Optics Test Review: Light Production and Reflection
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
medium
The substance through which light travels.
electromagnetic spectrum
The range of all types of electromagnetic radiation.
opaque
A material that does not allow light to pass through.
transparent
A material that allows light to pass through without scattering.
real image vs. virtual image
A real image can be projected on a screen, while a virtual image cannot.
radiation
The emission of energy as electromagnetic waves or as moving subatomic particles.
visible light
The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye.
Light ray
A straight line that represents the path of light.
translucent
A material that allows some light to pass through but scatters it.
plane
A flat surface where light can reflect.
electromagnetic wave
A wave of electromagnetic radiation that travels through space.
Luminous vs non-luminous
Luminous objects emit their own light, while non-luminous objects do not.
Incident ray
The ray of light that strikes a surface.
converge vs. diverge
Converge means to come together, while diverge means to spread apart.
normal
An imaginary line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence.
perpendicular
At an angle of 90 degrees to a given line or surface.
focus
The point where light rays converge or appear to diverge.
reflected ray
The ray of light that bounces off a surface.
angle of incidence
The angle between the incident ray and the normal.
angle of reflection
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal.
Specular vs diffuse reflection
Specular reflection occurs on smooth surfaces, while diffuse reflection occurs on rough surfaces.
Concave vs convex
Concave lenses curve inward, while convex lenses curve outward.
centre of curvature
The center of the sphere from which a mirror is made.
principal axis
The line that passes through the center of curvature and the focus of a lens or mirror.
vertex
The point where the principal axis meets the mirror or lens.
refraction
The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.
angle of refraction
The angle between the refracted ray and the normal.
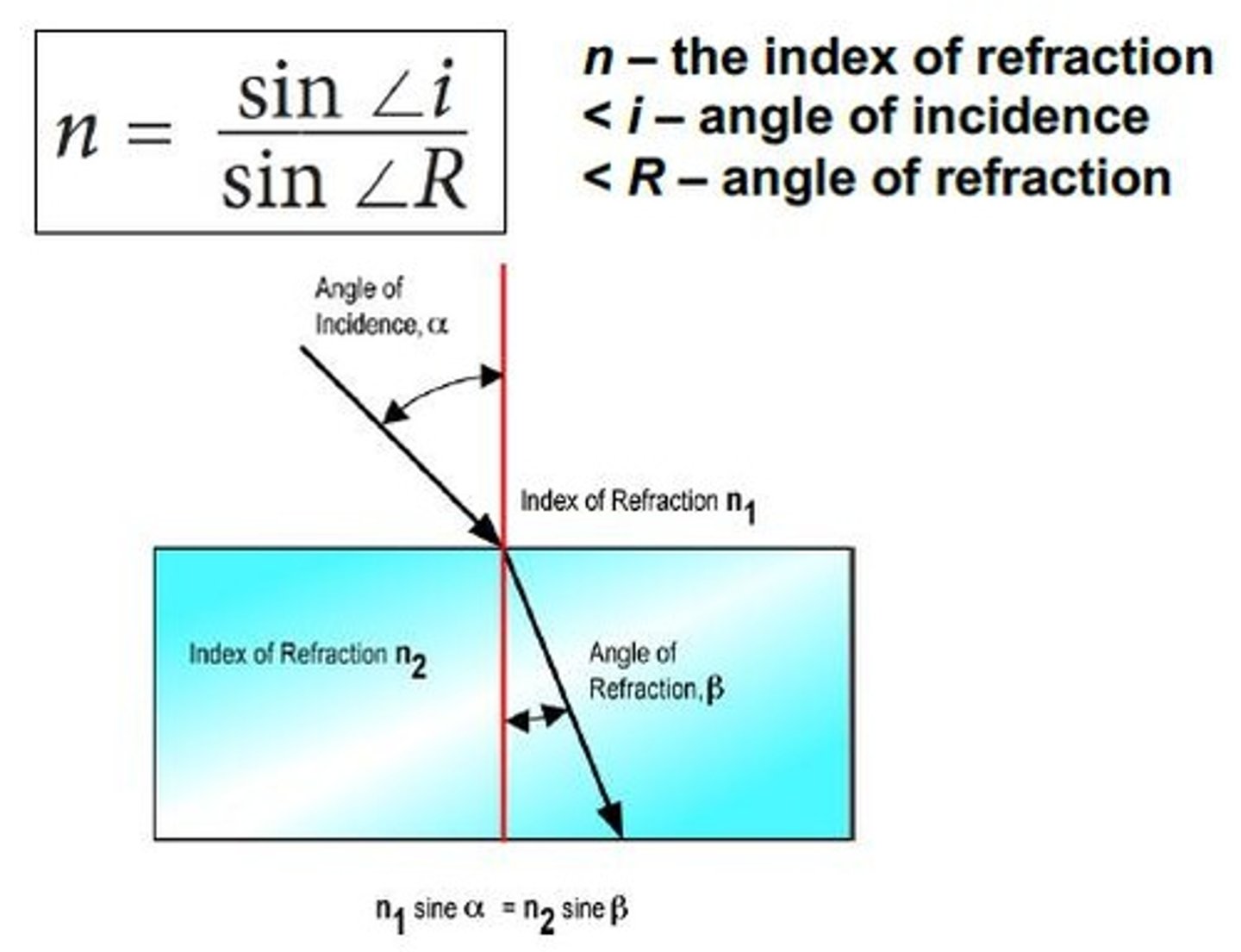
Index of refraction
A measure of how much the speed of light is reduced in a medium compared to vacuum.
