Greek Art and Architecture
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Who was Pericles
A political figure who led the building of the Parthenon
How was Pericles funded
By taxes from city-states in the Delian League
What was the Delian League
A group of city-states that the athens protected
When was the Greek Archaic Period
600-480 BCE
What happened in the Greek Archaic Period
a. Greeks were known for conquering coastlines / known for sea trades
b. Greek and Persia were regularly at war
c. Greeks united against a common enemy and won the battle of marathon
d. Greek city-states boned together
When was the Late Classical Period of Greek art
400-323 BCE
What happened in the Late Classical Period of Greek art
a. There was a movement towards humanizing statues
b. Greeks were completely defeated by the Persian empire
What marked the end of the Late Classical Period of Greek art
The death of Alexander the Great
Monumentality
Big, grand, and powerful art or buildings that show pride, importance, and lasting beauty.
What does Humanism mean
A philosophical concept that stressed the abilities of humans, apart from the divine, and inspired artists and architects to consider the viewers experience and to represent idealized forms.
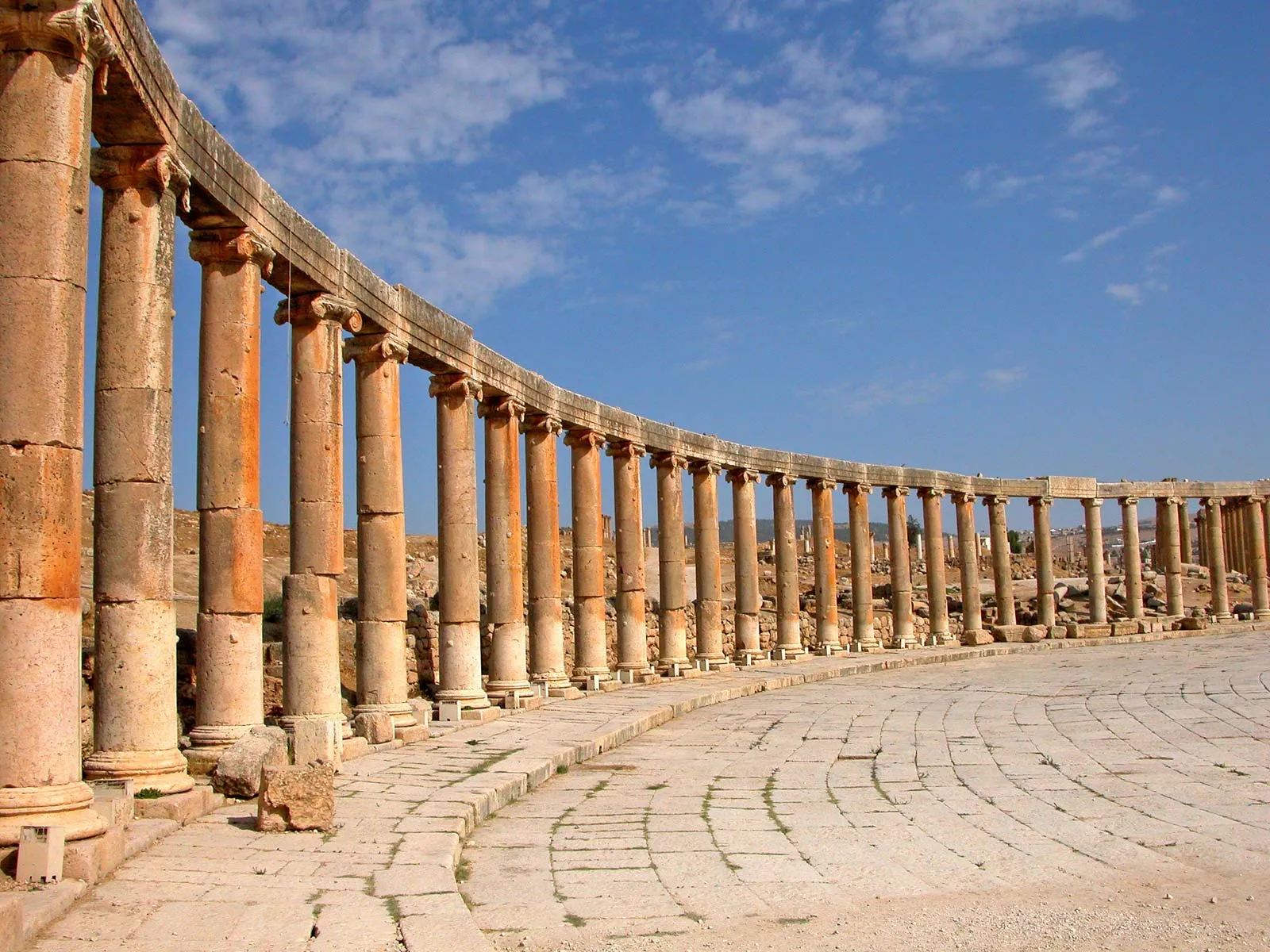
What is a Colonnade
Long sequence of columns supporting a roof

What is a Pediment
a. High relief sculpture
b. A triangular component that sits atop a columned porch, doorway, or window (roof).
