Weather and Climate of the Tropics
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about Weather and Climate of the Tropics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Annual mean top of atmosphere solar radiation
The average amount of solar radiation received at the top of the Earth's atmosphere annually.
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Climate
average over 30 years
Baede et al., 2018
weather
determined by the vertical structure of the atmosphere
constant changing of the atmosphere around us
Baede et al.,2018
Tropical band
A concentrated band of incoming solar radiation located in the tropical region.
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Hadley circulation
Circulation pattern in the tropics where warm air is efficiently mixed.
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Specific humidity
Measures the amount of water vapor in air for every kg of air
near the surface - specific humidity is high near the equator, but low over major deserts
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Latent heat of condensation
Energy released when water vapor condenses into liquid water.
abundance of water vapour in the tropics
water vapour - source of latent heat - drives thunderstorms
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Conditional Instability
Condition where air is stable until lifted to a certain point, after which it becomes unstable.
likely to occur in warm, moist air masses
Henderson and Robinson, 1999
Convectively Available Potential Energy (CAPE)
Amount of potential energy available for convection
the more convective available potential energy the more thunderstorms
Henderson and Robinson, 1999
Thunderstorms
crucial to how we view the functioning of the atmosphere
tropical convection pumps heat and moisture away from the surface to mid upper troposphere
Henderson and Robinson, 1999
Tropical convection
They transport heat and moisture away from surface to mid-upper troposphere
Henderson and Robinson, 1999
Local minima in solar radiation
Minimum levels of solar radiation reaching the surface coincide with tropical thunderstorm hotspots
