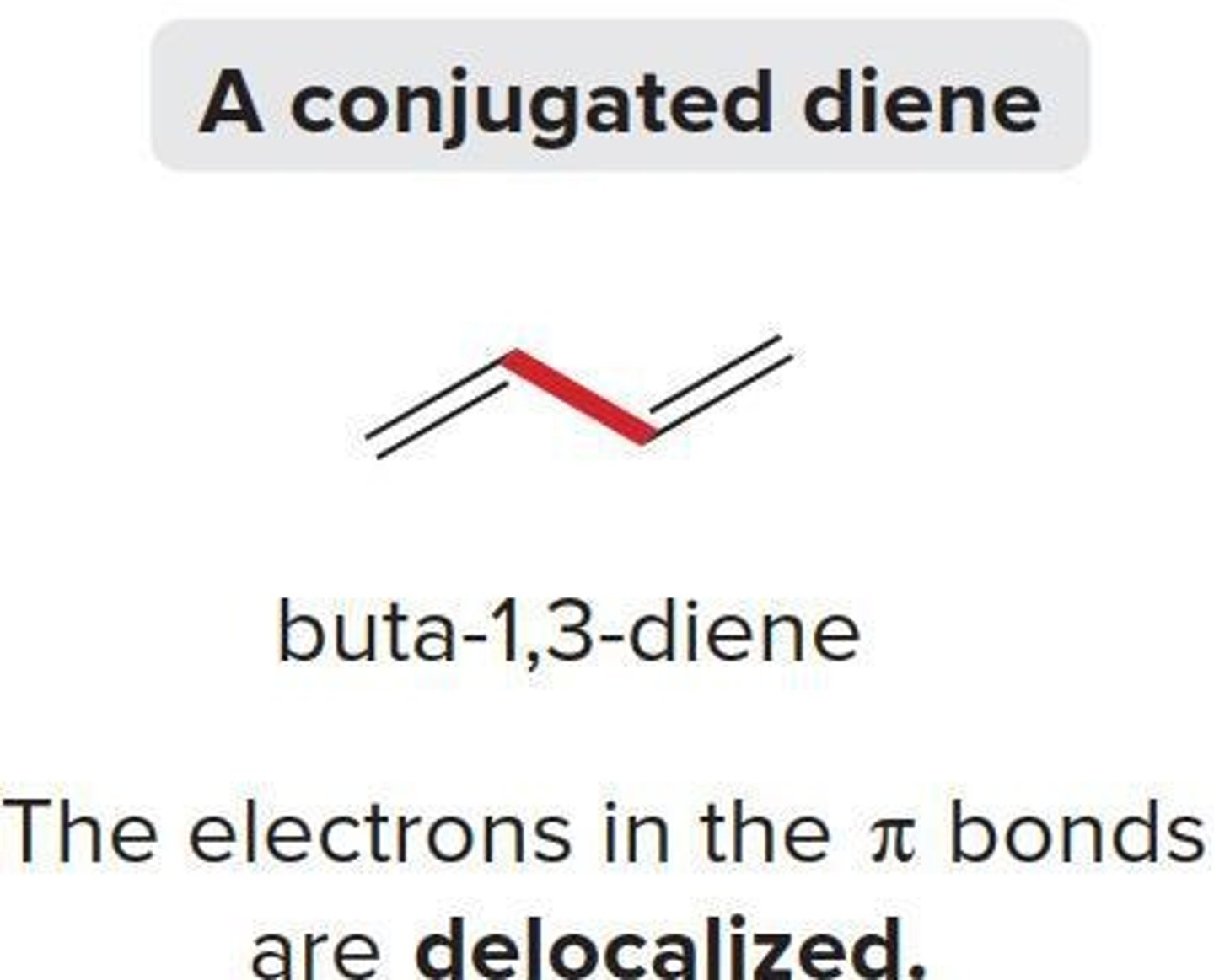
1,3-Diene
A conjugated system with alternating double bonds.
