Ch. 1 Managing and Performing
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Challenges that Characterize the Current Business Landscape
Globalization
Technology Change
Collaboration
Knowledge Management
Globalization
Corporations operate worldwide, transcending national borders by tapping international markets.
Technology Change
Engagement in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, data protection, 5G etc. The internet can be a threat and business opportunity. AI can interfere between humans and technology and society.
Collaboration
Requires productive communications among different departments, divisions, or subunits of the organization.
Coopetition: simultaneous competition and cooperation among companies with the intent of creating value.
Knowledge Management
The set of practices aimed at discovering and harnessing an organization’s intellectual resources – finding , unlocking, sharing, and capitalizing on people expertise, skills, wisdom and relationships.
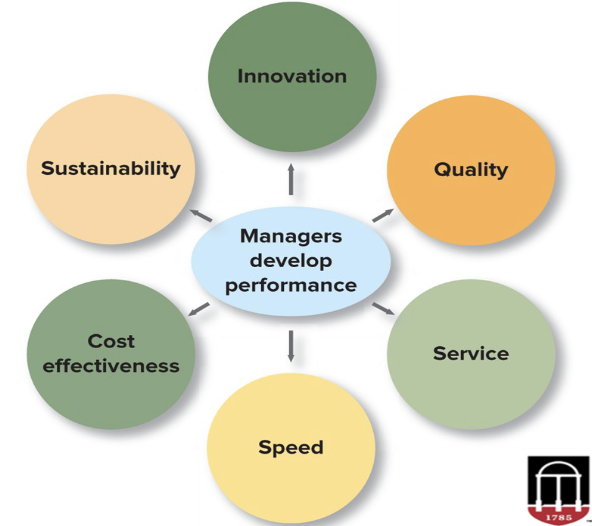
Managing for Competitive Advantage
A key to understanding the success of a company is how well it both creates
and sustains competitive advantage.
The Functions of Management
Management
Is the process of working with people and resources to accomplish organizational goals efficiently and effectively.
Gina, a sales manager, has increasing pressure from other vendors who have shifted production of their parts overseas. She calls one of his customers who normally buys at least once a month, but hasn’t placed an order with Gina in three months. Thecustomer states that they are buying from an alternate supplier based on price. Gina is competing for orders with companies who have reduced costs by shifting production overseas. Gina faces the management challenge involved with
A. Globalization
The FOUR Functions of Management
Planning
Organizing
Leading
Controlling
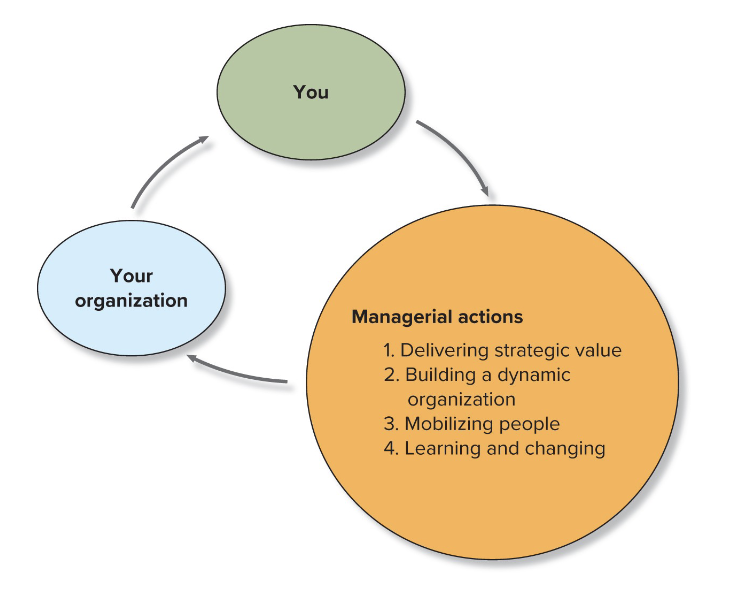
Planning: Delivering Strategic Value
Systematically making decisions about goals and activities to be pursued.
Organizing: Building a Dynamic Organization.
Assembling and coordinating resources needed to achieve goals.
Leading: Mobilizing People
Efforts to stimulate high performance by employees.
Controlling: Learning and Changing
Monitoring performance and making needed changes.
Through careful monitoring of the financial budgets of a firm, managers can detect
potential problems in reaching their financial goals and take actions to reverse the
problem. This is an example of the ________ function of management.
A: planning
B: controlling
C: leading
D: organizing
E: staffing
B. Controlling
The Three Levels of Management
Top-level managers
Middle-level managers
Frontline managers
Top-level managers
The senior executives of an organization and are responsible for its overall management. Often referred to as strategic managers.
Middle-level managers
Located in the organization’s hierarchy below top-level management and above the frontline managers. Sometimes called tactical managers, they are responsible for translating the general goals and plans developed by strategic managers into more specific objectives and activities.
Frontline managers
Also known as operational managers, are lower-level managers who supervise the operations of the organization. These managers often have titles such as supervisor, team leader, or assistant manager.
Roles of an Effective Manager
Decisional Roles
Informational Roles
Interpersonal Roles
Decisional Roles
Entrepreneur: search for new business, initiate new projects
Disturbance handler: take corrective action during crises
Resource allocator: provide funding and other resources, make significant organizational decision
Negotiator: negotiate with internal and external parties
Informational Roles
Monitor: seek information, serve as the center of communication
Disseminator: transmit information from source to source
Spokesperson: speak on behalf of organization
Interpersonal Roles
Leader: staffing, developing, motivating people
Liaison: maintain network of outside contacts
Figurehead: perform symbolic duties
Must-Have Managment Skills
Technical: ability to perform a specialized task involving a particular method or process
Conceptual and Decision: skills related to abilities that help identify and resolve problems
Interpersonal and Communication: people skills that represent the ability to lead, motivate, and communicate effectively with others
What is your Emotional Intelligence?
The skills of understanding yourself (including strengths and limitations), managing yourself (dealing with emotions, making good decisions, seeking and using feedback, exercising self-control), and dealing effectively with others (listening, showing empathy, motivating, leading, and so on.
Two Relationships: Which Will You Choose
You as a passive employee
You as an active contributor in a mutually beneficial relationship
Managerial Action Is Your Opportunity to Contribute
You → Your Organization → Managerial Actions
You and Your Career
Emotional Intelligence
The skills of understanding yourself, managing yourself, and dealing effectively with others.
Social Capital
Goodwill stemming from your social relationships
Be both a specialist and a generalist.
Be self-reliant.
Connect with people.
Actively manage your relationship with your organization.
Survive and thrive.
Which of the following job titles indicates that a person is a frontline manager?
A: Vice President
B: Chief Financial Officer
C: Human Resources Manager
D: Team Leader
E: Executive Assistant
D. Team Leader
T/F Emotional intelligence should be viewed as something you inherit and cannot change.
False