Ch. 13: The Blood, Heart and Circulation
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
207 Terms
What are the functions of the circulatory system
transportation, regulation, and Protection
functions of the circulatory system in regard to transportation is
Respiratory gases, nutrients, and wastes
functions of the circulatory system in regard to regulation is
Hormonal and temperature
functions of the circulatory system in regard to protection is
Clotting and immunity; blood clots, creating a barrier, protecting skin; WBC clean up dead cells
Major components of the Circulatory System are
The Cardiovascular System, and the Lymphatic system
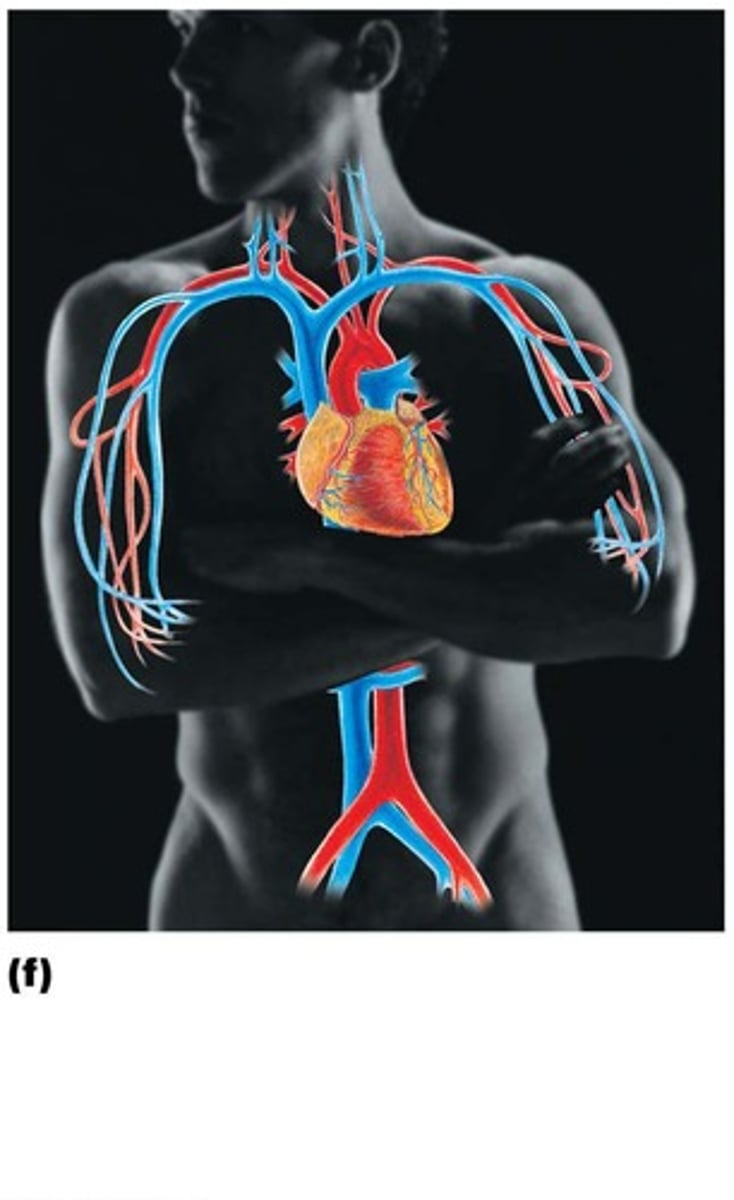
What is the cardiovascular system composed of
Heart: four-chambered pump; Blood vessels: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins
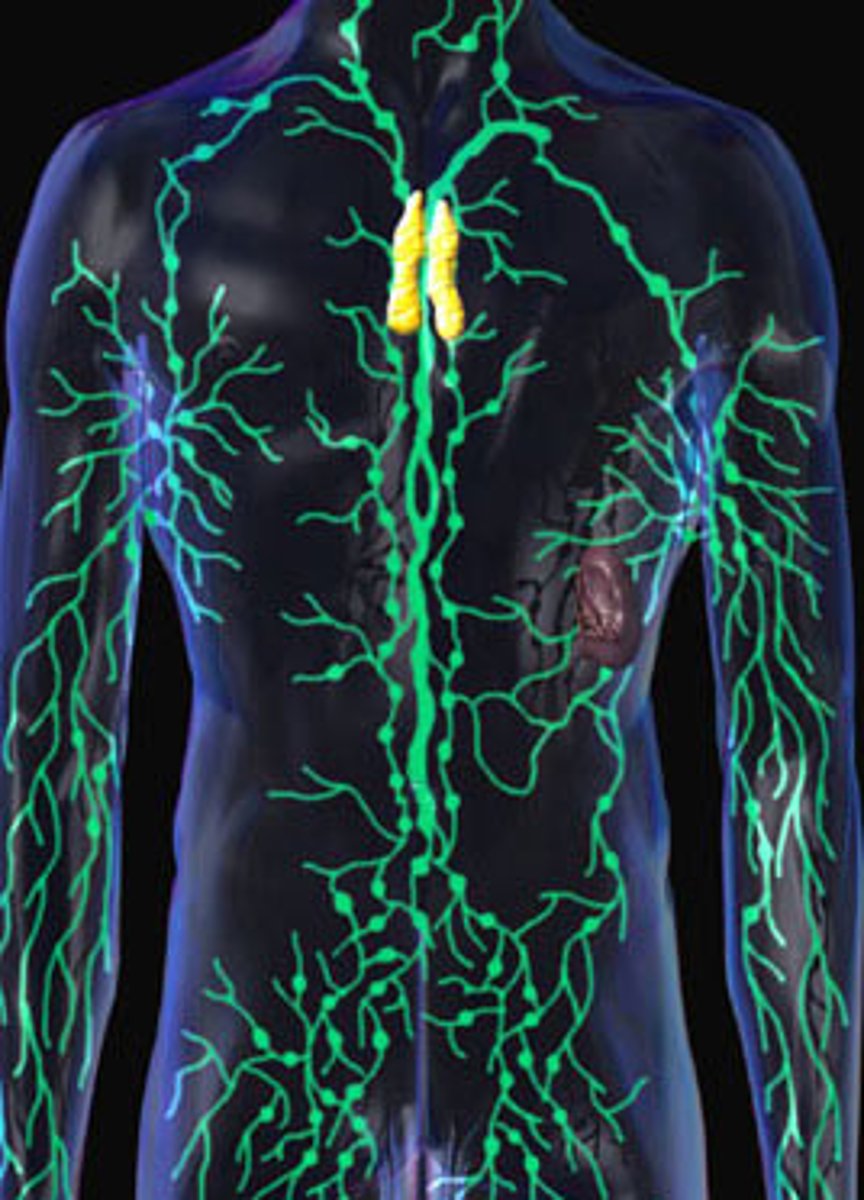
