A&P Ch. 12 Central Nervous System
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
The CNS develops from this
Embryonic Neural Tube
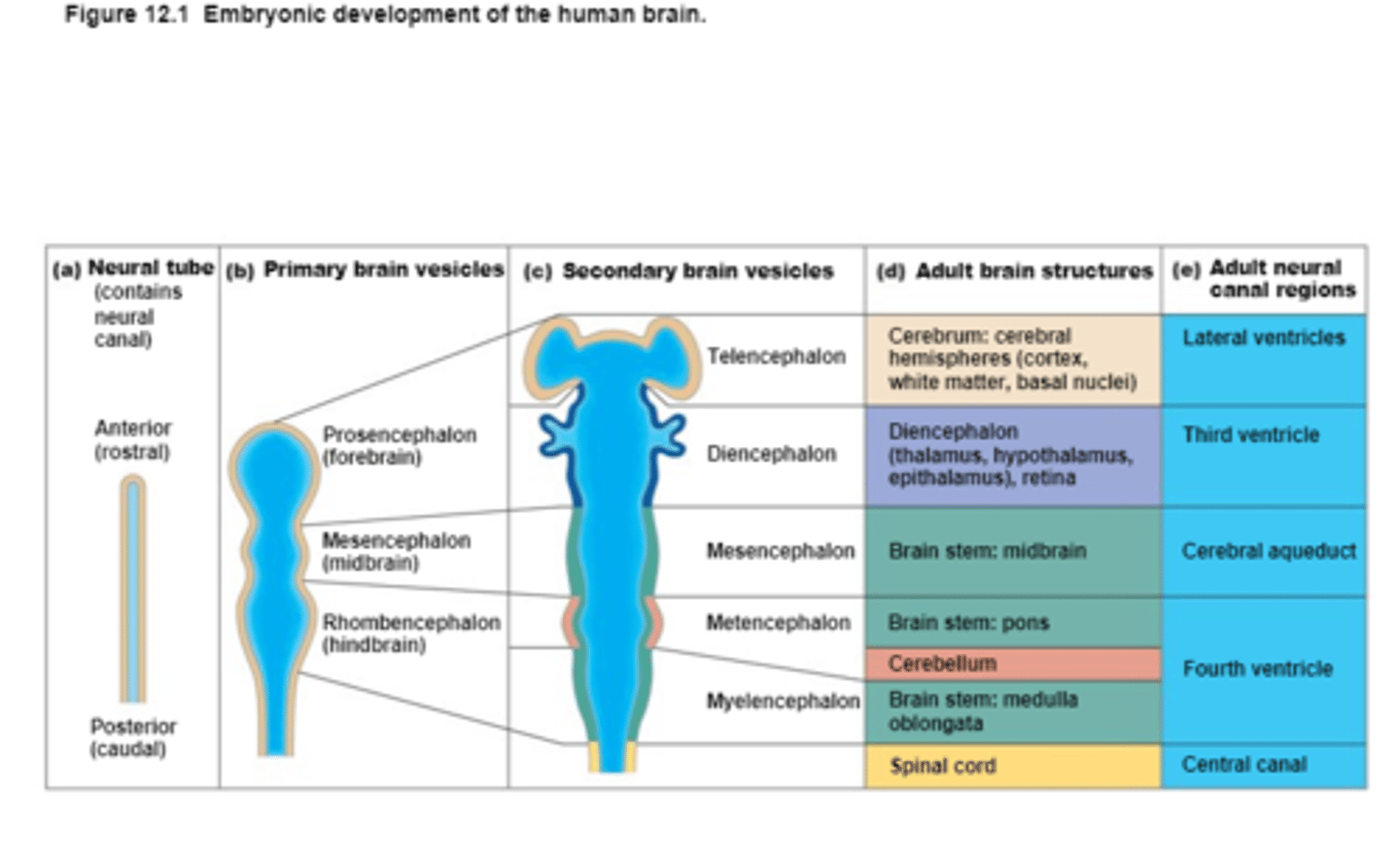
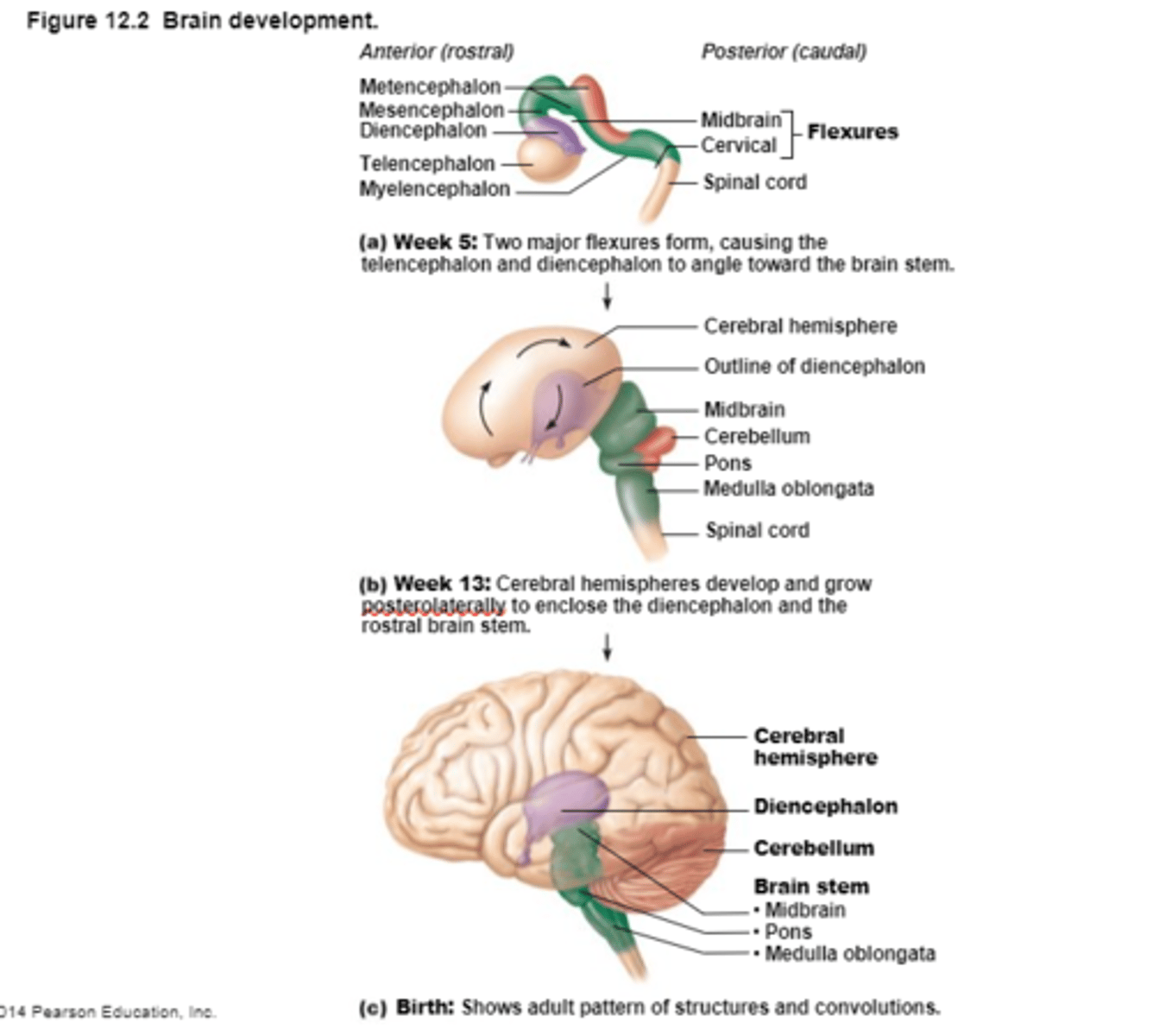
An Embryonic Neural Tube becomes the
Anterior end becomes the Brain and
Posterior end becomes the Spinal Cord
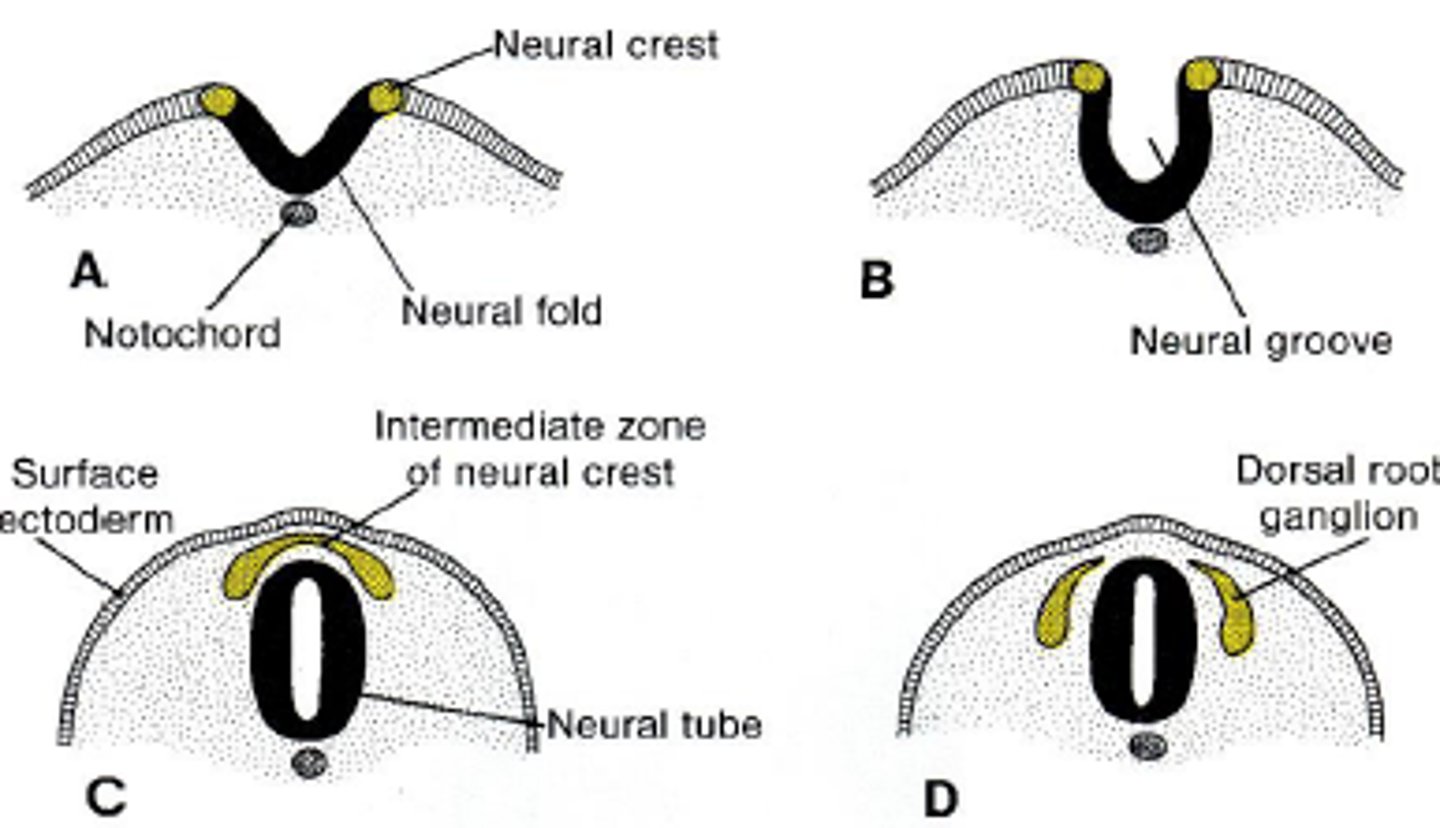
Neural Crest Cells
Give rise to sensory and autonomic neurons of the PNS
The opening of the neural tube become
Ventricles
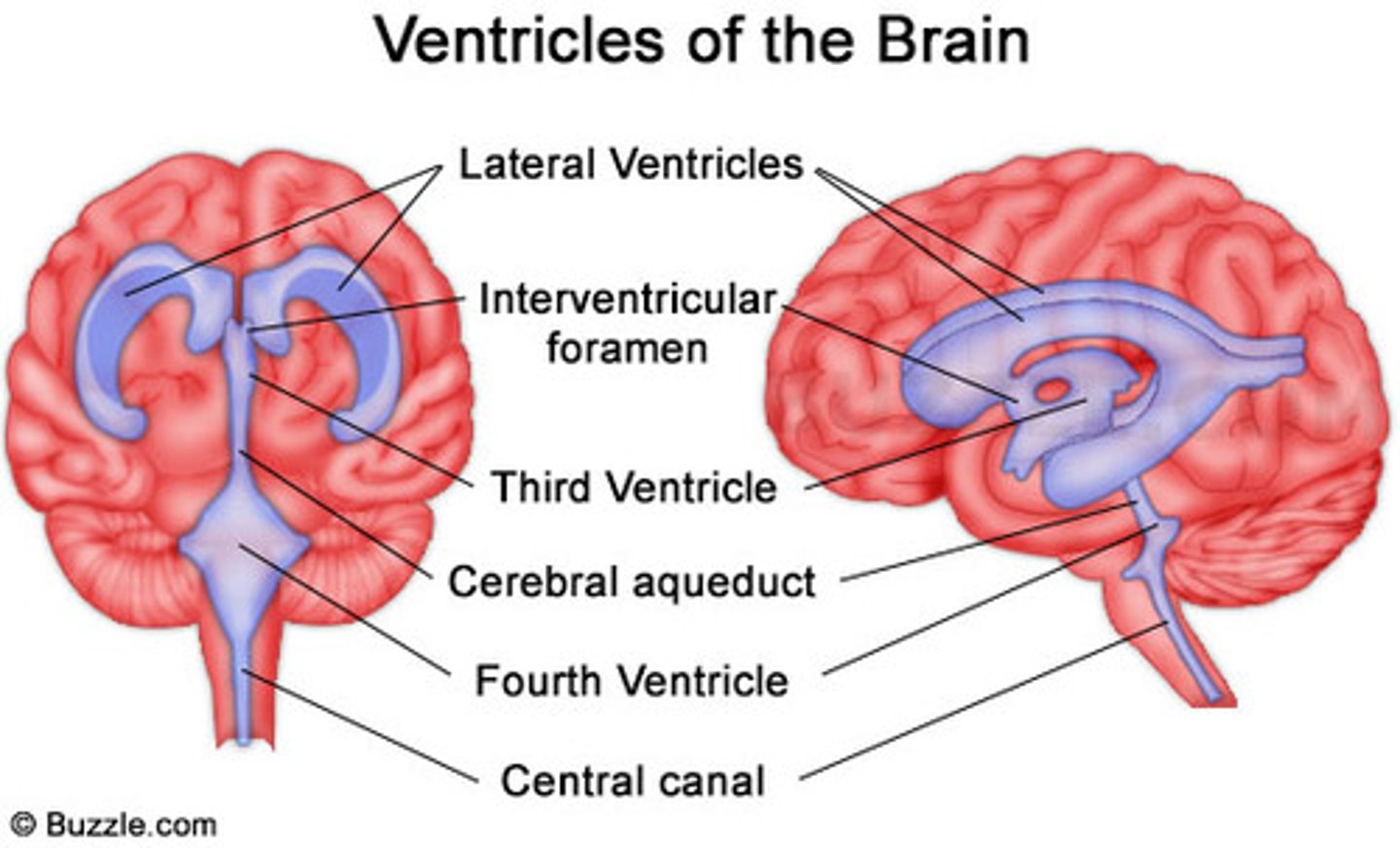
4 Chambers within the brain,
Filled with Cerebrospinal Fluid,
Continuous with each other and with the central canal of the spinal cord
4 Chambers within the brain,
Filled with Cerebrospinal Fluid,
Continuous with each other and with the central canal of the spinal cord
Cerebral Hemispheres (Cerebrum)
Paired (left and right) superior parts of the brain,
Largest Portion of the Brain,
The surface is made of elevated ridges called gyri and shallow grooves called sulci
How much does the Cerebrum weigh in females and males?
1450g in females,
1600g in males
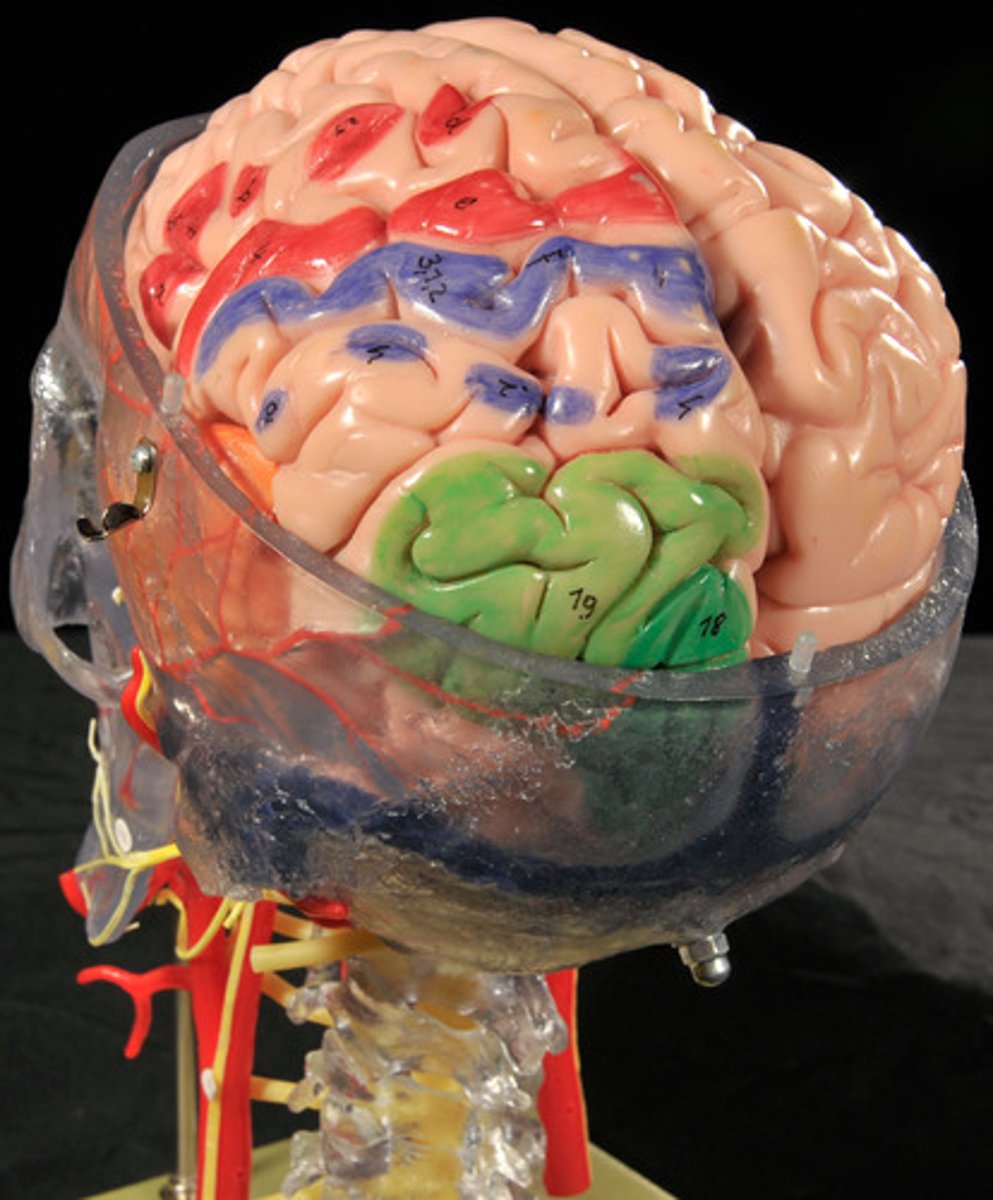
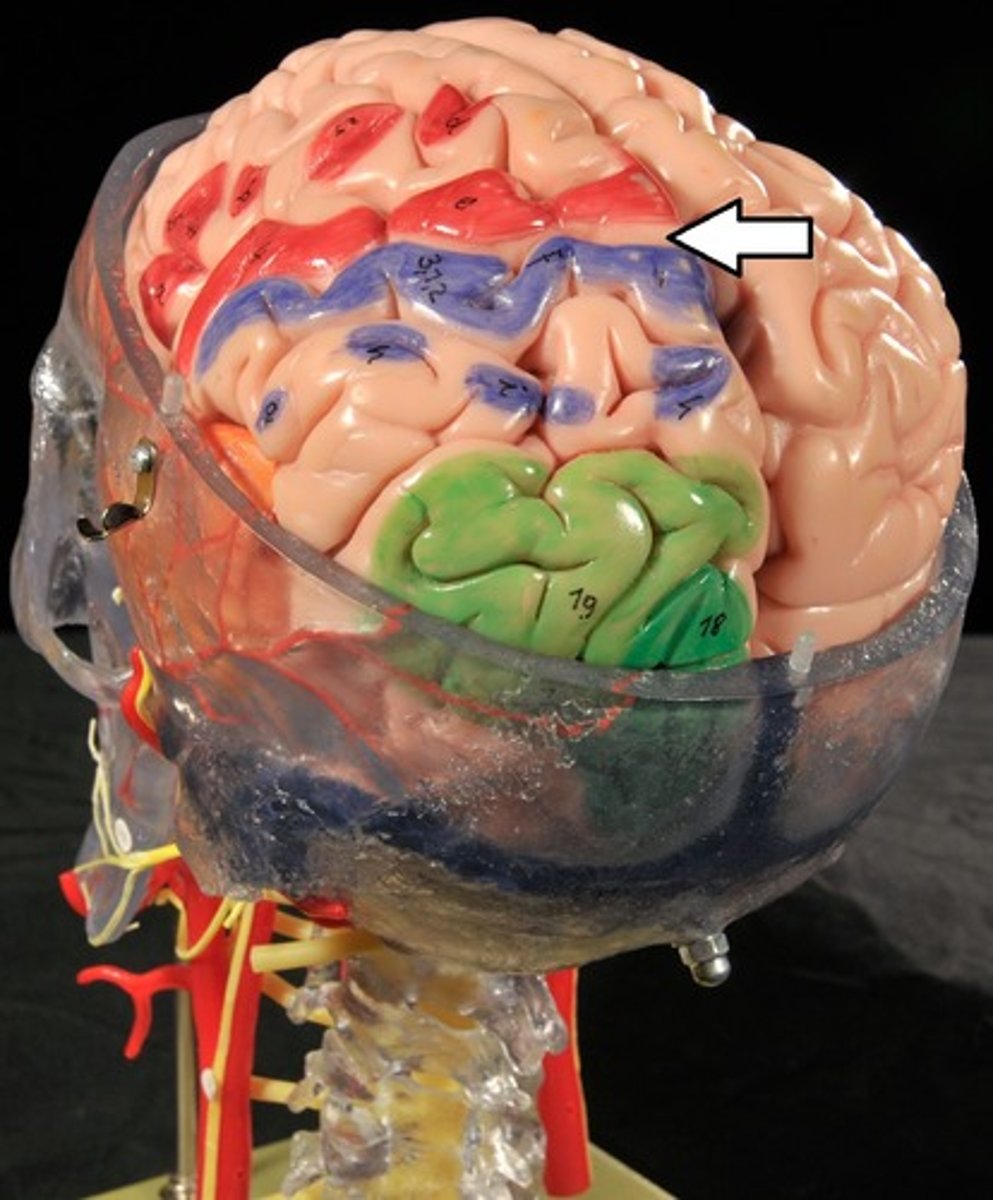
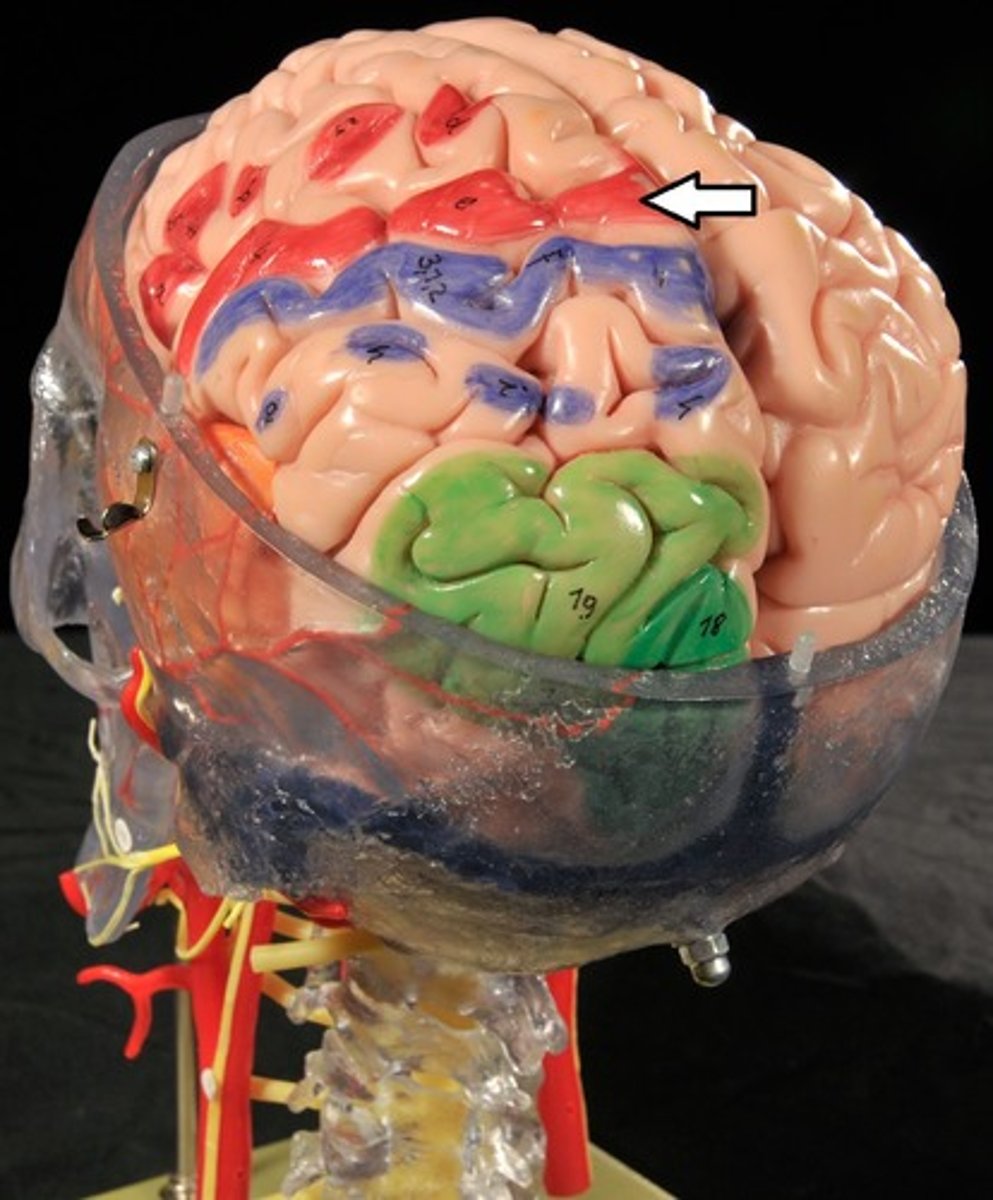
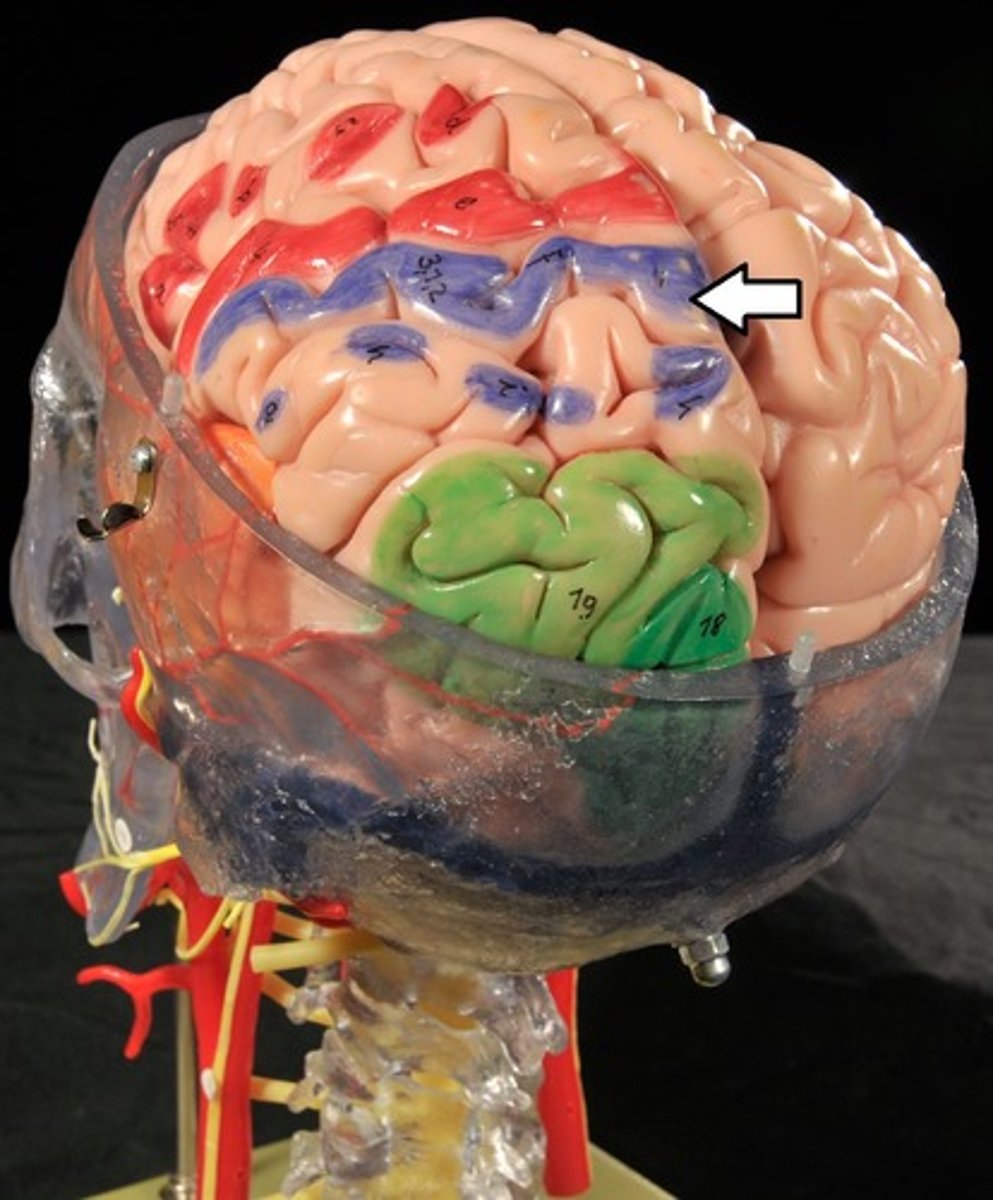
Cerebrum: Sulci and Gyri
Central Sulcus,
Precentral gyrus,
Postcentral gyrus
Central Sulcus
Precentral Gyrus
Postcentral Gyrus
Fissures
Deep grooves,
Divide the cerebrum into different regions of the brain
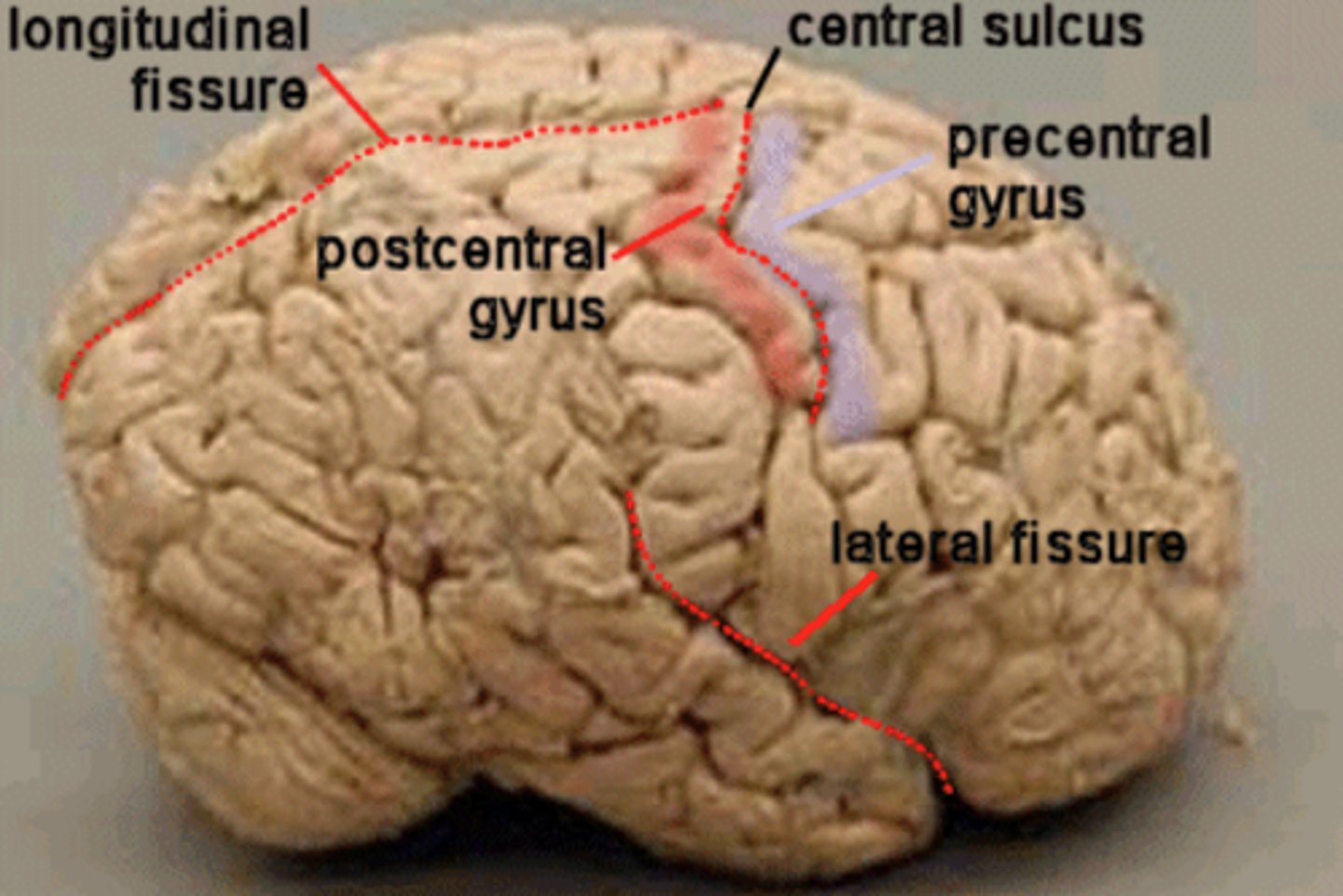
Longitudinal Fissure
Separates the left and right Cerebral Hemispheres
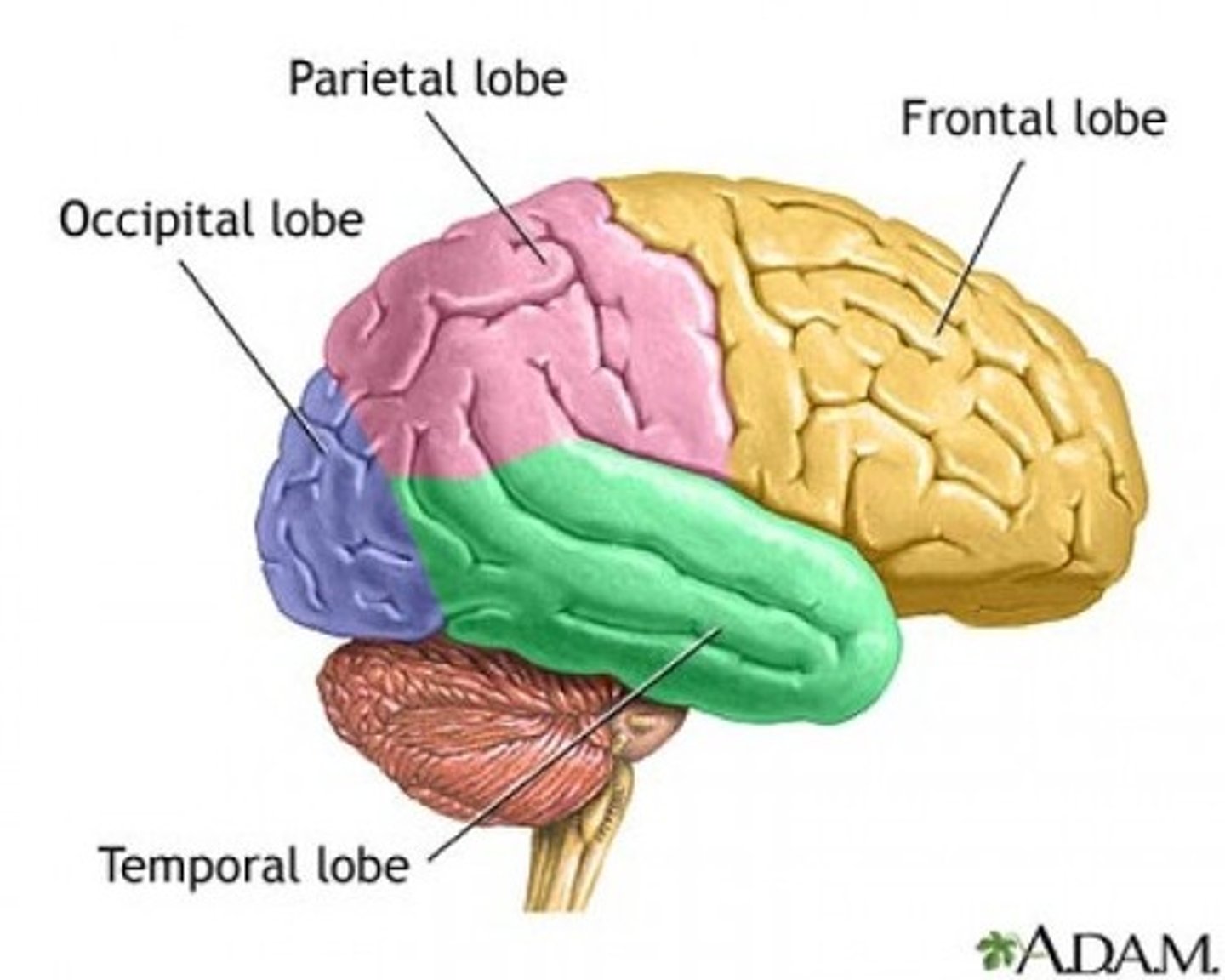
Surface lobes of the cerebrum
Frontal Lobe,
Temporal Lobe,
Parietal Lobe,
Occipital Lobe
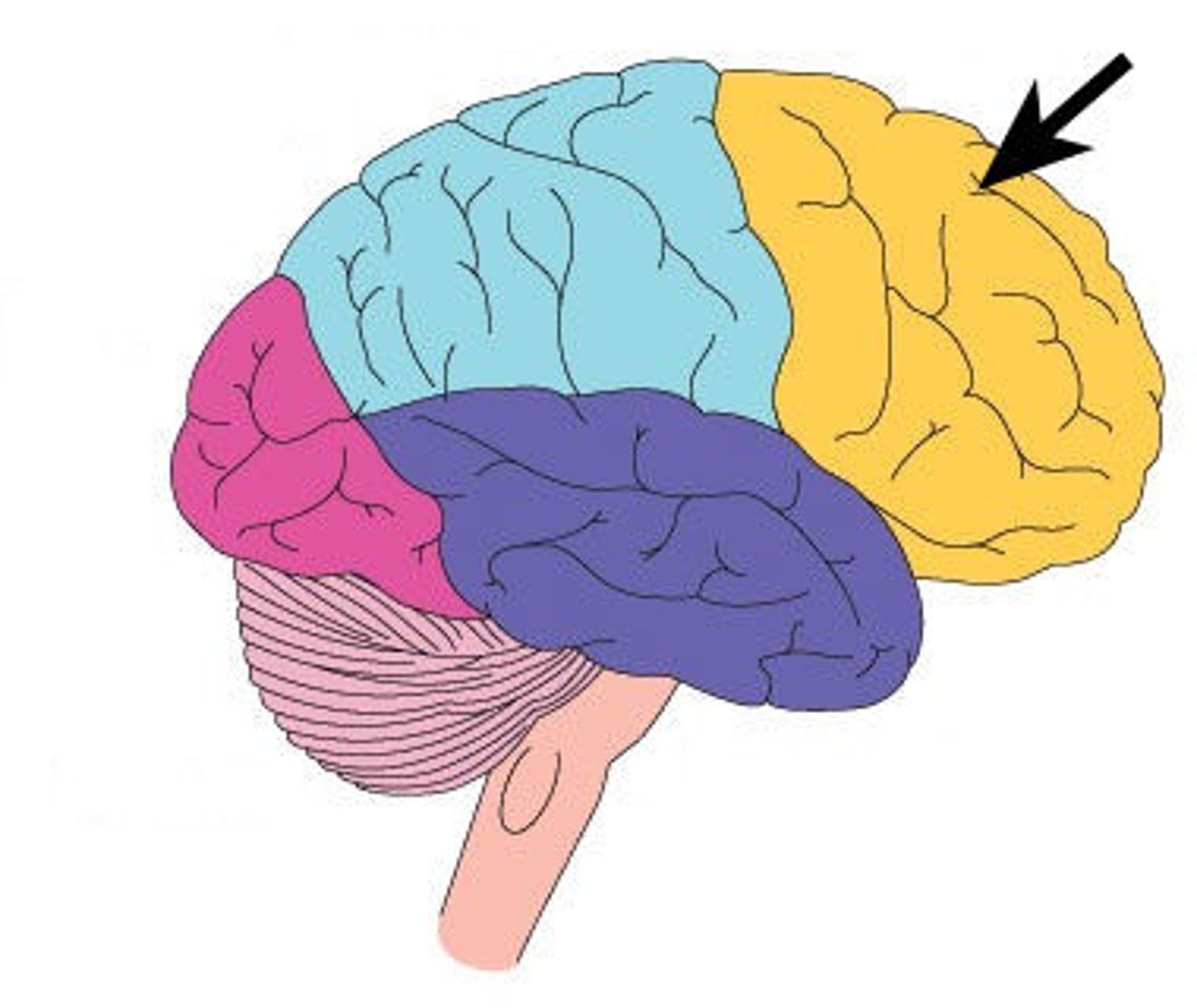
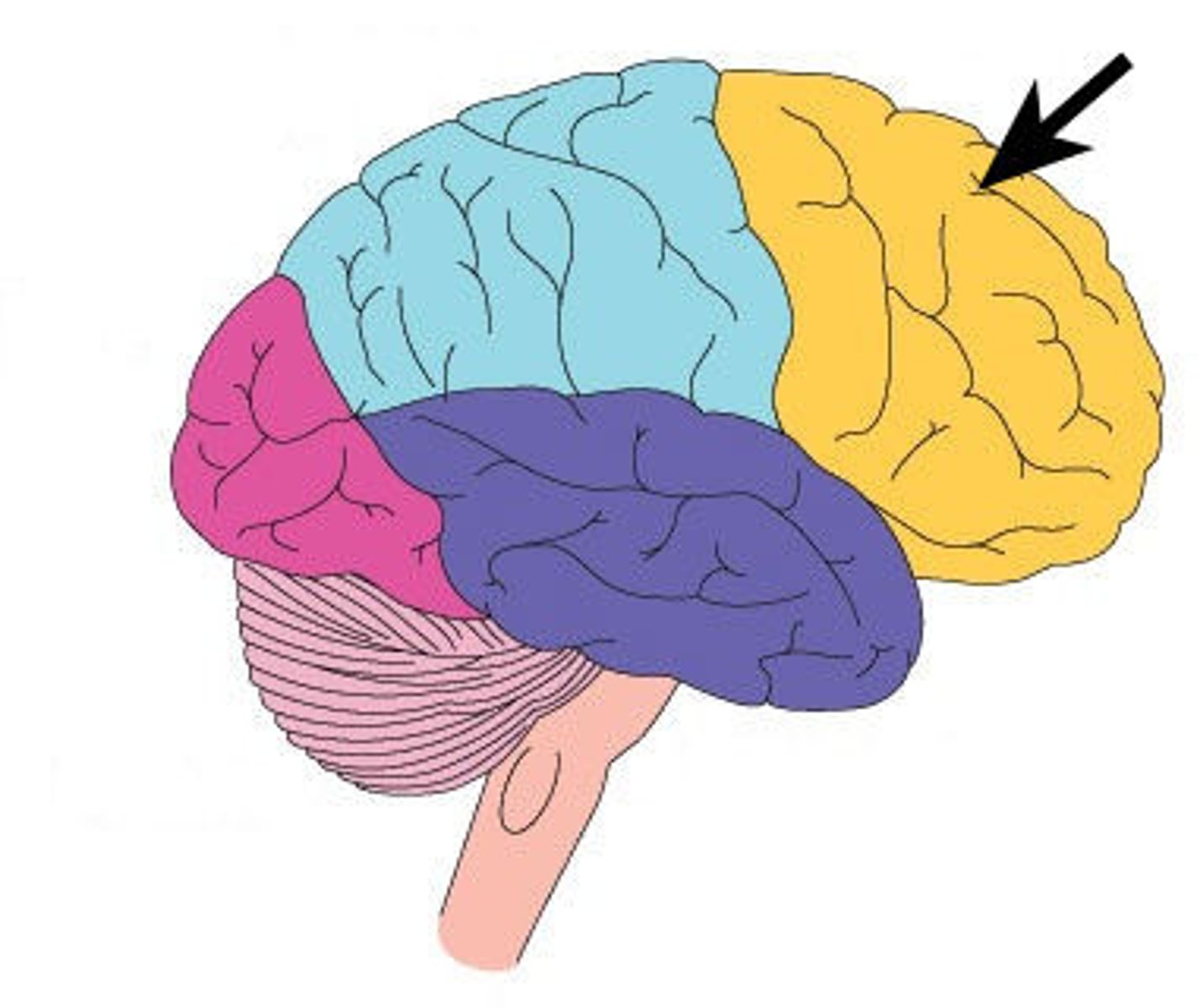
Frontal Lobe
Primary (somatic) motor cortex
Temporal Lobe
Olfactory and Auditory input
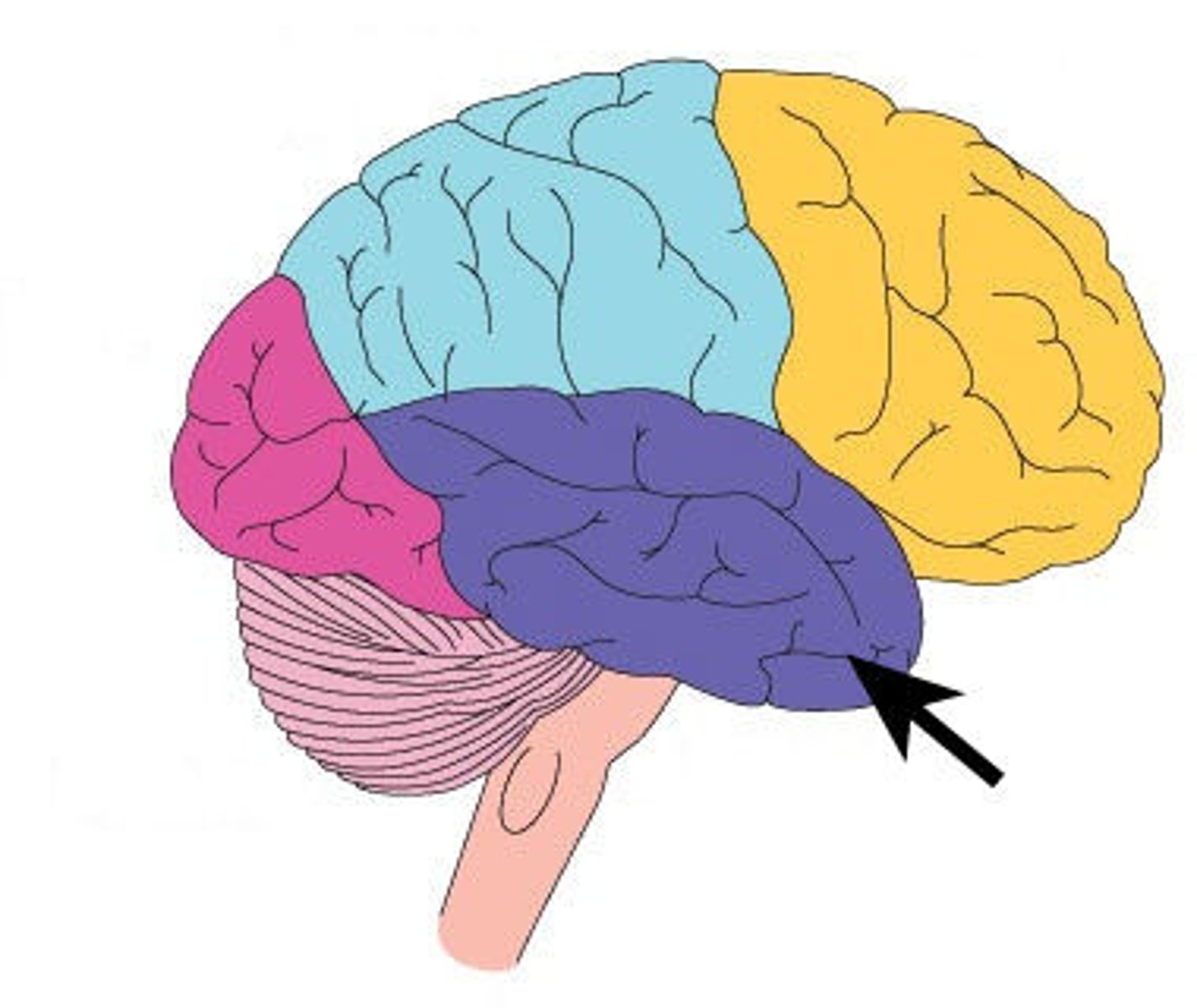
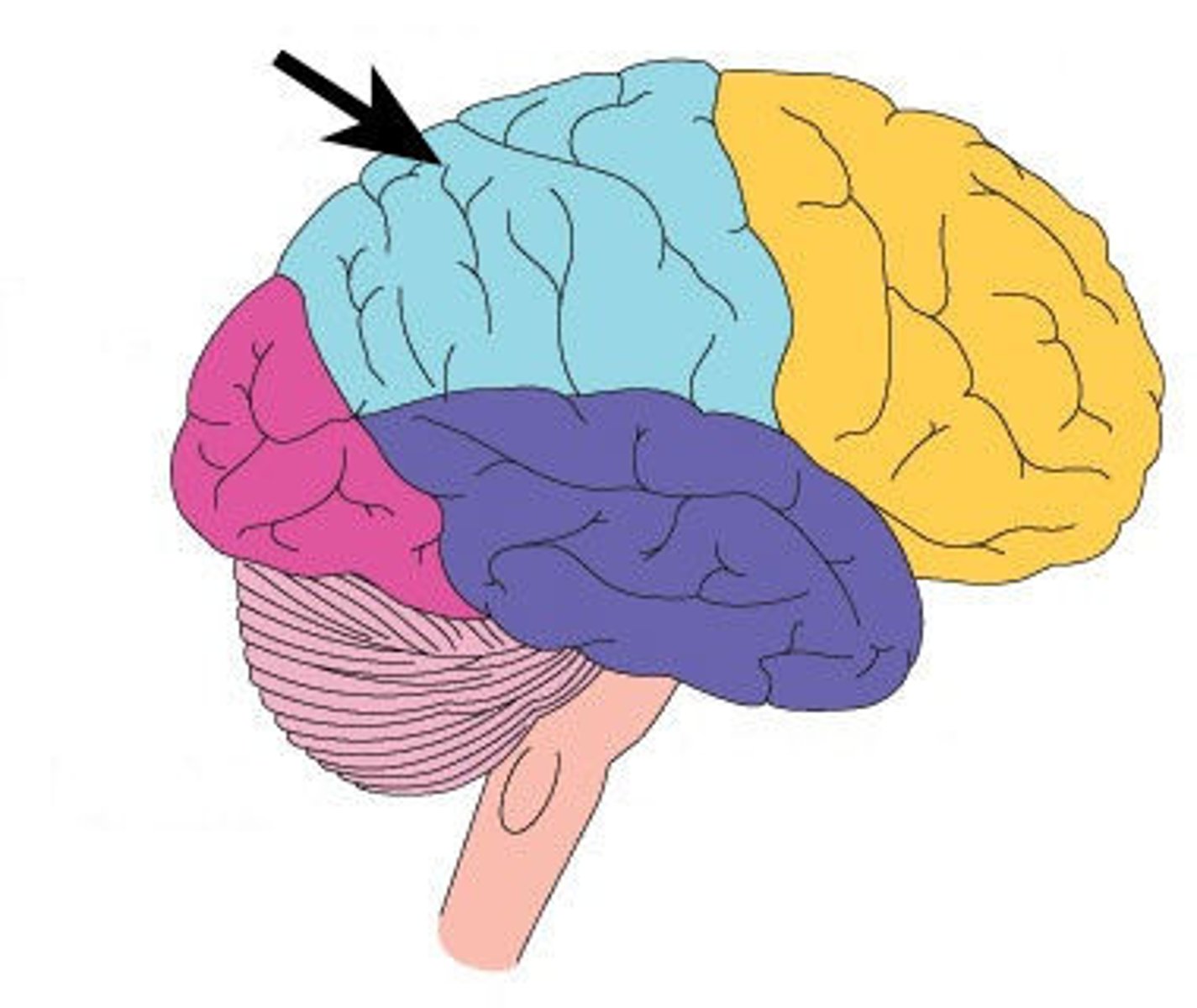
Parietal Lobe
Reception and evaluation (integration) of sensory information except for smell, hearing, and vision
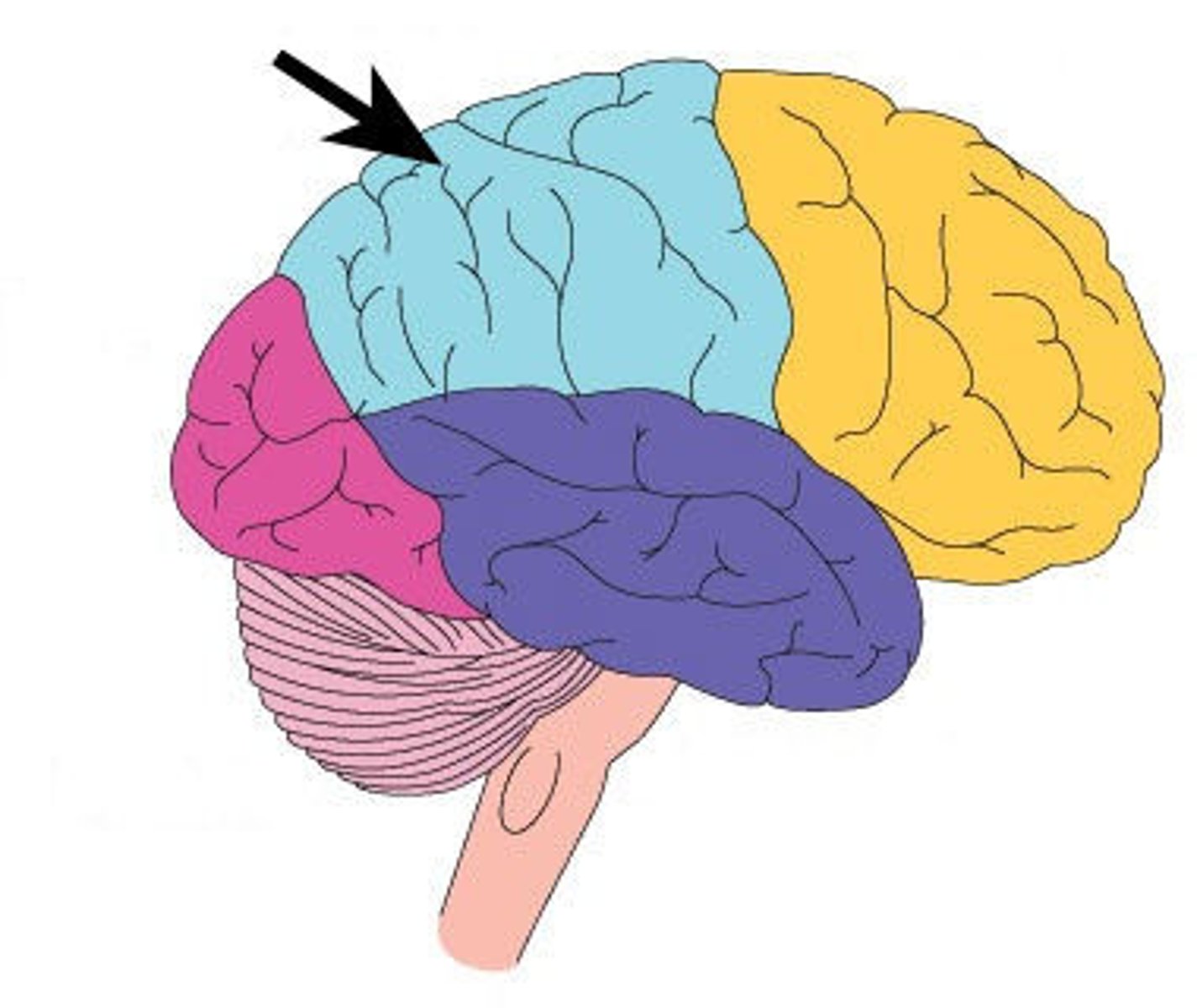
Occipital Lobe