Henderson and Robinson, 1999
Hadley circulation
Model of the tropics and subtropics near the equator with a high level of heating
explanation:
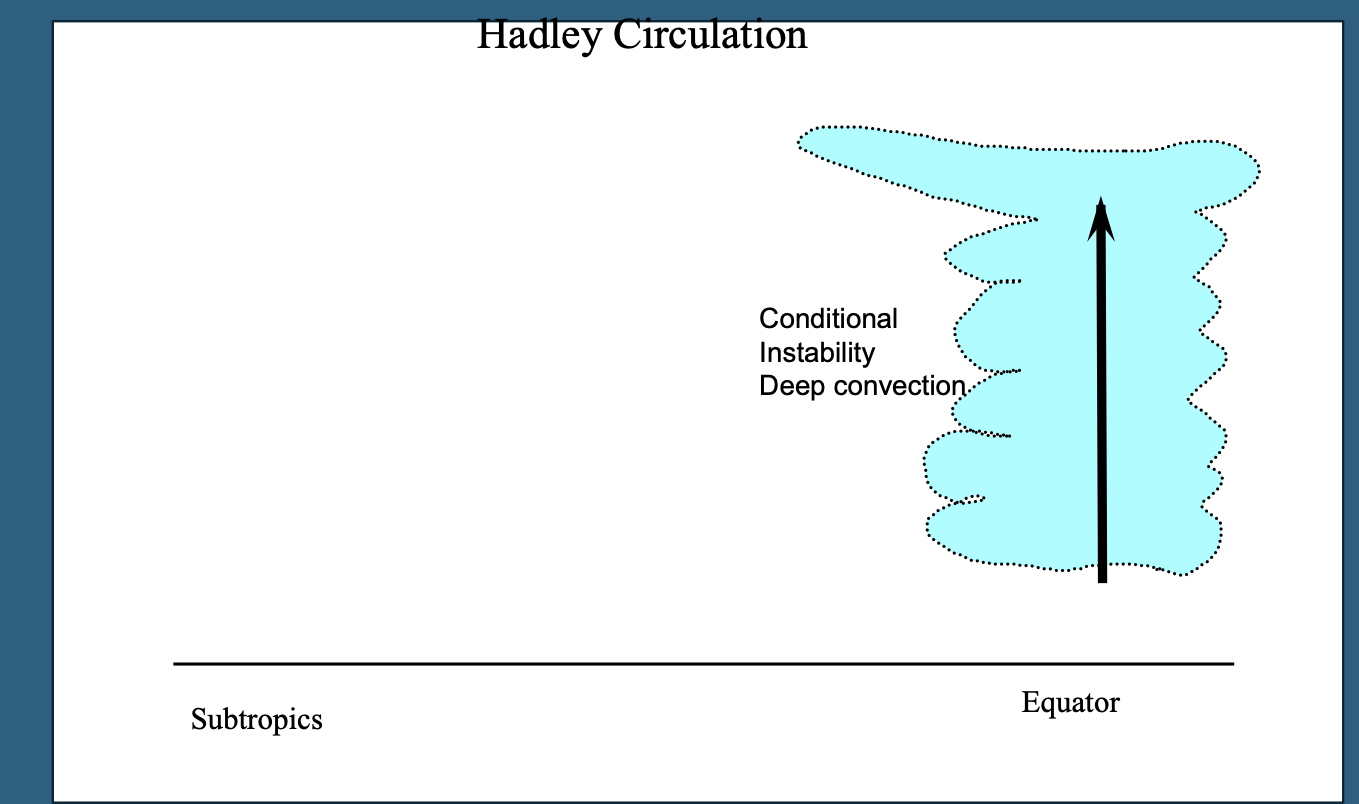
at equator have high surface heating - positive net radiation budget
heating fuels evaporating water vapour
warm moist air = more cape
= more thunderstorms
Continued
updrafts of air here
can reach up to 30m/s - fast
Continued …
explanation:
creates a low pressure system near surface
trade winds travel easterly
E —> W
feeds equatorial trough with more water vapour
more water vapour = more instability
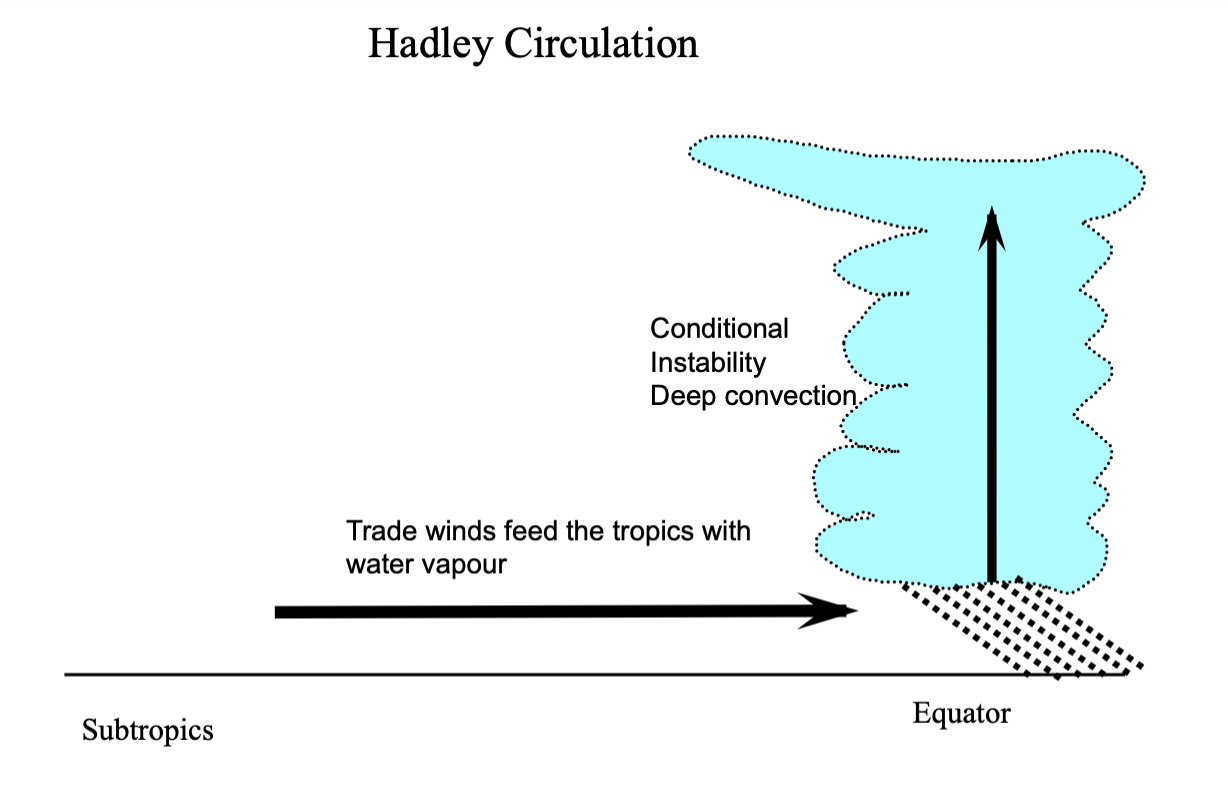
Continued…
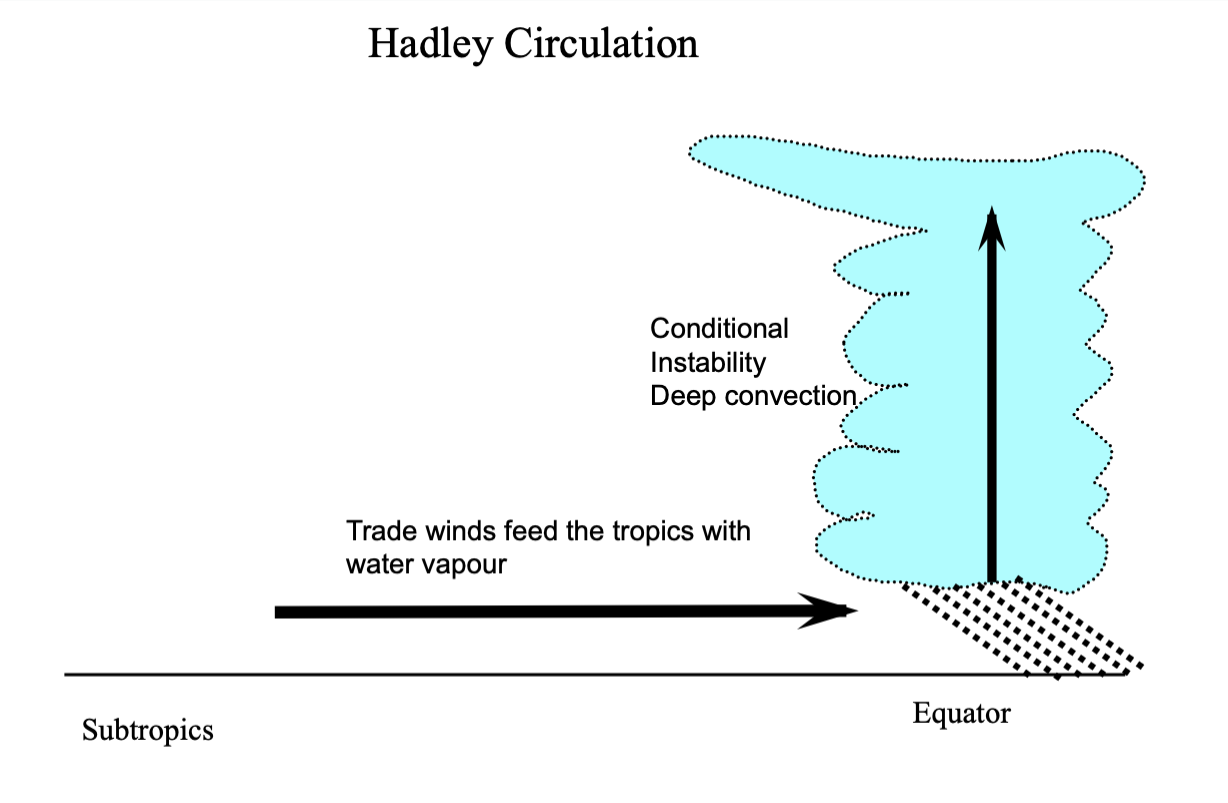
Continued…
Explanation:
top of atmosphere - stable lid
stratosphere - temperatures increase with height
air flowing out of thunderstorms meet stratosphere - get field of clouds as they spread out
air goes poleward - until it gets affected by Coriolis effect
after this is subsides through the depth of the atmosphere
