B cell & T cell development
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Y.Guilloux
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is the primary lymphoid organ (LO) of B and T lymphocytes
Bone marrow : pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells →
B lymphocytes : bone marrow ( I lymphoid organe)
T lymphocytes : Thymus ( ILO )

what type of selection occurs in the bone marrow (ILO) for B lymphocytes
negative selection
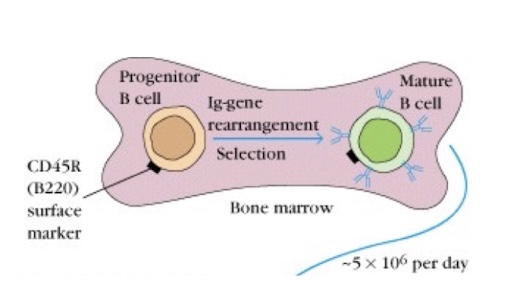
what type of selection occurs in the thymus (ILO) for T lymphocytes
negative and positive selection
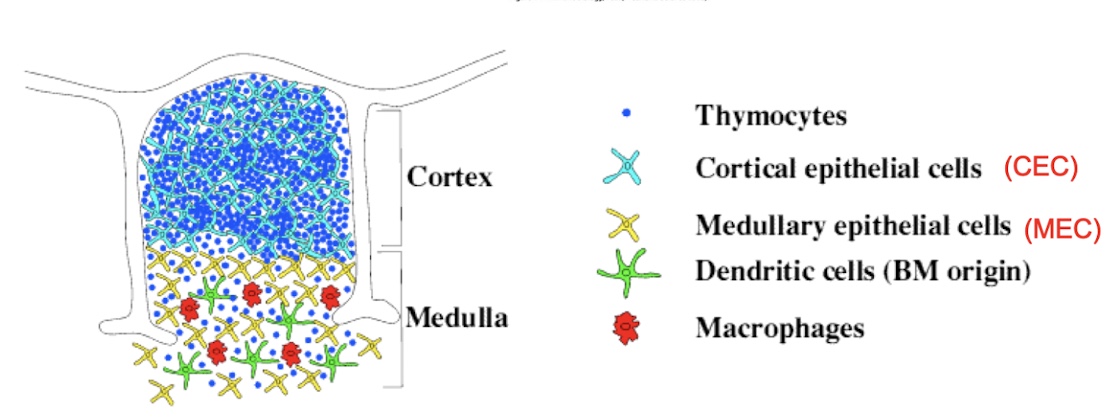
what are the 2 types of T cells
αβ : TCR chain are made up of α and β chains
γδ : TCR chain are made up of γ and δ chains
what is the order of V(D)J rearrangement for T lymphocytes
VDJ rearrangement of the DNA of the β and δ chains
VJ rearrangement of the DNA of the α and γ chains

