III: Bacterial Identification
1/247
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
248 Terms
S - -Size
S - Shape
A - Arrangement
M - Motility
S - Staining characs
Bacteria can be identified based on their morphology and appearance such a s
STAINING
the process of artificially coloring the organism with dye/ stains
STAINING
Its purpose is to observe and appreciate the appearance of bacteria
STAINING
Its purpose is to differentiate one organism from the other
STAINING
Its purpose is to reveal the chemical nature of bacteria
Simple / Direct
Differential
Indirect / Relief / Negative
Special Staining
Staining Techniques
Simple/ Direct
one dye; all organisms have the same color
Differential
two dyes; (GS and AFS)
Indirect/Relief/ Negative
Capsule
a. India Ink Test/ Borris Method
b. Nigrosin Method
2 types of Indirect/Relief/ Negative
Special staining
to demonstrate special features of the cell
Muir
Anthony's
tyle
Hiss
Welch's Grins
Special Staining
Capsule
Dorner's Schaeffer-Fulton
Wirtz and Conklin
Heat and Acetic Acid Method
Special Staining
Spores
Gray's
Fisher and Conn
Loeffler's
Leifson
Caesares
Gil
Van Ermenger
Special Staining
Flagella
Feulgen
Acridine orange
Special Staining
Nucleic Acid
Wayson
Special Staining
Polar Bodies
Levaditi
Fontana
Warthin- Starry
Special Staining
Spirochetes
Gimenez
Macchiavelo
Giemsa
Special Staining
Rickettsia
Neisser
Albert's
Ljubinsky
Lindergan
Ponder
Special Staining
Metachromatic Granules
Hans Christian Gram
GRAM STAINING is Developed by Danish bacteriologist - in 1884
teichoic acid
Gram staining Stains the - present on the cell walls of gram-positive
T
Gram staining is Not applicable to organisms that exist almost exclusively within host cells (Chlamydia) those that lack cell walls, and those of insufficient dimension to be resolved by light microscopy (Spirochetes) (t/f)
N - Neisseria
V - Veilonella
M - Moraxella
Al cocci are gram (+) except
M - Mycobacteria
C- Corynebacteria
C - Clostridia
B - Bacillus
E - Erysiphilotrix
L - Lactobacillus
L - Listeria
N - Nocardia
A - Actinomyces
Al bacilli are gram (-) except
gram -
All spiral organisms are reported as
gram +
Yeasts are reported as
Chlamydia/ Rickettsia
Cannot be gram-stained
- intracellular
Mycoplasma/ Ureaplasma
Cannot be gram-stained
- no cell wall
Spirochetes
Cannot be gram-stained
-- can't be resolved by LM
• Legionella & Spirochete
Cannot be gram-stained
