DNA and RNA part 1: includes triple content
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Diagram of our genetic makeup
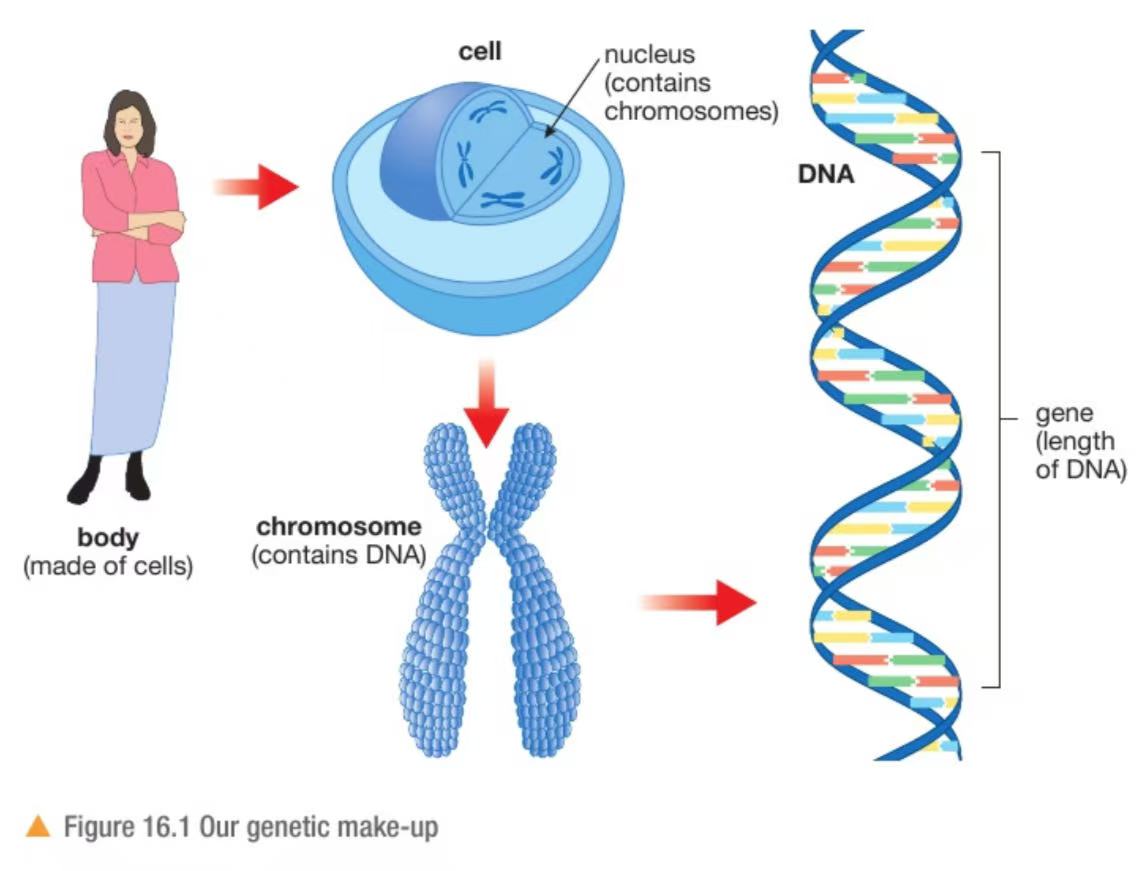
