Role of hair cells
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Differences between IHC and OHCs
number
innervation
function
vulnerability
Type 1 afferents make up (innervation)
95% of all spiral ganglion neurons
Our inner hair cell is innervated by
5-30 afferent nerve fibers
Most the information about the acoustic world reaches the brain
via the inner hair cells
The auditory efferent system
provides feedback to outer hair cells that helps regulate hearing sensitivity & protects hearing from intense noise
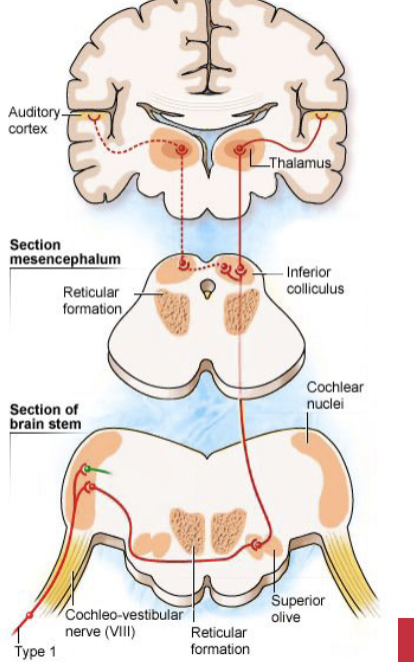
How many outer hair cells does an average person have?
12,500
Otoacoustic emissions
this pointed to a source of energy being generated inside the cochlea
Function of the IHCs
Inner hair cell’s primary function is to translate sound waves into electrical signals for the brain to interpret
Inner hair cells main job is to
send information from the Organ of Corti to the brain
Function of the OHCs
outer hair cells also generate force to improve auditory sensitivity and frequency selectivity
Inner hair cells primarily make up the
afferent system
Outer hair cells primarily make up the
efferent system
Electromotility
change in the length of the OHC in response to changes in the electrical potential of the cell
increases the displacement of the traveling wave
OHC motion causes an increase in the intensity of sound at the cochlea
it acts as a cochlear amplifier
OHCs are more susceptible to
damage from noise exposure and ototoxic medications
Damaged OHCs leads to…
hearing loss and reduced frequency selectivity
Cochlear amplifier
it’s amplifying vibrations
Frequency selectivity
OHC are connected to the basilar membrane tonotopically, if outer hair cells at the spot assigned is moving up and down and creating more energy, it makes the inner hair cell produce more information to the brain
Are Inner hair cells connected to the tectorial membrane?
No, they are not connected but the outer hair cells ARE connected
What part of the vestibular system is responsible for forward/ backward (horizontal) acceleration?
Utricle
When calcium crystals (otoconia) get dislodged
you can become dizzy, have vertigo
Vestibular system
detects changes in the head (movements)
Vestibular organs also
have hair cells
Otoconia sit in a
gel like substance