-- silver impregnation technique is most useful
I. Living state (unstained)
I. Fixed State (Stained)
Methods ofStudying Microorganisms
1. Wet mount Preparation Specimen mixed with NSS
2. Hanging drop preparation-
be uses concave slide; can used to demonstrate the motility of the organism
Steps in Living state (unstained)
1. Bacterial Smear Preparation
2. Fixation- Using heat or 70- 95 % alcohol; 95% methanol
3.Staining
Steps in Fixed state (stained)
heat or 70- 95 % alcohol; 95% methanol
Fixation is done using
Hanging drop preparation
uses concave slide; can used to demonstrate the motility of the organism
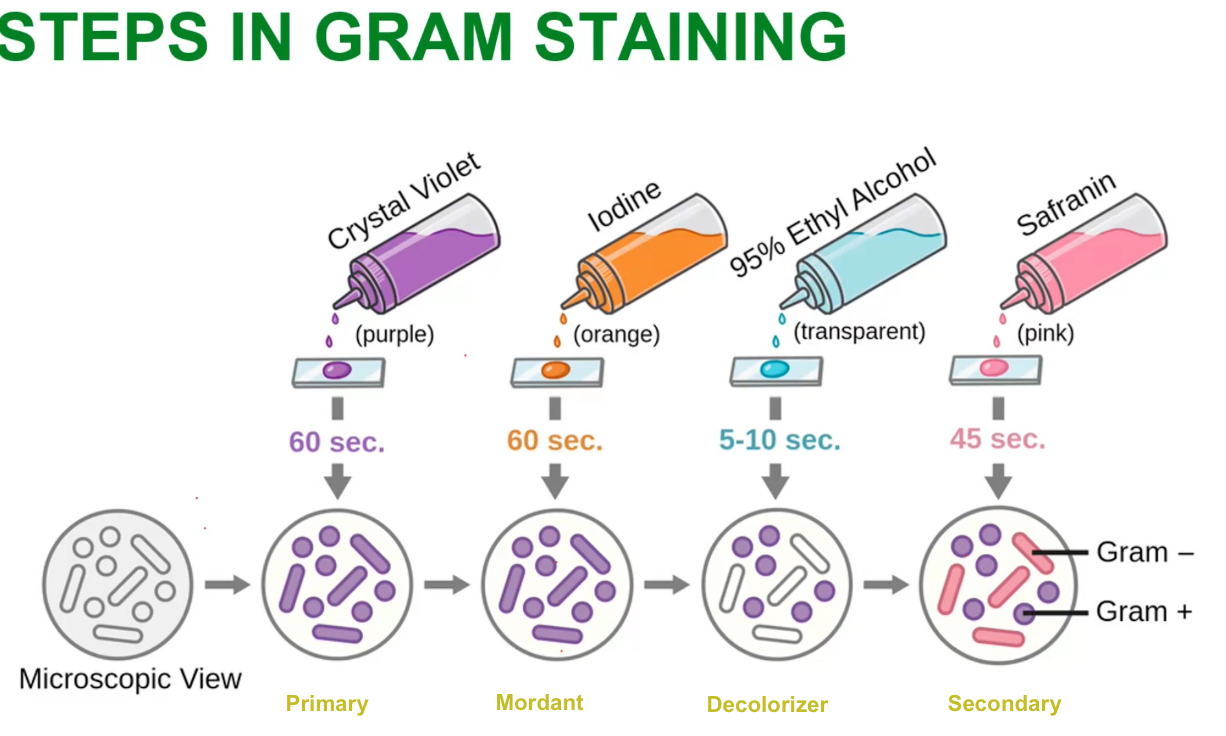
Steps in Gram Staining
G (+)becomesG (-)
ERRORS IN GRAM STAINING
Identify if G (+)becomesG (-) or G(-) becomes G(+)
Over-decolorization
G (+)becomesG (-)
ERRORS IN GRAM STAINING
Identify if G (+)becomesG (-) or G(-) becomes G(+)
Old, dying
G (+)becomesG (-)
ERRORS IN GRAM STAINING
Identify if G (+)becomesG (-) or G(-) becomes G(+)
Use of acidic iodine as a mordant
G (+)becomesG (-)
ERRORS IN GRAM STAINING
Identify if G (+)becomesG (-) or G(-) becomes G(+)
Penicillin (loss of cell wall integrity)
G (+)becomesG (-)
ERRORS IN GRAM STAINING
