TAMU BIOL111 - Exam 1 (chapters 1, 2, and 3 )
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
science
knowledge that covers general truths or the operation of general laws especially when acquired and tested by the scientific method
basic science
science that seeks to expand knowledge and understanding regardless of the short term application of that knowledge
applied science
form of science that aims to solve real world problems
discovery (descriptive) science
form of science that aims to observe, explore, and investigate
hypothesis based science
form of science that begins with a specific question and potential testable answers
inductive reasoning
form of logical thinking that uses related observations to arrive at a general conclusion
hypothesis
a tentative answer to a well framed question; an explanation on trial
deductive reasoning
form of logical thinking that uses a general inclusive statement to forecast specific results
scientific method
method of research with defined steps that include observation, formulation of hypothesis, testing, and confirming or falsifying the hypothesis
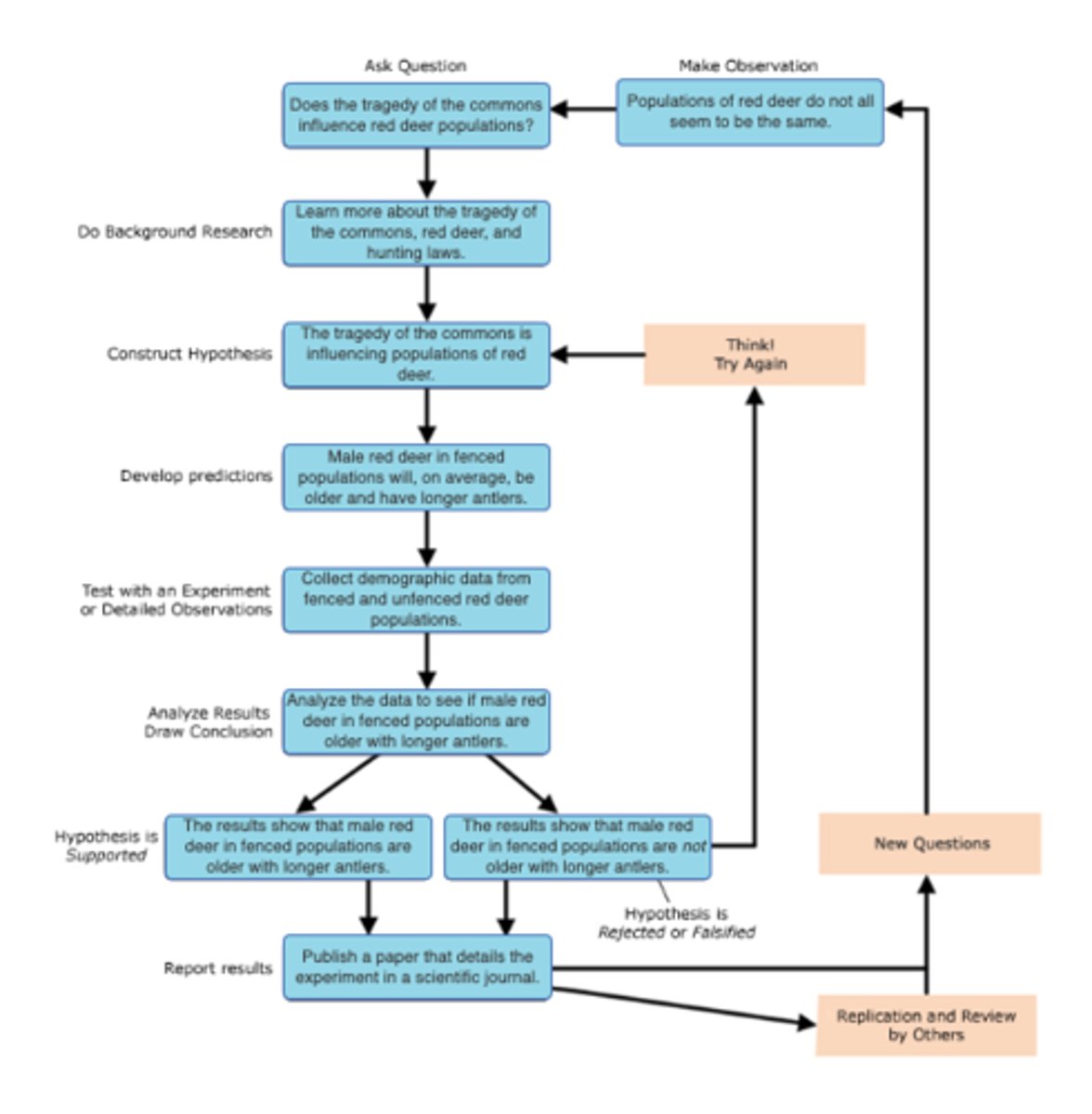
scientific theory
a carefully thought-out explanation for observations of the natural world that has been constructed using the scientific method and brings together many facts and hypotheses
