ChemLab Final
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
NMR
just for the hydrogens, to find what molecule it is
3 things to look for: chemical shift, integration, splitting
cs: where is it on spectrum, down or up on line, closer to Eneg atom makes H signal more down (left) further to Eneg is right, methyl groups are inherently less eneg due to amount of hydrogens
integration: equivalent protons (on same methyl,etc) makes peak higher (3H taller than 2H)
splitting: equivalent protons can be split into multiple peaks → depending on neighboring protons (n+1 rule), if neighbor present use n (neighbor H) + 1 rule to determine how many peaks will occur
spitting in shoes
splitting integration shift
IR
stretches and beards, tell connectivity btw molecules (C=C, C-H)
1500 and below IGNORE
look at 3 things: wavelength #, signal strength (not v important)
wavelength: look at chart C=C-H in aromatic ring, C-H
alkane C-C-H, alkene C=C-h, alkyne C≋C-H
ss: dips down further → strong signal below 30%, shorter dip → medium signal 60% - 30%, shorts dip → upper 60%
safety chart

12 principles of green chemistry
waste prevention → maximize amount of atoms → use less hazardous chemicals→ safer solvents → be energy efficient → use renewable chemicals → reduce derivatives → use catalysts to reduce energy and time → design for degradation → prevent pollution → choose safer procedures for reactions
Experiment 2 Lab
Summary: triglycerides (esters that connect 3 fatty acids chains to glycerol (3 alcohol groups) backbone), fatty acids are carboxylic acids with longgg hydrocarbon chains → unsat vs sat: unsat C=C vs sat C-C, unsaturated has kinks that make it harder to dissolve, esters from fatty acids
ester has C=O vs ether has C-O
Mechanism:
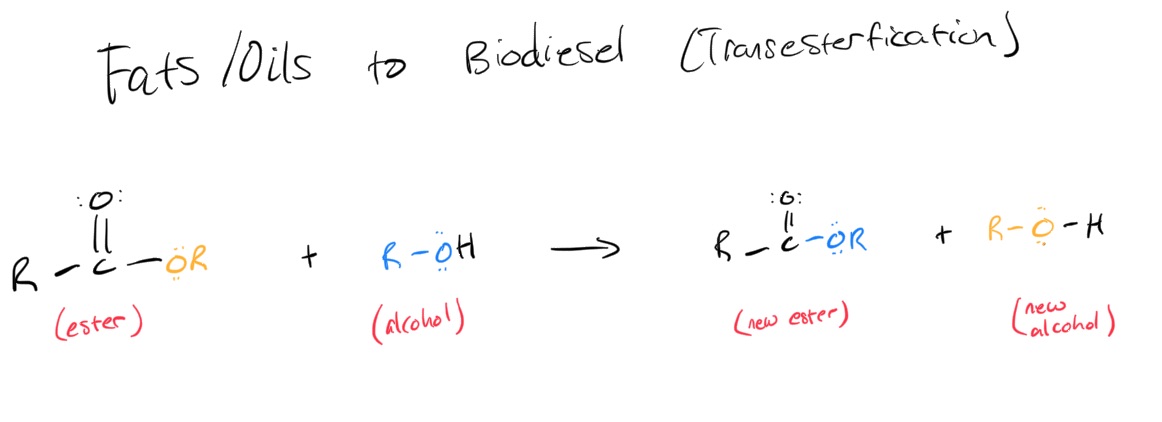
Methods: add methanol, potassium hydroxide, and sodium chloride (helps layers to separate) to tube w/ oil → shake and heat → poured top layer into candle and burned → biodiesel synthesis breaks bonds btw glycerol and fatty acid chains & adds methyl group to end of fatty acids → makes 3 monoesters from EACH tri-ester. react the esters of the triglycerides with alcohol(methanol) to create monoesters and glycerol
specific heat: q= m*C Δt or q= m ΔH → heat energy= mass * specific heat * change in temp
biodiesel is less viscous than canola oil because of triesteres converting into monoesters which allows more movement
KOH was cataylst that broke ester bonds btw glycerol backbone and fatty acids
temperature is measure of average kinetic energy, heat is thermal energy transferred due to temp
Green chemistry: biodiesel produces less energy than reg diesel BUT cleaner
Experiment 2 Math
Experiment 3 PreLab Liquid Liquid Extractions (purification)
summary: used separatory funnel to see difference btw 2 liquid (insoluble) layers → organic (hexanes/nonpolar/no charges) vs aqueous (water/polar/charged) → change the structure of molecules to influence solubility in organic vs aqueous (ex: carboxylic acid is organic soluble but when reacted with a base to make an - it is soluble aqueously, extraction is process of moving compound btw liquid layers.