when does the surrogate light chain intervene in the B cell development
during the large pre B cell stage
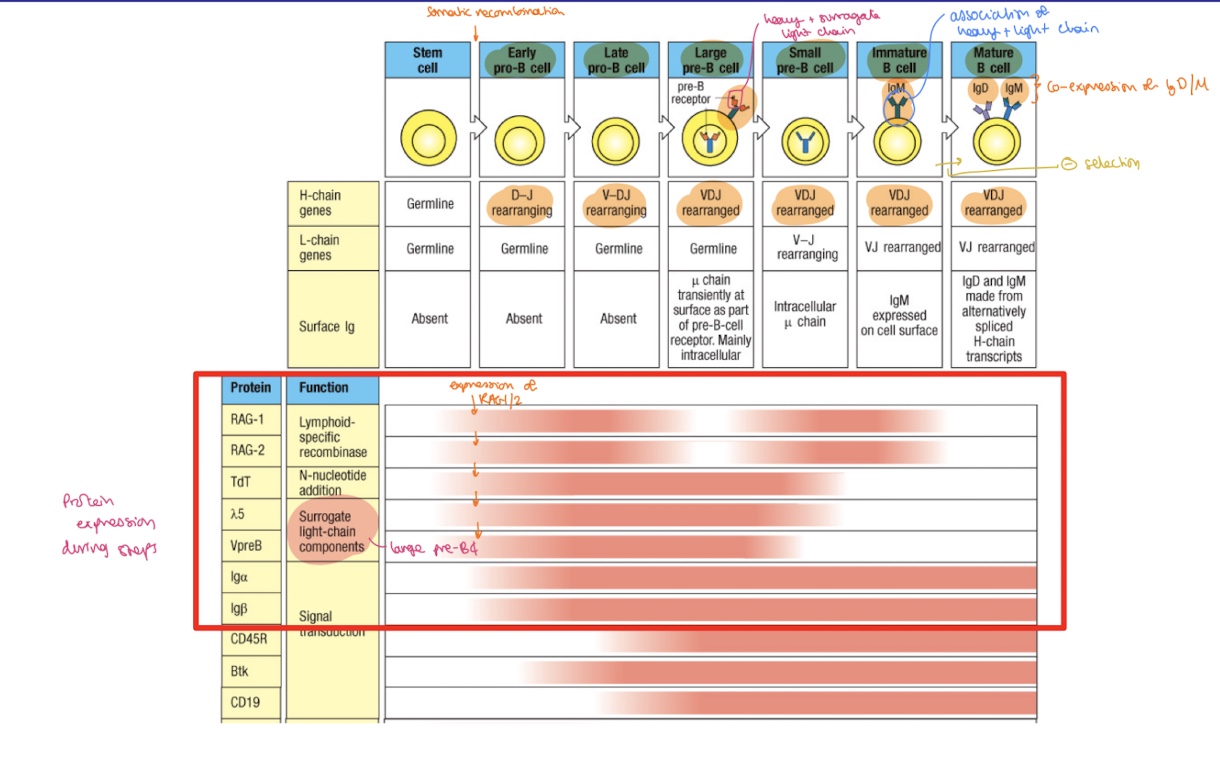
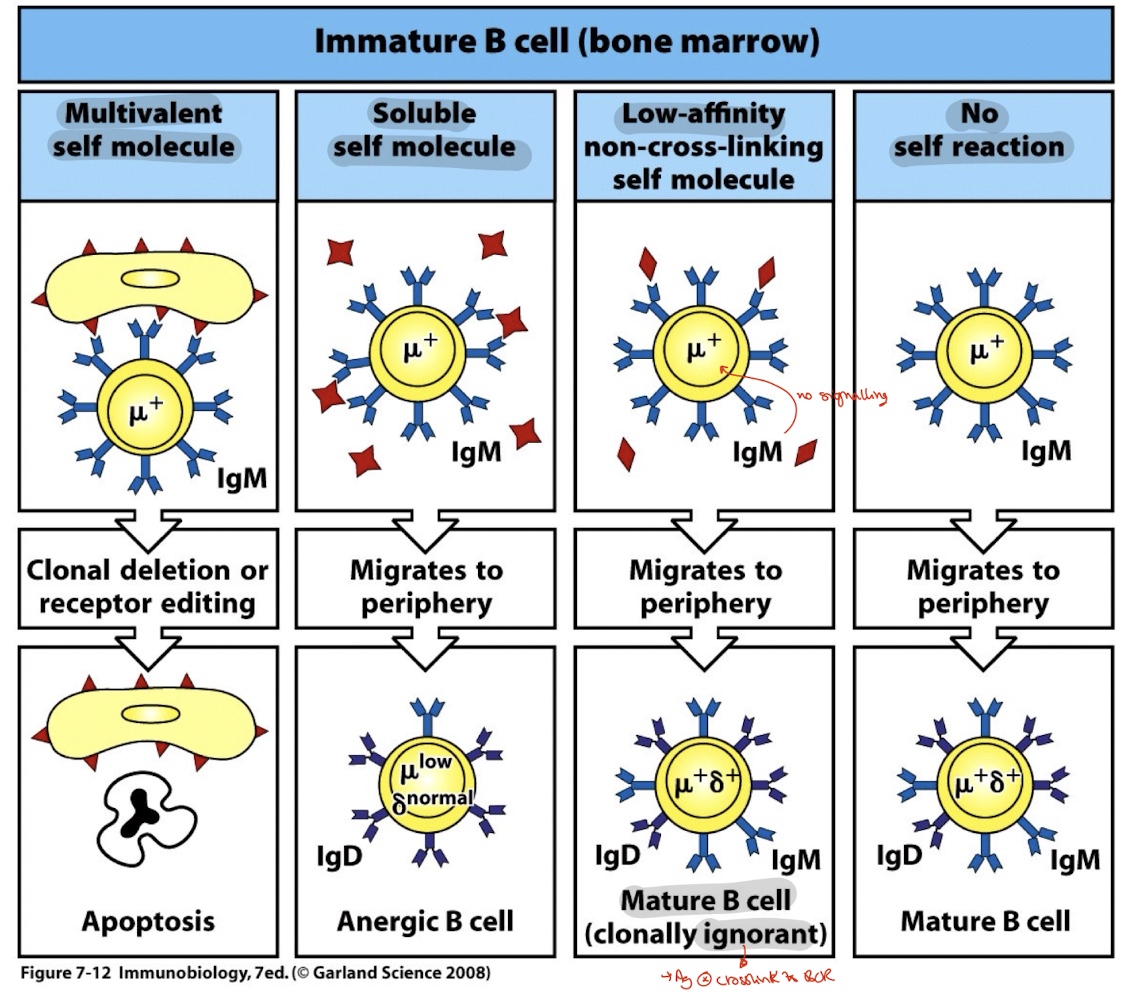
when does negative selection/clonal deletion occur in B lymphocytes
when a B cell recognises a self antigen
what is the name of MHC (major histocompatibility complex) molecules in humans and mice
HLA = MHC molecule in humans
H2 = MHC molecule in mice
what are the 3 classes of MHC class I molecules in humans
HLA A/B/C
what are the 3 classes of MHC class I molecules in mice
H2 K/L/D
what are the 3 classes of MHC class II molecules in humans
HLA DP/DQ/DR
what are the 2 classes of MHC class II molecules in mice
H2 IA/IE
what does it mean if the nomenclature/haplotype of the MHC is H2b
it means that all the MHC molecules have the allelic form of b (homozygote), so :
H2 Kb/Lb/Db (MHC I)
H2 IAb/IEb (MHC II)
what does it mean if the nomenclature of the MHC is H2b/d