theory
tested and confirmed explanation for observations or phenomena
generates new hypotheses
basic functions (properties) of life
1) order
2) sensitivity response to stimulus
3) reproduction
4) adaptation
5) growth and development
6) regulation/homeostasis
7) energy processing
8) evolution
levels of biological organization
1) organelles
2) cells
3) tissues
4) organs
5) organ system
5) organism/ population/ community
6) ecosystems
7) biospheres
hypothesis based science
form of science that begins with a specific question and potential testable answers
cell
the lowest level of organization that can perform all activities required for life
all cells:
are enclosed by a membrane
use DNA as their genetic information
2 major kinds of cells
prokaryotic + eukaryotic
organelles
small structure that exist within cells and carry out cellular functions
taxonomy
the branch of biology that names and classifies species into a hierarchical order
all life shares:
DNA, mRNA, tRNA
Ribosomes
Proteins of 20 amino acids
natural selection
Darwins second point about evolution: a process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
phylogenetic tree
a branching diagram that represents a hypothesis about the evolutionary history of a group of organisms.
decent with modification
Darwin's principle about evolution that each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time
matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
element
a pure substance made of only one kind of atom
atom
smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element
subatomic particles
protons: + charge
neutrons: neutral
electrons: - charge
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
atomic mass (mass number)
protons + neutrons
each has a mass close to 1 dalton (atomic mass unit = AMU)
isotope
differ in the number of neutrons in the atomic nucleus but have the same number of protons
radioisotopes
isotopes that have unstable nuclei and spontaneously give off particles and energy
molecules
groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Bhor model
indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell
hydrophilic
has an affinity for water (water loving)
polar molecules which contain O-H or N-H polar covalent bonds
hydrophobic
does not have an affinity for water
noncharged and nonpolar molecules
4 emergent properties of water
1) high heat capacity
2) heat of vaporization
3) cohesive and adhesive properties
4) versatility as a solvent
specific heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius
heat is absorbed when hydrogen bond breaks
heat is released when hydrogen bonds form
kinetic energy
energy of motion
thermal energy
