Bop Exam 3
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
E. All of the above choices are correct.
The energy and ability to move water through the body of the plant comes from the
___________________.
A. Evaporation of water (i.e., transpiration) of water from the leaves of the plant
B. Sun and wind
C. Cohesive and adhesive properties of water
D. Hydrogen bonding of water molecules
E. All of the above choices are correct.
D. Choices A, B, and C are all correct.
Sugar in the phloem moves from source to sink in a plant by means of _________.
A. Bulk flow.
B. Sugar being uploaded into the phloem across cell membranes from the source (e.g., leaf) through
active transport.
C. The movement of water into the phloem via osmosis.
D. Choices A, B, and C are all correct.
A. The gametophytic generation
A recurrent theme in the life cycle of plants is a phenomenon called Alternation of Generations. In terrestrial plants, such as gymnosperms (e.g., conifers) and angiosperms (i.e., flowering plants), which generation is most likely to be the more short-lived generation?
A. The gametophytic generation
B. The sporophytic generation
C. Alternation of generations does not apply to terrestrial or land plants; hence the question is
irrelevant.
D. The sporophytic and gametophytic generations are equivalent; neither can be considered short-lived.
E. None of the above choices are correct.
D. corolla
The collective term for all the petals of a flower is _________________.
A. androecium
B. gynoecium
C. calyx
D. corolla
E. receptacle
B. perfect and incomplete
Grasses and cereal grains produce flowers containing both stamens and carpels. These flowers lack sepals and petals. Each flower on such a plant would be considered ______.
A. perfect and complete
B. perfect and incomplete
C. imperfect and complete
D. imperfect and incomplete
E. sterile
D. inferior
When the calyx, corolla, and stamens of a flower are attached to the receptacle in a position above the ovary, the ovary of the pistil or carpel is said to be ___________.
A. superior
B. inflated
C. mediocre
D. inferior
E. average
A. meiosis; mitosis
In flowering plants, the process of _____________ is integrated into the formation of spores (sporogenesis) that develop into the male or female gametophyte, whereas the production of gametes (gametogenesis) is associated the nuclear division known as ________.
A. meiosis; mitosis
B. mitosis; meiosis
C. meiosis; meiosis
D. mitosis; mitosis
E. More than one of the above choices are correct.
E. All of the above are correct
Homologous chromosomes _______________________.
A. are similar in size and length
B. have the same centromere position
C. carry the same kinds of traits or genes
D. have different parental origins
E. All of the above are correct
A. prophase I
In which phase of meiosis does crossing-over occur and chiasmata are seen?
A. prophase I
B. prophase II
C. metaphase I
D. metaphase II
E. anaphase II
C. 128^2 or 1 in 16,384
Based on independent assortment of chromosomes during Metaphase I of meiosis, what is the the probability of two gametes being produced simple cell division (mitosis) by two gametophyte parents that originated from the sporophyte of a pea plant (2N = 14 or 7 pairs of chromosomes) that form the same assortment of chromosomes and these combining after fertilization to form an offspring identical to one of its siblings is at
least __________.
A. 2^2 or 1 in 4
B. 2^7 or 1 in 128
C. 128^2 or 1 in 16,384
D. 7^2 or 1 in 49
E. 49^7 or 1 in 67,822,000,000
E. All the above are correct
In sexually reproducing organisms, novel or new genetic combinations are produced through _____.
A. crossing-over and genetic recombination during meiosis
B. independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
C. the process of fertilization (the fusion of two gametes)
D. sporogenesis
E. All the above are correct
B. diploid (2n)
Through the process of "double fertilization", most flowering plants (approximately 70% of all species - Polygonum type) produce a ________________ zygote and a triploid (3n) endosperm.
A. haploid (1n)
B. diploid (2n)
C. triploid (3n)
D. pentaploid (5n)
E. hexaploid (6n)
E. Drupe
Botanically speaking a fruit, such as a cherry and an olive, with a fleshy exocarp and mesocarp, and a stony hard endocarp surrounding a single seed is a ________________.
A. Berry
B. Pepo
C. Hesperidium
D. Pome
E. Drupe
B. tomato, grape
Which of the following would be classified botanically as “true berries”?
A. apple, pear
B. tomato, grape
C. corn, wheat
D. orange, lime
E. cherry, peach
A. dehiscent
When the pericarp of the fruit is dry and splits open at maturity to release the seeds inside (e.g., legume, follicle, capsule), the fruit is said to be ______________.