it means that all the MHC molecules have the allelic form of b/d (heterozygote), so :
H2 Kb/Lb/Db and Kd/Ld/Dd (MHC I)
H2 IAb/IEb and IAd/IEd (MHC II)
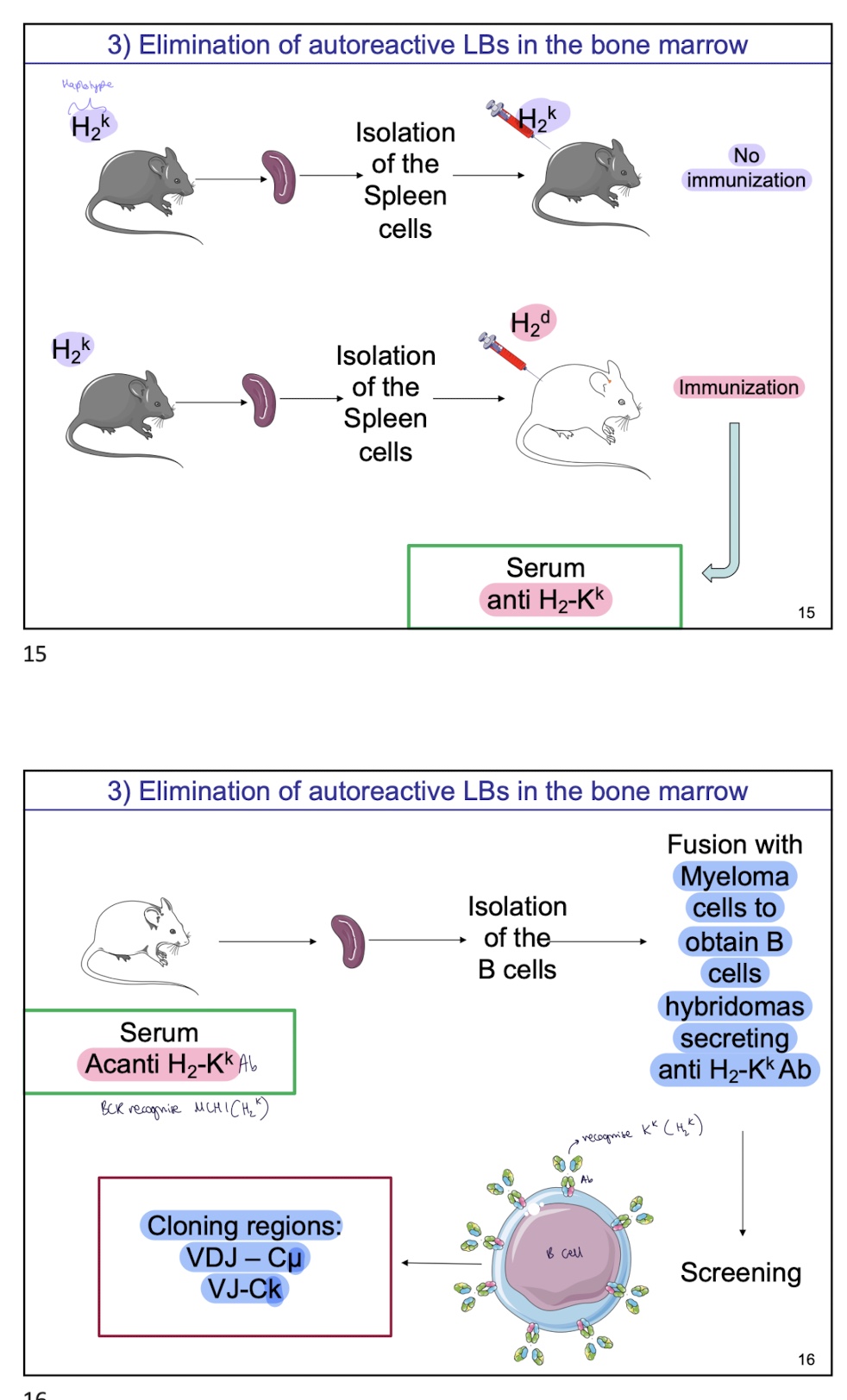
what experiment shows that self tolerance of MHC
Spleen cells are isolated of Mouse with haplotype H-2ᵏ
mouse w/ same haplotype is injected with spleen cells H-2ᵏ from previous mice
→ No immunisation as H-2ᵏ is self MHC so
B and T cells specific for H-2ᵏ were deleted or inactivated during development
next ,
Spleen cells are isolated of Mouse with haplotype H-2ᵏ
mouse w/ H2d haplotype injected w/ spleen cells H-2ᵏ from previous mice
→ immunisation and Serum contains anti–H-2Kᵏ antibodies as H-2ᵏ is foreign (allogeneic) to an H-2ᵈ mouse
T-cell help is available → B cells are activated
how is a transgenic mouse that recognises self Ag produced in the lab
