Lab 1 ULM A&P
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
What is a nontropic Hormone?
A hormone that have a direct effect on their target tissue.
What is a tropic hormone?
A hormone that causes the release of another hormone.
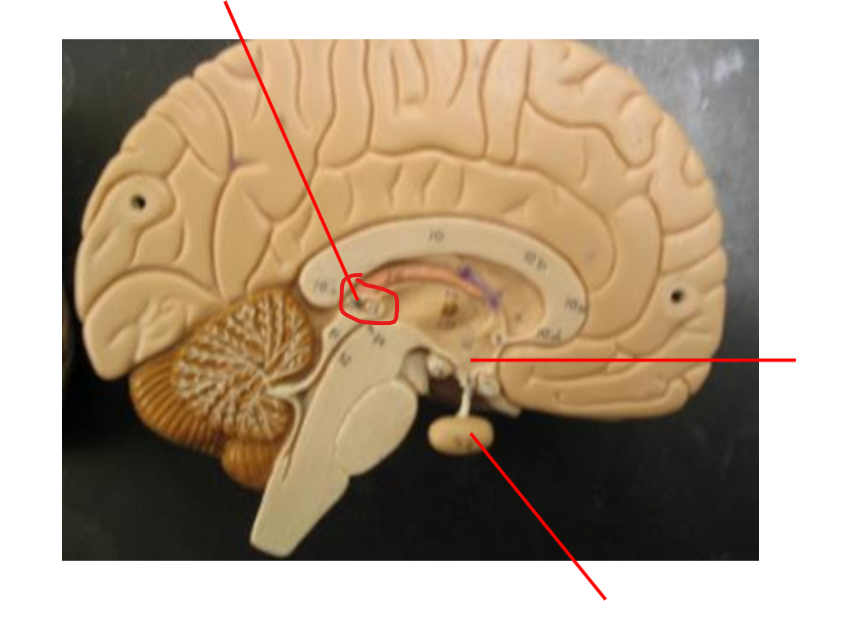
Pineal Gland
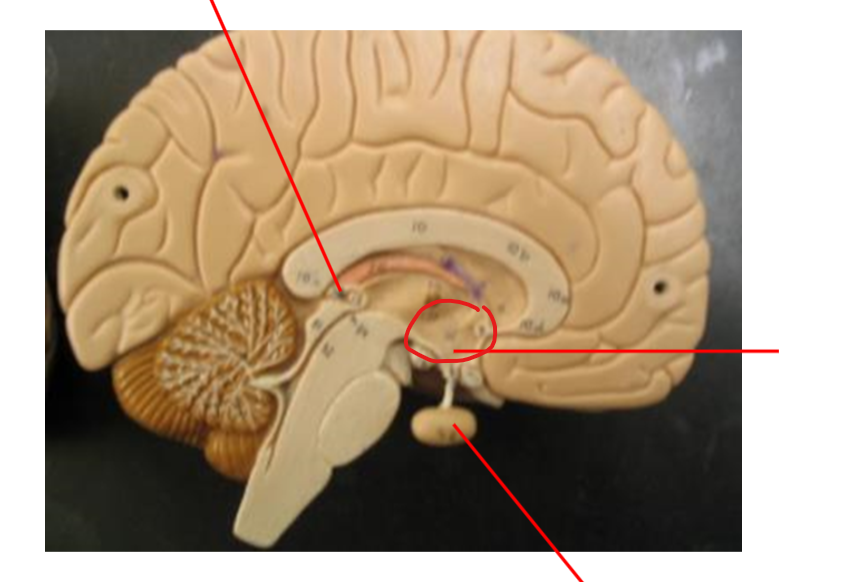
Hypothalamus
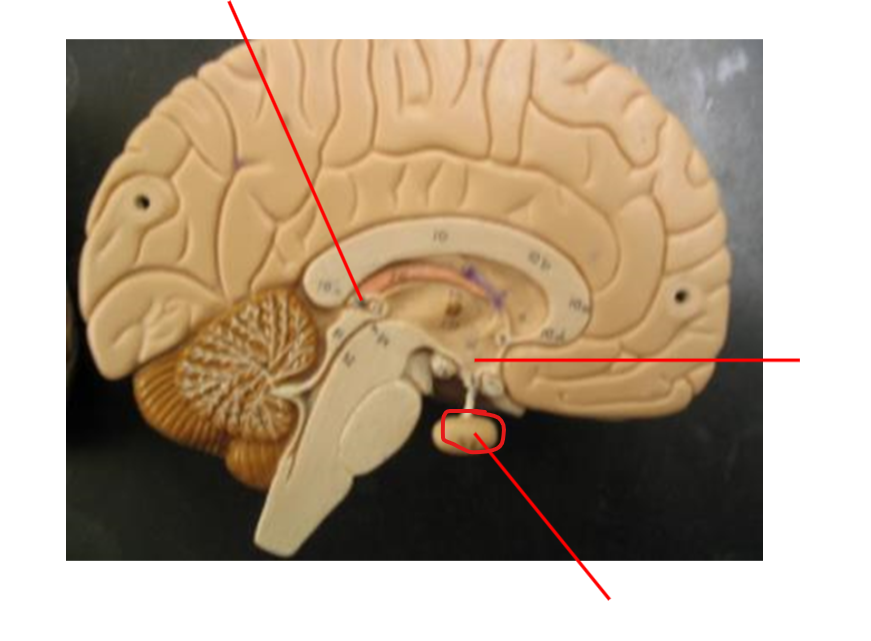
Pituitary gland
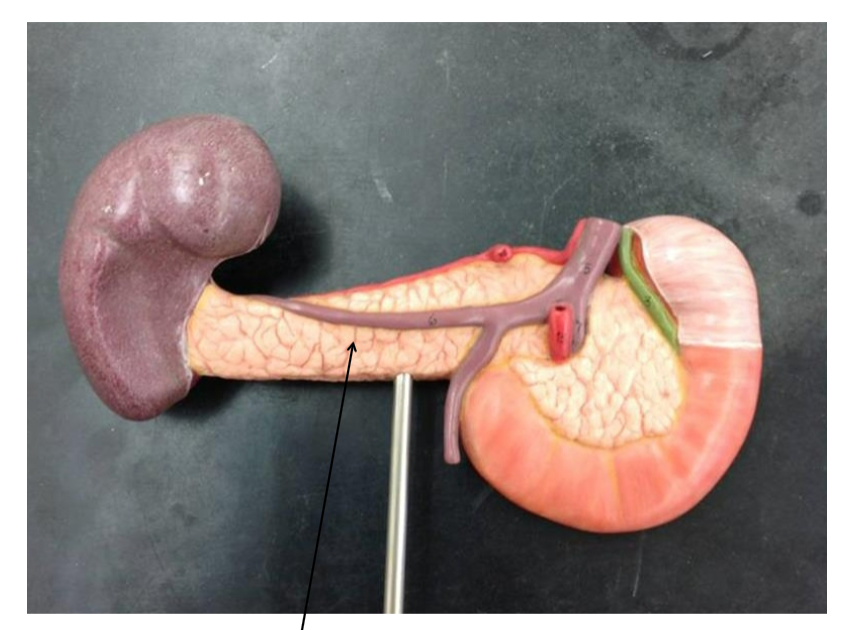
Pancreas
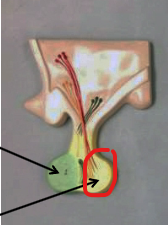
Posterior lobe of pituitary gland (neurohypophysis)
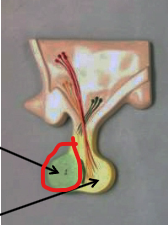
Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)

Thyroid Gland
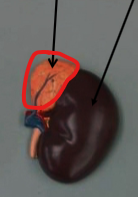
Adrenal Gland
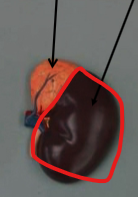
Kidney
Testes

Pancreas

Parathyroid
Ovaries
Thyroid
Parathyroid
What is the general function of Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)?
Stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin (PRL)
What is the general function Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
What is the general function Gonaciotropin-releasing hormone
Stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
What is the general function of Growth hormone-releasing hormone?
Stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete growth hormone (GH)
What is the general function of Somatostatin (Growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GIHIH))
Inhibits anterior pituitary secretion of growth hormone (GH) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
What is the general function of Prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH)
Inhibits anterior pituitary secretion of prolactin (PRL)
What is the general function of Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Water retention by kidney to help prevent dehydration
Oxytocin (OT)
Labor contractions; milk ejection in lactating mothers.
What is the general function of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Thyroid gland growth and secretion of thyroid hormone.
What is the general function of Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Adrenal cortex growth and secretion of glucocorticoids.
What is the general function of Prolactin (PRL)
Synthesis of milk in females and increases sensitivity of LH in males
What is the general function of Growth Hormone (GH)
Mitosis differentiation, and growth of tissue.
What is the general function of Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Follicle growth and secretion of estrogen in ovaries and sperm production in testes
What is the general function of Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Ovulation and progestogen production in the ovaries and testosterone production.
Where are releasing and inhibiting hormones located and where is there target tissue?
The hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland.
Where is Antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin made and stored?
The antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin are made in the hypothalamus but stored and released in the posterior pituitary gland.
Where is thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stored?
Anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)
Where is adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) stored?
Anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)
Where is Prolactin stored (PRL)?
Anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)
Where is Growth Hormone (GH) made?
Anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)
Where is Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stored?
Anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)
Where is Luteinizing Hormone (LH) stored?
Anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis)
What does melatonin do?
Plays role in sleep/wake cycle
Where is melatonin stored?
Pineal gland
What does thymosin do?
Stimulates the maturation of T-cells.
Where is thymosin stored?
Thymus Gland
What does T3 and T4 do?
Regulate metabolic rate, thermoregulation, and promote growth and development.
Where is T3 and T4 produced?
Follicular cells of thyroid gland.
What does calcitonin do?
Decrease blood calcium levels
Where is calcitonin produced?
Parafollicular cells in the thyroid gland.
What does parathyroid hormone (PTH) do?
Increases blood calcium levels.
Where is parathyroid hormone (PTH) produced?
Parathyroid Gland
Where is zona glomerulosa, fasciculata, and reticularis located?
Adrenal Gland (adrenal cortex)
What does Zona glomerulosa produce?
Mineralocorticoids
What does Zona fasciculata produce?
Cortisol (glucocorticoids)
What does the Zona reticularis produce?
Androgen (Testosterone/Estrogen)
Where is Epinephrine and Norepinephrine produced?
Adrenal Medulla of the Adrenal Gland
Where is alpha, beta, and delta cells located?
Pancreatic Islet
What do Alpha Cells produce?
Glucagon
What do Beta Cells produce?
Insulin
What do Delta cells produce?
Somatostatin
What does somatostatin do?
Regulates the release of glucagon and insulin.
Where is estrogen and progesterone produced?
Ovaries
What hormone disorder is associated with the hypersecretion of glucocorticoids (cortisol)?
Cushing’s Syndrome
What Hormone disorder is associated with hyposecretion of Glucocorticoids (Cortisol)
Addison’s Disease
What Hormone Disorder is associated with the hypersecretion of Growth Hormone during as a kid?
Gigantism
What Hormone Disorder is associated with the hypersecretion of growth hormone as an adult?
Acromegaly
What hormone disorder is associated with the hyposecretion of growth hormone?
Dwarfism
What hormone disorder is associated with hypersecretion of thyroid hormone?
Graves’ Disease
What hormone disease is associated with the hyposecretion of thyroid hormone as a child?
Cretinism
What hormone disorder is associated with the hyposecretion of thyroid hormone as an adult?