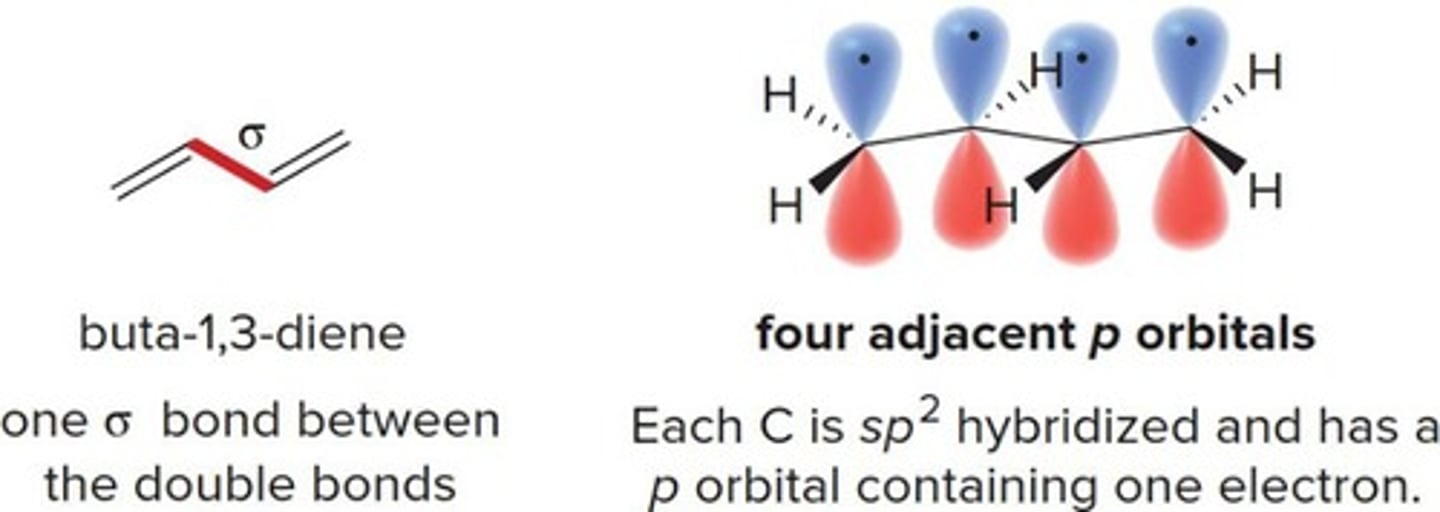
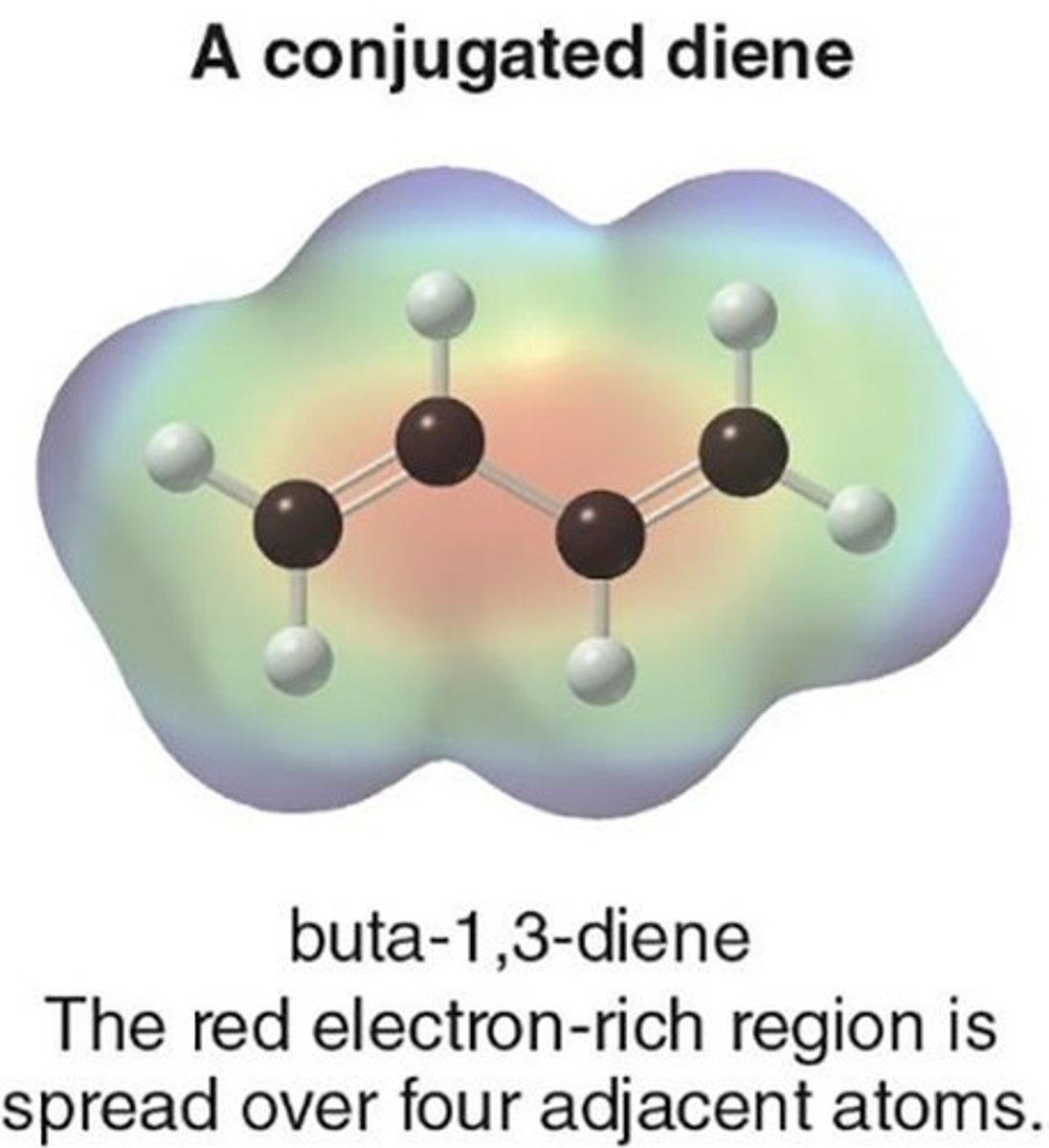
Delocalization
Spread of electrons across multiple atoms.
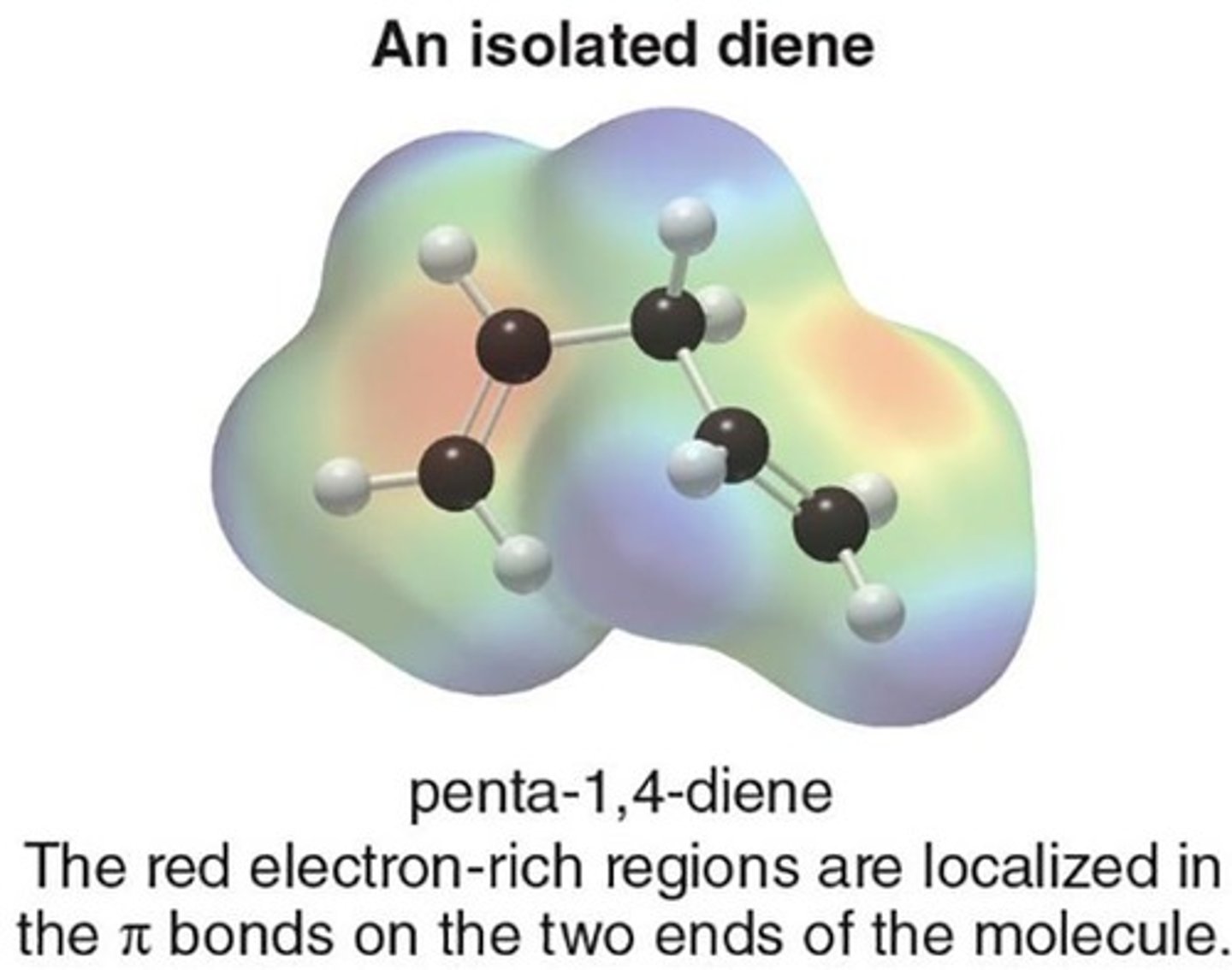
Isolated Diene
Diene with π bonds too far apart.
1,4-Pentadiene
An example of an isolated diene.
Allyl Carbocation
A cation stabilized by conjugation.
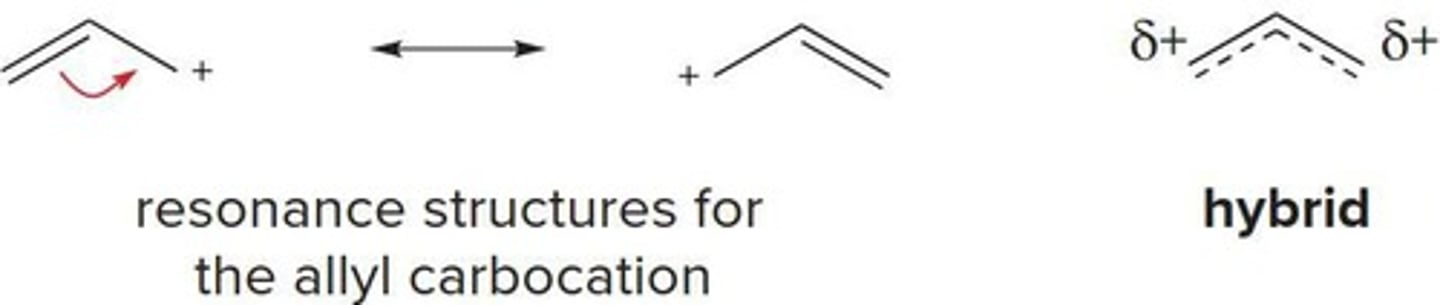
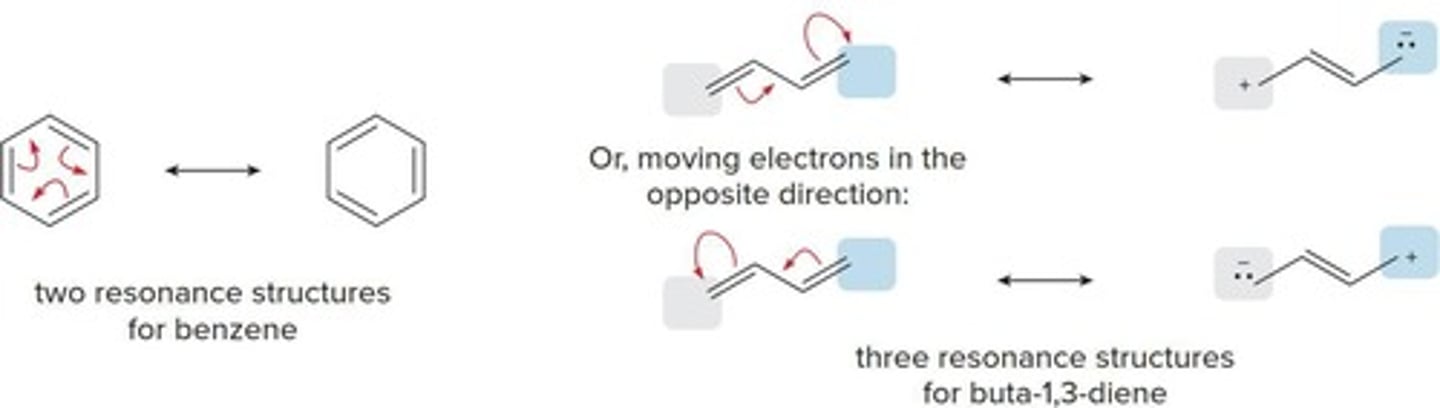
Resonance Structures
Different Lewis structures for the same molecule.
Delocalized Hybrid
Actual structure combining multiple resonance forms.
Stability of Allyl Cation
Comparable stability to a 2° carbocation.
Electrostatic Potential Map
Visual representation of electron density distribution.
Cyclic Conjugated Rings
Rings like benzene with multiple resonance forms.
Formal Charge
Charge assigned based on electron distribution.
Resonance Hybrid
Combination of all resonance structures.
Rule 1 of Resonance
More bonds and fewer charges are preferred.
Rule 2 of Resonance
Structures where all atoms have octets are better.
Rule 3 of Resonance
Negative charge on electronegative atoms is preferred.
Common Resonance Examples
Allyl cation and acetate anion are examples.
Conjugated Double Bonds
Double bonds that allow electron delocalization.
Electrostatic Potential Plots
Graphs showing electron-rich and electron-poor areas.
Resonance Contributions
Stability based on structure and charge distribution.
Hybridization
The mixing of atomic orbitals to form new ones.
sp2 Hybridization
Involves one s and two p orbitals.
p Orbitals
Required for overlap in conjugation.
Trigonal Planar Geometry
Shape of sp2 hybridized carbon atoms.
Conjugated Dienes
Compounds with two double bonds linked by σ bond.
