Fluoroscopy Exam
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
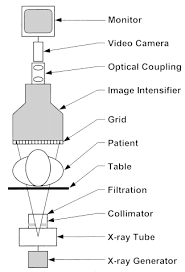
Name all parts of the Fluoroscopic Imaging Chain.
What are the characteristics of fluoro tubes?
Smaller focal spot
Lower mA
Longer exposure times
tube current between .5 to 5 mA
What is the purpose of a grid?
Improve image quality by reducing scatter radiation.
What type of grid does conventional Fluoroscopy use?
Linear grid
True or False?: Lower grid ratios are used for fluoro.
True
What happens when you move the II closer to the patient during an exam?
SID decrease
Patient dose decrease
Image quality improves
List all components of the I.I. tube in order.
Input phosphor
Photocathode
Electrostatic focusing lenses
Accelerating anode
Output phosphor
What is the job of the input phosphor?
Absorbs x-rays and converts their energy into light.
What is the input phosphor made of?
Cesium Iodide
What is the range in sizing for I.I.s?
4-16 inches in diameter.
What is attached to the input phosphor?
Photocathode
What is the photocathode composed of?
Cesium and Antimony
What is the job of the photocathode?
Turns light from the input into electrons.
What are both the photocathode and input screen slightly curved?
So electrons travel the same distance to prevent distortion.
What is the job of the electrostatic focusing lenses?
Accelerate and focuses electron stream onto output phosphor.
How do electrostatic focusing lenses change magnification?
By changing the focal point of electrons.
What is the job of the accelerating anode?
Allow electrons through to the output phosphor; speeds up electrons.
What role does the output phosphor play?
Converts high energy photoelectrons to light photons.
What is the output phosphor made of?
Zinc cadmium sulfide.
How many times brighter is the image after being processed through the output phosphor?
5000 times brighter.
Summarize the process of the image intensifier.
Input: X-rays → light photons
Photocathode: light photons → Electrons
Focusing Lenses: focus electrons
Accelerating Anode: Speed up electrons (Photoelectrons now)
Output: photoelectrons → light photons
What does ABC stand for and what does it do?
Automatic Brightness Control; Keeps the brightness of the image constant on the monitor by adjusting kVp & mA.
What is AGC stand for and what does it do?
Automatic Gain Control; System that takes over and continues to increase brightness once ABC hits “max levels'“ of technical factors. This is done by amplifying the electronic signal.
What is brightness gain?
Ability of I.I. to increase brightness level of image.
What is the common brightness gain of most I.I.s?
5000-30,000
What is minification gain?
Occurs when electrons from the large input phosphor are compressed into the smaller output phosphor.
What is the common size for an I.I’s output phosphor?
1 inch.
What is flux gain?
Measurement of increased light photons from output screen conversion efficiency
What are the formulas for:
Brightness Gain
Minification Gain
Flux Gain
BG = mini. gain * flux gain
MG = (input screen diameter)² / (output screen diameter)²
FG = Output light photons / Input x-ray photons
When are rods active?
At night (scotopic vision)
What are cones active?
In the daylight (photopic vision)
What are cones known to do better than rods?
Perceive color and small objects better.
What is Visual Acuity?
The ability to perceive fine detail.
What is the integration time for recognition of an image?
.2 seconds
What is the resolution of the I.I tube?
4-line pairs/mm
How are images magnified?
When the useful area of the input phosphor is decreased and the output phosphor remains the same.
How is the I.I designed to magnify images electronically?
By changing voltage on electrostatic lenses.
True or false: Mag. mode increases patient dose.
True
What is the I.I resolution in normal mode and mag. mode?
Normal = 4 lp/mm
Mag. Mode = 6 lp/mm
What are the happens as a result of mag. mode?
Better spatial resolution
Better contrast resolution
Higher patient dose
What is vignetting?
Decrease in image brightness due to curved input phosphor and increased OID.
What is the pincushion effect?
Caused by curved input phosphor to a flat output phosphor.
S-Shape distortion
Caused by curved input phosphor to a flat output phosphor. Creates a S shape instead of a “pin cushion” effect
What is blooming?
High energy photons hut input phosphor and results in loss of acuity. Shows up as white streaks.
What is veil glare?
Loss of visual sharpness, type of blooming.
What is lag?
Delay in response time of I.I due to change in beam intensity.
What is noise?
The result of not enough mAs and impacts image clarity, also called Quantum Mottle.
When is High-level control (boost) used?
During angiography and cardiac studies.
What is the maximum tabletop dose rate during boost mode?
20 rads/min unless recording devices are used.
What is pulsed mode?
Short pulses of x-rays (5msec or less) instead of constant output at timed increments.
Why is pulsed mode used?
To reduce patient dose and occupational exposure.
What size film does cinefluorography mode used?
35mm or 70mm
True or false: Cine. mode gives lower patient dose by lower quality images.
false (higher dose and better images.)
What is cine used?
For heart studies and angiography.
What are the two kinds of television coupling?
TV tube (fiber optics)
Charged coupled device (CCD) (lens coupling)
What is the advantage and disadvantage of fiber optics?
Advantage - compact assembly
Disadvantage - Cannot use other devices such as cine or photospot cameras
What is lens coupling?
Uses lenses and mirrors to split incoming signal in 2 signals.
What is the objective lens?
Accepts light from output phosphor and converts it to parallel beam
What is the purpose of the beam splitting mirror?
Sends the output phosphor image to both spot film camera and TV system
What are the two types of Camera tubes?
Vidicon
Plumbicon
What is the purpose of the camera tube?
Lens system that conveys image from output phosphor of I.I to TV camera where images are converted into video signal.
How do conventional and modern vidicon camera tubes work?
Old - Converts light → Electronic signal → monitor
New - CCD → converts light → electronic signal → ADC → monitor
What are the parts in order of a TV camera tube?
Glass envelope
Vacuum and provide mechanical support for internal components.
electron gun
Heated filament that supplies an electron current by thermionic emission.
electrostatic grids
Focuses and accelerates electrons.
target assembly
Serves as anode.
What are the 3 layers of the target assembly?
Face plate
signal plate
target
What does the TV monitor connect to?
To the camera and is a closed-circuit system
What does CRT stand for?
Cathode Ray Tube
What is the standard number of horizontal lines on a TV monitor?
525
What are the advantages of TV monitoring?
Controls brightness and contrast electronically
Many people can view the image at the same time
Allows electronic image storage and playback capabilities.
What is a raster pattern?
Pattern produced on the screen of TV picture tube by movement of electrons beam
What is active trace?
Electron beam moving from left to right side of screen
What is horizontal retrace
electron beam “blanks out” and returns to the left side of the screen.
What is vertical retrace?
This action takes place each time the beam has completed tracing the entire screen and then repeats itself back to the top to fill in gaps and keeps repeating this process.
What is interlace?
Combining 2 fields together to from/TV frame
What is vertical resolution determined by?
Number of scan lines
What is horizontal resolution determined by?
By bandpass
What is bandpass (bandwith)?
Refers to total number of cycles/sec available for display. Higher bandpass = better horizontal resolution.
What is video disc recording known as?
Last image freeze