Myxedema
What hormone disorder is associated with the hypersecretions of parathyroid hormone?
Hypercalcemia
What hormone disorder is associated with the hyposecretion of parathyroid hormone?
hypocalcemia
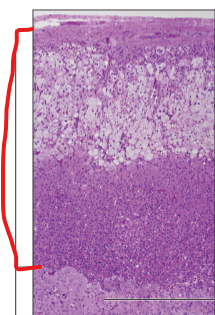
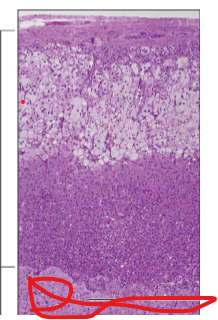
Adrenal Cortex
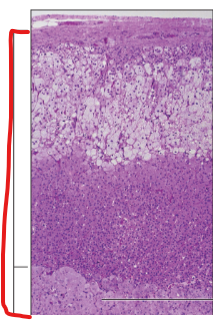
Adrenal Gland
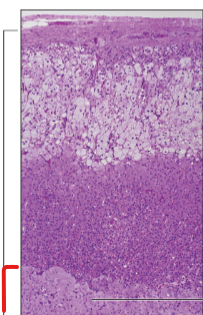
Adrenal Medulla
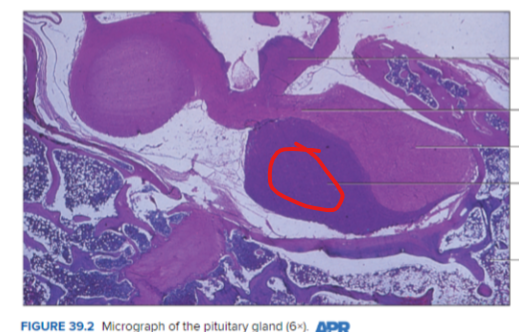
Anterior Lobe of pituitary gland (Adenohypophysis)
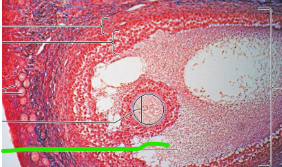
Antrum
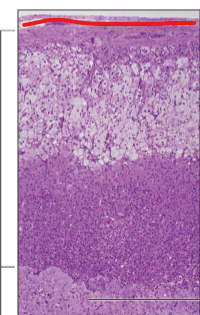
Capsule
Chromaffin Cells
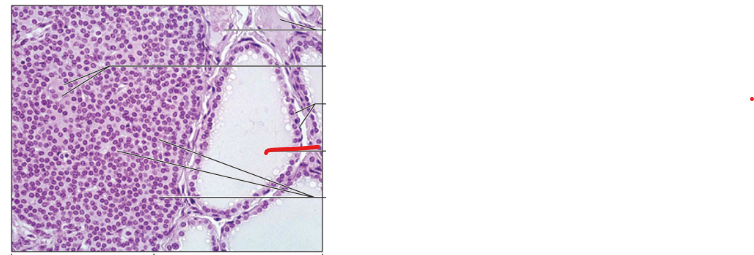