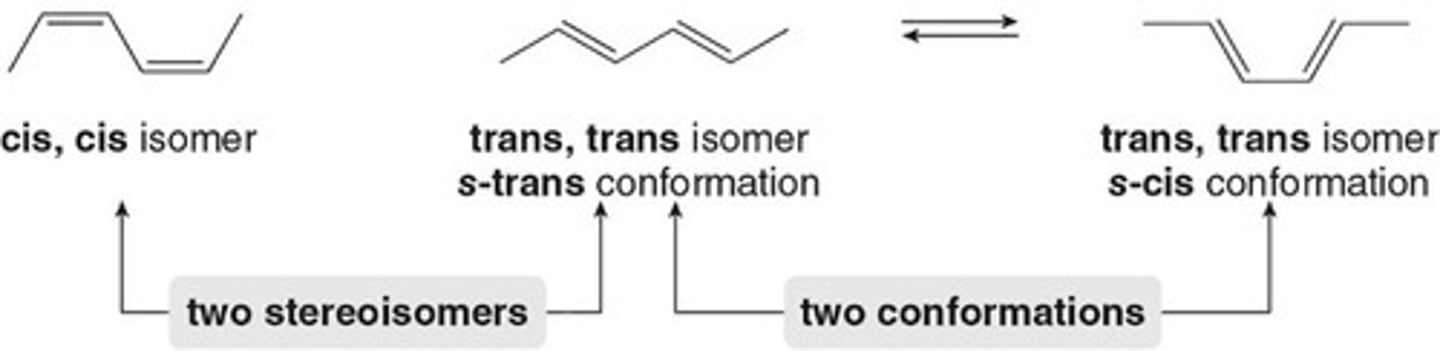
Stereoisomers
Discrete molecules with different spatial arrangements.
Conformations
Interconvertible arrangements of the same molecule.
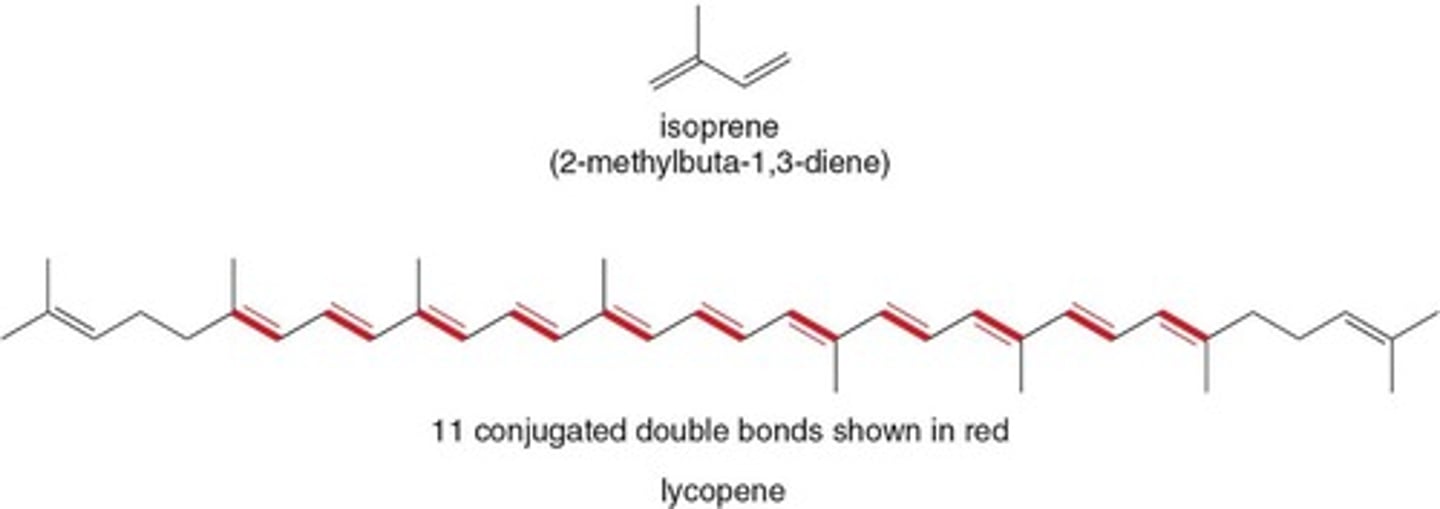
Isoprene
A plant compound released during heat stress.