Vision and integration of visual input
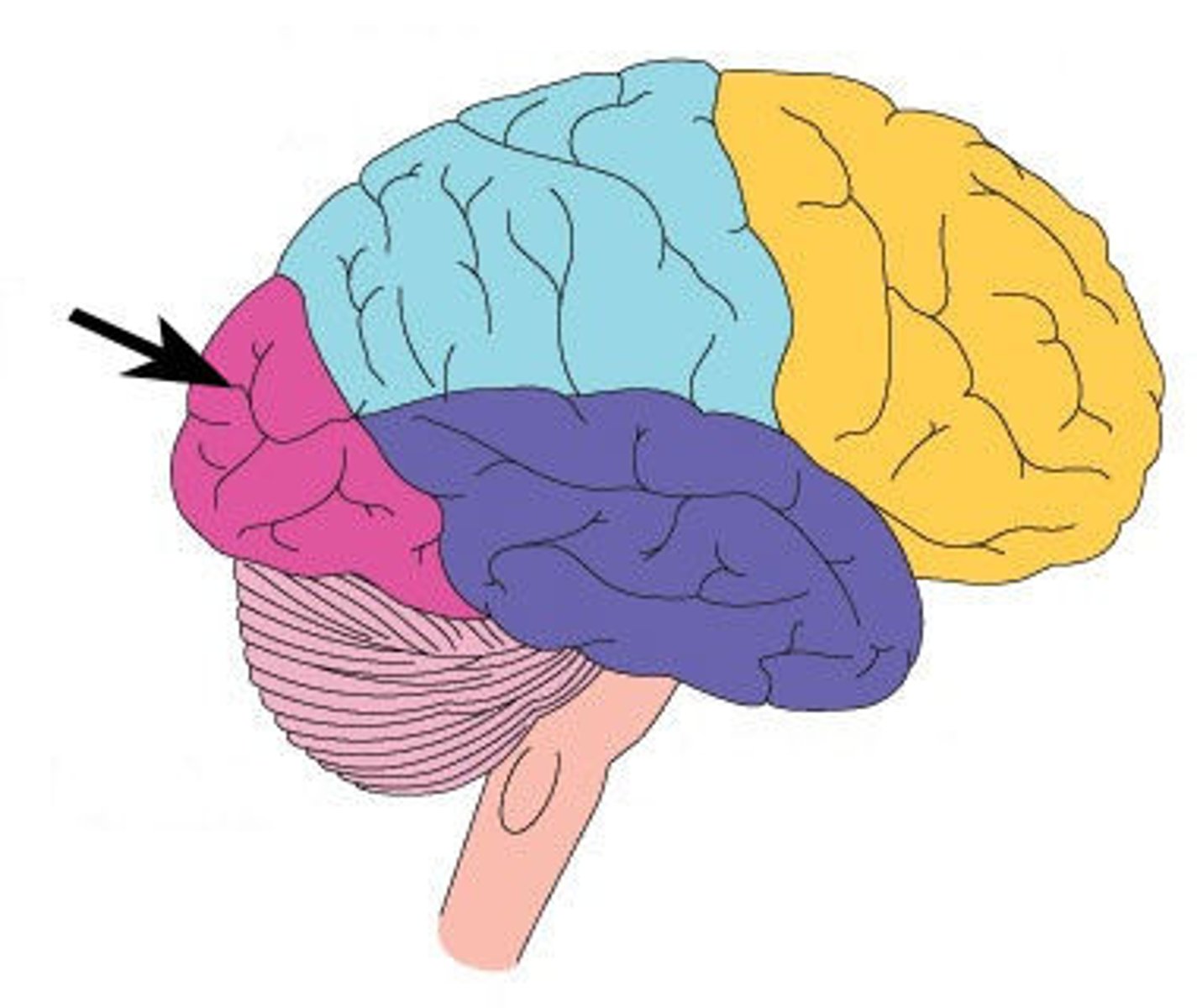
Frontal lobe: motor cortex
1) Controls precise or skilled voluntary movements of our skeletal muscles
2) Also learned motor skills (repititious or patterned nature) like playing an instrument or typing
3) Is contralateral: left primary motor cortex controls muscles on right side of body & vice versa
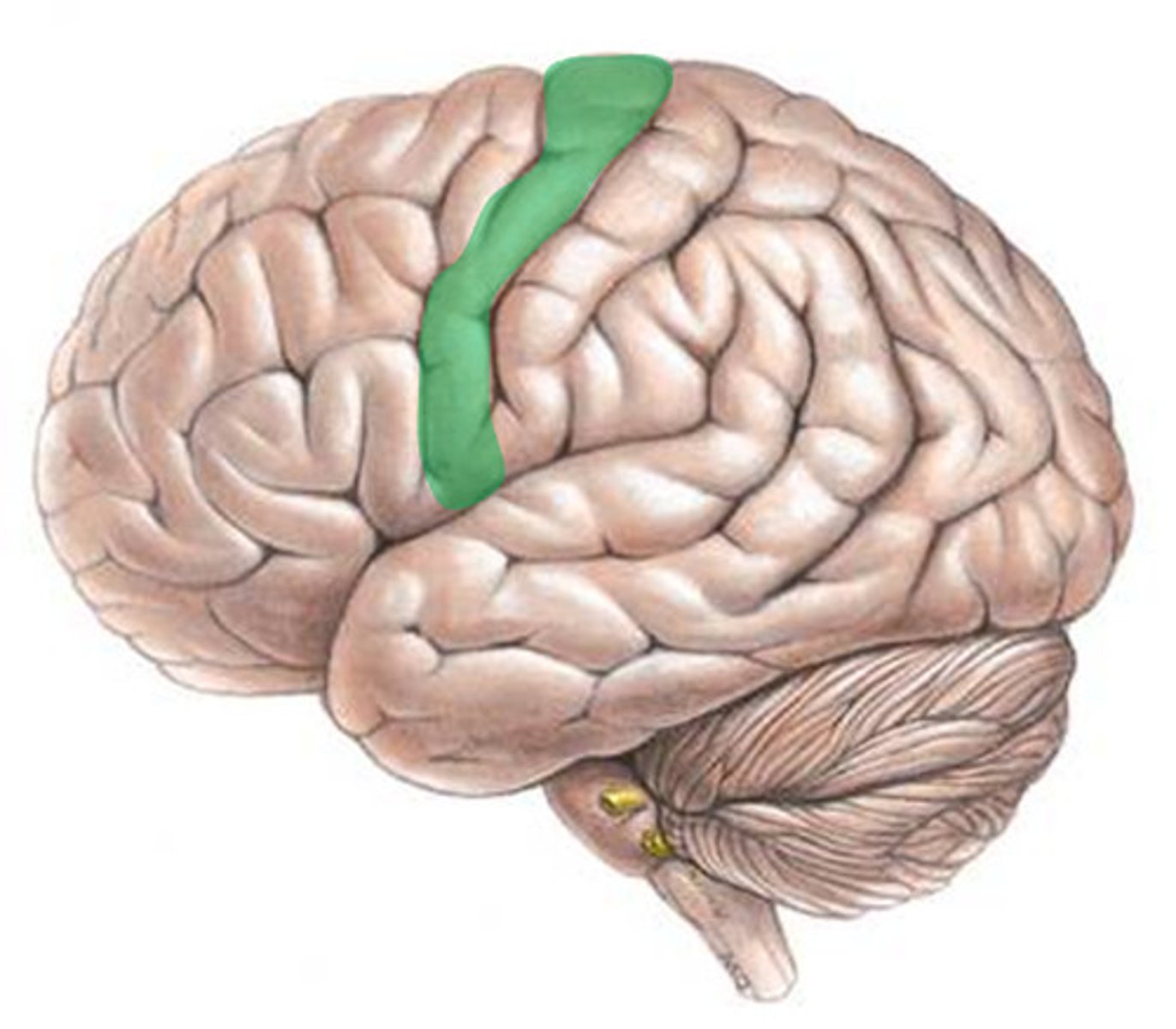
Contralateral
Left primary motor cortex controls muscles on right side of body and vice versa
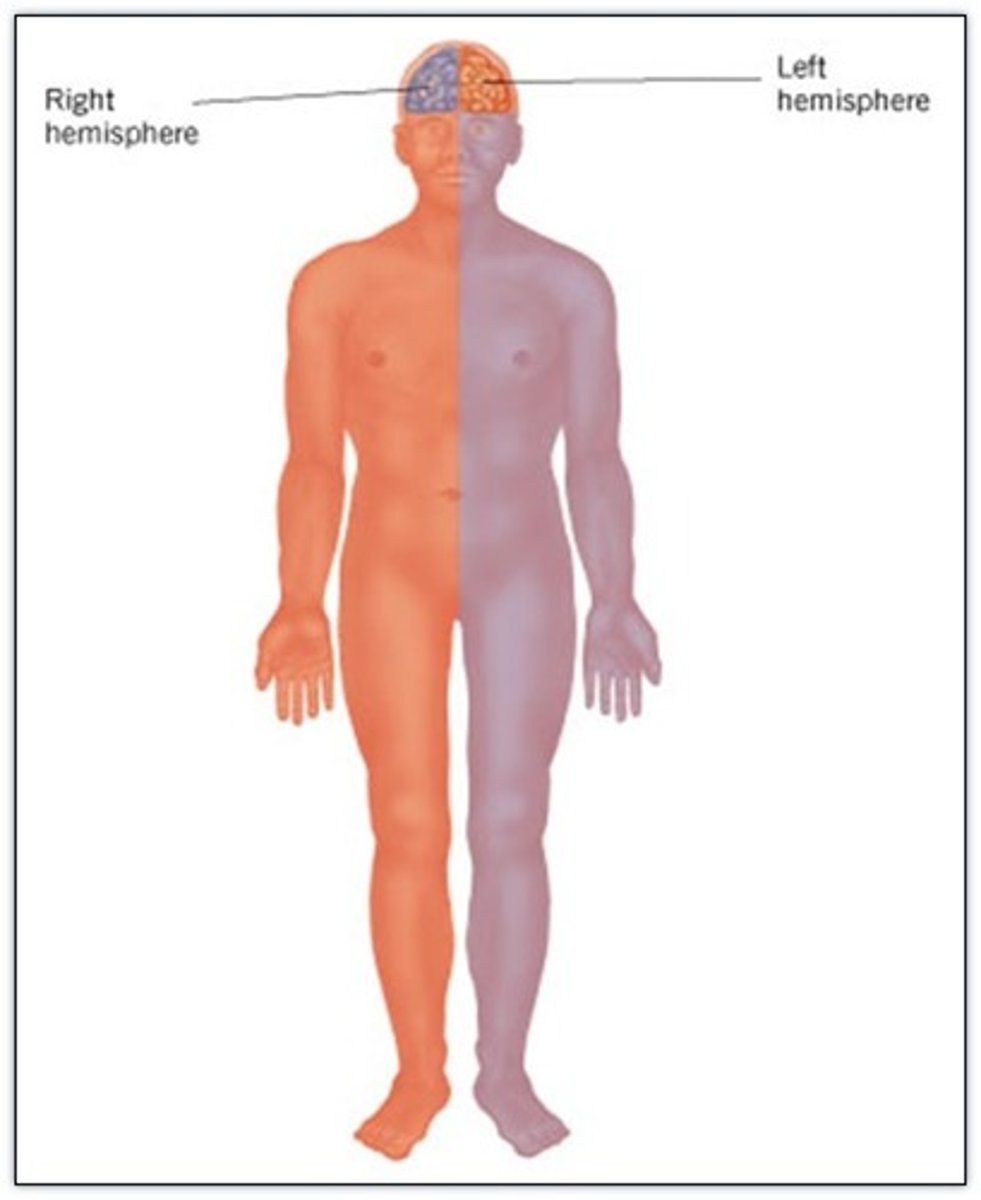
Clinical: damage to frontal lobe
Damage to localized areas of frontal lobe (such as from a stroke) paralyzes body muscles controlled by those areas.
Only voluntary control is lost, however, as muscles can still contract reflexively.
Sensory Cortex
Sensory Interpretation and Association
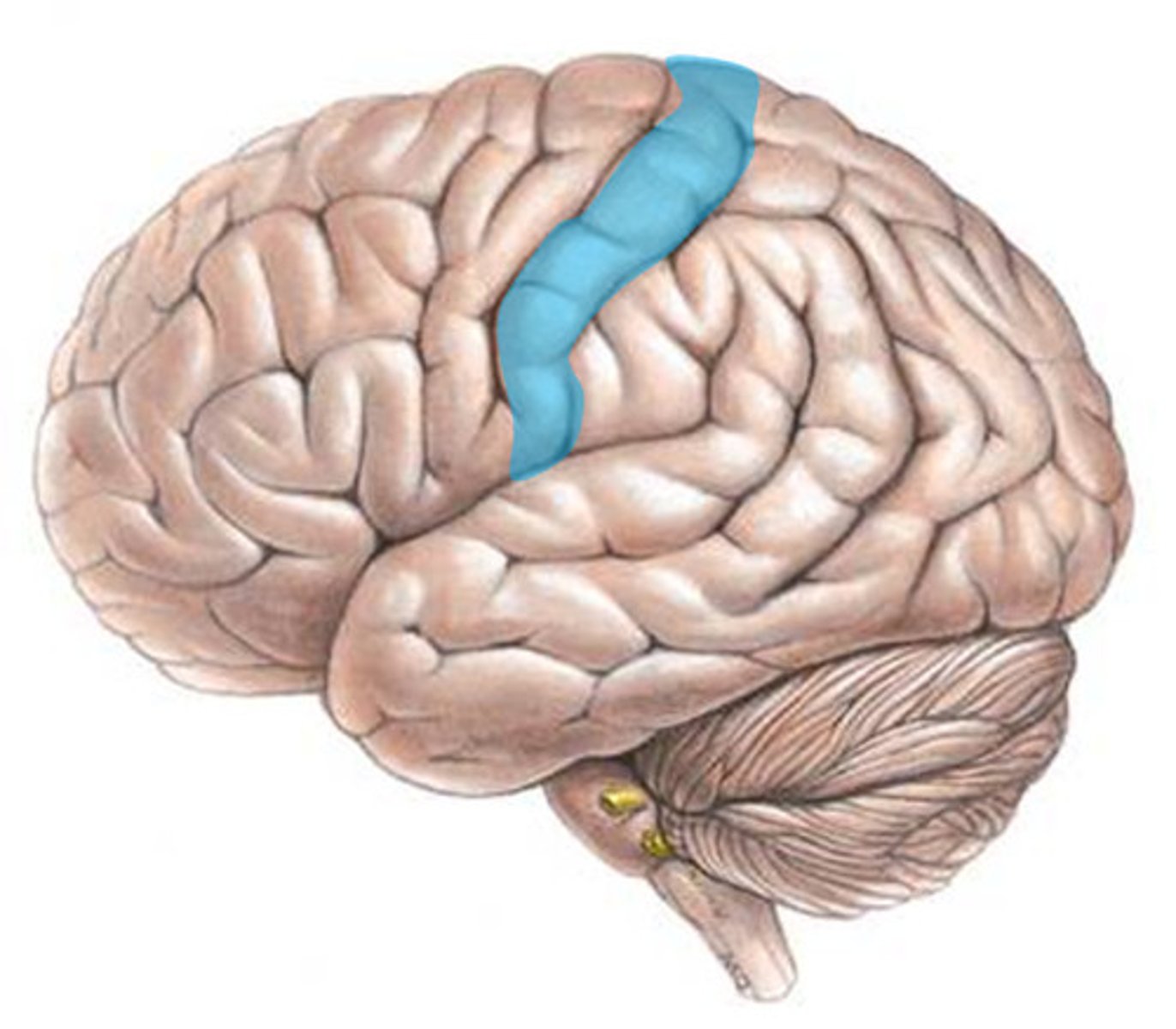
Sensory Interpretation
Integrates sensory inputs (temp., pressure, etc.) to produce an understanding of what is being felt or observed (size, texture, etc.)
Association of sensory cortex
Links sensory inputs above to past memories to provide meaning to what we fell or see
Lateralization of cortical functioning
Although we use both cerebral hemispheres for almost every activity and the hemispheres appear nearly identical, there is a division of labor as each hemisphere has unique abilities not shared by its partner.
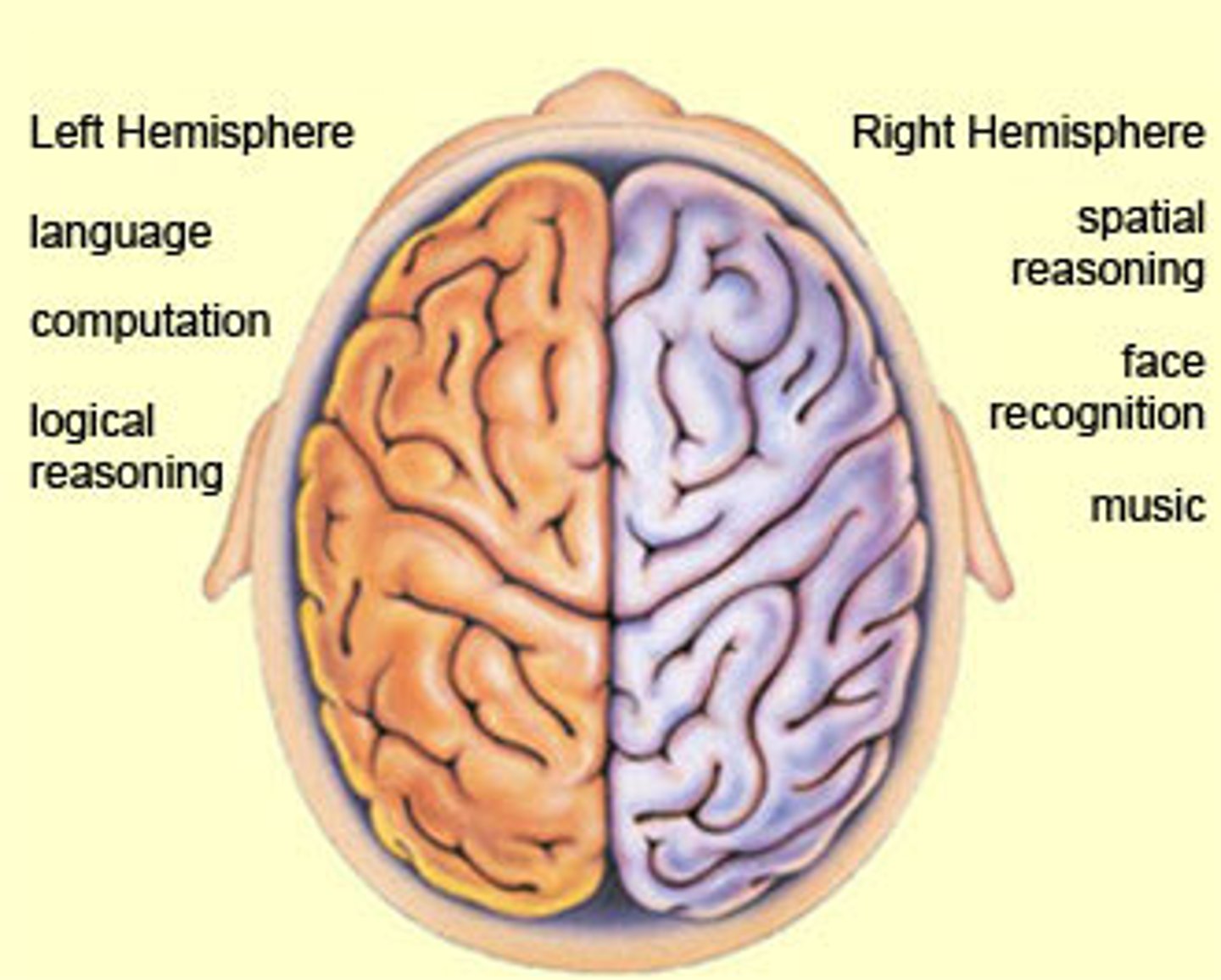
Left Cerebral Hemisphere (left brained people)
Has greater control over language, math, and logic,
Tend to be right handed
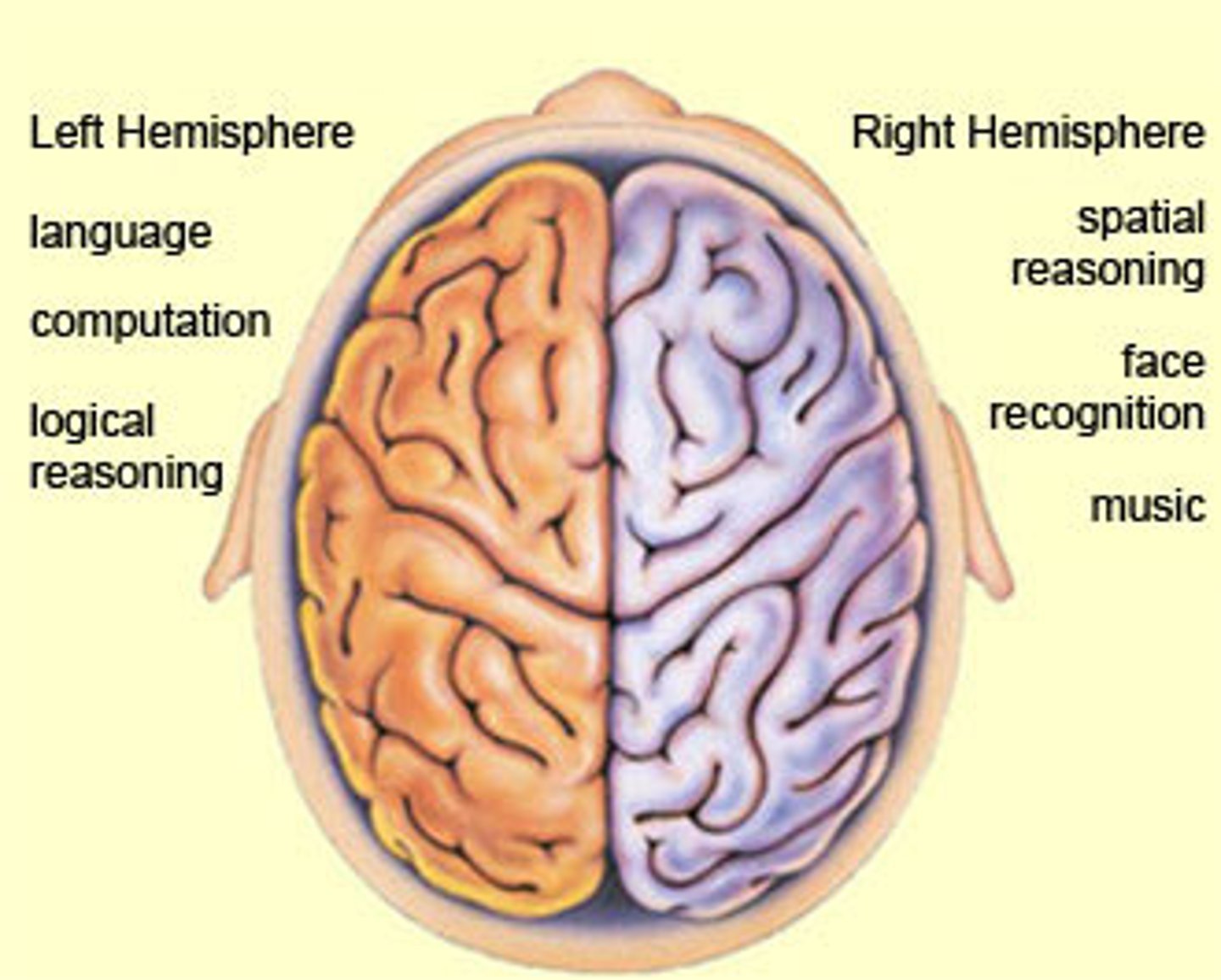
Right Cerebral Hemisphere (right brained people)
Is more free-spirited and more involved in intuition, emotion, and artistic and muscle skills,
Tend to be left handed
Layers of the Cerebrum
Cerebral Cortex (gray matter),
Cerebral Medulla (white matter),
Basal Nuclei
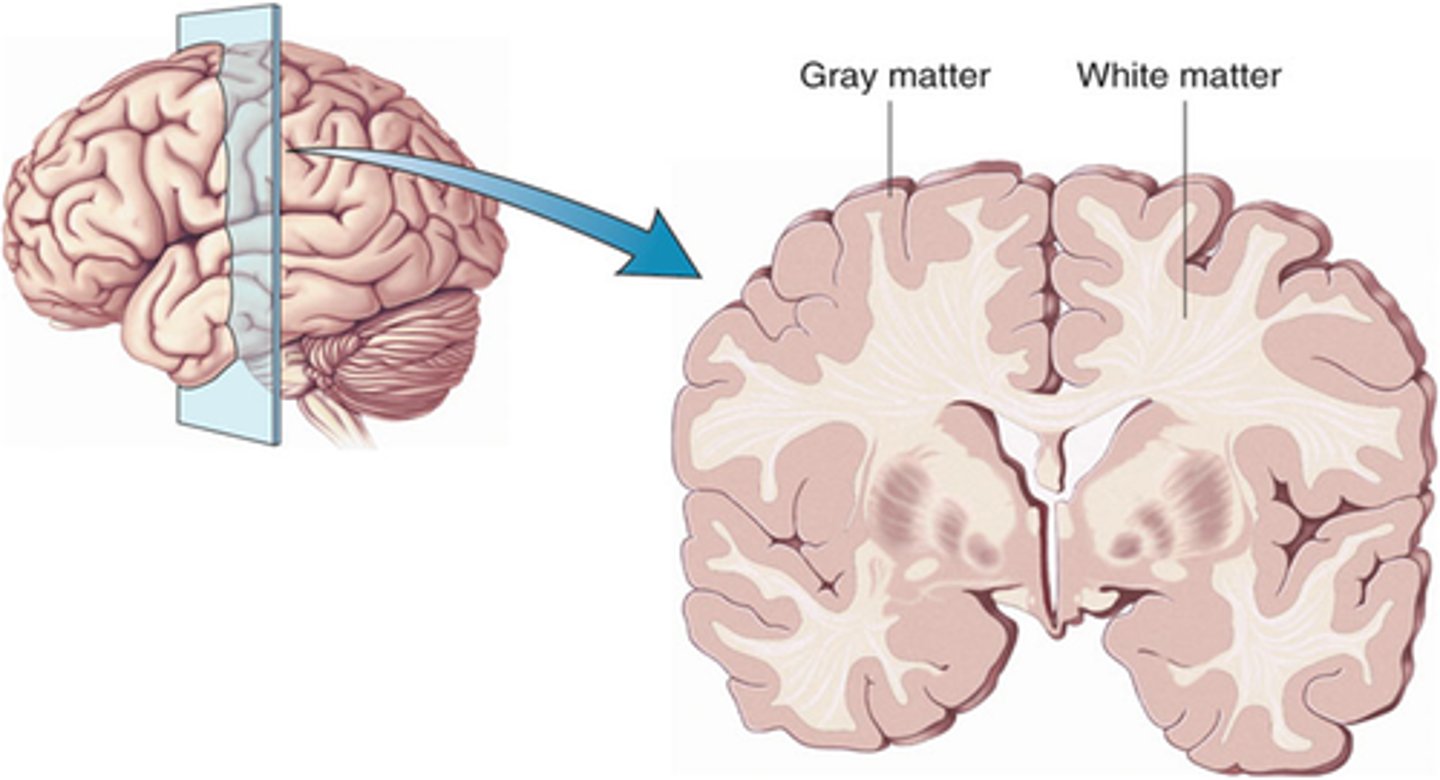
Cerebral Cortex
Gray matter,
Outer layer of cortex about 2-4mm thick and accounts for 40% of total brain mass,
Composed mostly of interneuronal cell bodies,
Highly convoluted,
Involved in higher brain functions (speech, memory, logic, etc.)