What is the lymphatic system composed of
Lymphatic vessels, lymphoid tissues, lymphatic organs (spleen, thymus, tonsils, lymph nodes)
The average adult blood volume is
5 liters
Arterial blood when leaving the heart is bright red and oxygenated, except for
blood going to the lungs
Venous blood when entering the heart is dark red and deoxygenated except for
blood leaving the lungs
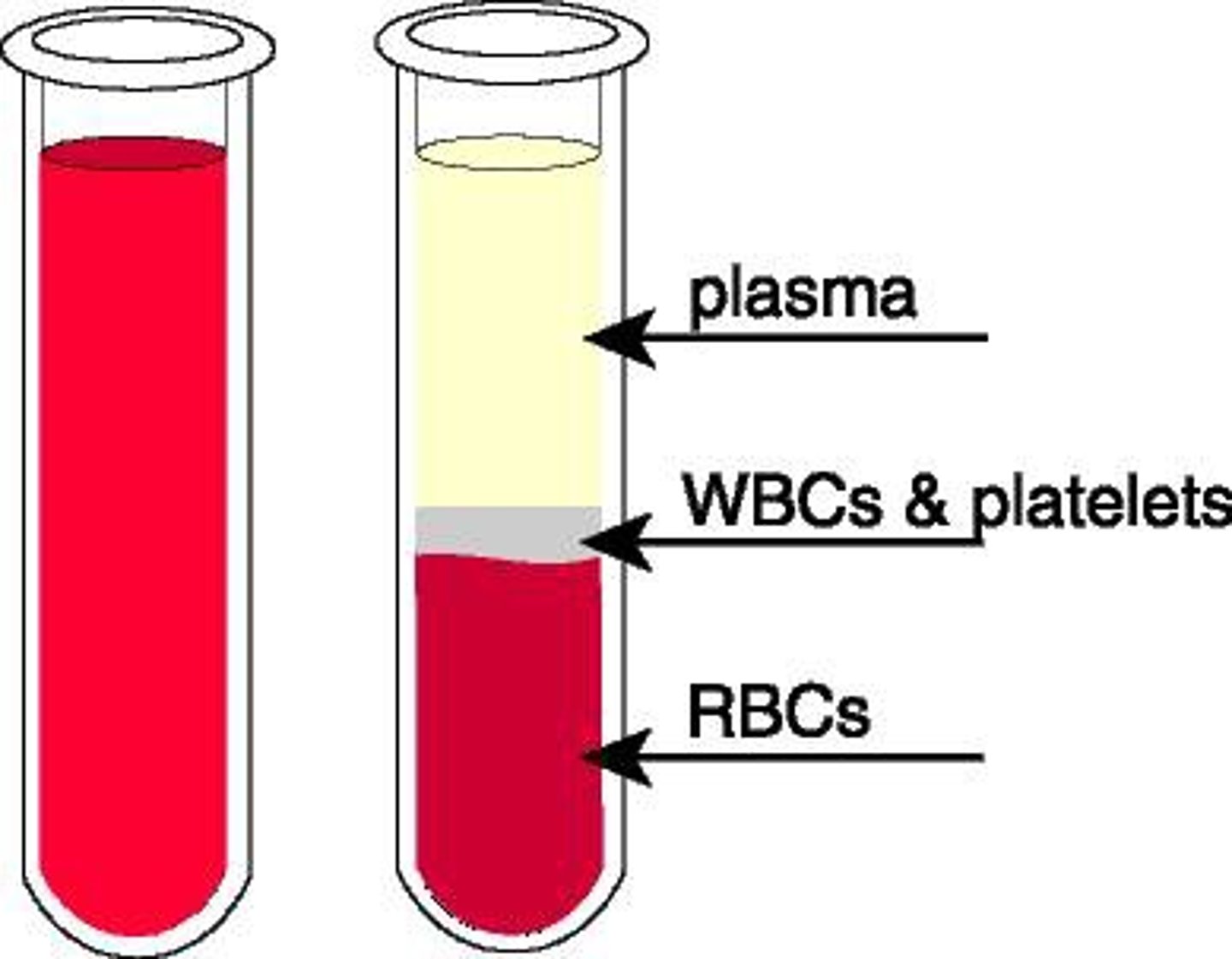
Blood is made out of
45% formed elements and ≈ 55% plasma (by volume)
What are some of the constituents of the blood
Plasma, Albumin, Globulins, and Fibronogen
Characteristics of blood plasma
Fluid part of blood, composed of water, Dissolved solutes
Plasma proteins make up ___of the plasma
7-8%
What does Albumin do
creates osmotic pressure to help draw water from tissues into capillaries to maintain blood volume and pressure
What are the three types of globulins
Alpha, beta, and gamma globulins
What do alpha and beta globulins do
transport lipids and fat-soluble vitamins
What do gamma globulins create
antibodies that function in immunity
What does fibrinogen do
helps in clotting after becoming fibrin
Blood without fibrinogen is called
serum
Regulatory mechanisms maintain plasma volume to maintain
blood pressure
Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus cause the release of Antidiuretic Hormone from the posterior pituitary gland if
fluid is lost, allowing fluid to be retained
What are the formed elements of blood
Erythrocytes(RBC), Leukocytes(WBC), and Platelets(thrombocytes)
Characteristics of Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
Flattened, biconcave discs; Transport oxygen; Lack nuclei and mitochondria; they carry oxygen to organs of the body, and carbon dioxide to the lungs for expiration.
