BIO 201 - Nervous System
1/430
Earn XP
Description and Tags
My nervous system is SCREAMING rn im gonna pass out
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
431 Terms
These immune cells of the nervous system respond to injury
microglia
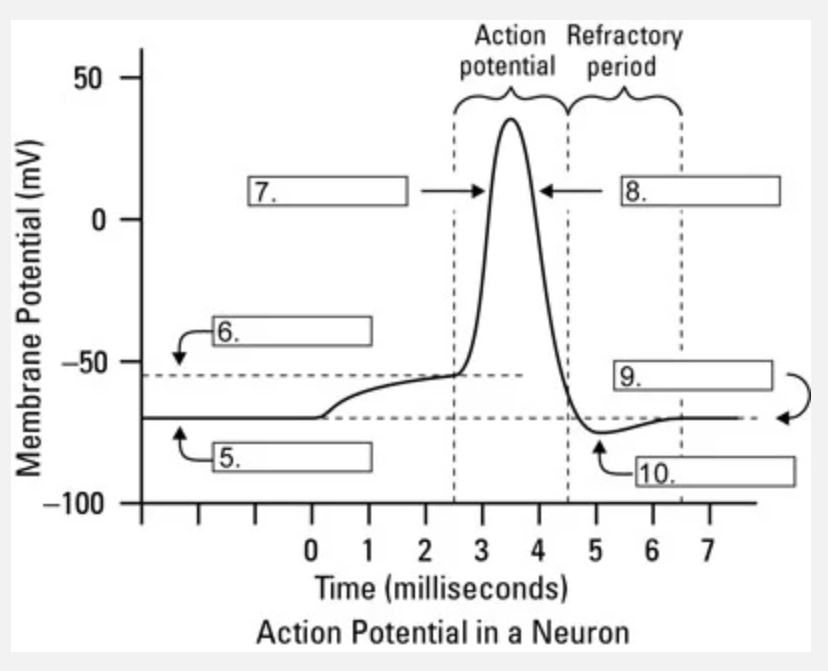
What is occuring at #5?
resting state
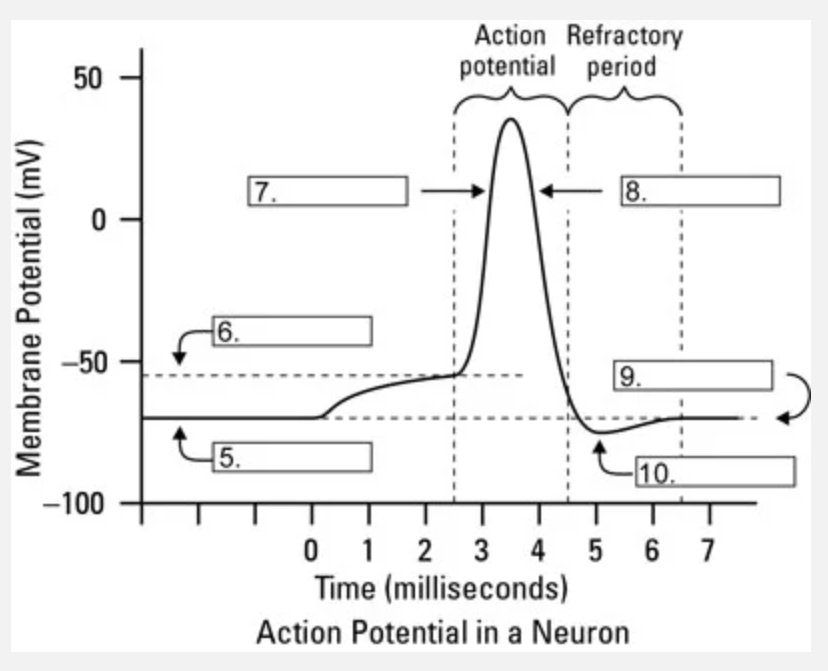
What is occuring at #6?
threshhold
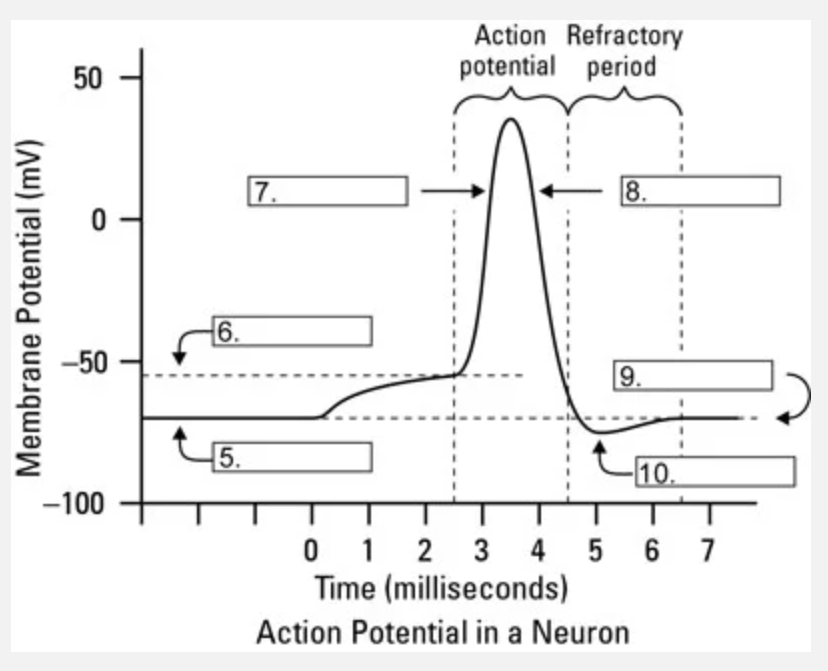
What is occuring at #10?
