AP Microeconomics Vocabulary
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Scarcity
a limited and desired product
Rationing
creation of a system to allocate resources
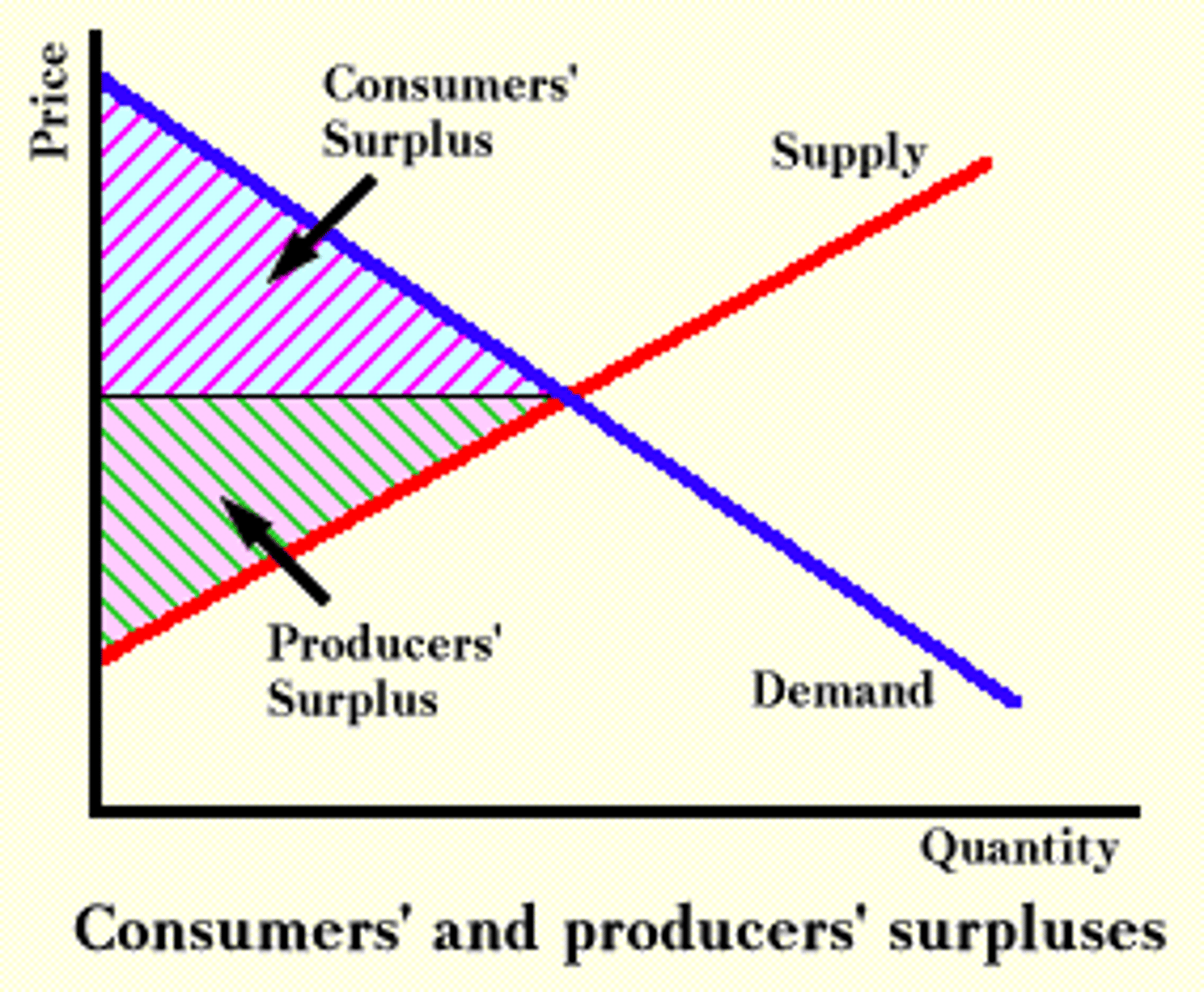
Consumer surplus
the difference between how much you are willing to pay and what you actually pay
The Basic Economic Problem
what to produce, how to produce it, who to produce for
Free goods
things that we desire but that are not limited
Economic goods
things that we desire but that are limited
positive economics
focuses on facts and cause-and-effect relationships, "what is"
normative economics
used for economic policy and incorporates judgment, "what ought to be"
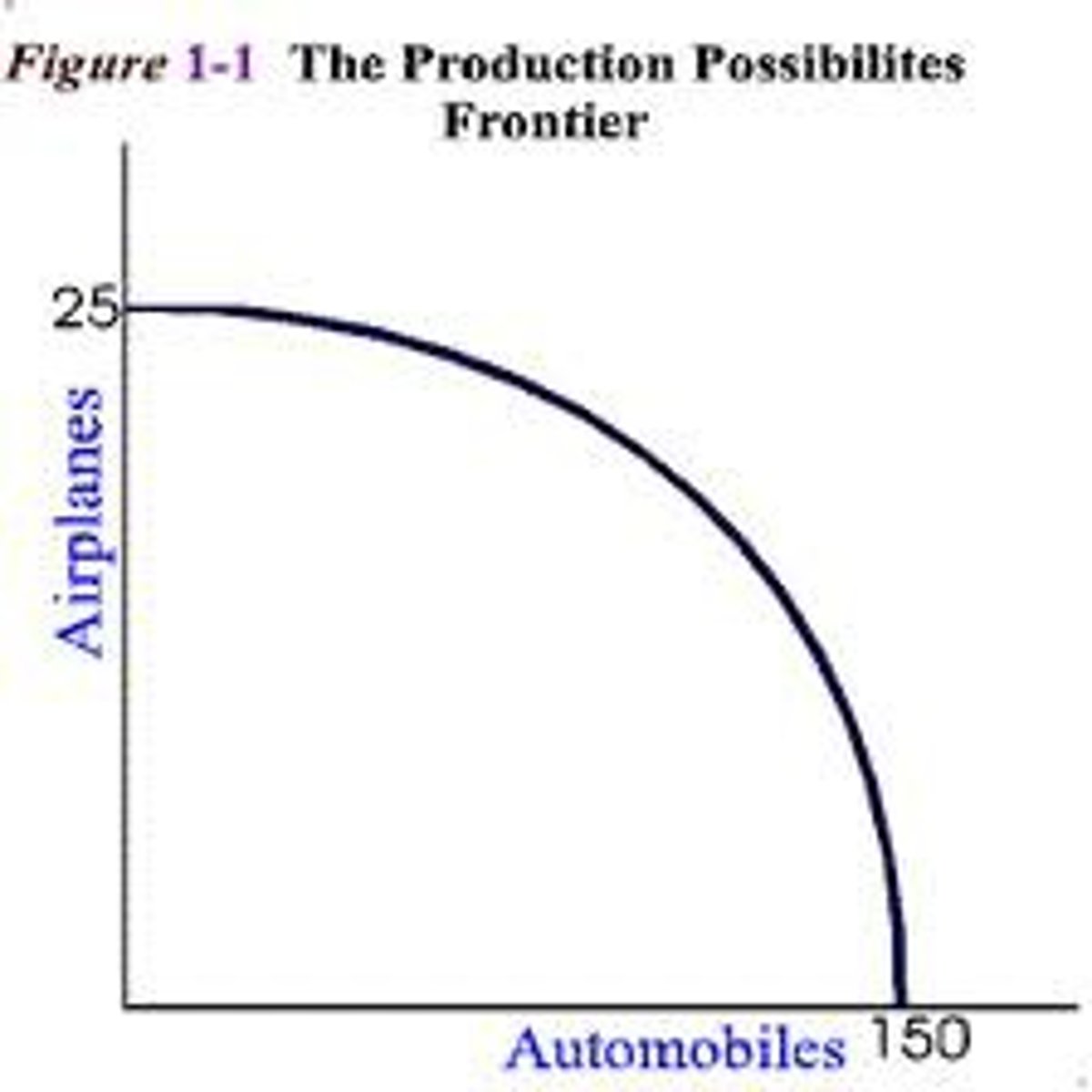
Production Possibilities Curve/Production Possibilities Frontier
illustrates the opportunity cost an economy makes when deciding what to produce and how to allocate resources
Utility
how much use a person gets from the consumption of something
Ceteris Paribus
"all things are the same/remaining equal"
Homo economicus
all people act in rational self-interest
Command Economy
the government answers all economic questions
Capitalism (Market Economy)
based on principles of supply and demand
Mixed Economy
a combination of command economy and market economy where the government answers some questions and the market answers others
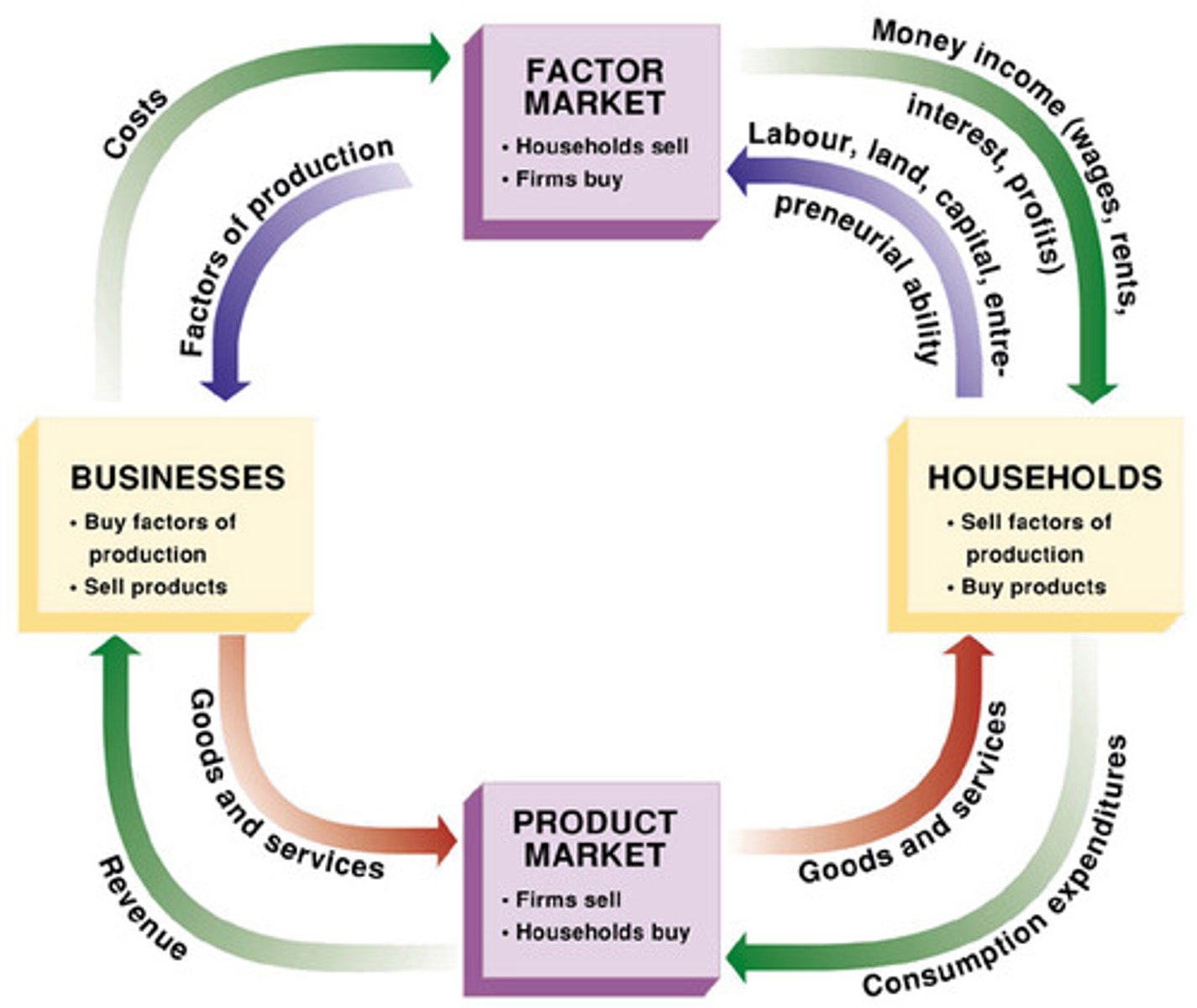
the circular flow model