mouse w/ H2k haplotype crossed w/ H2d Tg Ig anti H2-Kk Ab mouse that has BCR that recognises self Ag not expressed in the mouse → H2d/k Tg anti H2-Kk Ab ( transgenic mice that recognises self Ag)
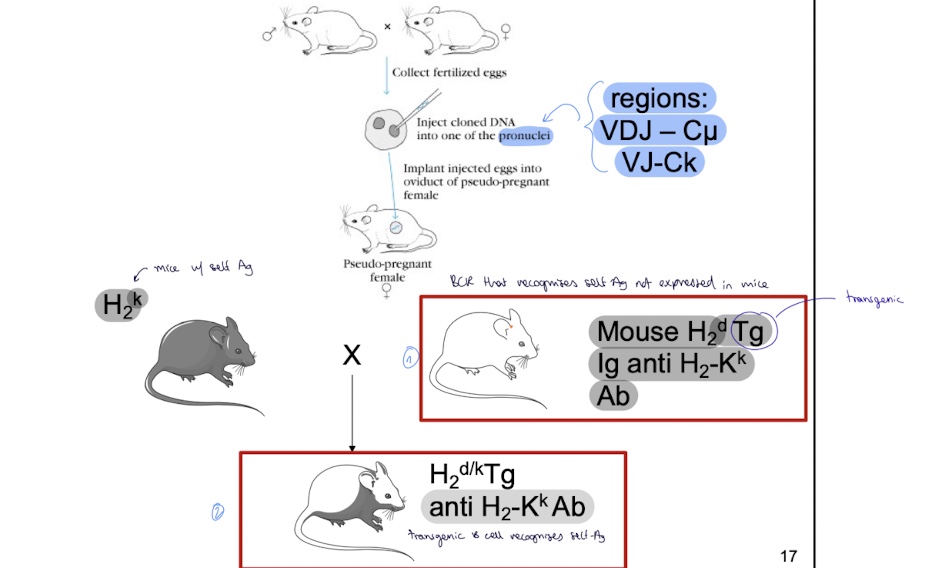
so in the H2d/k Tg anti H2-Kk Ab mouse (B cella against self Ag)
n mature B cells express anti Kk (self Ag) ans the BCR that recognises self Ag are deleted in the bone marrow due to negative selection
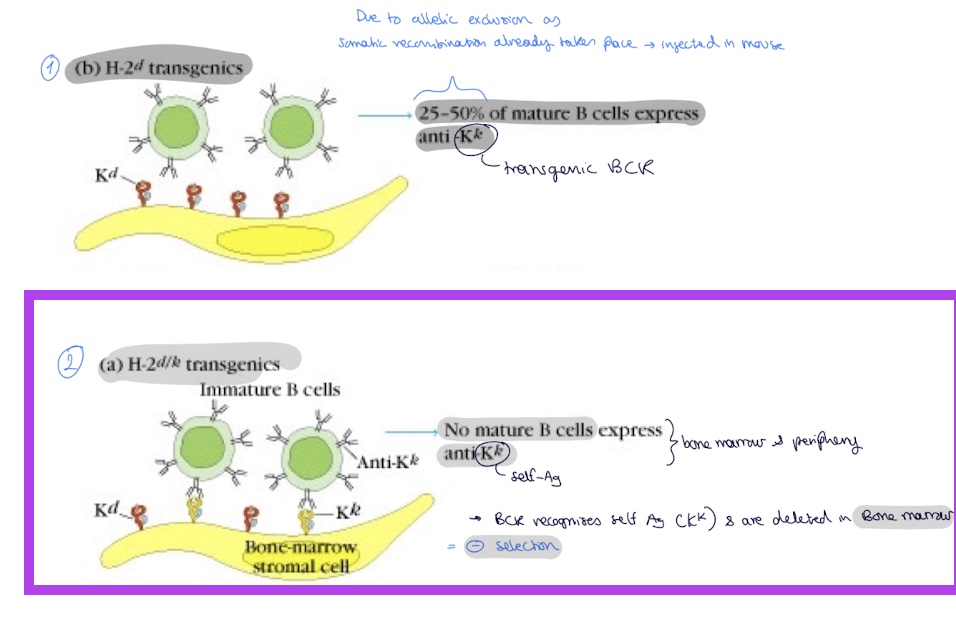
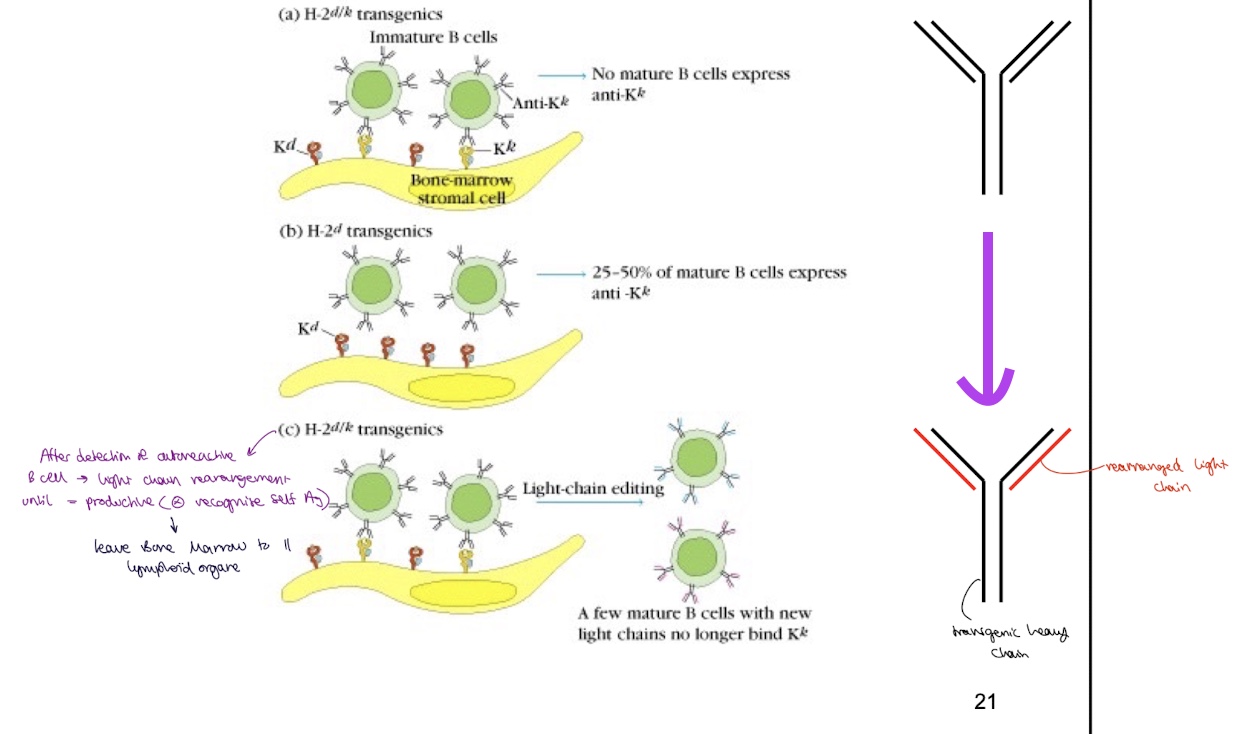
if self Ag recognised by B cell how does receptor editing allow the negative selection of B cells
after detection of autoreactive B cell → light chain rearangement unit productive rearrangement occurs → B cell can now leave bone marrow to II LO
what is an anergic state of a B cell
self reactive B cell remains alive but unable to be activated
to prove clonal anergy in mature B cells a HEL mouse (chicken egg white lysozyme) crossed w/ anti-HEL showed what results