hyperpolarization
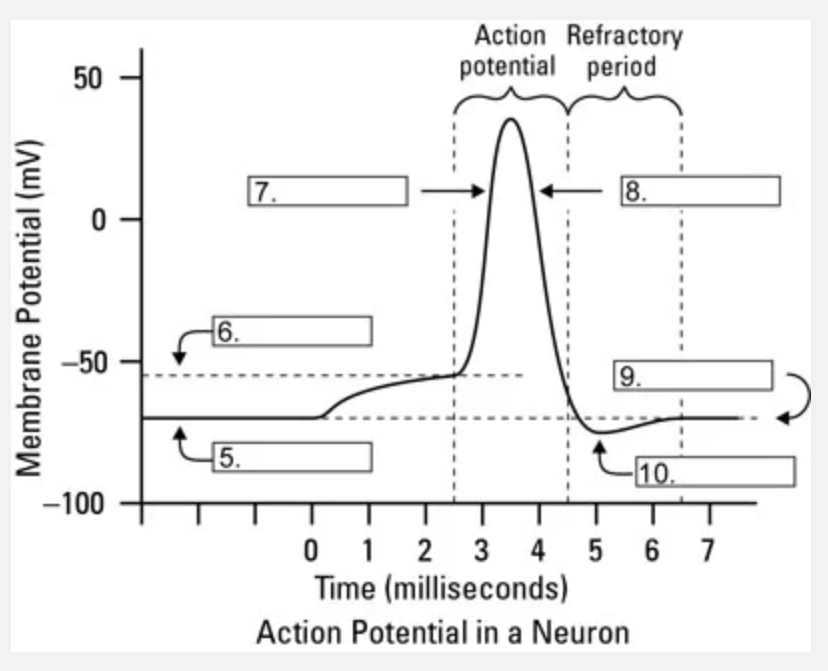
What is occuring at #8?
repolarization
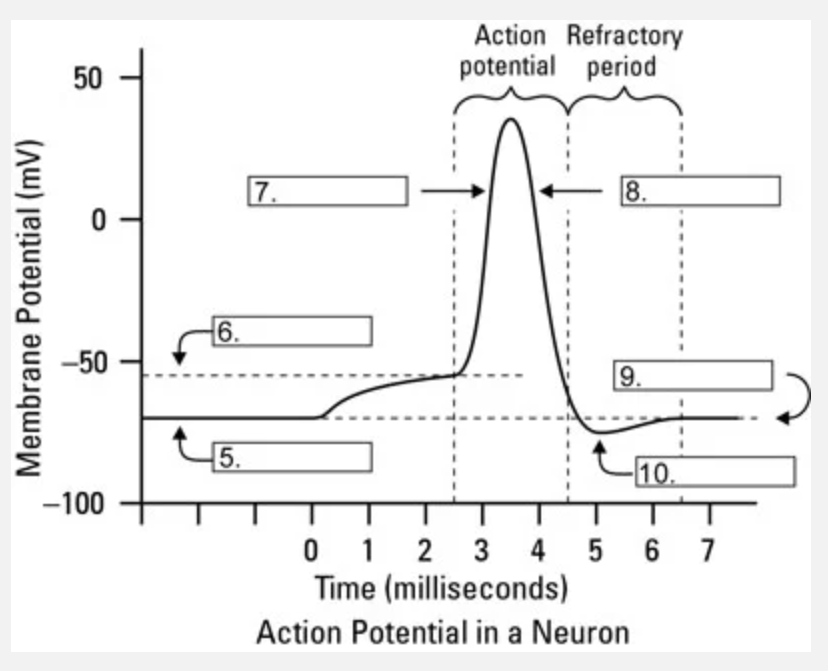
What channel is most likely responsible for area 10 going back to resting membrane potential?
