Chapter 8: Hormones & Sex
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made by @agreyr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Testes
Produce sperm cells
Ovaries
Produce ova
Steroid hormones produced by both gonads
Androgens (Testosterone), Estrogens (Estradiol), Progestins (Progesterone)
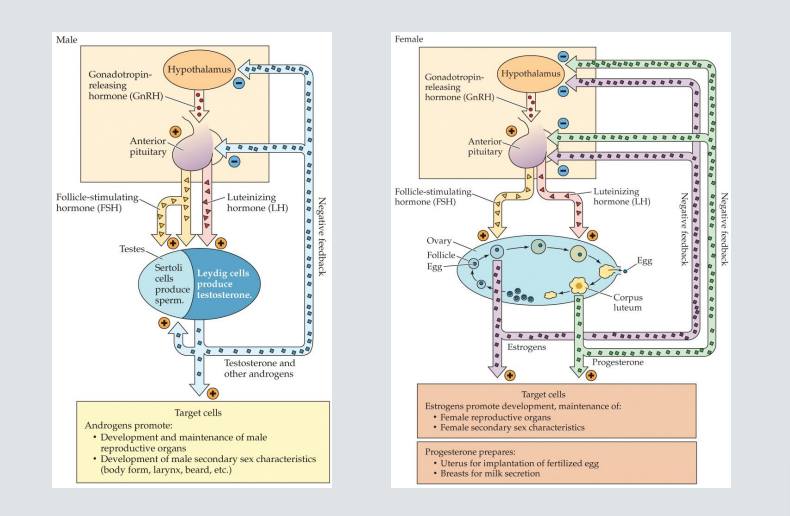
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
Produced by hypothalamic neuroendocrine cells, secreted into the blood vessels and carried to the anterior pituitary via hypothalamic-pituitary portal system (see Neuroendocrine System: Regions)
Gonadotropins
Released by anterior pituitary following GnRH
Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone
Drive the release of gonadal steroid hormones
Two major effects of sex hormones
Organizational (developmental) and activational
Organizational effects on gonads
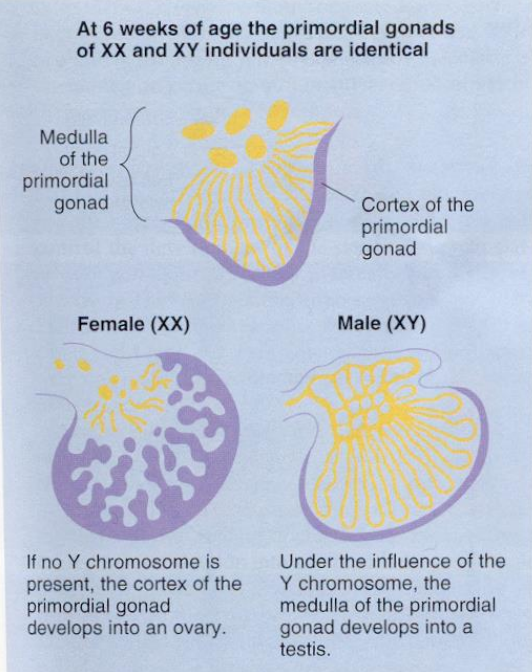
Indifferent (primordial) gonads
Presence of a Y chromosome triggers the synthesis of SRY protein at about 6 weeks of development; allows growth of the medulla into the testes while the cortex shrinks away
Organizational effects on internal organs
At 6 weeks, zygote contains two precursor duct systems (Wolffian system and Müllerian system)
Once formed, fetal testes release testosterone and Müllerian-inhibiting hormone (8 weeks of gestation)
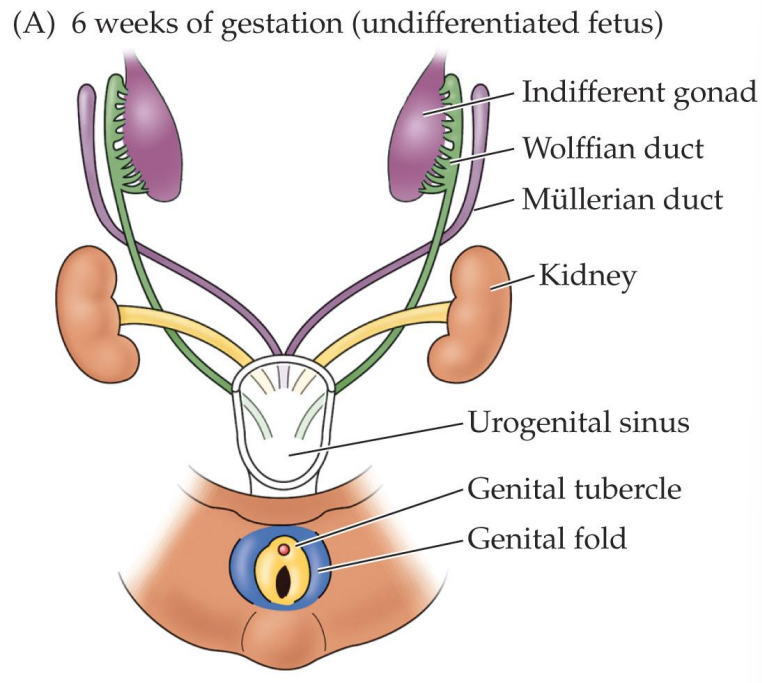
Wolffian system
