salivary glands
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
what are the three pairs of major salivary glands
parotid
submandibular
sublingual
the three sets of the major salivary glands produce __% of the saliva volume
90%
saliva is a complex fluid with multiple functions, like: (5)
wetting
lubricating
digestive
mineralization
protective
which major salivary gland is most active during stimulation
parotid
which major salivary gland is most active during non-stimulated times
submandibular
do the parotid glands produce mostly serous or mucous secretions
serous
the parotid gland only produces __% of daily saliva volume
20%
which major salivary gland will include SIgA in their salivary secretions
parotid
do the submandibular glands primarily produce serous or mucous secretions
more serous than mucous
the submandibular glands produce __% of daily saliva volume
65% → MOST
do the sublingual glands primarily produce serous or mucous secretions
mix of mucous and serous saliva
the sublingual glands produce __% of daily saliva volume
5%
when looking histologically at a cross section of a salivary gland, there will be…
numerous lobules within each of the lobes
what is surrounding the lobes of a salivary gland
a capsule made up of connective tissue that is rich in collagen
what separates the lobes within a salivary gland
connective tissue septa (is continuous w the capsule)
what runs within the connective tissue septa
blood vessels, nerves, and excretory ducts
salivary glands are composed of a capsule surrounding a branched duct system ending in…
acini
compound acinar gland
or tubules
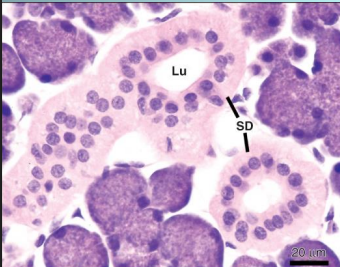
______ (serous/mucous) acinus and ________ (serous/mucous) tubules will drain into the ____________ (striated/intercalated) ducts, and this will then drain into the __________ (striated/intercalated) duct
serous acinus and mucous tubules will drain into the intercalated ducts, and this will then drain into the striated duct
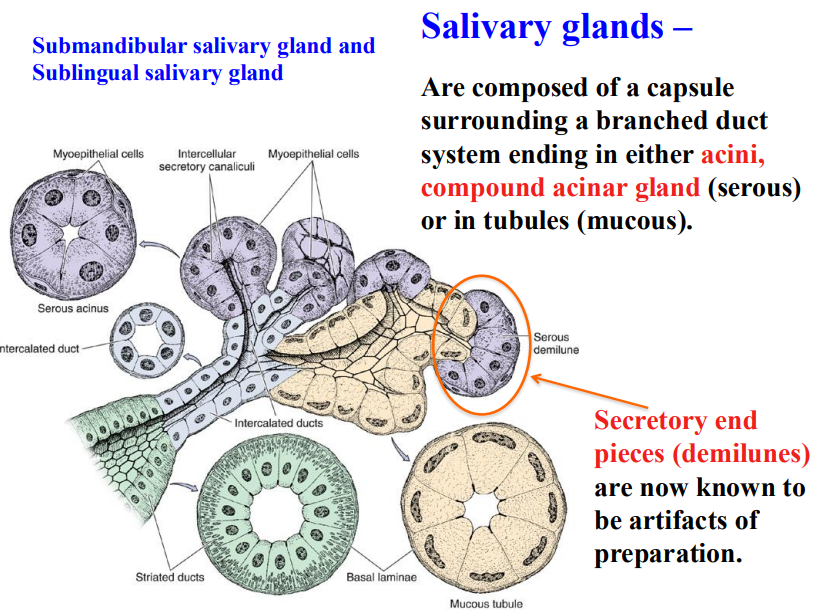
what are serous demilune
are artifacts created from incorrect preparation of the slide → ARE FAKE
how do serous cells present histologically
stain darker than mucous cells
pyramidal in shape
broad based attached to basal lamina
narrow apical end towards lumen
polarized cell
protein secreting cells
round nuclei
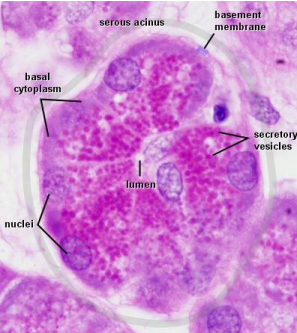
what do serous cells secrete
a watery fluid w proteins and an alpha-amylase
what is the funx of alpha-amylase
will digest dietary starch into maltose
how do mucous cells present histologically