Identify if G (+)becomesG (-) or G(-) becomes G(+)
lodine/ mordant was omitted
G(-) becomes G(+)
ERRORS IN GRAM STAINING
Identify if G (+)becomesG (-) or G(-) becomes G(+)
under-decolorization
G(-) becomes G(+)
ERRORS IN GRAM STAINING
Identify if G (+)becomesG (-) or G(-) becomes G(+)
Thick smear
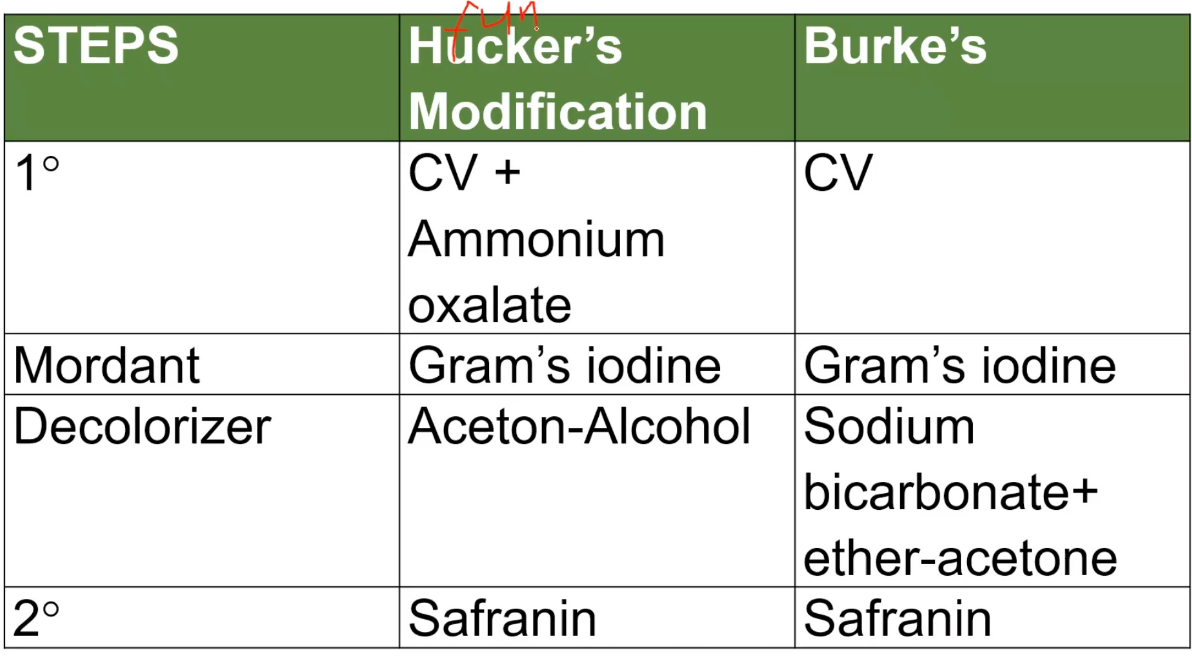
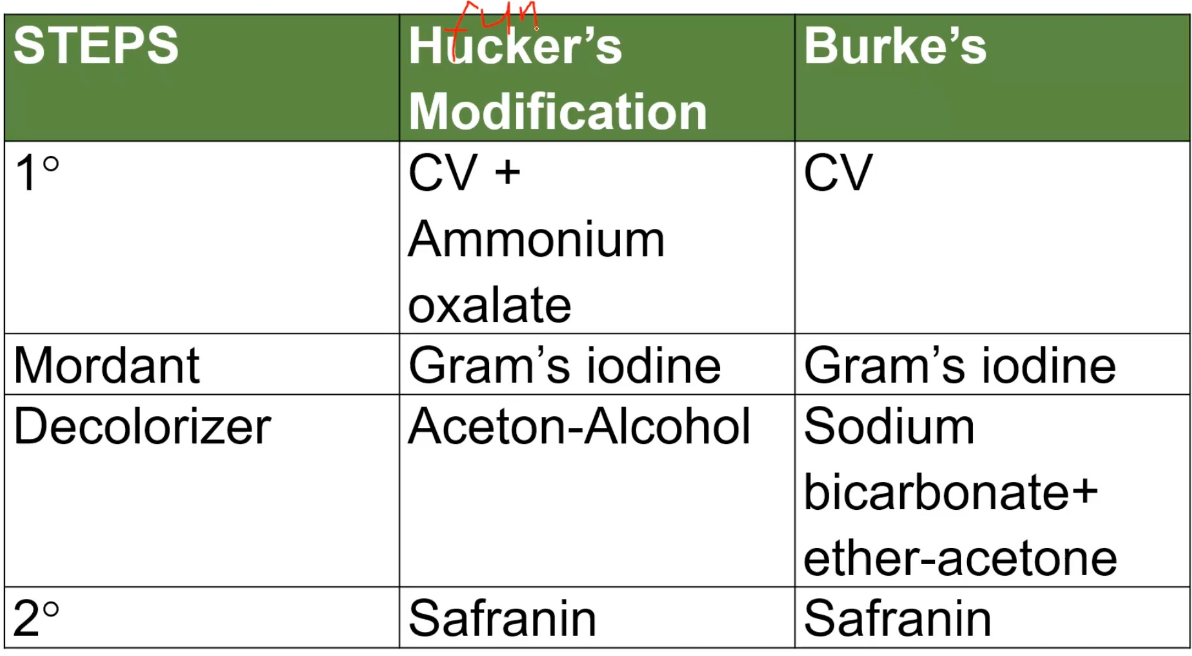
VAIAS
MODIFICATIONS OF GRAM STAINING
Hucker’s Modification Steps
VISES
MODIFICATIONS OF GRAM STAINING
Burke’s Modification Steps
Burke’s Modification
stain that shows the metachromatic granules
G (+)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Cell wall
THICK cell wall of composed peptidoglycan; TEICHOIC ACIDS may be present
G (-)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Cell wall
The outer membrane composed of lipids, protein, lipopolysaccharides, and inner thin peptidoglycan
G (+)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Shape
Spherical, rods, or filaments
G (-)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Shape
Spherical, ovals, straight, curve, rods, helical etc
G (+)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Teichoic Acid
PRESENT
