Genetics, Natural Selection and Genetic Modification
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
* The gametes are genetically different from each other
What does haploid mean?
Half set of chromosomes
What does diploid mean?
A full set of chromosomes
Stages of meiosis?
The cell making the gametes has a full set of chromosomes. These chromosomes copy themselves and stay attached to each other
The cell splits in two, with each new cell being haploid
Each cell divides into two again. Each of the four daughter cells have a half set of chromosomes (23 chromosomes)
What does meiosis produce and why?
4 genetically unique daughter cells
During meiosis, tiny changes are made to the chromosomes and they both only need half of the chromosomes because the other half comes from the other parent
When gametes fuse at fertilisation, what is the cell created called?
A zygote
Advantages of asexual reproduction?
Organisms do not have to find a mate making it faster and taking less energy
It exploits ideal conditions as a genetically identic offspring will have the same adaptations as the parent to the environment
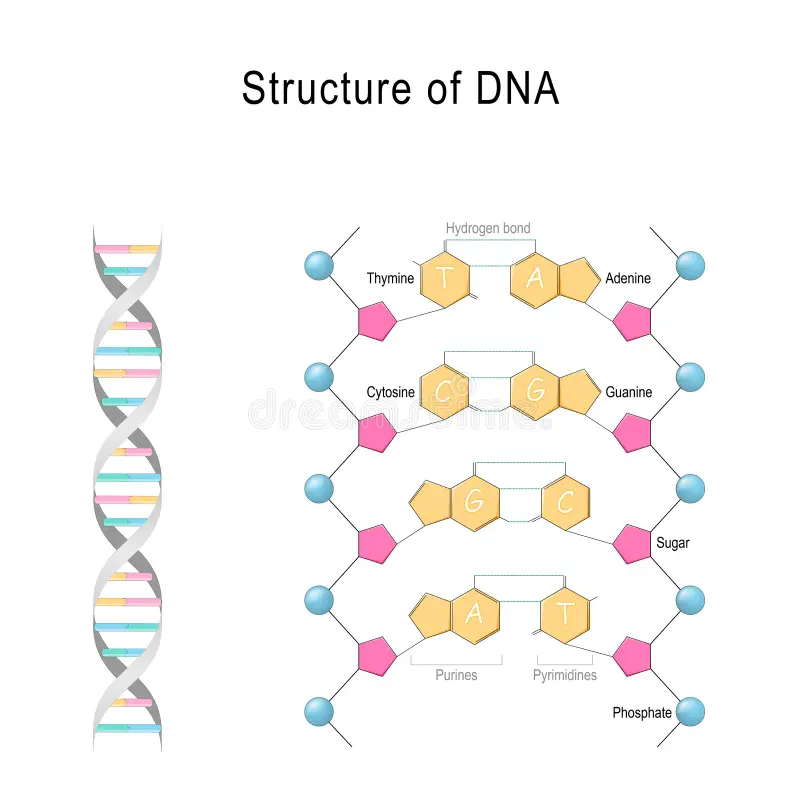
Cytosine-Guanine
How many hydrogen bonds between the base pairs?
Adenine and Thymine- 2
Cytosine and Guanine- 3
* This involves DNA bases being used to make a strand of RNA (ribonucleic acid)
* This takes place in the nucleus
What happens during transcription?
A section of DNA is unwound and the two strands separate
An enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to the non-coding region of DNA
RNA polymerase moves along the template stand and makes a strand of mRNA (messenger RNA) which has complimentary base pairs to the template strand
In mRNA, thymine is replaced with uracil
The RNA polymerase then detaches from the DNA and the mRNA leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores and goes to a ribosome
The two strands of DNA join back together
What is the second stage of protein synthesis and where does it take place?
Translation
The bases are read 3 at a time (a codon) coding for a specific amino acid to produce a protein
This takes place in the cytoplasm at a ribosome
What happens during translation?
The mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome
Amino acids are brought to the ribosome on carrier molecules called tRNA
The ribosomes now read the triplets of bases called a codon on the mRNA and matches them with an anticodon and uses this to join together the correct amino acids in the correct order
Once the polypeptide chain (a string of amino acids) is complete, it folds into a unique shape which creates a certain protein
* Mutations are the reason why genes exist in different forms called alleles
What is Gregor Mendel famous for?