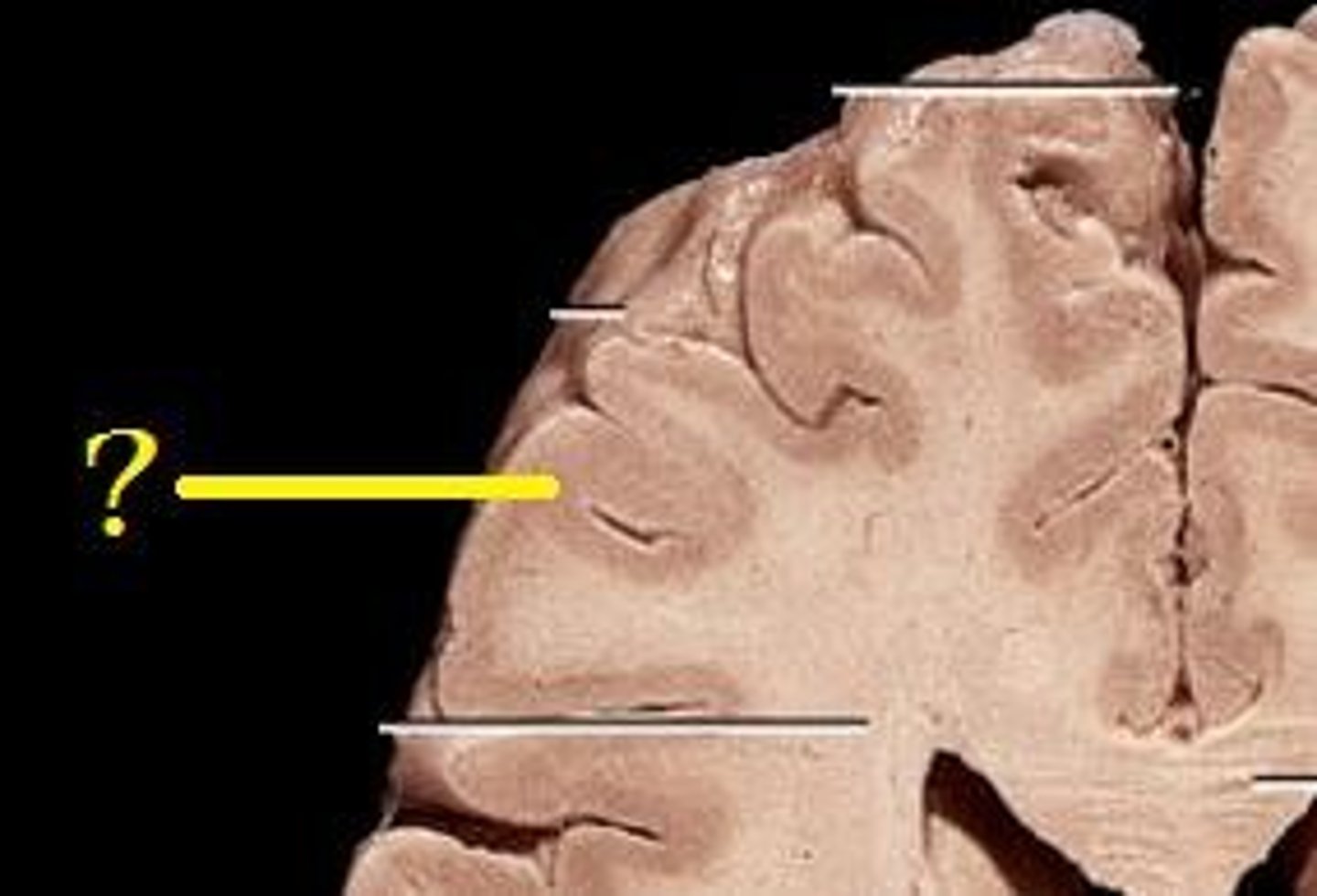
Higher brain functions
Speech, memory, logic, emotion, interpretation of sensory input, consciousness, etc.
Enables us to be aware of ourselves and our sensations, to communicate, remember, understand, and initiate voluntary movements.
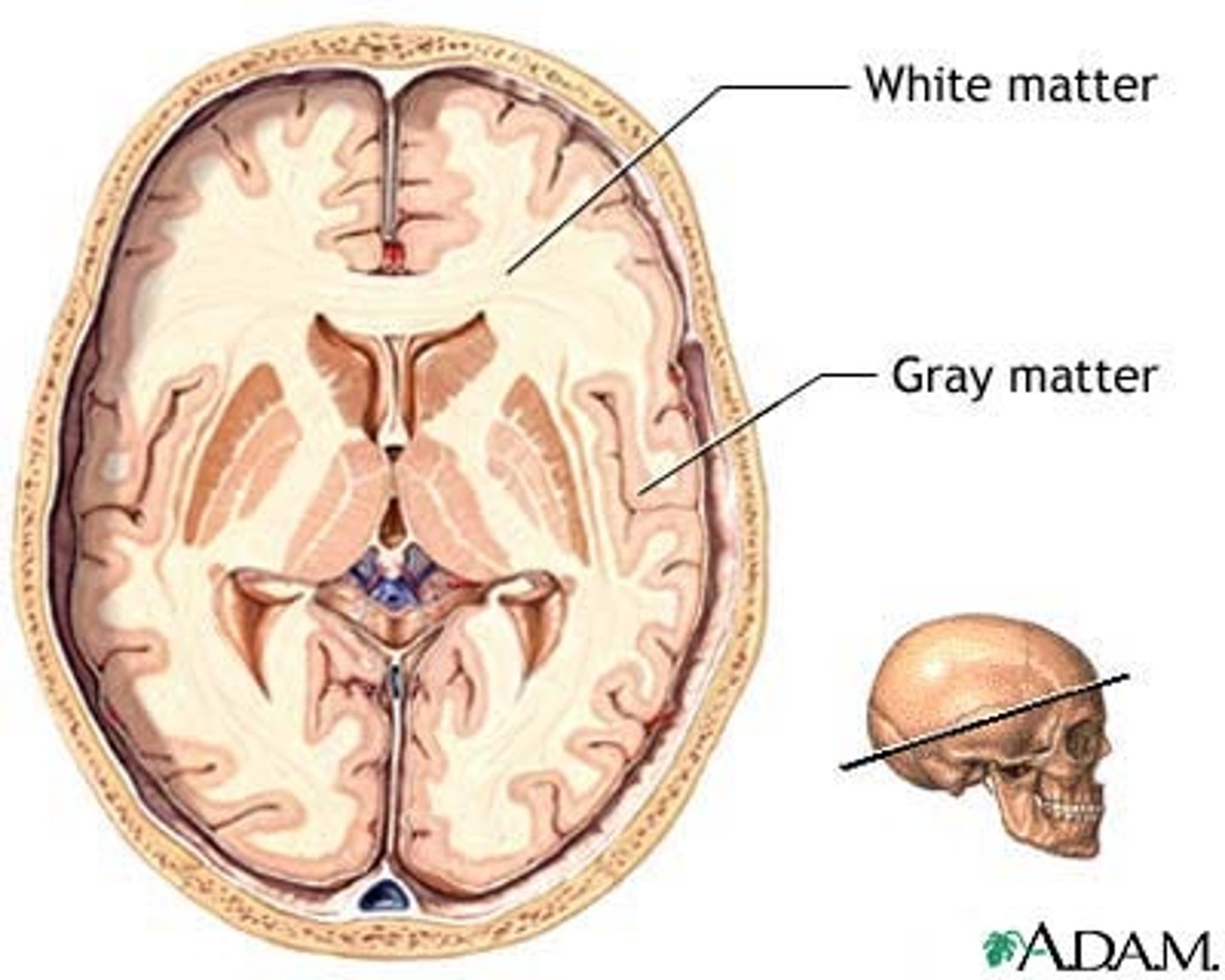
Cerebral Medulla
White matter,
Myelinated nerve tracts inside the gray matter that are responsible for communication between cerebral areas and between cerebral cortex and lower CNS centers,
Corpus callosum
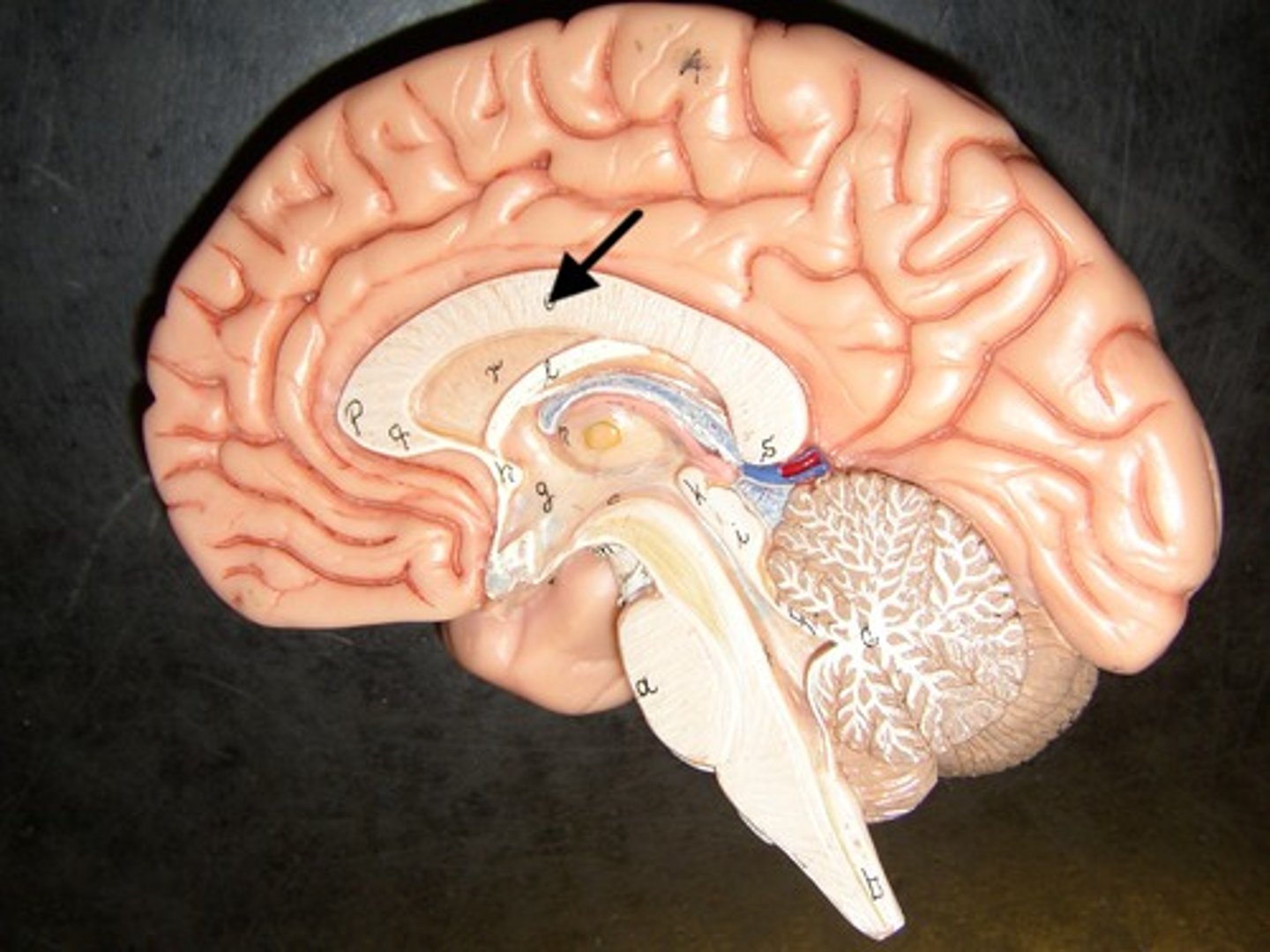
Corpus Callosum
Dense band of myelinated nerve tracts that allow communication between left and right cerebral hemispheres
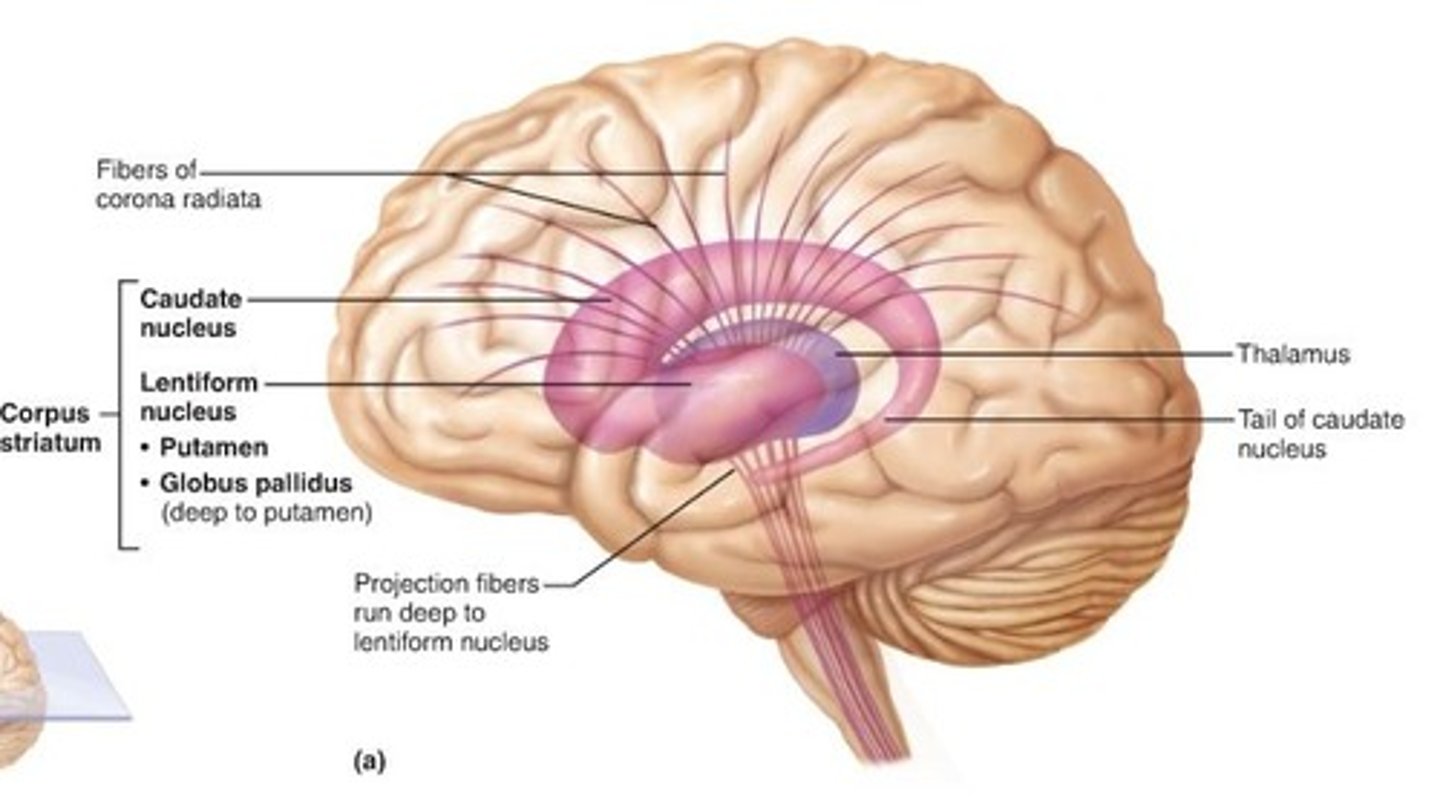
Basal Nuclei
Internal islands of gray matter dispersed bilaterally in the inferior cerebrum, diencephalon, and midbrain,
Not noted as distinct anatomical structures but functional areas,
Important in controlling and modifying motor functions
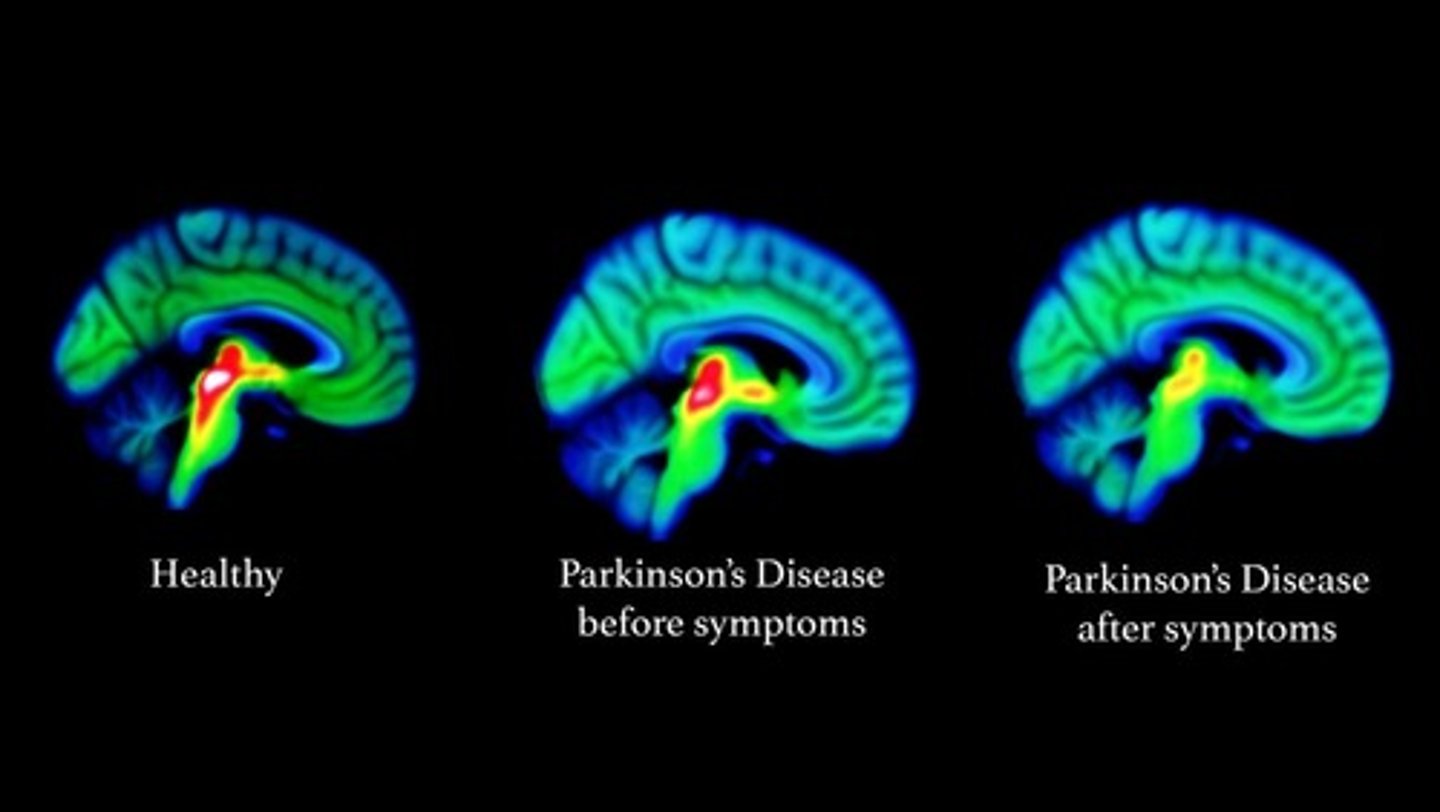
Basal Nuclei clinical: Parkinson's Disease
Results from degeneration of dopamine-releasing neurons, which causes the deprive basal nuclei they target to become overactive and produce the well-known symptoms of tremors at rest,
Cause still unknown, but may be environmental
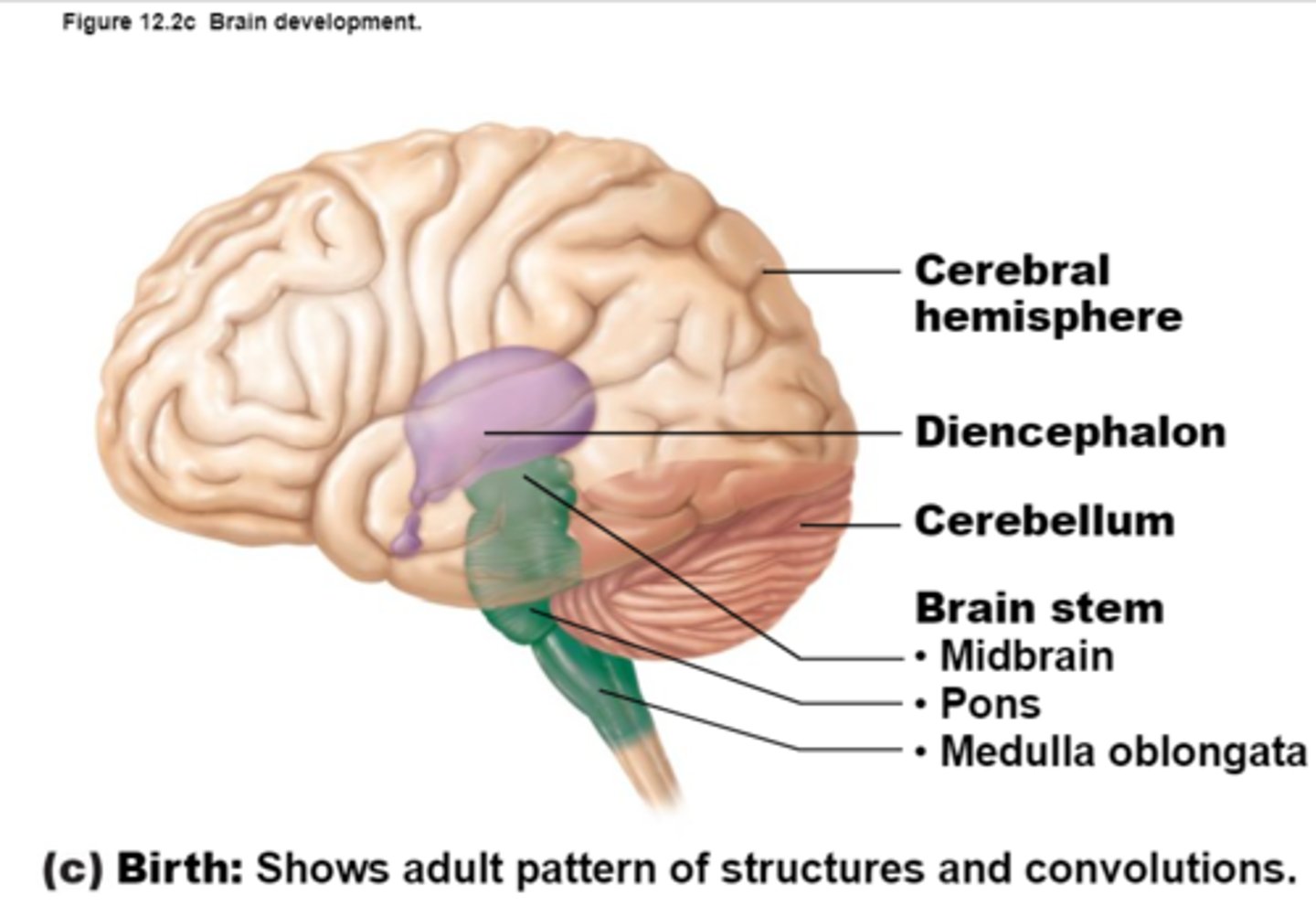
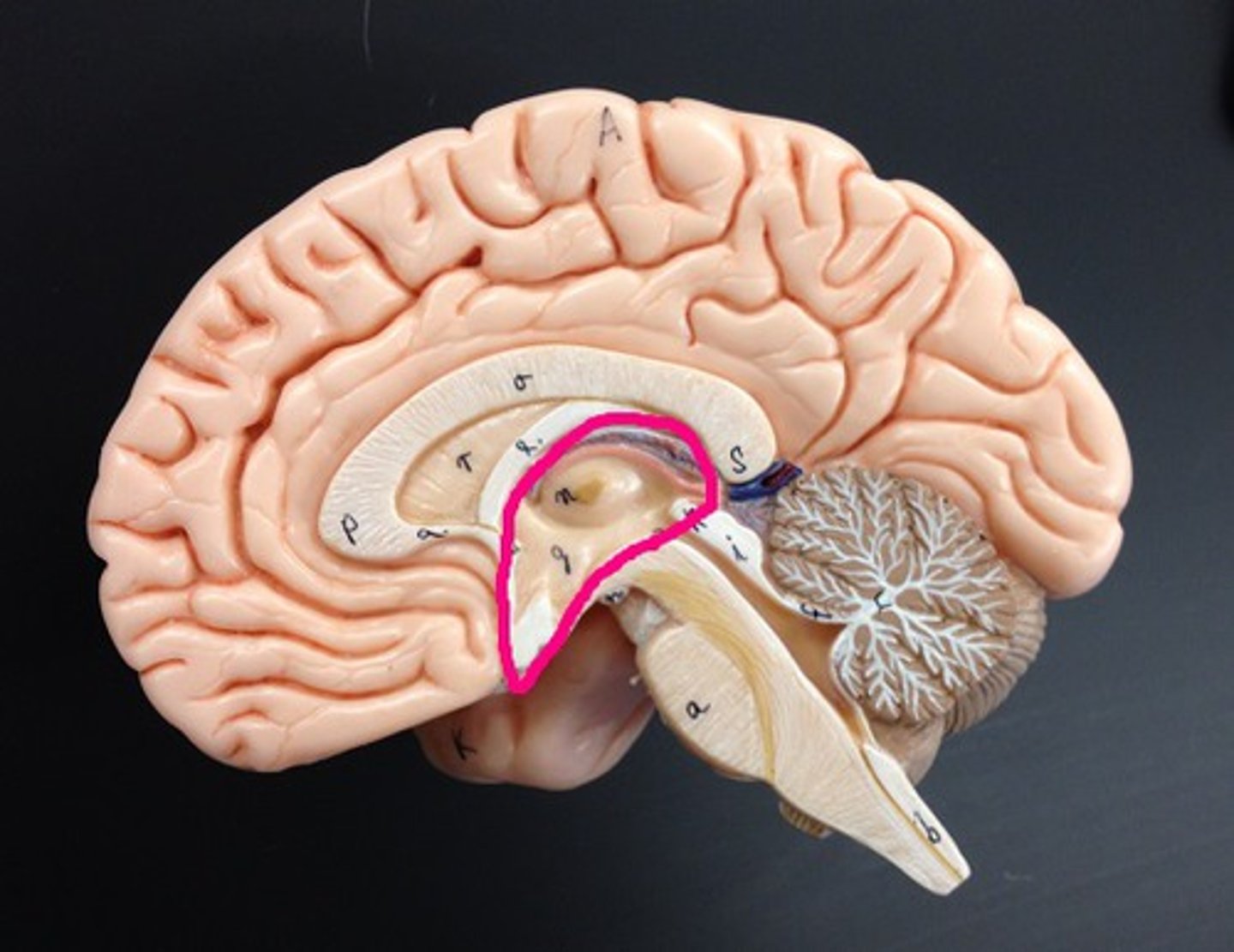
Diencephalon
Sits on top of the brain stem,
Enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres,
Made up of 3 parts: the Thalamus, Hypothalamus, and Epithalamus
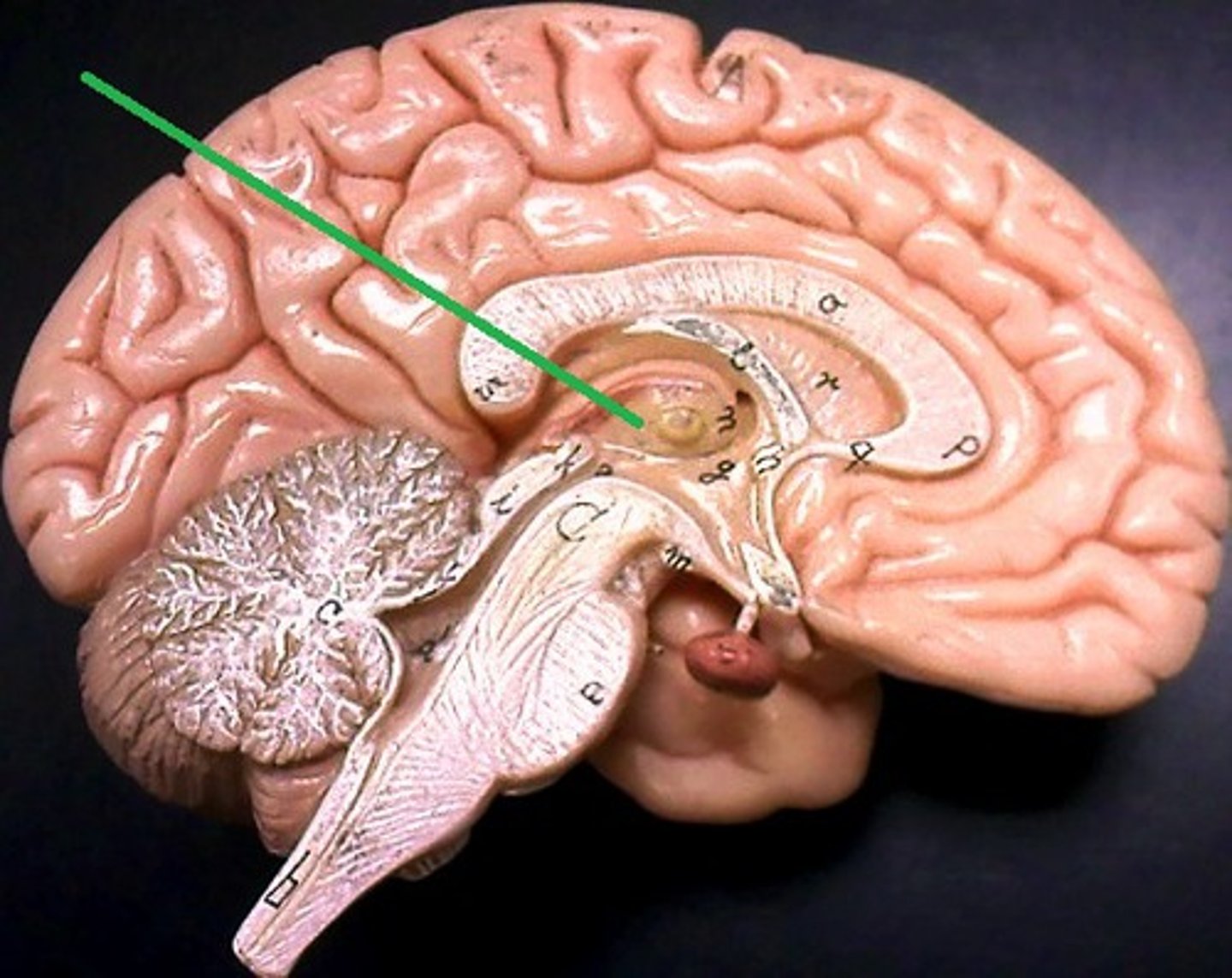
Thalamus
Bilateral egg-shaped nuclei, which forms superolateral walls 3rd ventricle,
Relay station for information coming into cerebral cortex:
-Will sort and edit the info
-Also provides a crude recognition of sensation as pleasant or unpleasant before it sends info on to cortex where specific stimulus localization and discrimination still occur
Hypothalamus
Located under thalamus where it caps the brain stem and forms inferolateral walls of 3rd ventricle,
Main visceral (involuntary) control center of body is vitally important to overall body homeostasis (few tissues in body escape its influence),
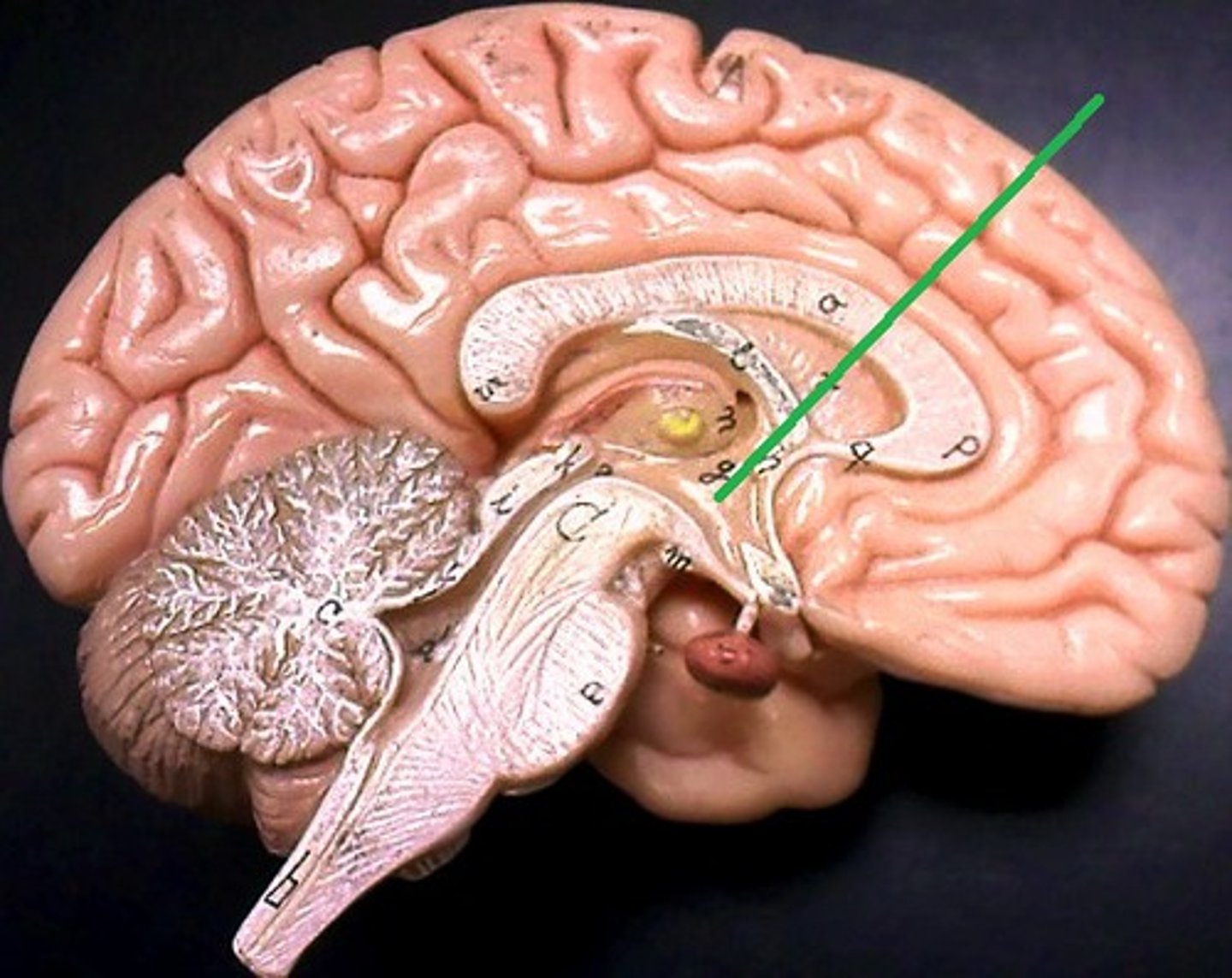
