2.3.2 Plant organ system
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the role of the stomata and guard cells?
to control gas exchange and water loss
What are root hair cells adapted for?
For the efficient uptake of water by osmosis, and mineral ions by active transport.
What is the function of xylem tissue?
Xylem tissue transports water and mineral ions from the roots to the stems and leaves
How is the structure of xylem tissue adapted for its function?
Xylem cells are composed of hollow tubes strengthened by lignin, adapted for the transport of water in the transpiration stream
What is the function of phloem tissue?
Phloem tissue transports dissolved sugar from the leaves to the rest of the plant for immediate use or storage
What is translocation?
The movement of food molecules through phloem tissue
How is the structure phloem tissue adapted for its purpose?
Phloem is composed of elongated cells. Cell sap can move from one phloem cell to the next through pores in the end walls
What is transpiration?
the loss of water vapour from inside a plant, from the surface of its leaves
What is the ‘transpiration stream’?
the constant movement of water through the plant
What affects the transpiration rate?
Light intensity, temperature, air flow and humidity
How does light intensity affect the transpiration rate?
more light means there will be an increase in the rate of photosynthesis, therefore increasing the transpiration rate, as stomata open wider to allow more carbon dioxide into the leaf. This also allows more water vapour to diffuse out, increasing water loss through transpiration.
How does temperature affect the transpiration rate?
the warmer it is, the faster the transpiration rate, as the particles have more energy to evaporate and diffuse out of the stomata
How does good air flow affect the transpiration rate?
windy conditions increase the rate of evaporation and keep a steep concentration gradient between the inside and outside of the leaf by blowing away the water vapour
How does poor air flow affect the transpiration rate?
If air flow is poor, the water vapour surrounds the leaf, meaning that a high conc. of water particles are outside of the leaf as well as inside it, so diffusion doesn’t happen as quickly
How does humidity affect the rate of transpiration?
the rate of diffusion of water from the leaf is faster in dry air than in damp air, as diffusion happens faster when there is a steep conc. gradient.
How are root hair cells adapted for their function?
hair-like projection: maximises surface area for water absorption, many mitochondria to provide energy for active transport of minerals and a thin cell wall for easy diffusion.
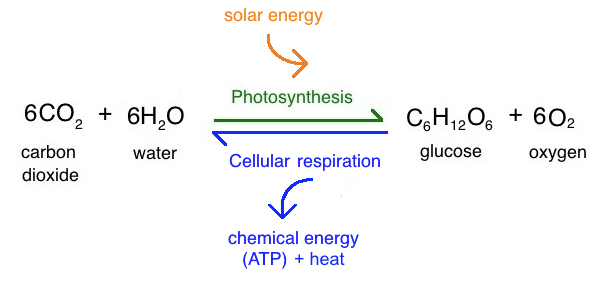
What is the word + symbol equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water - glucose + oxygen

What is the word + symbol equation for aerobic respiration?
glucose + oxygen - carbon dioxide + water