sodium/potassium pump
Oligodendrite is to CNS as ____ is to PNS
Schwann Cell
_____ is to CNS as Schwann Cell is to PNS
Oligodendrite
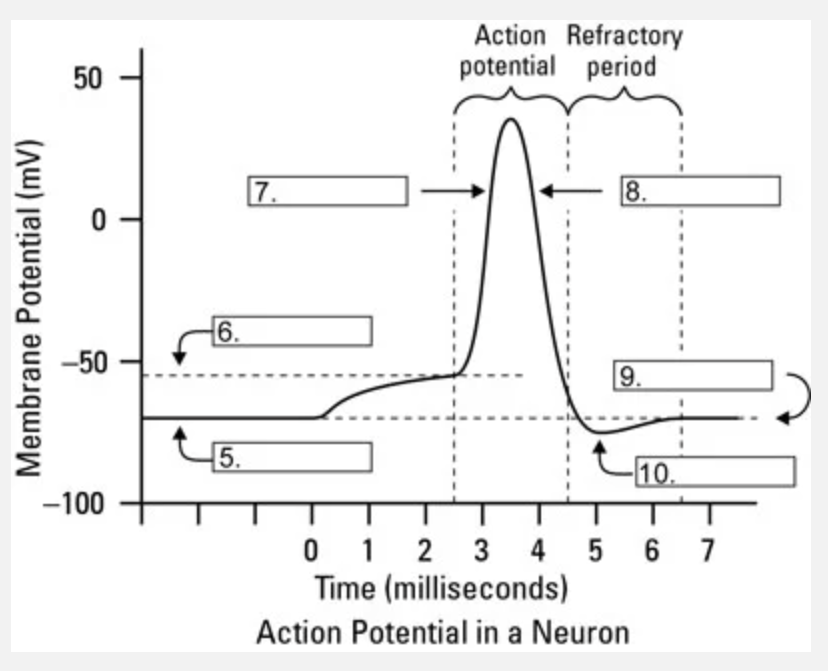
Ascending portion of the Action Potential graph represents
opening of sodium voltage gated channels
During ____ another action potential cannot occur
absolute refractory period
What happens in depolarization during action potential?
the inside of the cell becomes positive
In myelinated axons, action potentials occur where
only at the nodes of Ranvier
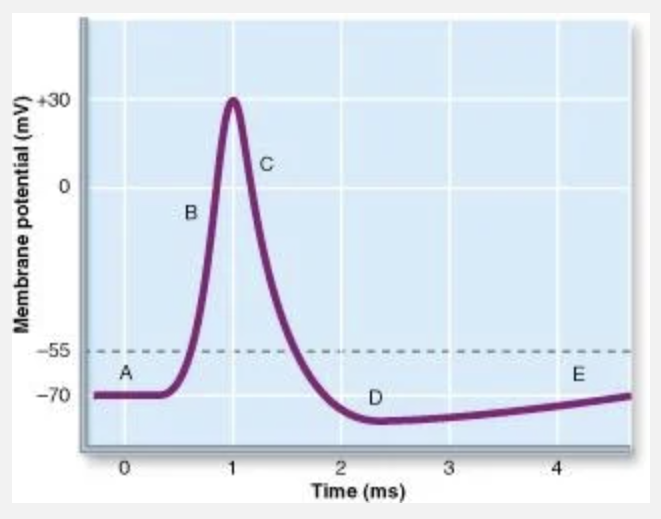
All Na+ inactivation gates are completely closed at
C
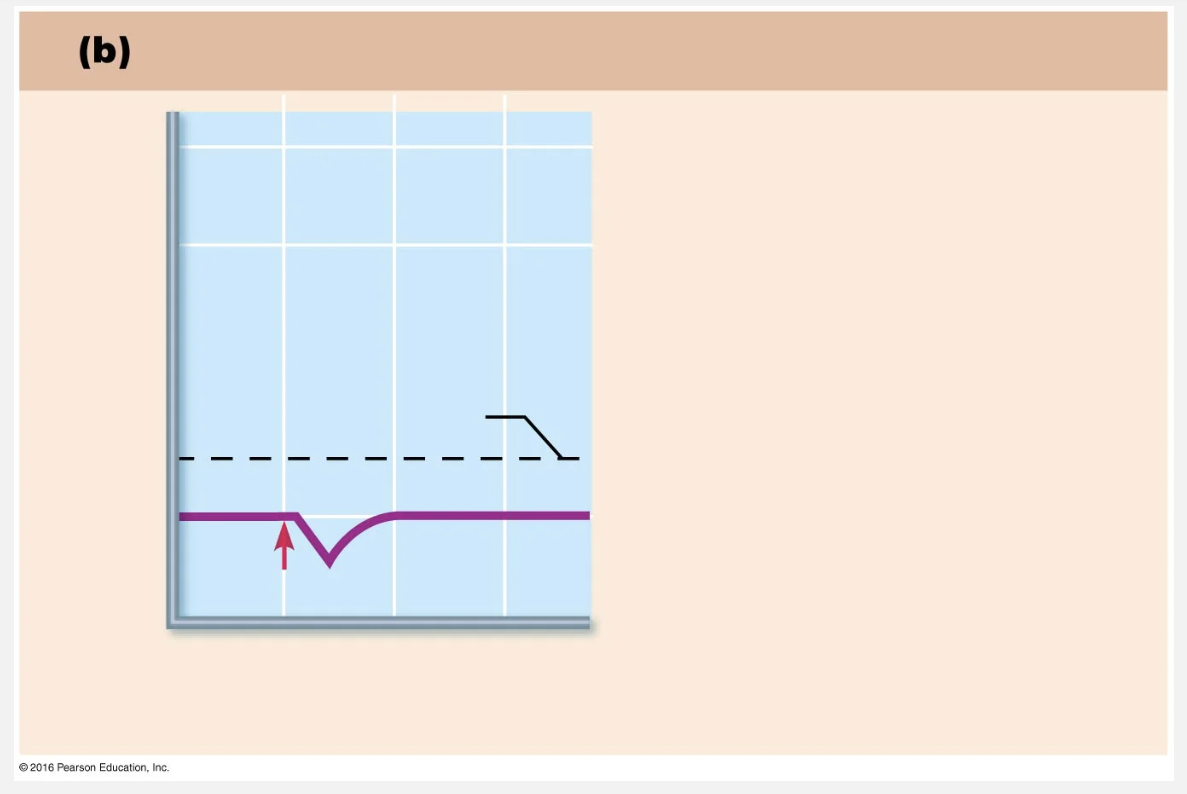
this graph shows (IGNORE THE ARROW)
hyperpolarization
At RMP leaky channels allow Na+ to move in what direction?
