Lab #3 Cardiac Conduction and EKG
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
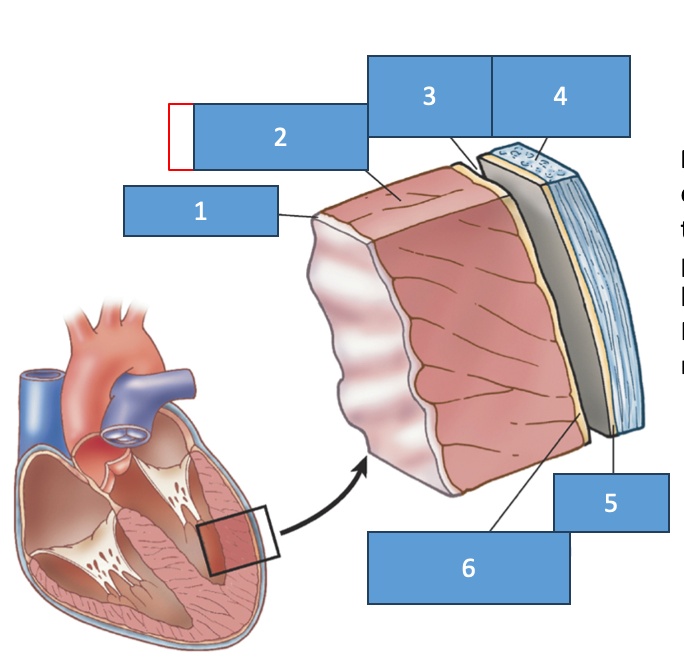
endocardium
myocardium
pericardial cavity
fibrous pericardium
parietal pericardium
visceral pericardium (epicardium)
cardiac muscle cells structure
intercalated discs between class that contain gap junctions. This is so action potential can be spread through a network of cells
what forms a functional syncytium
cardiac muscle fibers
functional syncytium
a mass of merging cells that function as a unit
2 functional syncytium in the heart
atrial synctium and ventricular synctium
what are cardiac muscle cells called
cardiomyocytes
what control cardiomyocytes
autonomic nervous system
what produces a current thorough the cardiac muscle cells
sinoatrial node
what do electrical changes in the heart tissue cause
mechanical changes (muscle contraction)
changes in membrane potential in heart tissue =
mechanical events
3 types of excitable cardiac muscle cells
pacemaker cells
specialized rapidly conducting cells
atrial and ventricular myocytes
what are the two types of pacemaker cells
SA and AV nodes
what are the specialized rapidly conducting cells in the ventricular walls called
purkinje fibers
cardiac conduction system def
group of clumps and strands of specialized cardiac muscle tissue, which initiates and distributes impulses throughout the myocardium
cardiac conduction system job
coordinates the events of the cardiac cycle
cardiac conduction system steps in the heart
SA node
atrial syncytium
junctional fibers
AV node
AV bundle
bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
ventricular synctium
sequence of electrical excitation in the heart
the SA node generates the impulse
the impulse pauses at the AV node
the AV bundle connects the atria to the ventricles
the bundle branches conduct the impulses the inter ventricular septum
SA node role
pacemaker that initiates rhythmic contractions of the heart
internodal atrial muscle
conducts impulses from SA node to aura
junctional fibers
conduct impulses form SA node to AV node
AV node
conducts impulses to AV bundle; delays impulse, so that atria finish contracting before ventricles contract
AV bundle
conducts impulses rapidly between AV node and bundle branches
Left and Right Bundle branches
split off from AV bundle, conduct impulses to Purkinje fibers on both sides of heart
Purkinje fibers
large fibers that conduct impulses to ventricular myocardium
EKG def
a recording of electrical changes that occur in the myocardium during the cardiac cycle
interval
waves that represent the depolarization and depolarization of the cardiac muscle
P wave
atrial depolarization; occurs just prior to atrial contraction
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization; occurs just prior to ventricular contraction
T wave
ventricular depolarization; occurs just prior to ventricular relaxation
arrhythmias
altered heart rhythms
fibrillation
uncoordinated, chaotic contraction of small areas of myocardium
atrial fibrillation danger
not-life threatening
ventricular fibrillation danger
often fatal
tachycardia
abnormally fast heartbeat
bradycardia
abnormally slow heartbeat
flutter
rapid, regular contraction of a heart chamber
premature beat
beat that occurs before expected in normal cardiac cycle; often originates from ectopic regions of heart
Ectopic pacemaker
damage to SA node may lead to AV node taking over, and act as secondary pacemaker, 40-60 min instead of 70-80
artificial pacemaker
device used to treat disorders of cardiac conduction system; implantable and battery powered
atrial fibrillation on EKG
will see multiple P waves before QRs complexes
Ventricular Fibrillation
all hell breaks loose
asystole
flatline
blood pressure
the force the blood pressure experts against the inner walls of the blood vessels
how does blood pressure change as blood moves throughout the system
moves from higher to lower pressure
when does arterial blood pressure rise
when the ventricles contract
systolic pressure
the maximum pressure reached during ventricular contraction
diastolic pressure
the minimum pressure remaining before next ventricular contraction
mean arterial pressure
average pressure in arterial system; represents average force driving blood to the tissues
blood pressure units
mm Hg
factors that increase blood pressure
blood volume increases
heart rate increases
stroke volume increases
blood viscosity increases
peripheral resistance increases
turbulent flow
when you open the vessel up after its been closed; the blood is hitting the walls of the vessels
laminar flow
when the sound disappears, flow is parallel and normal again