Washing vs Extraction: W→ desired compound stays in same layer, impurities move E→ desired compound moves, impurities stay, solute must be only soluble in ONE layer
pKa: high pKa= more basic, low pKa= more acidic
Partition Coefficient: to separate a mixture of 2 compounds dissolve mixture in organic solution, add water and two layers will appear, sometimes both layers are slightly soluble in both (called partitioned (P)). P= conc /solubility of compound in organic solution/ conc/solubility of compound in aq solution. If P is >1 compound is og soluble, if P <1 compound is aq soluble
Methods: mixed nile blue with hexane (stayed as 2 separate layers) → added NaOH (nile blue turned pink) → separated layers (took pink out) and readded it along with more hexanes → extracted pink again
to tell difference btw aq and og layers: add water and see which layer increases, check density
can convert organic acids & organic bases into water soluble salts
to find how much of a molecule is removed from extraction use x+y= grams given and x/y for conc
Green chemistry: control solubility to perform separations to isolate our desired product and minimize solvent use (solvents take a lot of energy and cannot be recycled usually)
Experiment 3 Math

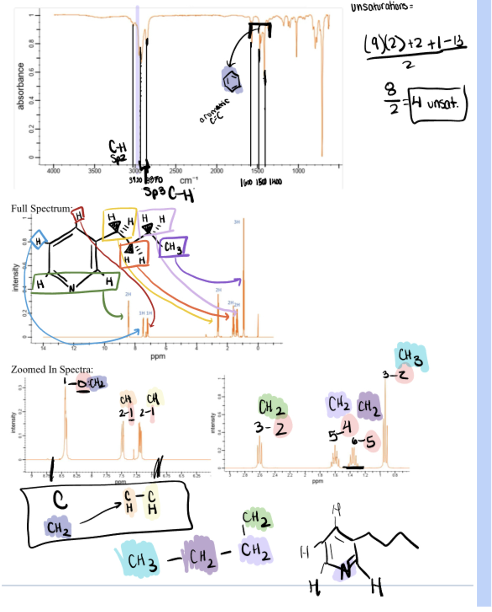
Experiment 4 IR & NMR
IR & NMR
NMR (diff resonances of Hs)
just for the hydrogens, to find what molecule it is
3 things to look for: chemical shift, integration, splitting
cs: where is it on spectrum, down or up on line, closer to Eneg atom makes H signal more down (left) further to Eneg is right, methyl groups are inherently less eneg due to amount of hydrogens, AROMATIC RINGS MAKE MORE LEFT TOO CAUSE OF SHIELDING
integration: equivalent protons (on same methyl,etc) makes peak higher (3H taller than 2H)
splitting: equivalent protons can be split into multiple peaks → depending on neighboring protons (n+1 rule), if neighbor present use n (neighbor H) + 1 rule to determine how many peaks will occur
spitting in shoes
splitting integration shift
IR (vibrations of diff stretching and bending of molecules as IR light passes thru)
stretches and beards, tell connectivity btw molecules (C=C, C-H)
1500 and below IGNORE
look at 3 things: wavelength #, signal strength (not v important)
wavelength: look at chart C=C-H in aromatic ring, C-H
alkane C-C-H, alkene C=C-h, alkyne C≋C-H
ss: dips down further → strong signal below 30%, shorter dip → medium signal 60% - 30%, shorts dip → upper 60%
unsaturations: degrees of unsaturation = (2#Cs + 2 #Ns - X -#Hs)/2