a theoretical model for a market economy detailing interactions between households, product markets, firms and resource markets
market
a place where goods and services are exchanged for liquid assets or other goods and services
competitive market
large number of firms, homogeneous goods or services, barriers to entry are few
oligopoly
a few interdependent, large firms dictate prices through collusion, whereby they set prices for their own behavior through working together, producing either a standardized or differentiated product in a market with a barrier to entry
monopoly
one firm has almost total control over a market, being the sole producer of a good with no close substitutes in a market with entry barriers
demand
the quantity of a particular good that consumers are willing and able to buy at a range of prices at a particular period in time
market demand
total demand; the sum of all the individual consumers' demands in a market
demand curve
a visual illustration of a demand schedule detailing prices and quantities
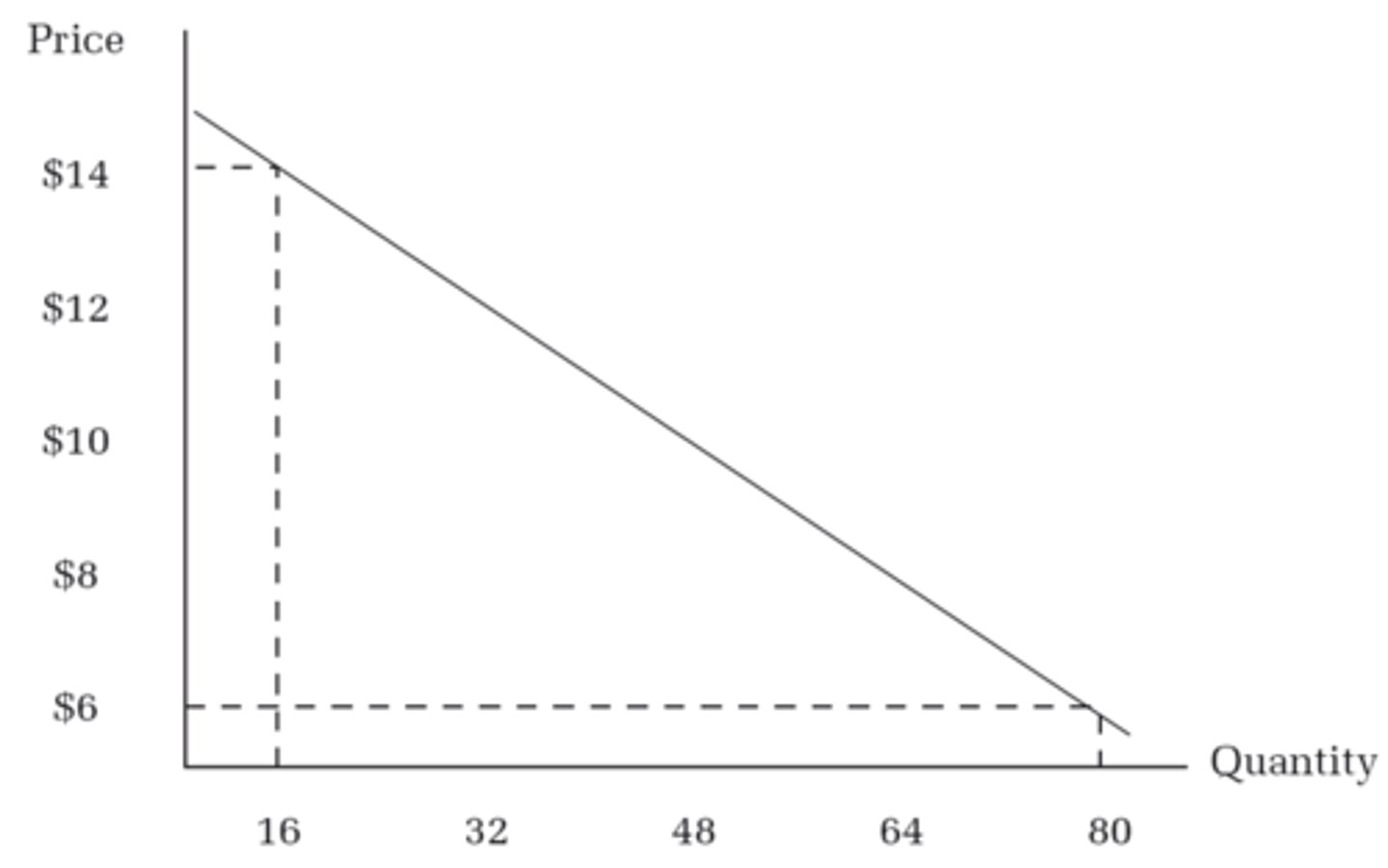
The Law of Demand
ceteris paribus, there is an inverse relationship between a good's prices and the quantity demanded by consumers
The Income Effect
as the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded increases because consumers now have more real income to spend
The Substitution Effect
as the price of a good decreases, consumers switch from other substitute goods because its price is comparatively lower