are much lighter (compared to serous cells)
pyramidal in shape
have a flattened nuclei
polarized cell
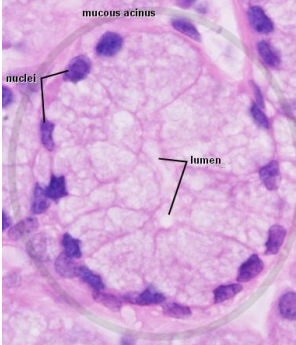
what do mucous cell secrete
a very mucus-rich secretion → mucin that is stored in large, light-colored vesicles
what does it mean to be a polarized cells
nuclei at one end (basal end) and secretory at the other end
are myoepithelial cells present in serous or mucous cells
serous cells ONLY
where specifically are myoepithelial cells
present between serous cells and their basal lamina in the serous acini as branched basket cells
along intercalated ducts
explain the origin of myoepithelial cells
are around the intercalated ducts resemble smooth muscle cells → are ectodermal in origin
what composes the duct system
intercalated ducts
striated ducts
intercalated ducts and striated ducts are the ___________________ ducts
intralobular ducts
what does intralobular duct mean
a duct located within a lobule of the salivary gland
characteristics of intercalated ducts
lining of cuboidal epithelial cells
act as stem cells for both secretory end piece cells and for the ductal cells
characteristics of striated ducts
connect to several intercalated ducts
are striated caused by infoldings of the basal plasma membrane for ion transport
in what duct is where the saliva composition changes
striated
excretory ducts are…
interlobular
have their own stem cells
are intercalated duct cells polar or nonpolar
nonpolar
intercalated duct cells are ___________ (small/big) in diameter and drain individual __________ units
small in diameter; secretory units
intercalated duct cells are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of…
lysozyme and lactoferrin
funx of lysozyme
normal protective type of enzyme
funx of lactoferrin
will slow bacteria growth: act as chelating agent, will bind to nutrient molecules on surface of oral cavity and make them unavailable to bacteria
what is the source of salivary gland stem cells
intercalated duct cells
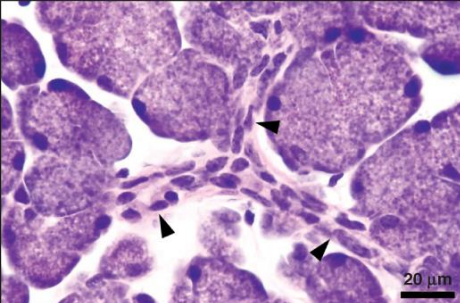
?
intercalated duct cells
where are striated duct cells mainly found
in parotid and submandibular glands
are striated duct cells polar or nonpolar
polar
striated duct cells are have a striated appearance in basal plasma membrane w many…
mitochondria
striated duct cells predominate role
in assembly and transcytosis of SIgA
?
striated duct cells
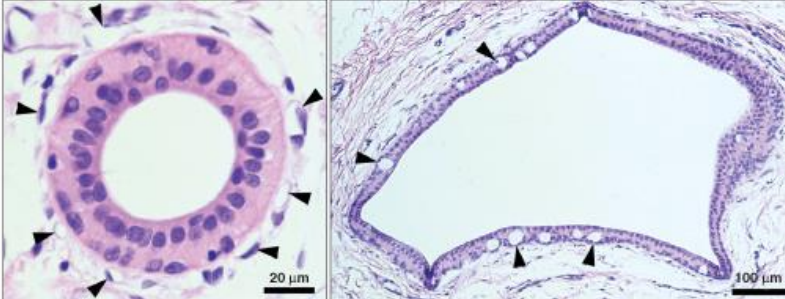
characteristics of excretory ducts (4)
are passive conducting tubes
maybe pseudostratified to stratified
contain both goblet cells and stem cells
bilayered
?