G (-)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Teichoic Acid
Absent
G (+)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Endospores
PRESENT in some groups
G (-)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Endospores
Absent
G (+)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Periplasmic Space
ABSENT
G (-)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Periplasmic Space
Present
G (+)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Flagellar structure
2 rings in basal body
G (-)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Flagellar structure
4 rings in basal body
G (+)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Resistance to Physical Disruption
HIGH
G (-)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Resistance to Physical Disruption
LOW
G (+)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Inhibition by Basic Dyes
HIGH
G (-)
Identify if G (+) or G (-)
Inhibition by Basic Dyes
LOW
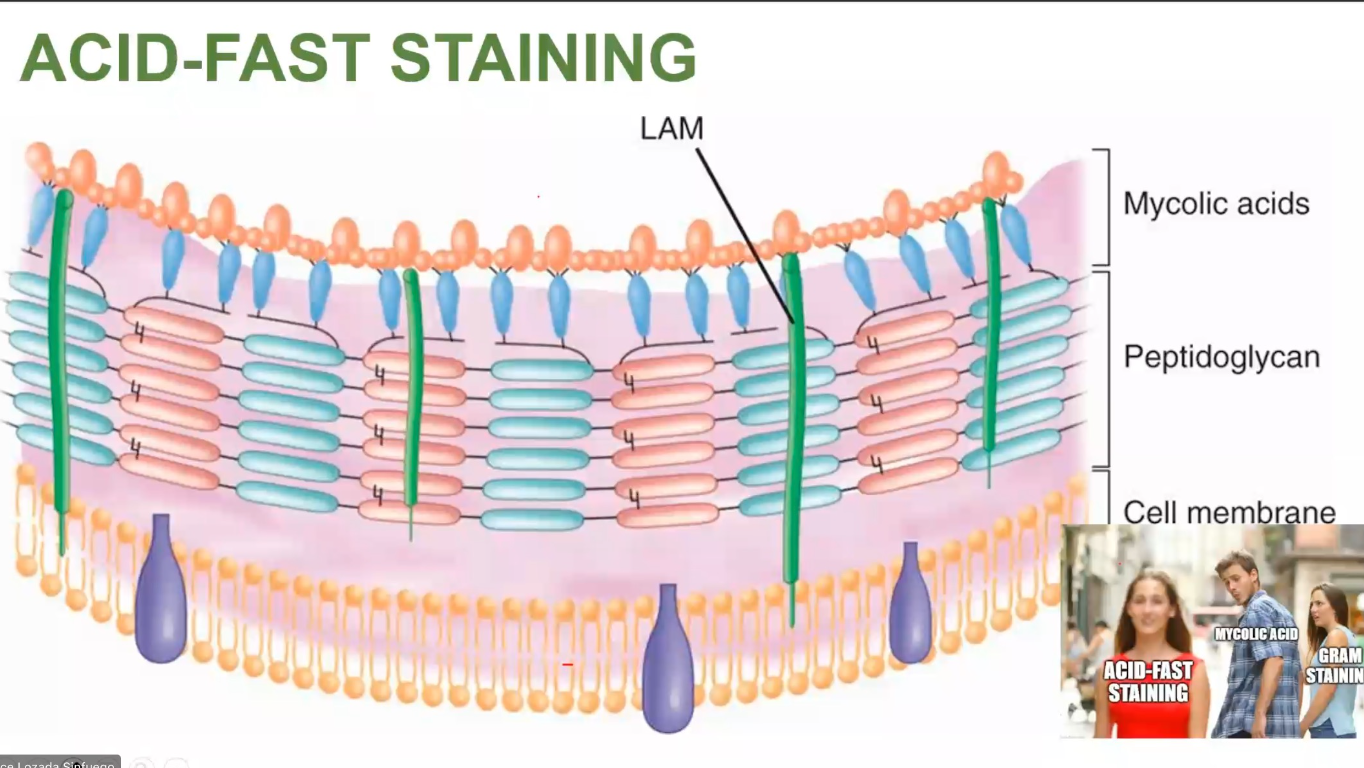
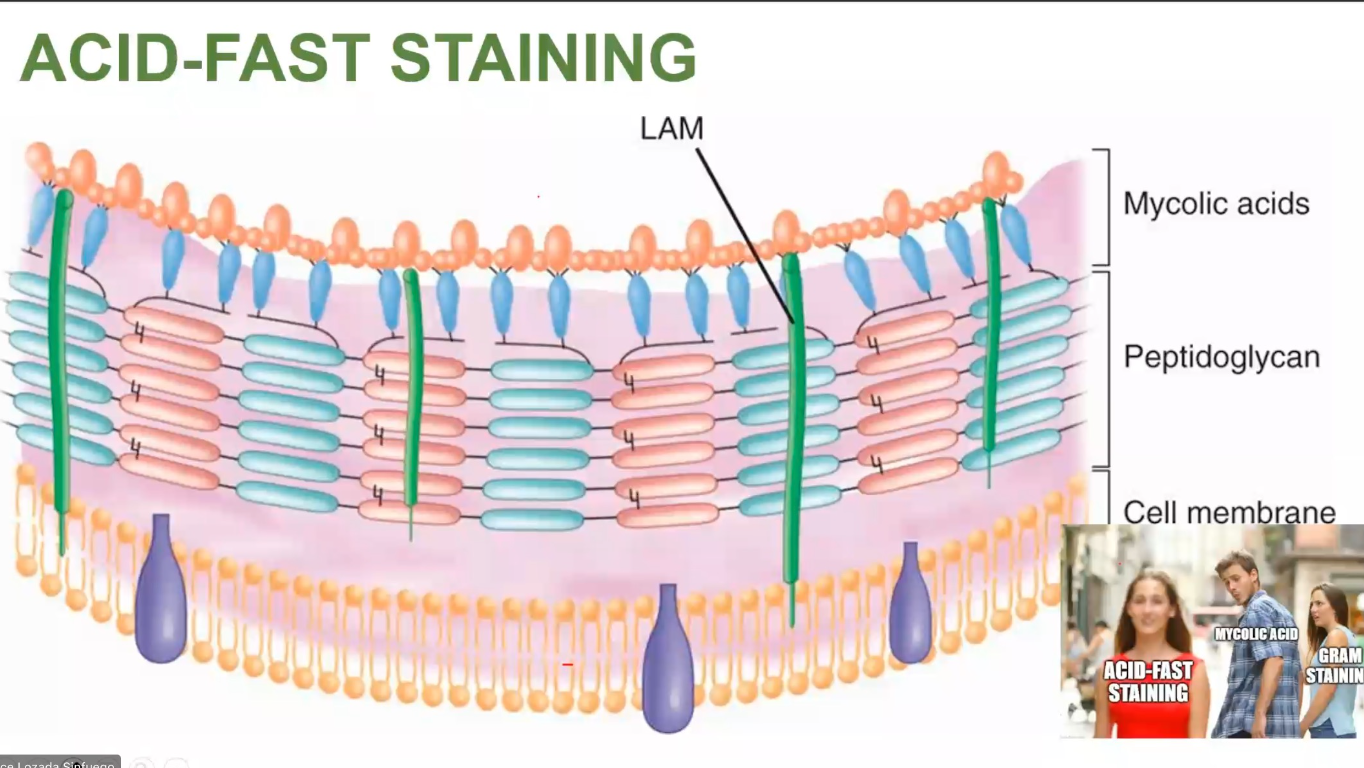
mycolic acid
ACID-FAST STAINING
Stains the - in the cell wall of bacteria
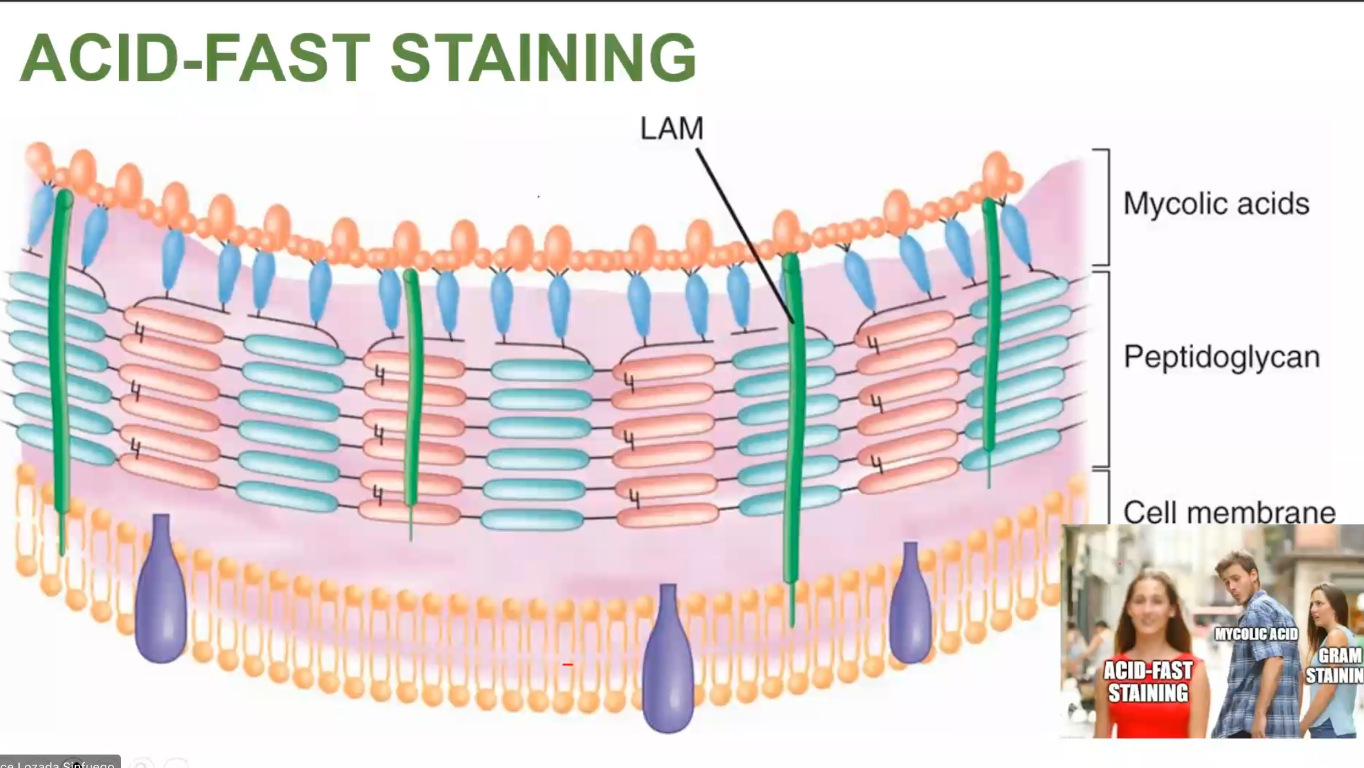
F
ACID-FAST STAINING