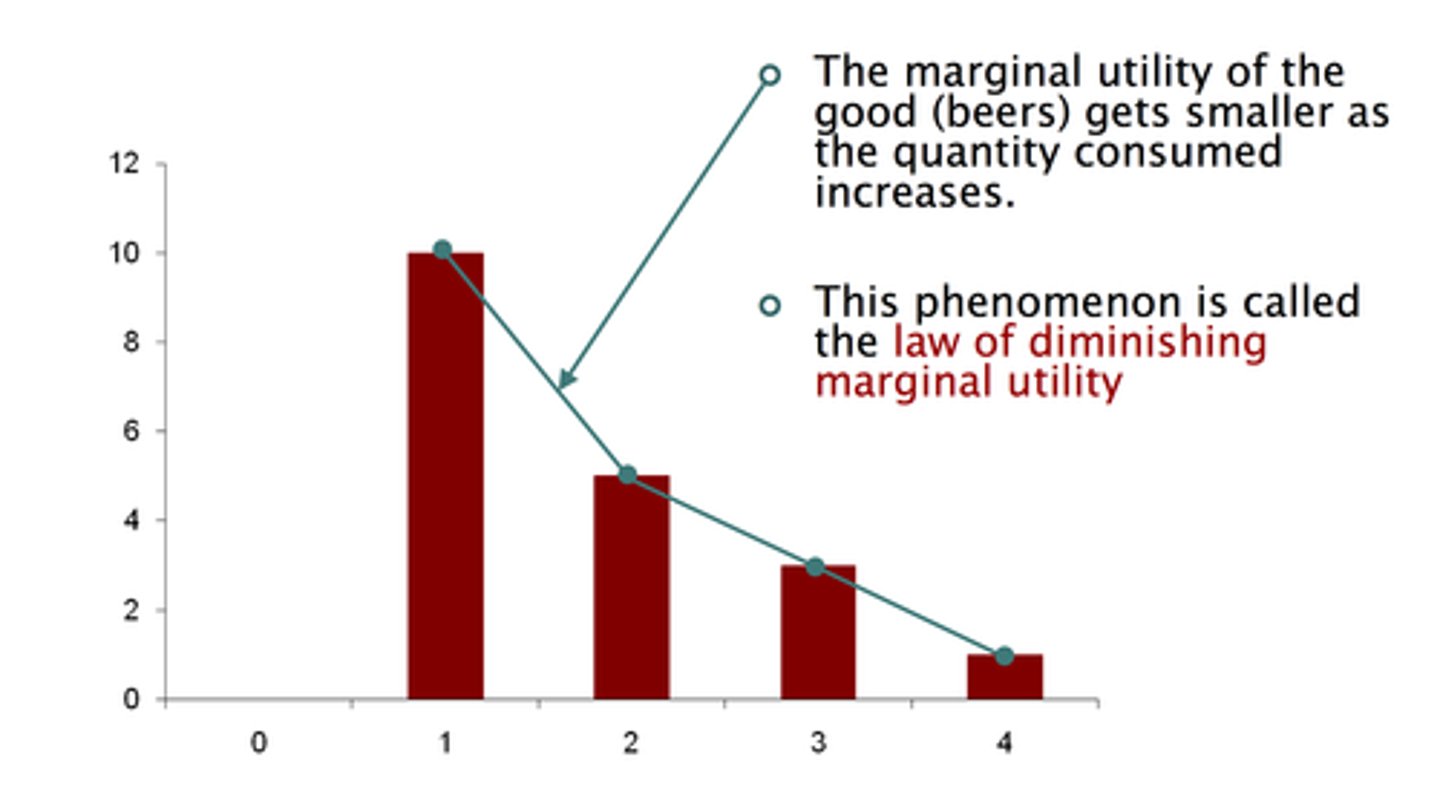
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
as we consume additional units of a good, the utility for each extra unit decreases
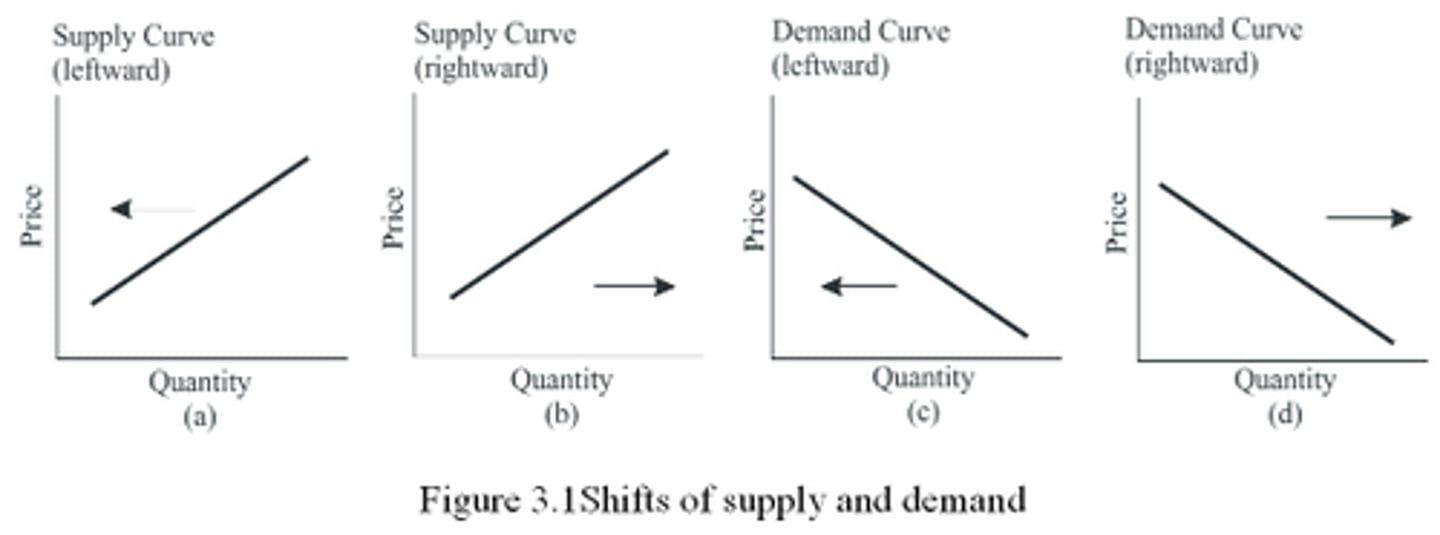
Non-Price Determinants of Demand (TOSISE)
Tastes, Other related goods' prices, Size of the market, Incomes, Special circumstances, Expectations
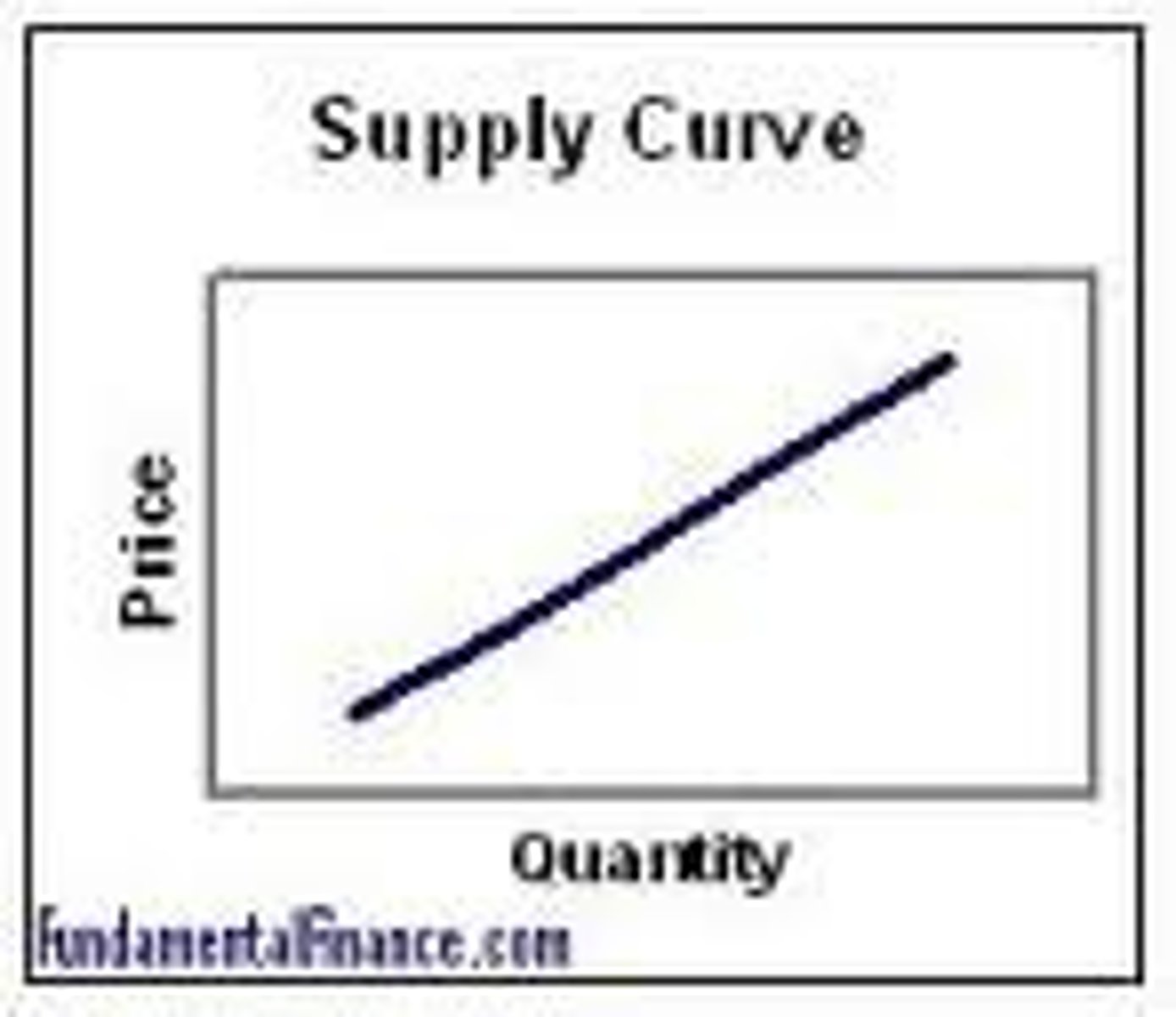
Supply
a schedule or curve showing how much of a product producers will supply at each of a range of possible prices during a specific period of time
Marginal cost
cost per additional unit
The Law of Supply
ceteris paribus, there exists an direct relationship between price of a product and quantity supplied. As the price of a good increases, firms will increase their output of the good and vice versa.
Non-Price Determinants of Supply (STOREN)
Subsidies and taxes, Technology, Other related goods' prices, Resource costs, Expectations of producers, Number of firms
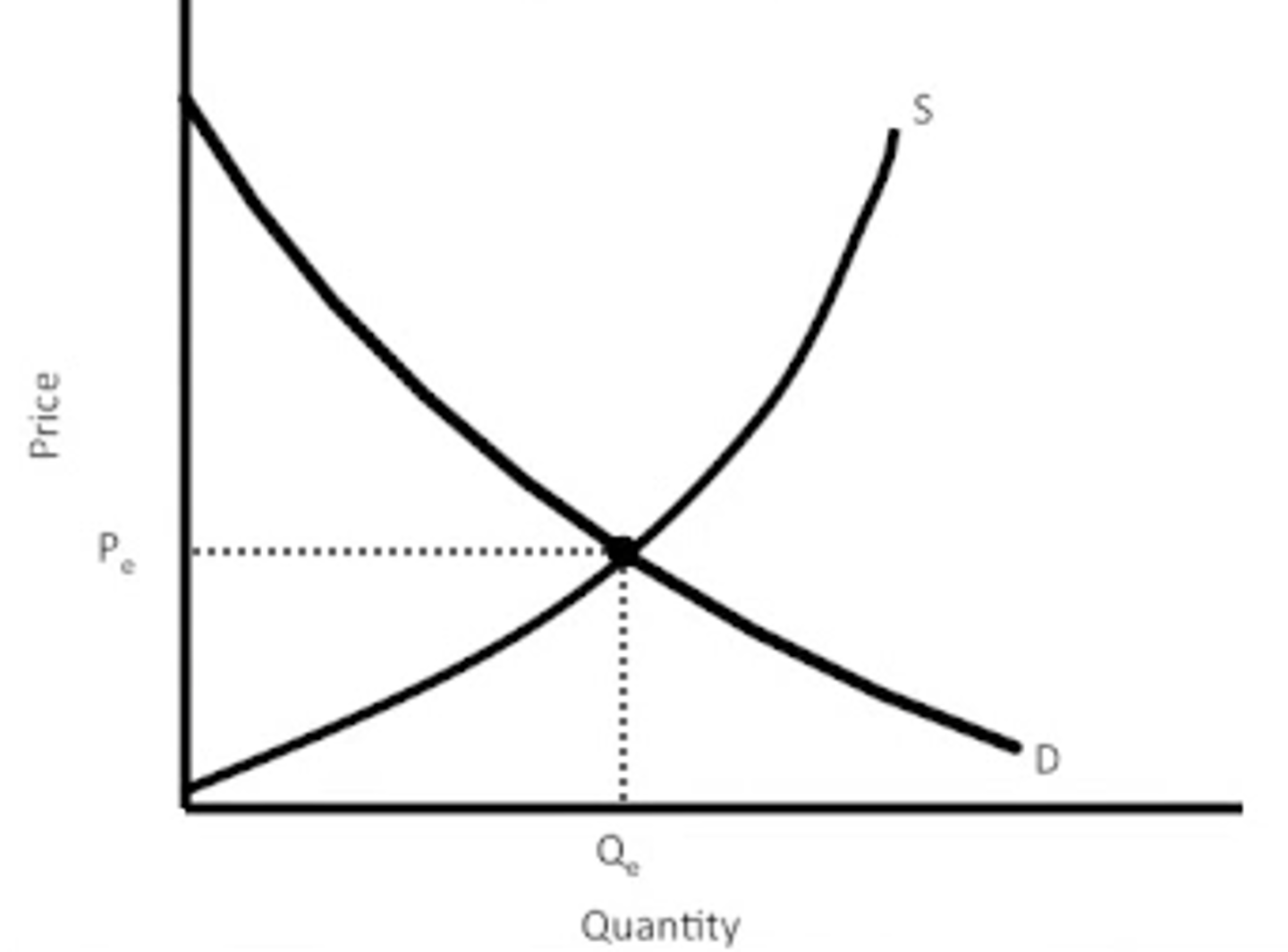
Market equilibrium
when the price and quantity are at a level at which supply equals demand and the market clears
Demand = Marginal Social Benefit (MSB)
the demand for any good represents the benefits that society derives from the consumption of that good
Supply = Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
the supply of a good represents the cost to society of producing that good. The more is produced, the more it costs to produce additional units.