excretory ducts
the parotid gland has the highest amount of ____ of all salivary glands
amylase
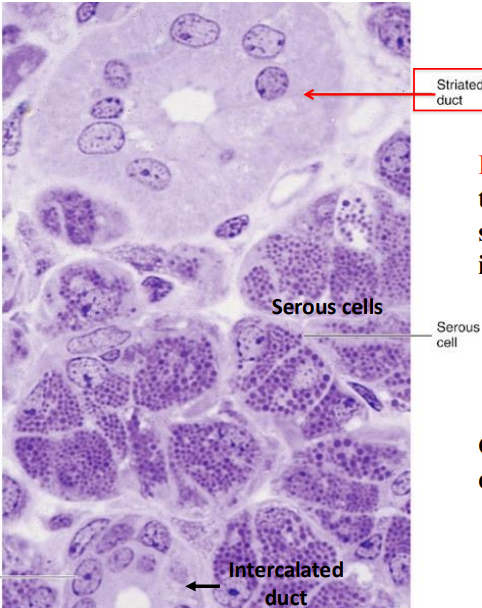
what gland is this
parotid gland
the submandibular gland is a mix of serous and mucous cells, which dominates
70% of the ducts end in serous acini and and 30% mucous acini (size will make it look like 50/50)
the submandibular and sublingual gland contains branched _____________ gland composed of serous and mucous cells
tubuloacinar gland
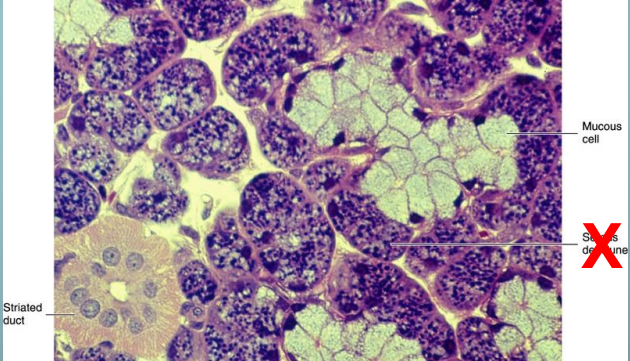
which gland is this
submandibular gland
the sublingual salivary gland is predominantly a mucous or serous salivary gland
predominantly mucous
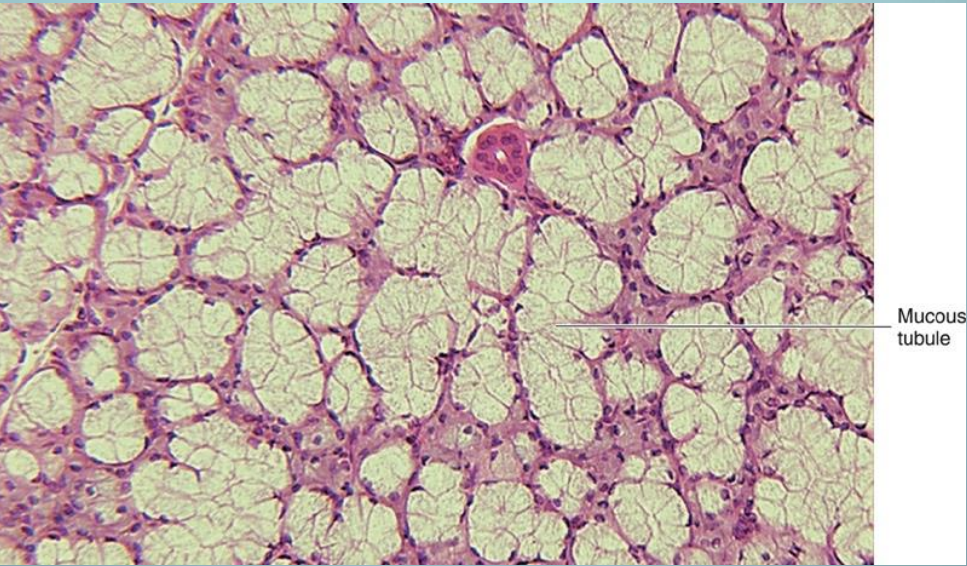
which gland is this
sublingual gland
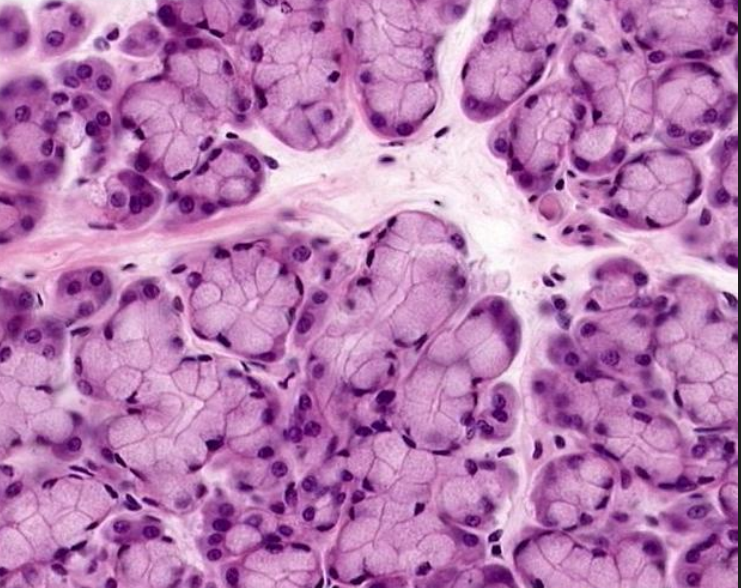
which gland is this
sublingual gland
what are the three minor salivary glands
mucous
serous
mixed
what are the mucous salivary glands
palatine glands
posterior lingual glands
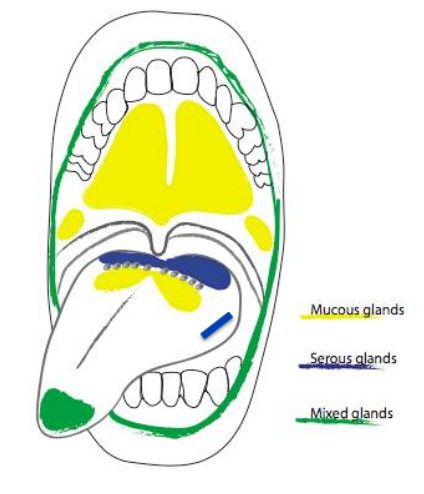
what are the serous salivary glands
glands of von ebner
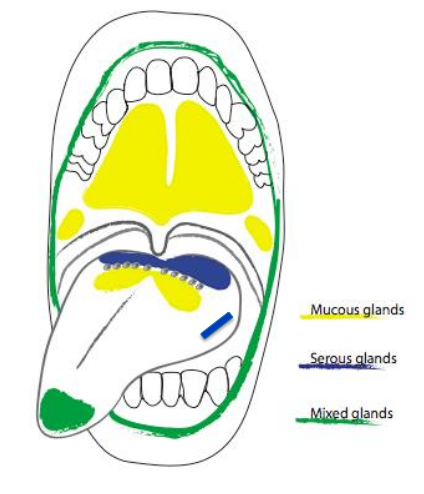
what are the mixed salivary glands
anterior lingual glands
buccal glands
labial glands
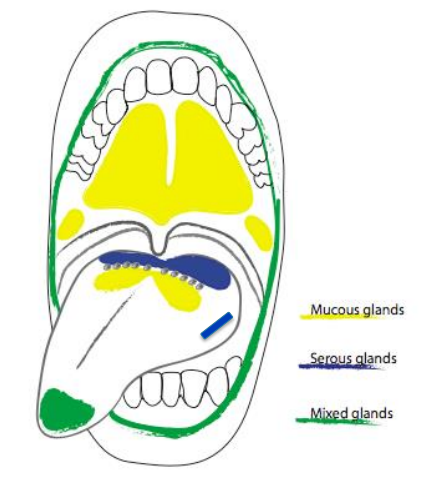
there are __________ (#) minor salivary glands in the oral cavity
600-1,000
what and where is the new salivary gland that scientist have discovered
tubarial glands → located near the tus tubarius, superior to the eustachian tube
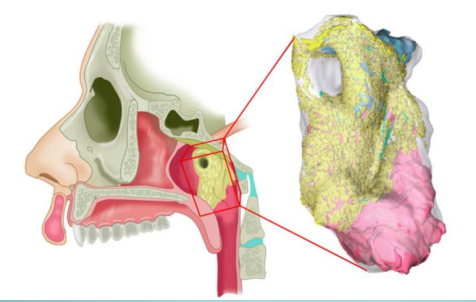
is the tubarial gland a minor or major salivary gland
minor, even though its size is huge
funx of the tubarial glands
assists in swallowing
is the tubarial salivary gland primarily mucous or serous
primarily mucous glands w minor serous output
the tubarial salivary gland is quite large, so what makes it a minor gland
the location in the submucosa, the diffuse nature of the glandular tissue, and the lack of a capsule
which glands are predominant in mucous secretions
minor salivary glands: 10% of salivary excretion but 70% of the mucous secretion