a measure of the total amount of kinetic energy due to molecular motion
temperature
measure of the average kinetic energy
heat of vaporization
quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 gram to be converted from a liquid to a gas
evaporation
the transformation of a substance from a liquid to a gas
cohesion
bonding of a high percentage of the molecules to neighboring molecules
due to hydrogen bonding
surface tension
measure of how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid
related to cohesion
adhesion
attraction between water molecules and other molecules
mole
6.023 x 10²³ molecules
the mass of 1 mole of a substance is determined by its atomic or molecular mass
molarity
number of moles of a solute per liter (M=mole/L) of solution
acid
any substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
base
any substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
pH
pH=-log[H+]
each pH unit represents a tenfold difference in H+ concentration
neutral solution: [H+] and [OH-] are both 10^-7 M
pH is low in an acid
pH is high in a base
buffers
substances that minimize changes in the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxide ions in a solution
consist of a weak acid base pair that reversibly combines with hydrogen ions
isomers
molecules that have the same chemical formula but differ in placement/arrangement of atoms or types of bond between atoms
structural isomers
have a different covalent arrangement of atoms
geometric isomers
have a different arrangement of atoms around a double bond
enantiomers
molecules that share chemical formula and bonds but differ in 3D placement of atoms; mirror images
6 functional groups
hydroxyl
carbonyl
carboxyl
amino
sulfhydryl
phosphate
methyl
functional groups
groups of atoms within a molecule that confer consistent specific properties to these molecules
4 major classes of macromolecules
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
organic molecules
all contain carbon
may also contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and some other minor elements
macromolecules
large molecules composed of smaller molecules
monomers
small unit that can join together with other small units to form polymers
polymers
molecules composed of many monomers; makes up macromolecules
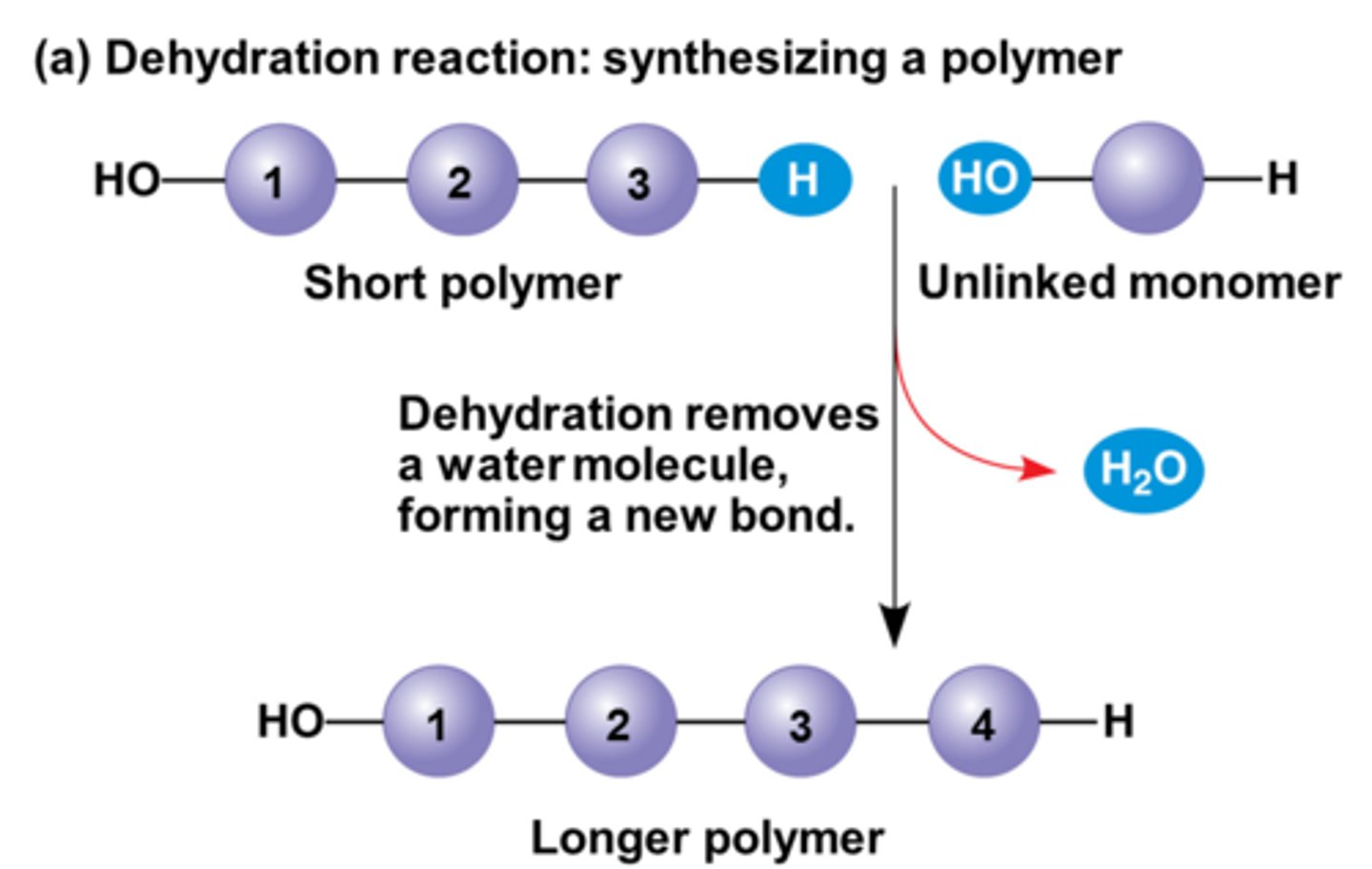
dehydration synthesis
the creation of larger molecules from smaller monomers when a water molecule is released
linked by covalent bonding
form new bonds/ require energy
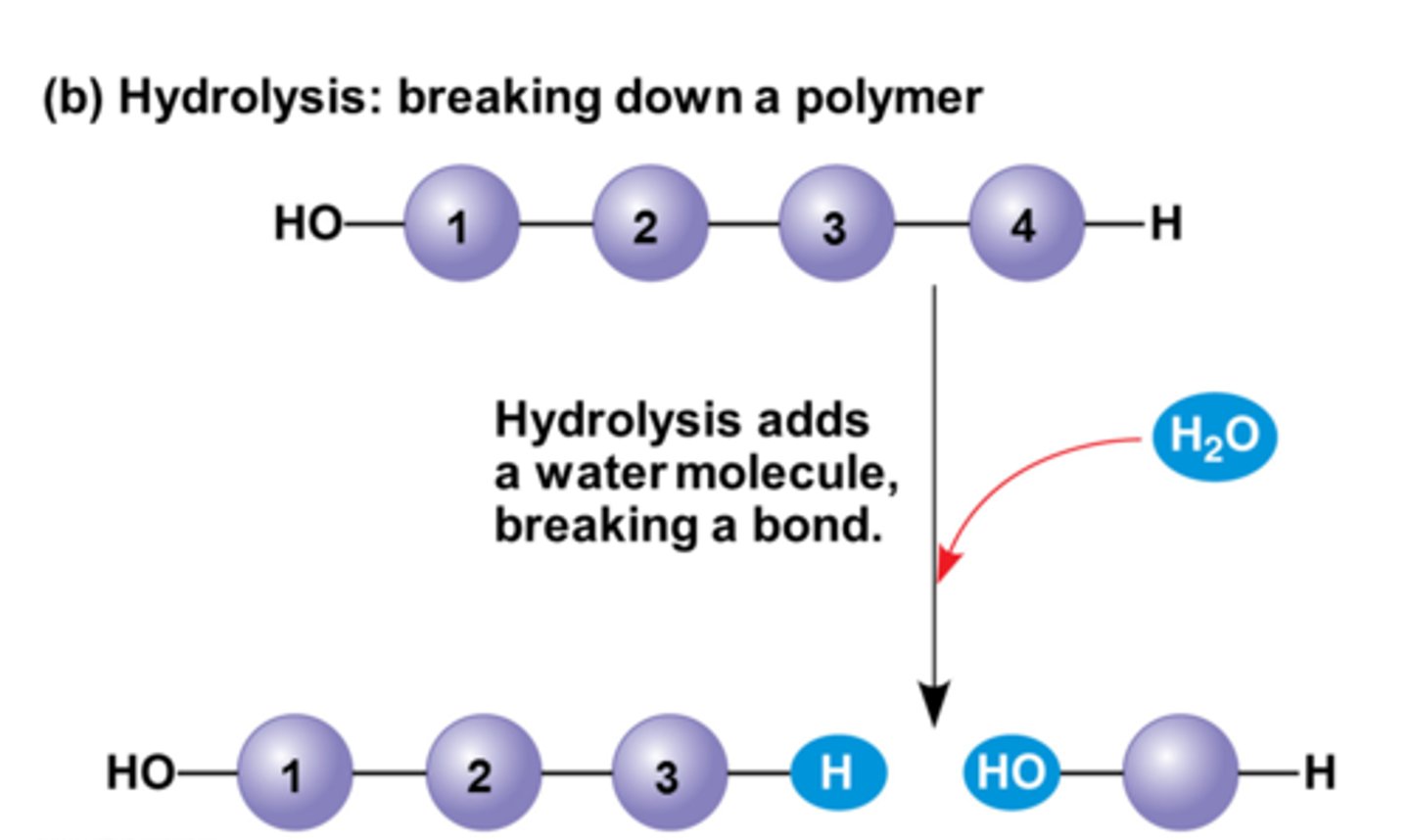
hydrolysis (dehydration reaction)
reaction that causes breakdown of larger molecules into smaller molecules by utilizing water
break bonds/ release energy
enzymes
