Computer Hardware
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Components of a computer
Computers consist of hardware (physical components) and software (programs that run on hardware)
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Brain of the computer performs all types of data processing operations from
simple arithmetic to complex tasks and all the
other important functions of a computer.
The CPU consists of 3 major units, which are:
Memory or Storage Unit
Control Unit
ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
Memory Unit
Data and instructions are stored in memory units which are required for processing.
All sorts of inputs and outputs are transmitted through the memory unit
Control Unit
Controlling of data and transfer of data and instructions is done by the control unit among other parts of the computer.
responsible for managing all the units of the computer
control unit fetches instructions from memory, interprets them, and directs computer operations accordingly.
also responsible for communication between input and output devices.
ALU
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) is responsible for performing arithmetic and logical functions or operations. It consists of two subsections, which are:
Arithmetic Section
Logic Section
Arthmetic Section
The ALU performs basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) and executes complex operations by repeatedly using these fundamental functions.
Logic Section
The ALU performs logical operations such as selecting, comparing, matching, and merging data.
What Does a CPU Do?
Fetch, Decode, Execute, Store
Fetch:
the first CPU gets the instruction. That means binary numbers that are passed from RAM to CPU.
Decode:
When the instruction is entered into the CPU, it needs to decode the instructions. with the help of ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit), the process of decoding begins.
Execute:
After the decode step the instructions are ready to execute.
Store:
After the execute step the instructions are ready to store in the memory.
Types of CPU
Single
Dual
Quad-core
Single Core
Oldest kind
used in the 1970s
means that the single-core CPU can only process one operation at a single time
Dual core
Dual-Core CPUs contain a single Integrated Circuit with two cores.
Faster
Quad core
A quad-core processor contains a chip with four independent cores. Quad Core CPU increases the overall speed of programs.
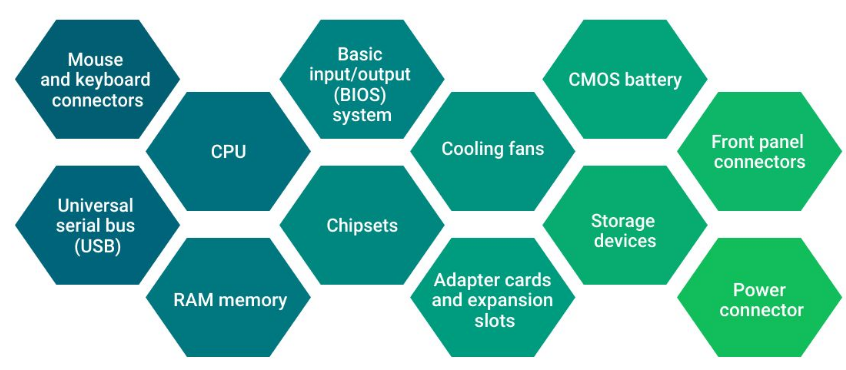
Motherboard
A motherboard is a circuit board inside computers that stores electrical components and helps them communicate.
Key Components of Motherboard
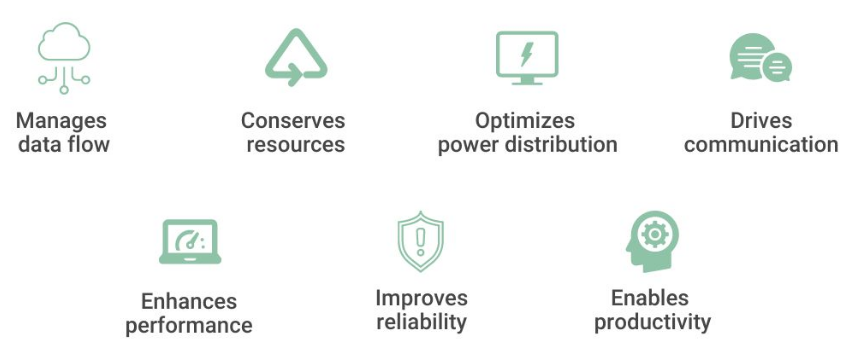
Functions of a Motherboard
Memory
Computer memory can be broadly classified into primary (main) and secondary (auxiliary) memory.
Primary Memory
primary memory further categorized into volatile (RAM) and non-volatile (ROM, flash memory)
RAM
It is a primary memory.
2 kinds.
DRAM
A common type of RAM used in most computers and other electronic devices.
SRAM
A type of RAM that retains data as long as power is supplied.
ROM
Read only memory, means it cannot be rewritten.
All the basic instructions for the computer are written on this.
PROM
Programmable ROM can we modified only once, and cannot be rewritten.
EPROM
Erasable Programmable ROM
can be rewritten by exposure to UV.
Secondary (Auxiliary) Memory:
refers to the storage devices and systems used to store data persistently, even when power is off.
Eg; HDDs, SSDs
Flash Memory
A non-volatile memory type that can be erased and reprogrammed electronically
Hard Drives (HDDs)
Traditional magnetic storage devices that store large amounts of data.
Solid State Drives (SSDs)
Modern storage devices that use flash memory for data storage.
Other Secondary Storage:
USB drives, CDs, and DVDs.
Cache Memory
A small, fast memory used to store frequently accessed data for quicker retrieval by the CPU.
Virtual Memory
A technique that uses hard disk space as an extension of RAM, allowing the computer to handle larger amounts of data.
Input Output Devices
Input devices send information to a computer, while output devices display or reproduce that information.
Input Devices
Keyboard, Mouse, Microphone, Lightpen, Joystick
Output Devices
Printer, Monitor, Speaker, Headphones
LCD/LED Monitor
LCD monitors use cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) for backlighting.
LED monitors use light-emitting diodes for backlighting.
LED Monitors are also known as
LED-backlit LCD Monitor
Keyboard
A keyboard is a panel of keys for entering text and commands into a computer.
Mouse
is a handheld pointing device used to control the cursor on a computer screen, select items, and navigate graphical interfaces.
Printers
A printer is an output device that produces a physical copy, or "hard copy," of electronic data from a computer or other device.
What does a printer do?
It transfers digital information, such as text, images, or a combination of both, onto a medium, most commonly paper,
Types of printers
Impacts and Non Impact
Impact Printer
These printers use a mechanism that physically strikes an ink ribbon against the paper to create an impression, similar to an old-fashioned typewriter.
Eg: Dot matrix
Non Impact Printer
These printers do not use direct physical contact to print.
Inkjet printers
spray ink from cartridges at close range to the paper.
Laser printers
use a laser beam to attract toner to specific areas of a rotating drum, which is then transferred and fused onto the paper.
Scanners
A scanner is an electronic device that converts physical documents, images, or objects into a digital format,
such as a file on a computer,
by using light and photosensitive sensors to capture their content.
Types of Scanners
Flatbed Scanners
Sheetfed Scanners
Handheld Scanners
Flatbed Scanner
The most common type, where documents are placed on a flat glass surface to be scanned.
Sheetfed Scanners
These move the pages through the scanner using rollers, often with automatic document feeders for scanning multiple pages at once.
Handheld Scanners
Small, portable devices that are manually dragged over a flat surface to scan text or images.
Hard Drive
A hard drive is a hardware component in a computer that provides non-volatile storage,
meaning it stores data permanently even when the device is turned off.
Location of Hard drives
internal, located inside the computer, or external, connected via cables for added storage and backups.
Types of Hard drives
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
Solid State Drives (SSDs)
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs):
The traditional type, using spinning magnetic platters and read/write heads.
Solid State Drives (SSDs)
A newer, faster type of storage that uses flash memory instead of mechanical parts.