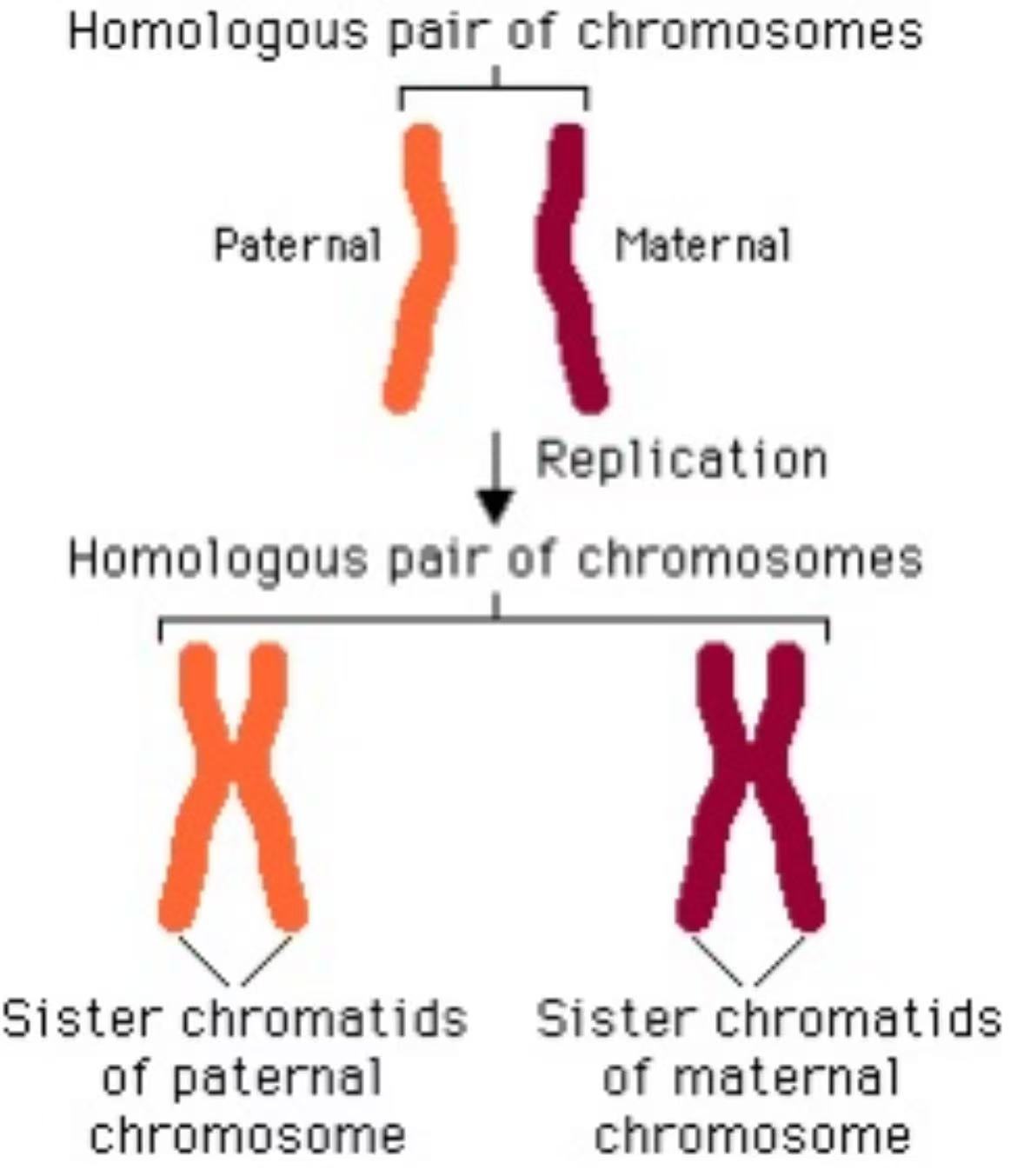
How many pairs of chromosomes do human body cells have and how do we get them? What is the name given to a chromosome pair?