biological molecules that catalyze or "speed up" reactions
carbohydrates
broken down to glucose to provide energy
3 main subtypes for carbohydrates
monosaccharides
disaccharides
polysaccharides
monosaccharides
3 structural isomers: glucose, fructose, galactose
3-7 carbons
disaccharides
form when 2 monosaccharides are linked in a dehydration reaction
joined by glycosidic bond
1-2 glycosidic bond
polysaccharides
long chain of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages
1-4 glycosidic bond
1-6 glycosidic bond
amylose
unbranched glucose monomers in a 1-4 glycosidic bond
amylopectin
branched glucose monomers in 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
starch
composed of amylose and amylopectin
cellulose
glucose monomers linked in unbranched chains by beta 1-4 glycosidic linkages
chitin
the hard exoskeleton of arthropods is composed of this polysaccharide
lipids
diverse group of hydrophobic non polar hydrocarbons
long term energy stores
building blocks for some hormones
important component of cell membranes
2 main components of fats
glycerol
fatty acids
triacylglycerol
formed by joining 3 fatty acids to a glycerol backbone
ester linkage
how glycerol molecules are attached to the fatty acids
saturated fatty acids
contain no C=C double bonds in the backbone
packed tightly and exist as solids at room temperature
unsaturated fatty acids
contain at least 1 C=C double bond in backbone
most unsaturated fats are liquids at room temperature referred to as oils
cis
acids have kink in the chain
they cannot be packed tightly
liquid at room temperature
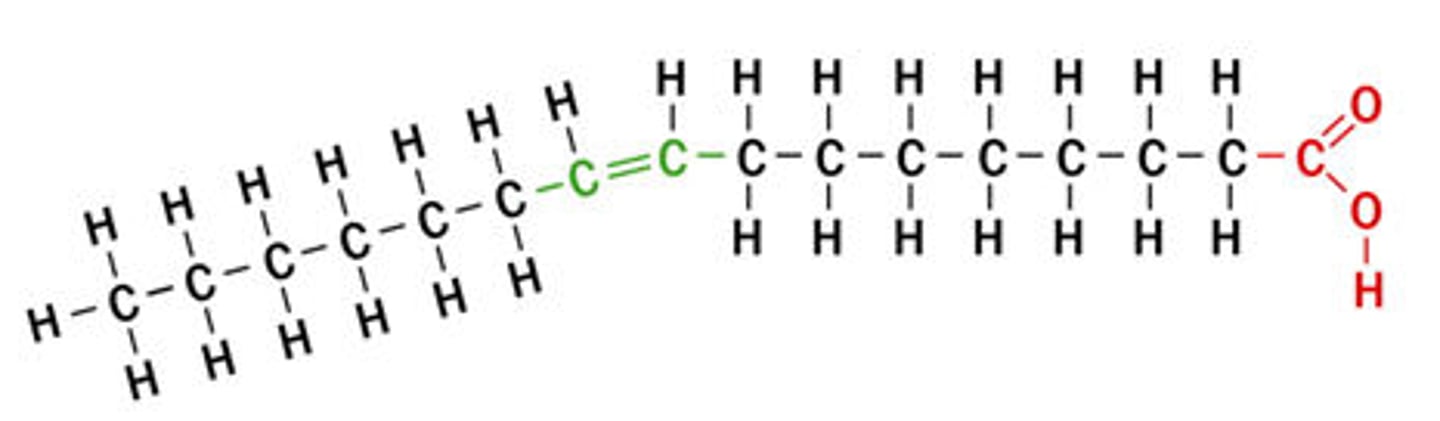
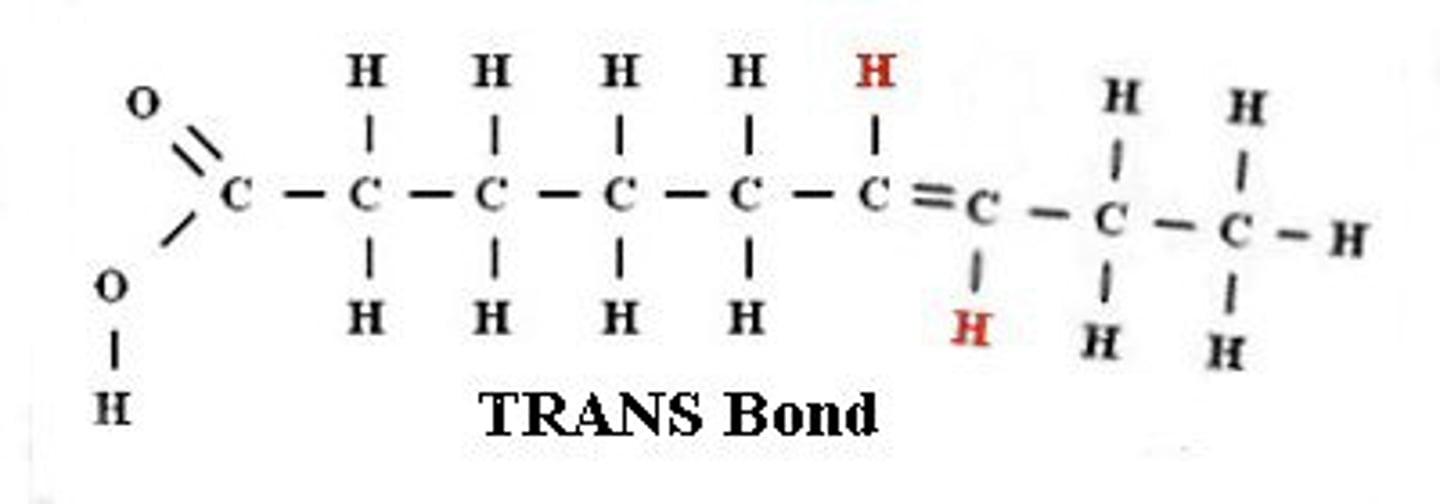
trans
acids have no kink
can be created through processing
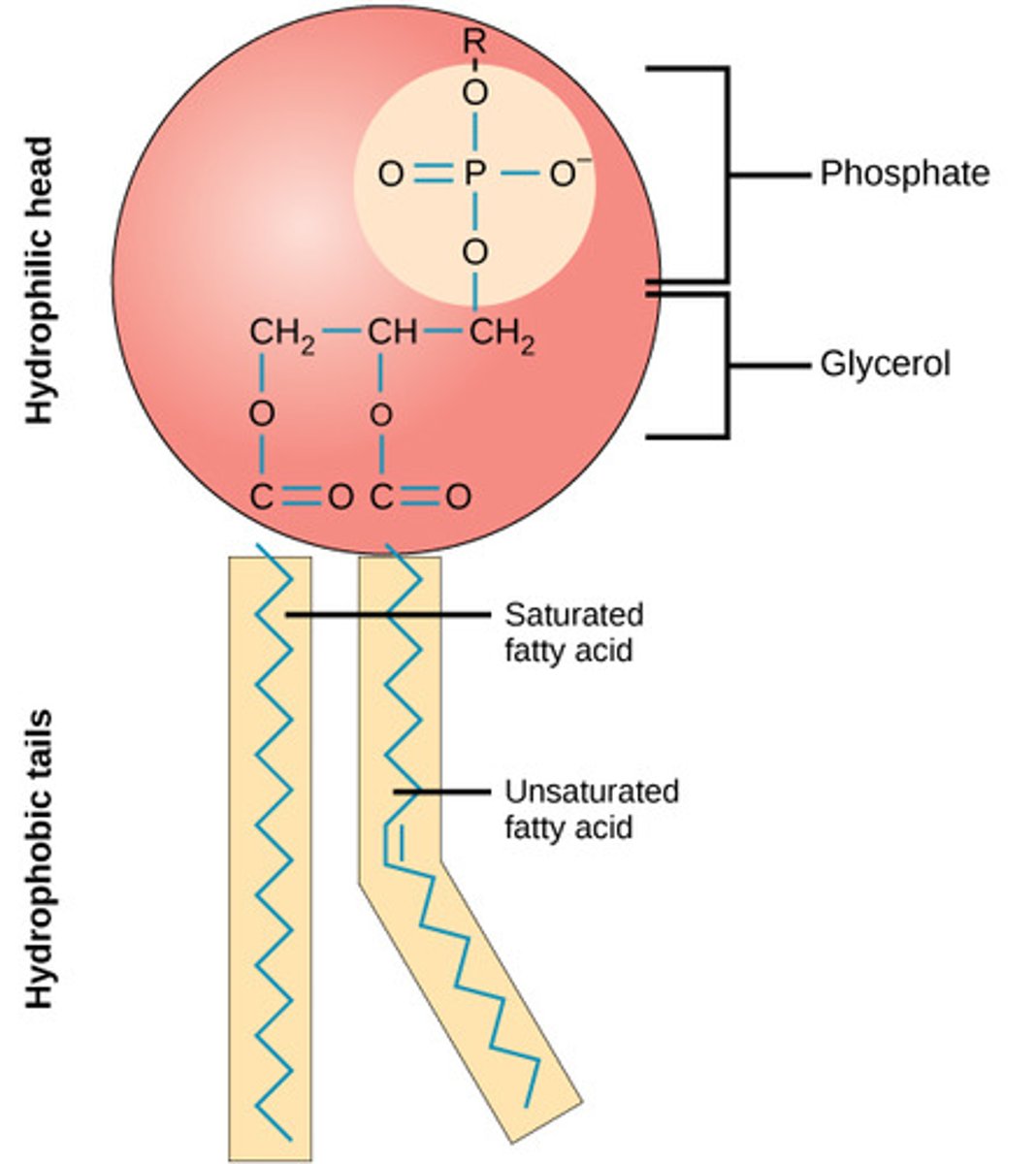
phospholipid
molecule with 2 fatty acids and a modified phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone
phosphate may be modified by addition of charged or polar chemical groups
2 common chemical groups that attached are choline and serine
proteins
most abundant organic molecules
have a diverse range of functions:
regulatory
structural
protective
transport
enzymes
toxins
multiple polypeptides
types of enzymes
catabolic
anabolic
catalytic
catabolic
break down substrates
anabolic
build more complex molecules
catalytic
affect rate of reaction
amino acids
monomers of proteins
the sequence and number of amino acids determine protein shape, size, and function
linked via peptide bond formation ( dehydration synthesis reaction
polypeptide
a chain of amino acids joined together in peptide linkages
protein shape has 4 levels of structure
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
primary protein structure