into the cell
Describe metabolism of neurons
very metabolically active
What three things play a role in the conduction velocity of an axon
presence of oligodendrocytes or Schwann cells, diameter of the axon, degree of myelination
How would you describe a membrane channel protein that opens when bound by a neurotransmitter?
ligand gated
If a stimulatory (excitatory) neurotransmitter bound to a protein, which would happen?
depolarization
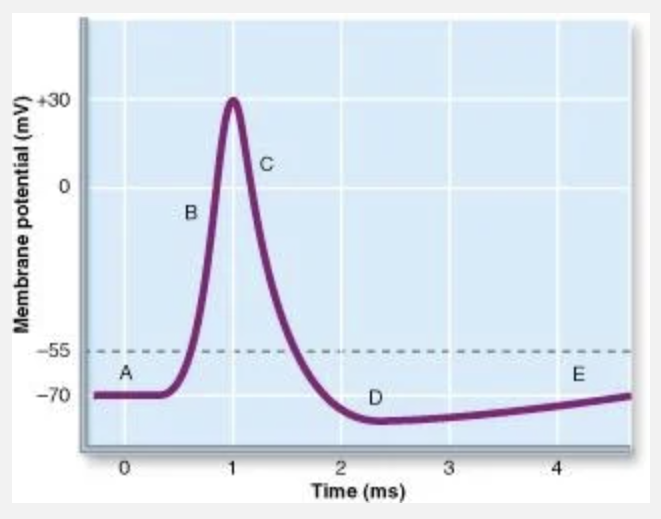
Which letter corresponds to Na+ RAPIDLY coming into the cell?
B
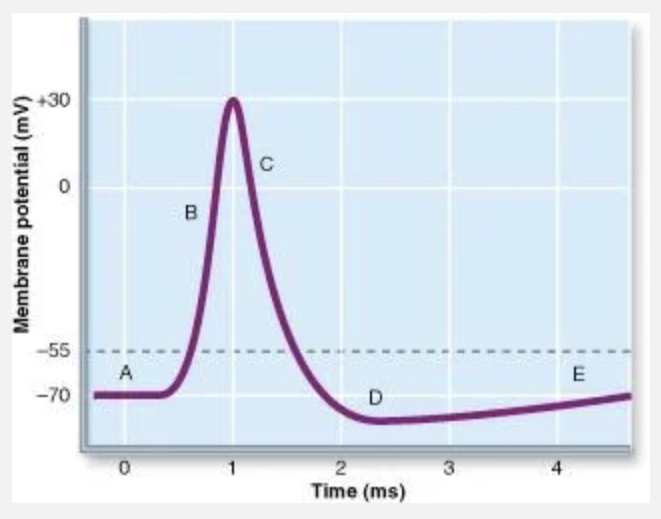
Which letter shows where K+ is leaving the cell?
Both B and C
During ____ a depolarization event can not occur
absolute refractory period
In terms of an AP, what is threshold?
its the voltage at which an AP will definitely occur
Which structure carries a signal away from a neuronal cell body?
axon
What two things GENERATE the RMP?
leaky Na+ channels and leaky K+ channels
Does Na+ or K+ have a greater concentration inside the cell?
K+
What are astrocytes?
cells that can provide nourishment to neurons
What is a synapse?
where two neurons meet
Place the events that occur at a synapse in order
I. Graded potential generated
II. Gates open on post-synaptic cell
III. Ca2+ enters an axon terminal
IV. Neurotransmitter released into cleft
III, IV, II, I
Do graded potentials summate? (Y/N)
Yes
Are Graded Potentials all-or-nothing? (Y/N)
No
Graded potentials travel (long/short) distances
short
Graded or Action Potential? These potentials have refractory periods.
Action
Graded or Action Potential? These potentials can be either a depolarizing or hyperpolarizing events.
Graded
These graded potentials cause the neuron to become more permeable to Na+ thus causing depolarization.
EPSP
These graded potentials cause the neuron to become more permeable to K+ thus causing hyperpolarization.
