Module 5 Electricity
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
define electrostatic force
the force of attraction or repulsion between charged objects/particles
Columbs Law states
theres a force in between all charged particles and its magnitude depends on the magnitude of the particles charge and their distance from eachother
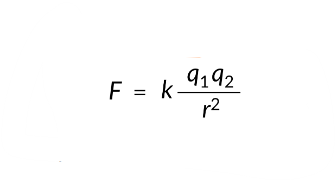
this measures what
electrostatic force (Columbs Law)
unit of charge
Coulumb (C)
μC
microcoulumbs
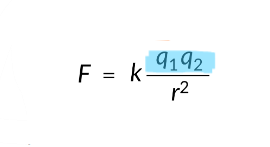
charge force in unit of C
elecric feild
the surrounding area of a charged object that exerts force on surrounding objects
electrons all have an elementary (or fundamental) _____
charge
define elementary charge
the smallest non 0 charge that can be carried by a particle
elementary charge is ____ for the electrons and _____ for the protons
negative, positive
all substances have a charged that is some multiple of _______
elementary charge
electric force increases as charge ____
increases
electric force decreases as distance ______
increases
define electric field (E) in equation
the force that 1C of charge feels in a field
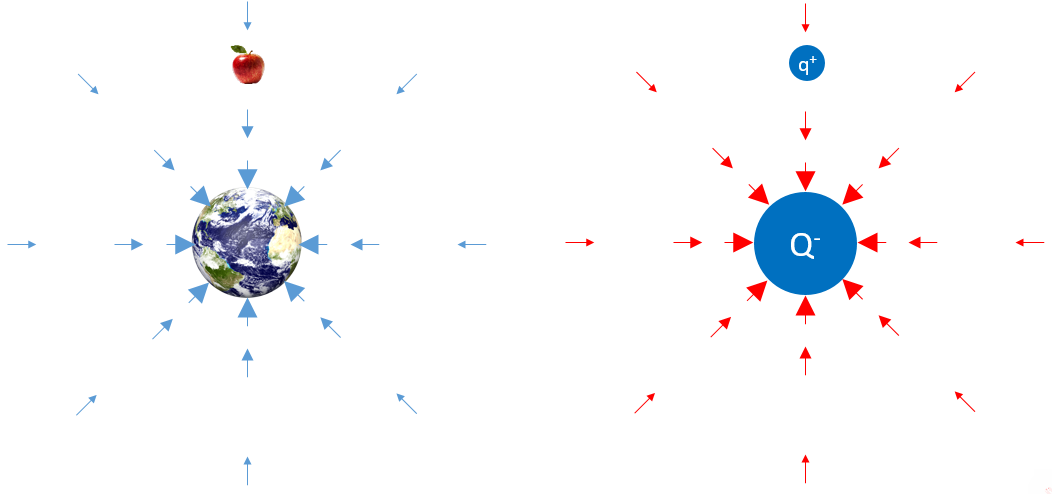
electrical feild works the same way as
gravitational feild
if an electrical feild were compared to earths gravitational feild, the charged object is
earth
any charged object has a
electric feild
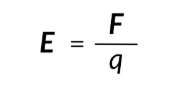
electrostatic force
the strength of electrostatic force ______ as distance from the source increases
decreases
as distance from source decreases, strength of electrostatic force _____
increases
how to find electric feild (E)
electrostatic force (F) times amount of charge placed in feild (q)
define point charge
the charge of the source of an electric feild
what does the point charge equation measure
The magnitude of the electric field at a specific distance away from the point charge
newtons 3rd law
for every action there is an equal opposite reaction
capacitor
a device that stores electrical PE
current flows from
pos term to neg term, high voltage to low voltage
electron flows
negative to positive
conventional current
flow of pos chargecu
current
rate of charge flow, deltQ/deltR
unit for current
amp
ohlms law
V= current times resistanve
electric power
voltage times current (VI) or I² R or V²/ R
1 watt
1 joule/sec
voltage=
IR
electric currents are basically the flow of
electrons
what is power dissipation
the thermal energy released by an electric current when its voltage drops after passing a resistor
unit of power dissipation
watts
unit of capacitors
Farads μF (= 10−6 F)