hypothalamus chief homeostasis controls
1) Important autonomic (ANS) control center,
2) Center for emotional response (limbic system),
3)Regulates Body tempt., food intake, water balance and thirst, and sleep-wake cycle
4) Control of endocrine system functioning: pituitary gland
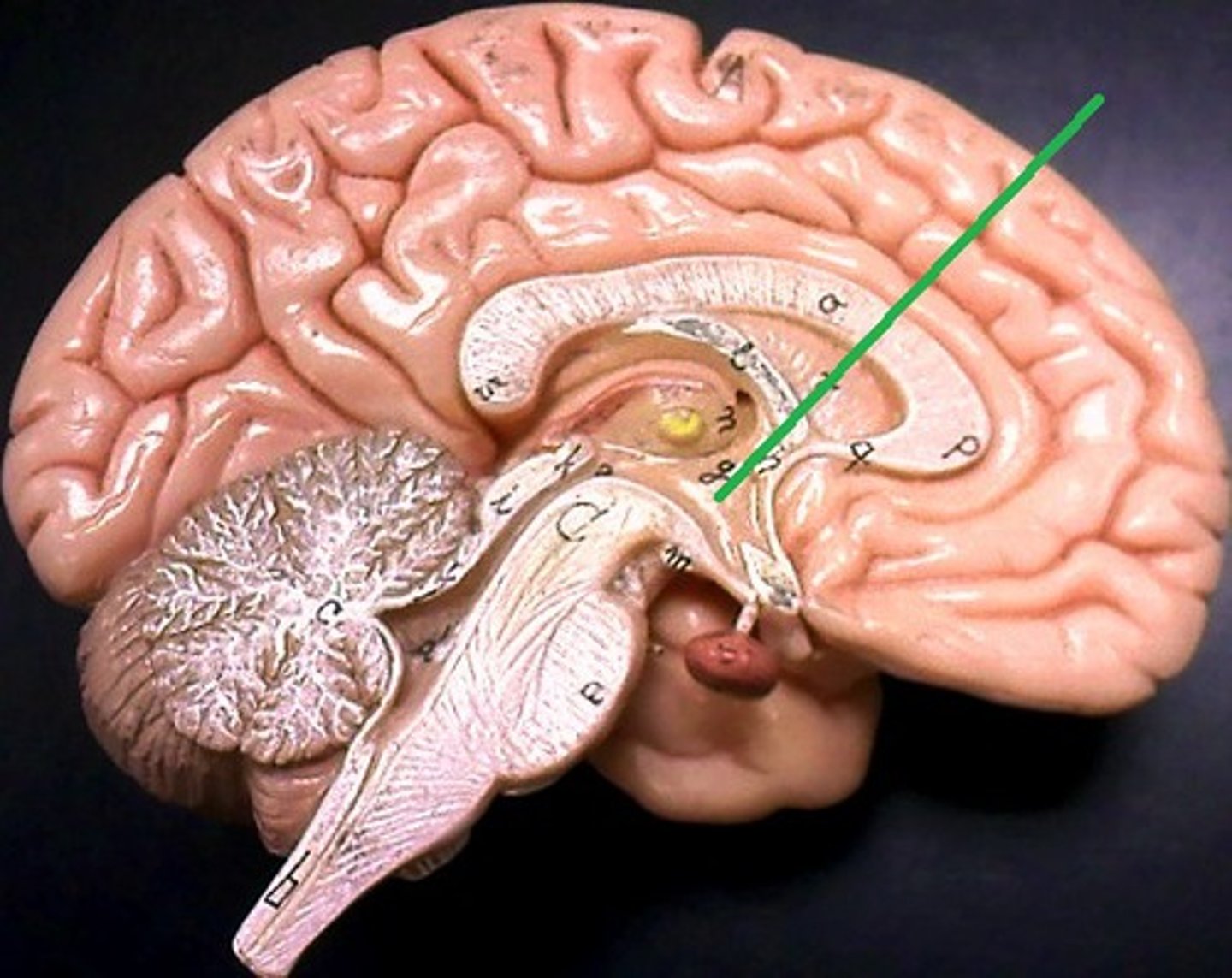
Pituitary gland
Is attached to the hypothalamus and the hypothalamus is therefore indirectly influences many body functions by sending signals through to regulate its secretion of hormones
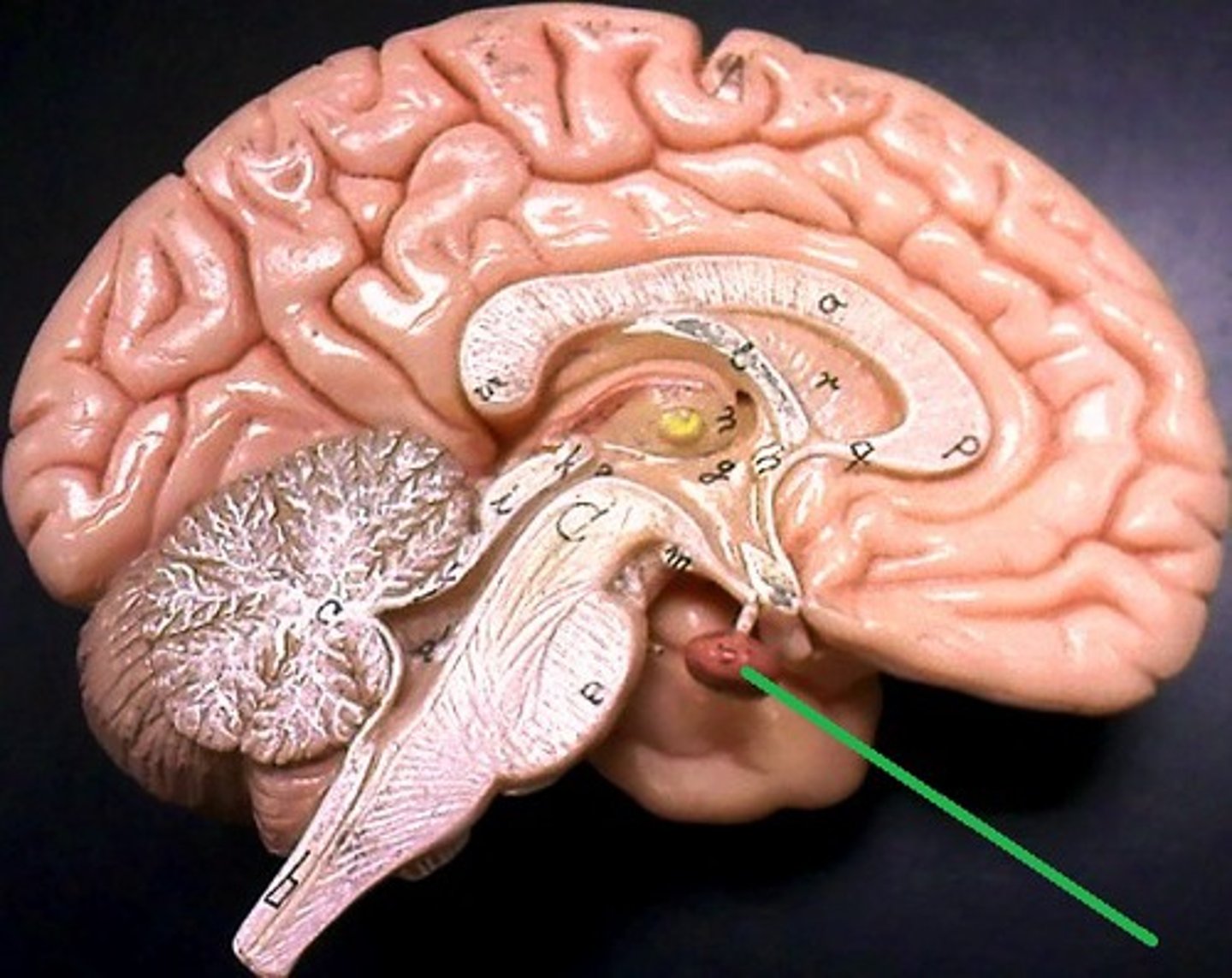
Epithalamus
Forms the roof of the 3rd ventricle,
Houses the pineal gland or body (an endocrine gland) (Melatonin production: sleep/wake cycle),
Includes the choroid plexus (forms cerebrospinal fluid- CSF)
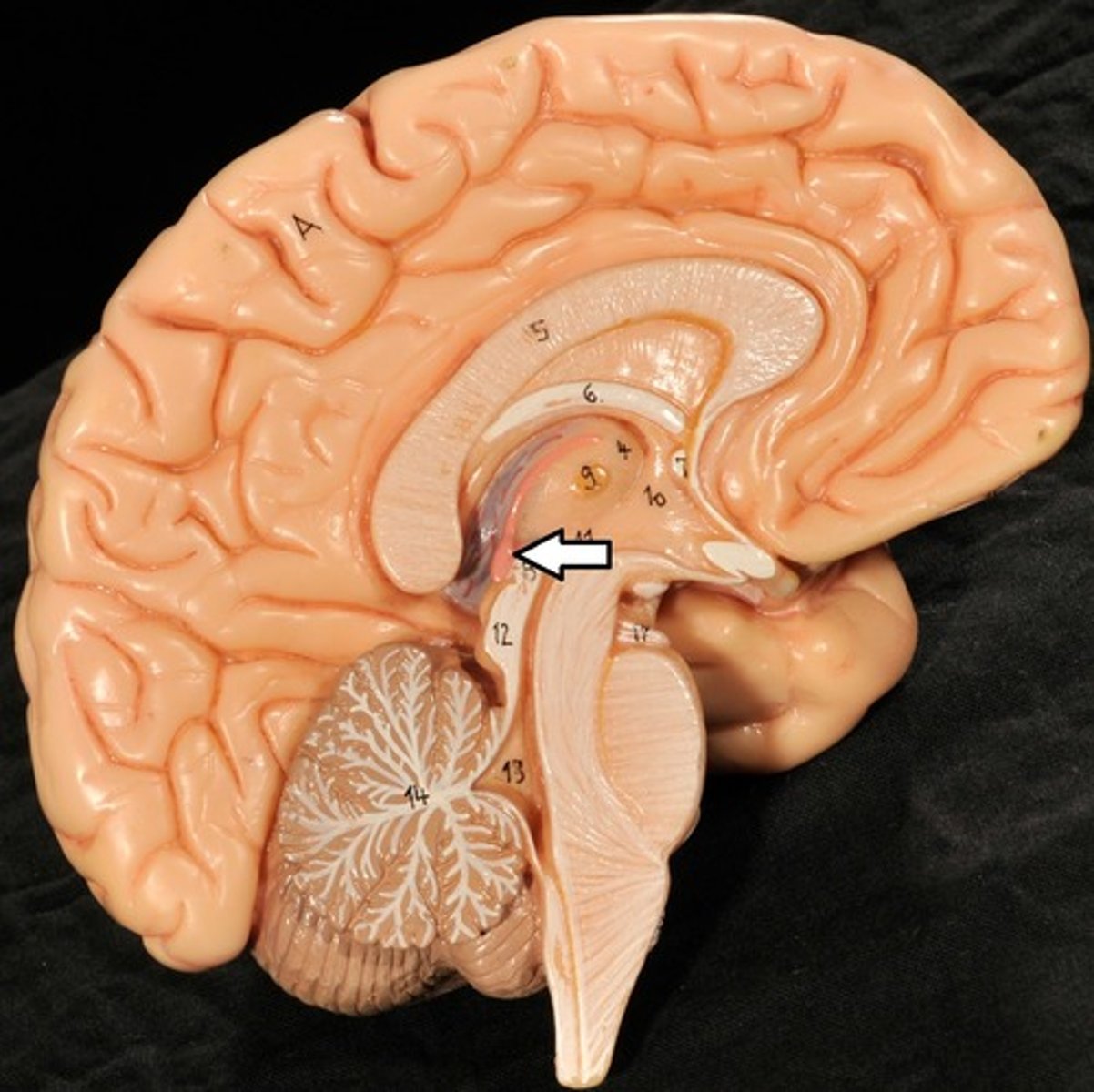
Choroid Plexus
Forms Cerebrospinal Fluid
Choroid Plexus
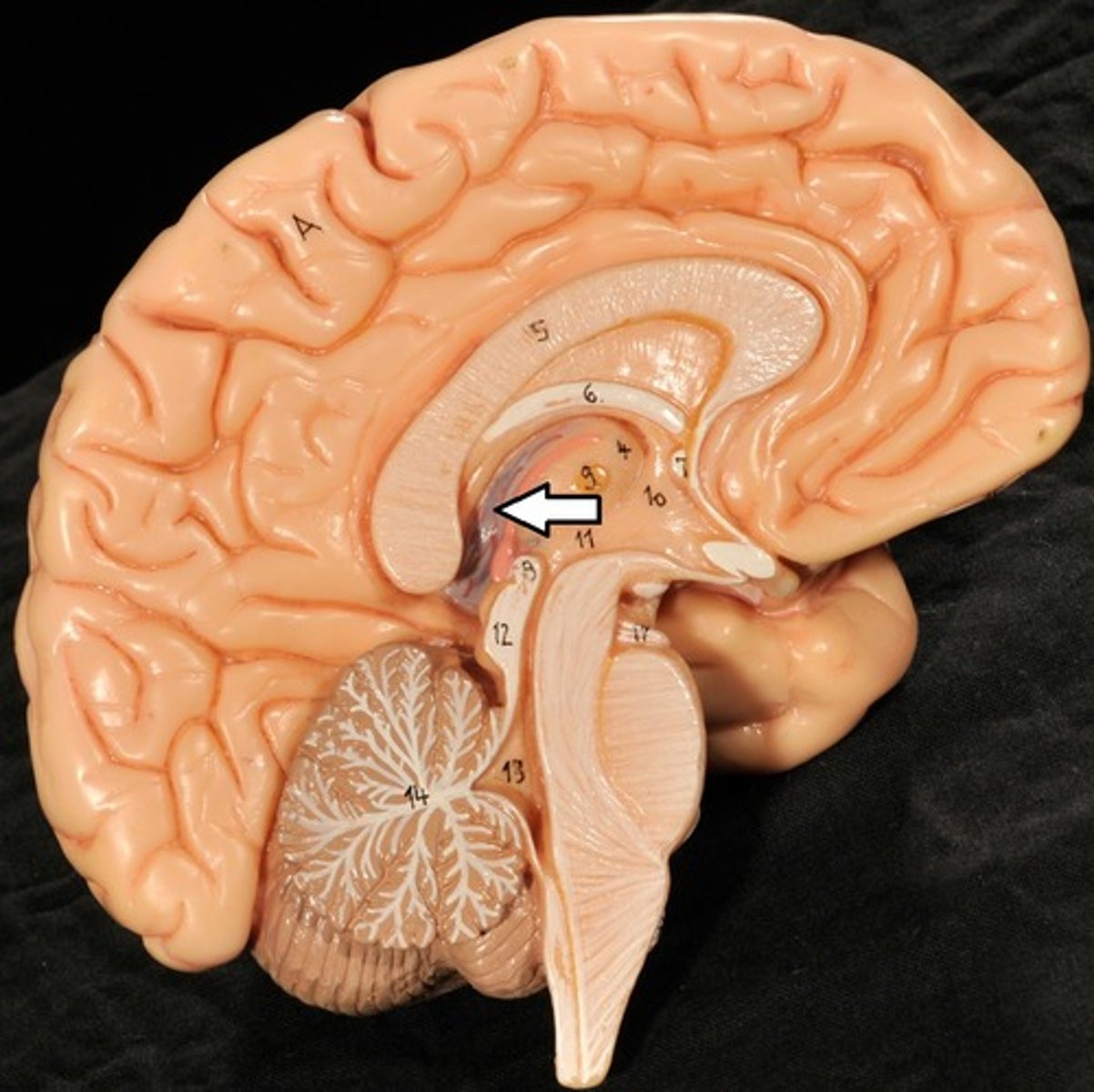
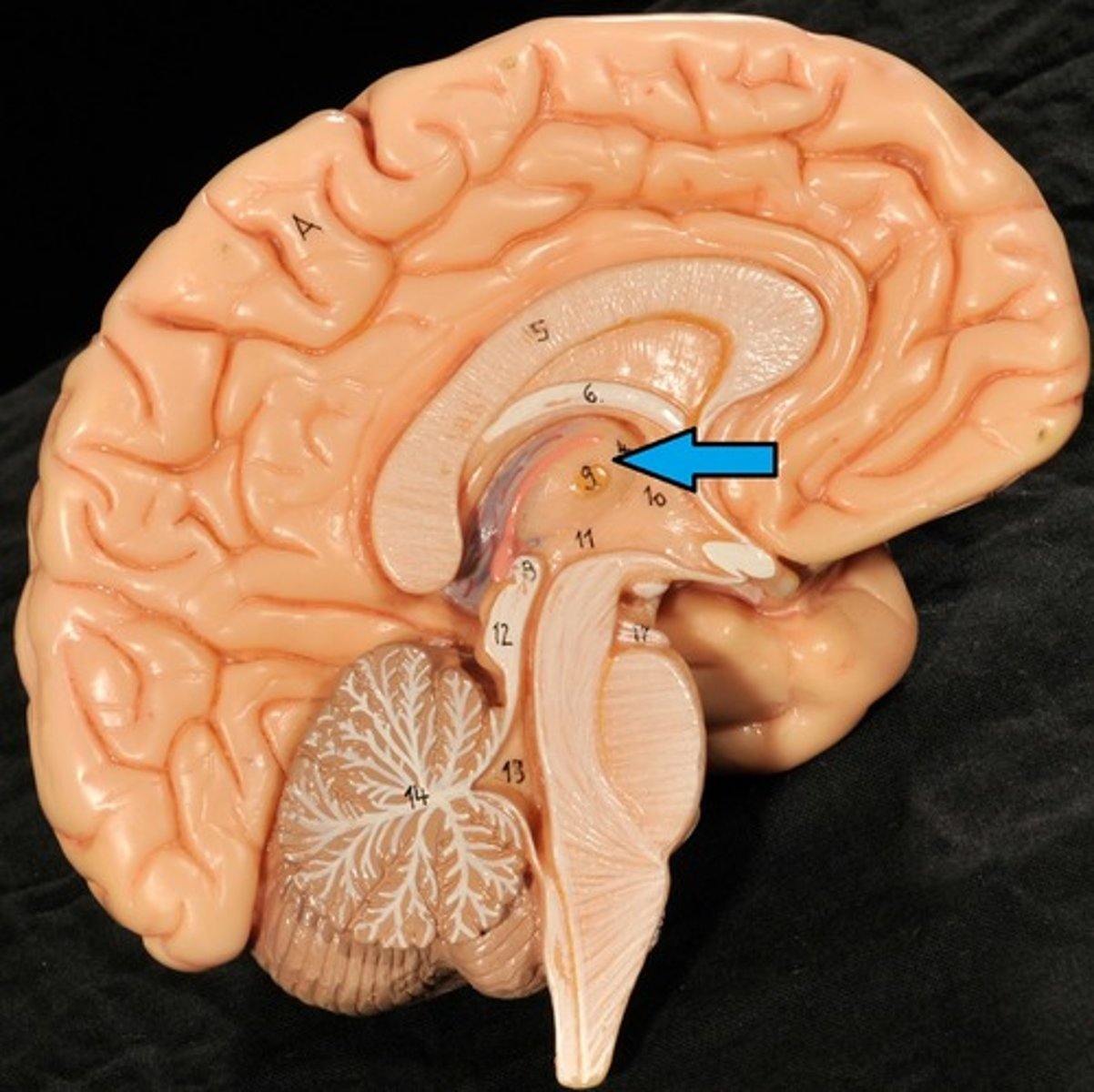
Pineal Gland
Melatonin Production (sleep/wake cycle)
3rd Ventricle
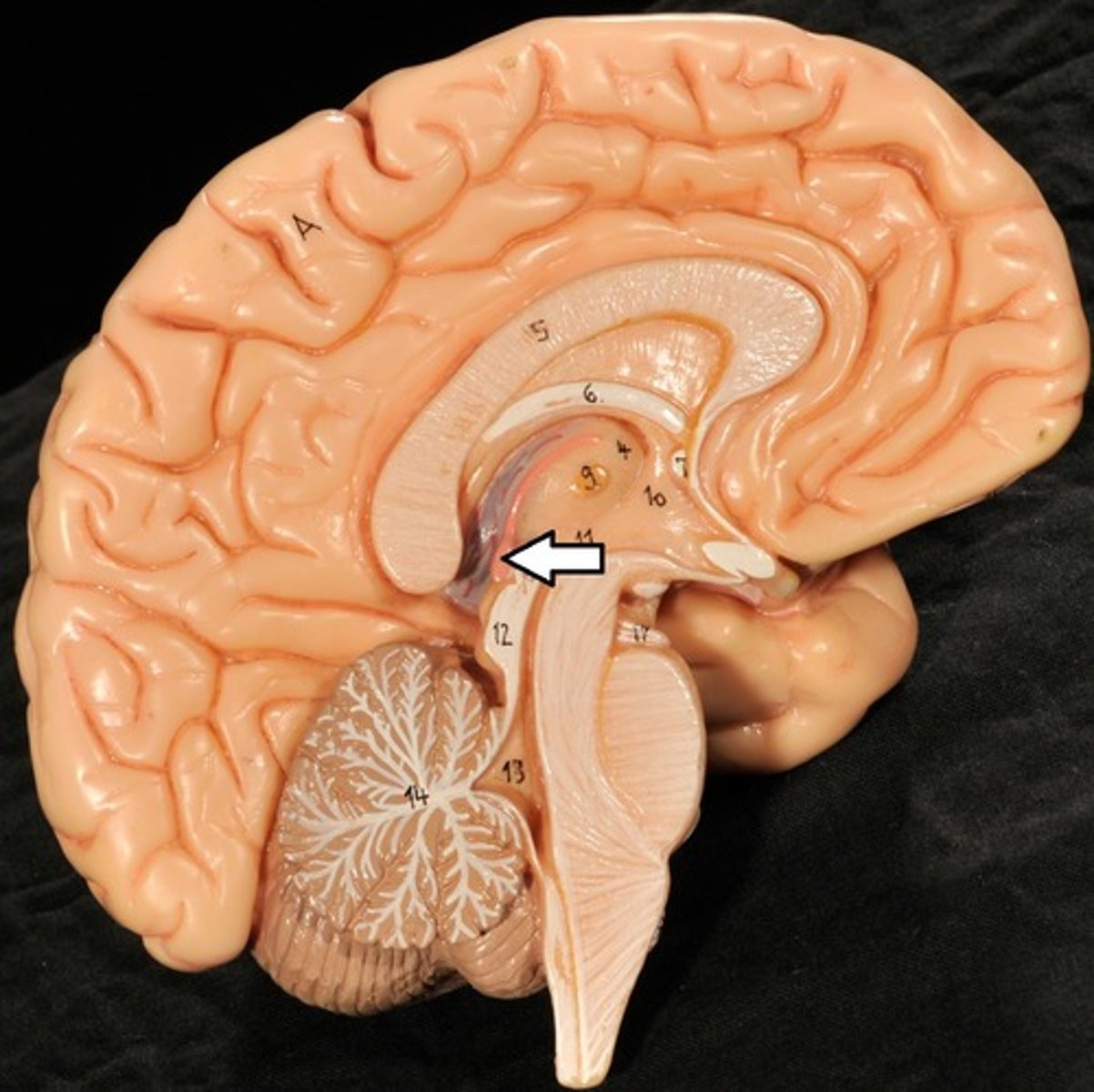
Brain Stem
1) Attaches to the spinal cord with no change in structure.
2) Only 2.5% of total brain mass but integrates many vital function.
3) Histologically similar to spinal cord (gray matter surrounded by white matter) but has nuclei of gray matter embedded in the white matter (which is not seen in cord).
4) Provides pathway for fiber tracts running between higher and lower neural centers and associated with 10 out of 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
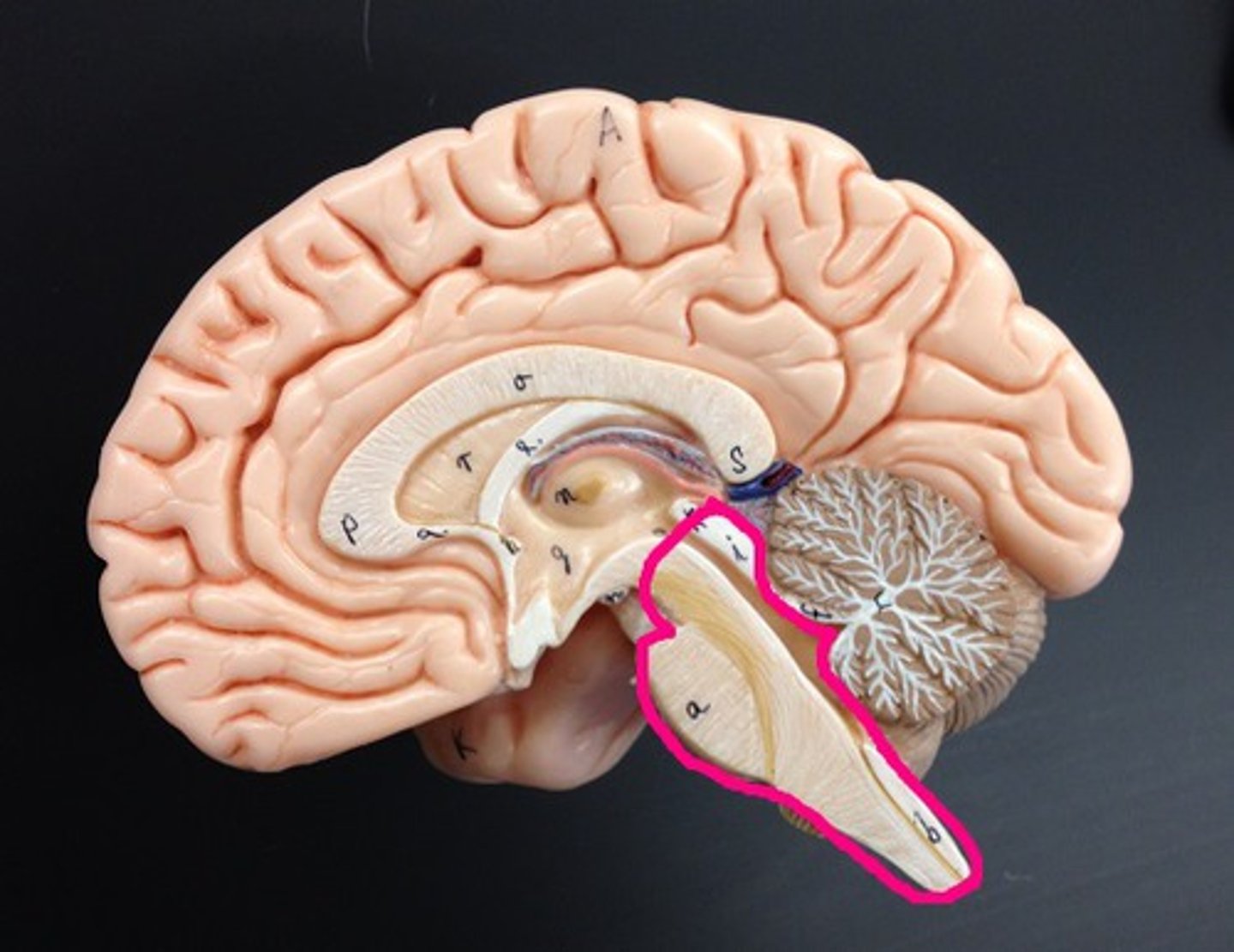
what can happen with Minor damage in brain stem?
Minor damage to the brain stem can result in death where as higher integration areas like the cerebellum can withstand major damage.
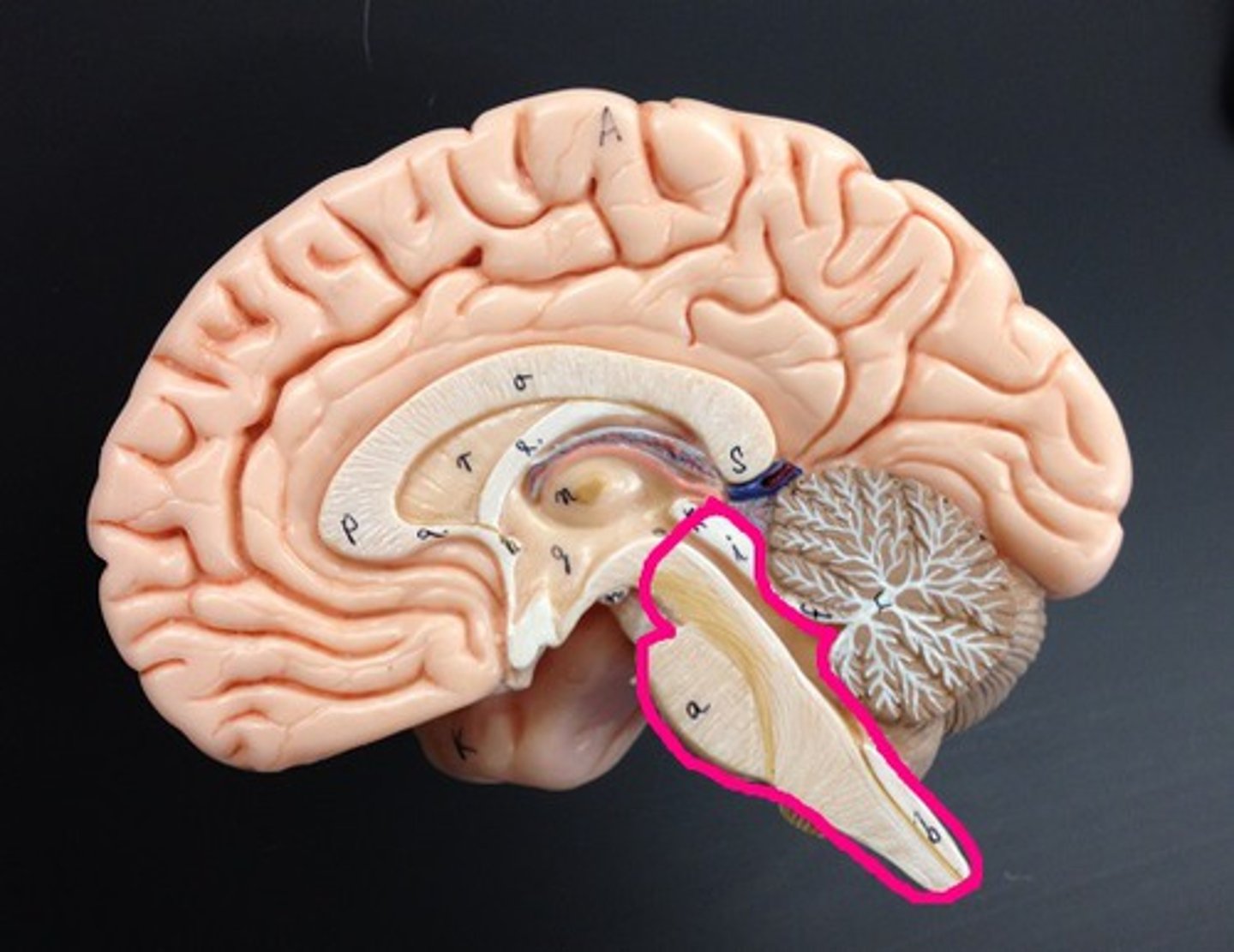
Parts of the Brain Stem
Midbrain,
Pons,
Medulla Oblongata
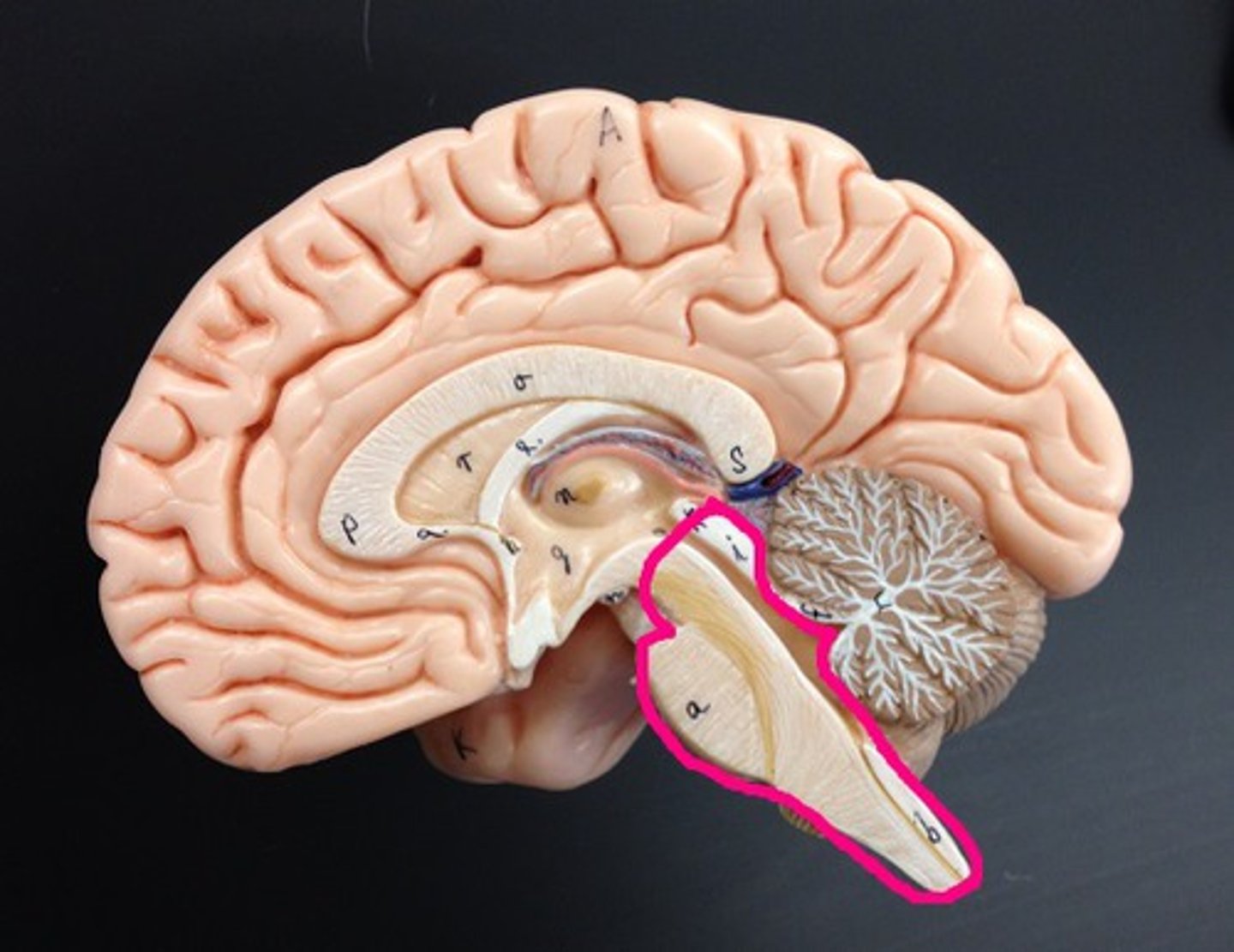
Midbrain
Composed mostly of tracts of nerves fibers
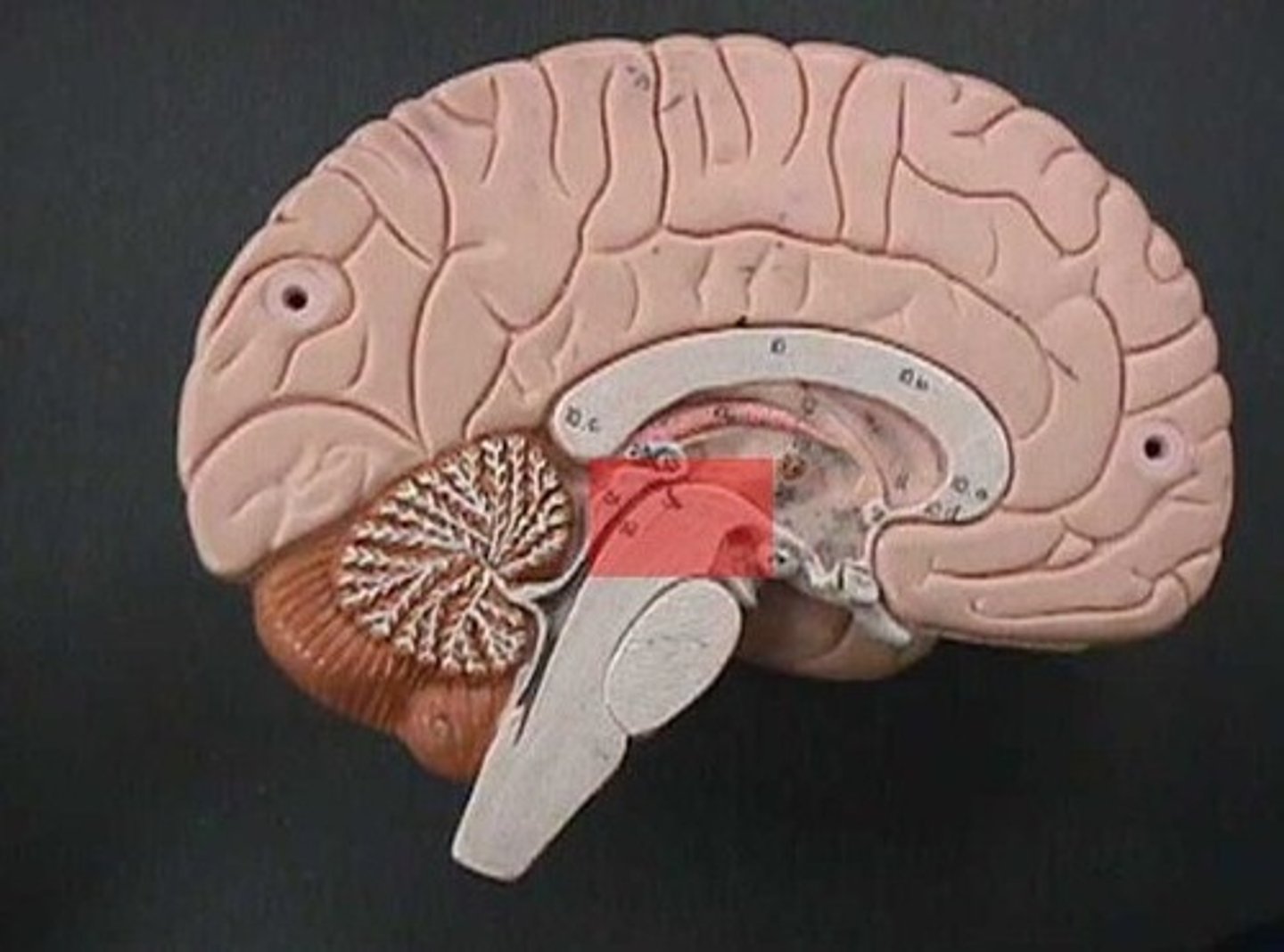
Cerebral Aqueduct

Pons
Includes nuclei involved in the control of breathing
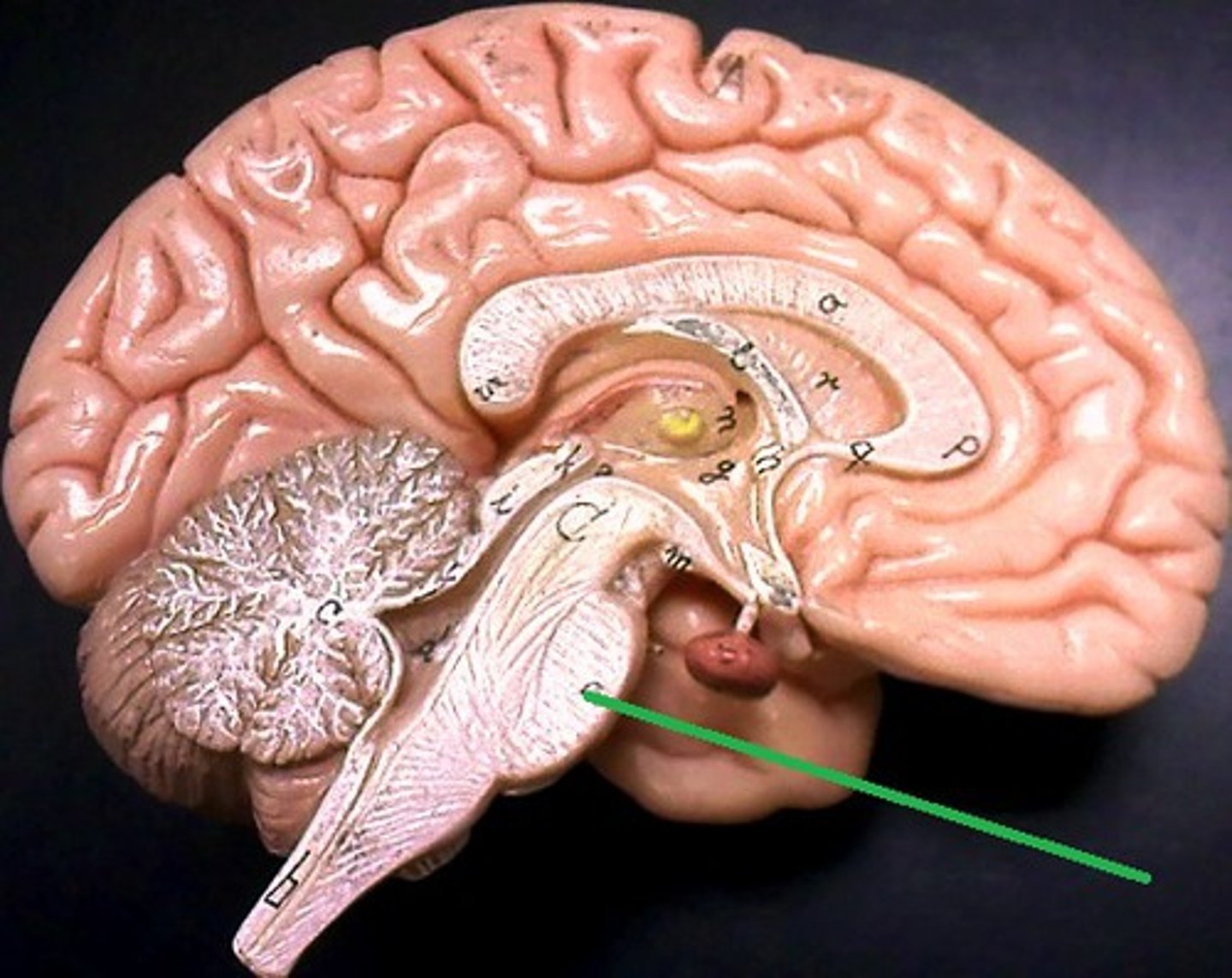
Medulla Oblongata
1) Most inferior part of the brain steam.
2) Merges into spinal cord.
3) Includes important ascending & descending nerve tracts.