this crossbreeding → double transgenic Tg carrying both HEL and anri-HEL transgenes and what is observed :
theres still the presence of HEL binding B cells but little to no IgM expression → anergic B cell
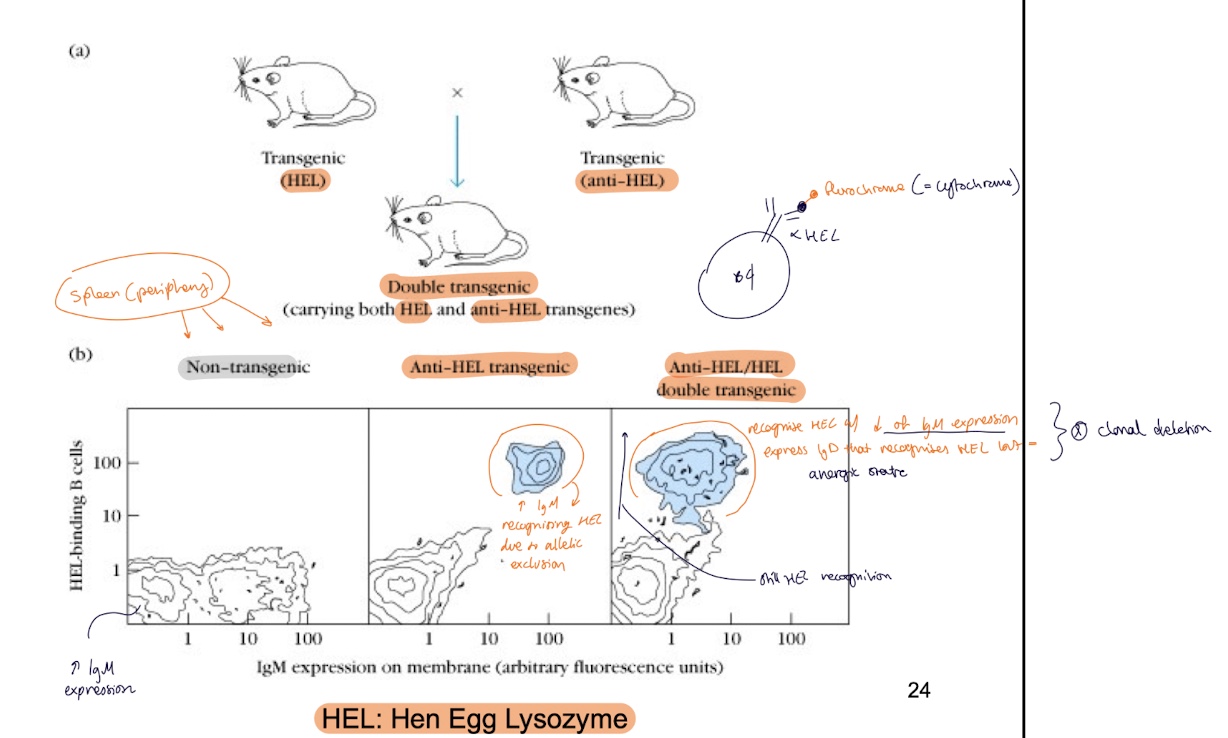
so what are the 3 main mechanisms if autoreactive B cell is detected
apoptosis
Anergic B cell
Mature B cell clonally ignorant
On BCR and TCRs there are structures associated to them that contain an ITAM domain, what do they allow
receive phosphorylation = phosphorylation domains
allows signal transduction
can bind w/ protein w/ 2 SH2 domains
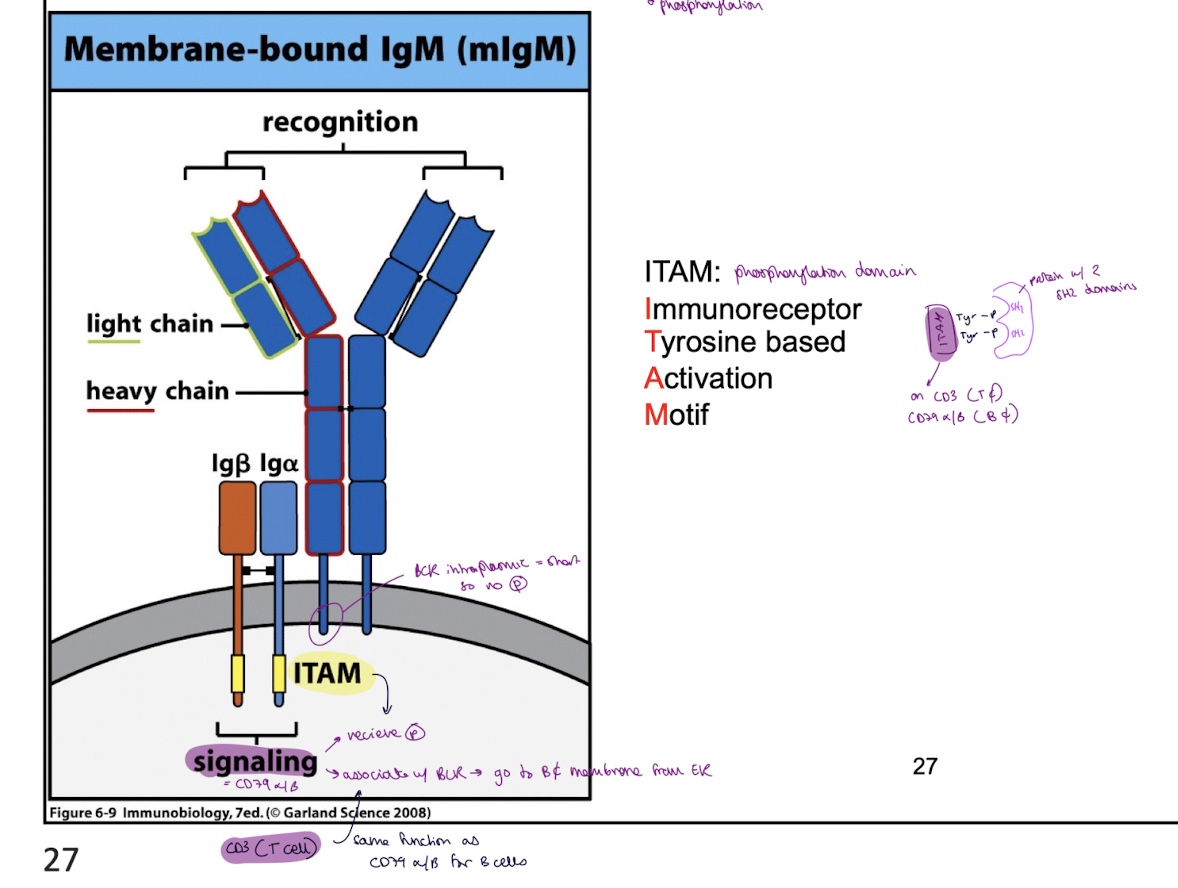
what structures are ITAM found in B and T cells
CD79α and β : B cells
CD3 : T cells
how does the Fab fragments of Ab binding to BCR alter the signal in B cells
Fab fragment of Ab bids to BCR but no crosslinking of BCR → no signal
Fab fragments crosslink BCR [F(ab)2] → weak signal
anti-F(ab)2 Ab cause extensive cross-linking → strong signal
![<ul><li><p>Fab fragment of Ab bids to BCR but no crosslinking of BCR → no signal</p></li><li><p>Fab fragments crosslink BCR [F(ab)2] → weak signal </p></li><li><p>anti-F(ab)2 Ab cause extensive cross-linking → strong signal </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2f4adce4-34a2-4e85-8960-644345834ee0.jpg)
what does a cytoxicity assay mesure
quantifies target cell death caused by cytotoxic immune mechanisms, most commonly by CD8⁺ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) or NK cells
if a H2b mouse is immunised by a virus and the T cells are isolated from spleen, what would the cytoxicity assay show compared to an uninfected mouse
infected mouse : high percentage of lysis for only MHC of the haplotype H2b will recognise and kill the virus
infected : no lysis as theres been no infection

the 3 CDRs recognises specific structures (MHC, peptide), which CDR recognises what ?
