22. Benign vs. Malignant vs. Metastatic Tumors
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the characteristics of neoplasia?
B
M
M
benign
malignant
metastatic
In general, how are benign tumors ultimately distinguished?
based on their invasiveness
Benign tumors typically have well ________ morphology. They similar structure to the cell or tissue of ________. They have little or no ________.
differentiated; origin; anaplasia
Benign tumors tend to be ________ growing, with ________ and ________ mitotic figures and ________ necrosis.
slow; rare; normal; little
Benign tumors are not ________ and frequently grow by ________ and _________ growth.
invasive; cohesive; expansile
What is often present with benign tumors?
capsule
separated from normal tissues by fibrosis connective tissue
encapsulation
Do benign tumors have metasiasis?
no
Malignant tumors have ________ differentiated morphologic features. The tissues of origin are sometimes ________. They also have variable degrees of ________.
poorly; unclear; anaplasia
Malignant tumors have ________ growth and ________ and ________ mitotic figures.
rapid; frequent; abnormal
Will malignant tumors have necrosis?
yes if there is poor blood supply
Malignant tumors have ________ invasion and are highly ________. A ________ is often absent or incomplete. ________ is sometimes present.
local; infiltrative; capsule; metastasis
What is the cellular criteria to determine malignancy?
W
C
C
A
A
K
M
M
M
well/poorly differentiated (how much do cells look like they should)
cellular pleomorphism (shape)
cytomegaly
anisocytosis (cell size)
anisokaryosis
karyomegaly
mitotic figures
multinucleation
multiple nucleoli
When taking a mitotic count, number the mitotic figures per how many fields of view? Why is this important?
10; the more you look at, the better average you get because it is a more representative sample
spread to another site from the site of origin and can occur hematogenously through blood or through lymphatics
metastasis
True or false: An example of metastasis is when a mammary carcinoma goes to a lymph node or an osteosarcoma goes to the lungs.
true
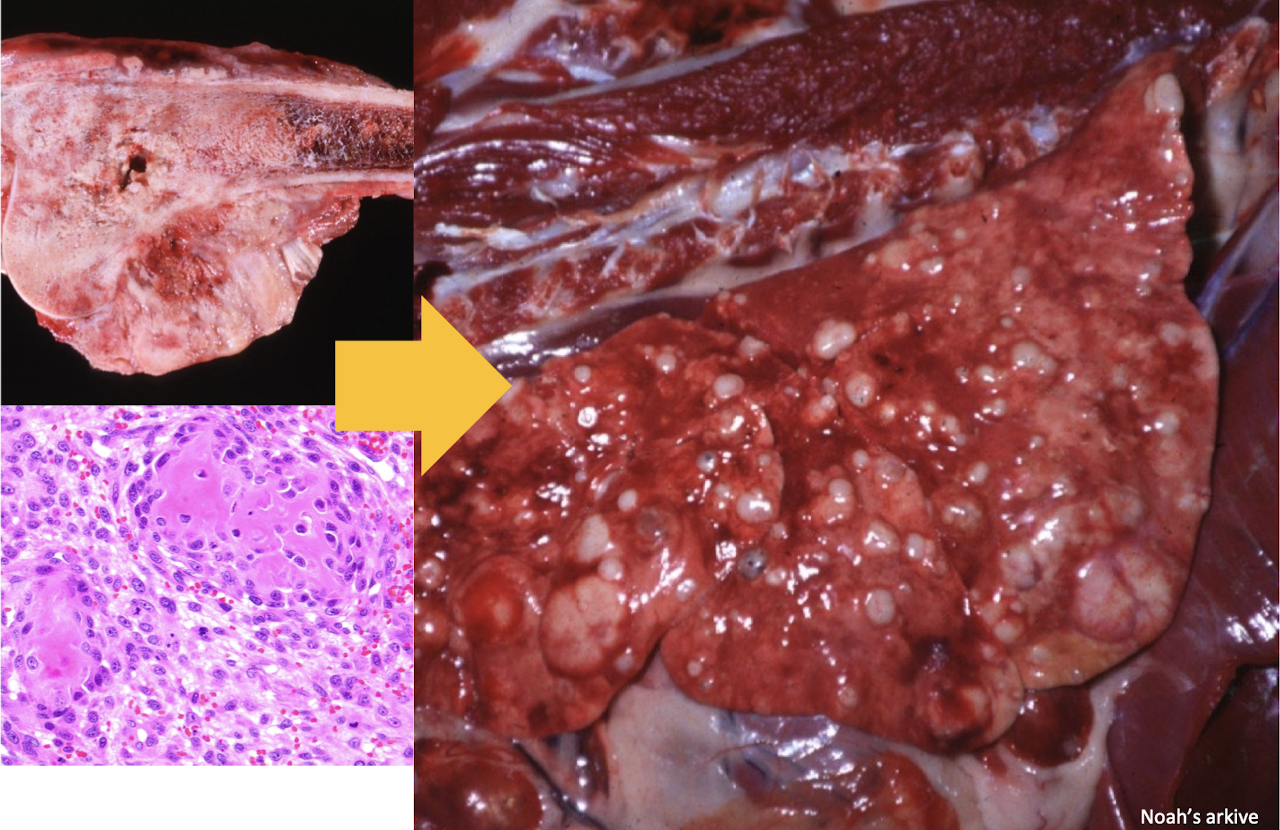
What is this an example of?
metastatic tumor
What are the steps to metastases?
A
I
M
F
E
C
adhesion
invasion
migration
formation of emboli
extravasation
colonization
What occurs during adhesion? What does this mean?
detachment; first, the tumor cells must detach from the main tumor mass, penetrate the basement membrane, and enter the ECM
What occurs during invasion? What do the tumor cells use to achieve this?
basement membrane is breached in order to enter the ECM; matrix metalloproteinases
What is used during migration?
growth factors
During migration, tumor cells migrate through the ________ through alterations in the ________ of the cell and cellular ________ structures and secretion of autocrine ________ ________.
stroma; cytoskeleton; adhesion; growth factors
What are the routes of metastasis?
L
H
T
lymphatic
hematogenous (vascular)
transcoelomic
metastatic cells can lie within distant or new sites until the right signals or set of environmental conditions occur
dormancy
What is responsible for most cancer mortality? What is it responsible for in humans?
metastasis; ~90% of cancer mortality from solid tumors
True or false: Metastasis is actually an inefficient process, as very few cells are capable of entering vessels or lymphatics for metastatic spread.
true
Lymphatic spread/ metastasis occurs most often with what tumor type?
carcinomas
During lymphatic metastasis, where does it often go to first?
draining lymphatics before distant sites
Hematogenous spread/metastasis occurs most often with what tumor type?
sarcomas
During hematogenous metastasis, are veins or arteries commonly used? Why?
veins; walls are much thinner than arteries, making them easier to penetrate
What is the common route of hematogenous metastasis?
veins → heart → capillary beds, particularly the lungs
Tumors which invade the portal vessels such as pheochromocytomas tend to metastasize to the ________ first.
liver
direct dissemination throughout a body cavity that commonly occurs with mesotheliomas or carcinomas and rarely sarcomatosis
transcoelomic metastasis
What would be an example of sacromatous spread?
ruptured splenic hemangiosarcoma, which can seed the abdomen
What are two specific tumor types that are the most common to spread via transcoelomic metastasis?
ovarian adenocarcinomas and pancreatic adenocarcinomas