23 pairs. One chromosome from a pair is inherited from each parent
Each chromosome pair is called a homologous pair
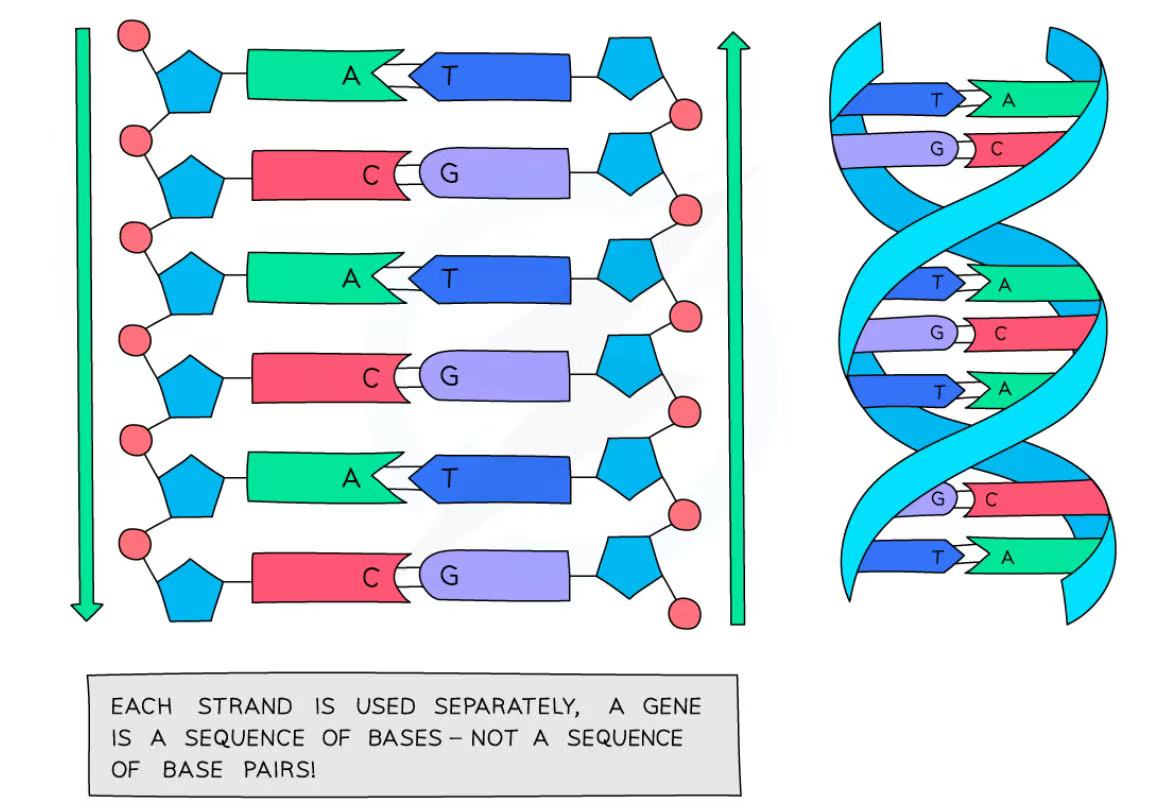
TRIPLE: What is the structure of a DNA molecule?
It is a polymer made up of two strands coiled into a double helix.
The strands are made up of nucleotides that consist of a sugar and phosphate backbone with nitrogenous bases.
The strands are linked by a series of paired complementary bases: A with T, C with G
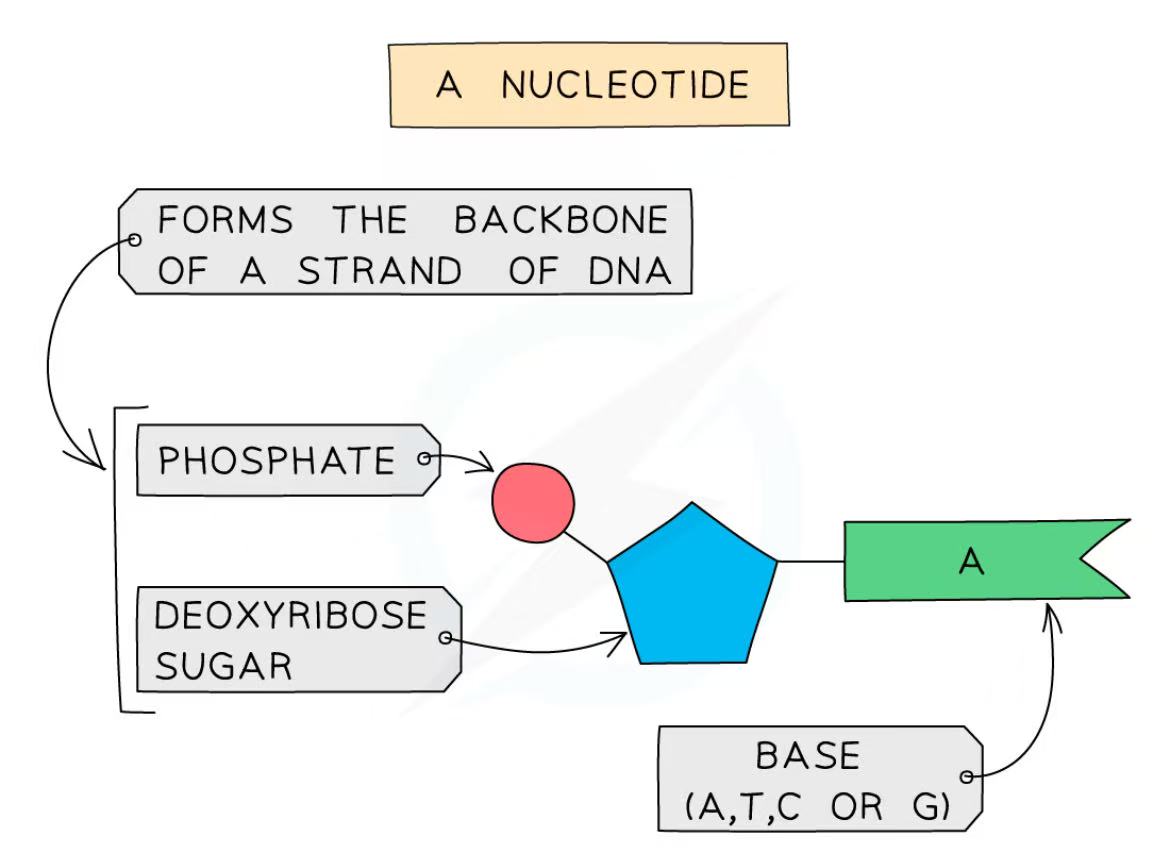
What is the structure of a nucleotide of DNA? Why is DNA a polymer?
The backbone of the DNA is formed from a sugar molecule (deoxyribose) and a phosphate
The backbone is connected to a base: A, T, G, C
A nucleotide is a type of monomer. That is why DNA is a polymer (a molecule made up of monomers
DNA is also a polynucleotide
What are the names of the bases? In savemyexams pone que deberíamos aprendérnoslo
Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) or Guanine (G)