Organisms with Mycolic acid/ hydroxyl methoxy acid in the cell wall are easy to gram-stain (t/f)
Mycobacteria
Nocardia (partially acid-fast)
Cryptosporidium
Cyclospora
ACID-FAST STAINING
Acid-fast organism:
Steaming
Addition of wetting agent (tergitol) prior to the stain solution
Increasing concentration of phenol (accentuator) and basic fuchsin
Prolonging contact of stain with the material
Ways to Facilitate Acid Fast Organisms

ACID-FAST STAINING
Ziehl-Neelsen Stain Steps
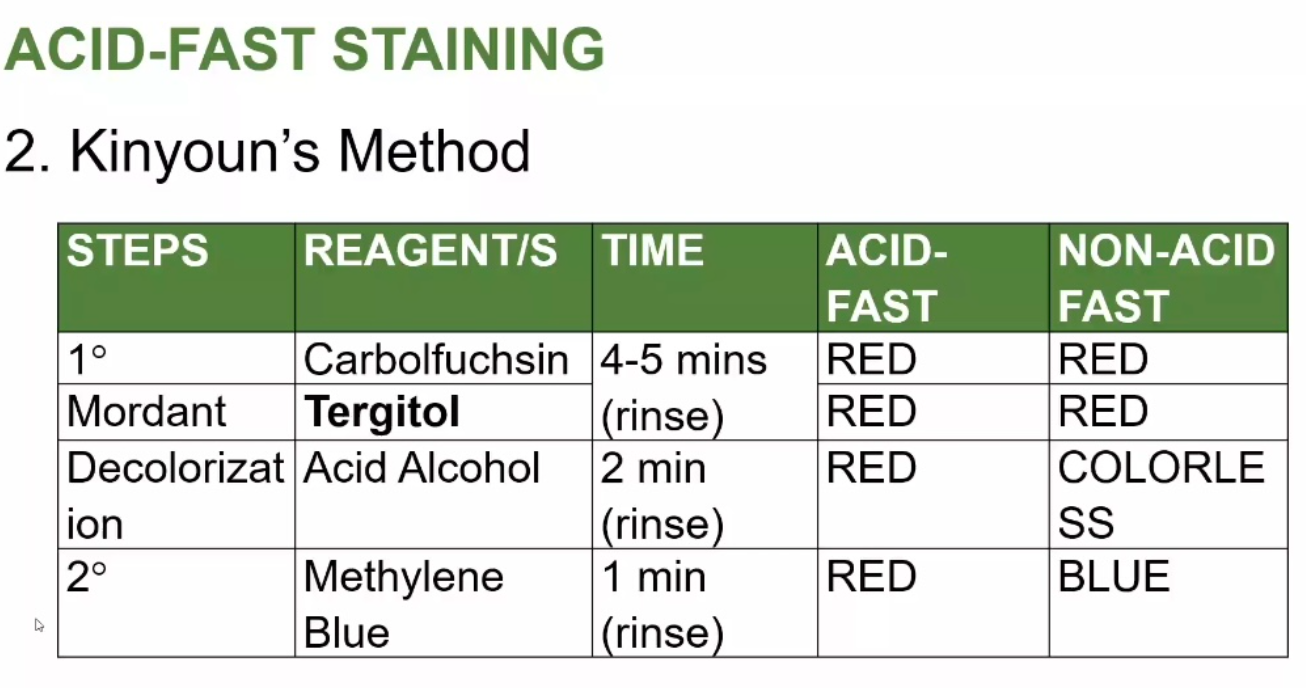
ACID-FAST STAINING
Kinyoun's Method
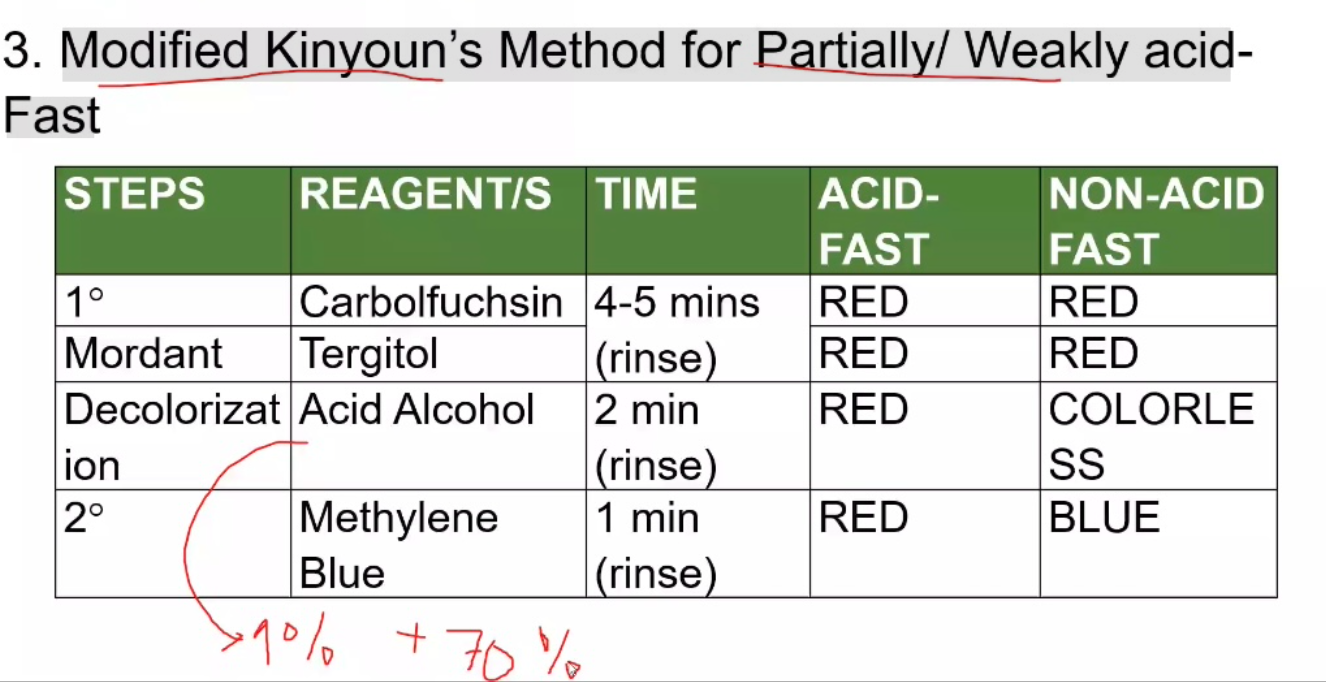
*1% H2SO4, 70% Ethanol
ACID-FAST STAINING
Modified Kinyoun's Method for Partially/ Weakly acid- Fast
Pappenheim's Method
Other Modifications of ACID-FAST STAINING
used to differentiate Mycobacterium smegmantis (neg) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (pos)
Fite-Faracos/Auramine-Rhodamine
Other Modifications of ACID-FAST STAINING
used to differentiate M. leprae (red-pos) from M. tuberculosis (blue- neg)
Culture
microorganisms in specimens can be cultivate and grown in artificial media
Culture medium
contains nutritional requirements needed for bacterial growth
1. Pure Culture
2. Mixed Culture
3. Stock Culture