IPSP
This divison of the nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord
Central Nervous System
Division of the peripheral nervous system involved with voluntary motor control.
somatic
Divisions of the autonomic nervous system. (2)
sympathetic and parasympathetic
What is the autonomic nervous system?
the system that is in charge of involuntary muscle
What nervous system encodes the “fight-or-flight” response?
Sympathetic nervous system
Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are associated with what?
hyperpolarization of the cell membrane
An IPSP from three neurons and two EPSPs from two other neurons at the same time describe ___ summation
spatial
What two things do EPSPs do?
depolarize the membrane and open cation channels
When the action potential reaches the axon terminal, Ca2+ does what?
ca++ rushes in
What happens once an action potential reaches the axon terminal?
Channels open and CA+ will enter the presynaptic cell
What three mechanisms can remove neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft?
degradation by enzymes, diffusion out of the synaptic cleft, reuptake by astrocytes or back into axon terminal
Why is it so important to remove neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft?
if they remain, the post-synaptic cleft will be continually stimulated.
During depolarization, the inside of the neuron becomes more (positive/negative)
positive
During repolarization the neuron gets more (positive/negative/sad/excited)
negative
Neuron repolarization occurs due to (potassium/sodium) diffusing (in/out)
potassium diffusing out
Hyperpolarization makes the neuron more (positive/negative) and (less/more) likely to fire
more negative; less likely to fire
Propagation of action potential is (unidirectional/bidirectional/multidirectional)
unidirectional
Why is propagation of action potential unidirectional?
inactivated sodium channels
True/False: Myelination slows down propagation of action potentials
False
The propagation of action potentials travels from ______ to ______
axon hillock to axon terminals
Dendrites ______ : Axon ______ (sends/receive)
receive, sends
What are sensory neurons that carry nerve impulses from sensory stimuli towards the central nervous system and brain.
Afferent Neurons
Leakage channels…
are always open
Two differences between oligodendrocytes and schwann cells...
is that the oligodendrocytes can wrap many neurons at once and that the schwann cell wrappings are the entire cell
Positive feedback in an action potential correlates to?
depolarization
What role does positive feedback play in the action potential
the influx of sodium causes more sodium channels to open
Strength of a stimulus is coded by
frequency of action potentials
what do interoceptors do
receive stimuli from internal visceral
Exteroceptors detect:
changes in our external environment
What three things do mechanoreceptors detect?
Vibration, pressure, and touch
Sympathetic preganglionic fibers release this
acetylcholine
in parasympathic fibers: preganglionic release _______ and postganglionic release_______
ACh, ACh
Parasympathetic postganglionic fibers release
acetylcholine
Most sympathetic postganglionic fibers release?
norepinephine
Sympathetic division stimulation causes (increased/decreased) glucose, peristalsis, hr & bp
increased glucose, decreased peristalsis, increased hr & bp
Autonomic Nervous System controls what muscle(s)
Smooth and Cardiac
All spinal reflex arcs start with?
a stimulus
A spinal reflex arc pathway is (6 parts)
Receptor, Sensory Neuron, Relay Neuron, spinal cord, motor Neuron, effector
What does autonomic nervous system do
coordinate and regulate internal organs
Ach can be stimulating or inhibiting. Why?
different postsynaptic cells will have different receptors
Axons of the peripheral nervous system are associated with neuroglia cells called…
Schwann cells
Schwann cells, wrapped repeatedly around the axon, form a coating called a ___
myelin sheath
The myelin sheath consists of multiple layers of the ___ of the neuroglia cells
cell membrane
Myelin consists of protein and large amounts of ___, giving heavily myelinated tissue a white appearance.
lipid
As the cells wrap around and around the axon, cytoplasm ends up in the outermost wrapping of the cell. Because myelin is nonpolar, it prevents ions from accessing the axon surface, serving as an electrical ___ to the axon.
insulator
Gaps between neighboring segments of the myelin sheath are called ___. At these points, the axon is not insulated.
nodes of ranvier
The ___ of a neuron release(s) neurotransmitters.