How are both strands of nucleotides bonded together?
By complementary base pairing (base pairing rule)
- A pairs with T
- G pairs with C
END OF TRIPLE: Key point: what is one consequence of the base-pairing rule?
In each molecule of DNA, there are equal amounts of adenine and thymine, as are the amounts of cytosine and guanine
Why and how is DNA able to pass genetic information from one generation to another?
Because DNA is the only chemical that can replicate itself exactly.
It passes the genetic info as a 'genetic code'
When a cell divides by mitosis, how are the replicated cells different from the og? What is the name given to this?
They are exactly the same. Each new cell receives the same type and amount of DNA.
They are genetically identical
TRIPLE: what is replication of DNA? When does it happen?
The copying of a DNA molecule. Happens when a cell is about to divide and each DNA molecule in the nucleus must be copied exactly (same amount and type of DNA)
Describe each stage of the process of DNA replication
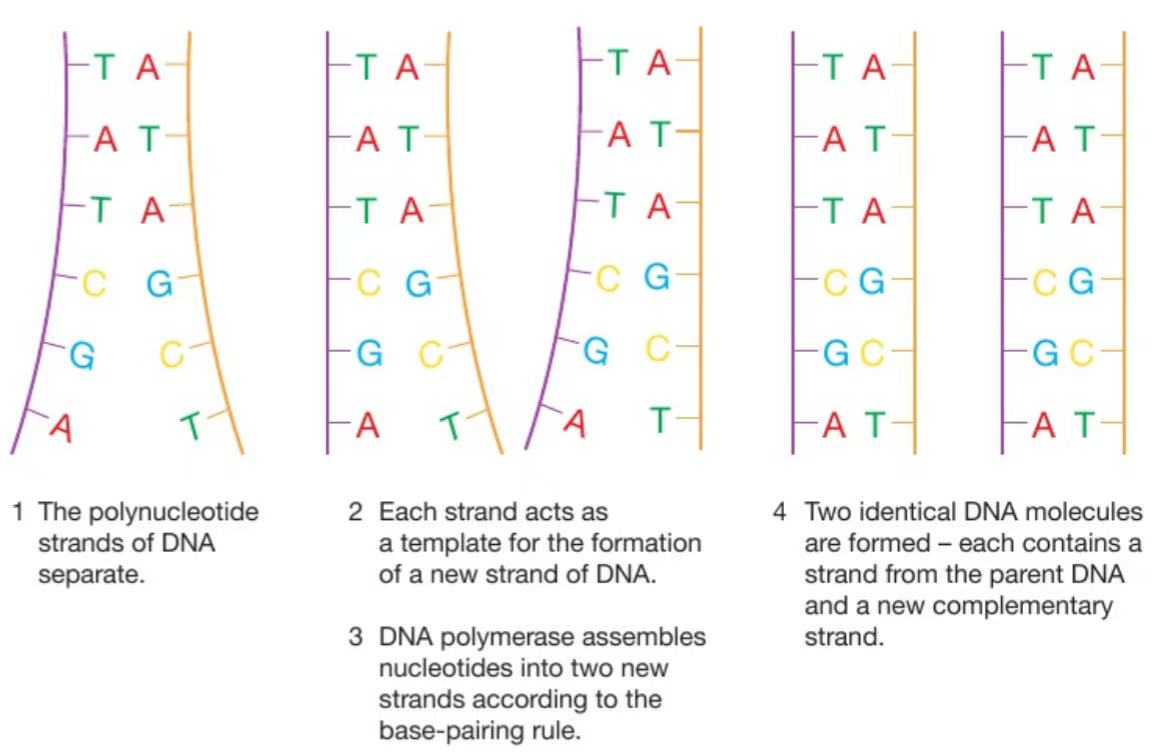
What is the template strand?
It is THE strand of a DNA molecule that actually codes for the manufacure of proteins in a cell. Only one of the strands is the one that codes the proteins.
The other one is called a non-template strand
Proteins are made of chains of amino acids. How is the coding for one amino acid look like?
A sequence of 3 bases in the template strand of DNA codes for ONE amino acid
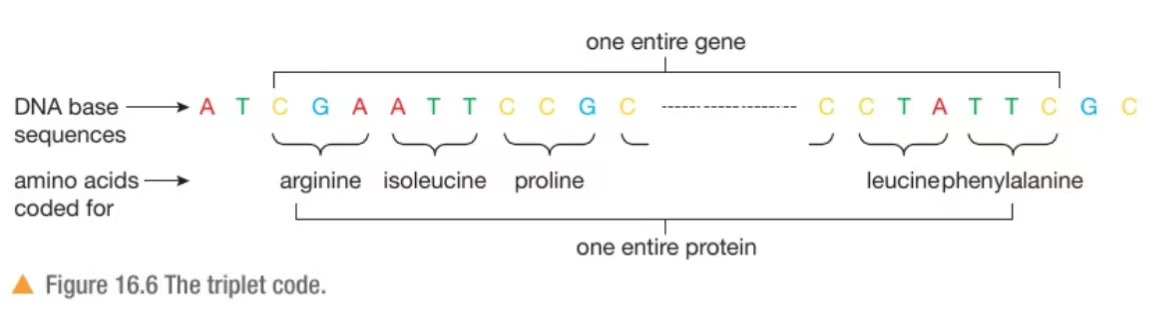
What does it mean that the DNA code is a universal code?
The triplets of bases that code for individual amino acids are the same in all organisms.
The base sequence TGT codes for the amino acid cysteine in humans, bacteria, bananas, fish, etc
Like DNA, the nucleic acid RNA is a
What is the structure of RNA?
polynucleotide (means made up of many nucleotides)
RNA molecule is a single stranded molecule made up of many nucleotides linked together in a long chain.