How many erythrocytes in blood
approximately 5 million/mm3 blood; Have a 120-day life span, Each contain about 280 million hemoglobin molecules
Iron heme is recycled from the
liver and spleen; carried by transferrin (globulin) in the blood to the red bone marrow
Characteristics of leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
Have nuclei and mitochondria, Move in amoeboid fashion
leukocytes Exhibit Chemotaxis which is
the movement directed by attraction to stimulus (seen in clotting)
Leukocytes also exhibit Diapedesis/Extravasation which is
movement through the capillary wall into connective tissue to site of infection/injury
How many leukocytes are in blood
approximately 5000-9000/mm3 blood
What are the types of leukocytes
granular and agranular leukocytes
What is leukocytosis
an increase of the number of white blood cells when we are fighting infections
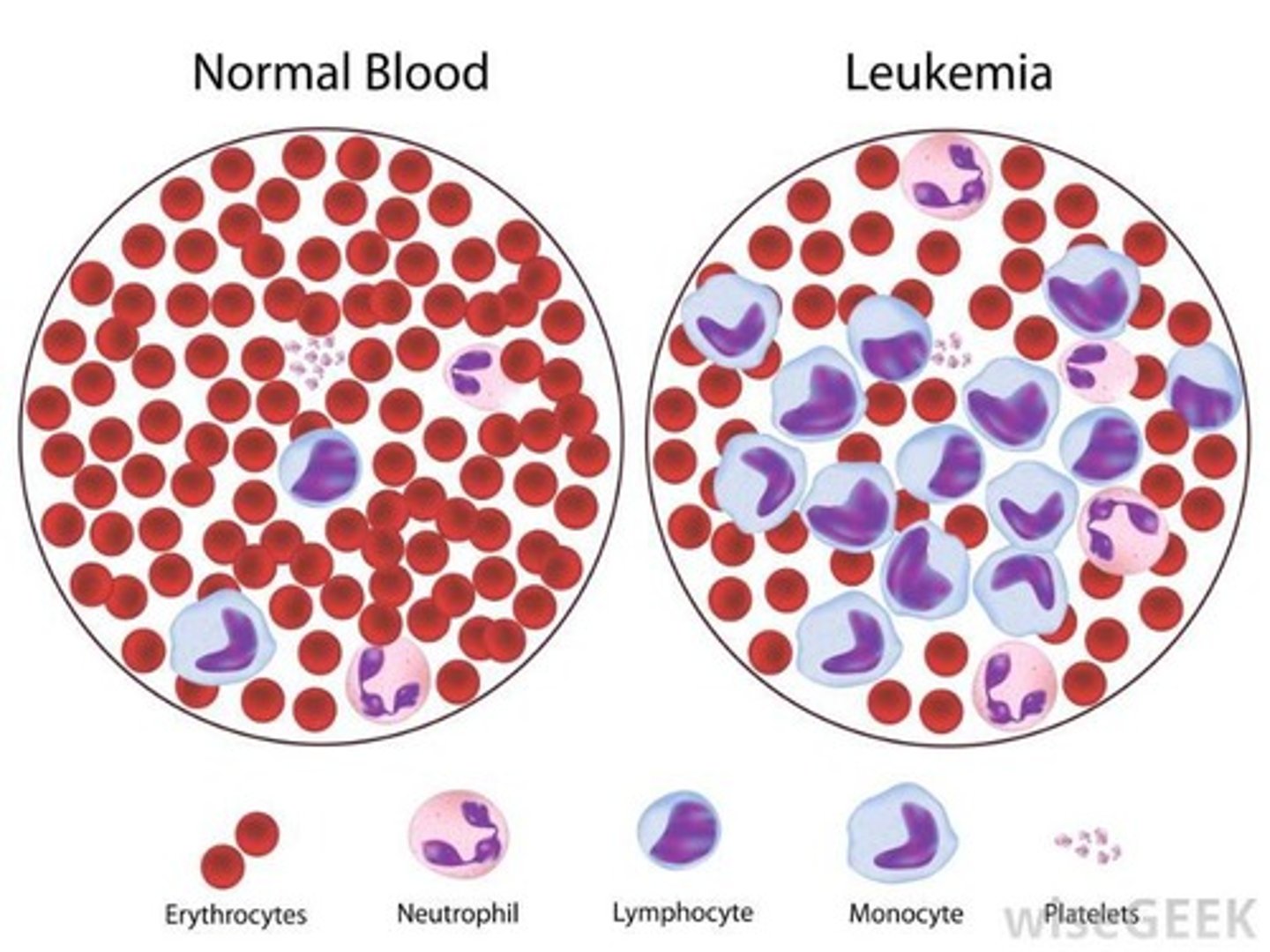
What is leukemia
many abnormal & immature leukocytes due to cancer of bone marrow
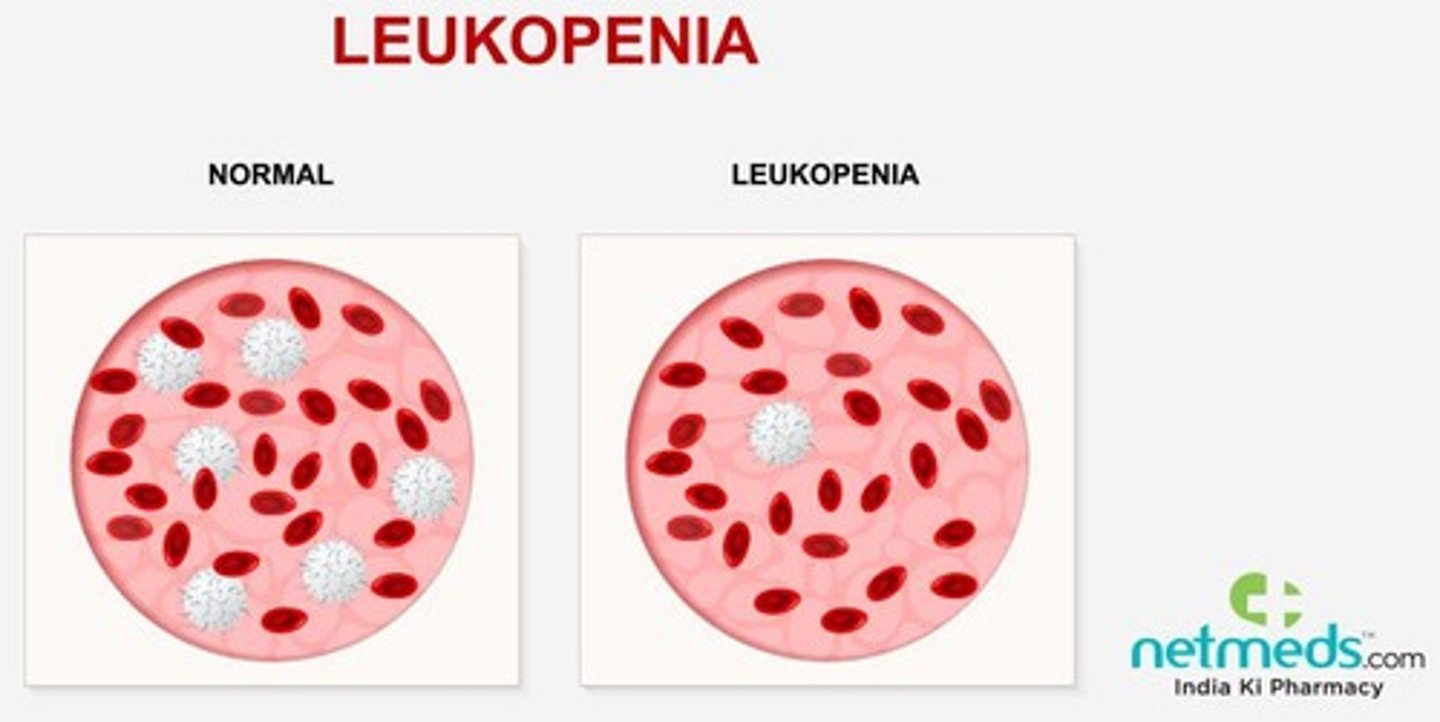
What is Leukopenia
a decrease in white blood cells die to radiation/chemotherapy; an increase in glucocorticoids happens alongside it