A. dehiscent
B. indehiscent
C. fleshy
D. robust
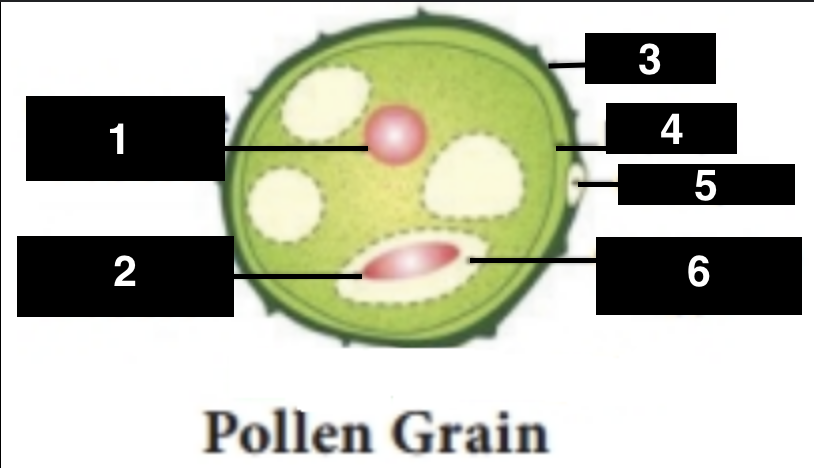
vegetative nucleus
1
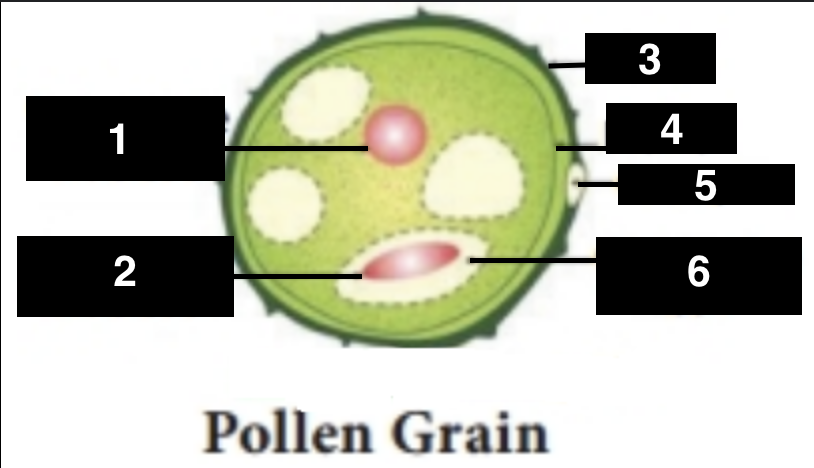
generative nucleus
2
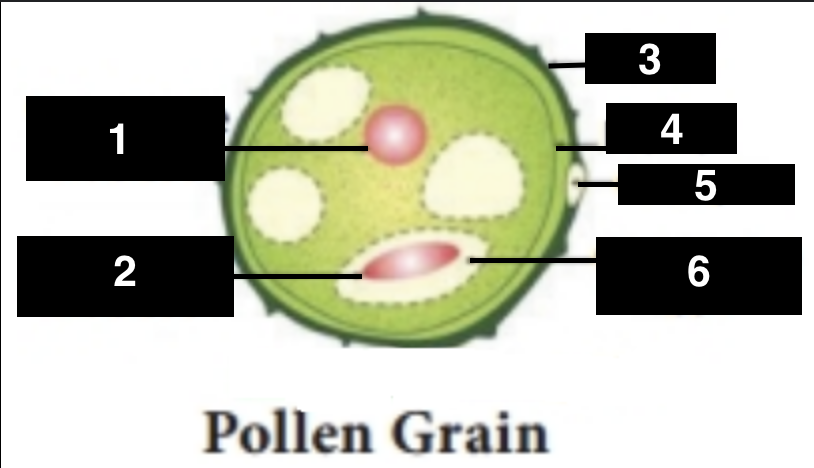
exine
3
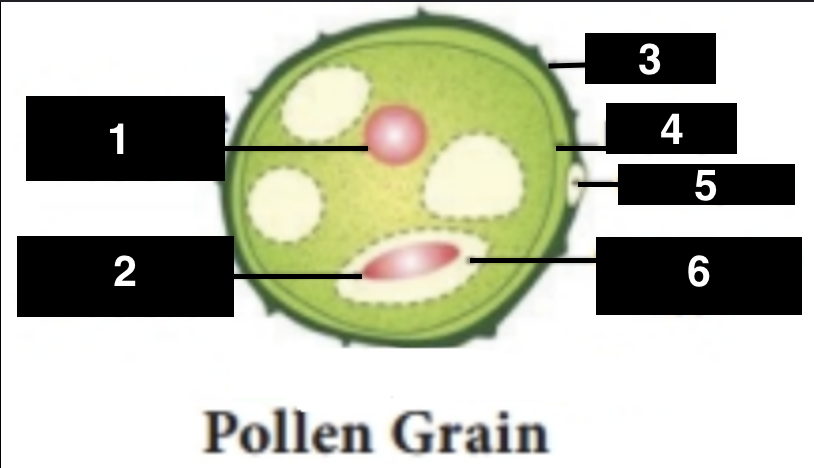
intine
4
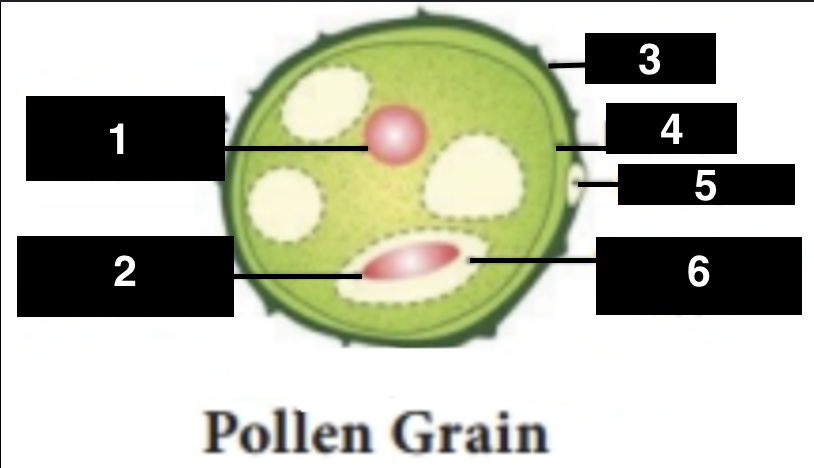
germ pore
5
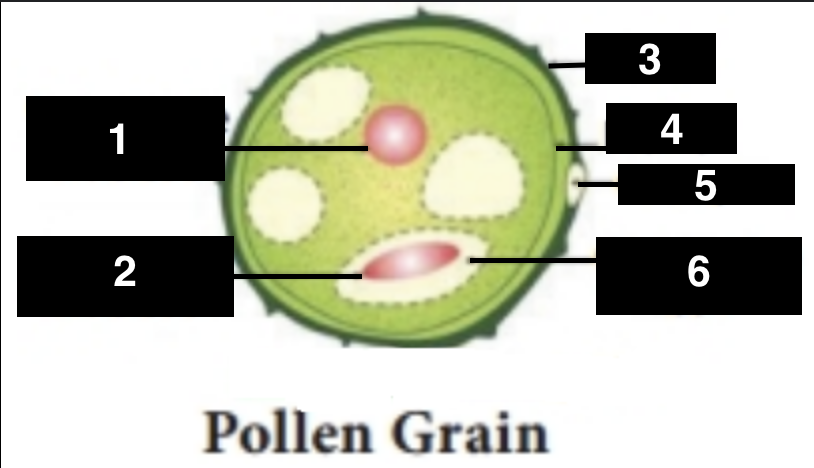
generative cell
6
prophase 1
Homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrads
anaphase 1
Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides
telophase 2 and cytokinesis
Nuclear membrane reforms, cytoplasm divides, 4 daughter cells formed
metaphase 2
Chromosomes line up along equator, not in homologous pairs
prophase 1
Crossing-over occurs
anaphase 2
Chromatids separate
metaphase 1
Homologs line up along equator
telophase 1 and cytokinesis
Cytoplasm divides, 2 daughter cells are formed
Loss of water vapor from plant leaves through stomata.
What is transpiration?
ray cells
What part of the xylem moves the water laterally in the stem?
Sugars move from source to sink via phloem, using pressure differences.
Pressure-Flow Hypothesis (food movement)?
Transpiration-Cohesion Hypothesis (water movement)?
Water pulled upward due to transpiration and cohesion of water molecules.
Leaf-like structures at the base of a leaf stalk.
what’re stipules?
Plant reproduction in angiosperms
Involves flowers, double fertilization, seeds inside fruits.
Alternates between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte
Major features of Alternation of Generations
sporophytic
Dominant generation in flowering plants?
gametophytic
Dominant generation in mosses?
Asteroid caused mass extinction ~65 mya, ending dinosaurs.
What does the Impact Hypothesis say?
Volcanism, climate change, plant shifts (e.g., decline of gymnosperms, rise of angiosperms)
Other extinction hypotheses?
angiosperms rose, gymnosperms declined.
what plant groups involved in extinction hypothesis
Food sources changed—herbivores and predators affected.