allocative efficiency
is achieved when MSB=MSC
Quantity demanded
price change
Demand change
demand curve shift
Quantity supplied
price change
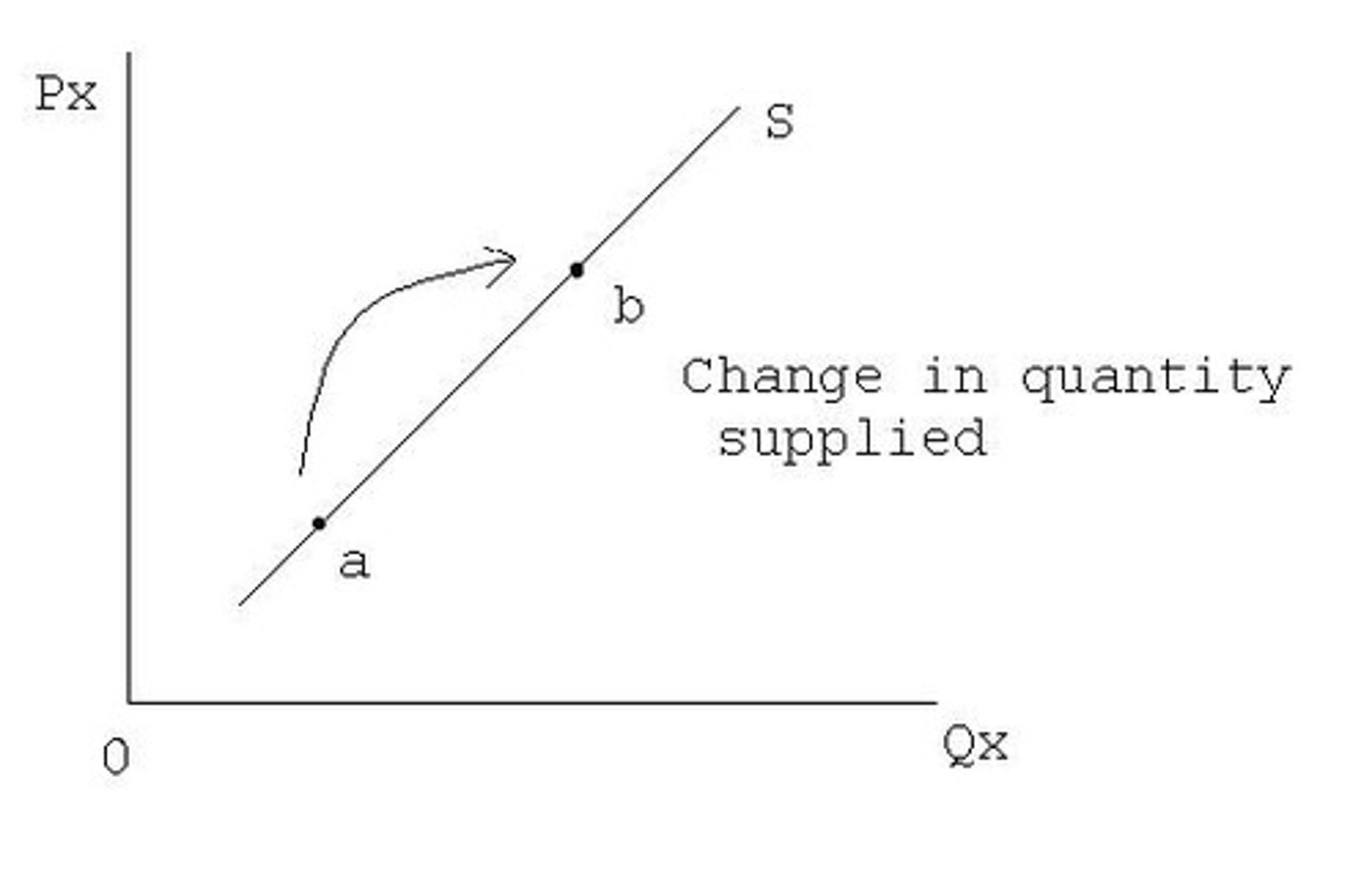
Supply change
curve shift
Producer Surplus
the difference between what you are willing to produce for and what the production cost was
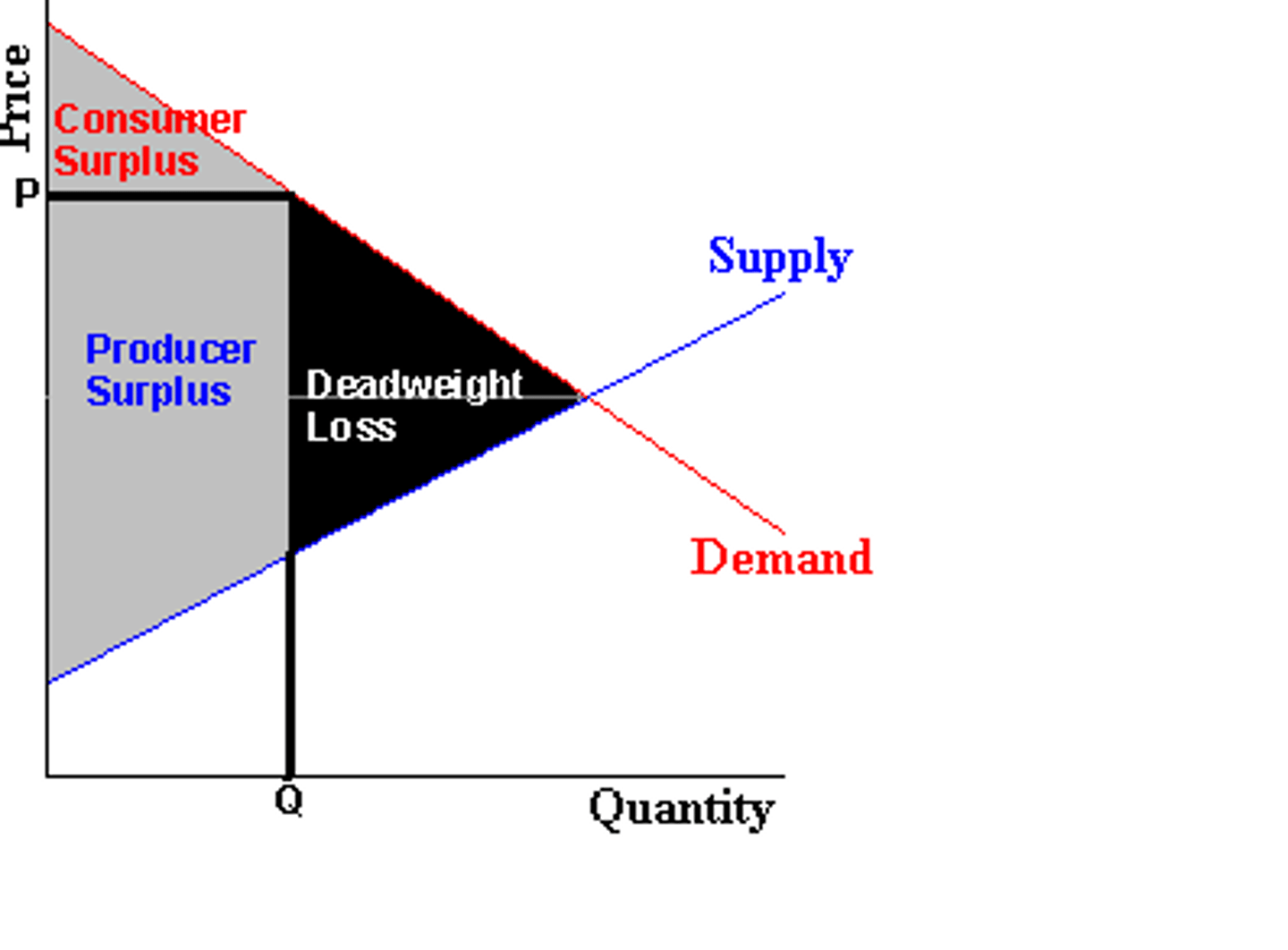
Deadweight loss
when producer surplus does not equal consumer surplus there is a waste
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
measures the responsiveness of consumers of a particular good to a change in price
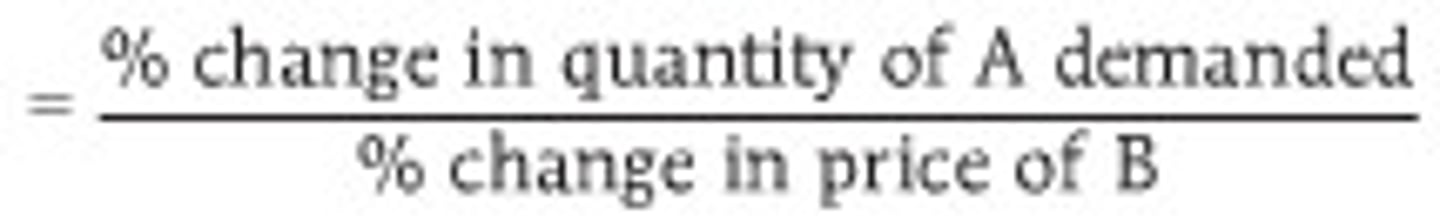
total revenue formula
price received x quantity
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand (XED)
measures the responsiveness of consumers of one good to a change in the price of a related good (either a substitute or a complement)
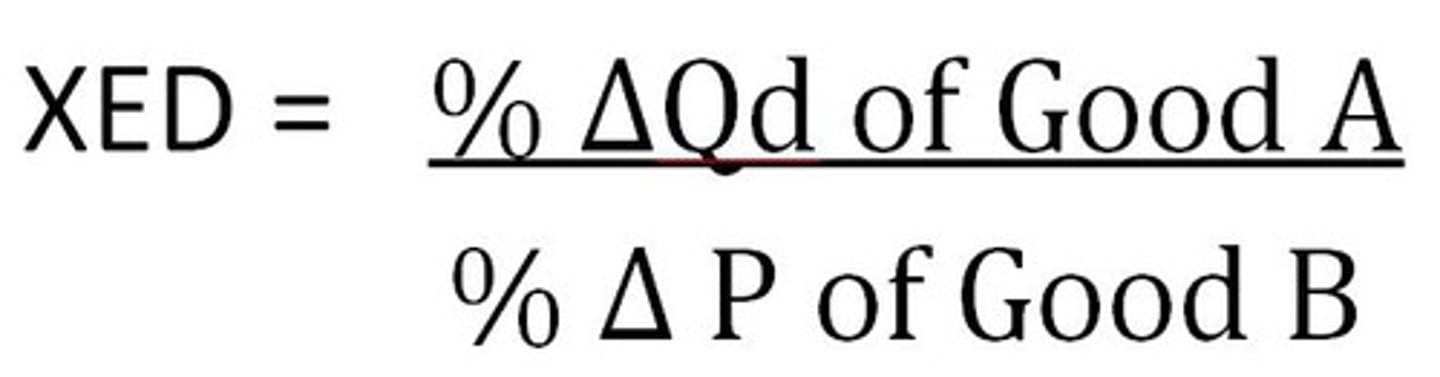
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
measures the responsiveness of consumers of a particular good to a change in their income
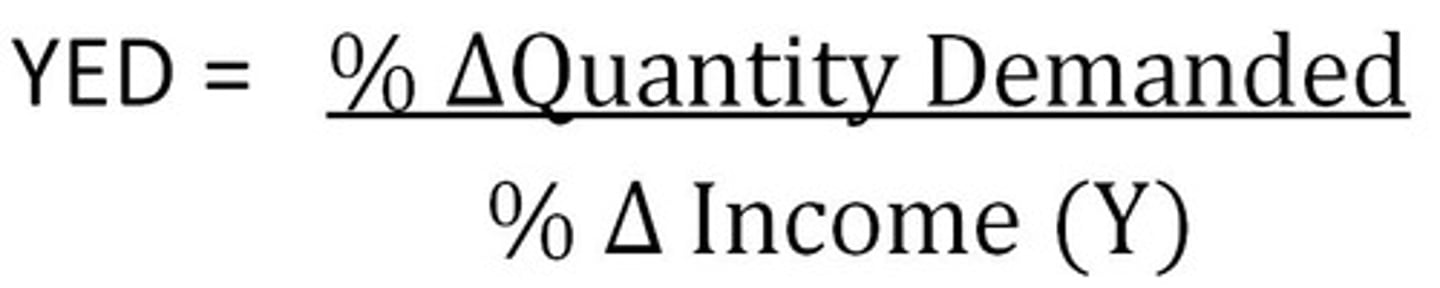
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
measures the responsiveness of producers of a particular good to a change in the price of that good
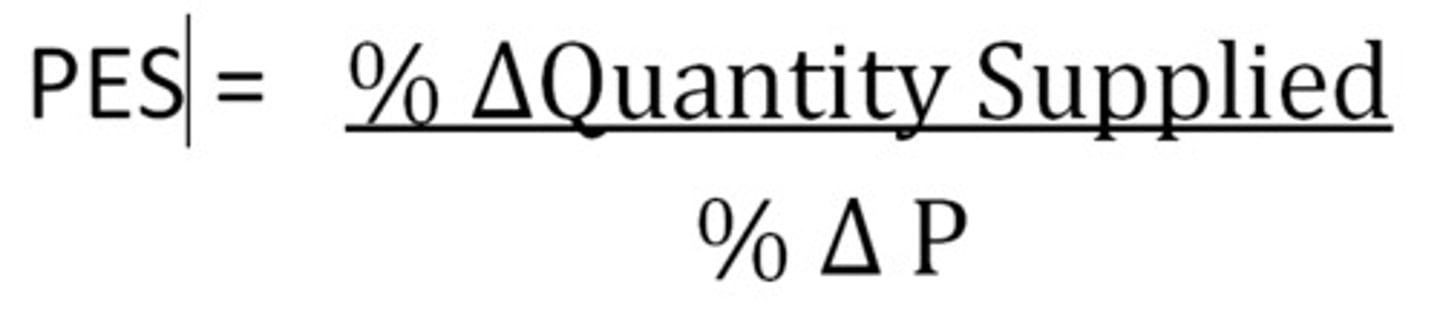
PED formula
