The movement of water and solutes in plants
Explain the quantitative importance of evapotranspiration in plants
Evapotranspiration is a significant process for plants as it accounts for a large portion of the water cycle, contributing to the movement of water from the soil to the atmosphere.
It plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature of plants and the surrounding environment through the cooling effect of water vapor release.
Quantitatively, evapotranspiration is a major factor in determining the water requirements of crops and natural vegetation, influencing agricultural practices and ecosystem dynamics.
The process of evapotranspiration also affects regional and global climate patterns, making it an important component of Earth's hydrological cycle.
List and explain three functions of evapotranspiration in plants.
Gas exchange
Evapotranspiration facilitates the exchange of CO2 and O2 for photosynthesis and respiration in plants
Cooling
Evapotranspiration plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature of plants and the surrounding environment through the cooling effect of water vapor release
Transport of photosynthates and nutrients
Evapotranspiration is essential for the transport of photosynthates and nutrients from leaves to other organs through the phloem
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Explain the quantitative importance of evapotranspiration in plants
Evapotranspiration is a significant process for plants as it accounts for a large portion of the water cycle, contributing to the movement of water from the soil to the atmosphere.
It plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature of plants and the surrounding environment through the cooling effect of water vapor release.
Quantitatively, evapotranspiration is a major factor in determining the water requirements of crops and natural vegetation, influencing agricultural practices and ecosystem dynamics.
The process of evapotranspiration also affects regional and global climate patterns, making it an important component of Earth's hydrological cycle.
List and explain three functions of evapotranspiration in plants.
Gas exchange
Evapotranspiration facilitates the exchange of CO2 and O2 for photosynthesis and respiration in plants
Cooling
Evapotranspiration plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature of plants and the surrounding environment through the cooling effect of water vapor release
Transport of photosynthates and nutrients
Evapotranspiration is essential for the transport of photosynthates and nutrients from leaves to other organs through the phloem
List and explain two mechanisms by which plants uptake water, and identify the one that is predominant
Cohesion-tension theory
This mechanism involves the evapotranspiration of water from the leaves, creating a negative pressure that pulls water up through the xylem.
The tension created by evapotranspiration is the predominant mechanism for water uptake in plants
Osmotic root pressure
In the absence of transpiration, roots can generate positive osmotic pressure, facilitating water absorption.
However, this mechanism typically represents less than 1% of the cohesion-tension mechanism and is not the predominant method of water uptake in plants
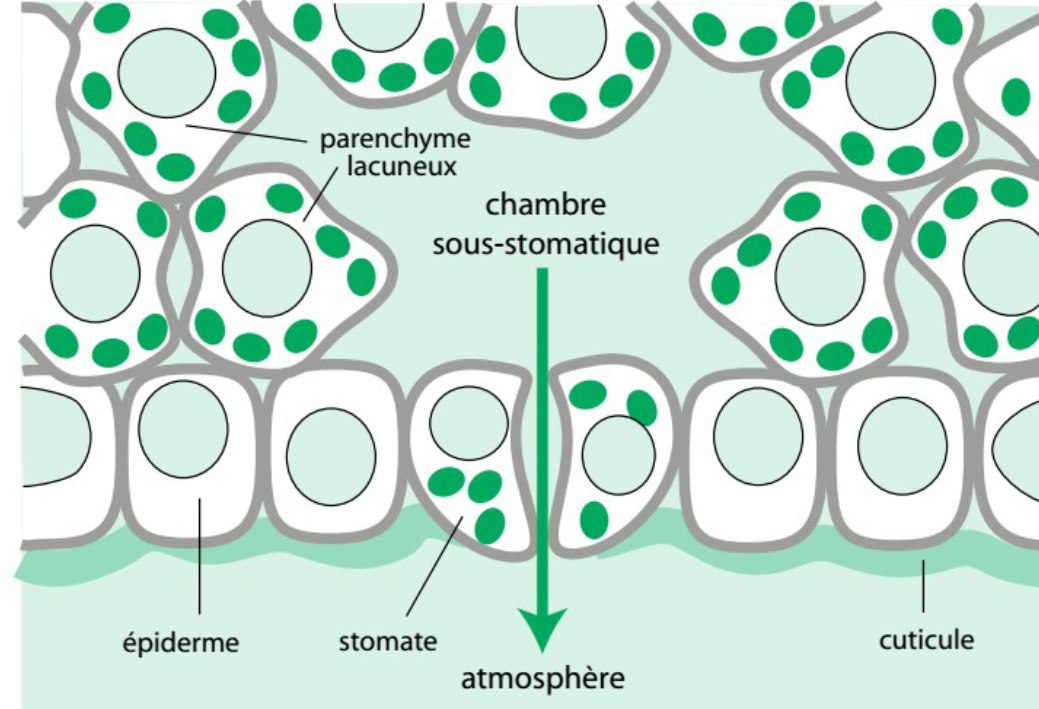
Make a drawing illustrating the anatomical features of a leaf that contribute at minimizing/controlling evapotranspiration
Anatomical adaptations
Waterproof cuticle coating the
epiderm
No intercellular space among epidermal cells
Disposal of stomata at the lower face
The substomatal space (air saturated with water vapor) prevents direct flowing of water through the stomatal aperture (only vapor can escape)
Physiological adaptations
Regulatory control of stomata opening and closing
Identify and explain two physiological adaptations to control evapotranspiration in plants
Regulatory control of stomata
Plants have developed physiological adaptations to regulate the opening and closing of stomata, such as the arrangement of cellulose microfibrils in guard cells and the presence of aquaporins
which control the movement of water and ions to adjust the turgor pressure and volume of guard cells, ultimately influencing stomatal aperture
Anatomical adaptations
Plants exhibit anatomical adaptations to minimize evapotranspiration, including the presence of a waterproof cuticle coating the epidermis, the absence of intercellular space among epidermal cells, and the disposal of stomata at the lower face of leaves. These adaptations help reduce water loss through transpiration