degrees of freedom (n is number of molecule): linear molecules→ 3n-5, nonlinear molecules→ 3n-6
Experiment 4 Charts/Examples
Experiment 5 DMAP
Summary: determining which pathway (ie which Nitrogen would get attacked) DMAP would take → only use NMR, different integrations depending on pathway
Methods: mix DMAP & methylene chloride, NO WATER (DMAP will react with water and result in no product) → add methyl iodide and reflux → cool in ice bath and vacuum filter
SN2 reaction btw amine and alkyl halide
methyl iodide is a carcinogen
Green chemistry: atom economy is 100%
Experiment 6 Fischer Esterfication
Summary: when clumping of drying agent occurs = dry, alcohol is better than water as a solvent because it doesn’t have to be removed from the solution (water will cause reaction to reverse)
Methods: mix transcinnamic acid, methanol, & H2SO4 → reflux → cool & move to seperatory funnel
→ add NaHCO3 to neutralize, add diethyl ether → add MgSO4 to DRY → filter out drying agent → heat to evaporate solution
Nomenclature
(alcohol)yl (acid)ate
Green chemistry: fisher esterfication uses less toxic chemicals to get product
TLC
Experiment 7 Grignard
Methods: make grignard, react grignard, work up grignard (remove MgBr)
make: Mg inserts itself inbtw Br, makes C attached to MgBr more Eneg
react: MgBr breaks off and bond attacks C=O on ketone and breaks =O to make O- , MgBr+ ‘attaches’ to O-
work up: MgBr is pulled off by acid/water to make Mg(OH)Br
NO WATER products will react with it
colors→ color we see is actually what is being reflected because the complement has been absorbed, if you see red = blue/green has been absorbed. 8 conjugated bonds needed for color
Malachite Green: transitions from yellow to green (0.2-1.8) & green to colorless (11.5-13.2)
Crystal Violet: transitions yellow to purple (0.0-1.8)
the higher the # of double bonds in conjugated system → the lower the HOMO LUMO gap → helps appear colored, a longer wavelength indicates a smaller HOMO LUMO gap
Green chemistry: grignard reactants are bases so they react to acids, reduce undesired byproducts
Experiment 8
Summary: arylboronic acid + an aryl/vinylic halide = suzuki miyaura coupling product (in basic conditions w/ Pd catalyst), needs a base KOH
insertion of initial Pd catalyst into Br-C bond (oxidative addition) → Pd turns into Pd II (rate determining step) → Pd II reacts with arylboronic acid (transmetallation), tranfers aryl group from arylboronic acid to palladium atom, this makes B → new C-C bond made btw aryl groups bonded to Pd II of B, also regenerates og Pd