4) Autonomic control center for heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, coughing, sneezing, vomiting
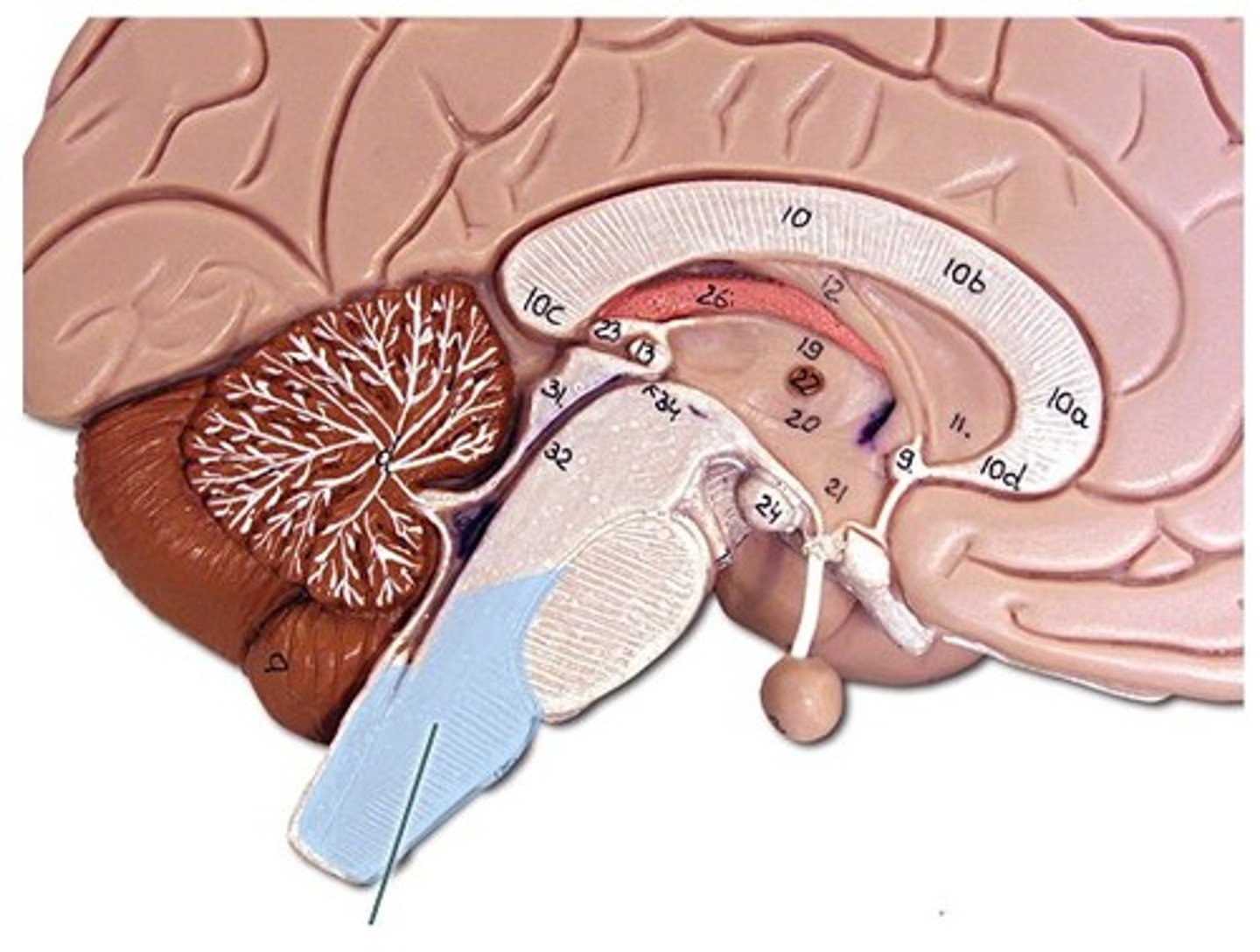
Cerebellum
Two hemispheres with convoluted surfaces,
Accounts for ~11% of total brain mass,
Provides involuntary coordination of body movements,
Also plays a role in posture and equilibrium
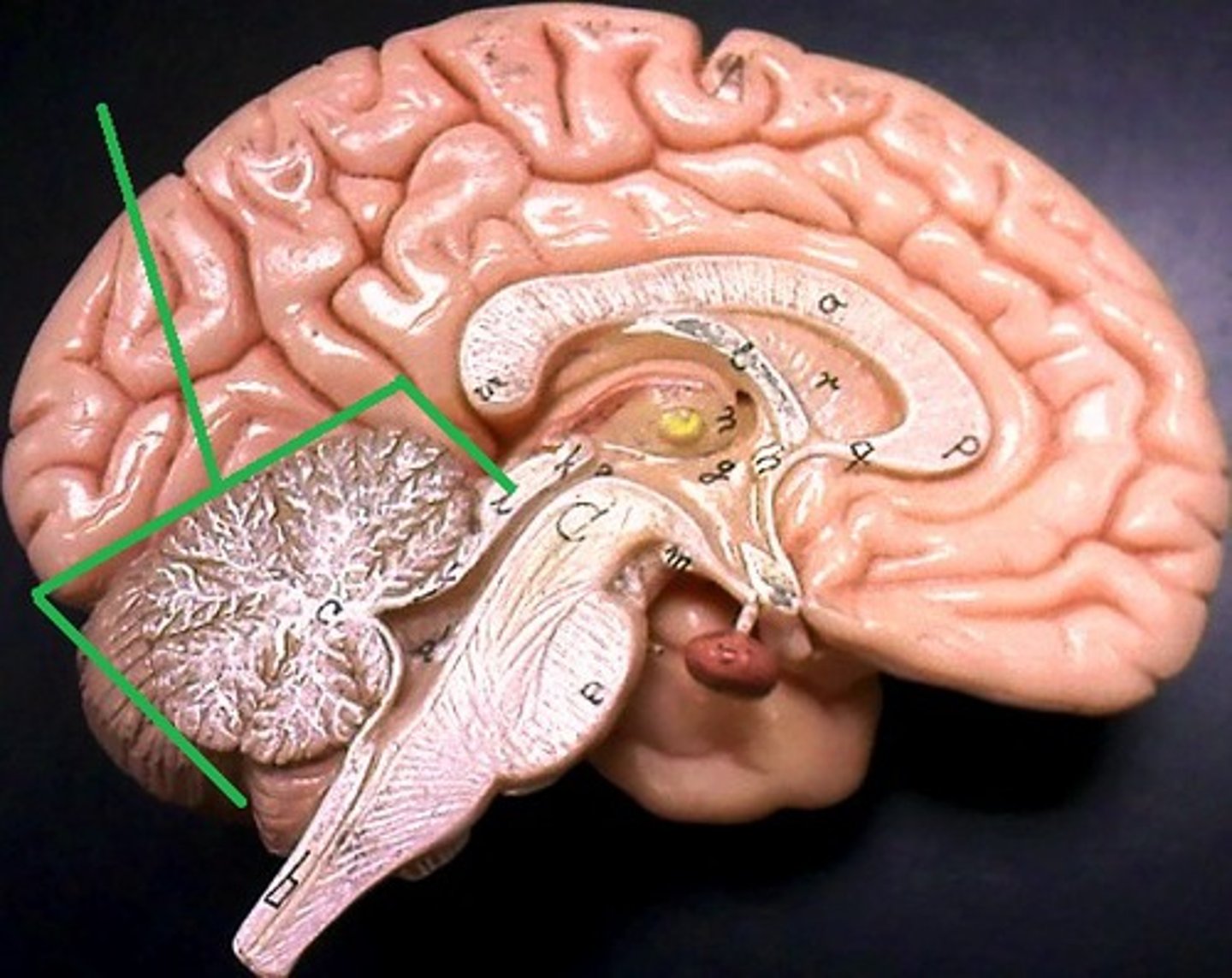
Cerebellum involuntary coordination
1) Receives input from motor cortex, brain stem (relays info from cortex), and sensory receptors to provide precise timing and appropriate patterns of skeletal muscle contraction,
2) Results in smooth, coordinated movements and agility (driving, walking, typing, etc.),
3) Completely subconscious (have no awareness of its functioning)
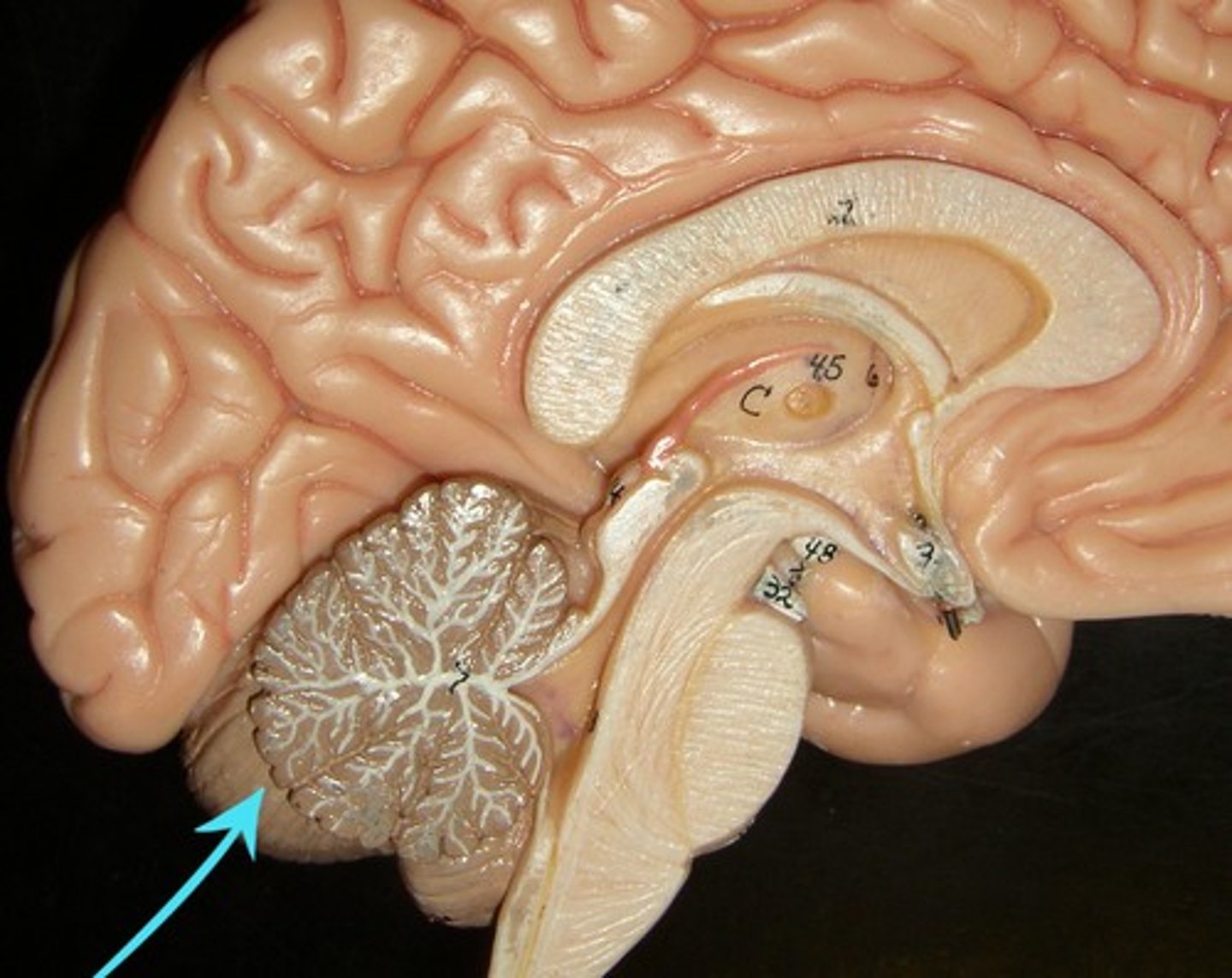
4th Ventricle
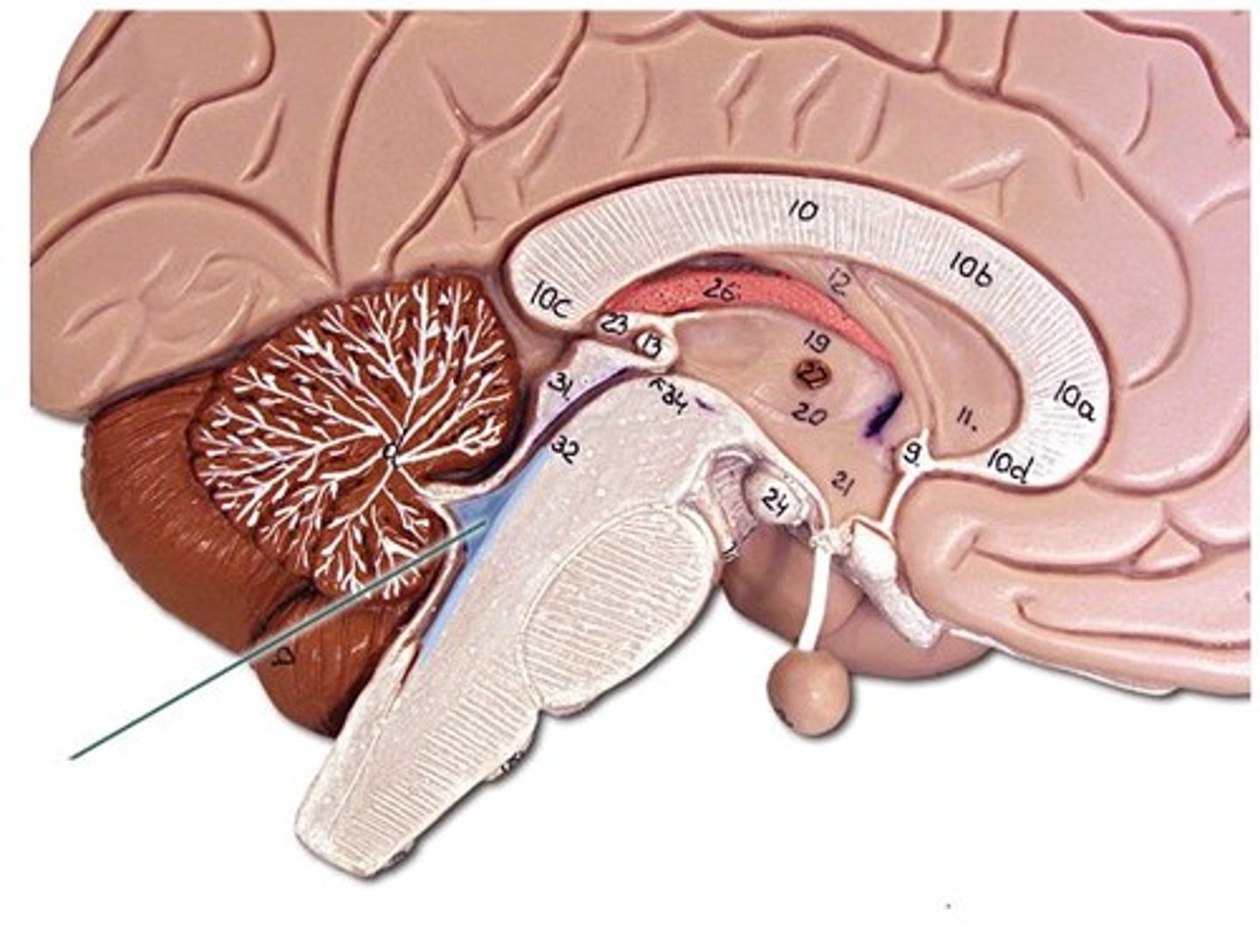
Protection of the CNS
1) scalp and skin
2) skull and vertebral column
3) meninges
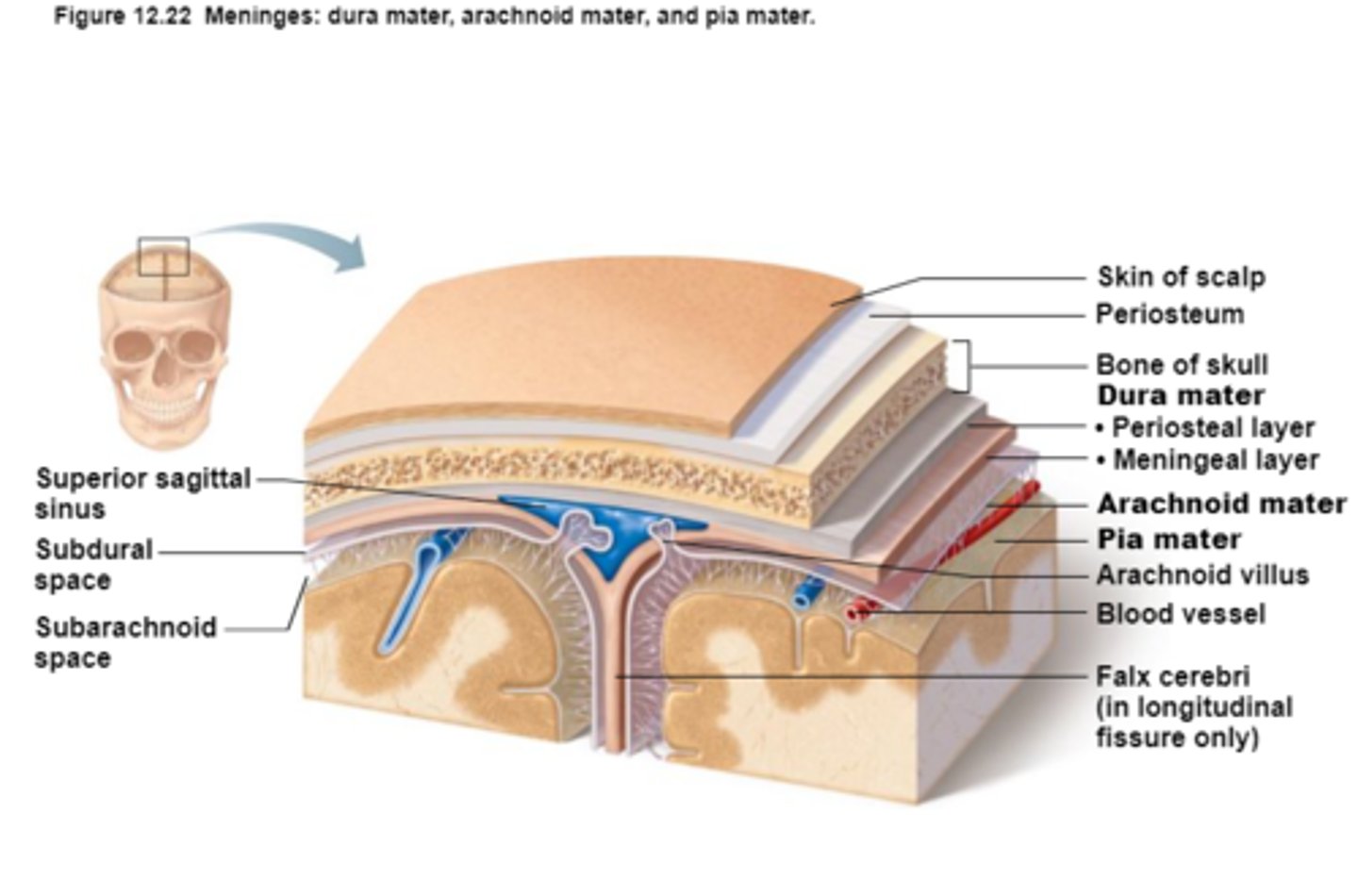
Meninges
Connective tissue membranes that lie just external to the CNS organs that:
-Cover and protect the CNS
-Protect blood vessels and enclose venous sinuses
-Contain cerebrospinal fluid
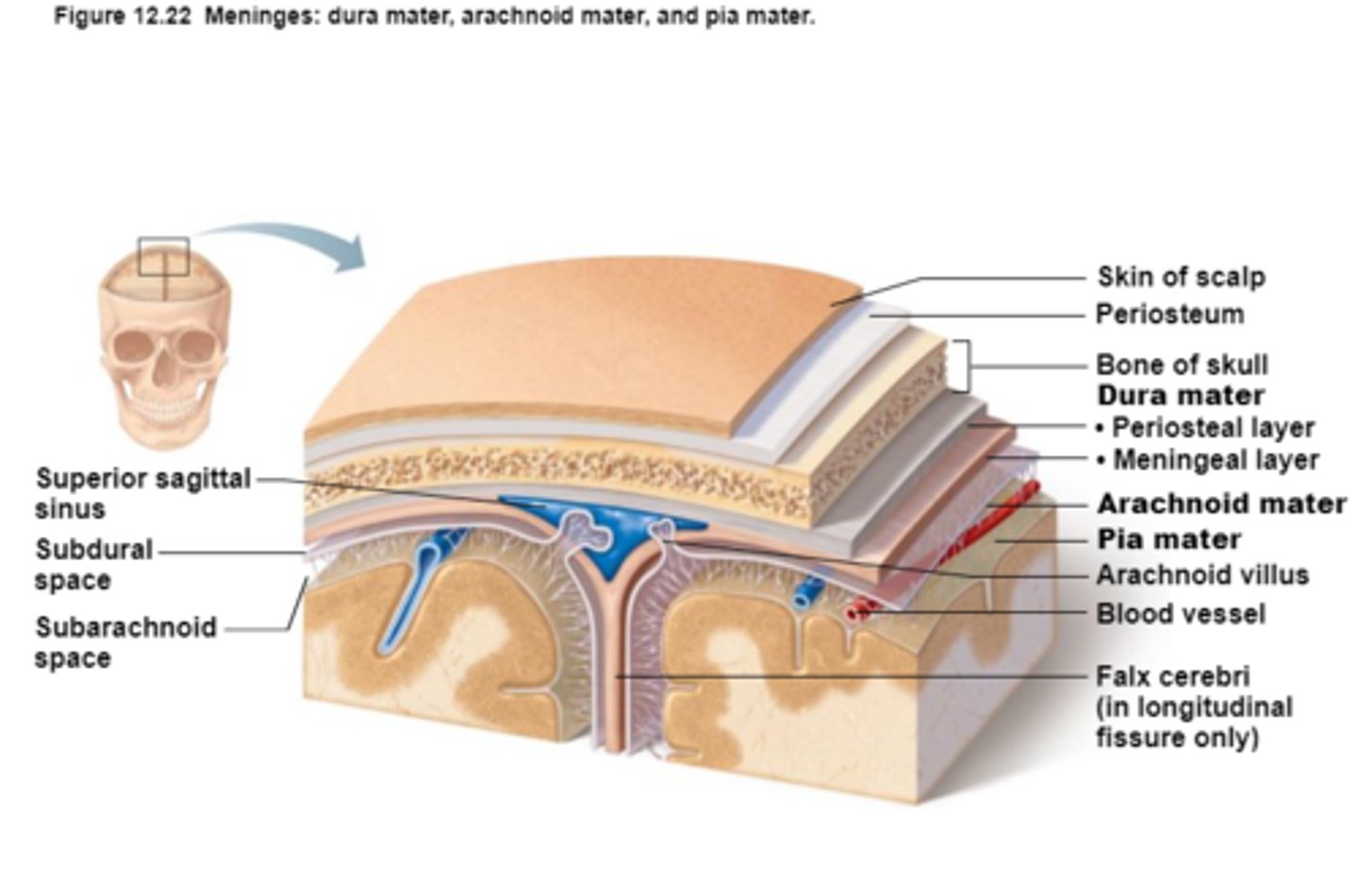
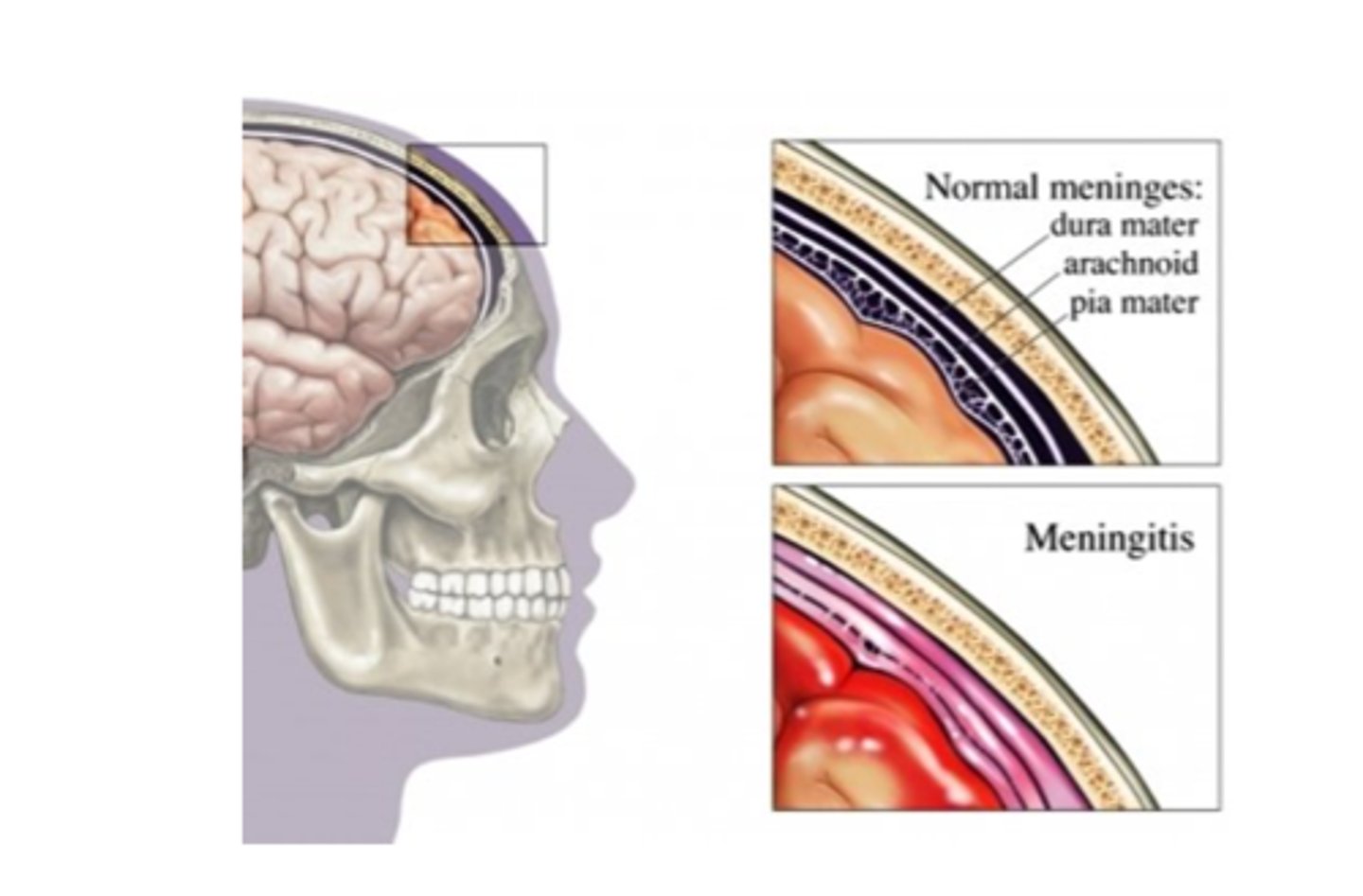
3 Layers (external to internal) of Meninges
Dura Mater,
Arachnoid Mater,
Pia Mater
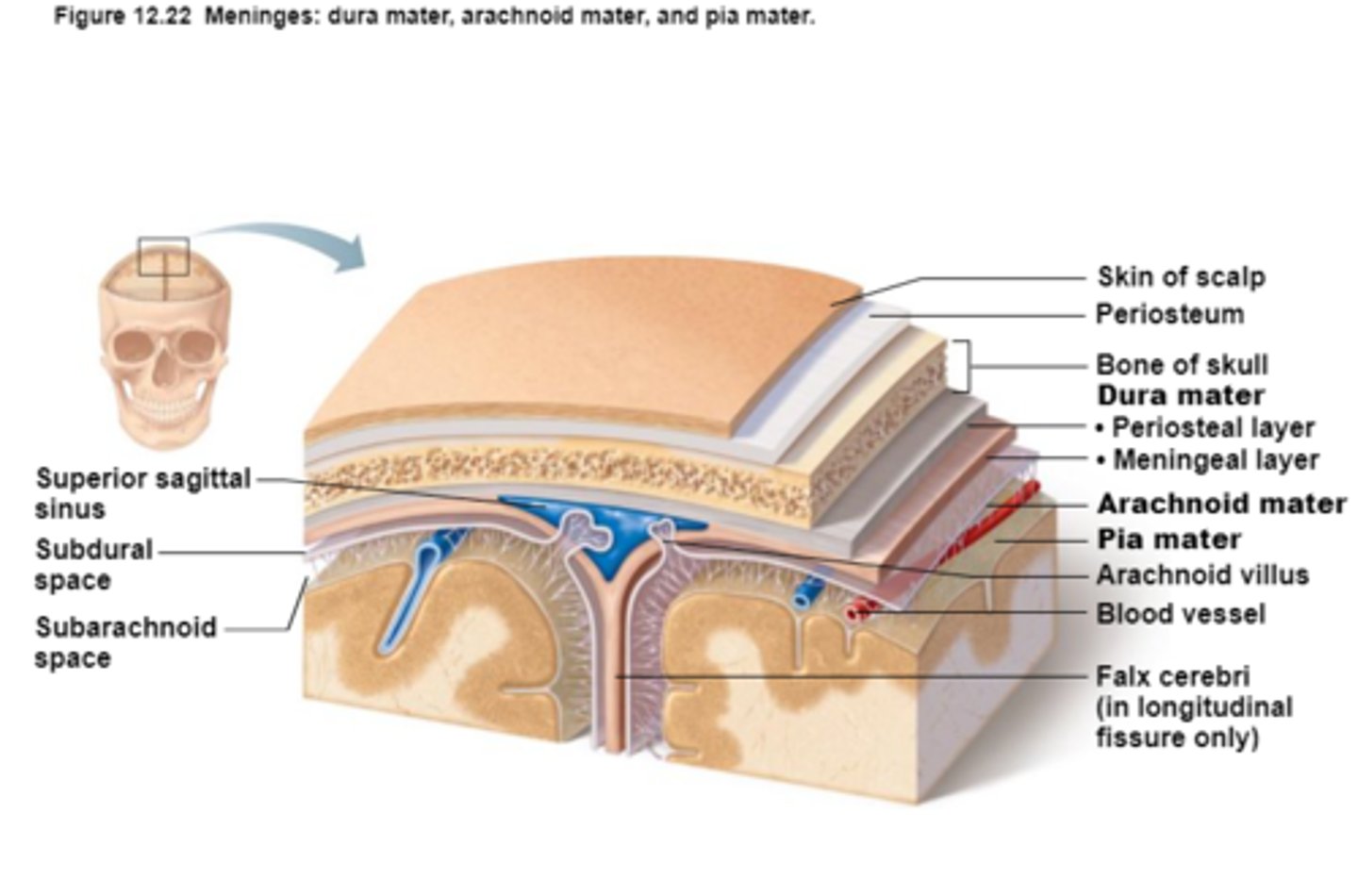
Dura Mater
First layer of Meninges,
Has layers that can separate to form dural sinuses:
-Periosteum
-Meningeal layer
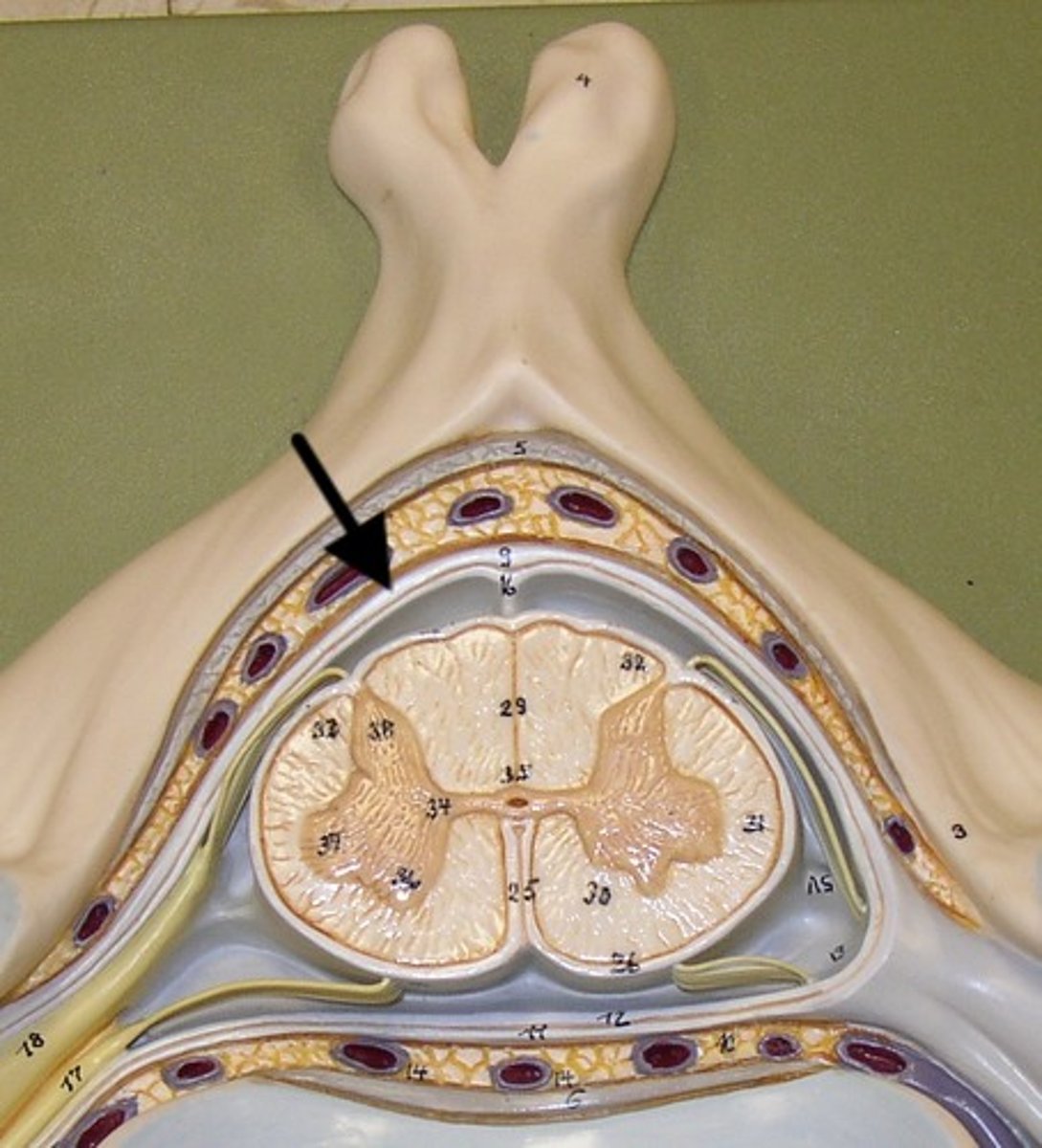
Arachnoid Mater
Second layer of the Meninges,
Subarachnoid space with cerebrospinal fluid
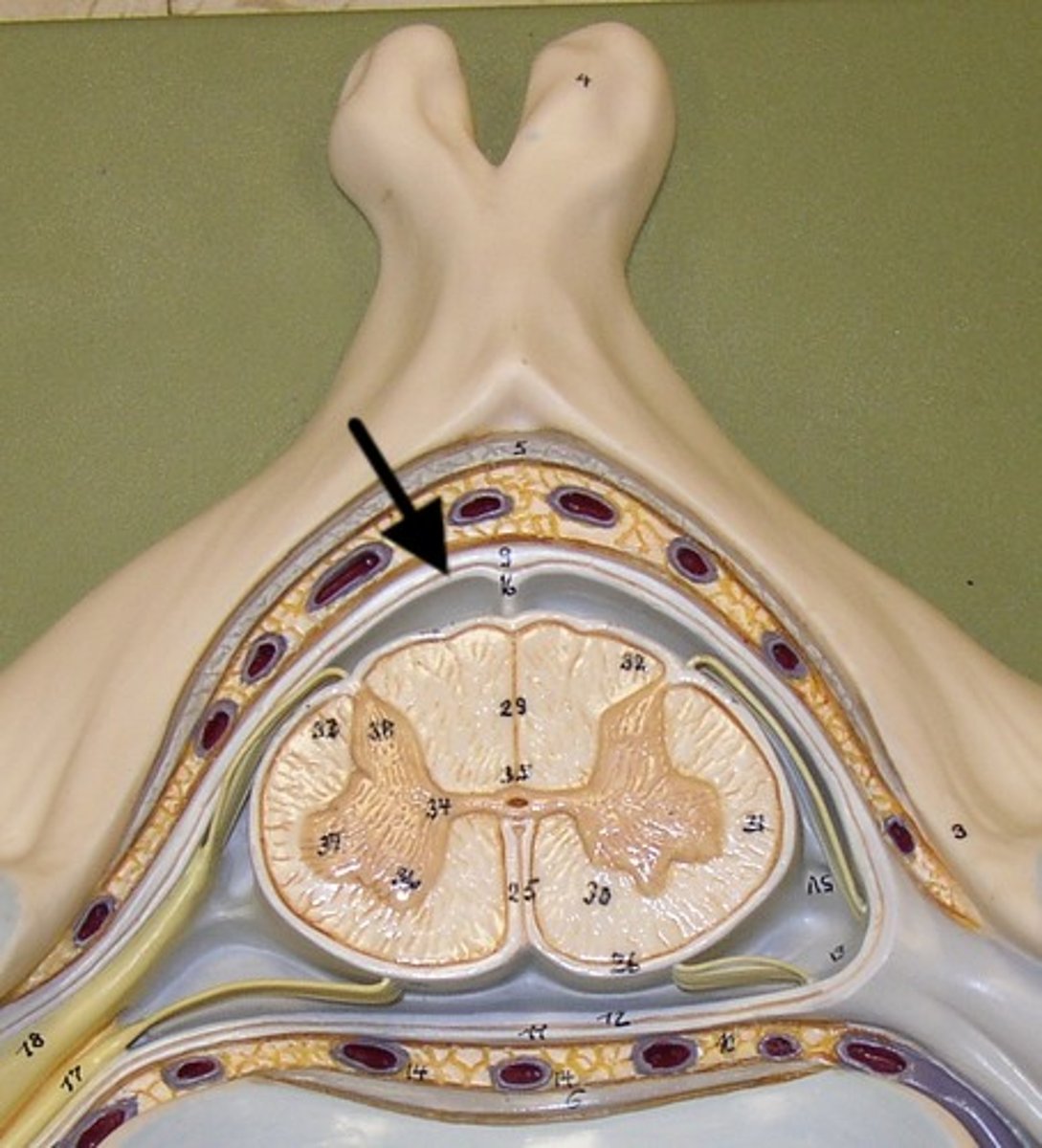
Pia Mater
Third layer of Meninges
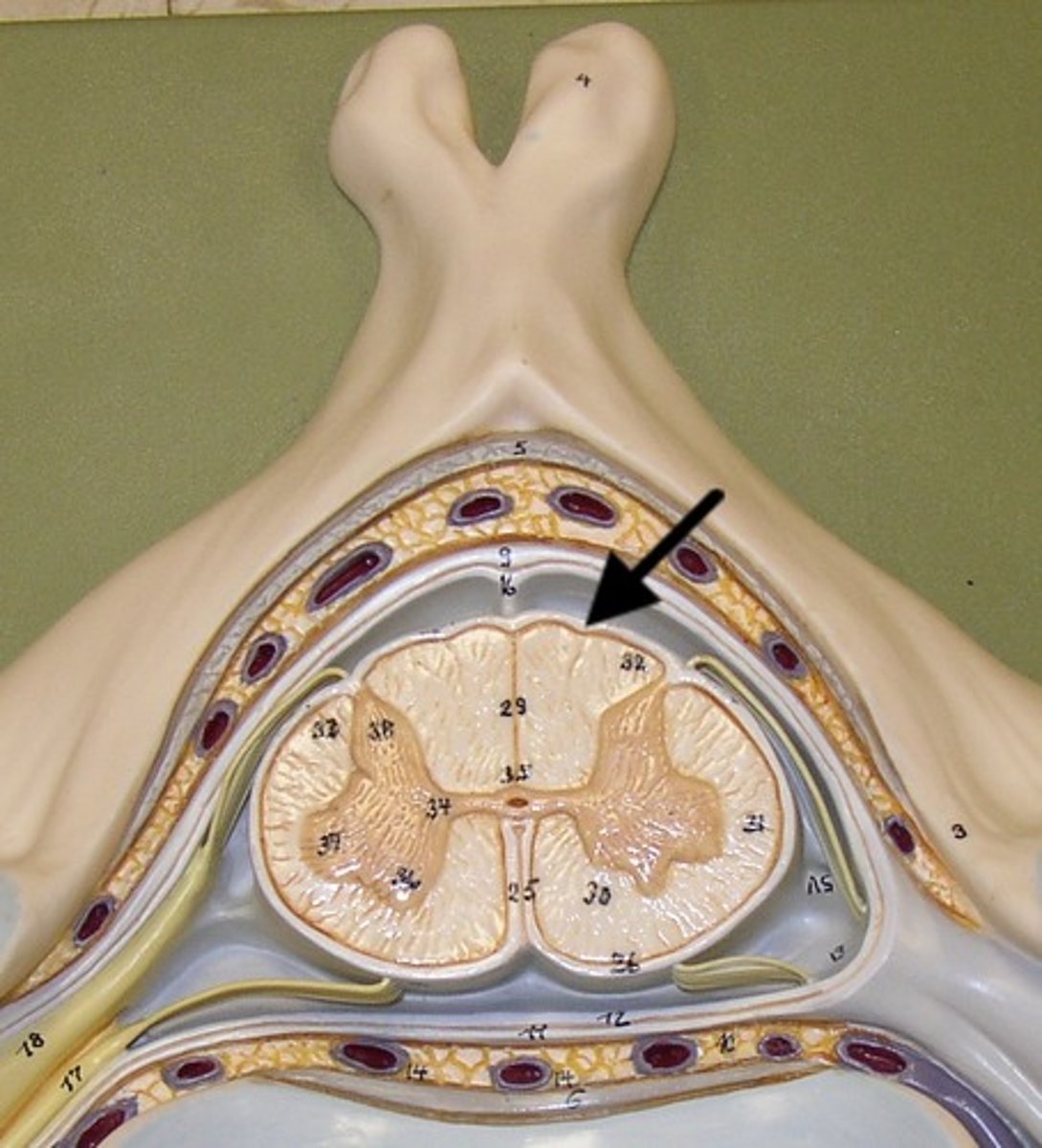
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
1) Formed by choroid plexus in each ventricle.
2) Similar to blood but no red blood cells and much lower protein level.