sinking air creates subtropical anticyclones
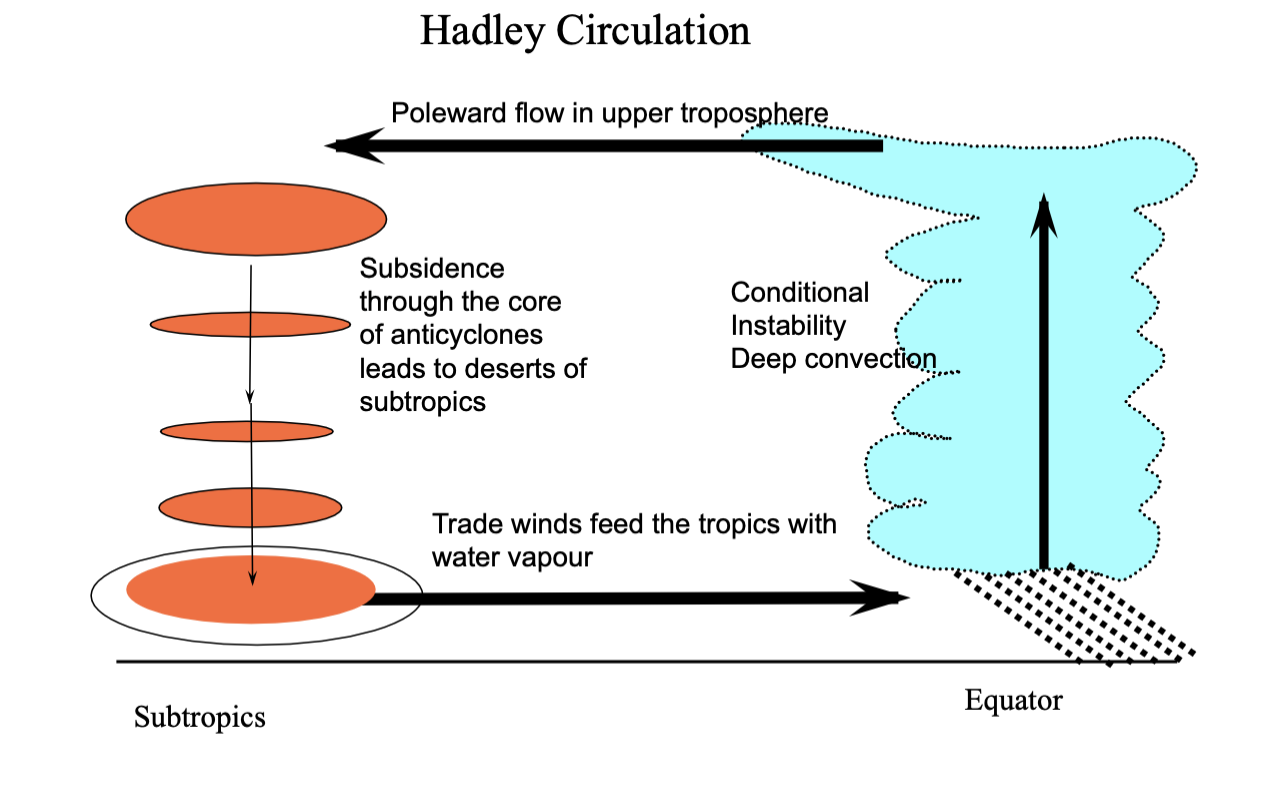
Energy sources associated with Hadley circulation
potential energy - something higher up = more potential energy
sensible heat - stuff you can feel
net radiation - driver of system

Hadley circulation again
convective updraft - water vapour that gets delivered to equatorial trough - condensing
condenation - gives energy for parcels to rise during thunderstorms
rising air = potential energy - you get long wave emission
latent heat by condensation is warming atmosphere
poleward upper branch - potential energy is high - get long wave emission
subtropics - air is sinking
potential energy is being converted by adiabatic compression
Barry and Chorley, 1998
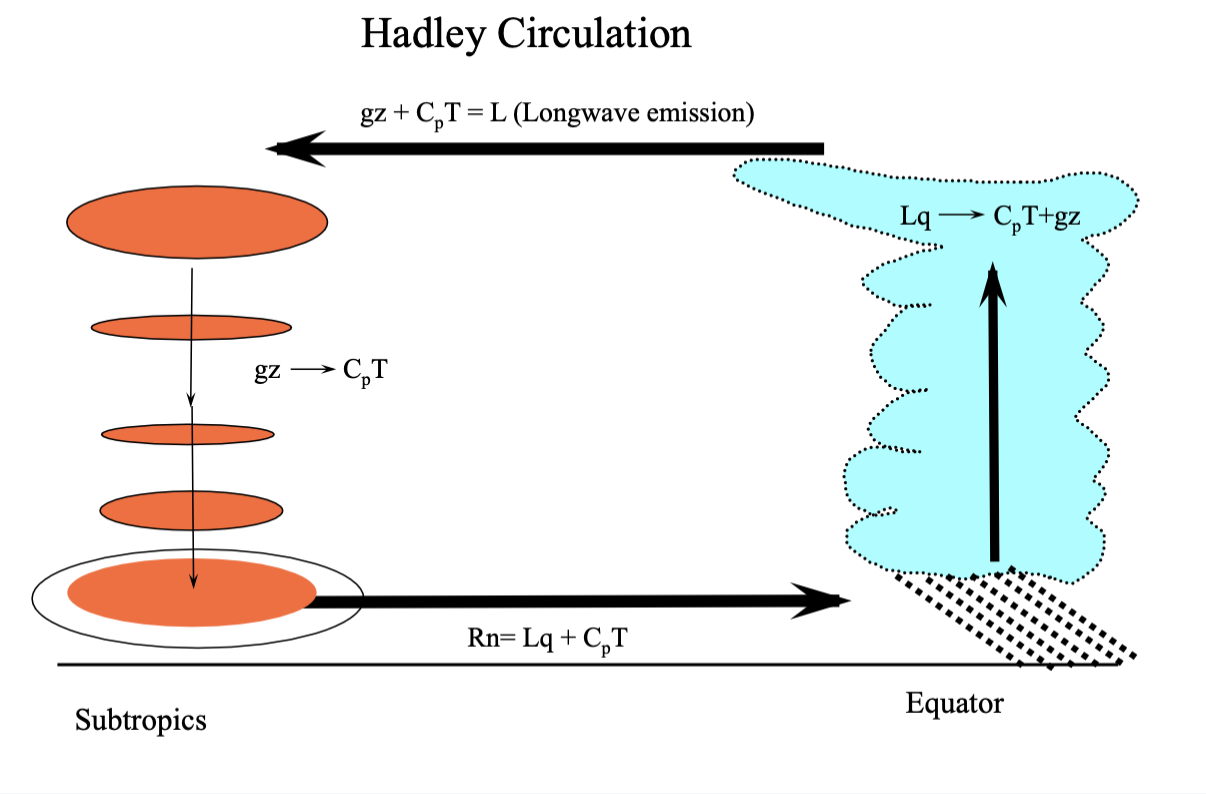
Warming
Adiabatic compression is the warming of air
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Energy transport by Hadley circulation
energy transferred poleward in the tropics
different set up to midlatitudes
Barry and Chorley, 1998
more on energy transport
transient eddies in midlattitdes transfer latent + sensible heat poleward
this latent energy is moved polewards
poleward transport of potential energy sets gradients on which transient eddies feed
Hadley - they are moved equator ward
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Subtropical highs
Located on the eastern sides of ocean basins
eastern side of ocean basins are colder than western sides
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Deserts
Located on the western sides of several continents
western side of continents are drier than eastern sides
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Tropical cyclones
Derive energy from high heat content and warm sea-surface temperatures
most damage from tropical cyclones occur close to the coast
do not form within 5 degrees latitude of the equator
heat source is warm sea surface temperatures
Barry and Chorley, 1998
Future change in the tropics
more rainfall in ascending belt of air
subtropics will get dryer and tropics will get wetter
Garstang and Fitzjarrald, 1999