Methods: added aryl halide to ethanol, add arylboronic acid, add Pd, stir, add ice cold water, vacuum filter, dissolve in CH2Cl2 add MgSO4, filter and evaporate
Green chemistry: catalytic reactants are superior to stoichiometric reagents, multiple uses, short time, lower temp
Experiment 8 math
reactivity C-X bond depends on strength of bond (inverse relationship) and depends on size of halogen (inverse)
the longer the bond the less energy needed to break it and the higher the reactivity
dihedral angle = angle btw two intersection planes, always less than 180
Experiment 9 Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
Summary: break and reform aromaciticity by adding nucleophile and making a nitrogen-anion, increased amount of EWG ortho or para to LG, replacing chlorine with fluorine increases reaction rate, soak shirt in sodium carbonate (removes
Methods: soak shirt in sodium carbonate → make dyes and dye shirt, let soak for a week → rinse and gather waste water → treat wastewater with charcoal and heat → filter with celite
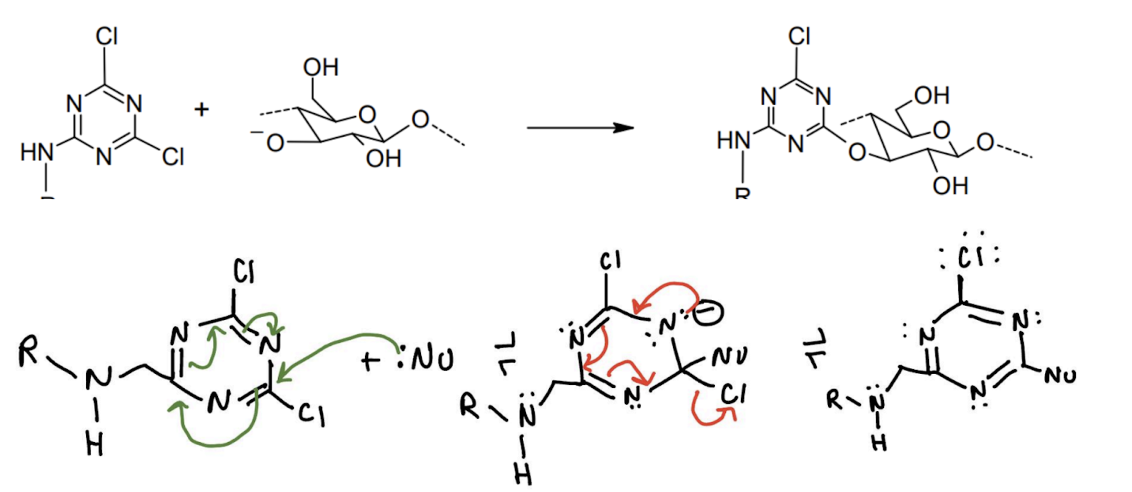
Green chemistry: literally all of them i aint writing that basically just treating waste water to release back to the fishies
Experiment 10 PTAD diel-alder
Summary: pericyclic reaction (everything happens at once), regioselective, stereoselective, PTAD is red and hetero-diels-alder is colorless, when color change occurs= reaction complete
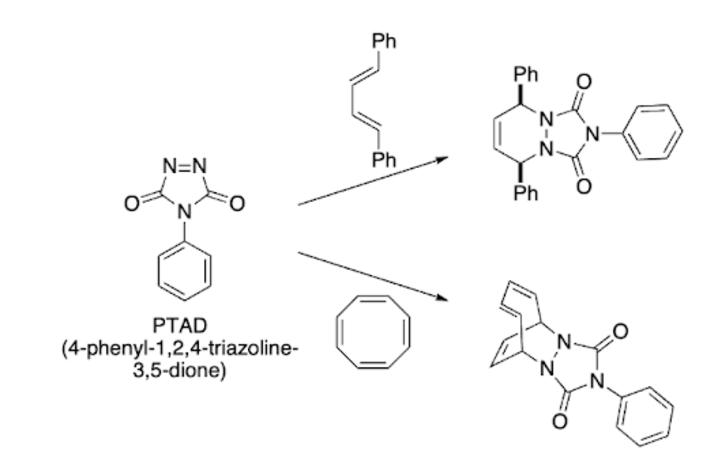
Methods: add 4-phenylorazole, oxone, potassium bromide, dichloromethane together → add water & stir → vacuum filtrate, gather liquid → add diene dropwise → boil off solvent → collect solid
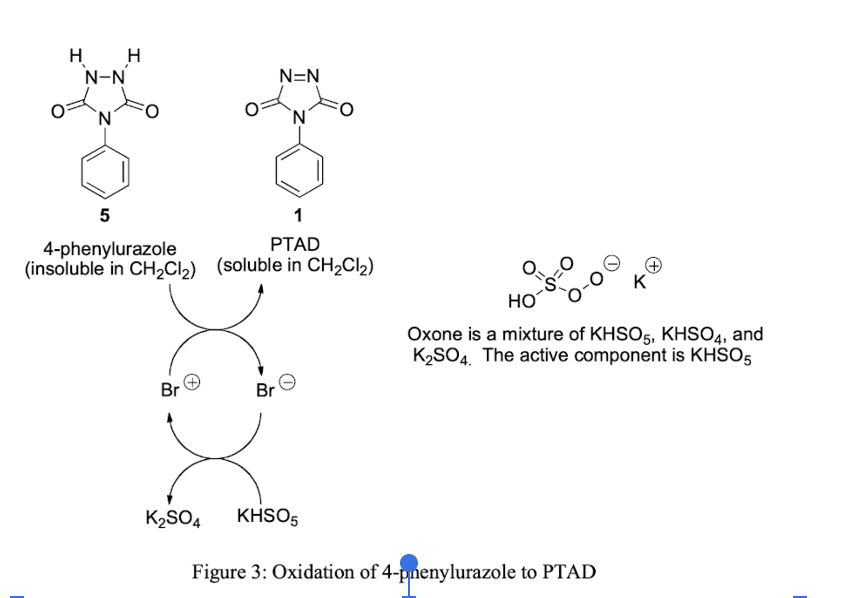
Green chemistry: chose reactants that will react at room temp, dienophile is conserved (cis to cis)
Experiment 11 Luminol
Summary: made chemiluminescent product, luminol lights up when detecting blood (reacts with iron), reaction needs base to deprotonate amines,
vacuum aspirator pulls out water vapor
Methods: heat water → add 3-nitrophthalic acid & hydrazine → heat & add triethylene glycol → heat, asperate water off → cool and add warm water to QUENCH → filter intermediate → add nitrto & NaOH in test tube → mix & add sodium hydrosulfate dihydrate → reflux → cool and quench → vacuum filter, dissolve in water & NaOH → add ferrieyanide, hydrogen peroxide & water→ mix 2 solutions
Magnesium Sulfate is DRYING AGENT
Hirsch Funnel vs Buchner Funnel: H→ smaller, filters small amounts B→ bigger, can filter out larger volumes
Green chemistry: luminol is v reactive needs little amount to get desired result
bumping
Experiment 11 math