presynaptic terminals
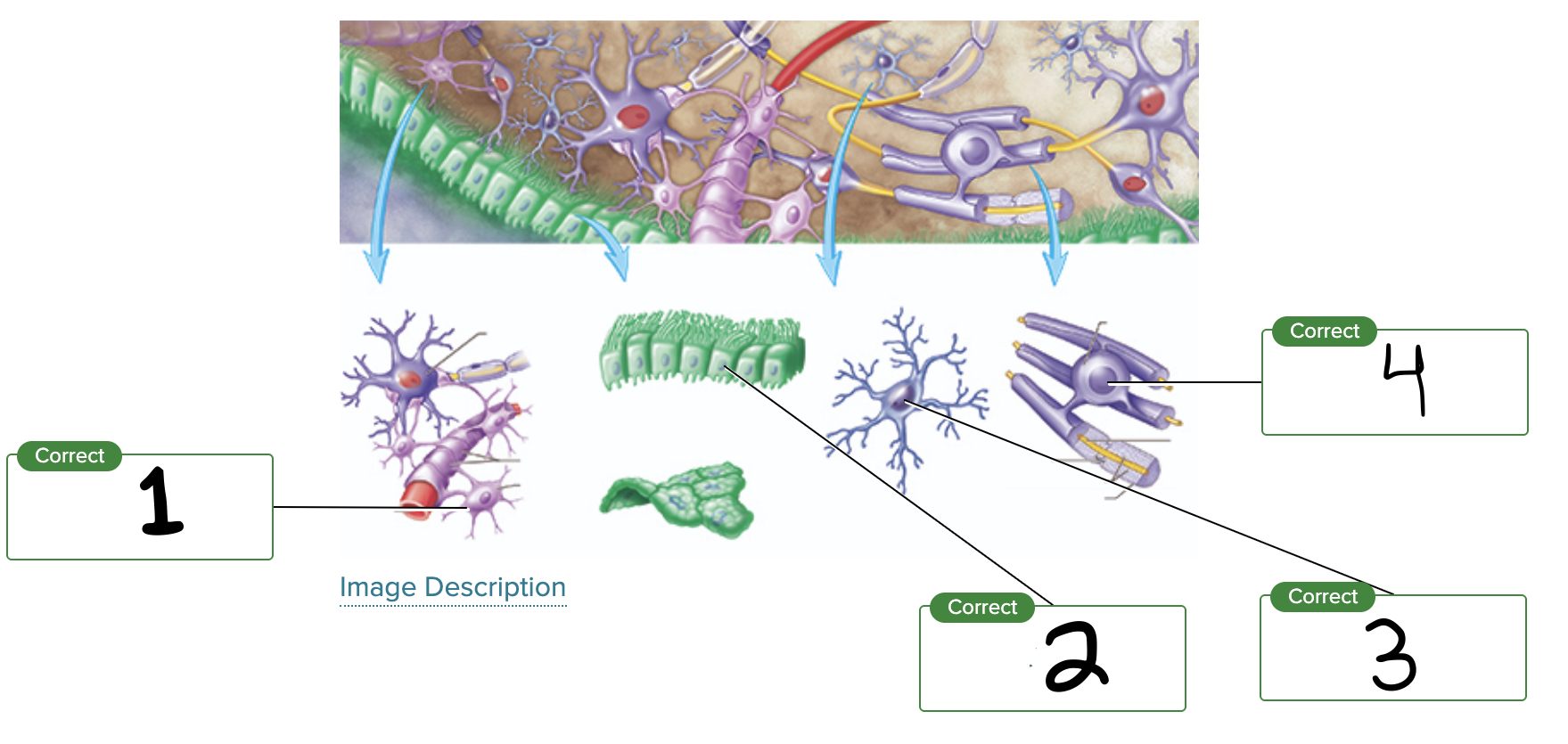
What is label 1?
Astrocyte
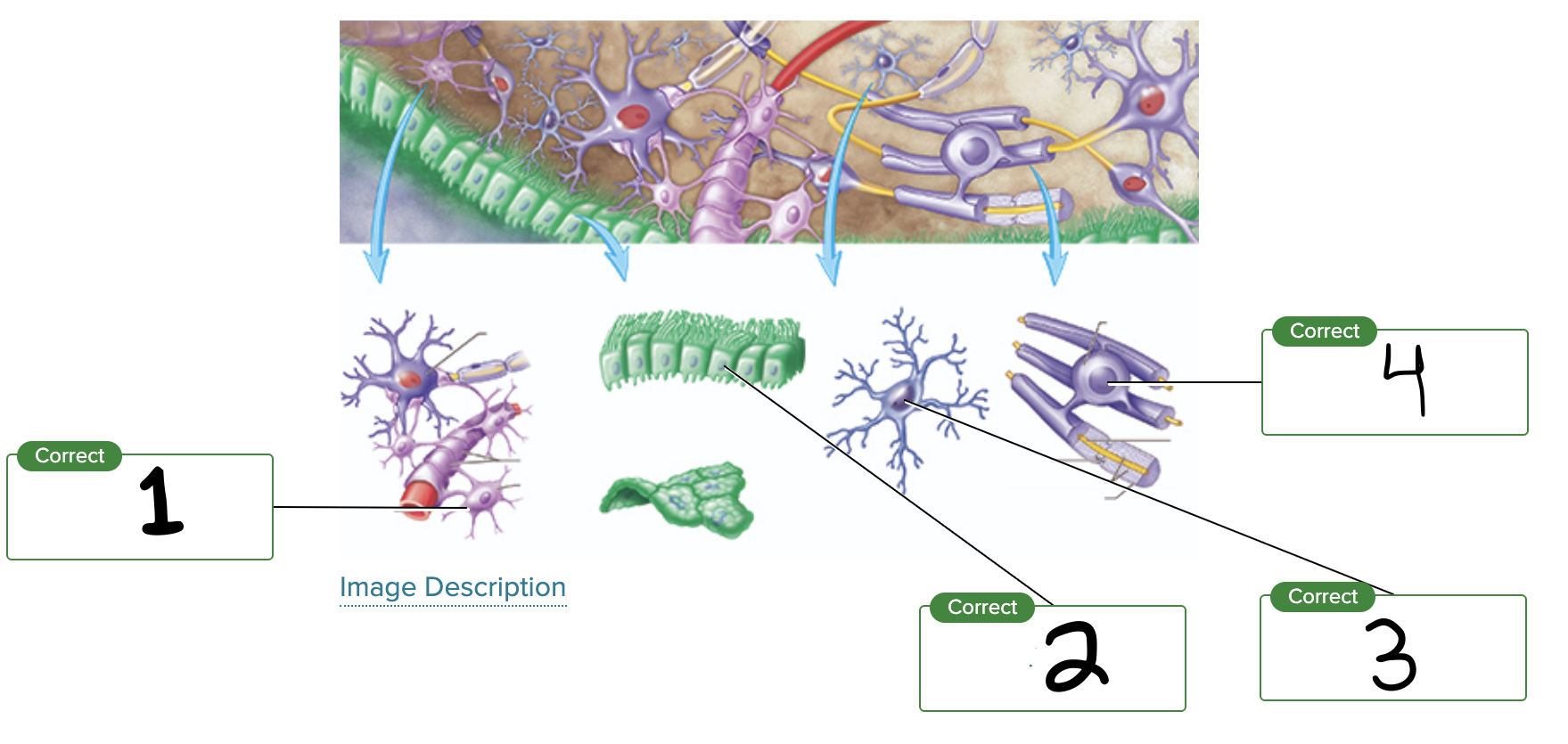
What is label 2?