Critical angle
The angle of incidence that results in total internal reflection.
Total internal reflection
The complete reflection of light back into a medium when it hits the boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle.
converging vs diverging lens
Converging lenses bring light rays together, while diverging lenses spread them apart.
emergent ray
The ray of light that exits a lens or medium.
optical centre
The point in a lens where light rays pass through without bending.
principal focus
The point where parallel rays of light converge after passing through a lens.
secondary principal focus
The point where diverging rays appear to originate after passing through a lens.
Converging and Diverging lens features
Diagrams and terminology that describe the characteristics of converging and diverging lenses.
Imaging rules for converging lenses and diverging lenses
The principles that govern how images are formed by different types of lenses.
Locating images in a converging lens and a diverging lens using the ray diagram method
A technique to determine the position and characteristics of images formed by lenses.
Describing the characteristics of an image using SALT
SALT stands for Size, Attitude, Location, and Type of the image.
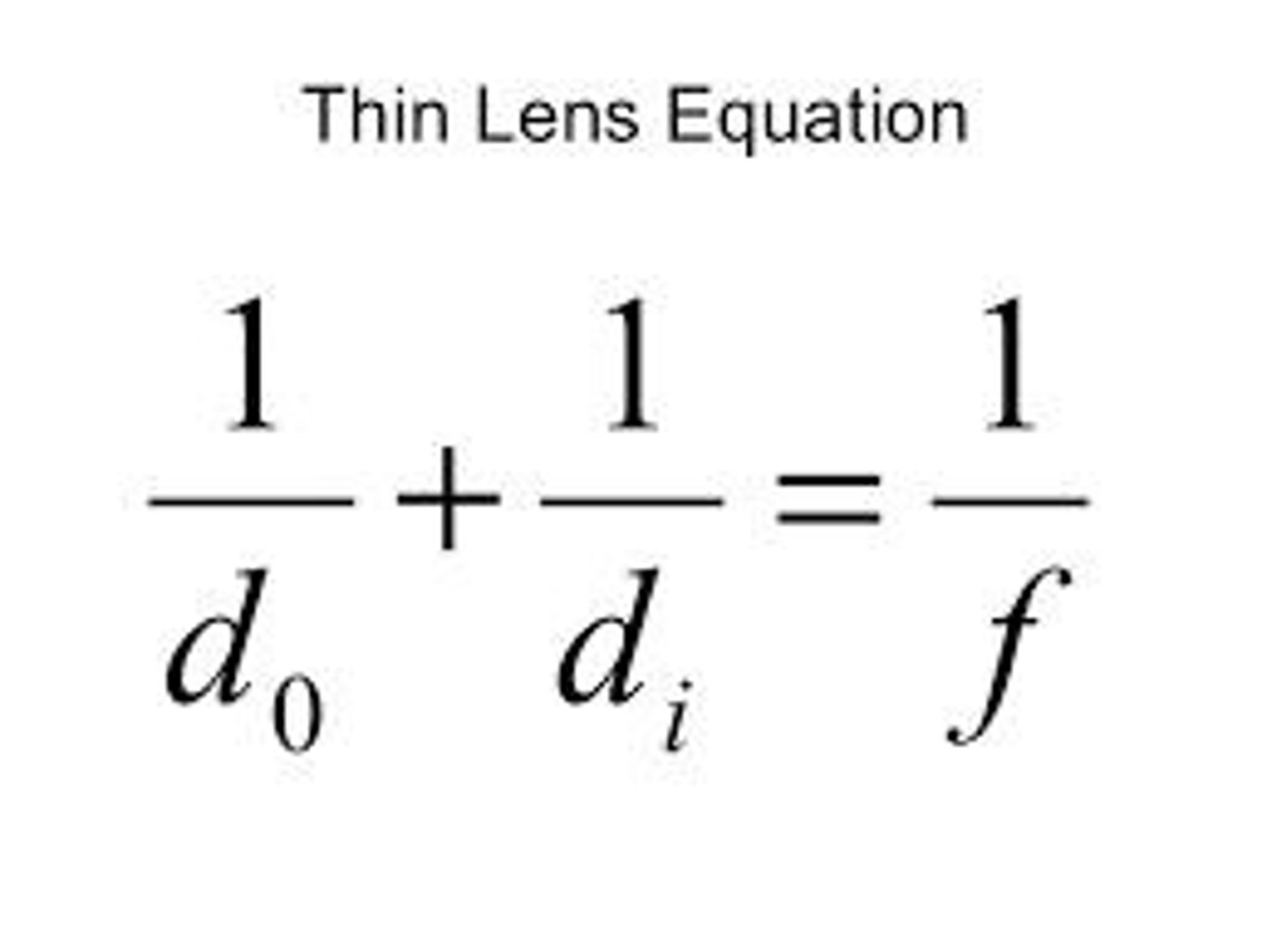
Solving problems using the 2 lens equations
Using the thin lens equation and magnification to find image characteristics.