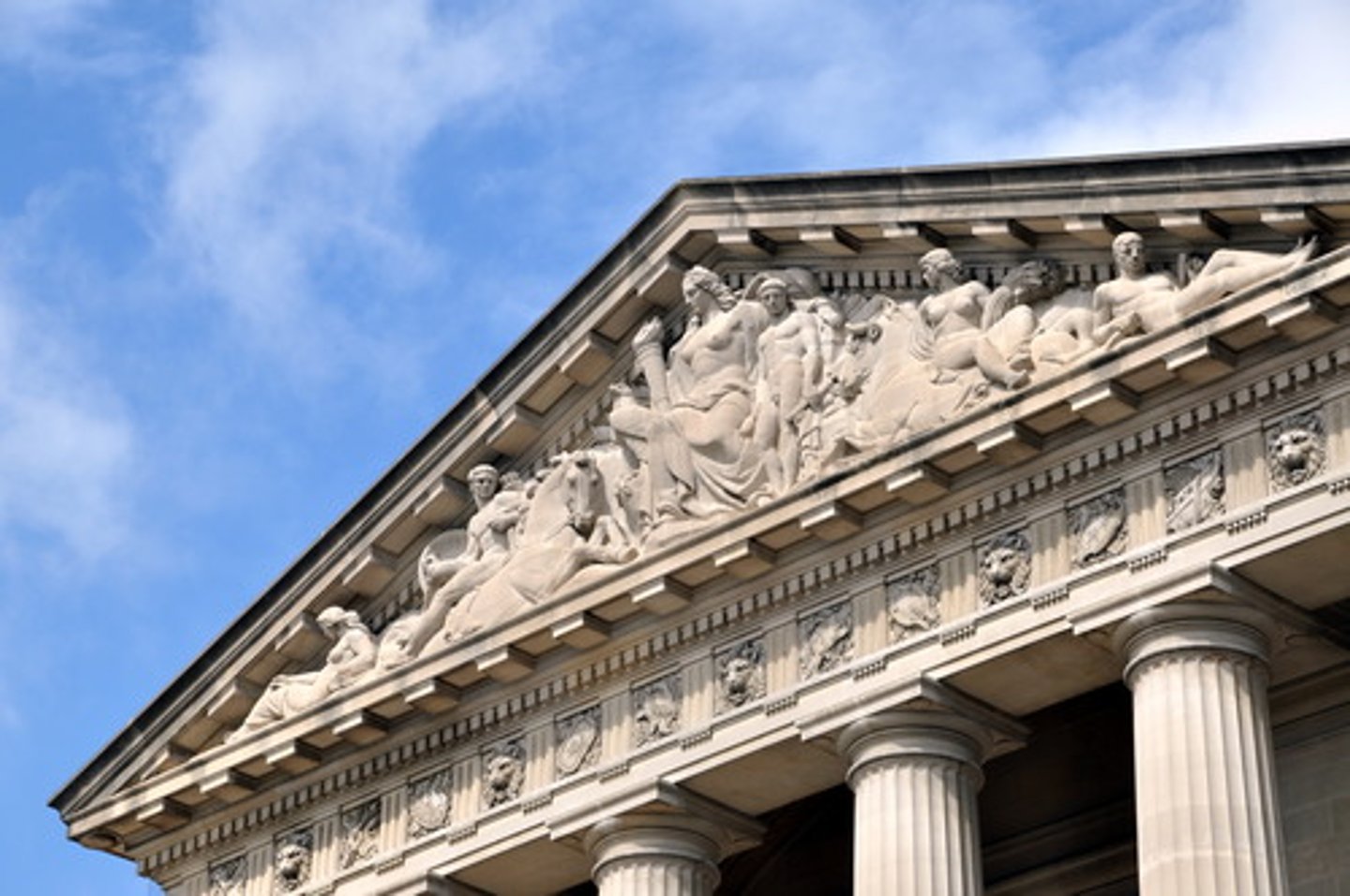

What does the Pediment at the entrance of the Parthenon show
Athena and Poseidan fighting to be patrons of the city
What is the sculpture in the round
A 3D sculpture that can be seen from all sides/angles.