3) Supplies nutrients and forms protective fluid cushion that gives buoyancy to CNS structures:
-Reduces brain weight by ~97% and prevents it from crushing under its own weight (very delicate)
4) Circulated in subarachnoid space, ventricles, and central canal (facilitated by ependymal cells that line each of these areas)
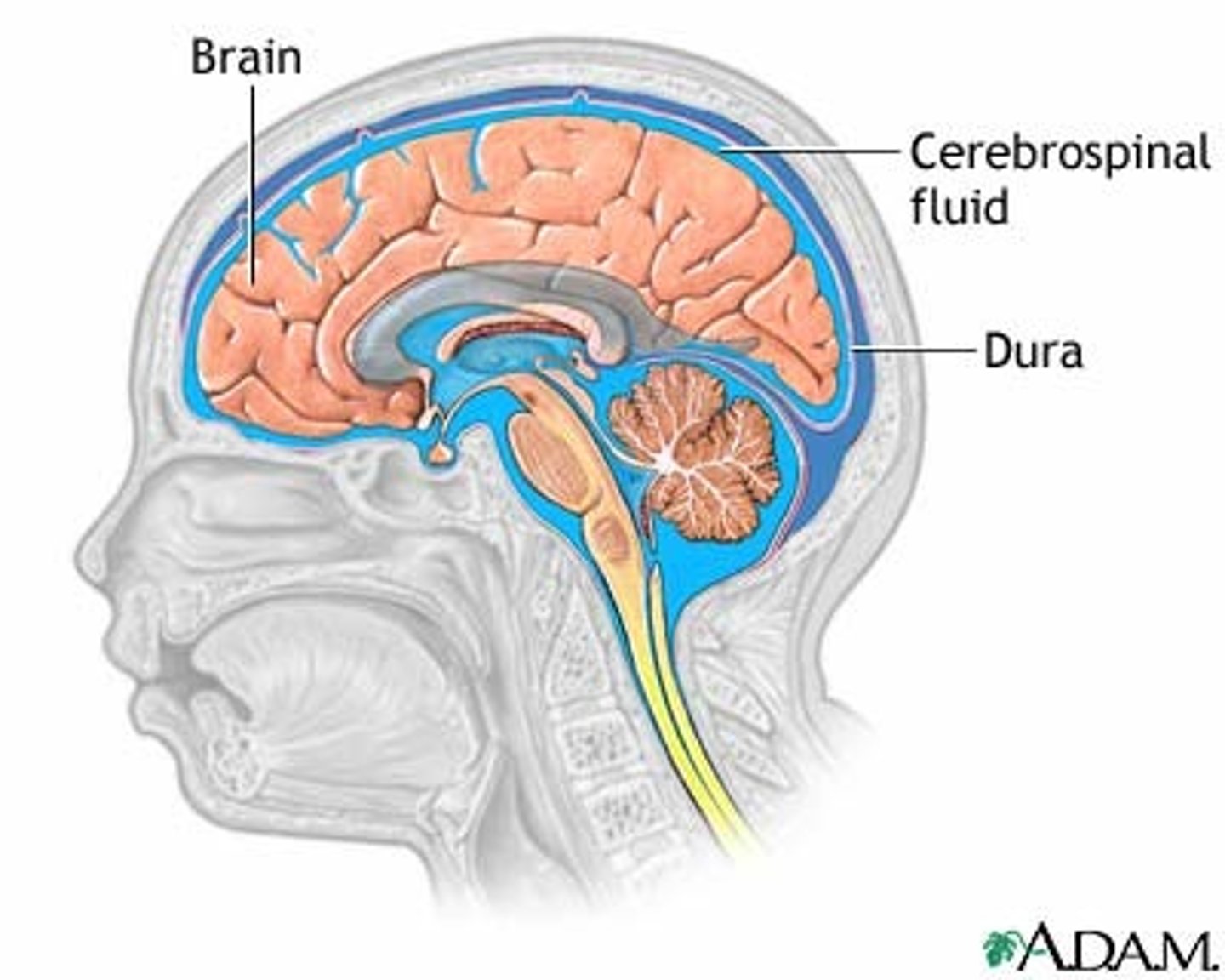
Ventricles
1) Right & left lateral ventricles:
-Anterior, Posterior & inferior horns
2) 3rd Ventricle, Cerebral aqueduct, 4th ventricles
4) Apertures (Narrow openings) into subarachnoid space of spinal cord
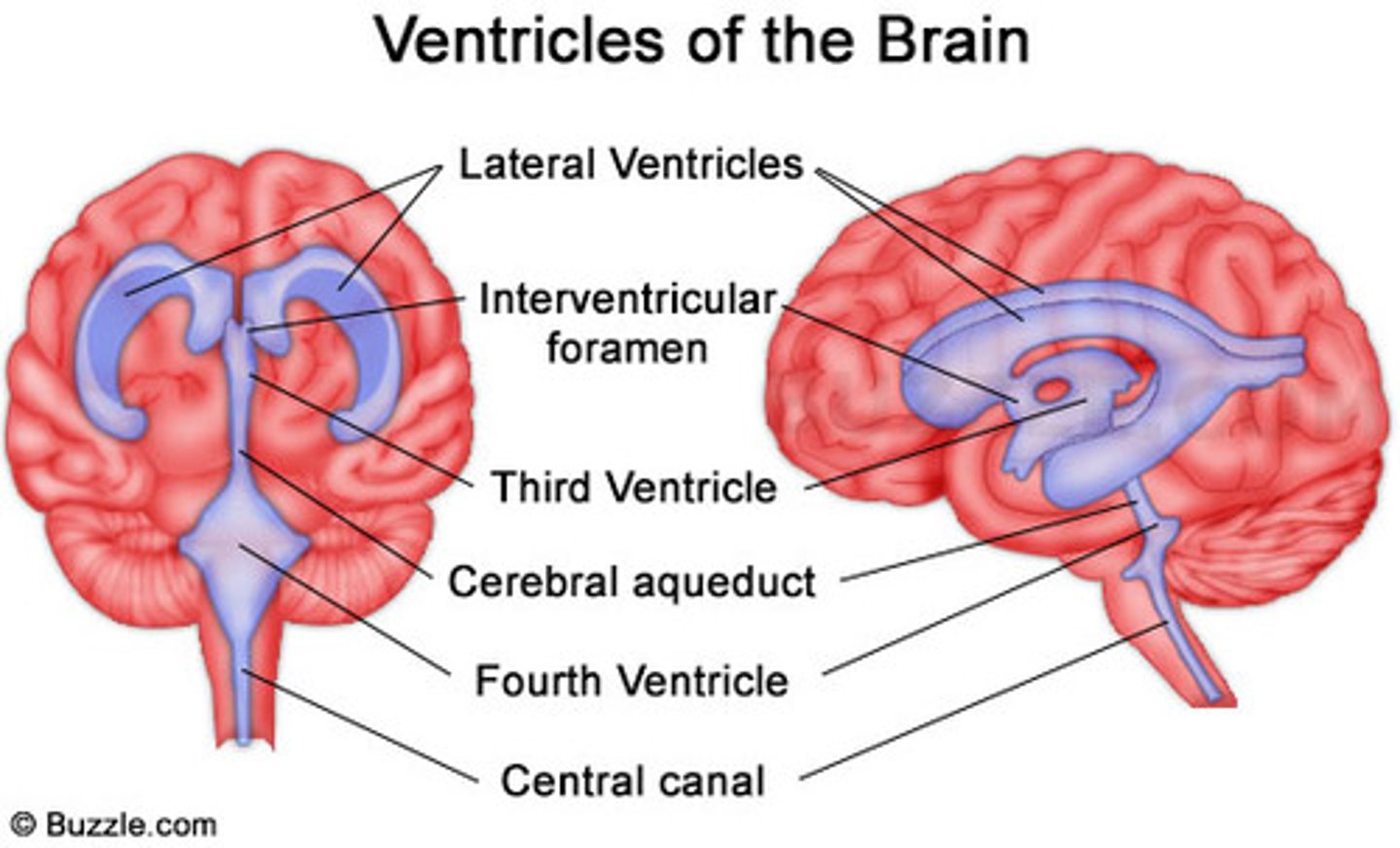
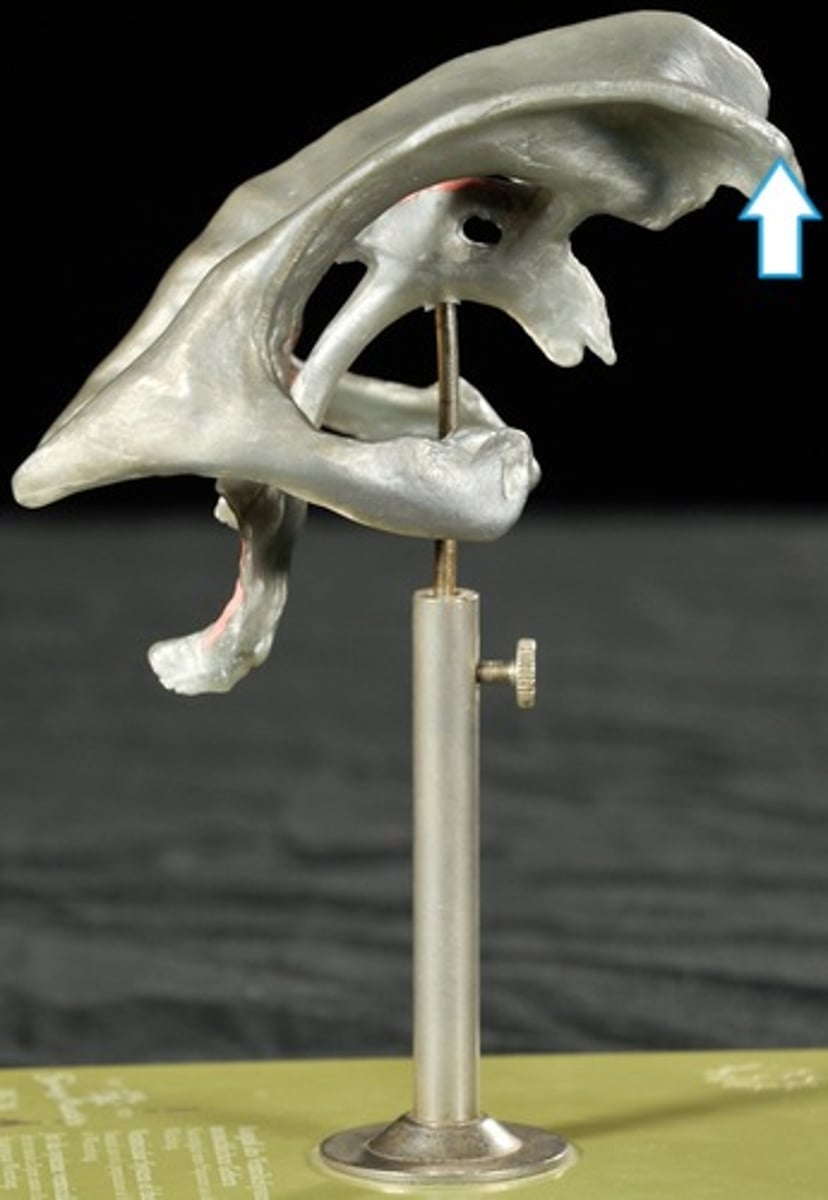
Anterior Horns
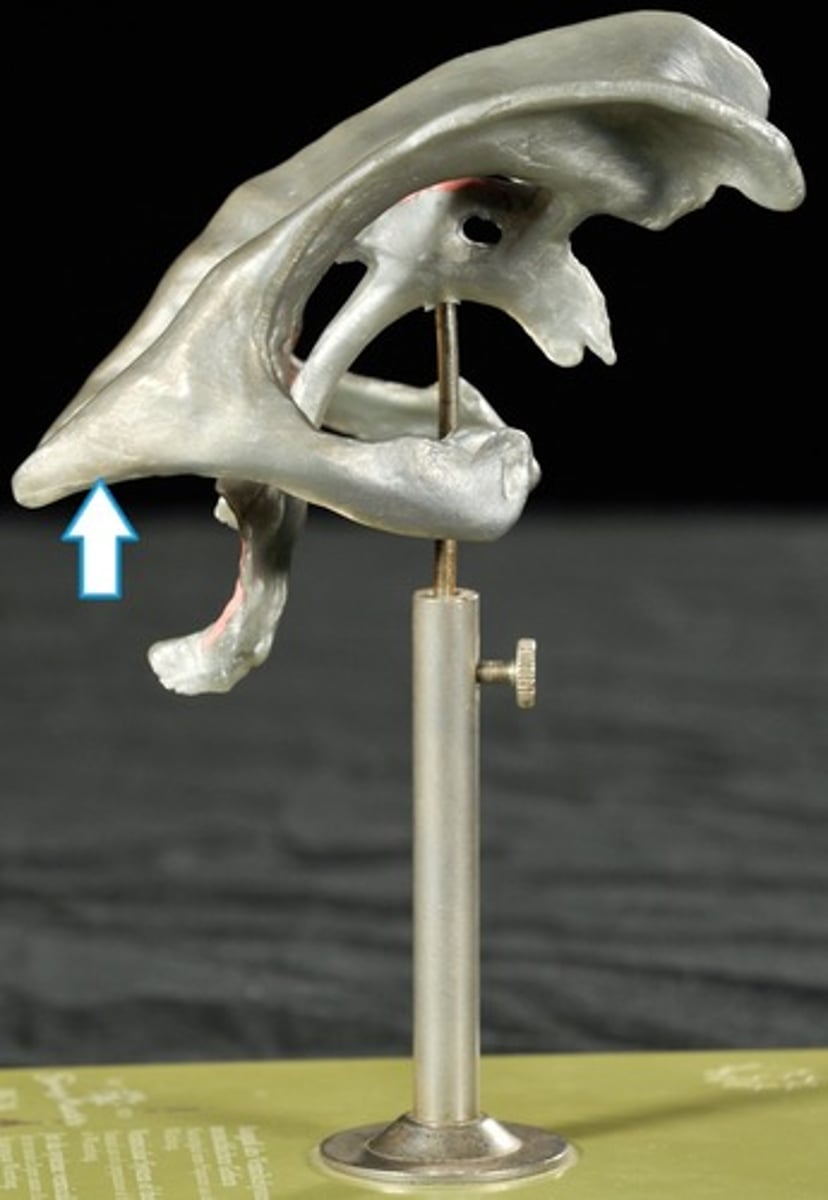
Posterior Horns
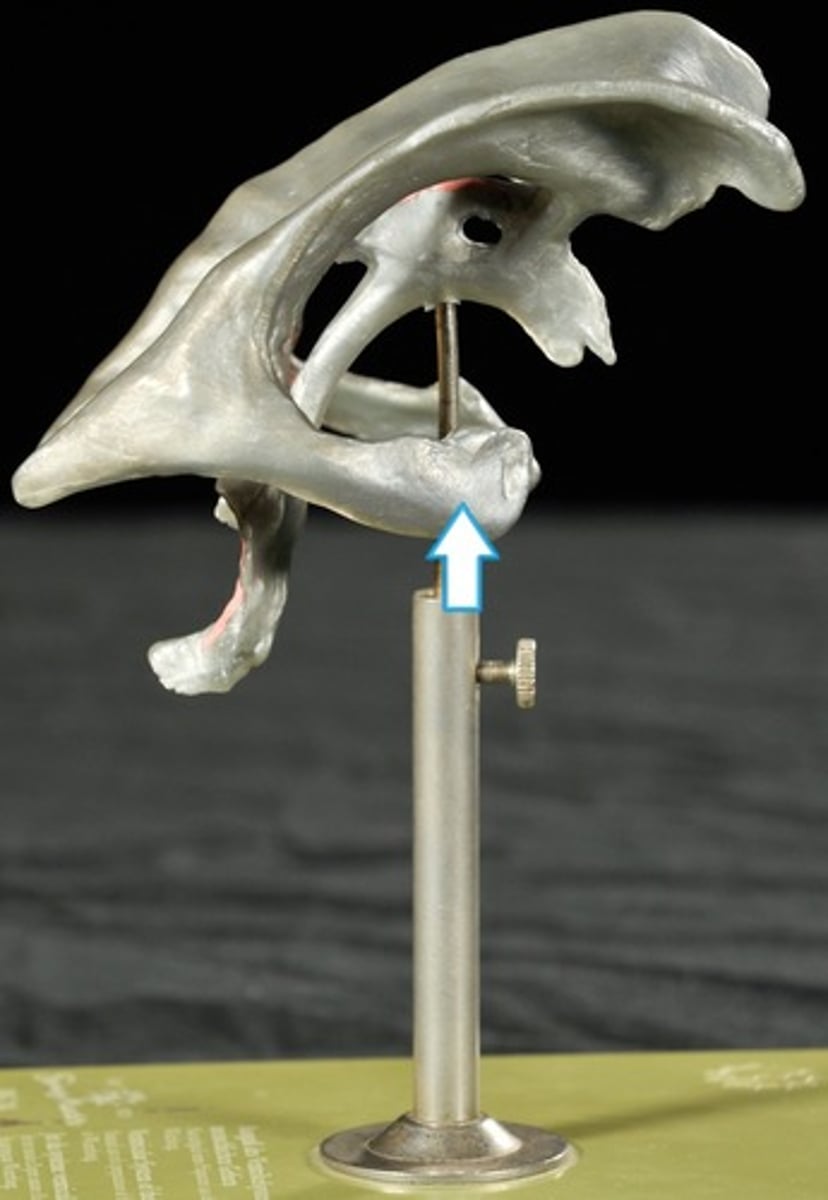
Inferior Horns
3rd Ventricle
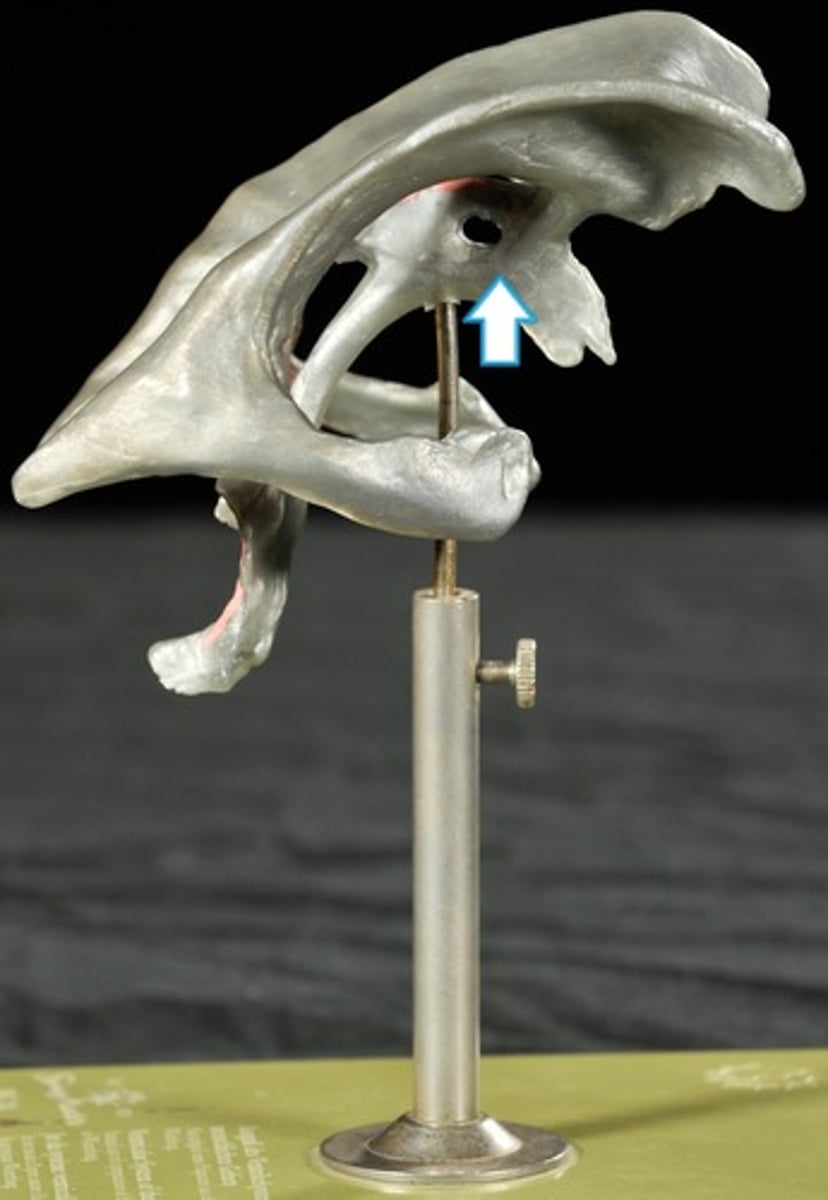
4th Ventricle
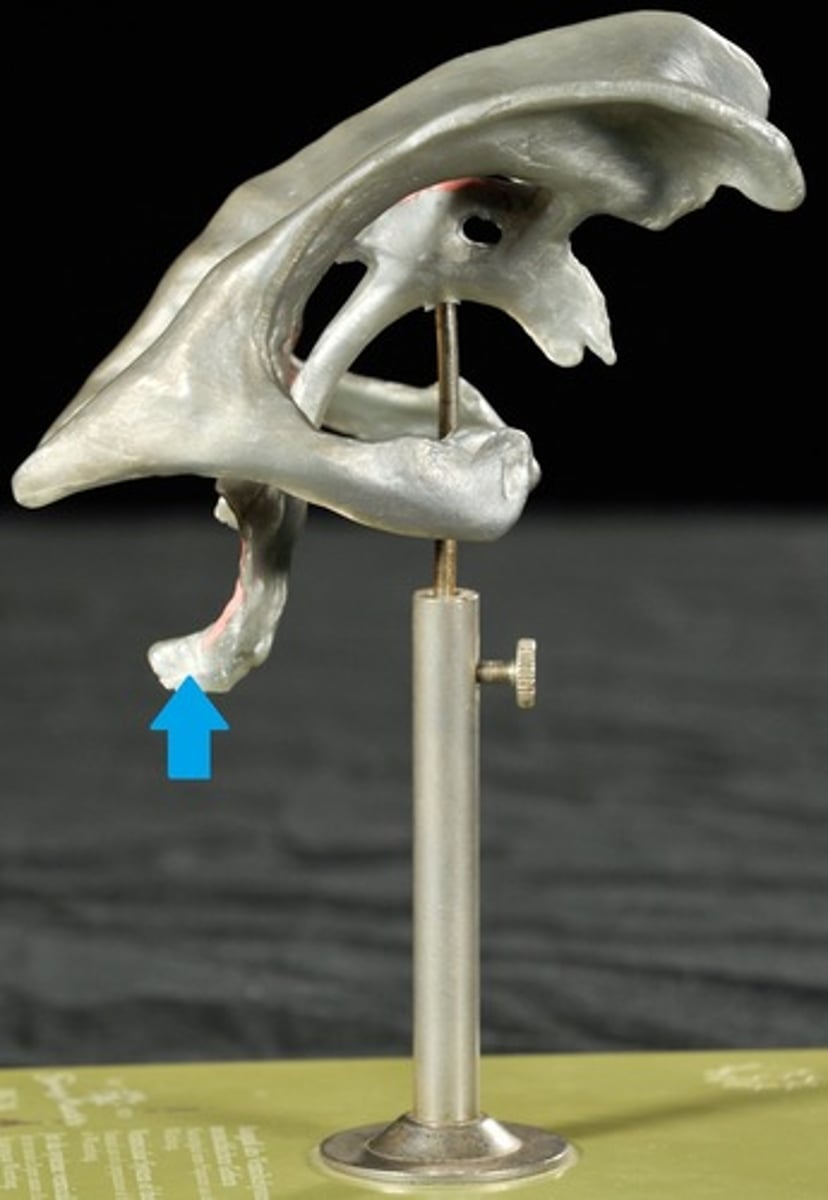
Dural Venous Sinuses
Blood and Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection for return to circulatory vessels exiting skull
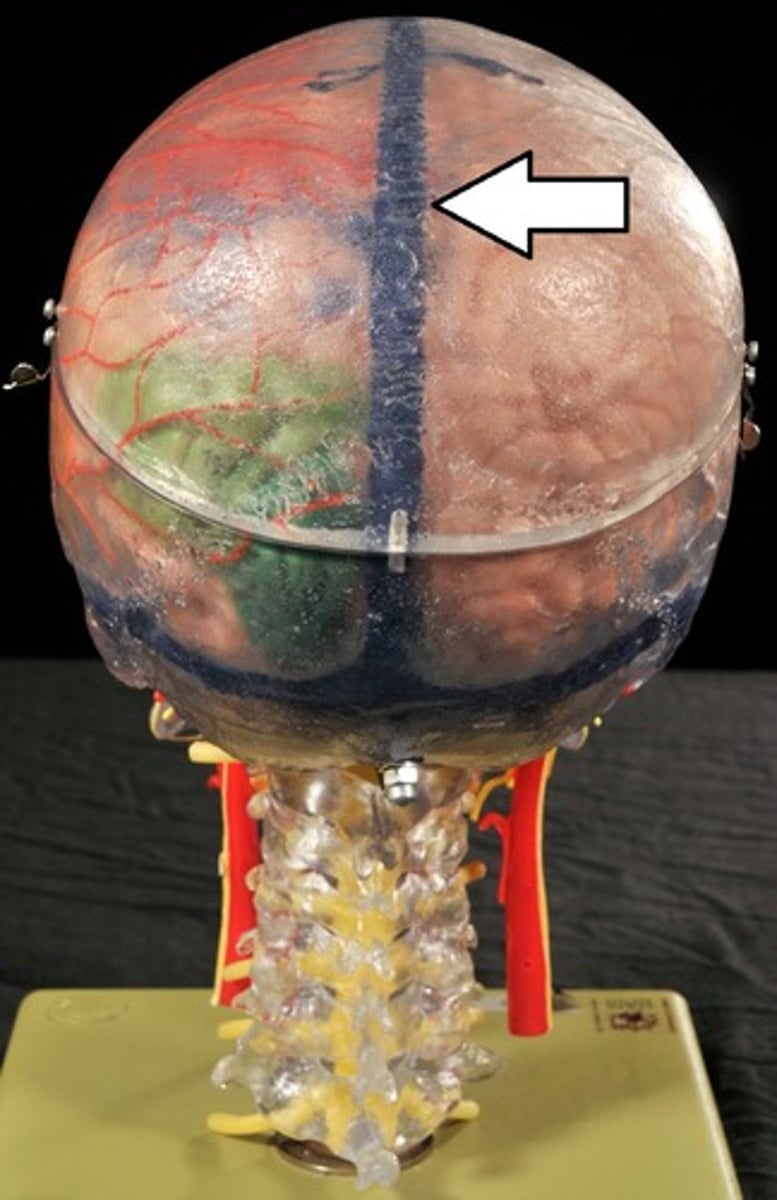
Blood Brain Barrier
Tight junctions between endothelial blood vessel cells cause substances to pass through cells to become Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF),
Not completely uniform in all areas
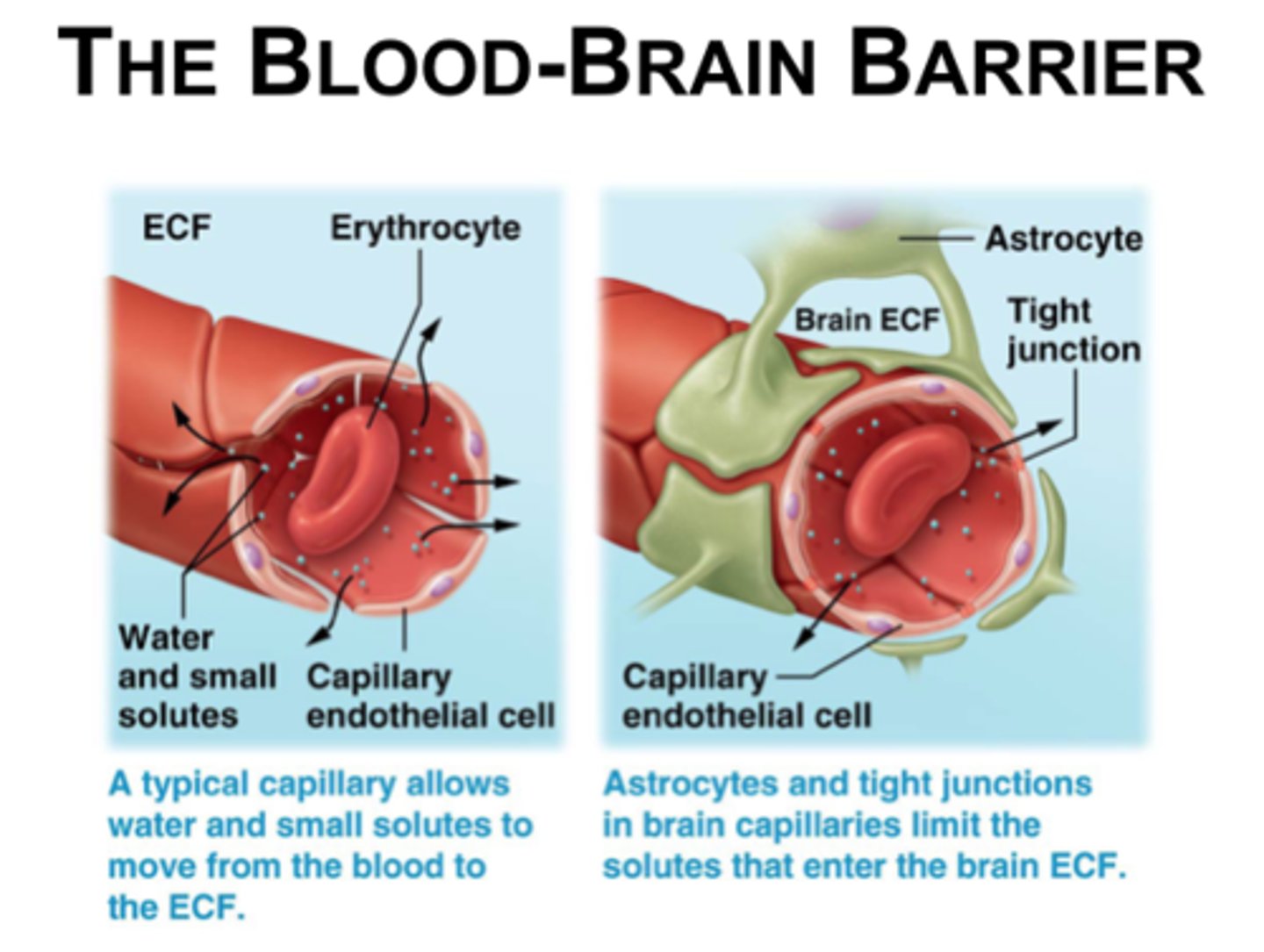
Blood brain barrier and tight junction/ substances becoming CSF
1) Large substances/molecules cannot utilize the route between cells and are barred from CSF.
2) Lipid-soluble substances, such as nicotine, ethanol, and heroin, can diffuse through the endothelial cell membranes and enter the brain.
3) Water-soluble molecules such as amino acids and glucose move across by mediated transport
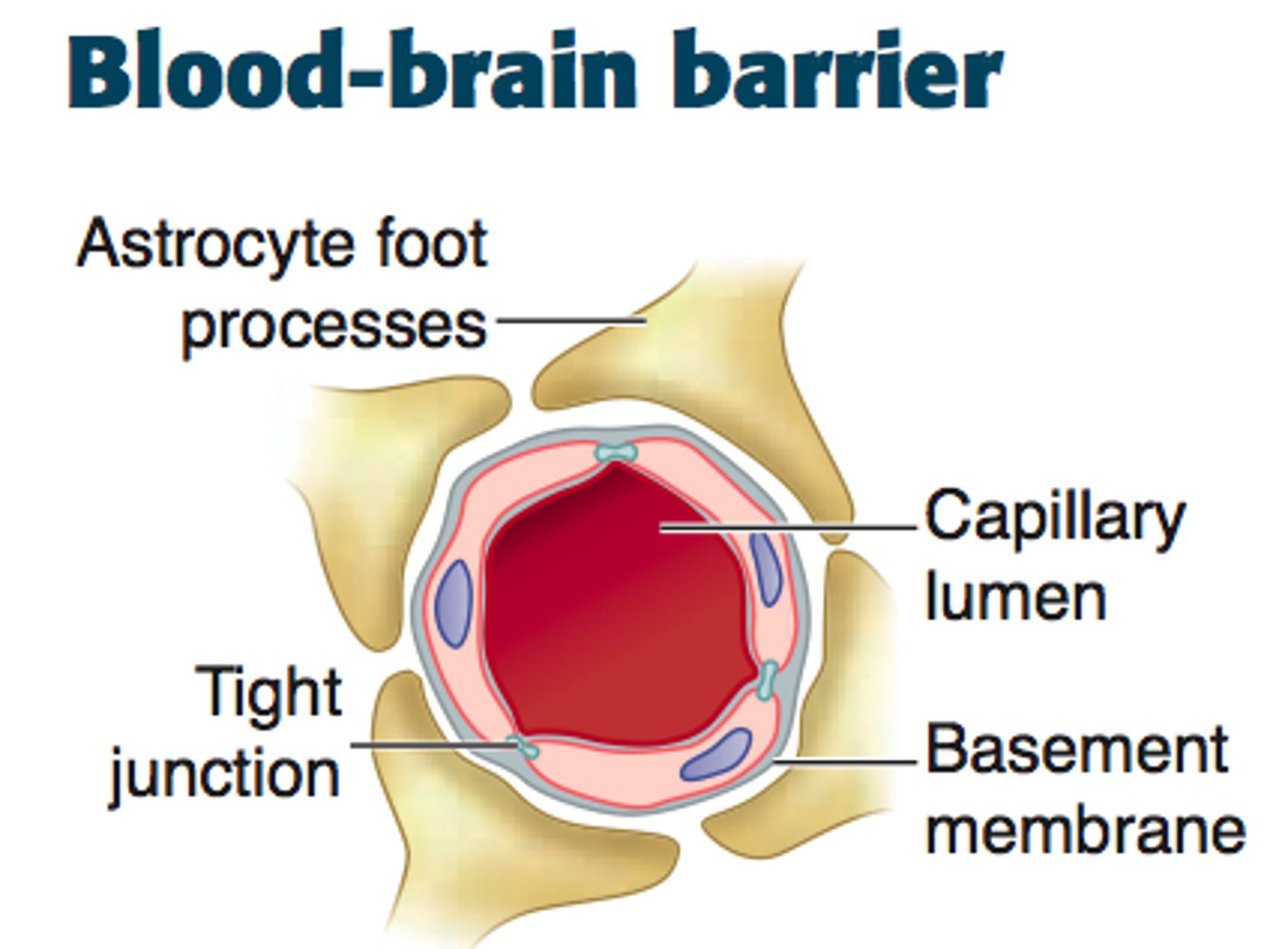
Blood brain barrier not completely uniform in all areas:
1) Very permeable in vomiting venter in brain stem
- allows monitoring of blood for poisonous substances
2) Very permeable in hypothalamus
- allows sampling of chemical composition of blood to regulate water balance, body temp, etc.
Blood supply to the brain
1) The brain is only 2% by weight but uses 20% of O2 consumption via carotid and vertebral arteries,
2) Nerve cells cannot store glucose or energy compounds like muscle tissue,
3) Interrupted blood flow to the brain can cause unconsciousness or irreversible brain damage if maintained for extended period of time
Meningitis
Bacterial meningitis (medical emergency) and viral meningitis,
inflamed meninges
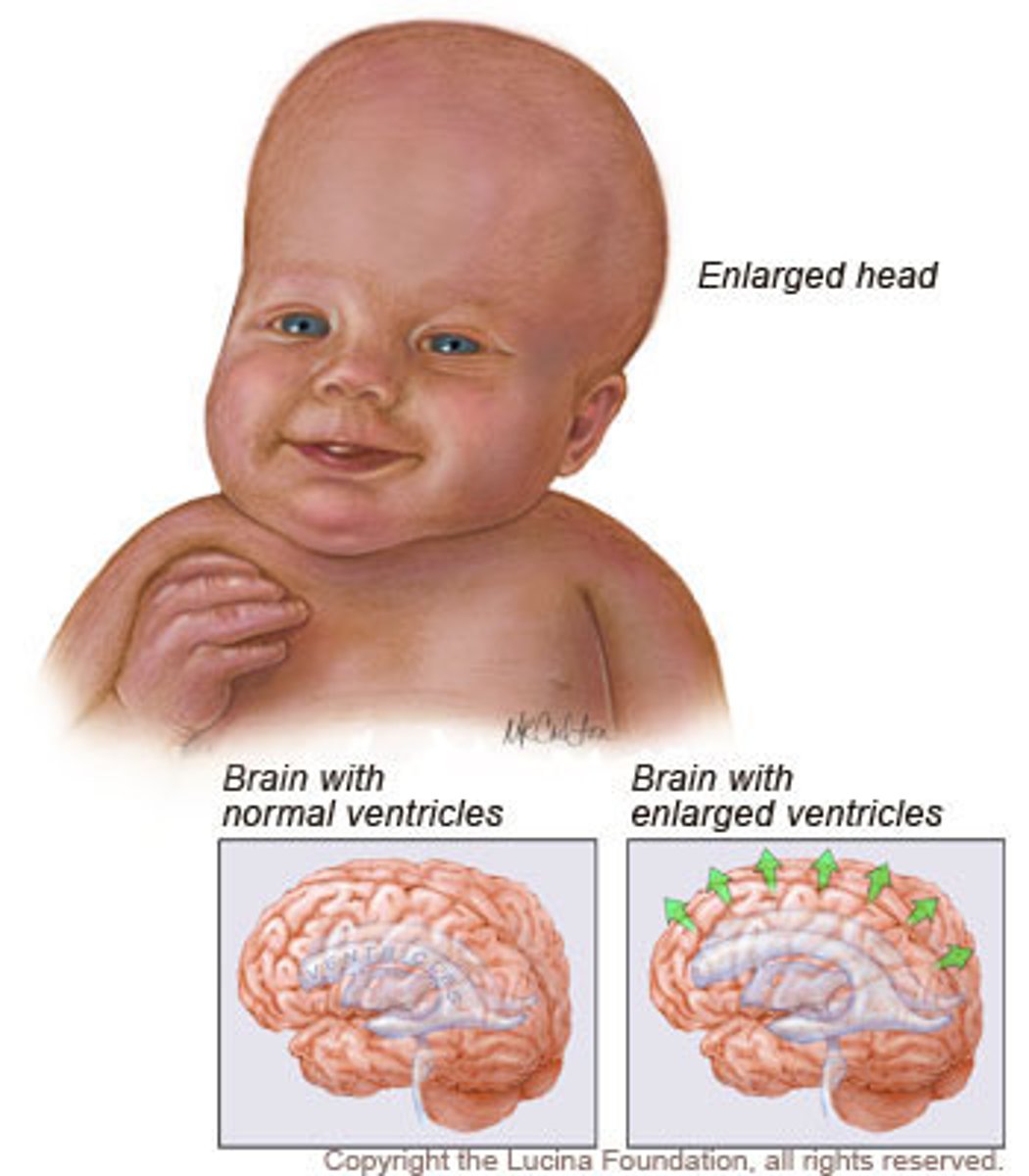
Hydrocephalus
water on the brain
Traumatic brain injuries (head trauma)
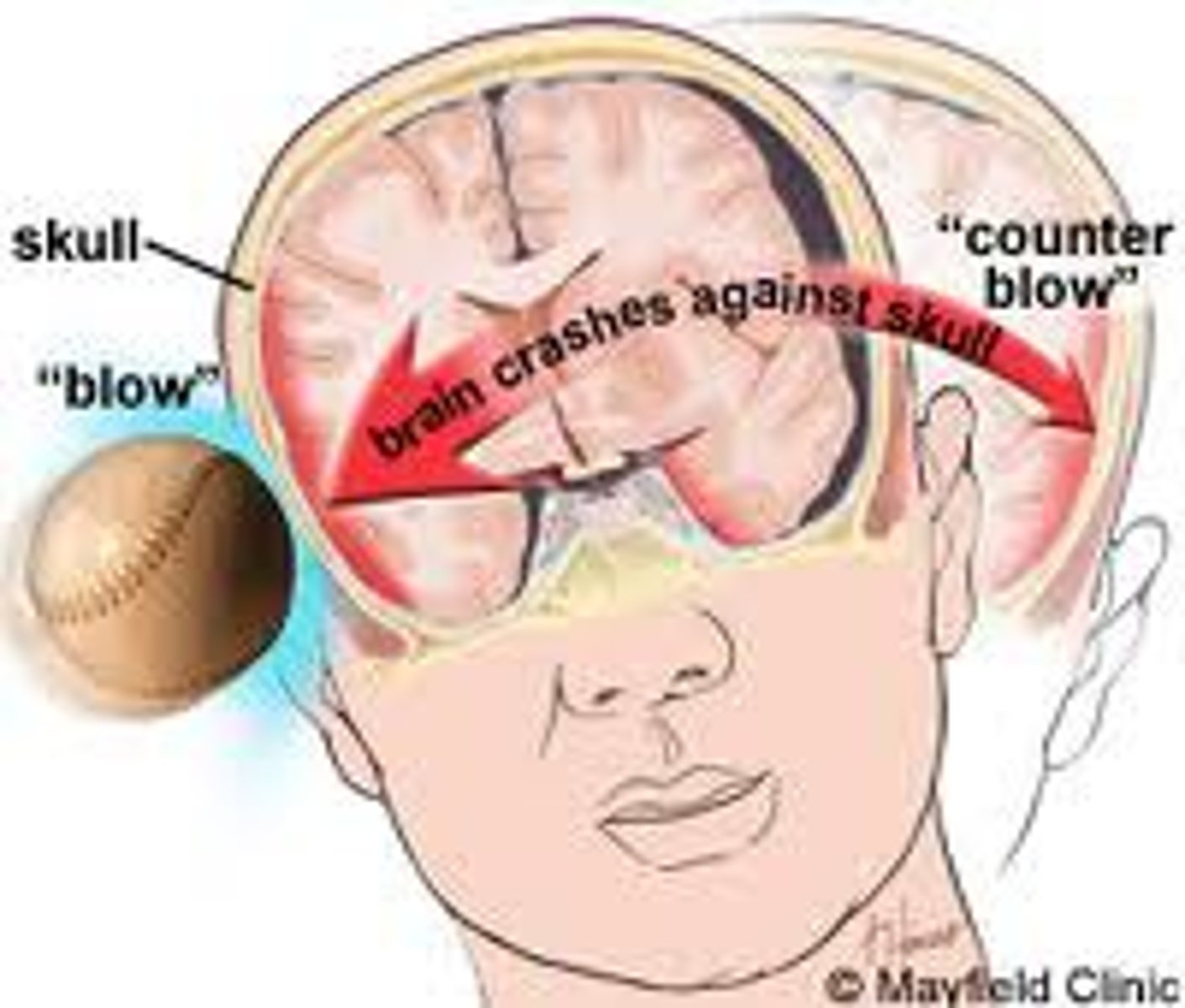
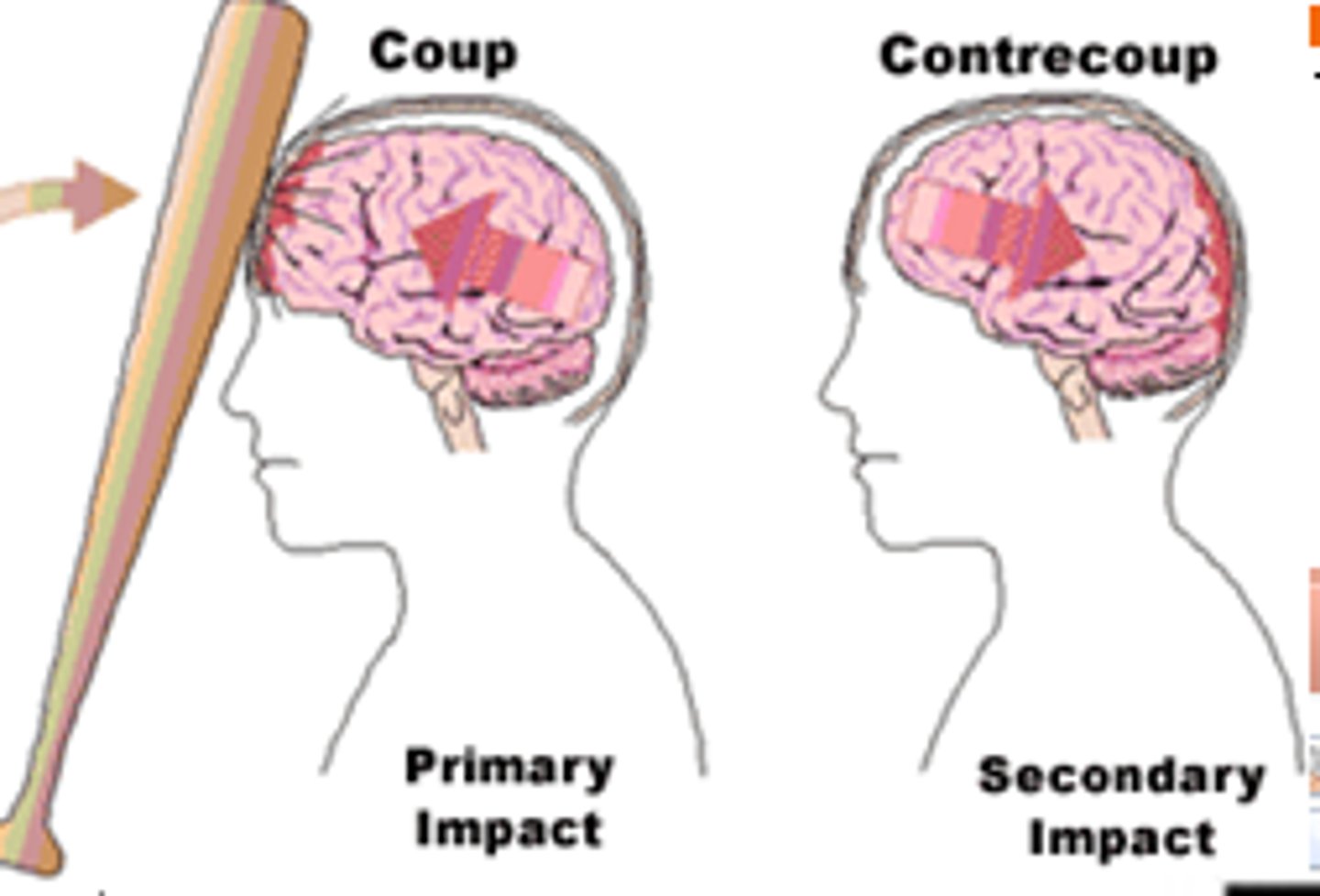
1) a leading cause of accidental death in U.S.
