McCain - parenteral
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Enteron means
a. Intestine
b. joint
c. skull
d. covering
a
Parenteral means _______ the _______
In practice, parenteral is understood to mean “by ________”
outside, intestine, injection
The three I’s of Parenterals
Imperative, invasive, irrevocable
Parenteral Advantages
Parenteral route would be indicated If drug is poorly absorbed or degraded by _____
_____ and predictable drug response
useful when patient is _______ or _______
useful when patient can’t absorb these ______
_____ drug therapy
______ acting drug delivery
______ pumps
GI
rapid
uncooperative, unconscious
orally
localized
long
implantable
Parenteral Disadvantages
Necessity of ______
Difficult and _____ to produce
Many require a ______ person to prepare and/or administer them
Once administered, it is difficult to _______ if adverse or toxic rxn occurs
_____ or risk of tissue ______ with administration
sterility
costly
trained
remove
pain, damage
USP Injectable Material Types (5)
injection → solution
for injection → dry solid, liquid upon prep
injectable emul
injectable susp
for injectable susp
Injectable suspensions are difficult to formulate because they must possess ________ and _______
syringeability, injectability
NDC Numbers
XXXXX-XXXX-XX
What does each group represent
company
product
size
Emulsions – relatively stable homogeneous mixtures of two __________ liquids
immiscible
IMPORTANT PARENTERAL CHARACTERISTICS (6)
sterile
particulate and pyrogen free
stable
pH
osmotic P
proper labeling and packaging
Sterility
Absence of living or ________ _______ form (ie. spore) of an organism
Cannot be 100% confirmed, is described using statistical probability known as __________ _________ _______
^ Each log reduction (10^-1) represents _____% reduction in microbial population
^ 6 log reduction represents that ____ unit(s) bacteria survived every 1,000,0000 units
5 methods used for pharmaceuticals
viable vegetative
sterility assurance level SAL
90%
1
steam, dry heat, filtration, gas, ionizing radiation
T or F:
Steam sterilization is useful for oils, fats, and other oleaginous preparations or powders that may be damaged by moisture
F (dry heat is)
Dry heat sterilization is the method of choice when _____ conditions are required or when not effectively sterilized by _____ heat
Good for ____ and ____
dry, moist, oils, fats
Filtration Sterilization
______ micron filter sterilizes a drug product
Advantages (3)
Disadvantages (2)
______ _____ testing is used to ensure filter integrity
0.2
speed, lower cost, complete removal of living and dead organisms
slow for large Vs, potential to retain drug in filter
bubble point
_____ sterilization interfere with cellular ________ function and can kill ______ known viruses, bacteria, fungi, and spores
Gas, metabolic, all
Radiation Sterilization may be ________ or ________
Advantages (2)
beam - electrical, ionizing - radioactive
cheap, nondestructive
Sources of particulates (6)
particulates can cause …. (5)
product itself, environment, equipment, personnel, packaging, administration devices
tissue injury, emboli, allergic rxn, tissue infarction, death
Pyrogen is any substance that can cause a _________
Endotoxin is the natural complex of lipopolysaccharide found in outer layer of live/dead gram-________ bacterial cell walls
Clinically important as can cause … (8)
fever
negative
fever, chills, nausea, malaise, pain, septic shock, respiratory distress, death
Pyrogen Testing
_________ test, cannot be precisely _______
Endotoxin Testing
_______ test, can be repeated
Aqueous extract of blood cells from the _______ _____ that reacts with lipopolysaccharide (forms a ________ gel)
rabbit, repeated
LAL
horseshoe crab, coagulation
Non sterile (“filthy”) vs pyrogenic
filthy → slow onset of fever, 100-102 F
pyrogenic → sudden onset of fever <20min and >104 F
IV Parenterals
Human blood plasma has pH of ______
Infusate pH btwn ______ can be tolerated by peripheral veins
________ of exposure is a contributing variable to tolerability
________ of vascular access is also a contributing variable
Blood has tonicity of _______ mOsm/L
7.4
5-9
duration
location
280-310
The 3 isotonic solutions
0.9% NS
5% dextrose → hypotonic in body after rapid oxidation to CO2 and free H2O
Lactated Ringers LR
D5W + anything else is always _________ (ex: D5W + LR or D5W + 0.45% NaCl)
hypertonic
For intravenous administration, osmolar concentration NOT LESS than _______ mOsm/L is essential to avoid _________ (cell rupture)
Osmolar concentration NOT MORE than _______ mOsm/L to avoid tissue injury/cell _______
112, hemolysis (hypotonic = burst)
600, shrinkage (hypertonic = shrink)
Result of HEPA + LAF (high efficiency particulate air filtration + laminar air flow)
Not “sterile”, BUT is _______ _____ and therefore a “_______” environment
The focus then becomes preserving the particle-free air flow at the ________ ____
2 types of hoods, which one for hazardous drugs?