percentage change in quantity demanded / percentage change in price
((Q2-Q1)/(Q1))/((P2-P1)/P1))
slope
consistent along the demand and supply curve
tax burden
proportion of tax spending that is paid by producers or consumers; changes based on elasticity
excise tax
tax on specific goods imposed to earn revenue, discourage consumption, redistribute income, and correct externalities
-results in a vertical shift in the supply curve by the amount of the tax
spending/sales tax
tax on all goods
Specific Tax
fixed amount, regardless of price of the product
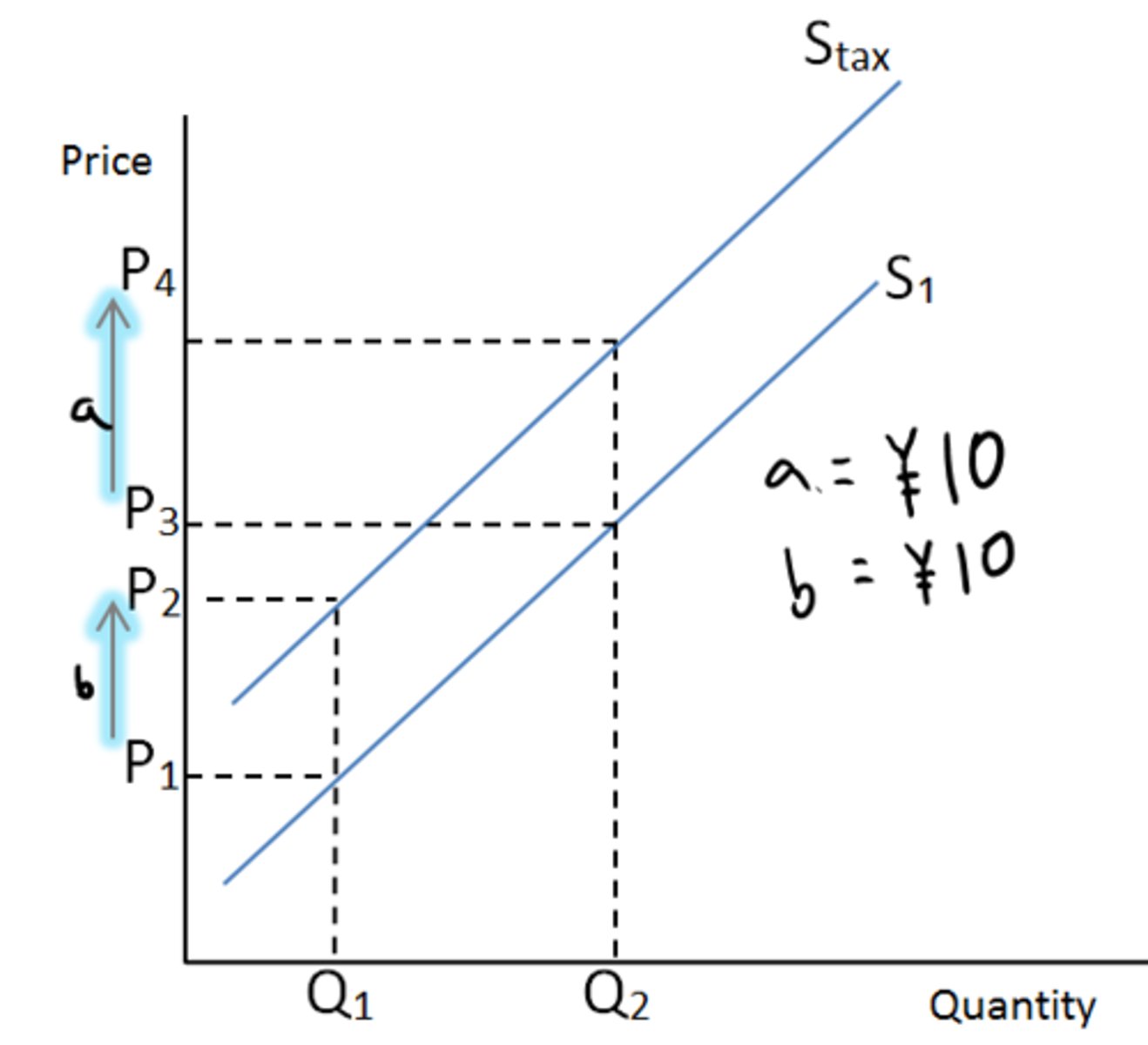
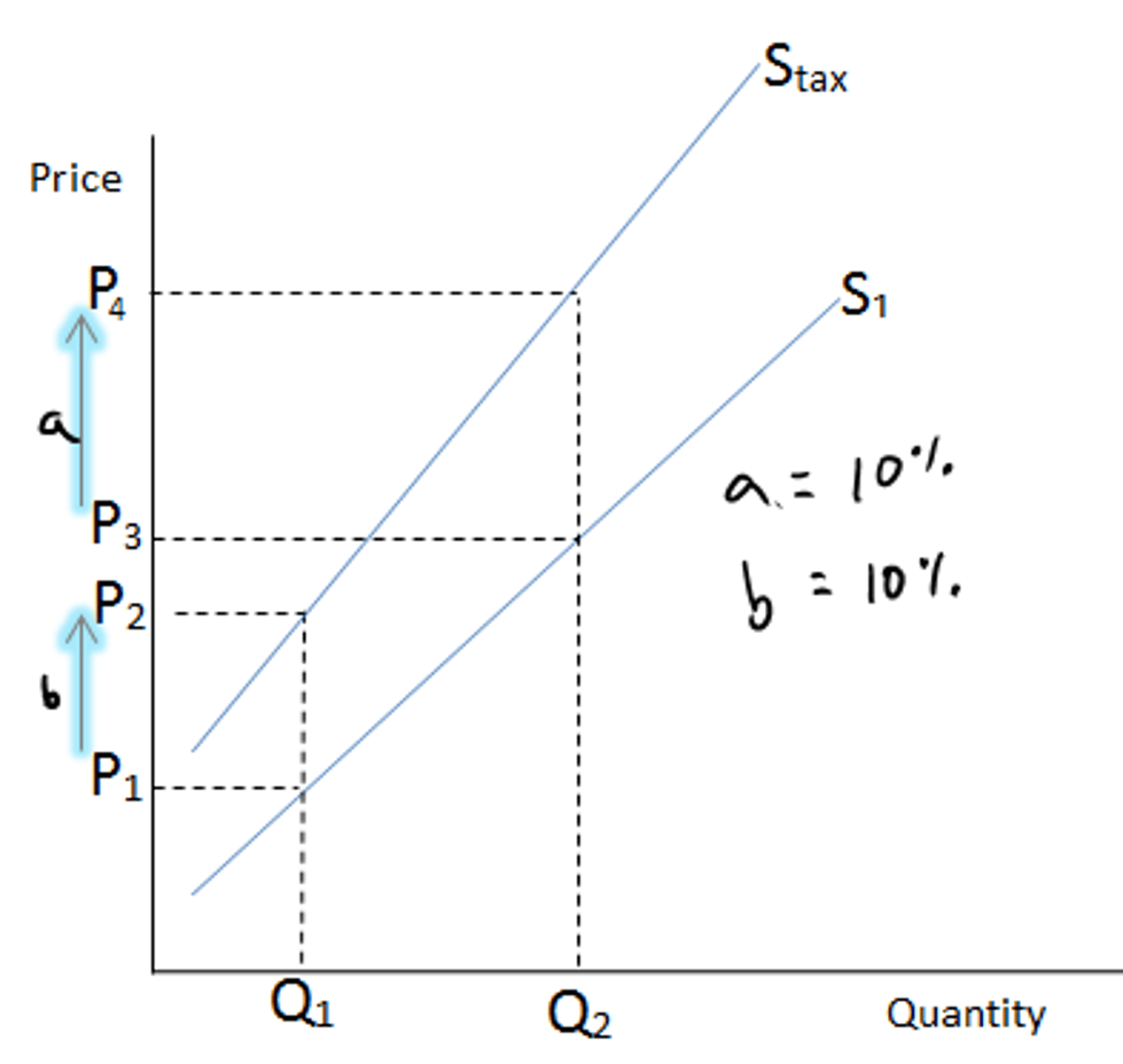
Ad Valorem Tax
fixed percentage of the good's cost
Subsidies
government financial assistance, often to firms, which influences prices as it signals change leading to a reallocation of resources
Total Tax Revenue Formula
- (Pc x Qt) - (Pp x Qt)
- (Pc - Pp) x Qt
-2 x Qt
-tax x Qt
Calculating consumer surplus after subsidy
((P-intc. Demand - Price S.) x Qsub) / 2
Calculating producer surplus after subsidy
((Price S. - P-intc. Supply) x Qsub) / 2
Price ceiling
a maximum price below market price
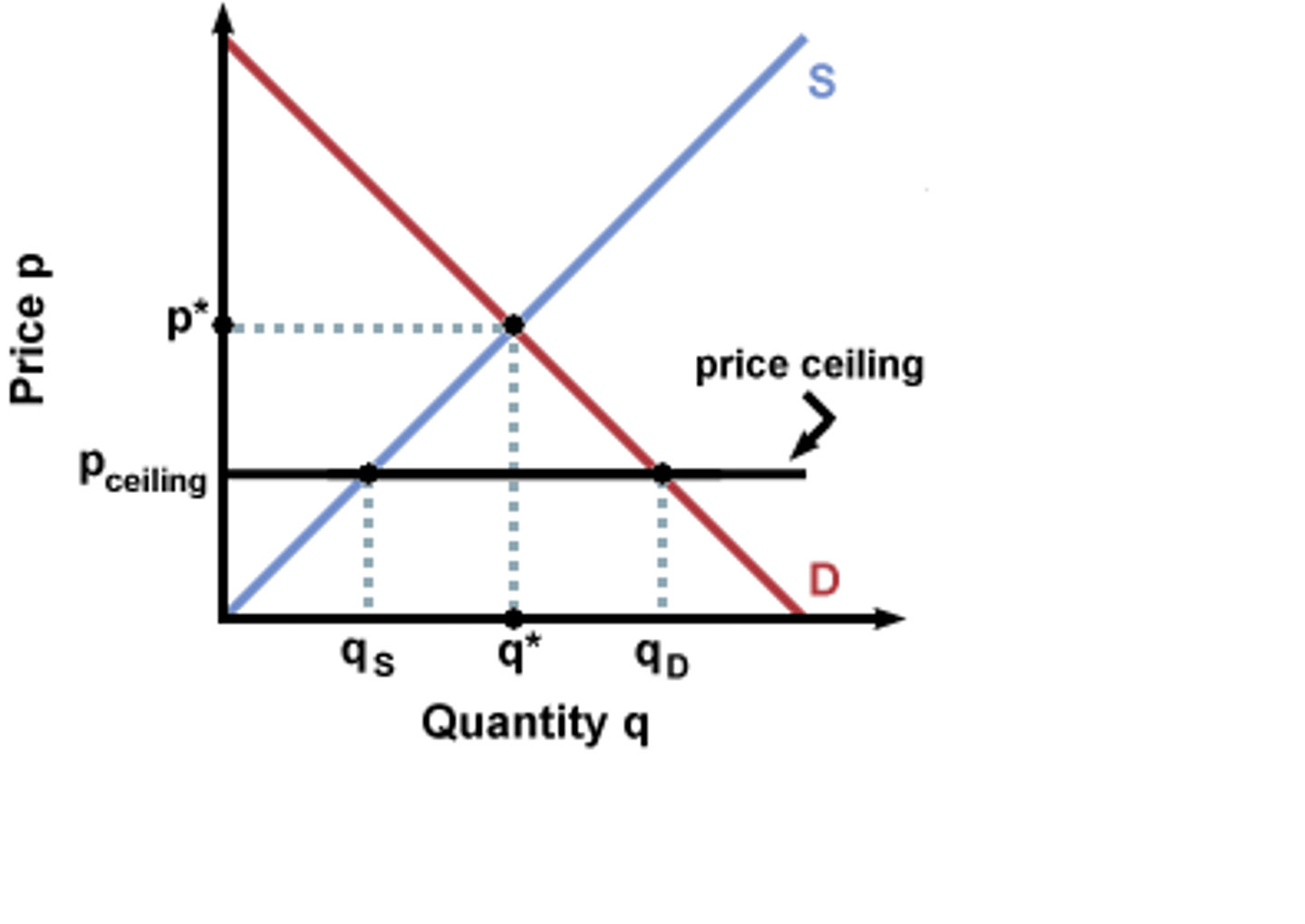
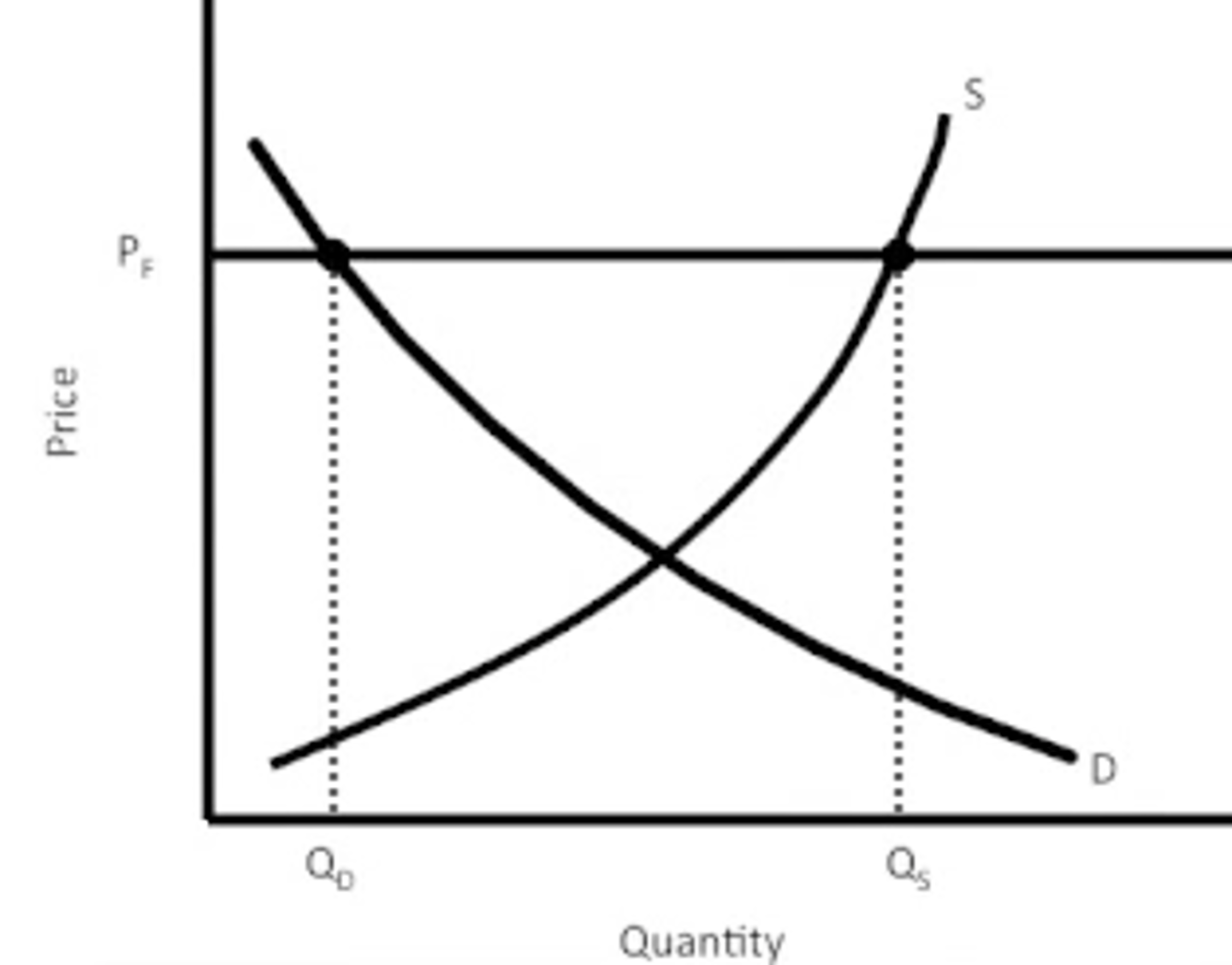
Price floor
a minimum price above market price
Benefits of a free market
-allocative efficiency
-consumer and producer surplus are maximized