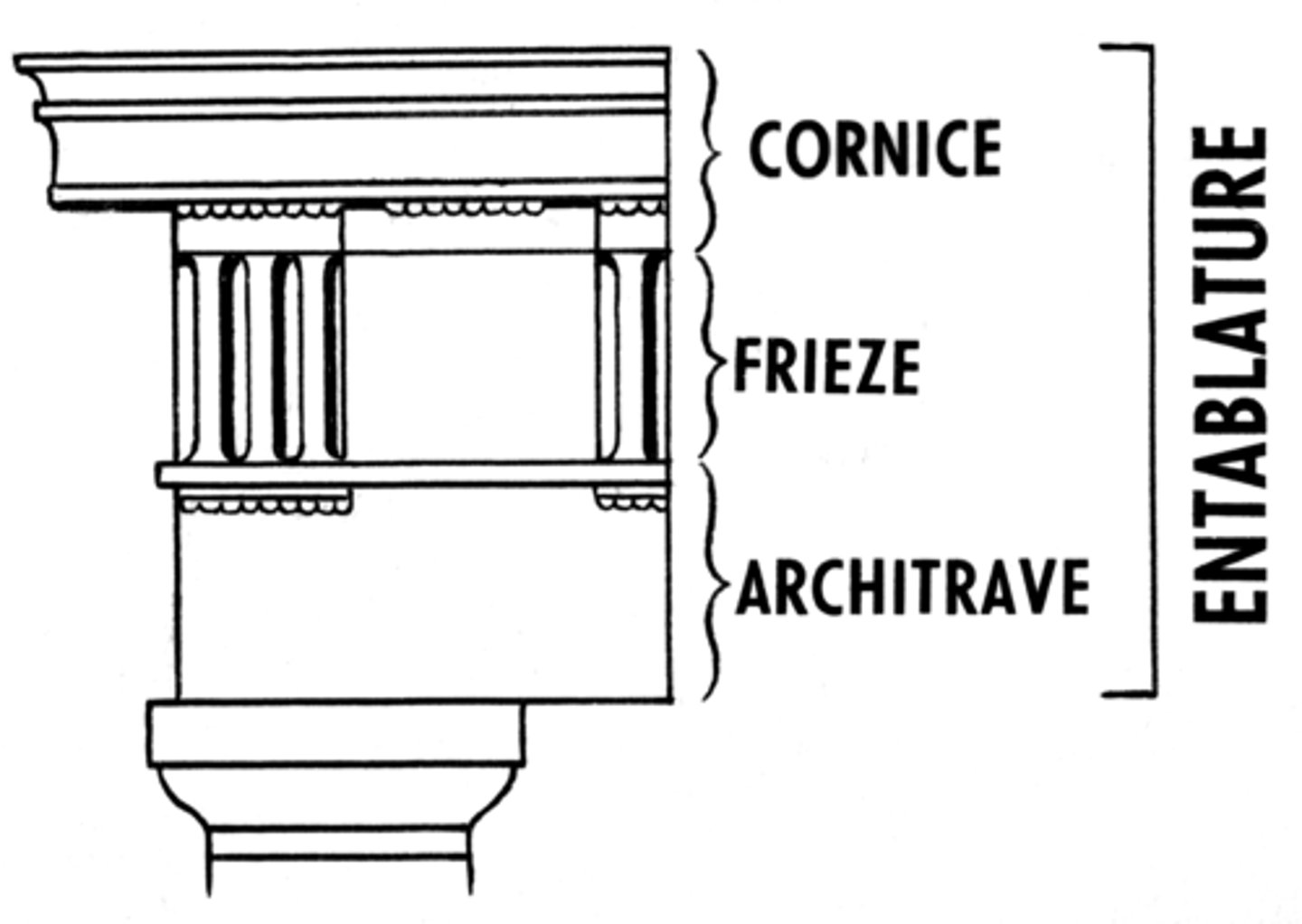
What is an Entablature
the part of a roof above the capital of the columns; has 3 parts: cornice, frieze, and architrave
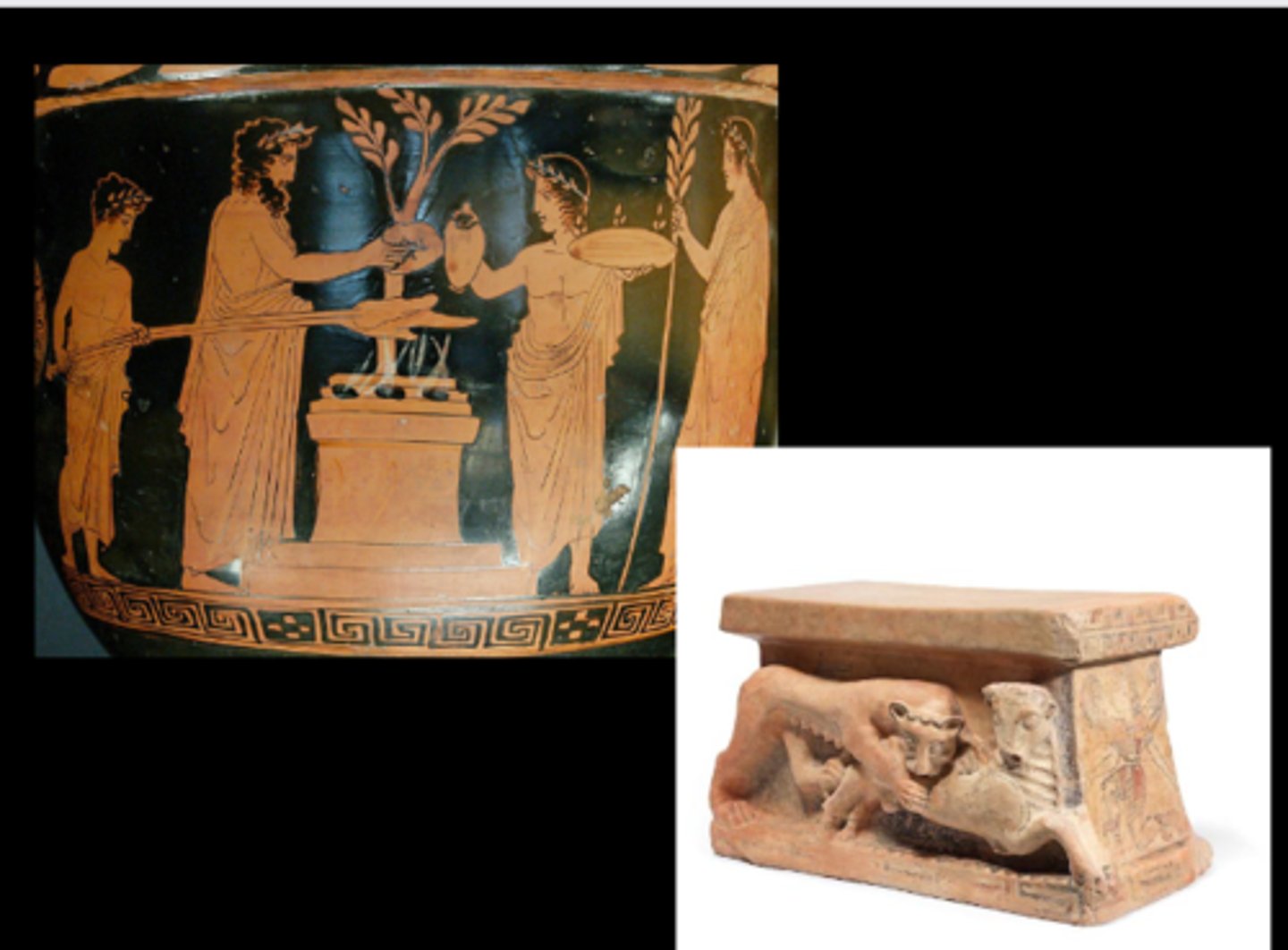
What is the Sacred Grove
a. They were part of sanctuaries—religious spaces reserved for worship.
b. These groves were usually natural wooded areas considered sacred, where rituals and offerings to gods might take place.
c. They were often associated with temples or sanctuaries, as places of divine presence.
What is the Temenos
Boundary marker of sacred space