What are some kinds of granular leukocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
What are some kinds of agranular leukocytes
monocytes and lymphocytes
What role do lymphocytes have
specific immunity
What role do monocytes have
phagocytosis
What role do basophils have
histamine/ inflammatory response, releases heparin
What role do Eosinophils have
allergy response & parasites
What role do Neutrophils have
they are 1st responders
What are the characteristics of platelets
Smallest formed element, fragments of large cells called megakaryocytic, Lack nuclei, Very short-lived (5−9 days), Clot blood with several other chemicals and fibrinogen,Release serotonin that stimulates vasoconstriction
How many platelets are in blood
approximately 130,000 - 400,000/mm3 blood
What is Hemopoiesis
Process of blood cell formation
What are hematopoietic stem cells
embryonic cells that give rise to all blood cells
Where does hematopoiesis happen
Process occurs in myeloid tissue (red bone marrow) and lymphoid tissue (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, thymus); As cells differentiate, they develop membrane receptors for chemical signals
What is erythropoiesis
Formation of red blood cells
Red bone marrow produces about ___RBCs/sec
2.5 million
Regulation of erythropoiesis is stimulated by
erythropoietin (EPO) from the kidneys that respond to low blood O2 levels; Process takes about 3-4 days; Most iron is recycled from old RBCs, the rest comes from the diet Intestinal iron secreted into blood through ferroprotein channels
All iron travels in blood bound to
transferrin
A Major regulator of iron homeostasis is the hormone
hepcidin which removes ferroprotein channels to promote cellular storage of iron and lowers plasma iron levels
What is leukopoiesis
Formation of white blood cells
What are cytokines
signaling molecules used for intercellular communication
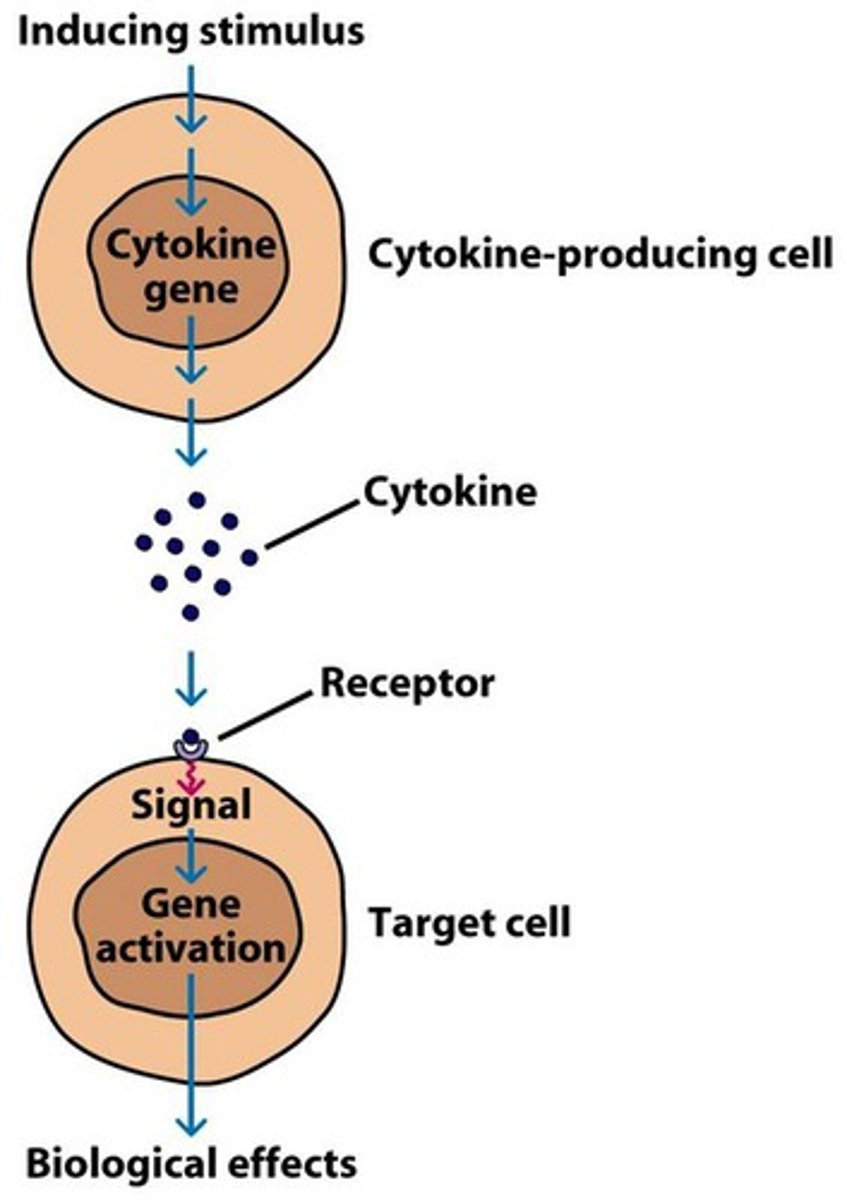
Cytokines include
Multipotent growth factor-1; Interleukin-1; Interleukin-3; Granulocyte colony stimulating factor, and Granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor
Several types of Cytokines stimulate the production of the different
WBC subtypes.