One of the two precursor duct systems present zygote at 6 weeks
Potential to develop into epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal ducts
Müllerian system
One of the two precursor duct systems present zygote at 6 weeks
Potential to develop into fallopian tubes, uterus, and inner vagina
Male reproductive organ development
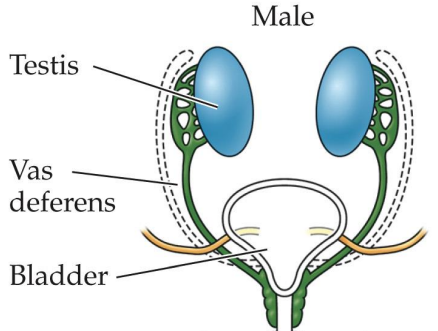
XY chromosome; Y chromosome being testis-determining factor
Primordial gonads develop into testes; anti-Müllerian hormone and androgens are produced
Defeminization and masculinization occur
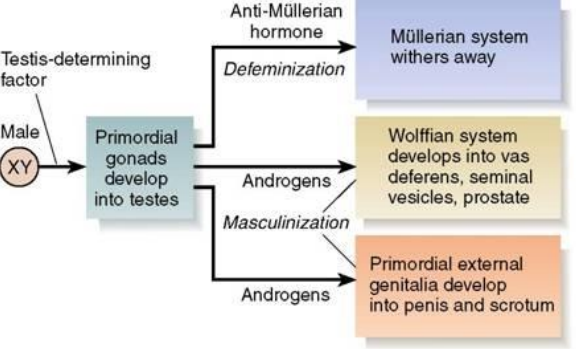
Defeminization
Triggered by anti-Müllerian hormone
Müllerian system withers away
Masculinization
Triggered by androgens
Wolffian system develops into vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate
Primordial external genitalia develop into penis and scrotum
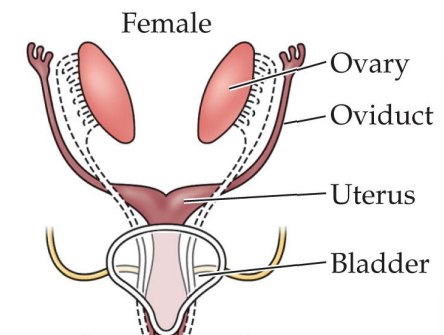
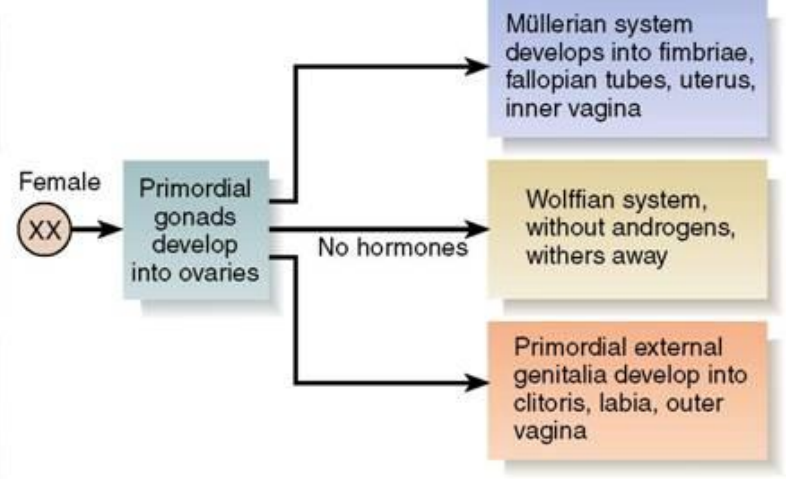
Female reproductive organ development
XX chromosome
Primordial gonads develop into ovaries; no hormones are produced
Müllerian system develops into fimbriae, fallopian tubes, uterus, inner vagina
Wolffian system, without androgens, withers away
Primordial external genitalia develop into clitoris, labia, outer vagina
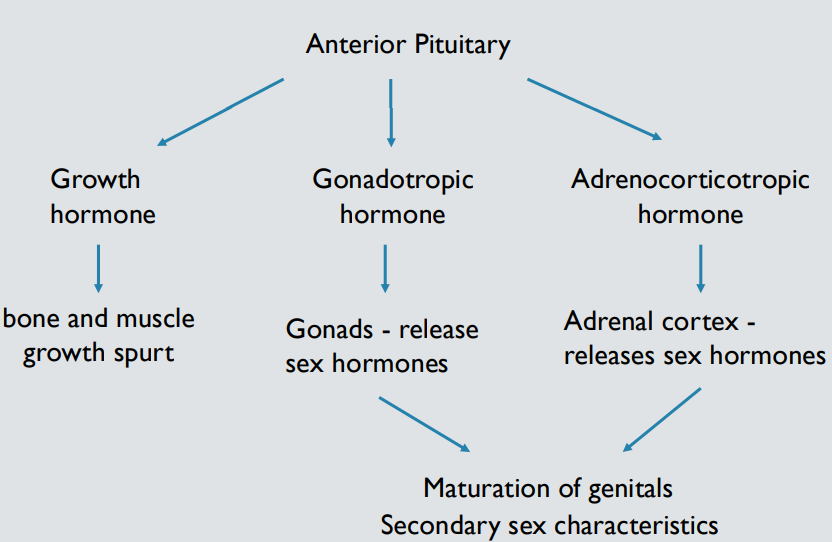
Activational effects
Puberty, a time period during which fertility is achieved, growth spurt occurs, and secondary sex characteristics develop; marked by surge in hormone release from the anterior pituitary