What is an Altar
a. Sacrifice place, most important site; sometimes inside Greek temples
b. Sacrifices were huge, people believed in larger sacrifices of more important things
c. Scent was very important to ritual sacrifices

What was Polis and the Greek city-state
a. It was a self-governing Greek State
b. Had constitutional and judicial reforms because of conflicts between the rich and the poor
c. Middle class had fights for citizenship / voting rights
d. Greater interest towards equality
e. Not just ruler class making decisions
What were Kouroi
a. Youth Sculptures
b. Unlike egyptians, much more female statues
c. Life sized
d. Patrons: Higher-class Families
e. Figures were not real portraits; they were idealizations of the youth of individuals
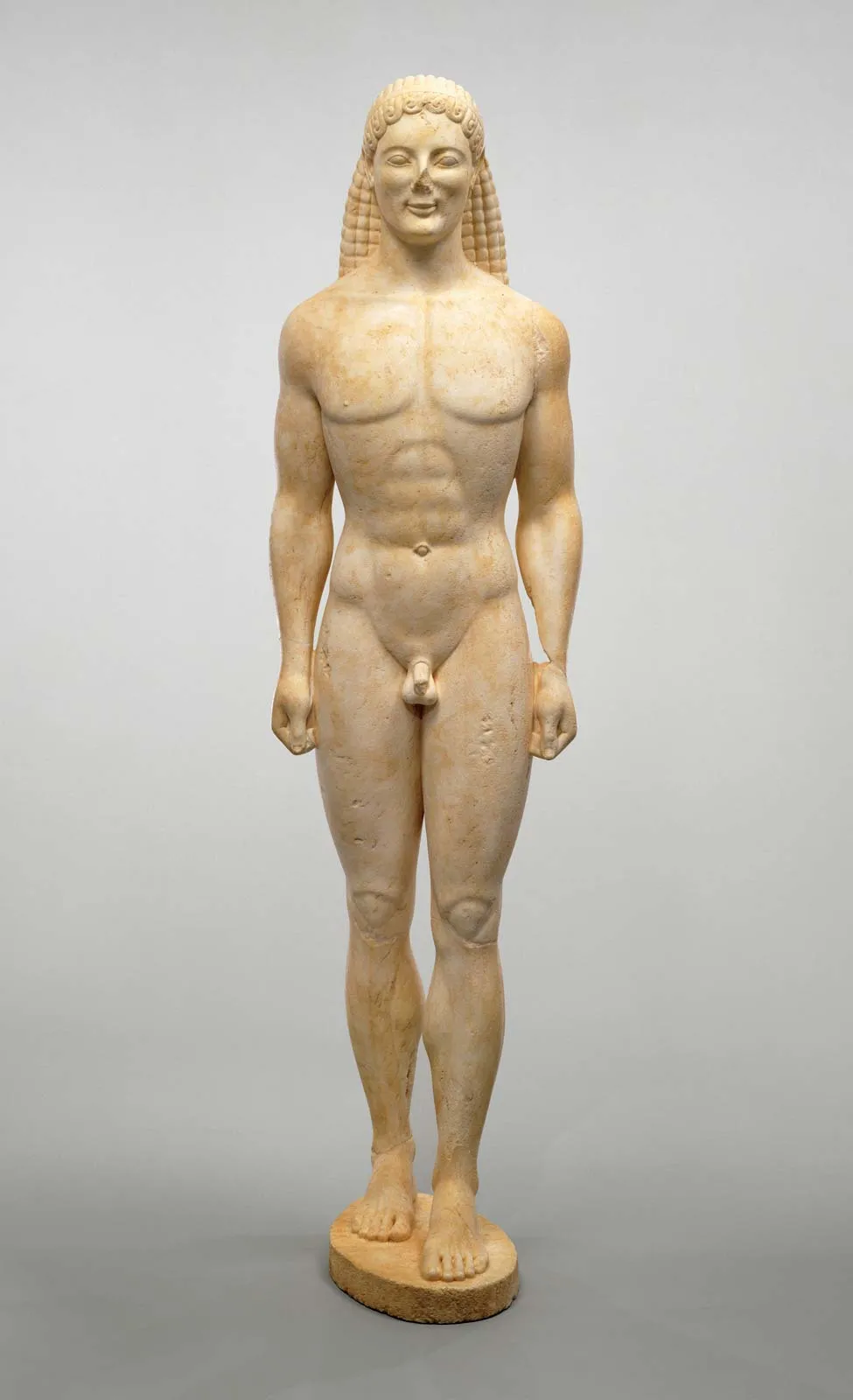

What were Male and female kouroi called
Male (Kurous), Female (Kore)
What was the Archaic Smile
A smile found on all Greek Archaic sculptures not to show happiness but used to animate the scluptures to be life like
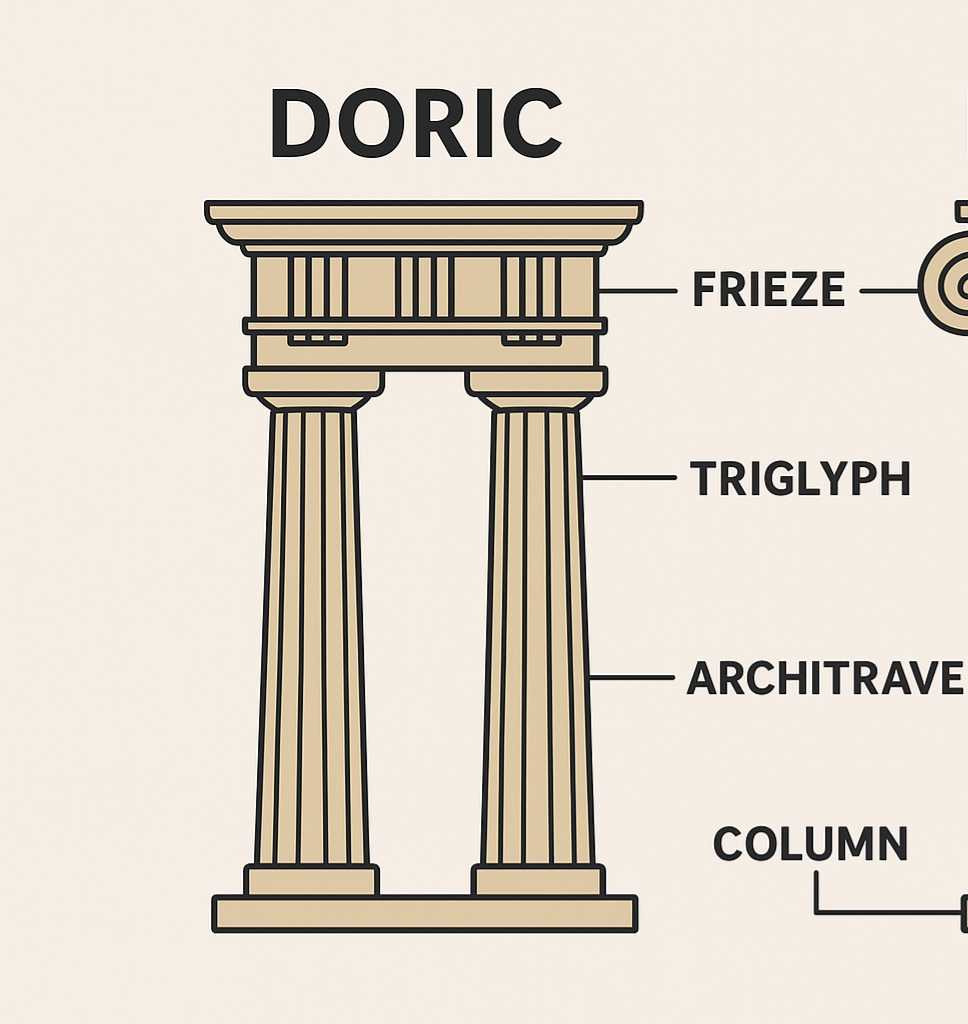
What was the doric temple
Oldest Greek style — strong and plain.