characteristics of minor salivary glands
have shorter excretory ducts
have poorly developed intercalated and striated ducts
are NOT surrounded by a connective tissue capsule
where are glands of von ebner located
posterolingual in the tongue
where do the secretions from the glands of von ebner go
are released in areas w significant # of taste buds → near the troughs and clefts of circumvallate and foliate papillae
do the glands of von ebner secrete serous or mucous saliva
serous fluid w digestive enzymes and other proteins
funx of the secretions from the glands of von ebner
to assist in the perception of taste
glands of von ebner can be associated w what other glands
webers glands, also posterolingual in the tongue
what does webers glands secrete in comparison to glands of von ebner
webers: mucous glands
VE: serous
what are the 6 steps of salivary gland development
bud formation
cord growth
branching of cords
lobule formation
canalization of cords
cytodifferentiation
what is hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
the abnormal development of structures including the skin, hair, nails, teeth and sweat glands; 63% have reduced salivation
what is the only other location that would support development of salivary glands from oral ectoderm
mesenchyme from urogenital ridge
does epithelium or mesenchyme dictate the morphogenic structure
mesenchyme
does epithelium or mesenchyme dictate the product that is secreted from the gland
epithelium
what are the four important signaling pathways and growth factors for salivary gland development
ectodysplasin A (EDA)
sonic hedgehog
FGF→ Fgf8/Fgf10
EGF
what is EDA
important in BUD FORMATION, branching morphogenesis, and histodifferentiation
in mice, what would happen if there was a mutation in EDA
lack minor salivary glands
what is sonic hedgehog
epithelial cell proliferation, survival and differentiation
important in embryonic submandibular salivary gland growth and branching morphogenesis
what would happen if there was no sonic hedgehog
fail to progress beyond “early pseudoglandular stage”
