physics info i need to learn
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
kirchhoff’s junction rule
Ienter = Iexit
in a circuit total current entering a junction equals the current exiting it
Ohm’s law equation
V = IR
V= voltage
I= current
R= Resistance
kirchhoff’s loop rule
V = V1+V2+V3+….. = 0
Sum of the voltage drops around any closed loop in a circuit equals 0
unit for current
Ampere(A)
unit for resistance
Ohms
unit for voltage
volts(V)
what is a Pa(pascal) equal to
N/m²
hydrostatic pressure equation
hydrostatic pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of a fluid
P = ρgh
ρ = density of fluid
g= 10m/s²(gravity acceleration
h= height
partial pressure equation
Pgas = Xgas+Ptotal
Xgas = mole fraction of the gass
Ptotal = total pressure
upward buoyant force and weight of the fluid relationship
buoyant force = W
Weight equation
W = mg
m = mass
g= 10m/s²(gravitational acceleration)
what is the doppler effect
observed frequency changes relative to motion
Ex. When an ambulance is stationary the frequency of its siren’s sound waves is stable to the observer
As the ambulance starts moving and gets closer to the observer they will notice that the frequency of the siren’s sound wave increases
wavelength and frequency relationship
they have inverse relationship
what is refraction
bending of light occurring at the boundary between 2 different mediums with different values of n
index of refraction(n) equation
n = speed of light in a vacuum( c ) / speed of light in a medium(v)
what is an incident angle
angle between the axis perpendicular to the surface and the ray
what happens when the incident angle increases
light is refracted closer to the surface
what occurs when a critical angle is formed
light is refracted at 90 degree angle and continues parallel to the surface
when does total internal reflection occur
when an incident angle is greater than the critical angle
ideal gas law equation
PV = nRT
P= pressure
V=volume
n= # of moles
R= 0.08 L x atm/mol x K
T= temp in kelvin
wave velocity equation
v = λf
λ = wavelength
f = frequency
for a standing wave how is the λ(wavelength) calculated
length of the string(L) and number of antinodes/nodes(n)
λ = 2L/n
what is snell’s law of light refraction
n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2
n1 = refractive index of medium 1(ex. air)
n2= refractive index of medium 2(ex. glass)
Work(w) formula
W = F x d
F= force
d= distance
kinetic friction force equation
Ff = μk * FN
μk = coefficient of kinetic friction
FN = Normal force
on a horizontal surface what is the normal force equal to
FN = mg
if a block slides down a ramp at constant velocity what happens to all the parallel forces
sum of all parallel forces is 0
Fparallel = Fw sin θ - Fk = 0
Fk = Fw sin θ
if a block slides down a ramp at constant velocity what happens to all the perpendicular forces
sum of all perpedicular forces is 0
Fperpendicular = FN - FW cos θ = 0
FN = FW cos θ
harmonic resonance frequency for standing wave on a string equation
fn = nf1
f1 = frequency of standing wave with one antinode
what are antinodes and nodes in standing waves
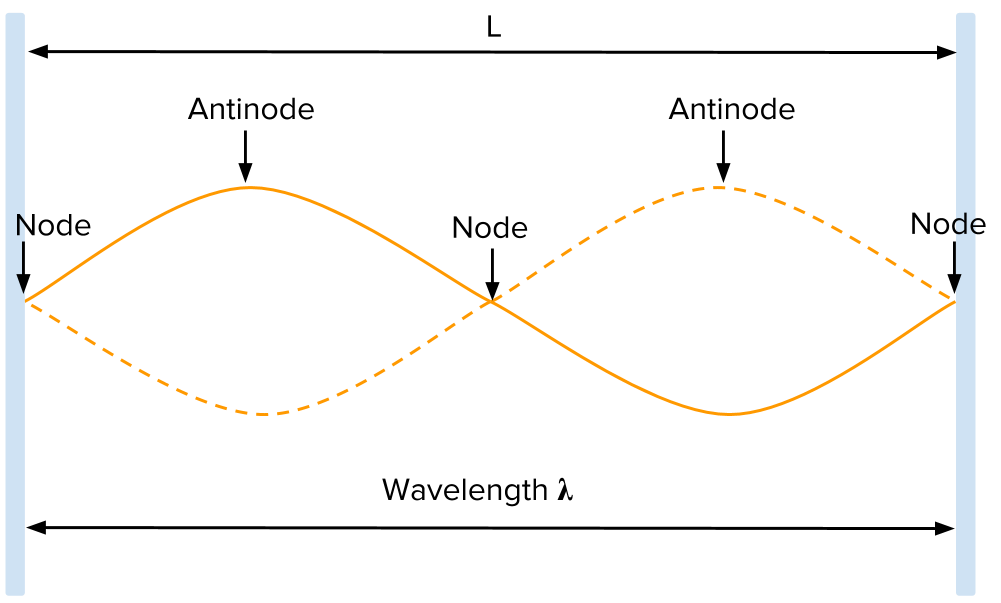
what is resonance
it generates standing waves on a string fixed at both ends
when a block that has a temp 35 degrees is submerged in water that has a temp of 25 degrees suppose the q value of water is 210J what is the q value of the block
q value of the block will be -210J because the heat of the block will transfer to the water
upper limit static friction force equation
Fs = μs N
N= normal force
what is static friction
frictional force that prevents 2 surfaces from sliding
if forces that promote sliding exceed the upper limit of static friction what happens
sliding will occur
is the coefficient of kinetic friction always greater or lower than coefficient of static friction
coefficient of kinetic friction is always less than coefficient of static friction
