Exam 3 Review: Contracts and Legal Capacity
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Voidable contract
Contracts that can be canceled by one party.
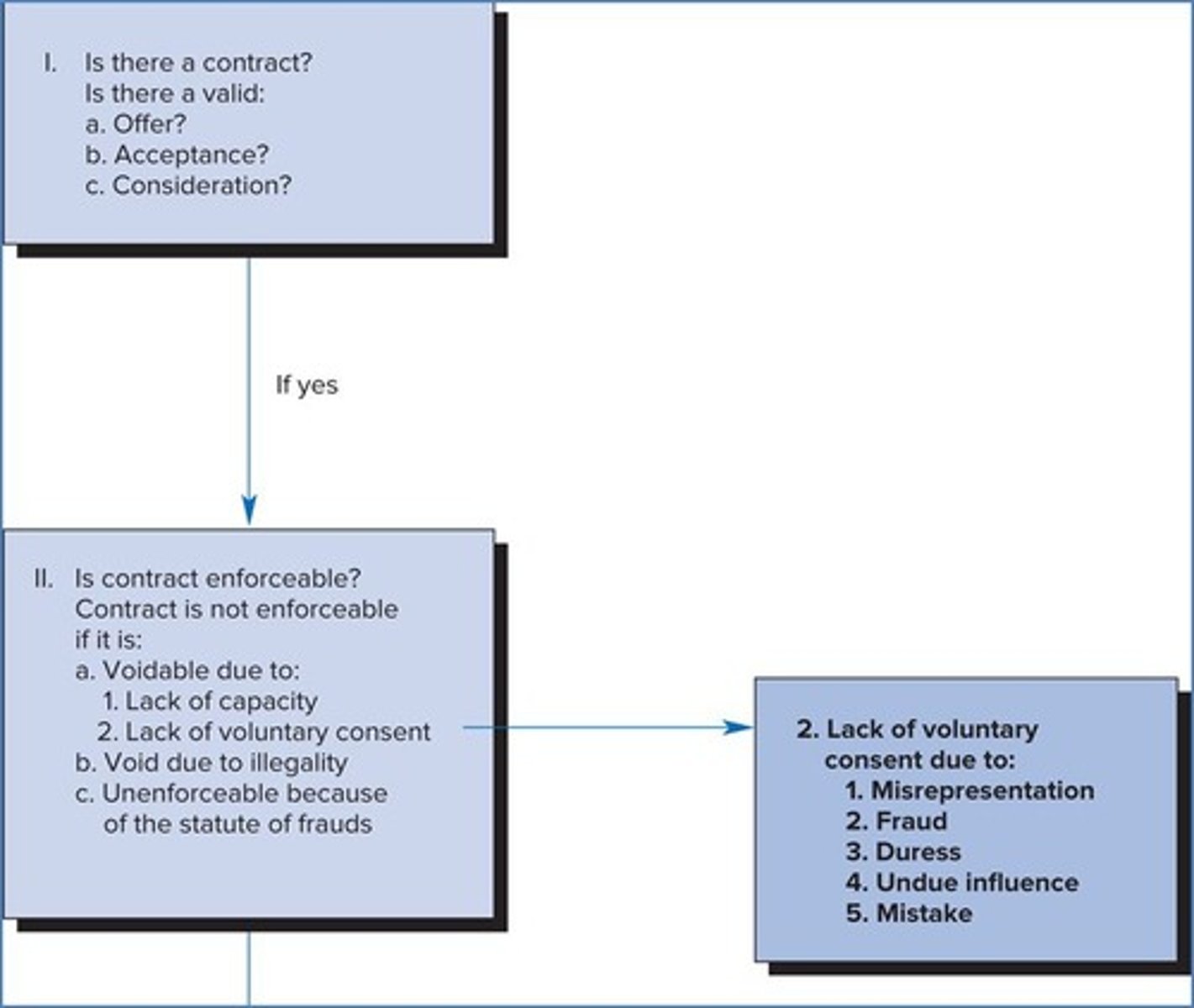
Void contract
Contracts that have no legal effect.
Unenforceable
Contracts that cannot be enforced in court.
Capacity
Ability to enter into a legal contract.
Disaffirm
Minor's right to cancel a contract.
Status Quo Ante
Return to pre-contract position.