amino acid sequence determined by gene encoding that protein
a change in that nucleotide sequence of DNA could lead to a change in amino acid
this could lead to a change in protein structure and function
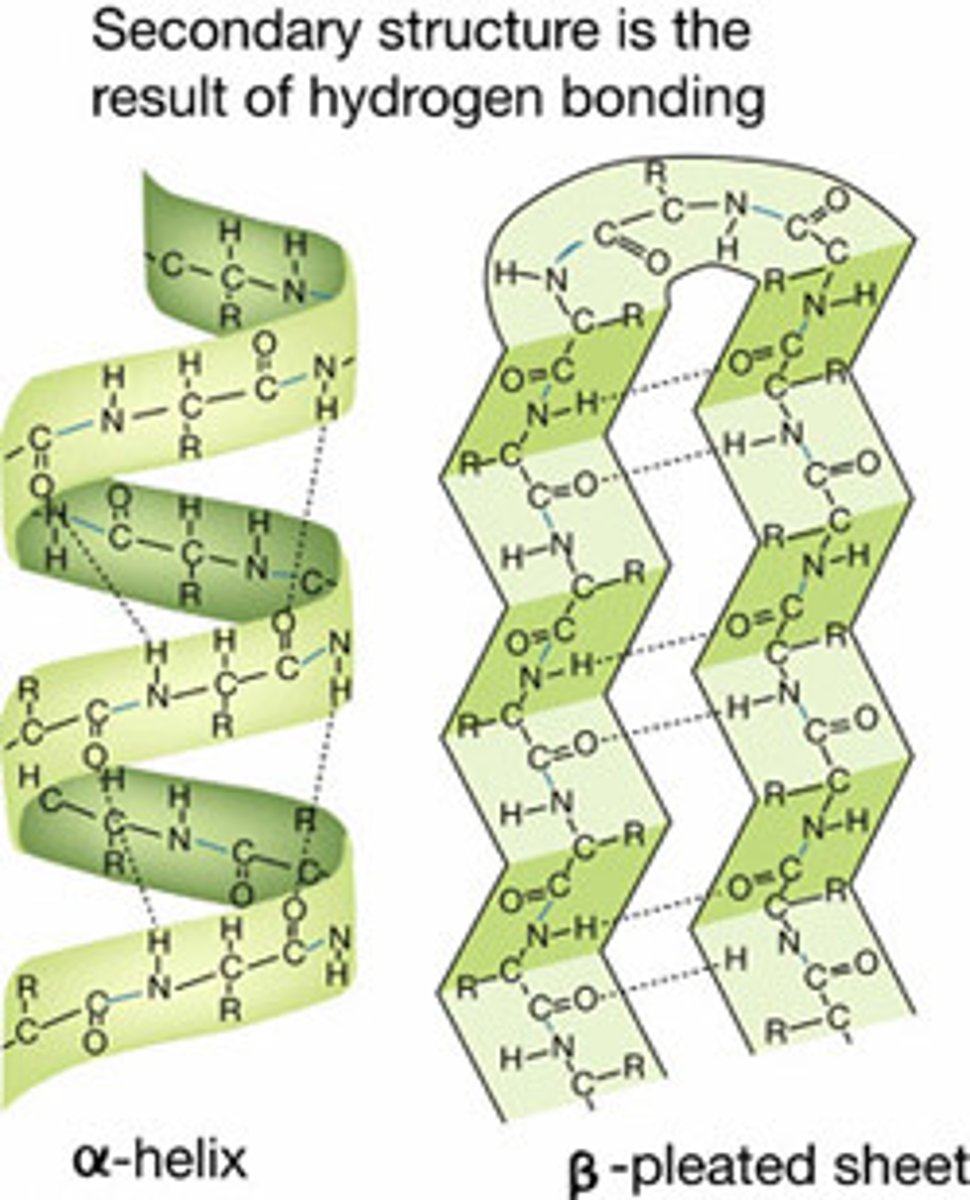
secondary protein structure
local folding of polypeptide
alpha helix- formed by hydrogen bond between oxygen in carbonyl group and an amino acid 4 positions down the chain
beta pleated sheet- hydrogen bonding between atoms on the backbone of the polypeptide chain
tertiary protein structure
unique 3D structure of polypeptide
chemical interactions between R groups on amino acids
determined by a variety of chemical interactions:
hydrophobic interactions
ionic bonding
hydrogen bonding
disulfide linkages
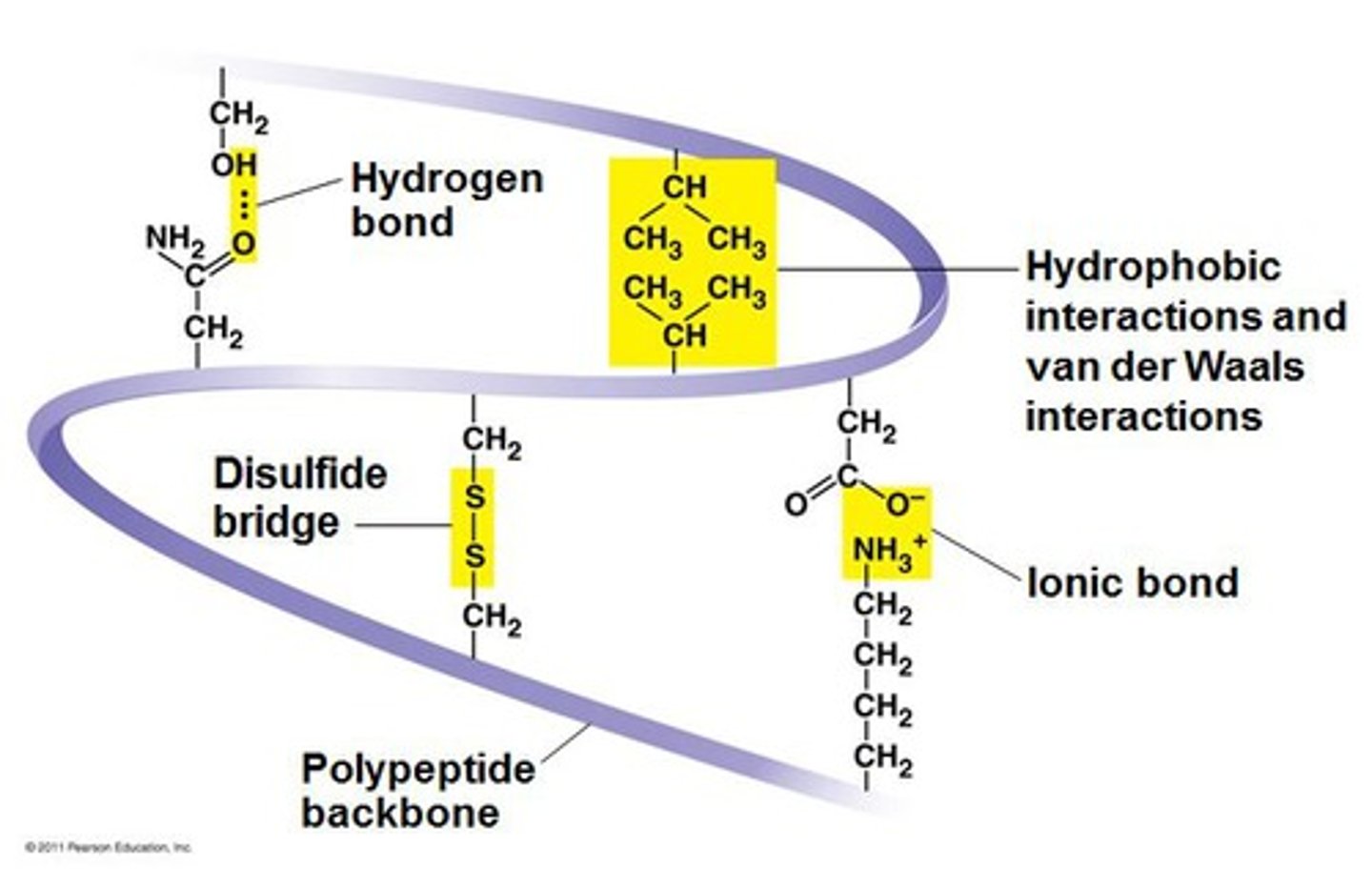
quaternary protein structure
interactions between several polypeptides that make up a protein
weak interactions between subunits help stabilize the structure
denaturation
changes in protein structure that leads to changes in function
changes in pH and temperature will alter primary structure of protein
nucleic acids
constitute the genetic material of living organisms
2 types:
DNA and RNA
locations:
nucleus of eukaryotic cells
mitochondria
chloroplasts
prokaryotic cells
DNA
codes for the genome of the cell
chromatin
complex of DNA and histone proteins