particle-free, clean
critical site
horizontal, vertical for hazardous
Tuberculin/TB vs Insulin syringes (3)
both are 1 mL
insulin typically have pre-attached needles
TB marked in 0.01 mL, insulin marked in 2 unit (100 U → 1 mL)
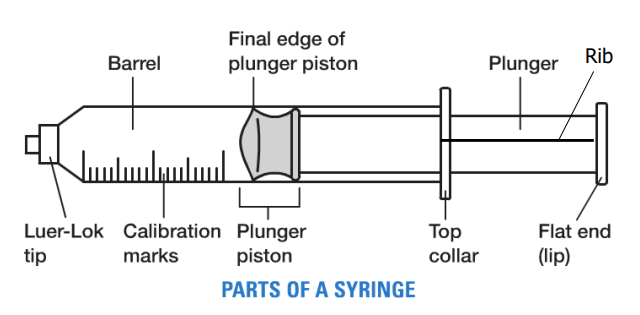
what 2 parts is NOT okay to touch while drawing a syringe? (contamination)
tip and rib/plunger
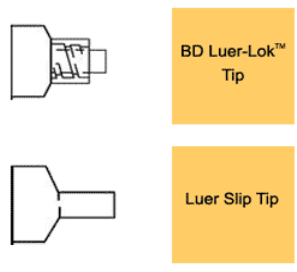
Difference btwn BD Luer-Lok and Luer Slip
Luer-Lok → locking fit
Luer Slip → push and twist
Syringes
Recommended V of solution drawn up typically to _____- _____ of syringe capacity
_______ ______ of plunger is used for measuring V
These syringes are accurate to ______of the smallest increment marking on the syringe
1/2-2/3
final edge
1/2
10 units is equivalent to _____ mL
0.1
Needles: ______ mL for priming
0.1 mL
T or F:
Needle gauges: The higher the number, the smaller the diameter
T
Insulin needles
micro fine =
ultra fine =
nano =
27-28 G
31 G
32 G
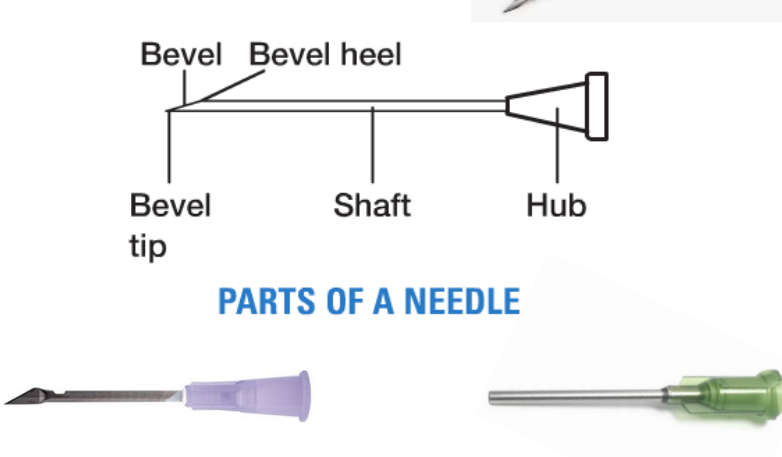
Which parts of the insulin needle should you NOT touch? (contamination risk)
ALL
T or F:
You can pull AND administer using filter needles
F
(always pull with the filter needle then change tip to administer OR pull with normal tip then change to filter and administer. always change tip)
Routes of Parenteral Administration
Intradermal ID → injection area just below the surface of the ____
^ used for …
Subcutaneous SC, SQ, SubQ → injection area of _____ tissue located beneath skin btwn dermis and muscle
^ used for ….