Columns: no base, thick, plain top (capital).
Frieze: has triglyphs (3 lines) and metopes (sculpted squares).
Looks solid and powerful.
🏛 Example: Parthenon, Athens.
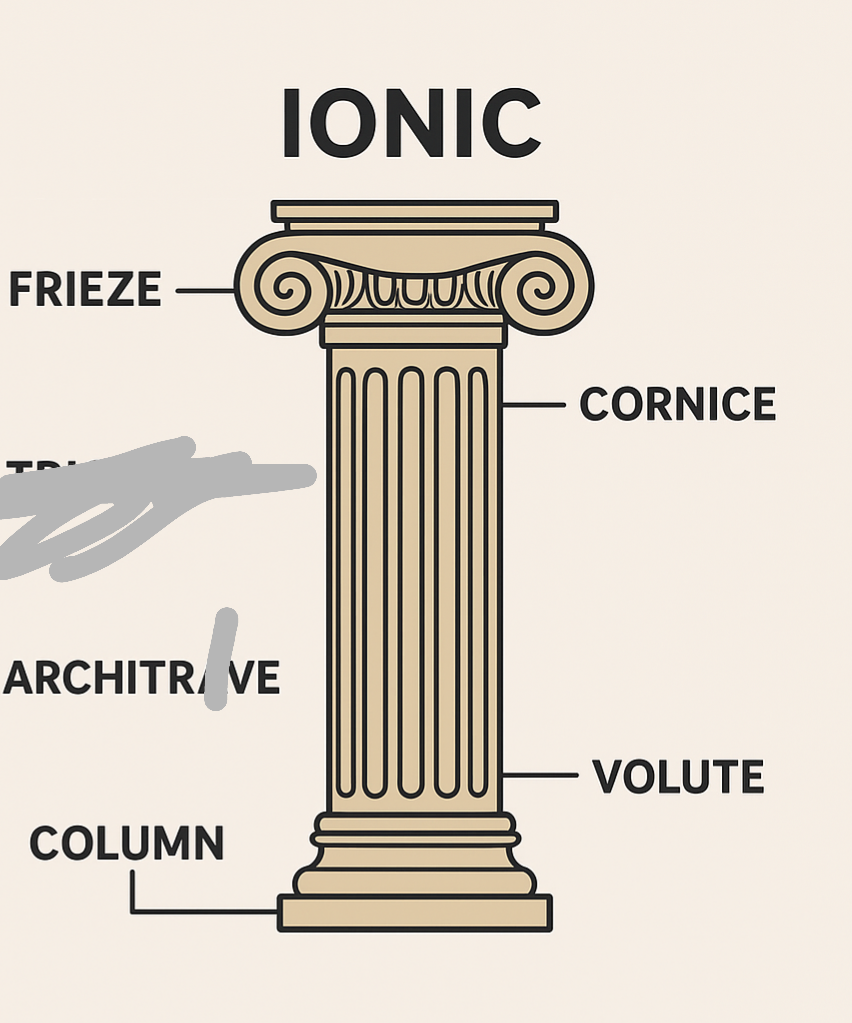
Ionic Elements
Lighter and more decorative style.
Columns: have a base, tall and thin, top has scrolls (volutes).
Frieze: continuous band (no triglyphs).
Looks elegant and graceful.
🏛 Example: Erechtheion, Athens.