What are antigens
A substance that triggers an immune response.
What are antibodies
A protein produced by the immune system to recognize and neutralize specific antigens.
What is Thrombopoiesis
the production of platelets (thrombocytes) in the bone marrow from hematopoietic stem cells
What does Thrombopoietin (cytokine from liver and kidneys) do
stimulates growth of megakaryocytes
To make a clot intrinsically
Factor XII leads to Factor X>leads phospholipids, calcium ions, and Factor Va, to forms a complex>his complex converts prothrombin into thrombin>Thrombin then converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin, which forms a mesh to create a stable blood clot
To make a clot extrinsically
Factor VII leads to Factor X> leads phospholipids, calcium ions, and Factor Va, to forms a complex>his complex converts prothrombin into thrombin>Thrombin then converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin, which forms a mesh to create a stable blood clot
What is a Tissue Plasminogen Activator
clot buster!; must be given within 3 hours of CVA onset; activates plasminogen to destroy the clot
Megakaryocytes are large, multinucleated cells that secrete ("bud off")
cell fragments = platelets
What is Hemostasis
cessation of bleeding when a blood vessel is damaged
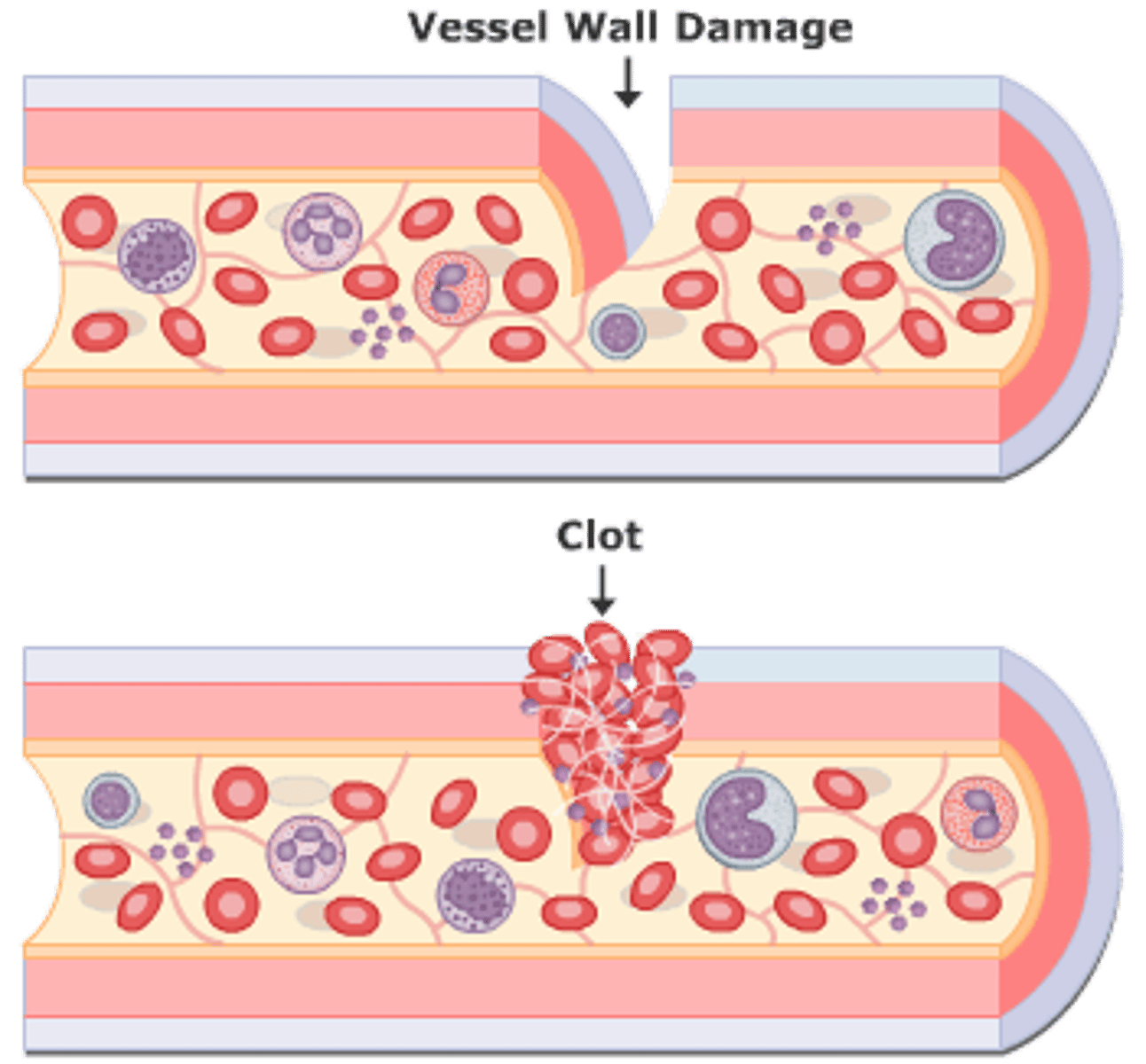
Damage to blood vessels exposes collagen fibers to blood, producing what
Vasoconstriction, Formation of platelet plug, Formation of fibrin protein web
Intact endothelium secretes prostacyclin (PG12 a prostaglandin) and nitric oxide (NO), which
Vasodilate, and Inhibit platelet aggregation
What does CD39 do
Breaks down ADP into AMP and Pi to inhibit platelet aggregation further
Damaged endothelium exposes collagen leading to
Platelets bind to collagen. Von Willebrand factor (protein produced by endothelial cells) holds them there. Platelets recruit more platelets and form a platelet plug by secreting: (Platelet release reaction); Activated platelets also activate plasma clotting factors
Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin via one of two pathways
instrinsic and extrinsic
How is Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin intrinsically
Activated by exposure to collagen. Factor XII activates a cascade of other blood factors.
How is Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin extrinsically (most direct pathway)
Initiated by tissue thromboplastin (factor III). Next, calcium and phospholipids (from the platelets) convert prothrombin to the active enzyme thrombin, which converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