-MC=MB
Pareto optimality
no one can be better off without making someone else worse off
Market failure
a failure to allocate resources efficiently
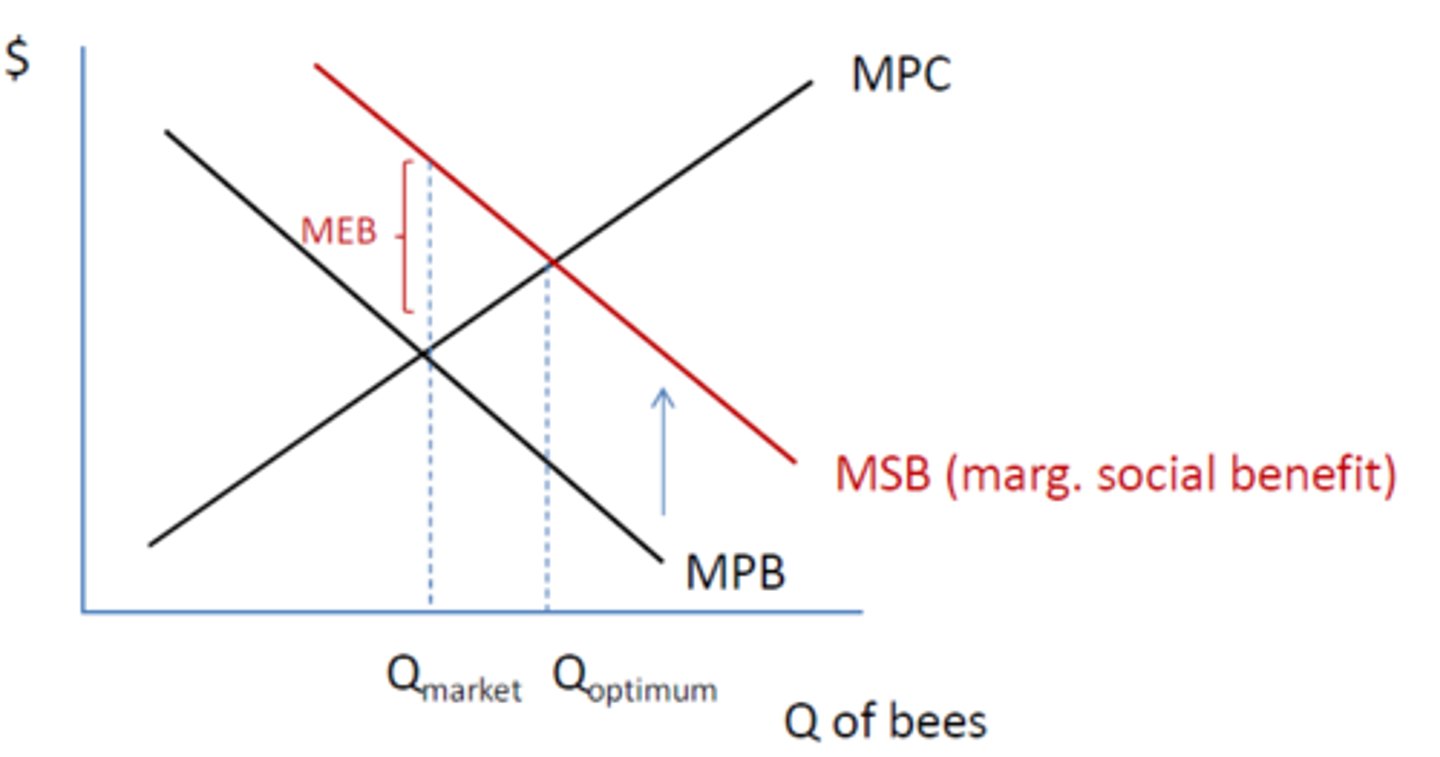
Marginal Social Benefit
benefit to SOCIETY of the consumption of a good
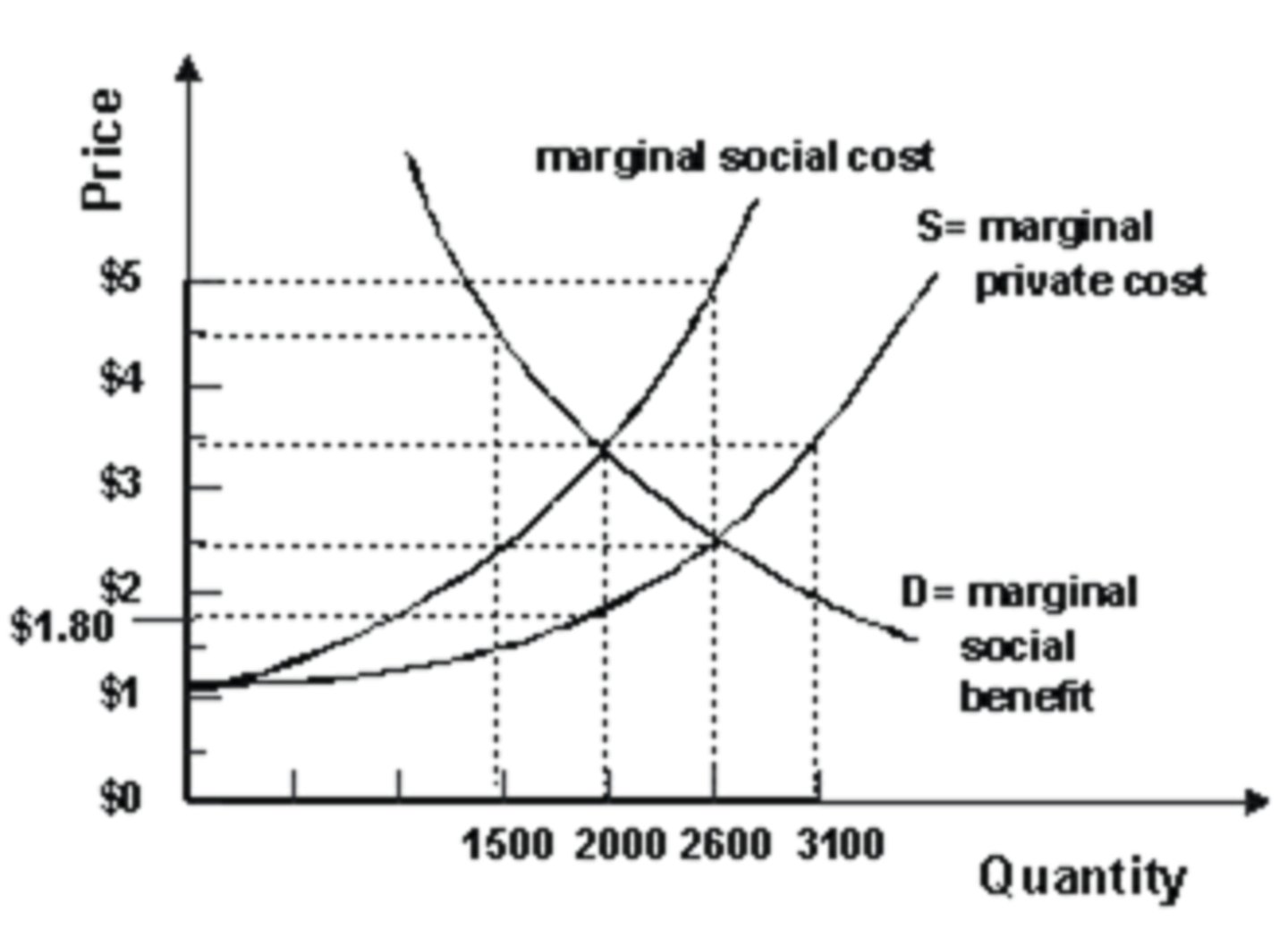
Marginal Social Cost
cost to SOCIETY of the production of a good
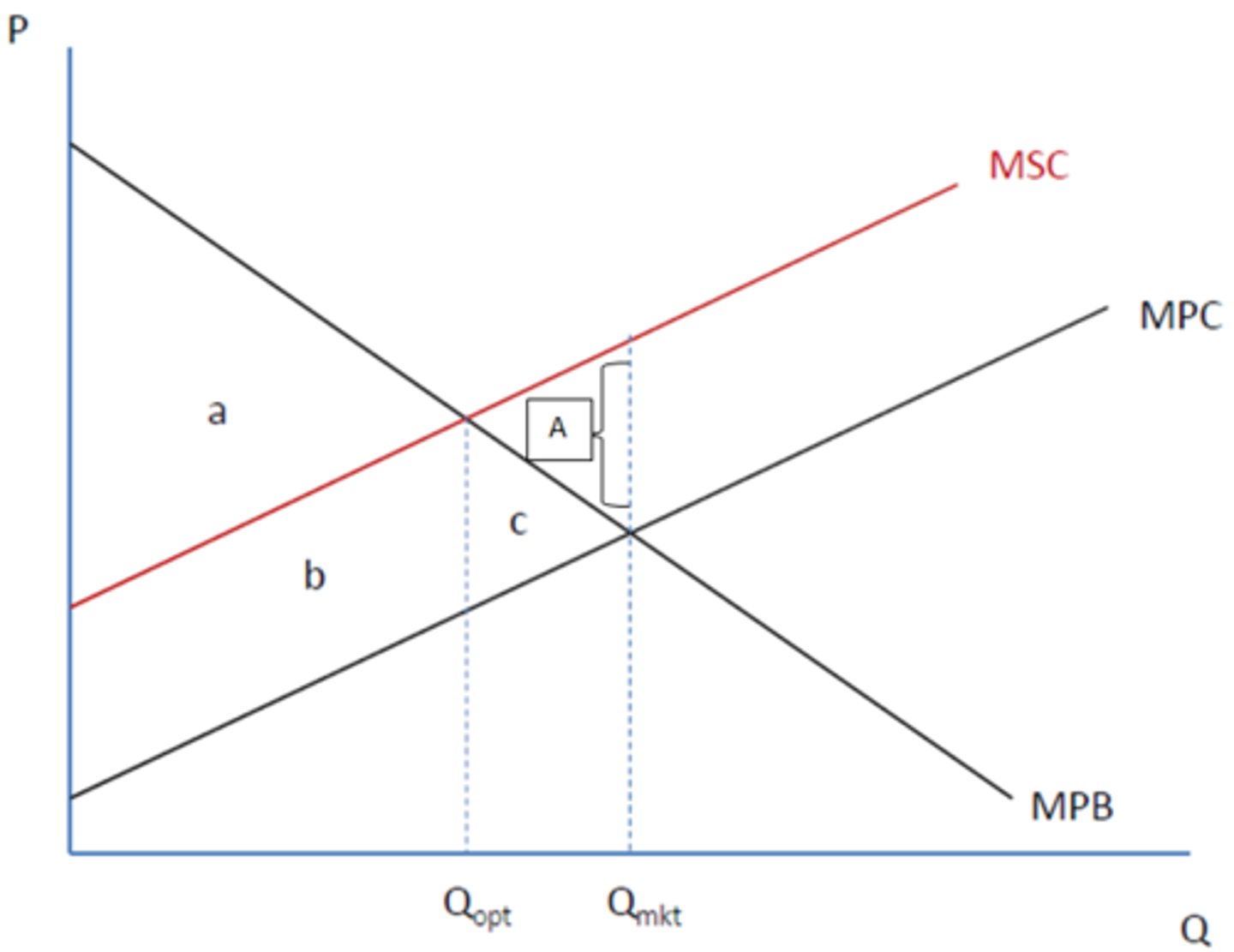
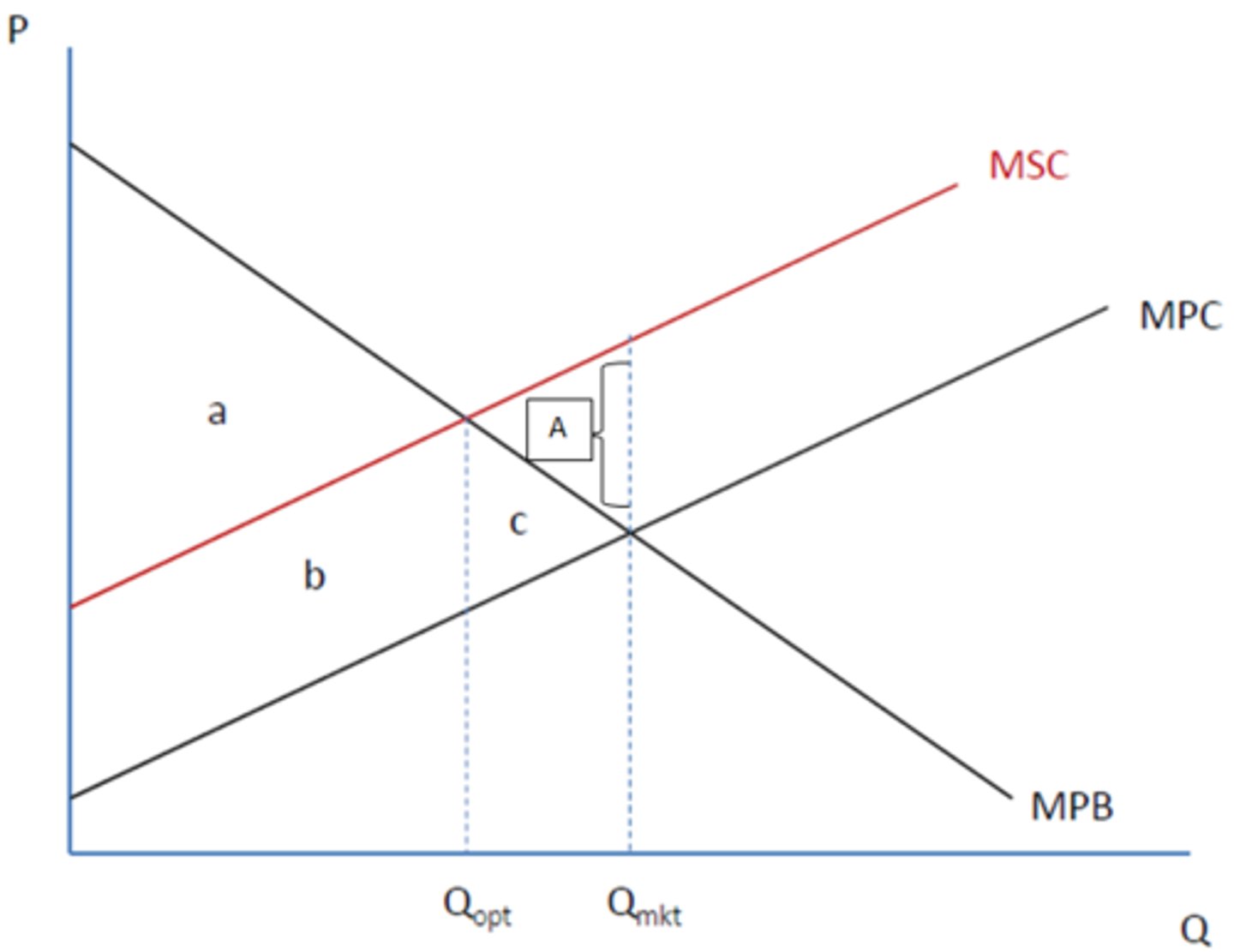
Marginal Private Benefit
benefits received by CONSUMERS for consumption of a good
Marginal Private Costs
costs for PRODUCERS for production of a good
Externalities
when a market outcome affects parties other than the buyers and sellers in the market
Positive externality
when the impact on the bystander is beneficial
Negative externality
when the impact on the bystander is adverse
Alternative correction for negative production externalities
-regulations and legislations; laws
-bans
Pigovian taxes
enacted to correct the effects of NEGATIVE externalities
Demerit goods
a good that is overvalued by society, typically restricted by government policies. Its consumption is often regarded as socially undesirable. If left to market forces, it will be over-consumed.
Lump-Sum Tax
a tax that is the same amount for every person
Regressive Tax