When was the Athenian Acropolis and Parthenon building built and where were they located
447-432 BCE. Athens, Greece
What was the Athenian Acropolis
a. Sacred site
b. Temple found next to Altar
c. Housed the statue of Athena and the olive tree
d. Destroyed by the Perisans
e. People mourned over the destruction by vowing not to build another temple (Parthenon was later built)

What was Parthenon
a. Temple built by Pericles against the will of the people
b. It was built when Athens was the strongest city-state
c. Only housed Athena
d. Not only a religious place but was also used to store valuable things such as offerings
e. Not every state had a Parthenon
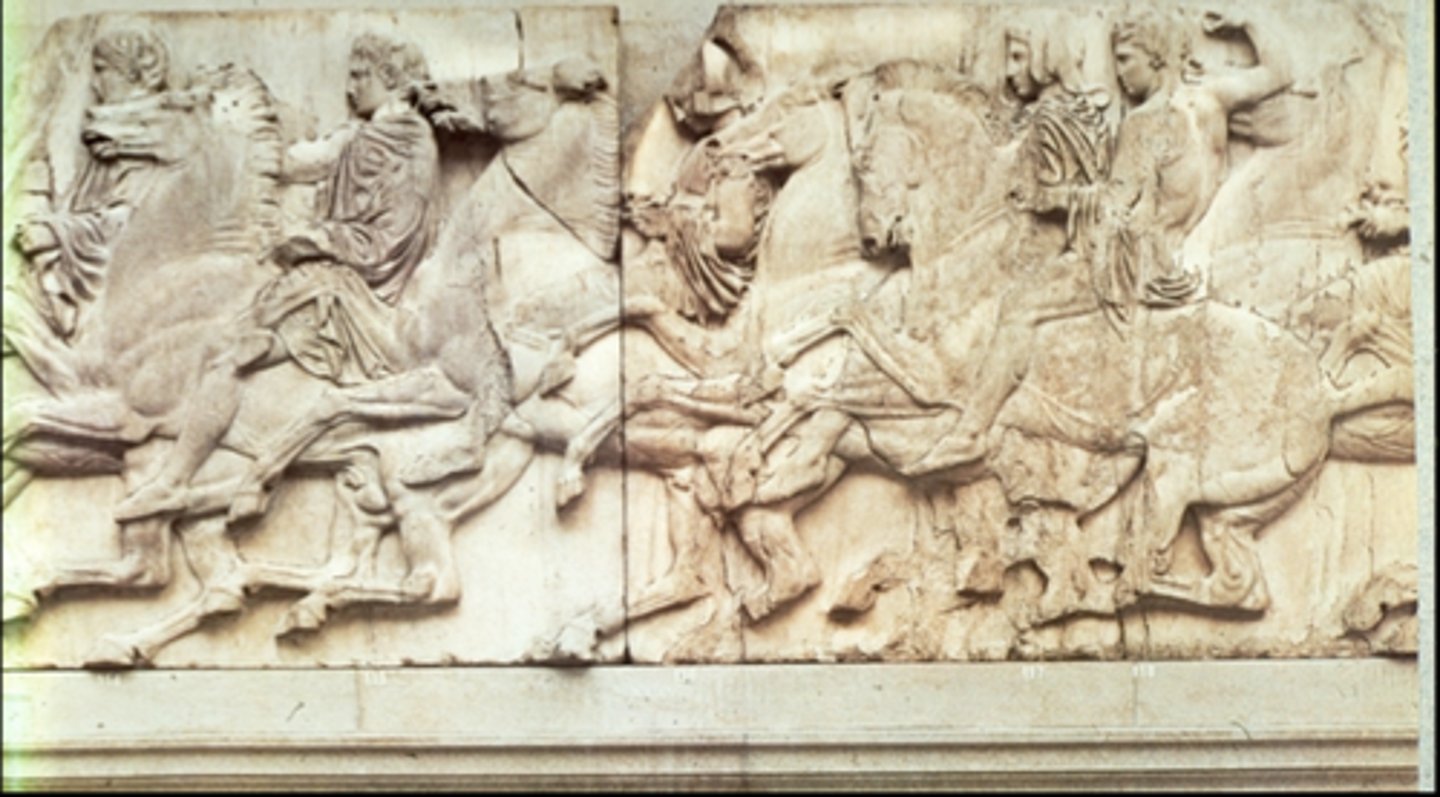
What are some details about the parthenon frieze
a. Date: 447-432 BCE
b. Material: Marble
c. Height: 90 cm
d. Location: British Museum, London
What was the Parthenon Frieze
a. Low relief sculpture
b. Had lots of sculptures about the Greeks fighting in battles
