ADH2 Exam 2: Pulmonary Embolism/ Anticoag Therapy
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Whats a PE? And ots most common cause??
obstx of pulmonary vessels by embolus (hypoxia)
d/t DVT
Risk factors of PE: (7)
DVT
Immobile
Recent surgery
Preggo
Obese
OCPs
Clotting disorders
List findings of PE:
resp (5)
cardiac (3)
other (3)
Respiratory:
dyspnea
crackles
cough
tachypnea
hemoptysis (pink frothy sputum)
Cardiac:
chest pain
tachycardia
syncope (faint)
Other:
anxiety
diaphoresis
pleural effusion

An ABG for early PE shows??
Respiratory ALKALOSIS!!
HYPERventilate
Whats the lab test specifically used to determine PE and what does it determine?*
D-Dimer!!
an increase suggest clot in body
Gold standard diagnostics for PE?
Whats the alternative?
CT Pulmonary Angiography
uses contrast so note allergies!!
Use VQ scan (Ventilation/Perfusion scan) if contrast contraindicated
Whats the ranges for
pH
CO2
HCO3
pH: (a) 7.35-7.45 (b)
CO2: (b) 35-45 (a)
HCO3: (a) 22-26 (b)
In ABG for PE pt, what does it show in Early, Progressive, and Late/Severe stage?
Early: Resp. ALKAlosis!!
Hyperventilation → blowing off CO2
Progression: Hypoxemia develops
Ventilation/ Perfusion (V/Q) mismatched
lungs are ventilated but blood flow is BLOCKED!!
Late/Severe: Resp. ACIDosis!!
fatigue
decreased ventilation → CO2 retention (acidic)
PE medication: (3)
Anti-coags
Heparin (IV)
Enoxaparin (SQ)
Warfarin (PO)
Antidotes for Heparin, Enoxaparin, Warfarin?
Protamine Sulfate for 2
Vitamin K for warfarin
What lab tests to monitor for Heparin and Warfarin and the values?
aPPT: 1.5-2.5x control
PT/INR: 2-3
Which of the 3 PE anticoagulants has rapid onset to prevent clot growth and should discountinue if cant control it?
IV heparin!!
Which ones considered low molecular weight heparin?
And would u need to moniotr labs for it?
Enoxaparin!!
more predictable, so less monitoring needed (no labs)
SQ—abd fat, rotate site, not by navel
Nursing care for pts w/ PE
airway/O2 (2)
monitoring (2)
support (1)
Airway/ Oxygenation:
High fowlers
give O2 as prescribed
Monitoring:
resp/ cardiac status
ABGs, labs (clotting, electrolytes)
Support:
Emotional to reduce anxiety!!
Surgical Procedures for PE: (3)
which ones for life-threatening PE?
which is for prevention of PE?
which is alternative to anti coagulant therapy?
Embolectomy:
takes out embolus from pulmonary artery (for life-threatening PE)
Thrombectomy:
takes thrombus from deep vein (DVT tx → prevents future PE)
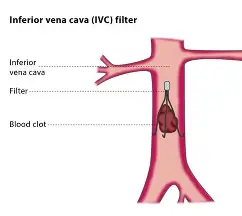
IVC Filter: (basically filters bloodstream)
device placed in Vena Cava to trap emboli and prevent PE (option if anticoag isn’t possible)
Complications of PE: (4)
Pulmonary HTN:
increased pressure form blocked pulmonary circulation
R.S. HF (Cor pulmonale)
RV can’t pump against high pressure!
Shock
impaired O2 and CO
bad perfusion
Death
if untreated or massive embolus!
PE Pt education and Prevention (8)
lifestyle (3)
mobility (3)
meds (2)
Lifestyle
quit smoking
maintain healthy weight
hydrate!
Mobility
regular physical activity
no prolonged immobility (traveling, bedrest)
use compression socks!
Meds
adhere to anti-coagulation regimen
keep regular lab checks!! (INR, aPPT, etc)

PE key points!!
Risk (5)
Findings (5)
Labs/Diagnostics (3)
Tx (4)
Prevention (5)
mostly from DVT
immobility
surgery
OCPs
Obese…
Sudden dyspnea
CP
Tachypnea
Tachycardia
anxiety
D-Dimer (increased= clot)
ABG
Early ALKAlosis→ HYPOxemia→ ACIDOsis
CT Angiography (gold standard)
Anti-coags
give O2
Positioning
possible embolectomy!
Keep them mobile
hydrate!
no smoking!
compression socks!
anti-coag adherence