Discovering the fundamental laws of inheritance
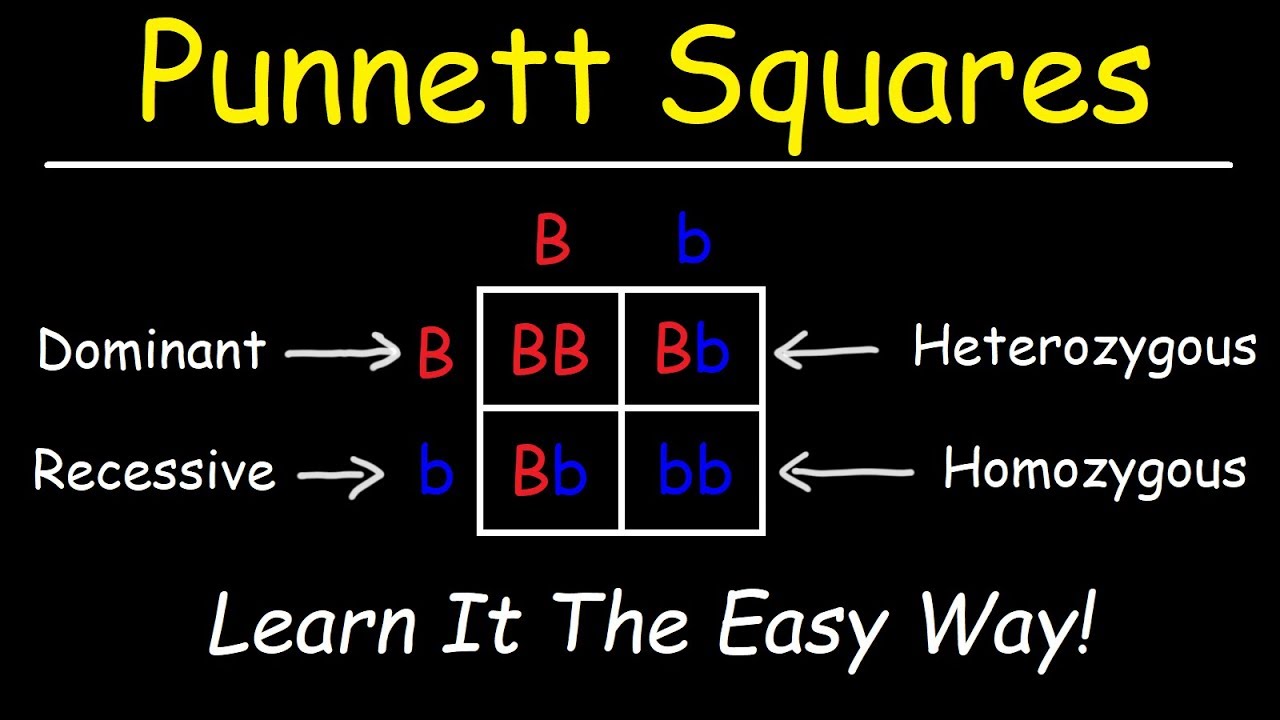
What is a gene?
A small section of DNA that gives instructions for producing a particular characteristic
How do we show dominant alleles and how do they work?
We show it with a capital letter (D for example)
You only need one copy of the allele to express a particular characteristic
How do we show recessive alleles an how do they work?
Written using lowercase letters (d for example)
You need two copies of the recessive allele to express certain characteristics
What is a phenotype?
The characteristic expressed due to the combination of alleles (basically what you see)
Females have two X chromosomes and males receive one X and one Y chromosome. What does this mean?
That boys received a Y chromosome from their father and girls received an X chromosome from their mother and father but not the Y chromosome from their father
* Could be a unit of measurement for example centimetres
* A set name for something for example eye colour- blue, green, brown, black
* An organism has 2 latin words referring to the genus and species
* Example: Homo(genus) and Sapiens(The species)
* Organisms that share the first name are closely related
Evidence of evolution?
Fossils and stone tools found showing how humans gained more intelligence and were able to make more complex tools
What is the organism that many other organisms originate from called?
The common ancestor
What is the binomial system and what is the order?
The section where animals come from they range in specificity:
(Least specific to most specific): Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
* Examples: roses, algae, ferns, trees
* Examples: Humans, dogs, birds, reptiles, fish
* Examples: Moulds, mushrooms
* Examples: amoeba, paramecium
* Examples: Bacteria
What is inbreeding and what can it lead to?
When animals and plants are bred within a small gene pool, which can lead to some breeds being prone to inherited diseases or defects
How does genetic engineering work on a basic level?
Enzymes are used to ‘cut out’ or isolate the required gene,
This gene is inserted into a vector, which is usually a bacterial plasmid
The vector inserts the gene into required cells in the nucleus
The genes are transferred to animal, plant or microorganism cells, during early development. This allows them to develop with the desired characteristics.
* Improve crop yields or crop quality
* Introduce herbicide resistance, which results in less herbicides being used, as weeds are quickly and selectively killed.
* Insect and pest resistance can be developed and inserted into the plants. The plant produces toxins
* Sterile insects could be created such as a mosquito. They would breed, which would lead to infertile offspring. This may help with spread of diseases, such as malaria, dengue fever and the Zika virus.
* Some people believe it is not ethical to interfere with nature in this way. Also, GM crop seeds are often more expensive and so people in developing countries cannot afford them.