Each RNA strand is made up of a backbone of alternating ribose sugars and phosphate groups linked together
Nitrogenous bases (A, U, C, G) of each nucleotide are projecting out sideways form the single stranded RNA molecule
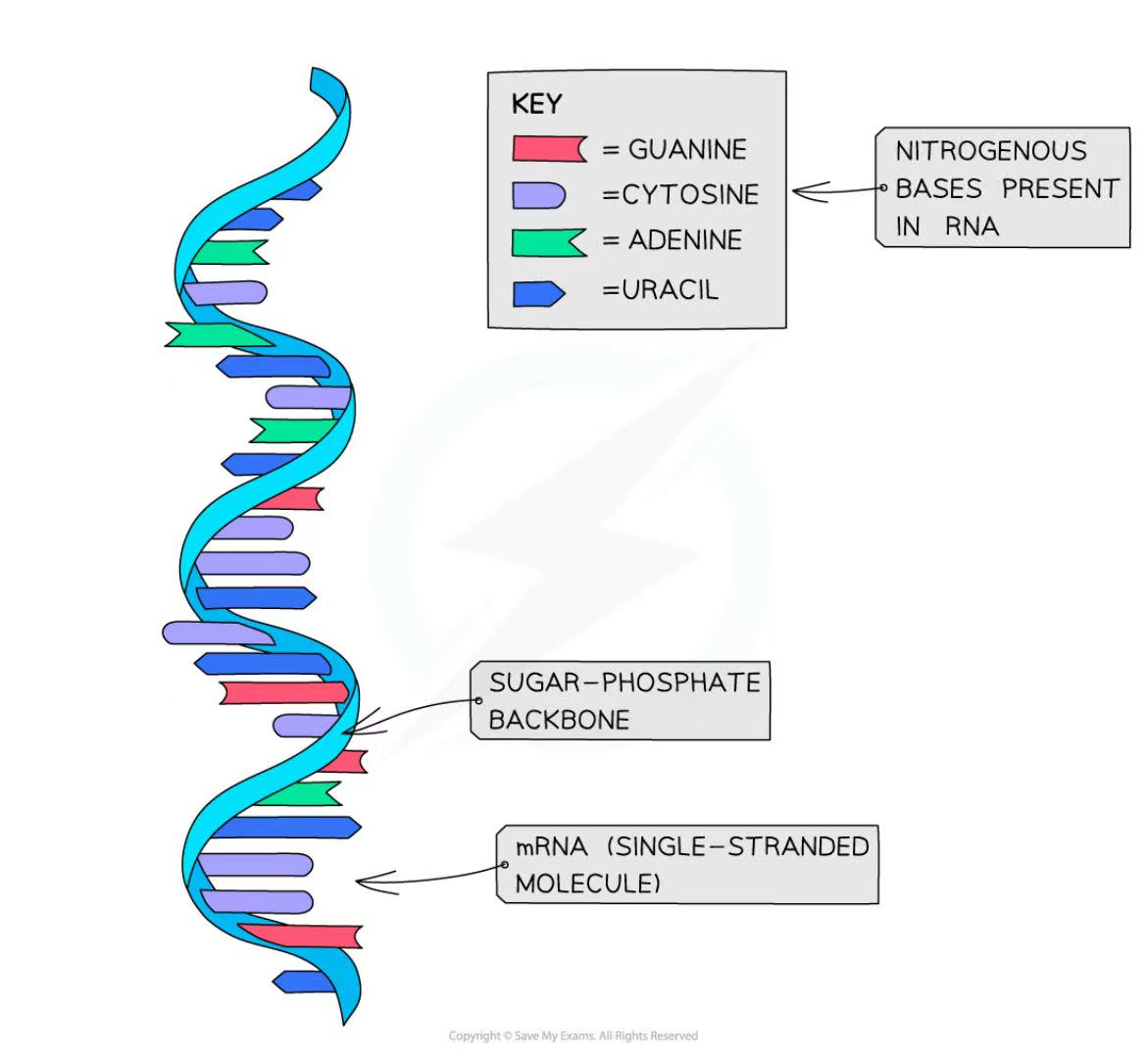
What are the nitrogenous bases for RNA? And their complementary bases? (base pairing rule) -- need to know for protein synthesis
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
A binds to U
- If on the DNA it says T then the one pairing with it is A on the RNA side
G binds to C
What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
RNA is single stranded while DNA is double stranded
RNA contains the base uracil instead of thymine while DNA contains thymine instead of uracil
DNA has deoxyribose sugar while RNA has ribose sugar
Those are main three but sometimes you can say that DNA is longer