Ependymal cell
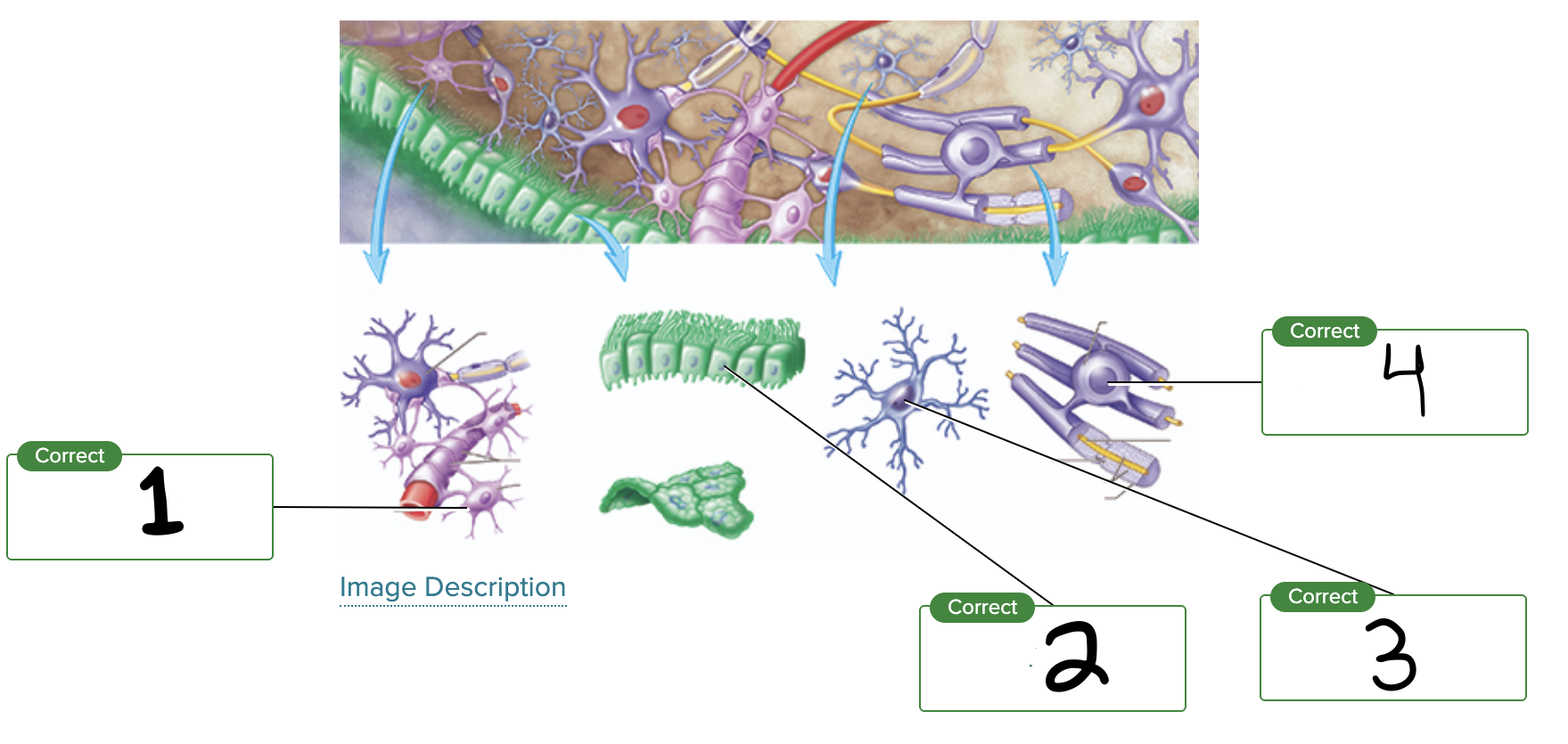
What is label 3?