TYPES OF CULTURE
Pure Culture
one species
Mixed Culture
- more than one species
Stock Culture
- for ATCC (known stain bacteria)
1 Weigh
2. Dissolve in deionized or distilled water
3. Sterilize
4. Dispense
WDSD
STEPS IN PREPARING CULTURE MEDIA
Plated (Petri Dish)
1. Weigh
2. Dissolve in deionized or distilled water
3. Dispense
4 . Sterilize
WDDS
STEPS IN PREPARING CULTURE MEDIA
Tube (Test Tube)
A. According to the Physical State
Liquid
Semi-solid
Solid
Biphasic
B. According to Composition (SNT)
Synthetic/ Defined
Non-synthetic/ Complex
Tx cells
C. According to Purpose (DTESSS)
Simple /General Isolation
Enriched
Enrichment
Selective
Differential
Transport
TYPES OF CULTURE MEDIA
0 % or none
Amount of solidifying agent of Liquid
0.5-1%
Amount of solidifying agent of Semi-solid
2 - 3%
Amount of solidifying agent of Solid
Solid & liquid
Amount of solidifying agent of Biphasic
Liquid
Identify if what type of culture media according to physical state is the examples
Nutrient Broth
Brain Heart Infusion
Alkaline Peptone Water
Thioglycolate
Semi-solid
Identify if what type of culture media according to physical state is the examples
S I M
Gelatin Media
Solid
