Heat
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
SI unit of temperature
K
What is temperature?
Measurement of how hot an object is
What is the measuring instrument?
Thermometer, thermocouple
Why cant we use our hands to measure temperature?
Inaccurate
when pouring a liquid of different temperature into another liquid, what affects the temperature?
Volume of water
Temperature of water
How is temperature affected by pressure
Higher pressure = higher boiling point
lower pressure = lower boiling point
Why do we need to install expansion gaps on floor tiles, railway tracks, bridges (rollers) etc?
To provide space for the track to expand without damage (crack) on hot days.
What do expansion joints do in concrete bridge?
Expansion joints provide space for expansion and contraction during hot and cold weather conditions to prevent the bridge from damaging
How does climate change affect the sea level? As a result what happens?
Oceans absorb more heat
Water expands, polar ice caps and glaciers melt, thus sea level rises
As a result, more coastal land washed away
How do solids expand? (particles)
When a substance is heated, their particles gain kinetic energy and vibrate more vigourously about their fixed positions due to the increase in kinetic energy. The distance between the particles increases. This causes the volume of substances to increase as a result the substance expands
How do solids contract? (particles)
When the substance loses heat, the particles lose kinetic energy, vibrate less vigorously about their fixed positions and the distance between particles decreases. This causes the volume to decrease and the substance contracts.
How do liquids expand?
When it is heated, its particles gain energy and move much faster gaining kinetic energy. The distance between the particles increases this causes the volume of the substance to increase as a result the substance expands
How do liquids contract?
When the substance loses energy, the particles move slower and the distance between the particles decreases, this causes the volume to decrease and the substance contracts.
Metal pipes what?
expand and contract depending on the surrounding temperature and the substances they carry like steam or hot water, oil and gases, have bends which enables the pipes to expand or contract safely without breaking.
How do gases expand
When a gas gains heat, their particles gain kinetic energy and zoom past each other much faster. The distance between the particles increases, this causes the volume of the substance to increase as a result the substance expands
How does gases contract
When the substance loses energy, the particles move less slowly and the distance between particles decrease. This causes the volume to decrease and the substance contracts
What happens to particles during contraction and expansion?
Number of particles remains the same so the mass remains the same
The size of the particles does not change
Upon heating the particles does not change
Upon heating the particles gain heat energy and vibrate more vigorously. The distance between the particles increases as a result the substance expands and the volume increases
Upon cooling the particles lose heat energy and vibrates less vigorously about their fixed positions. The distance between the particles decreases as a result the substances contracts and the volume decreases.
Rate of expansion of matter from fastest to slowest
Gas
Liquid
Solid
What is weird about water?
Maximum density at 4dc
from 0dc to 4dc, it contracts when heated
from 4dc and above, it expands when heated.
What are the factors that affect heat transfer for conduction?
Rate of conductivity
State of matter
What mechanism does the bimetallic strip and bimetallic thermometers work based on?
Expansion rate
How does it work?
Made up of two metals that expand or contracts at different rates upon the same change in temperature. One mental in the bimetallic strip expands or contracts more than the other. This makes it curve.
e.g. Brass expands more than steel.
Bimetallic strip in thermometer how does it work?
As the temperature changes, the different expansion rates of the metals causes the coil to unwind when the temperature increases and it tightens when the temperature decreases. Thus the pointer moves over the scale.
How does a hot air balloon work?
When air is heated, it volume increases while its mass stays constant, hence the density decreases. Since the air in the balloon is less dense than the surrounding air, it rises and pushes the balloon up.
What are the modes of heat transfer?
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
How is heat transferred?
Net transfer of heat from a hotter region to a colder region,
How does conduction work?
Particles contact to transfer heat
What affects conduction?
Type of material and state of matter
What state of matter conducts heat faster? From descending order
Solids, liquids, gas
Why does solids generally conduct heat better than fluids?
Solid particles are very closely packed and collide more frequently.
Why are metals the best heat conductor
Metals are the best heat conductors as they also have mobile valence electrons to transfer heat through the metal.
Fluids are?
Poor heat conductors
Why does paper over metal burn slower?
Metal is a good conductor of heat, so more heat is transferred to the metal, slowing down the amount of heat the paper has.