Why plant shifts matter to animals?
protect bud
function of sepals
attract pollinators
function of petals
male (produce pollen)
function of stamens
female (make ovules/seeds)
function of carpels
androecium
collective term for stamens
gynoecium
collective term for carpels
corolla
collective term for petals
calyx
collective term for sepals
leaves
flower parts are modified what?
Perfect = both stamens + carpels.
Imperfect = only one.
Perfect vs. imperfect flower?
lily, rose
examples of perfect flowers
corn, cucumber
examples of imperfect flower
A perfect flower contains both male and female reproductive organs, while an imperfect flower has either male or female organs but not both.
Complete vs. incomplete flower?
yes
Can a flower be incomplete and perfect at the same time?
hibiscus
Example of a flower with radial symmetry?
orchid
Example of a flower with irregular/bilateral symmetry?
dioecious
Plants and flowers that represent a specific gender are called...
monoecious
Plants and flowers that contain both male and female parts are called...
ovary is superior (buttercup)
definition of hypogynous
ovary is halfway inferior (cherry)
definition of perigynous
ovary is inferior (apple)
definition of epigynous
radial
symmetry around a central axis (star-shaped)
bilateral
symmetry along one plane
a cluster or group of flowers arranged on a stem.
What is an inflorescence?
the diploid, spore-producing phase of the plant lifecycle.
What is a sporophyte?
A spore is a haploid reproductive cell that can grow into a new organism, while a gamete is a haploid cell (sperm or egg) that fuses during fertilization.
What is the difference between a spore and gamete in a plant?
the haploid phase of a plant that produces gametes.
What is a gametophyte?
Sporophyte: Diploid (2 sets of chromosomes).
Gametophyte: Haploid (1 set of chromosomes).
How many sets of chromosomes do the nuclei of cells in a sporophyte and gametophyte have?
No
Is the plant gametophyte the same thing as a gamete?
the fertilized egg formed from the fusion of a sperm and egg gamete.
What is a zygote?
No
Are pollination and fertilization equivalent terms?
Pollination is the arrival of pollen on the stigma, and fertilization is the union of sperm and egg within the ovule.
What is the difference between pollination and fertilization?
Haploid has one set of chromosomes, diploid has two, and triploid has three sets.
What is the difference between a haploid, diploid, and triploid nucleus?
Interphase, specifically in the S phase.
In which phase of the cell cycle does DNA and protein synthesize to transform unduplicated chromosomes into duplicated chromosomes?
chromosome pairs, one from each parent, that are similar in shape and size.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Synapsis
What is the pairing of homologous pairs during prophase I called?
a pair of homologous chromosomes during prophase I, and crossing-over is the exchange of genetic material between them.
What is a bivalent, and how is this related to crossing-over?
the region where chromatids are joined, and spindle fibers attach during mitosis and meiosis
What is the centromere of a chromosome?
Metacentric, acrocentric, and telocentric.
What are the different positions of the centromere along the chromosome?
Homologous chromosomes separate into different cells, including processes like crossing-over during prophase I.
Describe major events in Meiosis I:
Similar to mitosis, where sister chromatids are separated into daughter cells.
Describe major events in Meiosis II:
Homologous chromosomes pair, and crossing-over occurs, exchanging genetic material.
What happens during Prophase I?
crossing over
What is one way genetic recombination occurs during Prophase I of meiosis?
a haploid spore that develops into a male gametophyte, produced by meiosis.
What is a microspore and how is it produced in angiosperms?
a haploid spore that develops into a female gametophyte, produced by meiosis.
What is a megaspore and how is it produced in angiosperms?
the pollen grain grows a pollen tube, and sperm cells travel to the ovule for fertilization
What happens after pollination in a plant?
Pollen tube, generative nucleus, sperm nuclei, micropyle, embryo sac, egg, and polar nuclei
Parts of the plant involved in pollination and fertilization:
Meiosis occurring in the pollen grain and embryo sac.
Gametogenesis is a result of what?
Generative cell and tube cell.
What types of nuclei or cells are found within a pollen grain?
false
Most types of plants exhibit the phenomenon of double fertilization. Is this True or False?
A zygote (embryo) and a triploid endosperm
What does double fertilization produce in a flowering plant?
the female reproductive organs of a flower that contain the ovary, style, and stigma.
What are carpels?
A simple pistil consists of a single carpel, while a compound pistil has multiple fused carpels.
Difference between simple and compound pistil in an angiosperm?
the entire female reproductive structure (carpels included).
Difference between carpel and pistil?
seeds
What does a ripened fruit of an angiosperm contain when mature?
Exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
Names of three major layers of the pericarp:
Fleshy fruits have soft tissue (e.g., berries), while dry fruits are hard or papery (e.g., nuts).
Difference between fleshy and dry fruit types?