c. Used to represent Triumphs of Athens and greeks

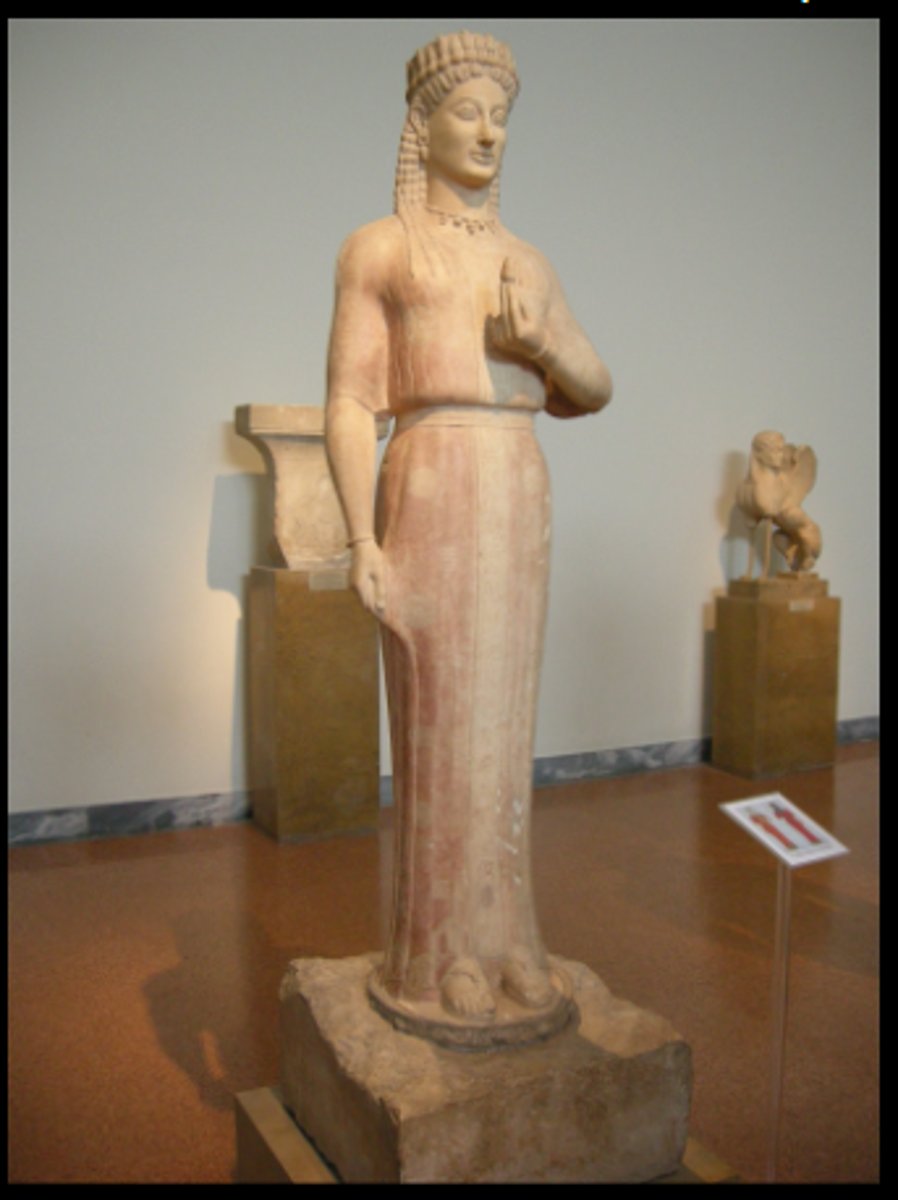
What are some details about the Phrasikleia Kore
a. Date: 550 BCE
b. Material: Marble
c. Height: 179 cm
d. Location: National Archaeological Museum, Athens

What was inscripted on the bases front of the Phrasikleia Kore
The name of the deceased Phrasikleia: [Grave marker of Phrasikleia. I shall forever be called maiden (kore), since i will never marry ]
![<p>The name of the deceased Phrasikleia: [Grave marker of Phrasikleia. I shall forever be called maiden (kore), since i will never marry ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2fb00a3c-9bf7-418f-9fc0-8dbc557b9889.jpg)
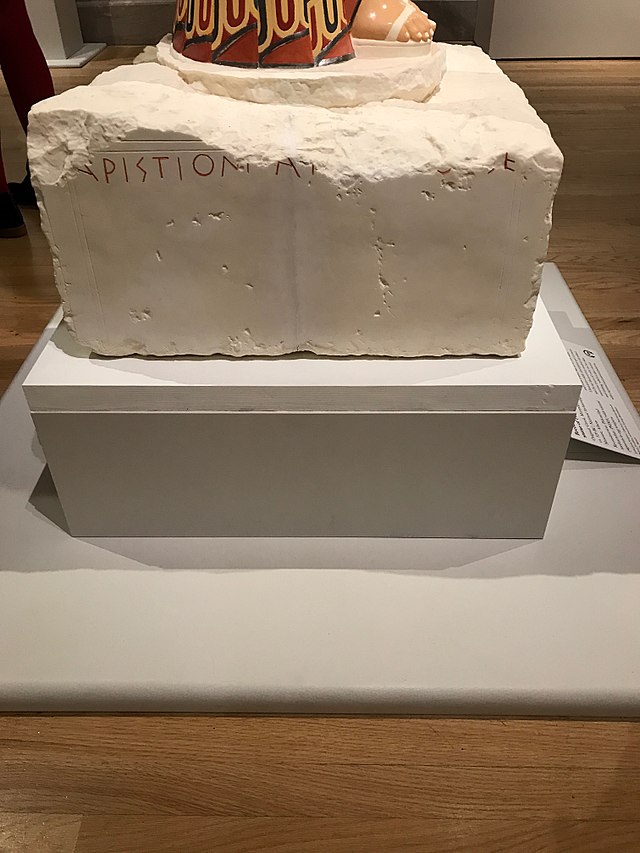
What was inscripted on the left side of the Phrasikleia Kore
The name of the sculptor: (Aristion of Paros made me).

athens was the most powerful city-state in which century bce
5th