Colloid
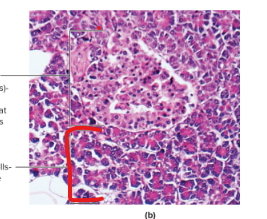
Exocrine Cells
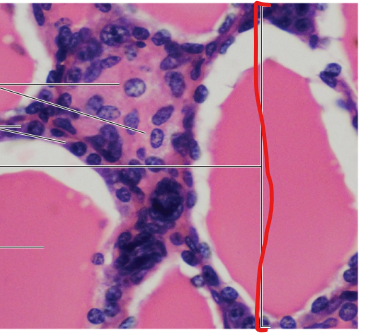
Follicle
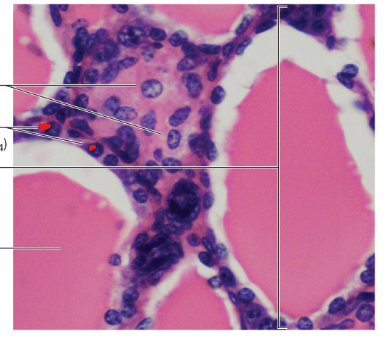
Follicular Cells
Granulosa Cells
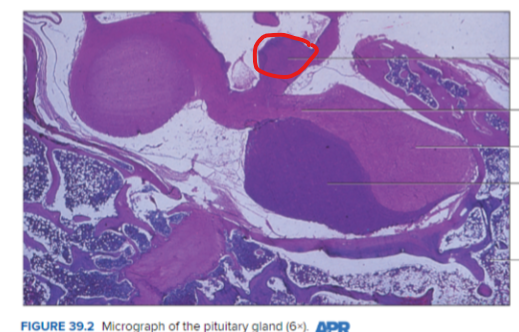
Hypothalamus
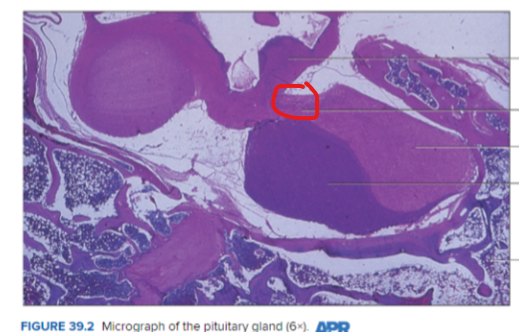
Infundibulum
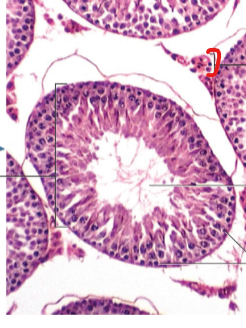
Intestinal Cells
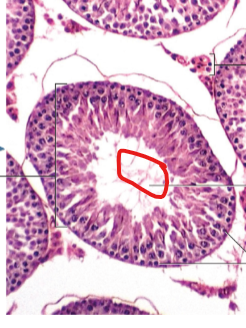
Lumen
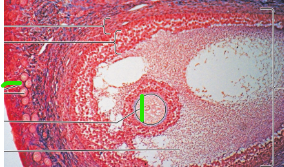
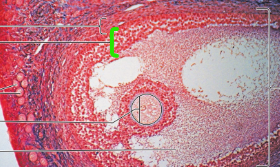
Oocyte
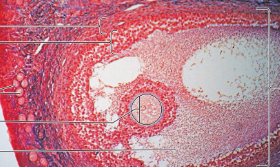
Ovaries
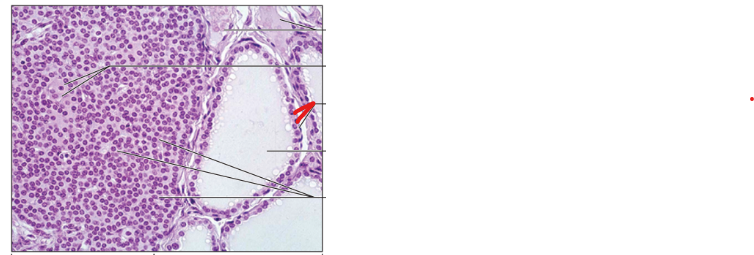
Follicular Cells
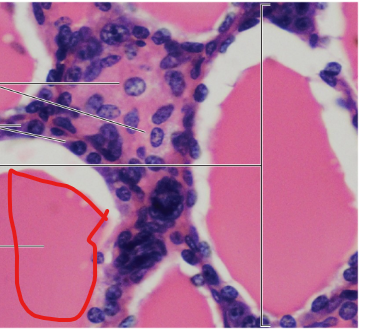