what is FGF
stimulates secretion of collagen- cleft formation
lobule formation
capsule formation for major glands
important for branching to occur → elongation
what is EGF
stimulates epithelial proliferation and differentiation
what two way can lead to hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
deficient EDA being made by mesenchymal cells
deficient receptors being made by epithelial cells
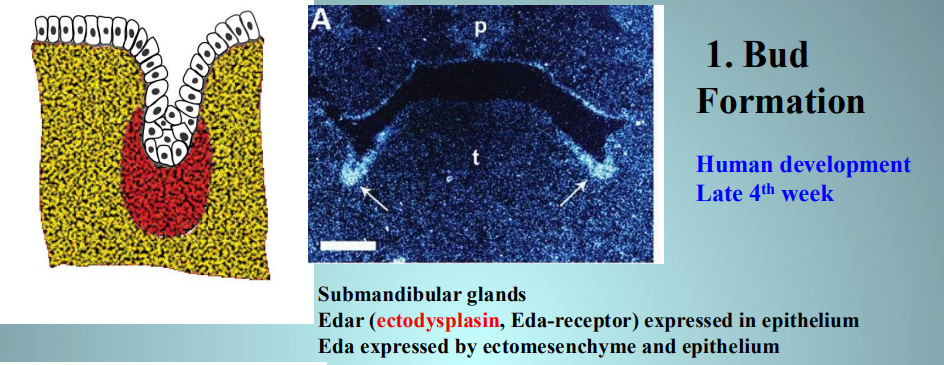
what week of development is bud formation happening
late week 4
what is happening in bud formation
submandibular glands
EDAr expressed in epithelium
EDA expressed by ectomesenchyme and epithelium
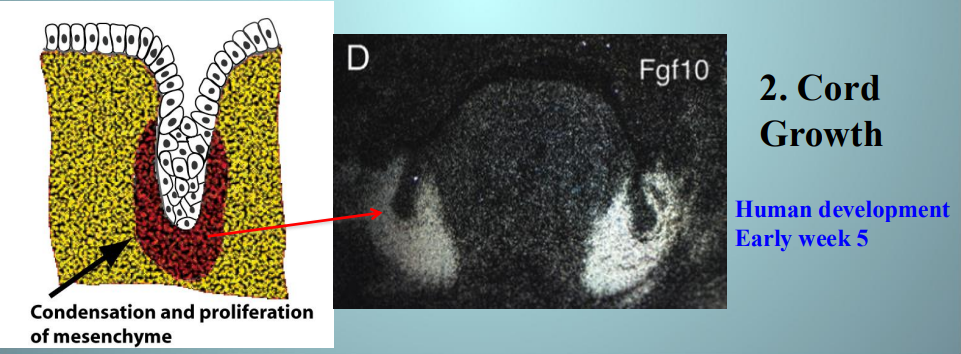
what week of development is cord growth happening
early week 5
what is happening in cord growth
bud growing into ECM bc of FGF from ECM
origin of parotid gland epithelial cells
ectodermal origin
origin of submandibular and sublingual gland epithelial cells
endodermal origin
what is happening during branching of cords in salivary gland development
clefts develop in the bud forming 2/or more buds
growth factors Shh and TGFb from mesenchyme result in clefts from changes in epithelial cell shape
why is the ECM important for cleft formation during the branching of cords stage of salivary gland development
ECM has fibronectin and collagen III (reticular fibers) → non-muscle myosin
what is happening during lobule formation of salivary gland development
repeated branching and budding along major branches of the cord stimulated by FGF and EGF
E-cadherin → acinar formation
why is E-cadherin important in acinar formation
will hold the structure of the clefts in place as these will eventually become serous or mucous cells
_______________ is a requirement in branching morphogenesis
fibronectin
what components are important for branching and lobule formation to occur: (5)
collagen III→ cleft formation
fibronectin → cleft formation
collagen IV→ branching, acinar morphogenesis
proteoglycans→ branching
laminins→ basement membrane assembly