* GM crops could be harmful, for example toxins from the crops have been detected in some people’s blood.
* GM crops could cause allergic reactions in people.
* Pollen produced by the plants could be toxic and harm insects that transfer it between plants.
Advantages of fertilisers?
They are quick in providing plant nutrients and restoring soil fertility.
They are portable and easy to transport.
Plants easily absorb fertilizers.
Fertilizers improve and increase the productivity/crop yield of many crops such as wheat, maize, and rice.
Disadvantages of fertilsers?
They get washed away by water easily and cause pollution.
They are expensive.
They provide only short term benefits.
They change the nature of soil, making it either too acidic or too alkaline, reducing soil biodiversity
One natural alternative to fertilisers?
Animal dung
What is a family pedigree?
A diagram showing the inheritance of a genetic condition within a family. It is used to predict the chance that someone will inherit a faulty allele
How is the sex/gender of humans controlled?
By one pair of sex chromosomes
The genotype XX produces a female
The genotype XY produces a male
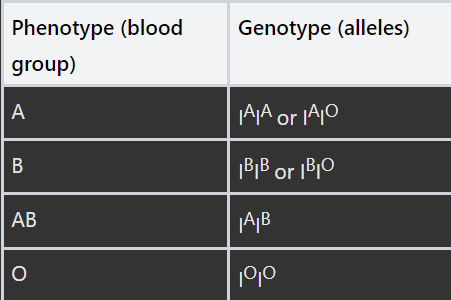
What are the four blood groups and what are their alleles?
Phenotype (blood group) | Genotype (alleles) |
|---|---|
A | IAIA or IAIO |
B | IBIB or IBIO |
AB | IAIB |
O | IOIO |
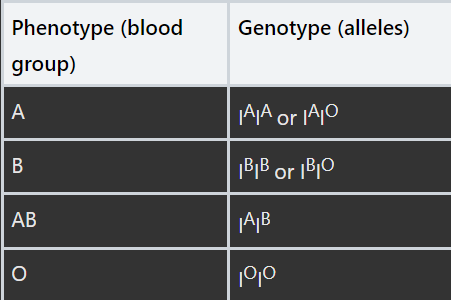
What does this table show us about the dominant and recessive alleles in blood?
See image
I stands for the blood group gene and the letter above the I shows the allele of that gene
IO is recessive to IA and IB because it is not expressed in the heterozygote
IA and IB and codominant. This occurs when the heterozygous individual shows the effect of both alleles that they carry in the gene
What is haemophilia?
A sex-linked genetic disorder where blood doesn’t clot properly
What are the alleles for haemophilia?
XH and Xh
XH is the chromosome that produces normal blood clotting
Xh is the chromosome that produces poor blood clotting
Because boys have a Y chromosome, they can only inherit haemophilia if their mother is a haemophiliac or a carrier for the disease
What are some causes of variation?
The different alleles and organism inherits
Caused by the environment such as riding a bike or scars
Combination of both such as weight and skin colour which are affected by both genetics and the environment
Lifestyle
How do mutations work?
A mutation is created if the sequence of bases in a gene is changed
A mutation in the gene’s coding DNA can affect the phenotype of an organism
If the amino acid sequence is altered, the activity of the protein produced may also be altered
How dangerous can a mutation be?
Some mutations can be harmless or have little effect, but others can significantly affect the phenotype
A mutation may also cause a large change in a protein produced
How can a mutation in the non-coding region of DNA affect proteins produced?
A mutation may increase or decrease the ability of RNA polymerase to bind to DNA
This could increase or decrease the amount of protein produced
What is the human genome project?
A collaboration between scientists to decode the human genome (the order of bases or all human chromosomes)
The results are being used to develop new medicines and treatments for disease
What are the advantages for the human genome project?
Alerting people that they are at risk of a certain disease so they can make lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of the disease developing
Distinguishing between different forms of diseases such as leukaemia or Alzheimer’s disease, as some drugs are beneficial for some but not others
Allowing doctors to tailor treatments for some diseases to the individual, where different alleles effects how someone will respond to treatment
What are the disadvantages of the human genome project?
People at risk of certain diseases may have to pay more to obtain life insurance
It may not be helpful to tell someone they are at risk of a condition that has no cure
How does Darwin’s theory of evolution work?
Adults produce more young than the environment can’t support leading to a ‘struggle for existence’ for the young
Some individuals inherit characteristics that help them survive in the environment while others will be less adapted to the environment
Individuals who have not adapted as well will either die out and will not produce young or they will produce less young than the adapted individuals
Individuals with advantageous characteristics will pass on their genes to the next generation and will be more likely to survive
More individuals in the next generation will have same gene
What two groups can prokaryotes be split into and why?
Eubacteria and archaea
This is because the genes or organisms in archaea work more like eukaryotes while eubacteria work a little differently