Lycopene
Antioxidant responsible for red color in tomatoes.
Cholecalciferol (D3)
Vitamin D3, important for calcium metabolism.
Simvastatin
Medication used to lower cholesterol levels.
Calcitriol
Treats hypocalcemia, increasing blood calcium levels.
Features of Conjugated Dienes
Distinct properties compared to isolated dienes.
C-C Single Bond
Unusually short in conjugated dienes.
Stability of Conjugated Dienes
More stable than isolated dienes due to conjugation.
Heat of Hydrogenation
Lower value indicates greater stability of diene.
1,2-Addition Product
Product formed in electrophilic addition to conjugated dienes.
1,4-Addition Product
Alternative product formed in electrophilic addition reactions.
Reaction Conditions
Influence the ratio of addition products formed.
Kinetic Product
Formed faster but less stable than thermodynamic product.
Thermodynamic Product
More stable product formed at equilibrium.
Energy of Activation (Ea)
Determines the reaction rate.
Ultraviolet Light Absorption
Conjugated dienes absorb longer wavelengths than isolated dienes.
1,4-Product
More stable due to two alkyl groups.
1,2-Product
Less stable with only one alkyl group.
Proximity Effect
Influences stability of 1,2-products.
Energy Diagram
Illustrates energy changes in reactions.
Two-Step Mechanism
Lower activation energy at low temperatures.
Kinetic Energy
Higher temperatures allow reaching both transition states.
Diels-Alder Reaction
Addition of 1,3-diene and alkene to form a ring.
Six-Membered Ring
Product of Diels-Alder reaction.
π Bonds
Three π bonds break during the reaction.

σ Bonds
Two σ bonds and one π bond form.
Energy Release
Typical release of ~40 kcal/mol.
s-cis Conformation
Diene must adopt this for reactivity.
s-trans Conformation
Diene is unreactive in this form.
Electron-Withdrawing Groups
Increase dienophile reactivity in Diels-Alder reaction.
Nucleophile
Diene acts as this in the reaction.
Electrophile
Dienophile acts as this in the reaction.
Carbonyl Group
Effective electron-withdrawing group in dienophiles.
Cis Fused
Bicyclic product with cis hydrogen atoms.
Bridged Ring System
Shares nonadjacent carbon atoms in two rings.
Dienophile
Alkene that reacts with 1,3-diene.
Bicyclic Product
Formed from cyclic dienophile in Diels-Alder.
Reactivity of Dienophile
Increases with stronger electron-withdrawing substituents.
Endo Orientation
Preferred arrangement in Diels-Alder products.
Dienophile
Substituted alkene reacting with diene.
Endo Product
Product with substituent oriented towards diene.
Exo Product
Product with substituent oriented away from diene.
Transition State
High-energy state during chemical reaction.
Dicyclopentadiene
Dimer formed from cyclopentadiene via Diels-Alder.
Retro Diels-Alder Reaction
Heating dicyclopentadiene to regenerate cyclopentadiene.
Steroid
Tetracyclic lipid with four fused rings.
C Ring of Estrone
Formed using Diels-Alder reactions in steroid synthesis.
B Ring of Cortisone
Constructed via Diels-Alder reactions in steroid synthesis.
Ultraviolet Light
Light that promotes electron to higher energy state.
UV Light Wavelength
Useful range for absorption is 200-400 nm.
Ground State
Lowest energy state of an electron.
Excited State
Higher energy state after light absorption.
Conjugated Dienes
Compounds with alternating double bonds.
λmax
Wavelength of maximum light absorption.
UV Spectrum
Plot of absorbance versus wavelength for UV light.
Visible Light
Light absorbed by compounds with many conjugated bonds.
Lycopene
Pigment absorbing light at λmax = 470 nm.
SPF Rating
Measure of sunscreen effectiveness against UV radiation.
PABA
Sunscreen ingredient that absorbs UV light.
Padimate O
Another sunscreen compound that absorbs UV light.