Concrete - Masonry
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Etech 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Masonry is
the building of structures from individual units laid in and bound together by mortar
the common materials of masonry construction are (5)
brick
stone (granite, travertine, and limestone)
concrete block
glass block
tile
Masonry is generally a highly durable form of construction. However,
the material used, the quality or mortar and workmanship, and the pattern i which the units are laid can strongly affect the durability of the overall masonry construction
4 masonry advantages
Thermal mass - the use of materials such as brick and stone can increase the thermal mass of a building, giving increased comfort in the heat of summer and cold of winter
fire resistant - fire resistance and heat resistance is very high
maintenance free - brick typically will not require painting, providing a surface with reduced life-cycle costs
appearance - masonry’s appearance can give an impression of solidity and permanence
5 masonry disadvantages
expensive
absorbs moisture
color deteriorates
requires a heavy foundation
requires skilled labor for installation
Masonry Brick - Grade SW (severe weathering)
is used in areas of heavy rain, snow, or continual freezing
Grade MW (moderate weathering)
is used in areas of average rain or moderate freezing
Grade NW (no weathering)
is used in areas of minimal rain and no freezing, in sheltered or indoor locations
Face Brick
is brick that will be exposed to view; made with a controlled mixture of clay and shale
fire brick
is made with great resistance to high temperatures for use in fireplaces or similar
paving brick
is very hard and dense for use in pavements
adobe brick
is made from a mixture of clay and straw, placed in molds, and dried in the sun. requires protection from rain and moisture
Mortar
a material composed of cement and a fine aggregate (sand) used to hold masonry units together. It must be compatible with the masonry units being used, the strength required of it, and the environmental conditions.
it is distinguished from ‘concrete’ by lack of large aggregates.distinguished from ‘concrete’ by lack of large aggregates
Grout
Similar to mortar, but is mixed to a pouring consistency and used to fill cavities or cores of masonry units
Efflorescence
a white powdery crystallization on a masonry surface caused by soluble salts in the units or in the mortar
when it appears it can be removed by washing with high pressure water, light sandblasting, or most commonly washing with a 5% solution of muriatic acid water
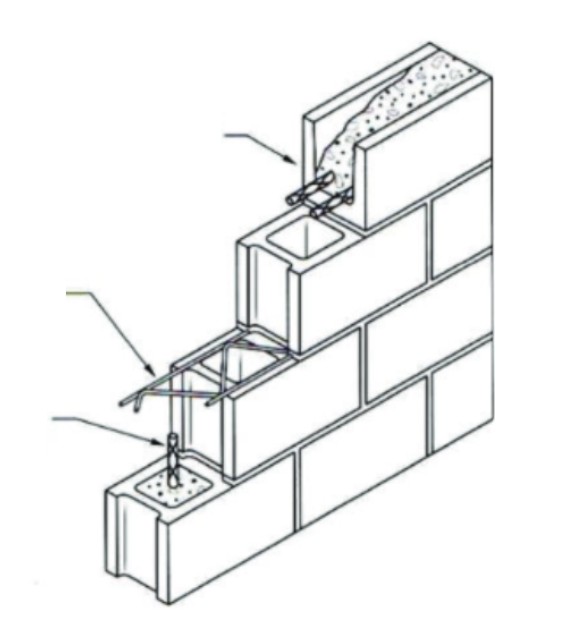
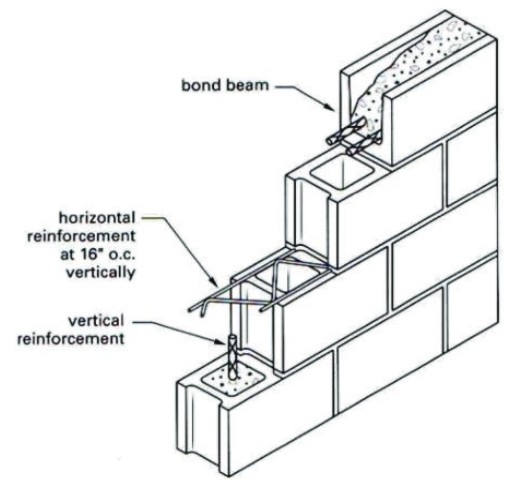
Joints
are a critical part of a masonry wall.
The mortar in the joints not only holds the entire wall together, it also prevents the infiltration of water and air
After the brick is laid, the joints must be
tooled
Tooling imparts a decorative effect on the wall, but more importantly, it makes the joint more watertight by compressing the mortar near the exposed surface.