Intramuscular IM → Injection area in _______ mass
Formulations must be ________, V limited by ______ of injected muscle and _____
Intravenous IV → injection area: _________
Administration of drug that needs immediate _________ circulation, is _____, and/or requiring controlled ______ levels
skin
skin tests, small Vs
fat
acute/continuous therapies, insulin, heparin, 2.5 mL V
muscle
nonirritating, mass, age
vein
systemic, irritating, blood
Parenteral suspensions in oil have pharmaceutically _______-acting effect
These are administered ONLY ________ (not miscible w blood, _______ risk)
long, intramuscularly, embolic
Venous Access Devices
-
-
Peripheral catheters → most common, short duration/days, limitations on content and rate
Central catheters → more complicated, longer duration/days to months, fewer limitations
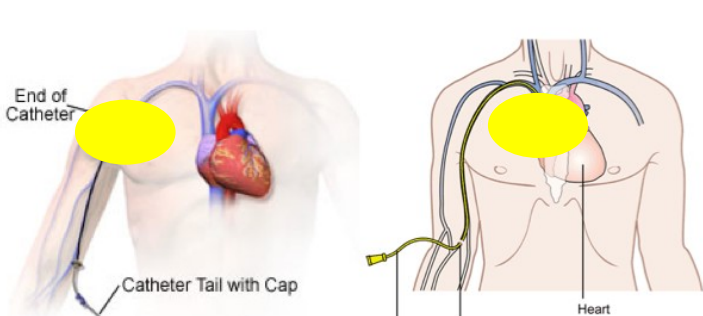
midline vs PICC line vs Implanted port
Midline → ends around shoulder
PICC → longer
implanted port → under skin
2 types of IV administration
bolus
infusion → continuous or intermittent
Bolus IV Push
advantages (5)
disadvantages (3)
shortest duration, not prolonged, immediate blood lvls, no pump, less expensive
drug toxicity, stability, blood fluctuation
infiltration vs extravasation
the type of medicine/fluid that is LEAKED
infiltration → non vesicant
extravasation → vesicant (irritating to tissues)
Continuous IV → simultaneous fluid + drug therapy
advantages (2)
disadvantages (4)
constant blood lvls, minimize vein trauma
greater monitoring, may require central catheter, infiltration or extravasation leaks, potential of adverse drug event ADE
Intermittent IV
advantages (4)
disadvantages (4)
limited admin time, less monitoring, less potential for ADE, inc stability
V/conc limits, less constant blood lvls, inc prep time, inc infection risk
Complications of IV administration (5)
phlebitis - vein inflammation
thrombosis - vein clot
air emboli
particulate emboli
infiltration/extravasation
commonly utilized for analgesia and/or anesthesia → __________ (space in spinal column)
MUST BE __________ ______ and have __________
used for analgesia/anesthesia AND select chemotherapeutic, injects INTO the spine → ____________
also must be ________ _____ and have _______
epidural
preservative-free, labeling for epidural use
intrathecal
preservative-free, labeling for intrathecal use
Vincristine should NEVER be given ________
intrathecally
Parenteral solutions are packaged as ….
large volume parenteral LVP > 100 mL
small volume parenteral SVP 100 mL or less
pharmacy bulk package → NOT intended for direct infusion, contains many single doses
3 types of containers for LVP
glass bottles
glass bottles with air vent tube
plastic bags → graduation marks roughly estimate (should not be used to measure), collapse as they empty and do not require venting
Before withdrawing contents from a vial, an equal volume of _____ is FREQUENTLY injected into the vial to pressurize the vial and aid in withdrawing the contents
air
BLACK “flip off” cap and a BLACK FERRULE with _______ ____ _______ warning
must be diluted
T or F:
Vial entry → use slight lateral P at 45 angle and move to 90 to prevent coring
T
Ampoules are ______ dose glass containers with elongated neck that must be broken off
Ampoules require use of a _________ filter
single
5 micron
Single dose containers may be ______ or ____
they contain NO ________
________ MUST BE discarded immediately
Multiple dose containers are limited to _______ volume
Must be discarded within ______ days unless specified by manufacturer
ampoules, vials
preservatives
ampoules
30 mL
28
T or F:
For reconstitution, all drugs should be shaken
F (some should NOT be shaken)