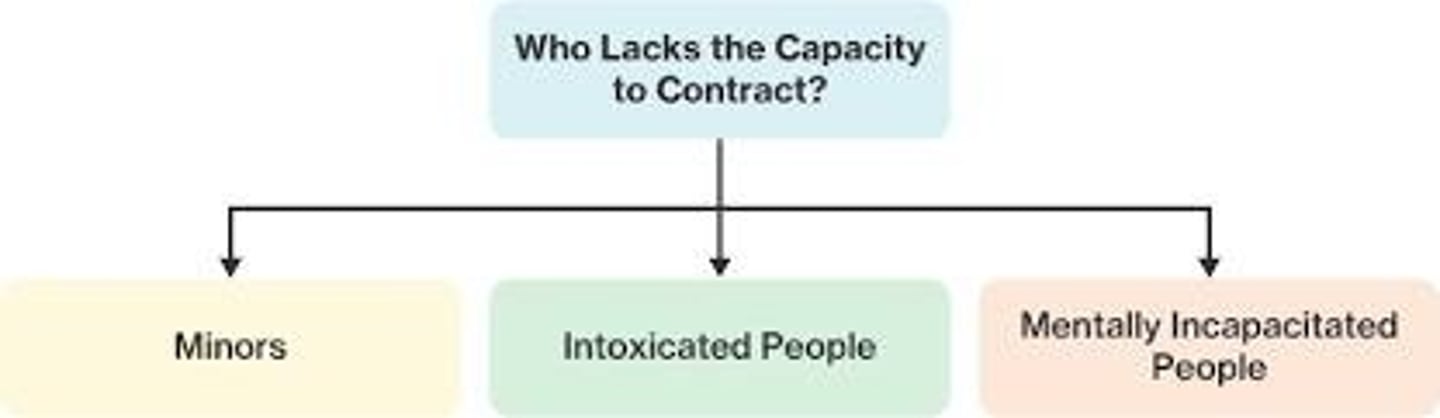
Minor's Contracts
Voidable contracts that minors can disaffirm.

Parental Binding
Parents cannot bind minors to voidable contracts.
Misrepresentation of Age
Lying about age affects disaffirmation rights.
Tort of Deceit
Liability for lying about age in contracts.
Mental Incapacity
Lack of mental capacity to enter contracts.
Lucid Moment
Time when a person can legally contract.
Intoxication
Ability to contract when not under influence.
Voluntary Consent
Agreement must be made without coercion.
Meeting of the Minds
Mutual agreement between parties in a contract.
Rescind
To cancel a contract and return received items.
Ratification
Approval of a contract after a delay.
Necessaries
Essential items for which reasonable value must be paid.
State Statutes
Laws governing contracts vary by state.
Fair Contracts
Contracts that may be enforced despite minor status.
Barriers to Disaffirming
Conditions limiting a minor's right to disaffirm.
Adult Responsibility
Adults must return minors to status quo ante.
Misrepresentation
False statement of material fact affecting decisions.
Material Fact
Present fact, not opinion or future prediction.
Justifiable Reliance
Trusting a misrepresentation without public information.
Harm/Detriment
Negative impact on the person relying on misrepresentation.
Fraud
Intentional misrepresentation to deceive another party.
Scienter
Intent to deceive inferred from actions.
Caveat Emptor
Buyer beware; common law principle.
Duty to Disclose
Obligation to reveal certain information in transactions.
Unseen Defects
Latent issues not visible to buyer during sale.
Duress
Coercion to force agreement or action.
Undue Influence
Excessive pressure affecting free will in agreements.
Mutual Mistake
Both parties share incorrect belief about contract.
Unilateral Mistake
Only one party holds a mistaken belief.
Rescission
Cancellation of a contract due to mistakes.
Illegal Agreement
Contract violating law or public policy.
Wagering Statutes
Laws regulating or prohibiting gambling activities.
Risk-Shifting Contract
Agreements transferring risk of loss, like insurance.
Speculative Bargaining
Contracts based on uncertain future events.
Usury Laws
Prohibit excessive interest rate charges.
Sunday Blue Laws
Restrict business activities on Sundays.
Regulatory Statutes
Laws regulating activities for public protection.
Unlicensed Agreements
Illegal contracts by unlicensed professionals.
Unconscionable Contracts
Contracts with unfair terms, unenforceable by law.
Procedural Unconscionability
Unequal bargaining power affecting contract fairness.
Substantive Unconscionability
Unfair terms in a contract, oppressive to one party.
Statute of Frauds
Requires certain contracts to be in writing.

Oral Contracts
Enforceable unless statute of frauds applies.
Quasi Contract
Recovery for reasonable value of performance without contract. Implied contract to prevent unjust enrichment.
Promissory Estoppel
Prevents withdrawal from a promise causing reliance.
Executory Bilateral Contracts
Contracts not fully performed within one year.
Lifetime Contracts
Agreements lasting for the lifetime of a party.
UCC Sale of Goods
Contracts for goods over $500 require writing.
Plain Reading Standard
Interprets contracts based on reasonable person understanding.
Parol Evidence Rule
Limits use of prior agreements to interpret written contracts.
Ambiguities in Contracts
Unclear terms resolved against the drafter.
Exceptions to Parol Evidence Rule
Includes lack of consent and proving ambiguities.