CDR1 : recognises MHC-peptide
CDR2 : recognises the MHC only
CDR3 : recognises peptide only
what is the positive selection of T cells
in the thymus : the survival of T cells that recognise self MHC molecules
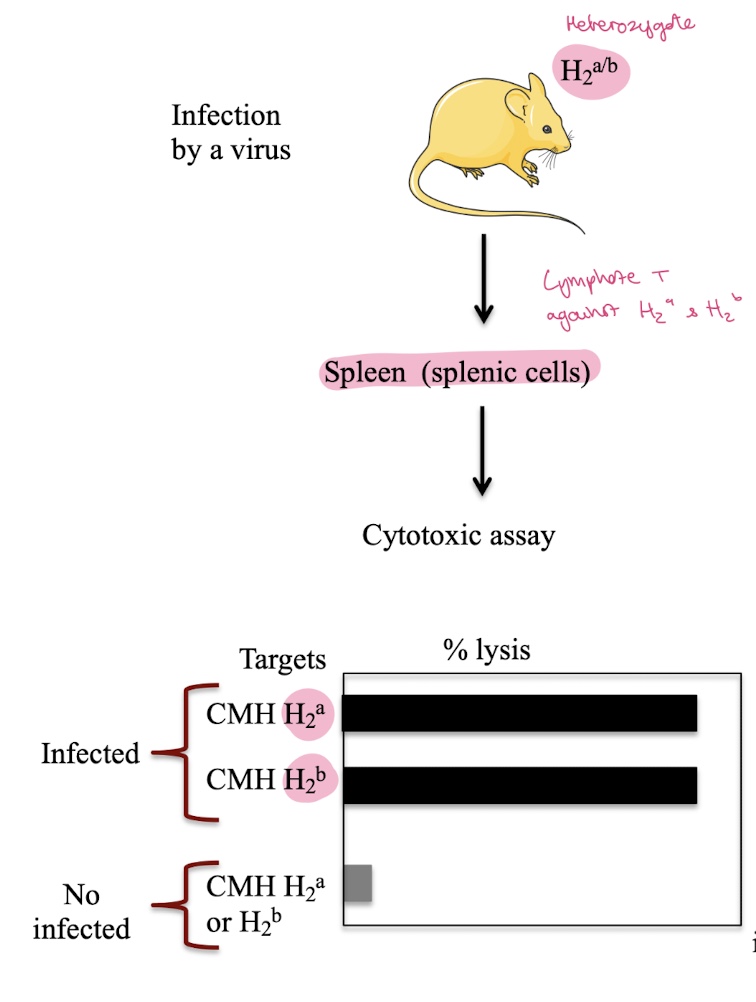
what cytotoxicty assay is observed if a heterozygote mouse H2a/b is infected w/ a virus
T cells kill infected target cells presenting antigen on:
H-2ᵃ
H-2ᵇ
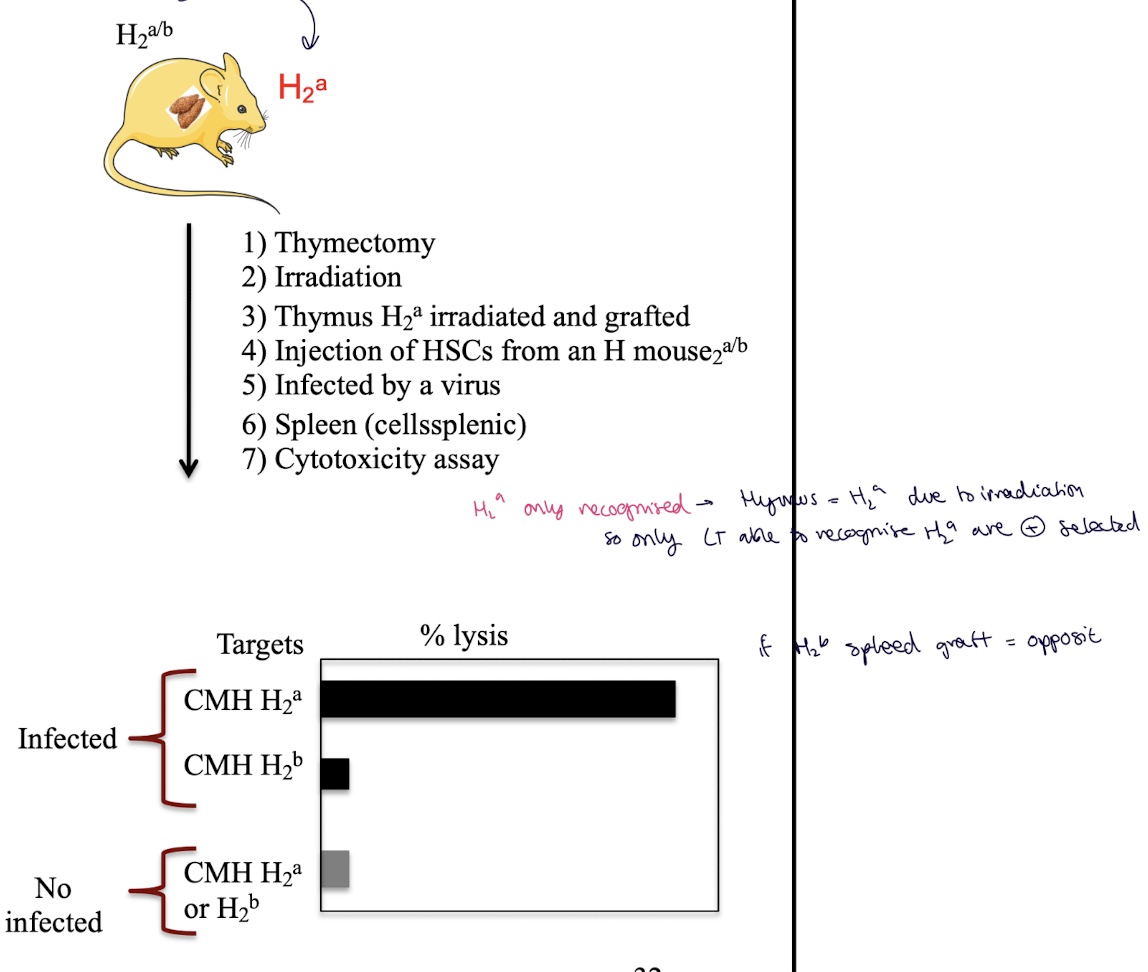
what cytotoxicty assay is observed if a heterozygote mouse H2a/b that is irradiated and grafted w/ a thymus from H2a mouse which is infected w/ a virus
irradiation of the mouse is to remove all hematopoietic cells (HSCs)
Graft a thymus from an H-2ᵃ mouse : Thymic epithelial cells express only H-2ᵃ
HSCs from H2a/b are injected in the mouse
→ T cells kill infected target cells presenting an Ag on H2a
Only T cells whose TCRs can bind H-2ᵃ survive = positive selection (T cells capable of recognising H-2ᵇ die by neglect)
Spleen cells from an H-2ᵏ mouse are isolated and transferred into two recipient mice, one H-2ᵏ and one H-2ᵈ. In which recipient will the transferred T cells function, and why?