How does convection work
Fluid that is heated/cooled will expand/contract, causing density to increase/decrease and resulting in hotter fluid rising/colder fluid sinking to take up the space of the hot/cold air. This sets up convection currents for heat transfer.
When can fluids transfer heat via convection?
If heat source is at the bottom or the cooler is at the top.
How is heat transferred via radiation?
Electromagnetic waves emitted from surroundings, no need for medium
What affects emission and absorption of radiation?
Surface area
Texture
Colour
Elab
Black rough surfaces are good absorbers and emitters of radiation
White shiny smooth surfaces are poor emitters and absorbers of radiation but are good reflectors of radiation
Why should we have air between surfaces?
heat cannot transfer through conduction QUICKLY. This reduces heat transfer to the surroundings.
Why should we have a cover covering a thermoflask?
Cover must be poor conductor of heat
Prevent convection with the surroundings - reduces heat loss to the surroundings
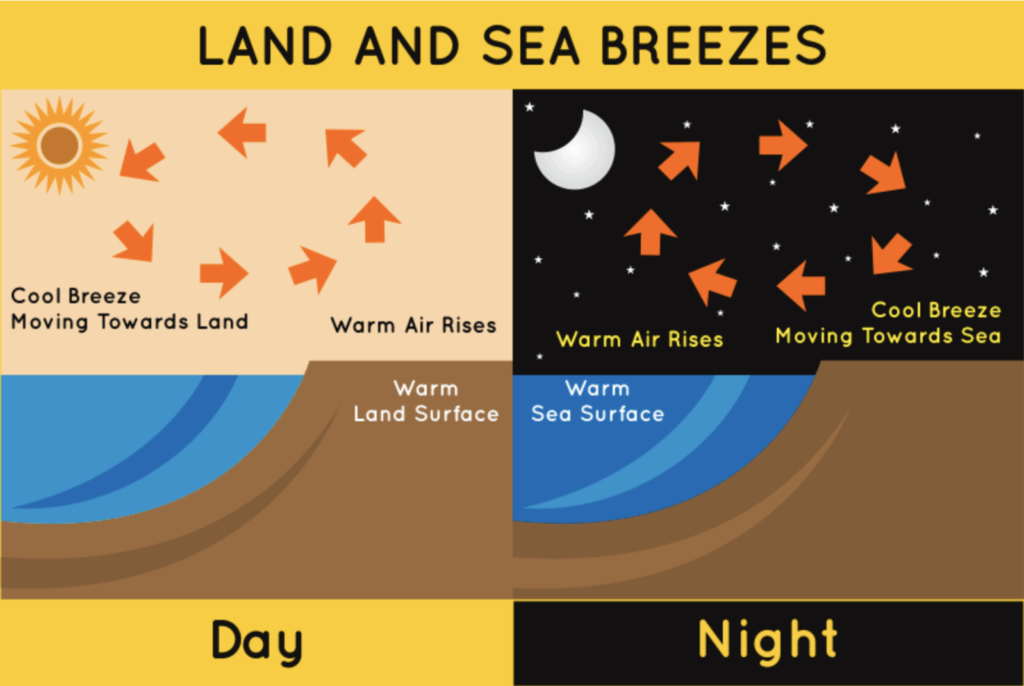
Movement of land and sea breezes
What doesnt occur and occurs in vacuums?
Not in vacuum
Conduction
Convection
Vacuum
Radiation
Air spaces in objects are?
Poor conductors of heat - this prevents quick heat loss via conduction.
small beaker containing a coloured liquid was placed into a large beaker containing water at room temperature. The other was placed in a beaker at 80 dc. The smaller beakers are covered with aluminium foil secured with a rubber band and a small hole is made. How will the water move in the beaker filled with room temperature water?
Diffusion
Movement:
The coloured liquid will escape from the hole in the aluminium foil covering the small beaker and spreads out
How about the water at 80dc?
Convection
Movement:
Coloured liquid escapes the hole in the aluminium foil covering the beaker, and moves upwards in a stream before spreading out, with a little liquid spreading out near the hole.
where is the heat source in order for radiation to occur?
- Radiation occurs in all directions.
- If the heat source is near/beside the object, then there is only radiation.
- If the heat source is touching the object, then there is conduction.
- If the heat source is below the object, there is convection and radiation.
- If the heat source is above the object, there is only radiation.