2) Caused not only by localized injury at site of blow but also by ricocheting effect as brain hits opposite end of skull

Types of Head Trauma
Concussion,
Contusion,
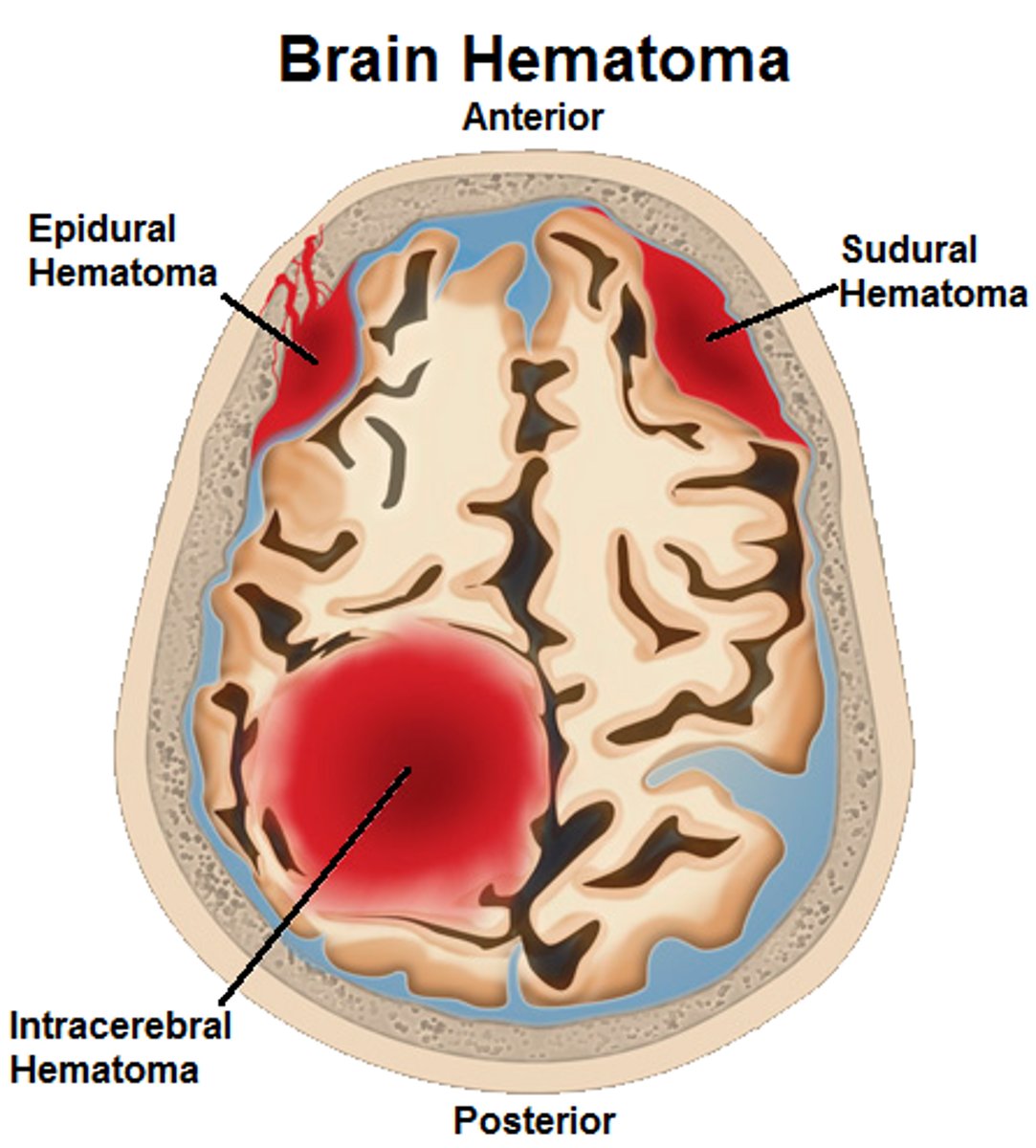
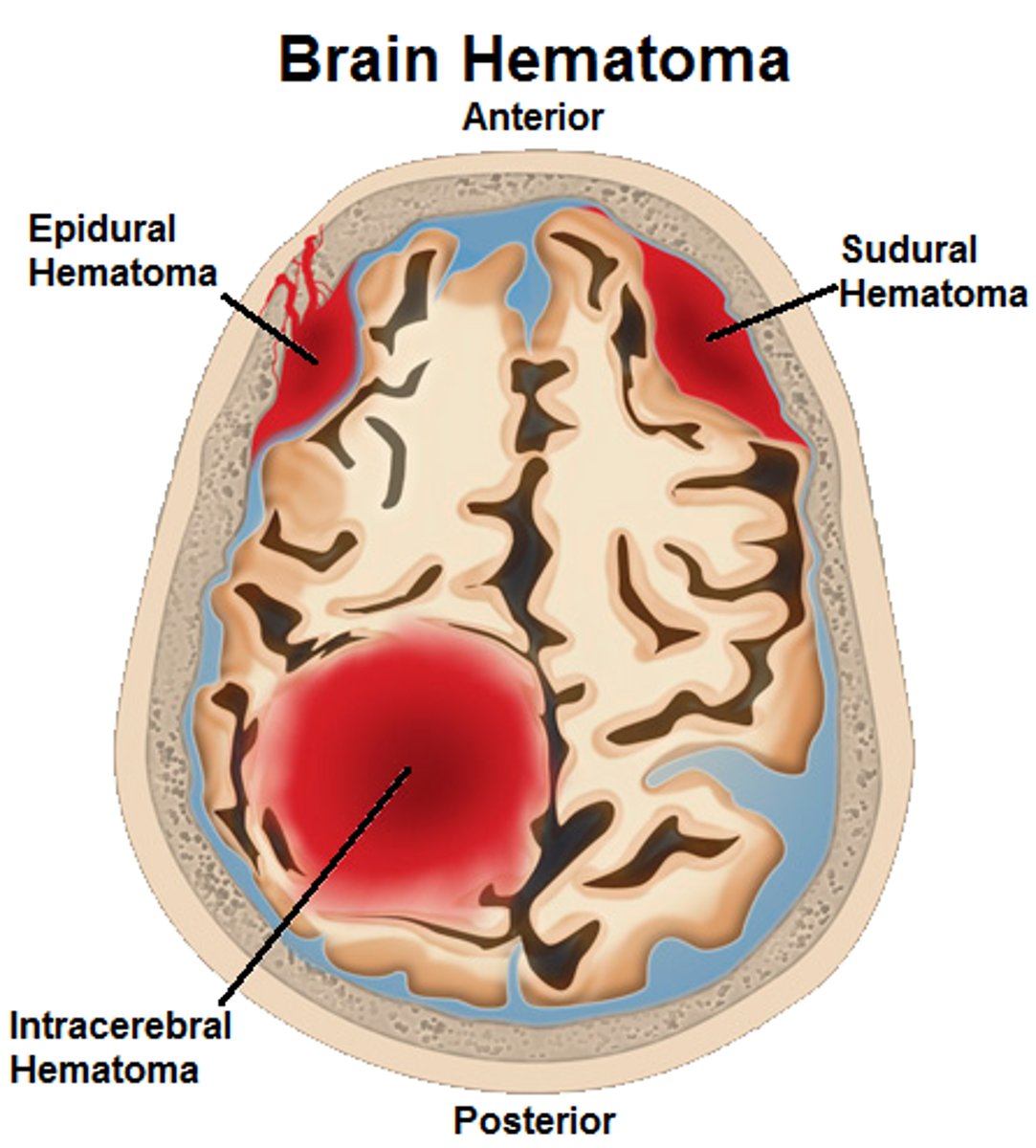
Subdural Hematoma,
Cerebral Edema
Concussion
Alteration in brain function following blow to the head
Contusion
Bruising in the brain and can cause permanent Neurological Damage
Subdural Hematoma
Blood vessels are broken in the brain
Cerebral Edema
Swelling on the brain
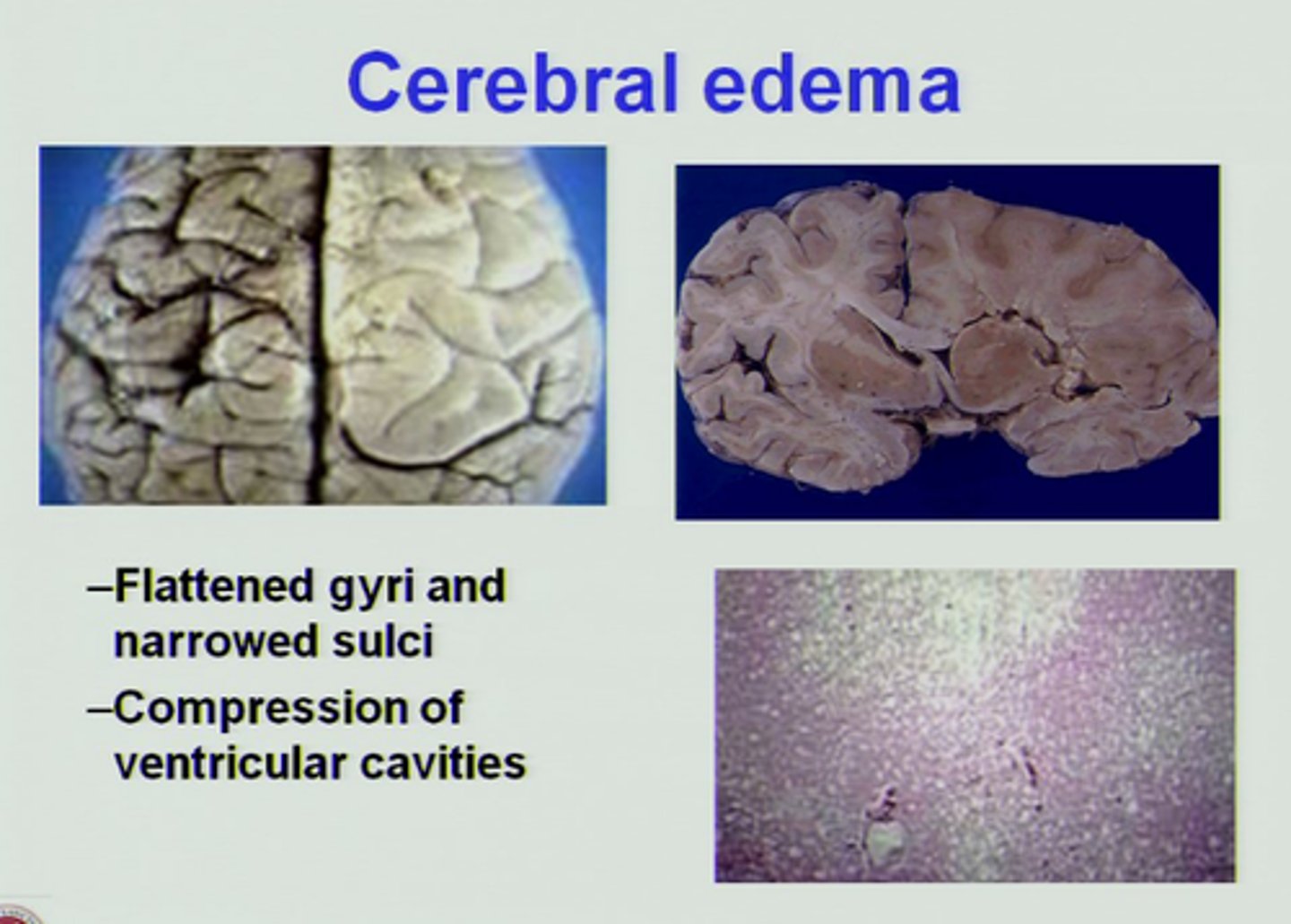
Degenerative injuries
1) Cerebrovascular accidents (CVAs or strokes)
2) Alzheimer's Disease
3) Parkinson's Disease
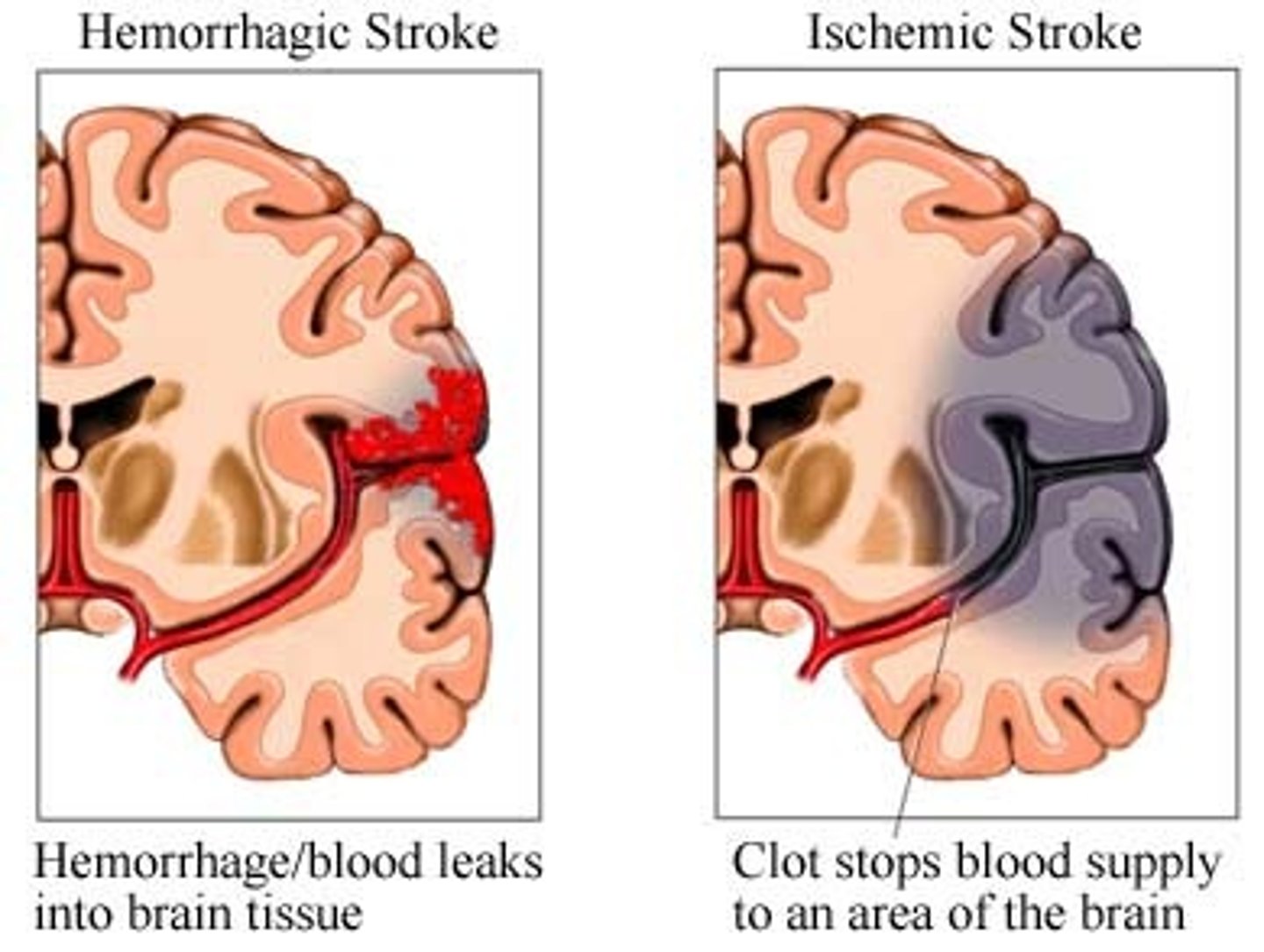
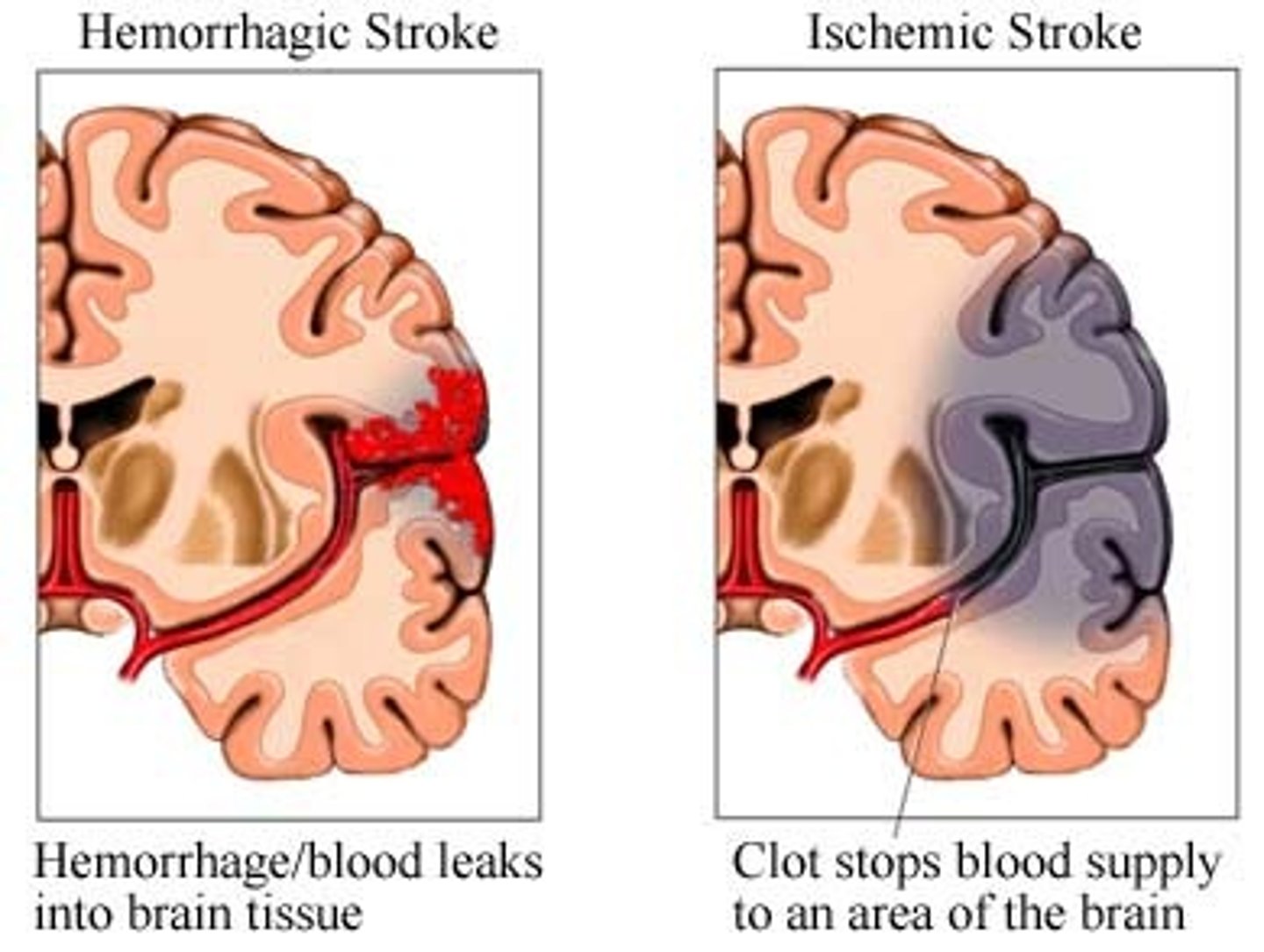
Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVAs and Strokes)
1)Death of brain tissue because of blood depravation,
2) Causes: Hemorrhagic & Ischemic
3) The glutamate cascade which lead to neural frying
-Rationale for rapid treatment
Alzheimer's Disease
1)Progressive degenerative brain disease that eventually results in dementia (mental deterioration)
2) Characterized by abnormal (beta-amyloid) protein deposits and twisted fibers (neurofibrillary tangles) within neurons
3) Symptoms: memory loss, irritability, confusion & ultimately hallucinations & death

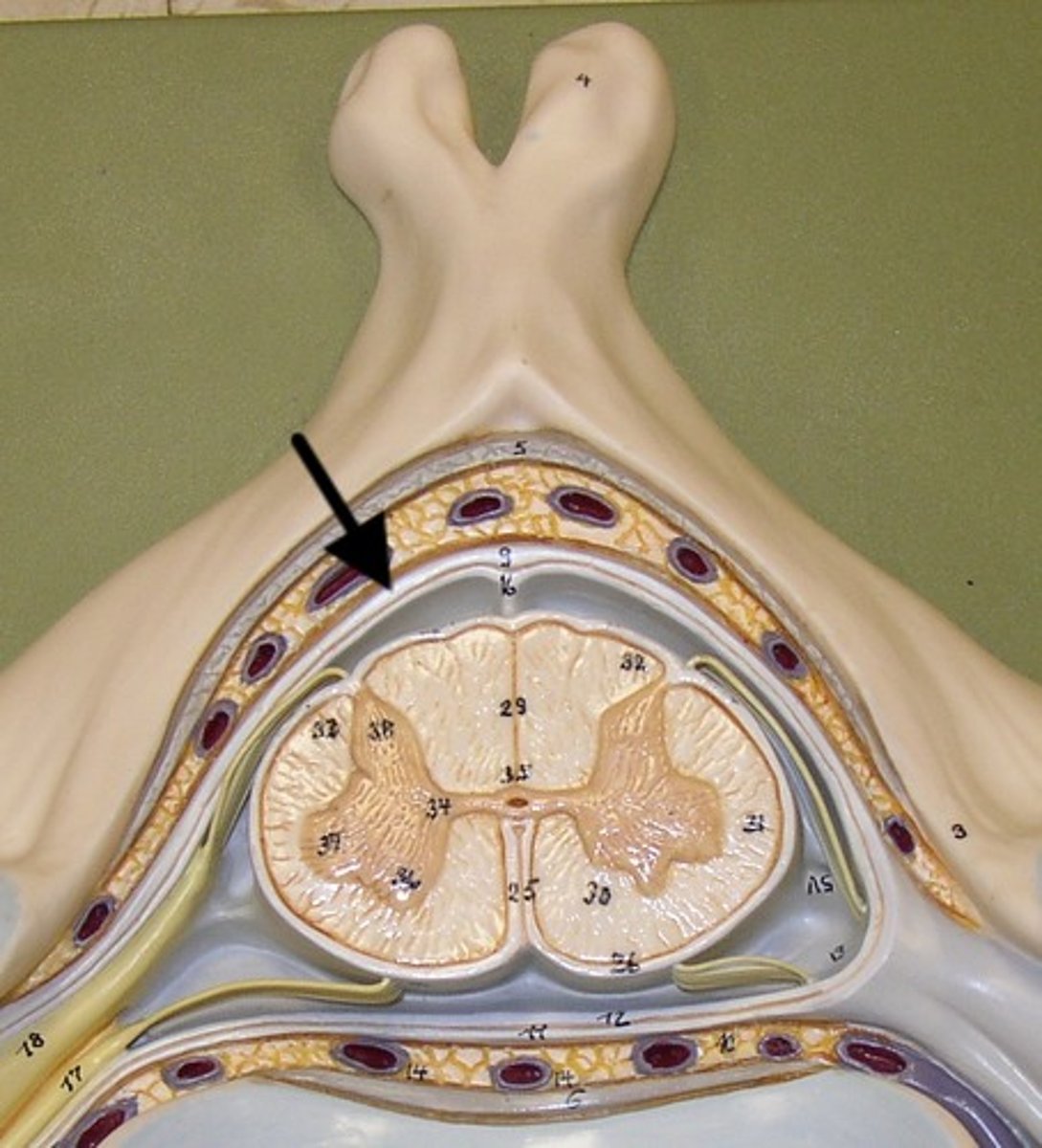
Spinal Cord .
1)Two-way conduction system of nerve pathways to & from the brain
2) Major Reflex center; Spinal reflexes initiated and completed at level of the cord
3) Extends from Medulla Oblongata at level of foramen magnum to the region of L1 or L2
4) Below L2 is the cauda equina
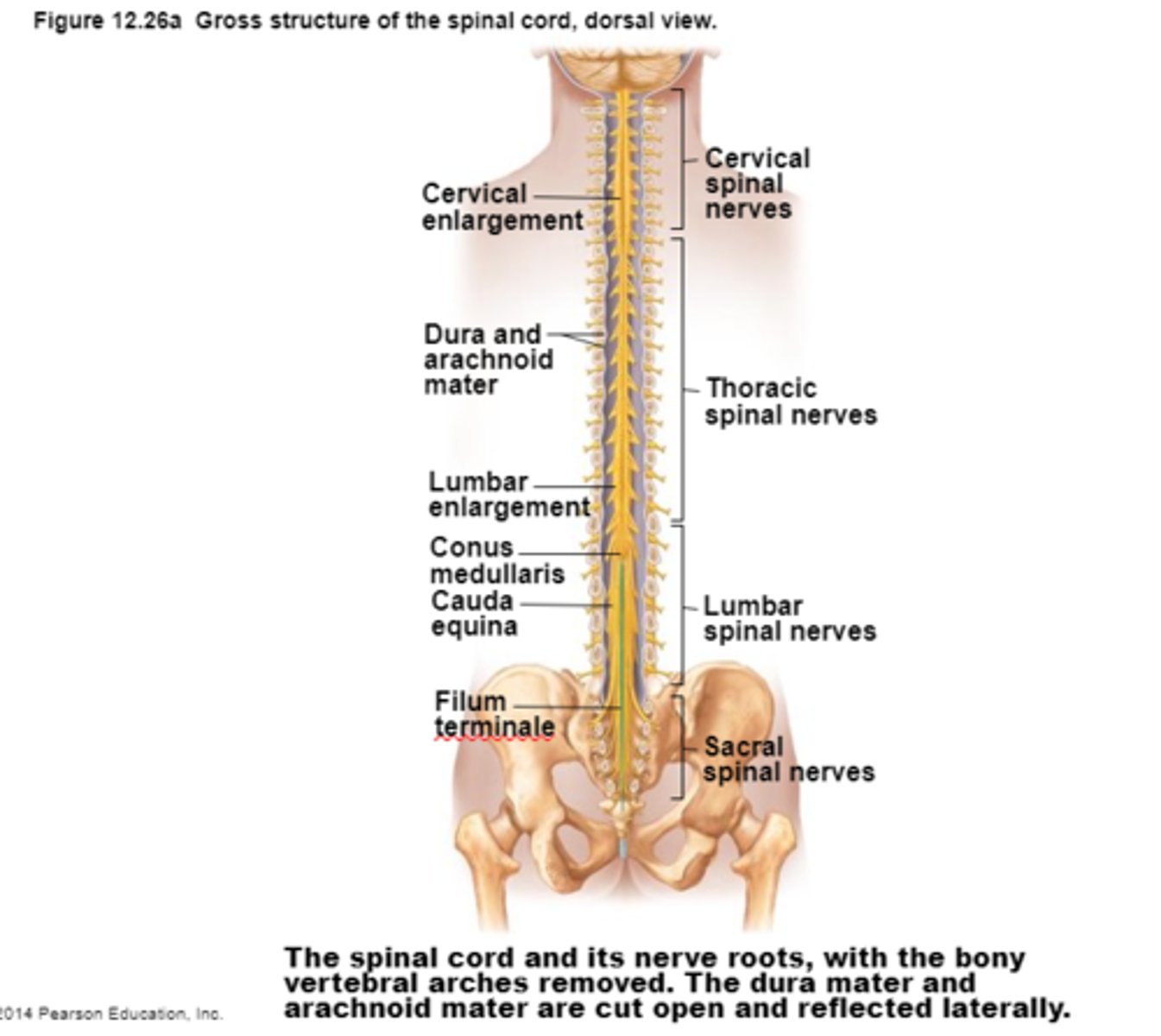
Spinal Cord