The transferred T cells will function only in the H-2ᵏ recipient, because they are MHC-restricted to H-2ᵏ and can recognise antigen presented on H-2ᵏ MHC molecules. In the H-2ᵈ recipient, the T cells will not respond because they cannot recognise antigen presented on H-2ᵈ MHC.
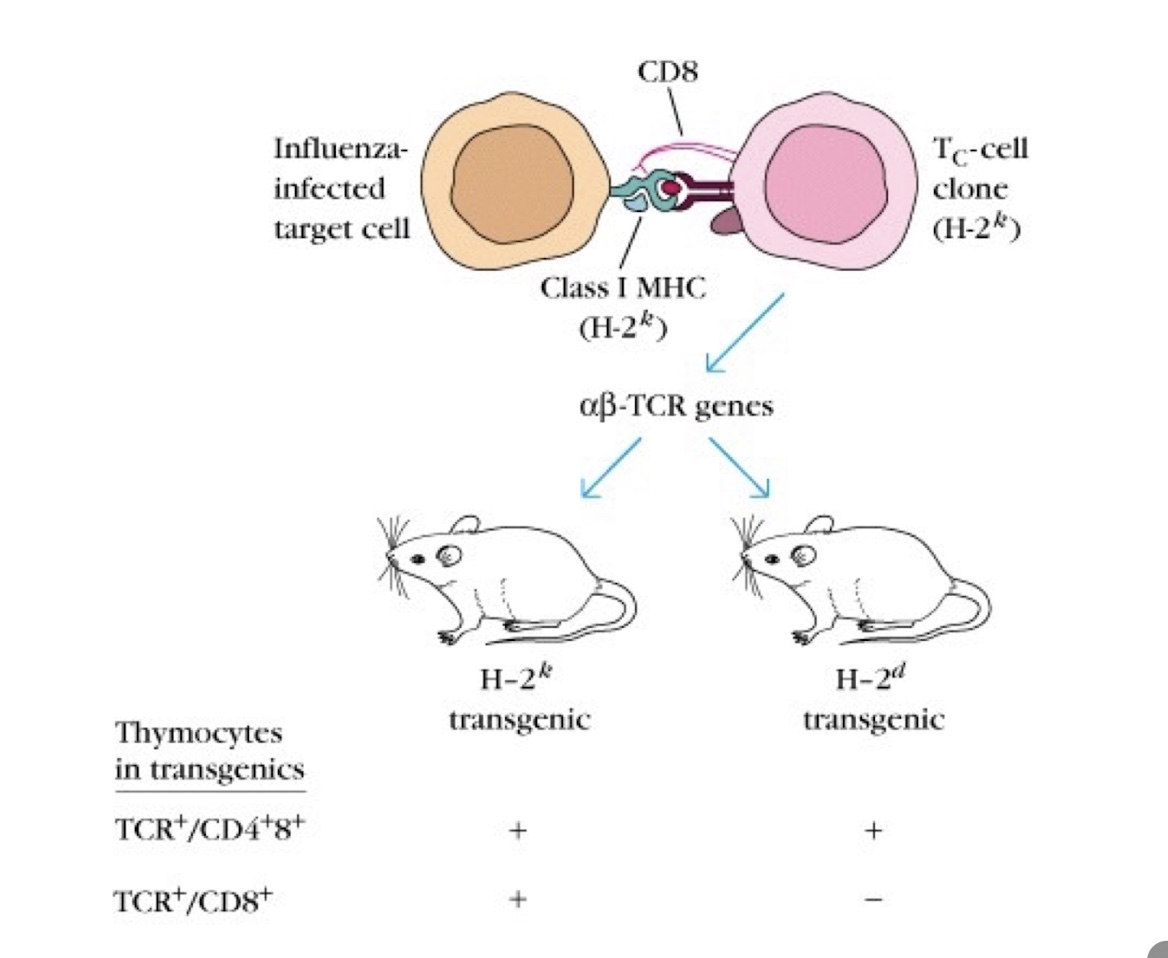
what MHC class does CD8+ T cells recognise
MCH I
what MHC class does CD4+ T cells recognise
MHC II
what type of cells present MHC I and II
MHC I : all nucleated cells
MHC II : professional APCs s B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells
what is negative selection
the deletion of developing T cells w/ TCRs that recognise self peptide-MHC complexes w/ high affinity