Microglial cell
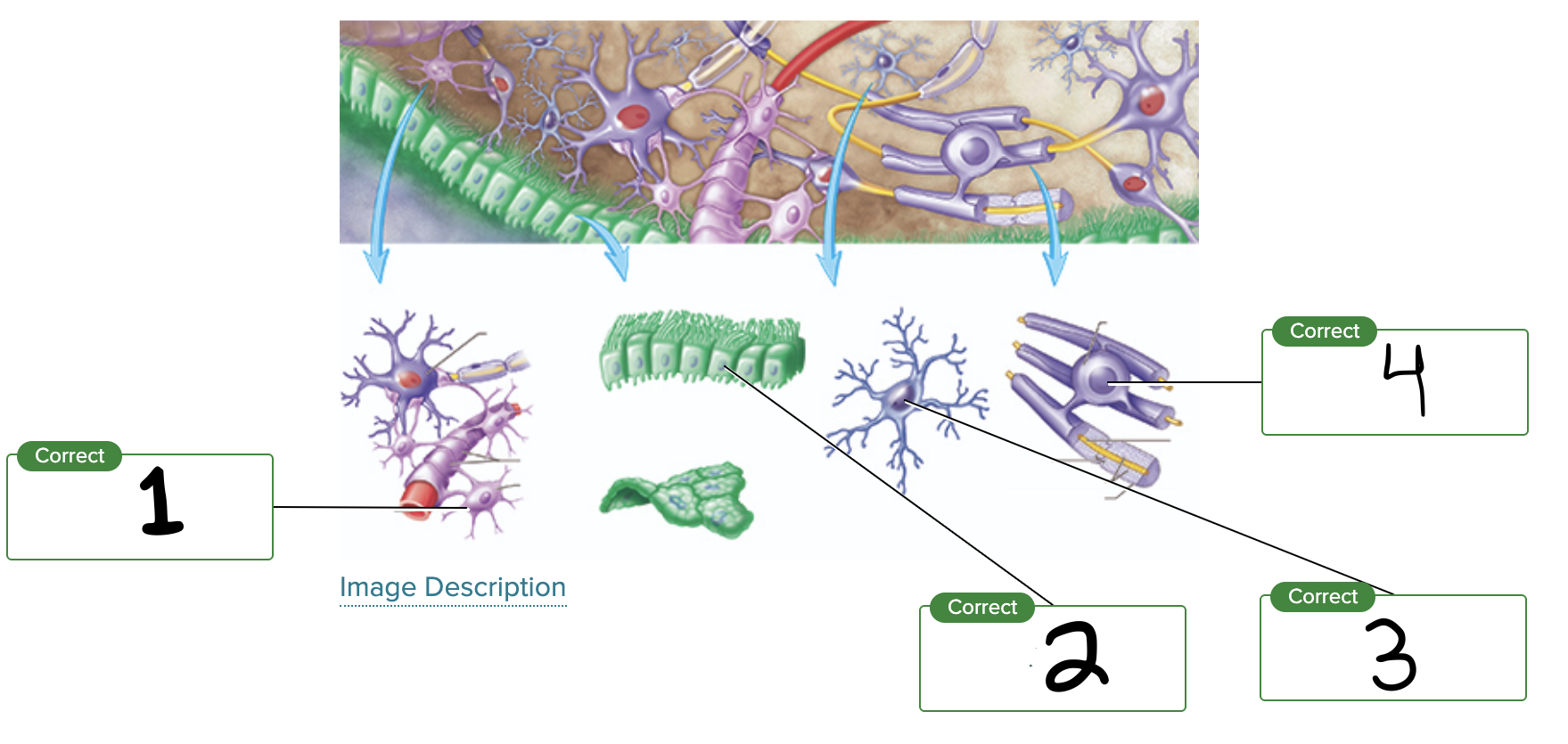
What is label 4?
Oligodendrocyte
What cells for myelin sheaths in the CNS?
Oligodendrocytes
What cells function in the production and circulation of CSF
Ependymal cells
What cells are the macrophages of the CNS?
Microglia
What cells are multi-functioning cells involved with neurogenesis, scar formation, BBB maintenance, etc.
Astrocytes
What cells form myelin sheaths in the PNS?
Schwann cells
What cells are support cells in the PNS that surround neuronal cell bodies?
Satellite cells
The nervous system functions in detecting ___, some of which we are aware and others of which we are not aware.
sensory inputs
The nervous system receives information both internally and from the environment, responding so as to maintain ___.
homeostasis
The nervous system can respond to stimuli using ___ and ___ ___.
muscles; secretory glands
The nervous system functions in mental activities such as solving ___
problems
the nervous system is able to ___ information in order to either respond to or ignore it.
integrate
(Multipolar/Bipolar/Unipolar) Many dendrites extend from the soma
Multipolar
(Multipolar/Bipolar/Unipolar) Most motor neurons are this type
Multipolar