Vitamin K is needed by the liver to make
several of the required clotting factors; without it, it could lead towards a tendency of excessive bleeding.
What do plasmalogens do
break down blood clots
What is the hematocrit
percentage of red blood cells in whole blood; males typically have more RBC in comparison to women
What is anemia, why does iron deficiency cause anemia
abnormal low hemoglobin or low hematocrit; an iron deficiency impairs the body’s ability to produce red blood cells
What is aplastic anemia
damage to bone marrow
What is Hemolytic Anemia
RBC destruction increases
What is sickle cell anemia
an inherited blood disorder that causes red blood cells to become abnormally shaped (sickle-shaped)
What does Factor XII do
activates kallikrein
What does kallikrein do
activates plasminogen activators like TPA
What do Plasminogen activating factors do
it activates plasminogen into plasmin
What does Thrombin do
it activates fibrinogen into fibrin
What does Plasmin do
dissolves the blood clot
how does the dissolution of clots happen
Factor XII activates Kallikrein > plasminogen > plasmin digests fibrin
Clotting can be prevented with certain drugs including
calcium chelators, heparin, coumadin, and aspirin
What does heparin do
blocks thrombin
What does Coumadin do
inhibit vitamin K
What does Aspirin do
COX Enzyme, inhibits prostaglandin production (TXA2)
What is INR
the relative time it takes for blood to clot
What are the contents of the heart
Four chambers; two upper (atria), two lower (ventricles)
The right atrium receives
deoxygenated blood from the body
The left atrium receives
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
The right ventricle pumps
deoxygenated blood to the lungs
The left ventricle pumps
oxygenated blood to the body
Fibrous skeleton Separates atria from
ventricles.The atria therefore work as one unit, while the ventricles work as a separate unit.
Pulmonary Circulations happen between the
heart and lungs
Pathway of Pulmonary Circulations
Blood pumps to lungs via pulmonary arteries; Blood returns to heart via pulmonary veins.
Systemic Circulations happen between the
heart and body tissues
Pathway of Systemic Circulations
Blood pumps to body tissues via aorta; Blood returns to heart via superior and inferior venae cavae.
Atrioventricular (AV) valves are located between
the atria and the ventricles including the bicuspid and tricuspid valves