Pituitary
Anterior and posterior
Hypothalamus
Supraoptic and paraventricular
Posterior pituitary
Major hormones (Vasopressin and Oxytocin) signaled via neural connections and released into the blood; negative feedback signaling
Controls the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones via its own set of hormones; releasing and inhibitory factors
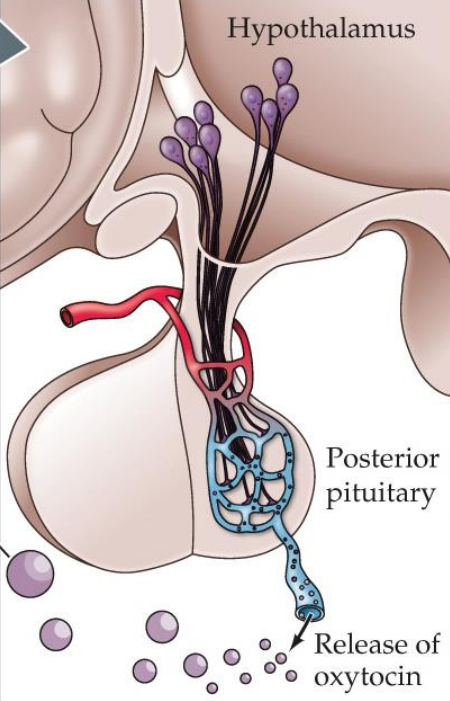
Vasopressin
Facilitates water reabsorption in the kidney
Oxytocin
Parental behavior
Releasing factors
Stimulate the release of an anterior pituitary hormone
Inhibitory Factors
Inhibit the release of an anterior pituitary hormone
Anterior pituitary
Considered to be the master gland because it releases tropic hormones
Part of the hypothalamic-pituitary portal system
Releases gonadotropins (see Neuroendocrine System: Gonads)
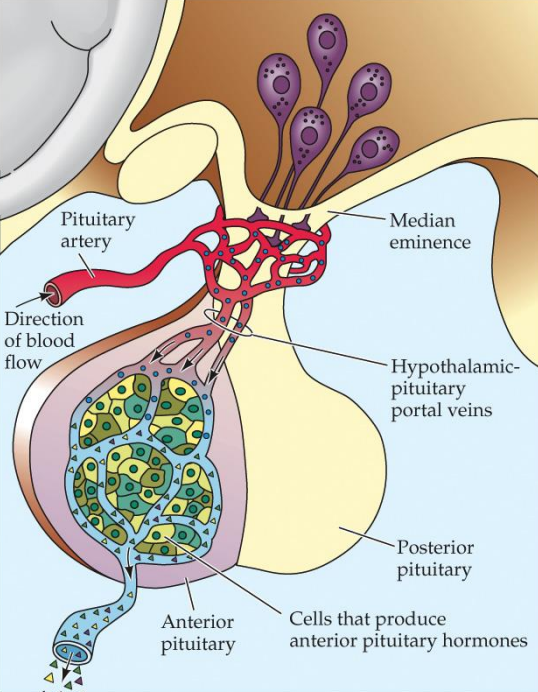
Hypothalamic-pituitary portal system
Carries GnRH from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary (see Neuroendocrine System: Gonads)
Tropic hormones
Primary function is to influence the release of other hormones
Prolactin, gonadotropic hormones (FSH and LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone, ACTH, growth hormone
Neuroendocrine cells
Special category of cell
Hormones
Chemicals released by endocrine glands into blood circulation