a tax for which high-income taxpayers pay a smaller fraction of their income than do low-income taxpayers
Alternative correction for negative consumption externalities
-bans
-limit behaviors
-advertising and persuasion
Alternative correction for positive consumption externalities
-subsidies
-government provisions
-vouchers/promotions
-legal mandates
Merit good
a commodity or service that is regarded by society or government as deserving public finance as it is a necessity, i.e. education or health care
Promotion
marketing focused on 4 elements: advertising, sales promotions, personal selling, and public relations
Trade-offs
scarce resources imply that individuals, firms, or governments are constantly faced with difficult choices that involve benefits and costs
Law of Increasing Costs
the more of a good that is produced, the greater the opportunity cost of producing the next unit of that good
Absolute advantage
this exists if a producer can produce more of a good than all other producers
Comparative advantage
a producer has comparative advantage if he can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than all other producers
Normal goods
a good for which higher income increases demand
Inferior goods
a good for which higher income decreases demand
Price elastic
the responsiveness of the consumer exceeds the initial change in price
Price inelastic
the initial change in the price exceeds the responsiveness of the consumer
Unit elasticity
the initial change in price is exactly equal to the responsiveness of the consumer
Perfectly inelastic
No matter what percentage increase or decrease in price, the quantity demanded remains the same
Perfectly elastic
Even the smallest percentage change in price causes an infinite change in quantity demanded
Determinants of elasticity
-number of good substitutes
-proportion of income
-time
Incidence of tax
the proportion of the tax paid by consumers in the form of a higher price for the taxed good is greater if demand for the good is inelastic and supply is elastic
Midpoint Method
(difference QD/ average Qd) / (difference P/ average P)
absolute advantage
the ability to produce more of a good than all other producers
absolute prices
the price of a good measured in units of currency
accounting profit
the difference between total revenue and explicit cost
ceteris paribus
all else equal; the assumption that all other variables are held constant so that we can predict how a change in one variable affects a second
average fixed cost (AFC)
total fixed cost / output
average product of labor (APL)
total product / labor employed
average tax rate
the proportion of total income paid to taxes