newtons 2nd law of motion
F = ma
m= mass
a= acceleration
when velocity is positive and you need to calculate acceleration using kinetic friction equation, is Fk negative or positive
Fk is negative because friction acts in the opposite direction
on an incline what is the perpendicular component of the weight of an object
W cos θ
on an incline what is the perpendicular component of the weight of an object equal to
the normal force
Work equation
Wf = Fd
F = force
d= displacement
what is the pressure equation
P = F/A
Capacitance equation
C = Q / V
Q = quantity of stored charge
V= voltage
in a parallel place capacitor, what is the equation used when there is a dielectric between the parallel plates
C = k · C0
k = dielectric constant
C0 = Capacitance when there is nothing in between
in a parallel plate capacitor why is C proportional to area of the plates
As the area of the plates increase more charge can be stored on it(increase in Q value)
Resistance of a resistor equation
R = ρ · L/A
ρ = resistivity
L= length
A= area
how to add resistors that are in a series
Req = R1 + R2 + R3….
how to add resistors that are parallel
1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3….
in a pulley system what is the weight of the large block resting on the surface equal to
Weight largeblock = FN + Ty
FN = Normal force of the large block
Ty = y component of the rope attached to large block
in a pulley a large block is resting on a surface what is its Fs equal to
Fs will be equal to the x component of the rope attached to the large block
when an object is at rest or moving at constant velocity how do you calculate tension of the object’s supporting rope
Tension of the object’s rope is equal to the weight of the object
hooke’s law
Fel = -kx
k= spring constant
x= displacement
when a force is applied to a spring whether it may be by extending the spring or compressing the spring, how will the elastic force of the spring behave
the spring will apply elastic force equal to the force that was applied to it but in the opposite direction
Ex. if a force of 5 N is applied
the elastic force of spring will be -5N
unit for Work
joules(J)
unit for force
Newtons(N)
Power equations
P = Work/time(s)
P= Energy/Time
unit for power
watts(W)
what is watt equal to
joule/second
what is a joule equal to
1 kg⋅m2⋅s−2
N · m
Pa ·m³
Watt · second
Coulomb · volt
Torque equation
torque = rFsin(θ)
r= distance between pivot point and location where force is applied
F=force
elastic potential energy
Uel = ½ kx²
k= spring constant
x= displacement
what is ampere equal to
1 coulomb/second
current equations
I = Q/t
I = V/R
Q = charge
V= voltage
R= resistance
decibel and intensity relationship
for every 10dB increase the intensity increases by a factor of 10
Ex. 10dB = 101 times more intense
20dB = 10² times more intense
how does the velocity of sound waves change in different mediums
velocity of sound waves is fastest in solids
velocity of sound waves is faster in liquids
velocity of sound waves is slowest in gases
when a sound wave enters a solid, liquid, or gas what happens to its intensity
intensity decreases
frequency of sound wave and pitch relationship
as the frequency increases the pitch increases
for a pipe that is open at both ends what is the L value equal to
L = wavelength / 2
for a pipe that is closed on one end and open on the other end what is the L value equal to
L = wavelength / 4
frequency equation
f = velocity / wavelength
if a gas has a high partial pressure in a mixture what does that mean
high concentration of the gas is present in that mixture
how does gas move during simple diffusion
moves from area of high gas concentration to low gas concentration
in terms of change in potential energy what is Work equal to
W = mg∆h
kinetic energy equation
KE = ½ mv2
energy of a photon equation
E = hc/λ
h = planck constant
c = speed of light
λ = wavelength