Identify if what type of culture media according to physical state is the examples
Liquifiable:
Liquid-> Solid-> Liquid
Ex. SSA, BAP, MAC
Non-liquifiable:
Will no longer liquefy when heated again
Ex. Rice medium
Bipahasic
Identify if what type of culture media according to physical state is the examples
HBT- Human Blood Bilayer Tween (G. vaginalis)
Castanedas- Brucella
Synthetic/ Defined
-All components are KNOWN to the user
-for research
BG-II Cyanobacteria
eg Synthetic/ Defined
Non-synthetic / Complex
-composed of some UNKNOWN
-substance (peptone, meat broth)
-very useful for isolation of bacteria
Nutrient Broth
TSB
MacConkey Agar
eg Non-synthetic / Complex
Tx cells
-uses living cell
- we look for CYTOPATHIC EFFECT
HeLA cells
A549
McCoy Cells
Vero Cells
Hep2 Cells
eg Tx cells
Simple /General Isolation
It is known as supportive media, supports the growth of most non-fastidious bacteria
Simple /General Isolation
No growth advantage is given to any group of bacteria
Nutrient agar
trypticase soy agar
nutrient broth
eg Simple /General Isolation
Enriched
Used for growing FASTIDIOUS ORGANISMS
Enriched
For general isolation with added nutrients like blood, serum, peptone, and vitamins
BAP
CAP
eg of Enriched