Act on target tissues throughout the body (including the brain) to produce physiological effects
Three main categories of hormones
Peptides, Amines, Steroids
Peptide hormones
Small protein molecules made of a string of amino acids
Bind to receptor proteins on the surface; activate second messengers; fast, but not as fast as synaptic signals
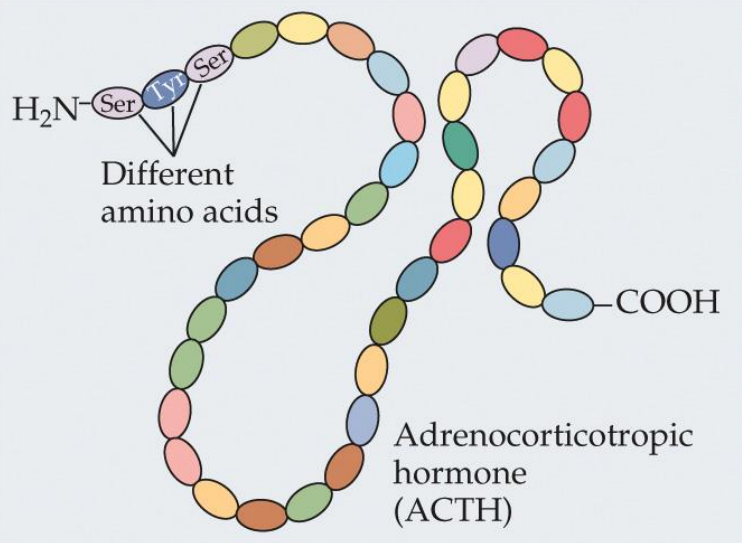
Amine hormones
Modified versions of single amino acids; smaller and simpler
Bind to receptor proteins on the surface; activate second messengers; fast, but not as fast as synaptic signals
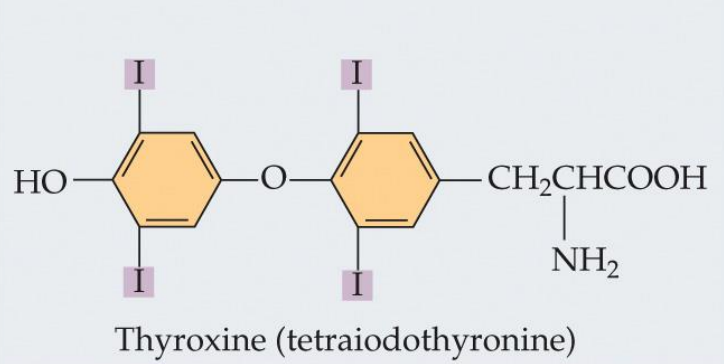
Steroid hormones
Derived from cholesterol; most important for sexual development and behavior
Bind to receptors inside the target cell; binds to DNA and controls expression of other genes
Hypothalamus
Control of hormone secretions
Pineal gland
Reproductive maturation; body rhythms
Anterior pituitary gland
Part of the pituitary gland
Hormone secretion by thyroid, adrenal cortex, and gonads; growth
Posterior pituitary gland
Part of the pituitary gland
Water balance; salt balance
Thyroid
Growth and development; metabolic rate
Adrenal cortex (outer bark)
Part of the adrenal glands
Salt and carbohydrate metabolism, inflammatory reactions
Adrenal medulla (inner core)
Part of the adrenal glands
Emotional arousal (epinephrine)
Pancreas
Sugar metabolism
Gut
Digestion and appetite control
Gonads (testes/ovaries)
Body development; maintenance of reproductive organs in adults