Colloid
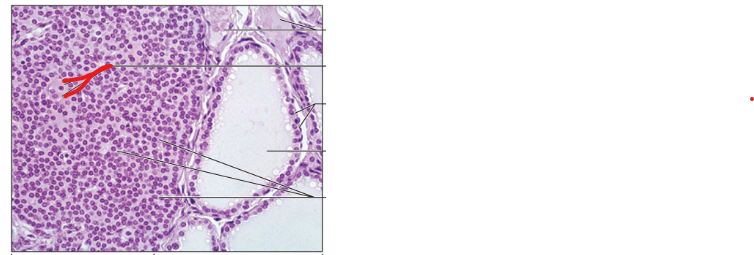
Oxyphil Cells
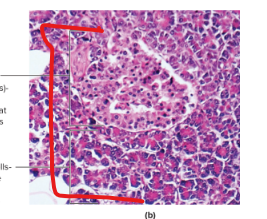
Pancreas
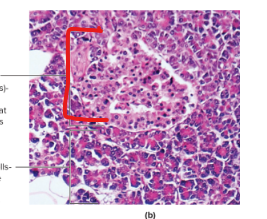
Pancreatic Islet
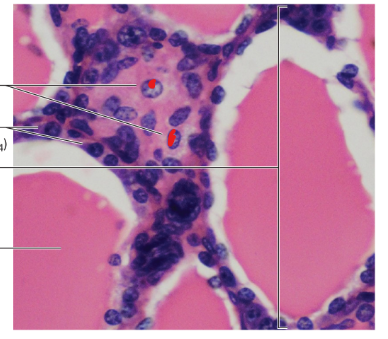
Parafollicular Cells/C Cells
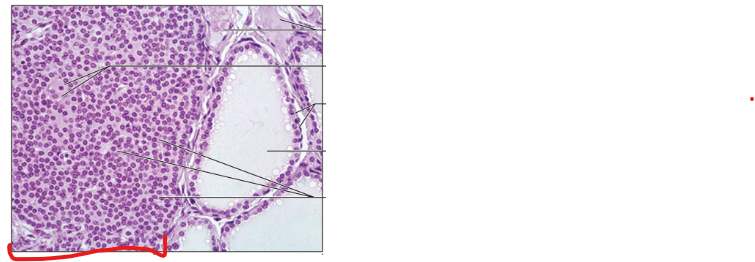
Parathyroid Gland
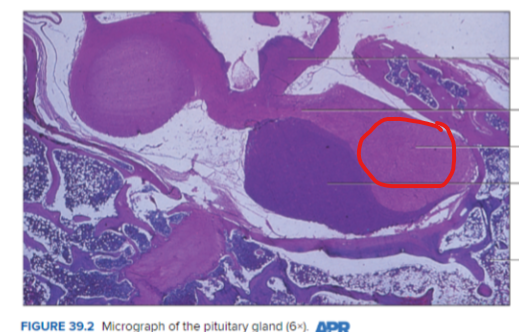
Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary gland)
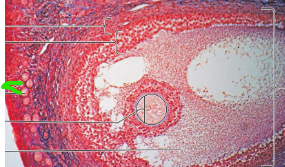
Primordial Follicles
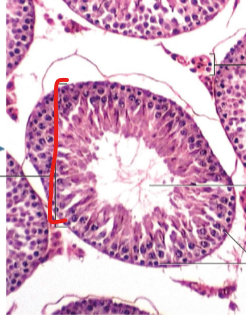
Seminiferous
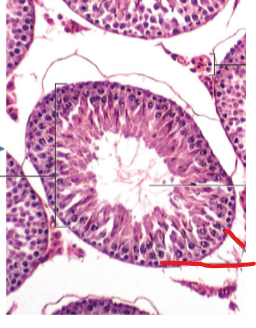
Spermatogonia
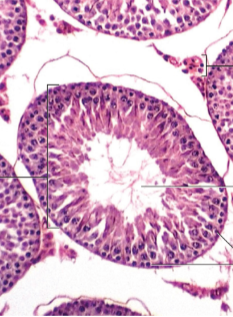
Testes