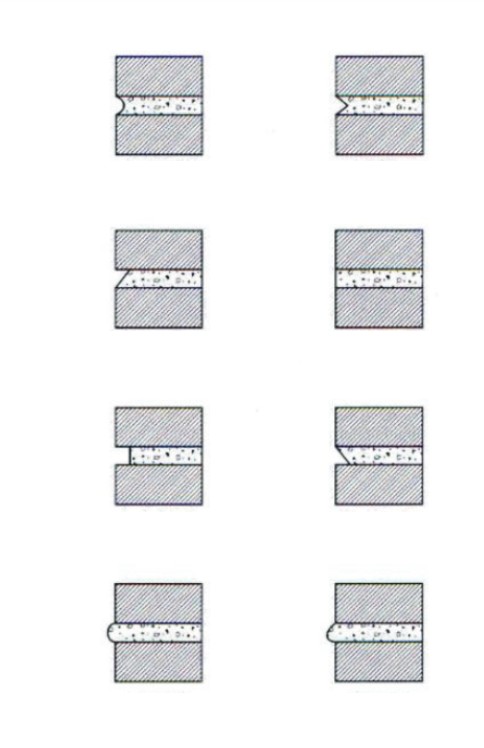
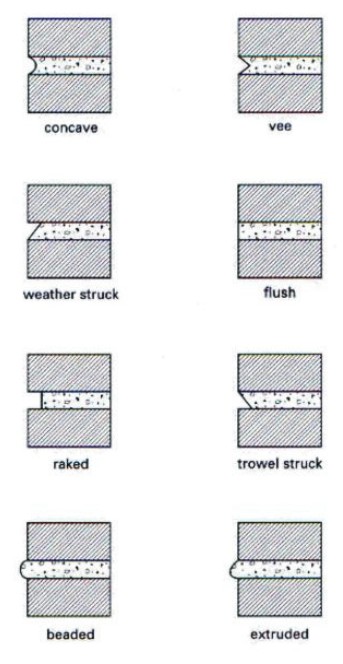
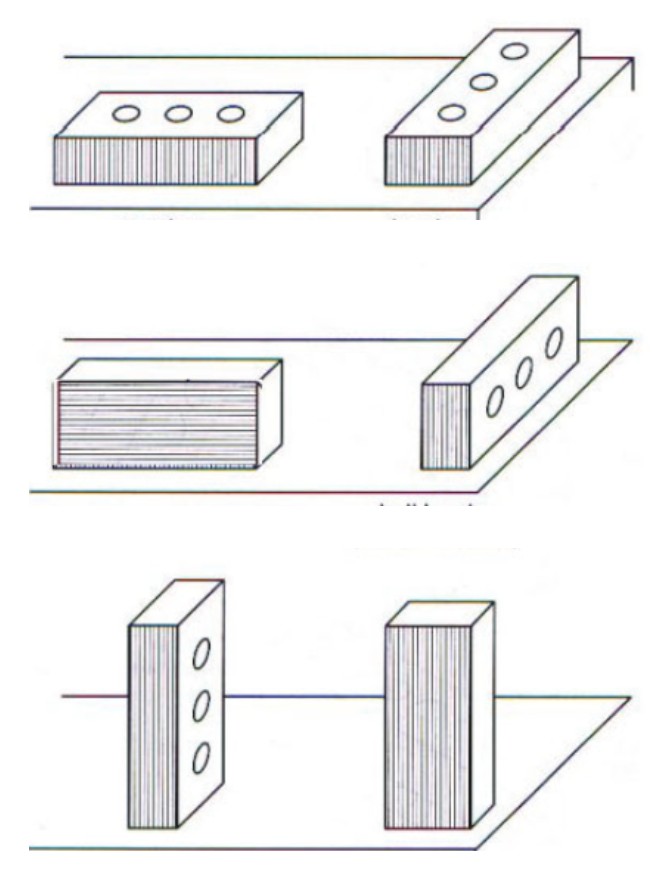
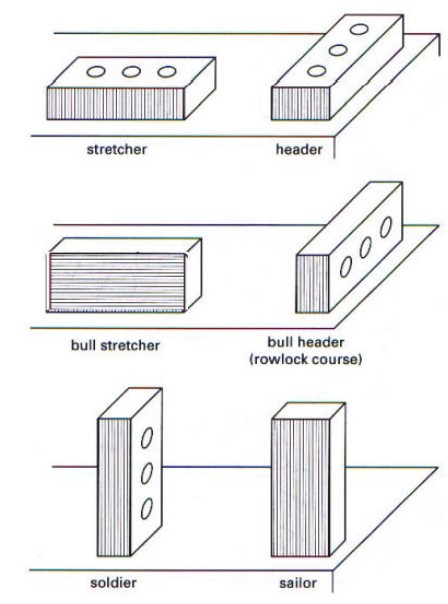
A course is (define + name 6 types)
one continuous horizontal layer of masonry
stretcher course (typical course style)
header course
bull stretcher course (decorative)
bull header course (rowlock)
soldier course (decorative)
sailor course (decorative)