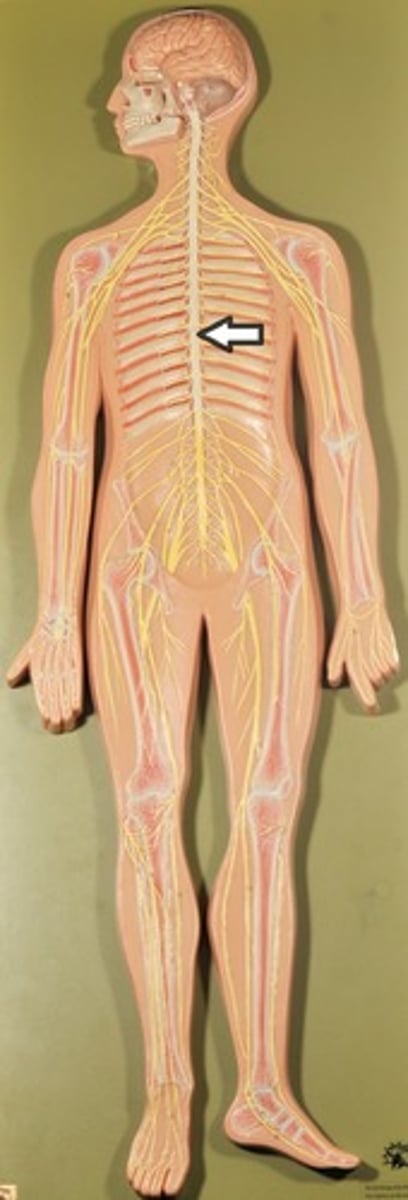
Cauda Equina
Bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve roots and is below the L2
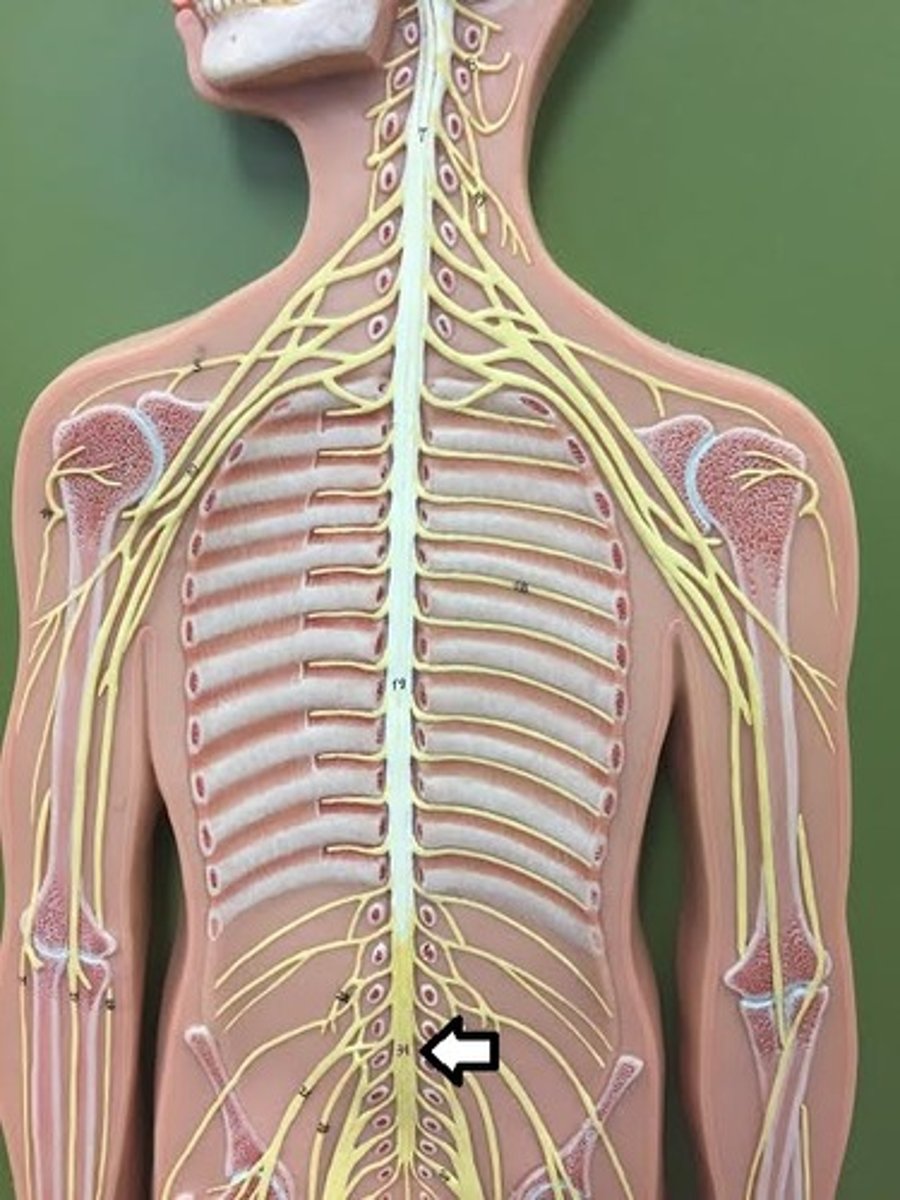
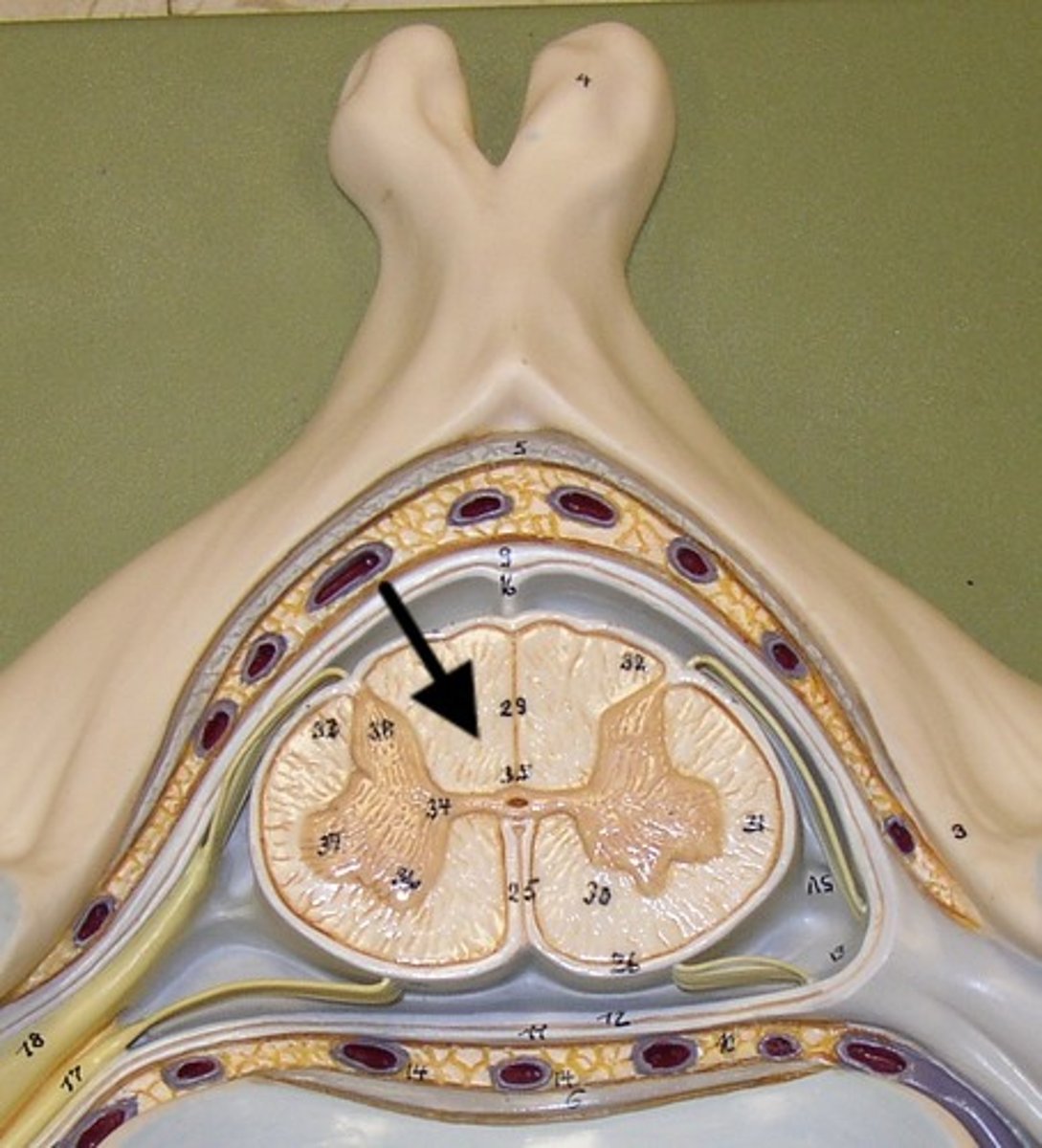
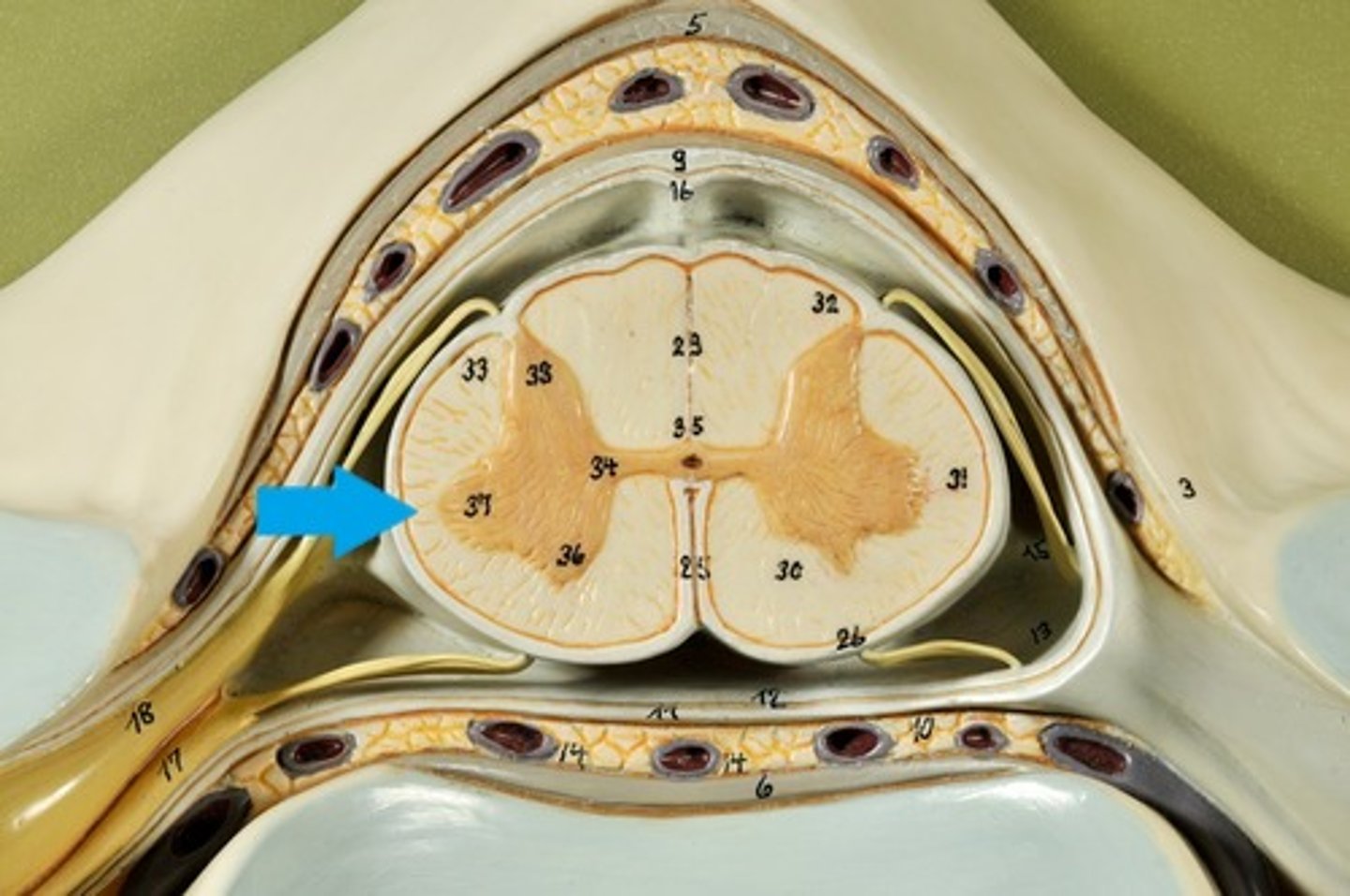
Spinal cord Anatomy (cross-sectional)
1)Internal butterfly shaped gray matter,
2)Exterior white matter,
3)Central canal filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF),
4)Cushioned & protected by meninges,
5)Pia mater,
6)Spinal nerves leave at the level of each vertenrae
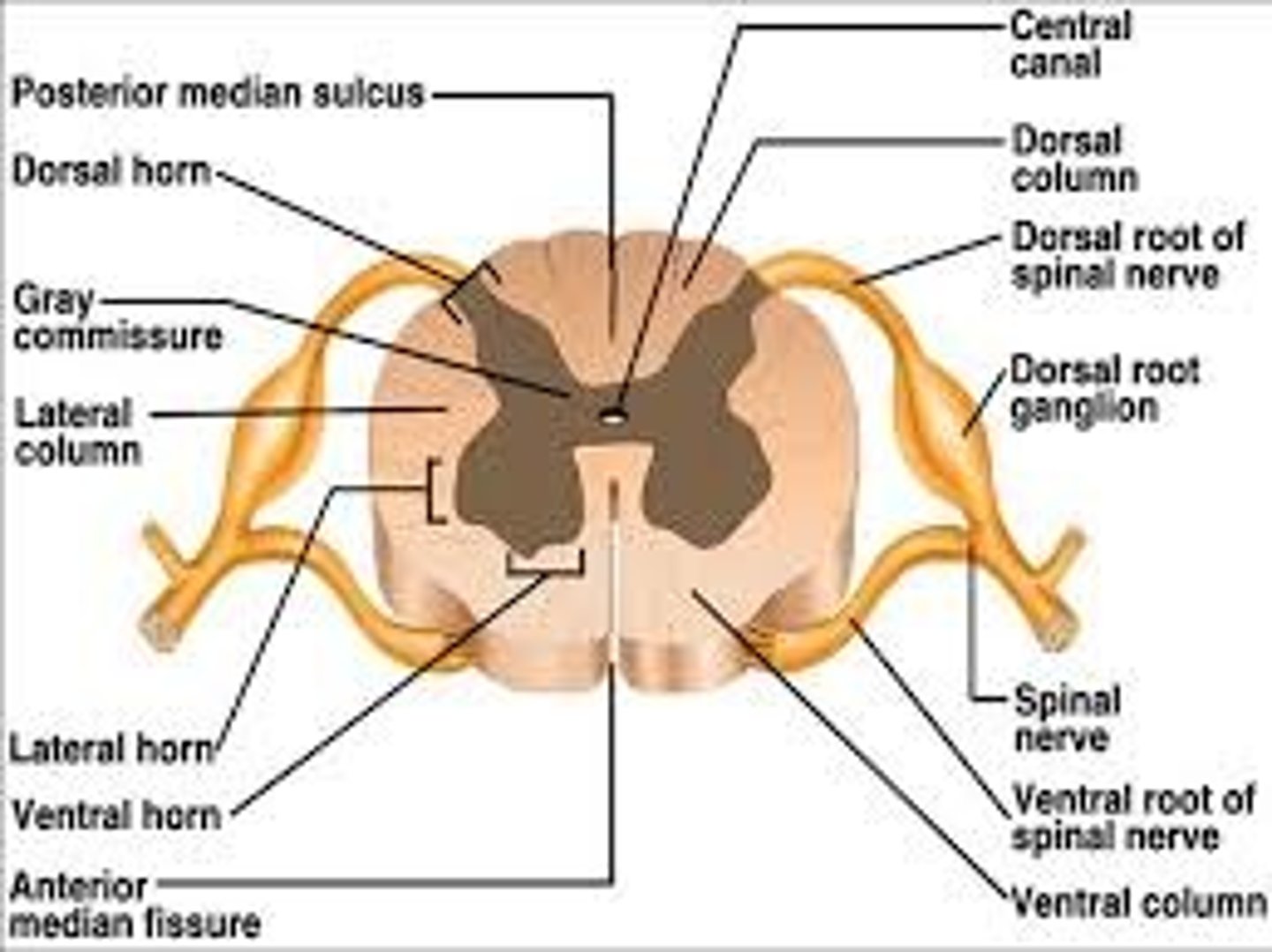
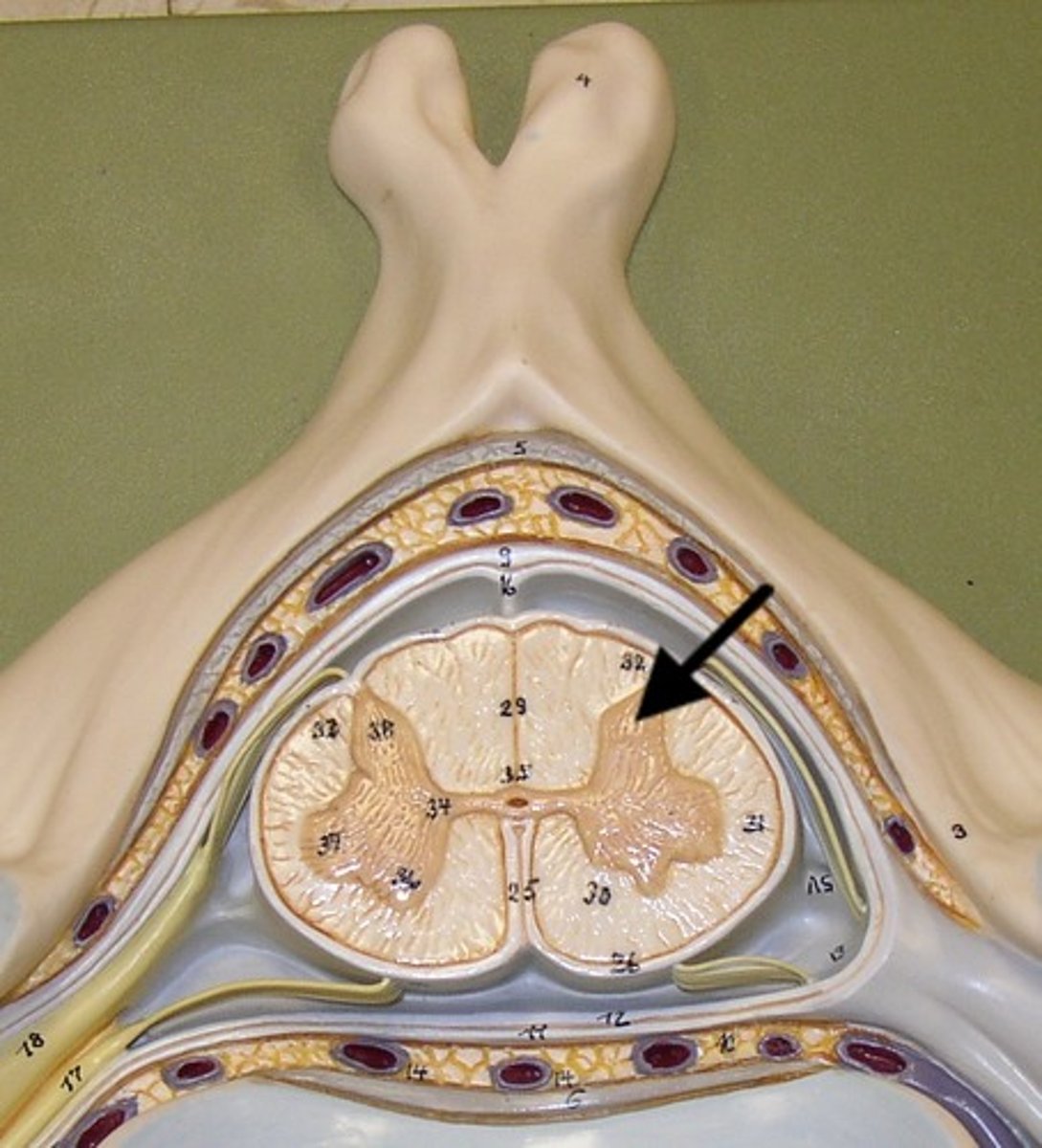
Horns of Spinal Cord Anatomy
Dorsal Horns,
Ventral Horns,
Lateral Horns
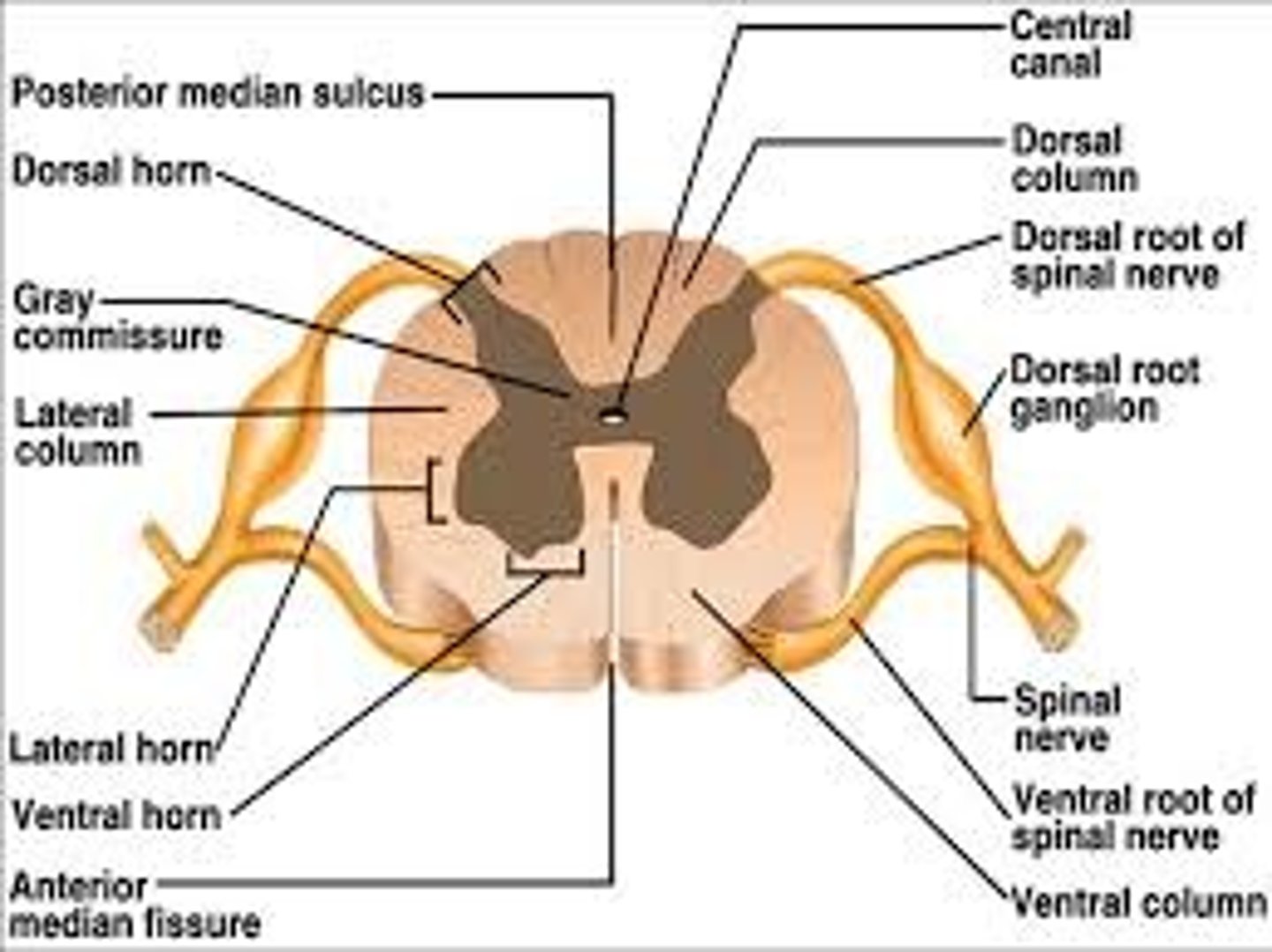
Dorsal Horns
Lateral Horns
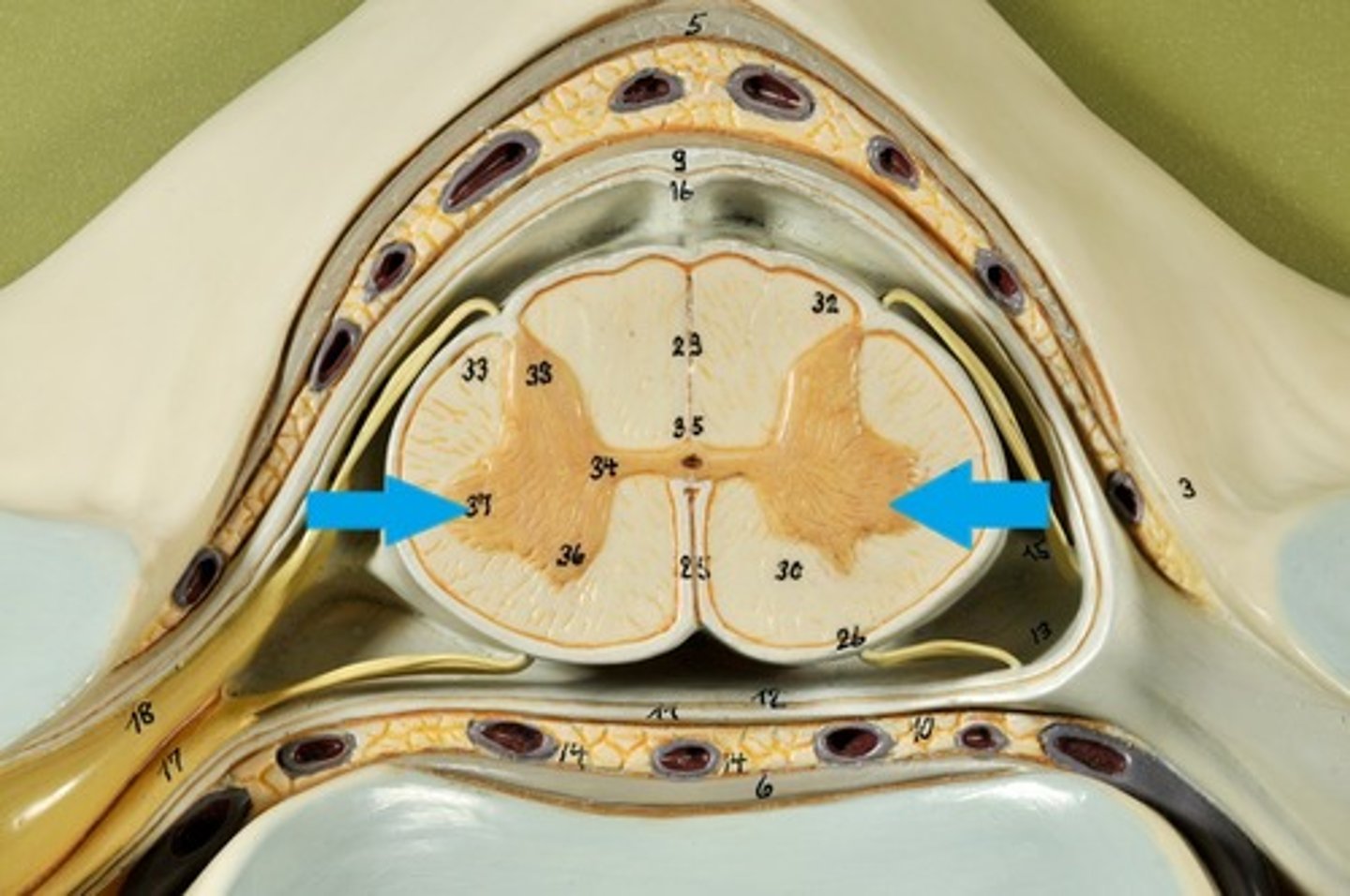
Ventral Horns
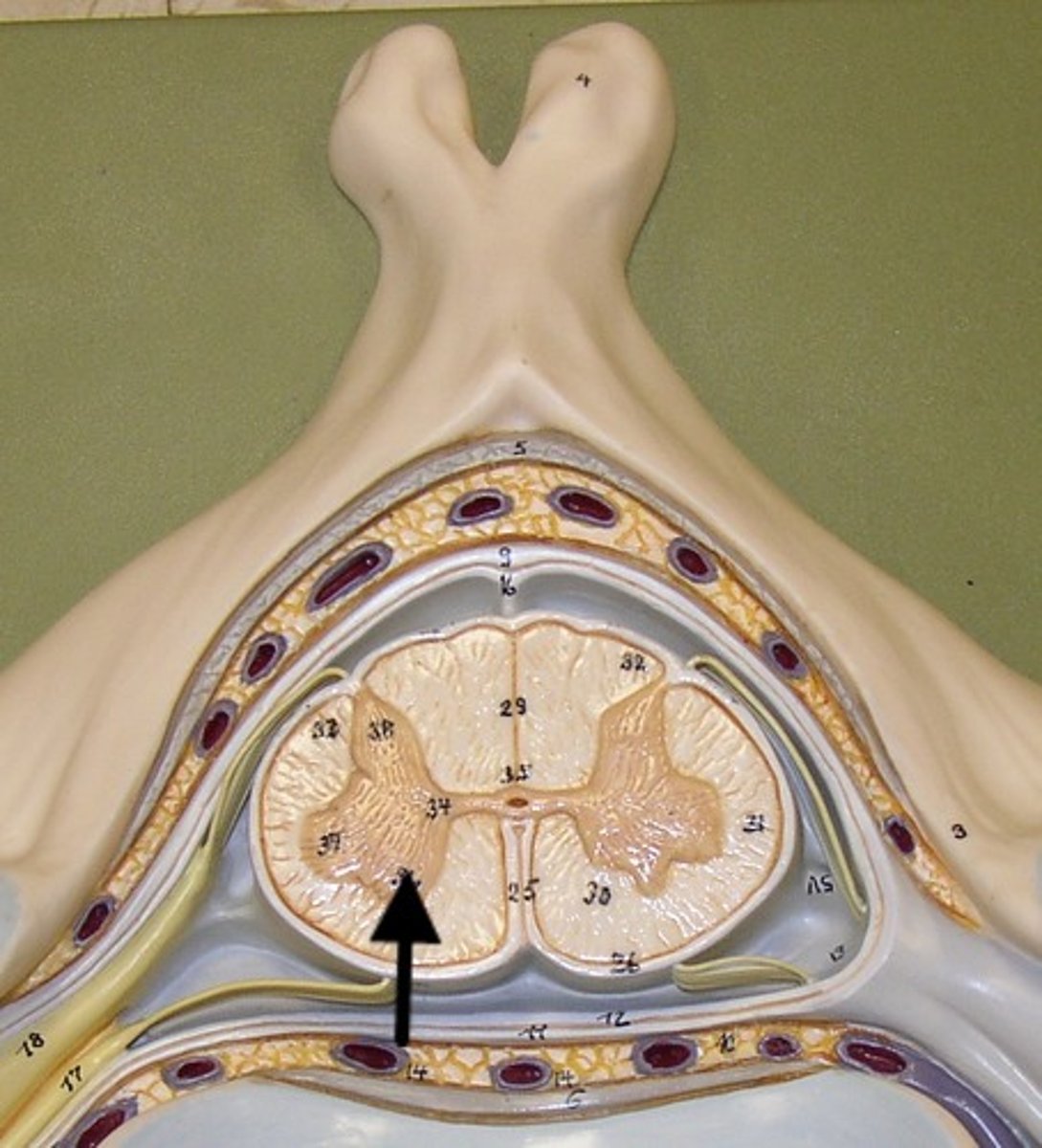
Interneurons
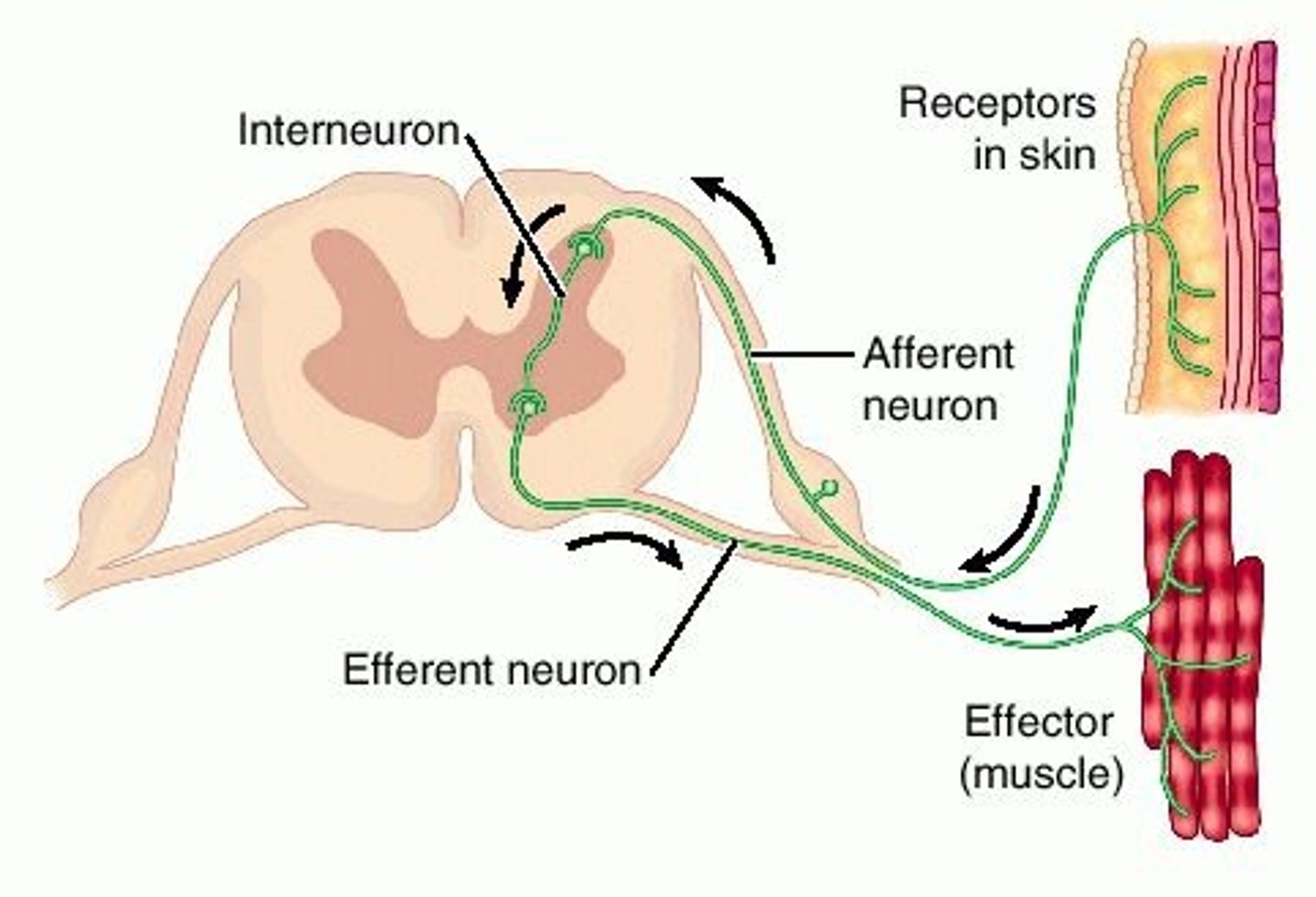
exterior white matter of the spinal cord
Ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) myelinated nerve tracts,
Posterior, anterior, lateral columns or funiculi
Posterior Columns
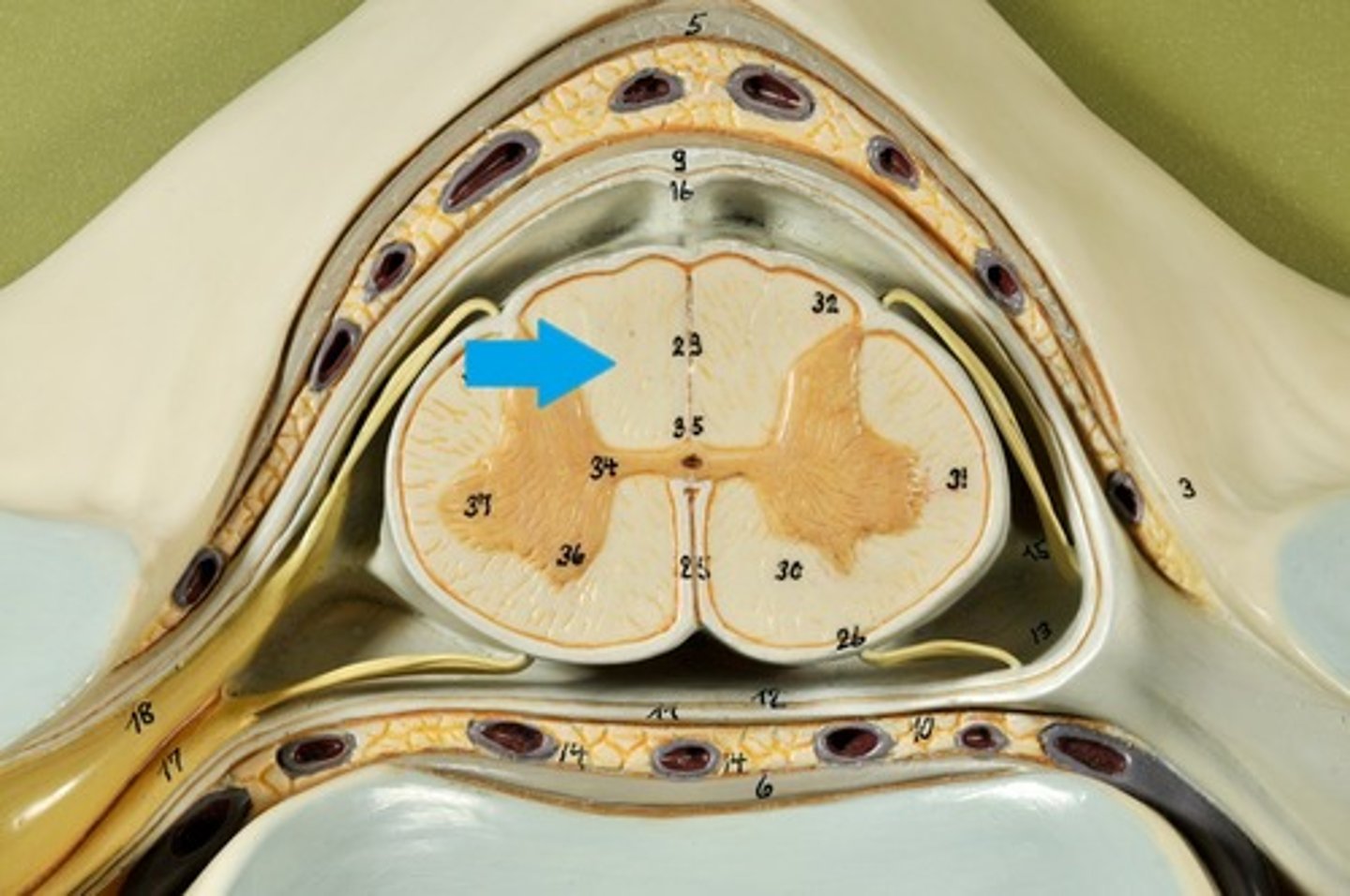

Anterior Columns
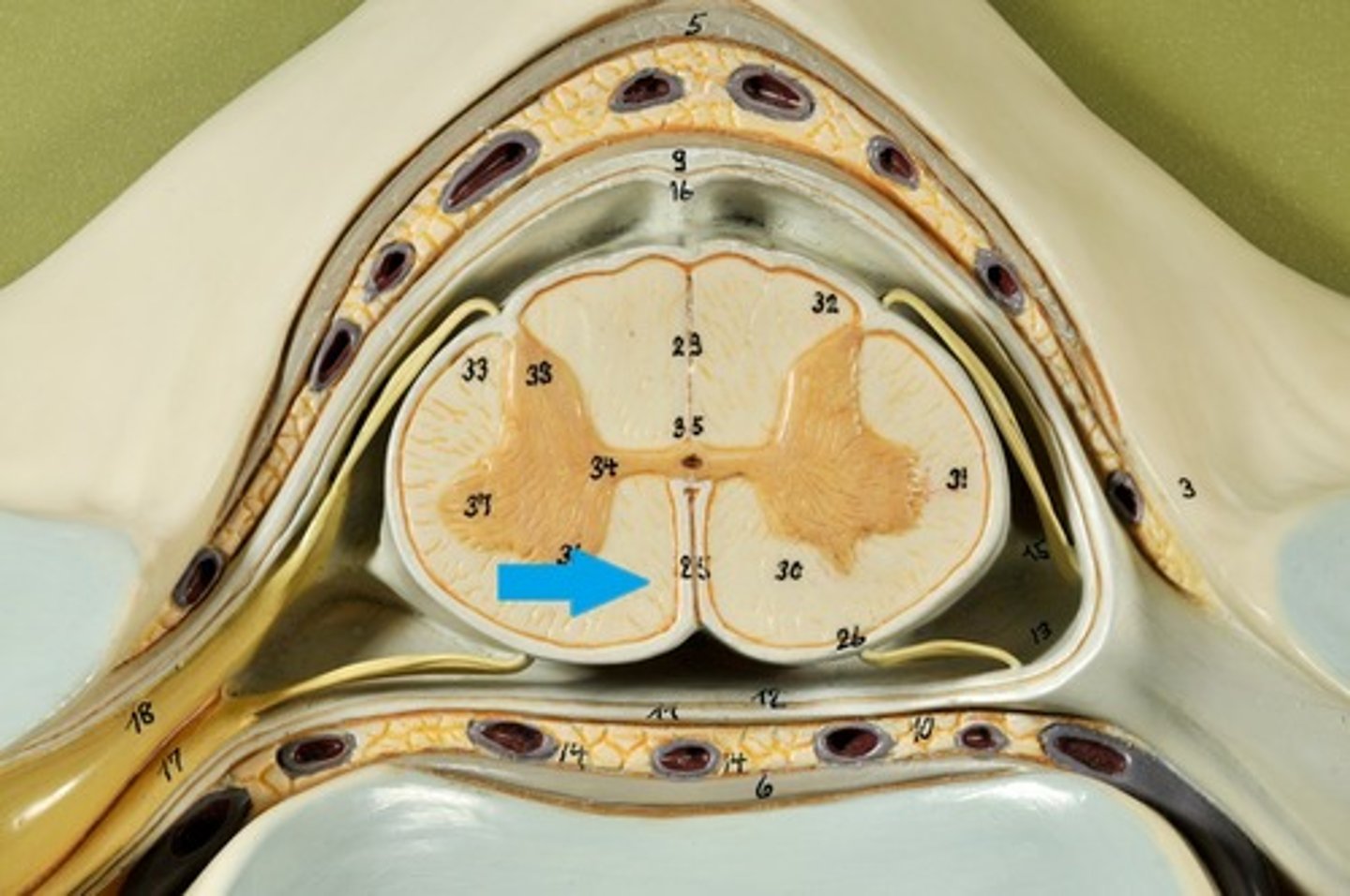

Lateral Columns/ funiculi
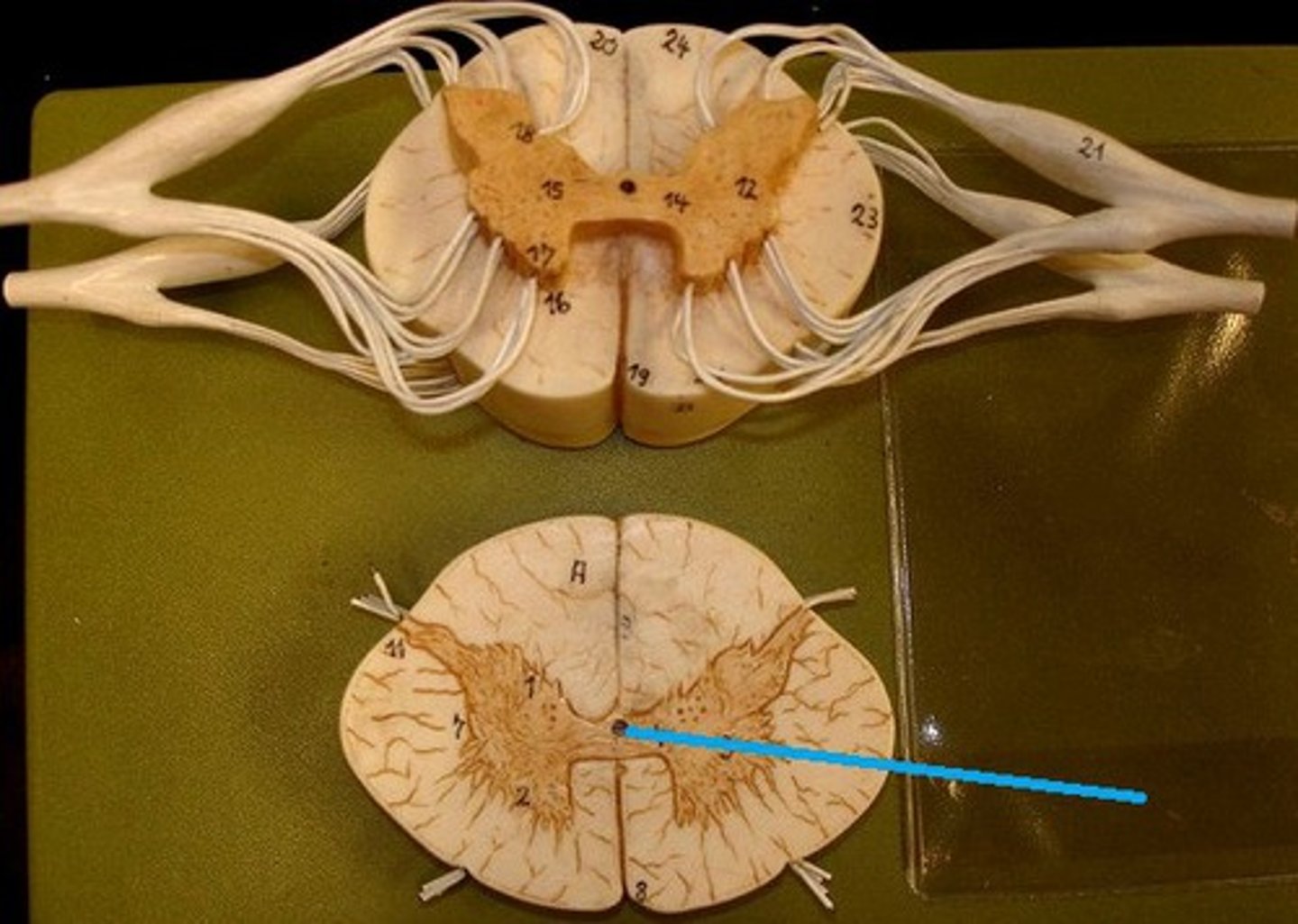
Central canal filled with what?
Central canal filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Cushioned and protected by meninges
1) Cover the spinal cord
2) Dura mater, Arachnoid & Pia mater
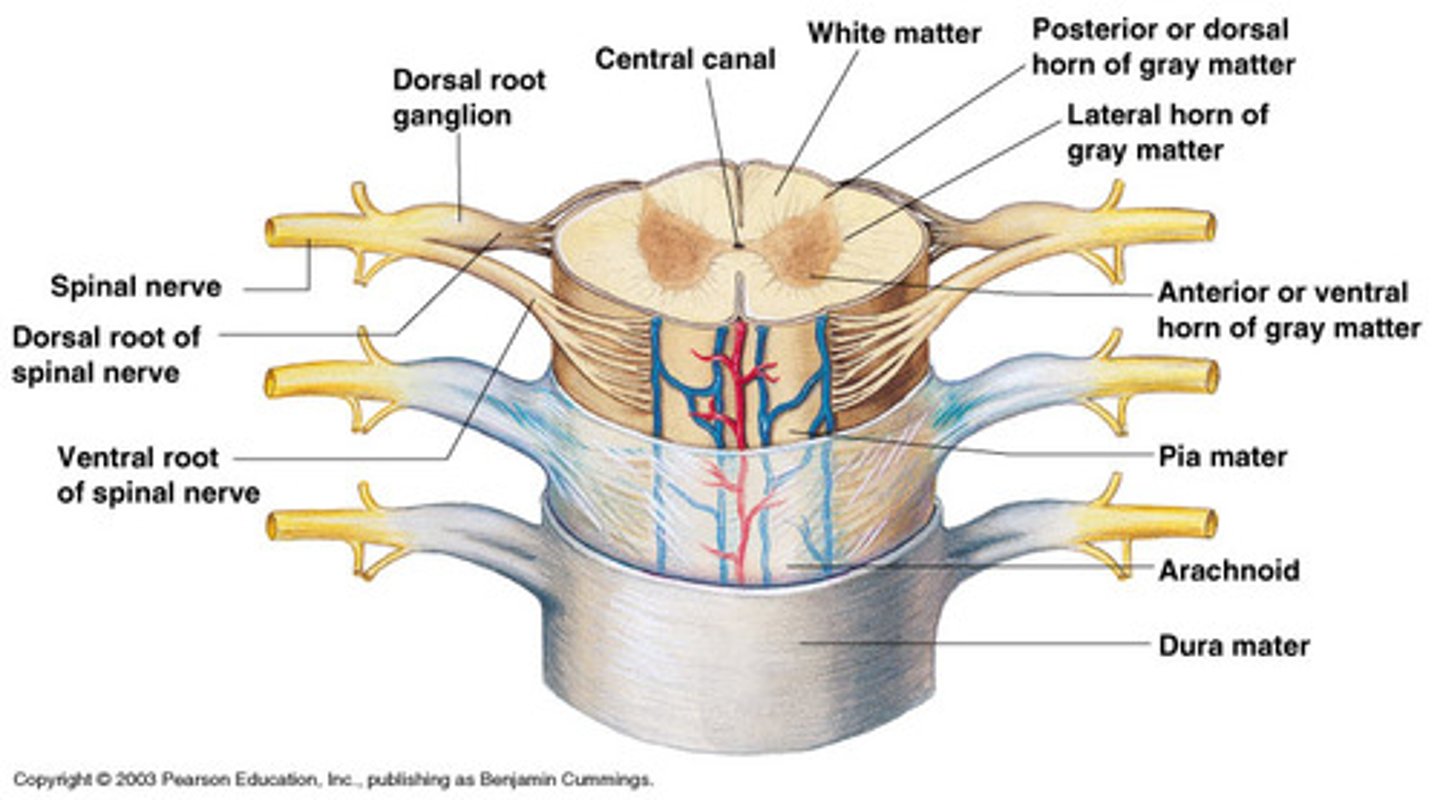
dura mater of spinal cord
1) Separated from the periosteum by the epidermal space (fat, blood vessels)
2) Subdural space between dura and arachnoid mater
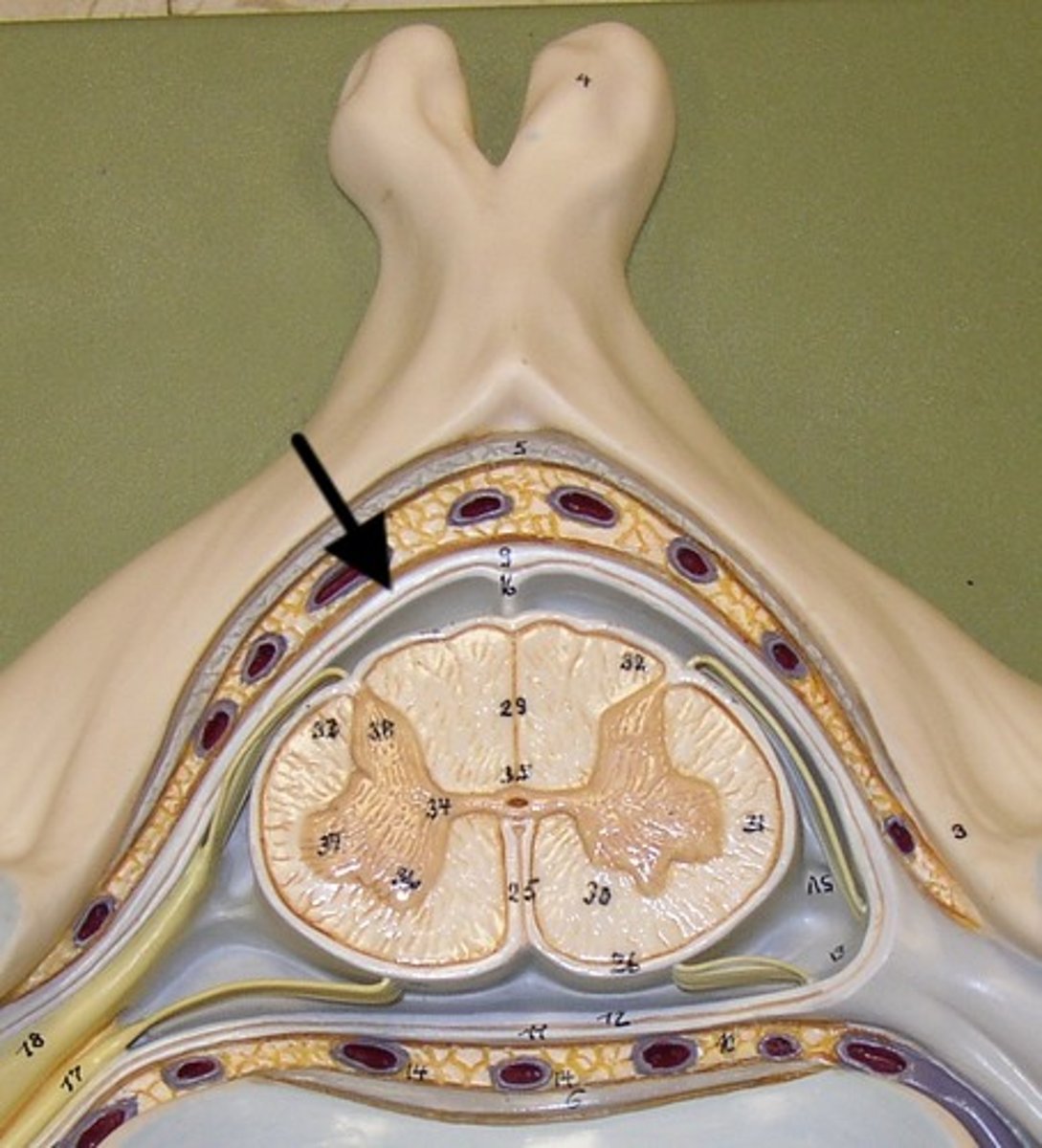
Dura Mater